Abstract
(1) Background: The acute effects of ozone, cold temperature and particulate matter less than 2.5 μm (PM2.5) in size related to asthma attacks are well known worldwide. The adverse effects of ozone and cold temperature on asthma morbidity in Taiwan are still inconclusive. (2) Methods: This retrospective study included patients who had asthma emergency room visits (ERVs) from 1 January 2016 to 31 December 2019 in a regional hospital in Taiwan. The short-term negative effects were estimated using Distributed Lag Non-Linear Models (DLNMs) for the relative risks (RRs) of asthma ERVs associated with PM2.5, ozone and cold temperature exposures within 5 days. (3) Results: There was a significant association between a 10 ppm increase in PM2.5 exposure and asthma ERVs at a 2-day lag (RR 1.166, 95% confidence interval (C.I.): 1.051–1.294). There was a significant association between ozone and asthma ERVs at a 1-day lag (RR 1.179, 95% C.I.: 1.034–1.345). The ambient temperature in cold weather compared with the temperature of minimum asthma ERV showed an RR of 1.214, 95% C.I.: 1.009–1.252 at a 1-day lag. (4) Conclusions: This study provides evidence that short-term exposure to fine suspended particulates, ozone and inverse temperature is associated with asthma exacerbation.
1. Introduction
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that affects more than 350 million people worldwide, and its incidence is on the rise. It is reported to kill approximately 383,000 people each year [1]. Acute asthma attacks cause dyspnea, which requires emergency management visits to emergency departments, resulting in a healthcare burden. Acute asthma exacerbation is an important public health problem that induces patients’ respiratory discomfort and increases burdens on their families, health professionals, health care institutions and even the development of the nation [2]. Asthma contributed 13.2 million years of life lived with disability and 10.5 million years of life lost due to premature death across all ages, as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2016 [3].
For chronic asthma, the estimated prevalence is the highest in the African region (11.3%), but the lowest in the Southeast Asia region (8.8%) [3]. Up to 36% of children younger than 18 years old with asthma reported emergency department visits for asthma in the past year in the United States [4]. The prevalence of asthma was 11.53% in Taiwan in 2011 [5]; the estimated number of asthma patients was approximately 2 million. The prevalence rate of asthma in children under 12 years old was 5.6%, and 9.2% of them went to the emergency department due to an asthma attack within one year, according to the National Health Interview Survey as reported by the Taiwanese Ministry of Health and Welfare National Health Service [6]. The 55.1/100,000 hospitalization rate of asthma is still higher than other countries, and policies are needed to improve the result [7].
Exposure to air pollution can lead to respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, lung cancer [8,9,10,11] and sudden hearing loss [12]. Particulate matter (PM) is the largest cause of air pollution; the higher the concentration of fine suspended particulates (PM2.5) in the air, the higher the relative risk of respiratory diseases [13]. In 2013, the International Agency for Cancer (IARC) listed PM2.5 as a first-class carcinogen [8].
Motor vehicle combustion, fossil fuel (traffic exhaust), power plants or other industrial processes may be the main sources of PM2.5 and ozone (O3). Traffic and power generation are the main sources of urban air pollution, and traffic-related air pollution (TRAP), as well as the air pollutants O3, nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and PM2.5, can induce airway inflammation [14].
A past study found that PM2.5 was related to asthma emergency room visits (ERVs) in Taipei [15]. Younger patients, below 18 years old, with asthma had significant risk associations with ambient levels of PM2.5 and ozone in southern Taiwan [16]. Studies on the associations between ambient temperature and ERVs vary due to differential areas with different climates and terrains [16,17,18,19]. Females and younger patients were more vulnerable to the effects of low temperatures. Adults are at a higher risk of asthma ERVs associated with extremely high temperatures due to outdoor work [16].
Taoyuan City is an urban area of Taiwan located in southern Taipei, and New Taipei cities have higher TRAPs. Longtan District is located in southern Taoyuan. In the special terrain surrounding the U sharp mountain, the seasonal wind carries air pollutants from mainland China and Linkou District that is difficult to clean out in the winter. Several factories for wafer manufacturing which use ozone water for wafer washing are located in the Longtan District. The air pollution and climate factors that may cause asthma attacks with delayed effects need to be studied. The relationship between asthma ERVs and air pollution or climate conditions in special areas is worthy of study.
The aim of this study focused on the relationship between asthma ERVs, ambient pollutants and climate conditions for a period of four years in Taiwan. The unique terrain caused air pollutants to gather via seasonal winds in winter, which resulted in asthma attacks. Although the government has focused on reducing air pollution for years, some air pollutants are still not targeted by the WHO’s air pollution guideline values, and aggressive policies to reduce them that would promote citizens’ health have not yet been introduced.
2. Materials and Methods
We analyzed daily asthma ERVs data for the time period 1 January to 31 December from 2016 to 2019 at Taoyuan Armed Forces General Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan. The regional hospital is located within the southern area of Taoyuan City in Taiwan and has more than 60,000 ERVs yearly; it is the only hospital with an emergency department in southern Taoyuan City. The Longtan District is a sector of hilly terrain located in the southern region of Taoyuan, with the highest height in the southeastern part, the lowest height in the northwestern part, higher terrain on both sides and 124,442 residents in 2021 [20].
The daily air pollutant gas data were obtained from the Taiwanese Environmental Protection local air quality monitoring station in Longtan of Taoyuan City (24°51′50.8″ N, 121°13′00.2″ E), which is the nearest station (approximately 2.35 km) to Taoyuan Armed Forces General Hospital. Air pollutants include PM2.5, O3, NO2, sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), relative humidity (RH) and ambient temperature. The data were obtained from the Environmental Protection Administration’s (EPA) Taiwan Quality Monitoring Network [21].
We used ERVs data, including information from 1 January 2016 to 31 December 2019. The occurrence of ERVs was retrieved via International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) codes 493 and ICD-10-CM code J45. The flowchart of this study is described in Figure 1. This study was approved in TSGH by the TSGHIRB No.: C202105149.
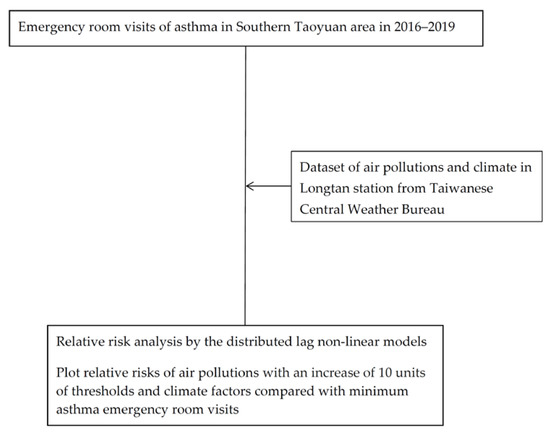
Figure 1.
The flowchart in this study.
Descriptive statistics of asthma ERVs, air pollutants and meteorological factors were evaluated (Table 1). The distributed-lag nonlinear model (DLNM) was performed for the association between asthma ERVs, air pollutants and meteorological factors (PM2.5, PM10, O3, CO, NO2, SO2, air temperature and relative humidity). The correlations between air pollutants and meteorological factors were assessed. We set the exclusion criteria at |r| > 0.8 to reduce the collinearity problem between each variable. The correlations were above 0.8 between PM2.5 and PM10 as well as between NO2 and CO, and we excluded PM10 and CO (Table 2). The levels of SO2 were not more than 10 units higher than the median and were excluded. The relation of ERVs and individual air pollution (PM2.5, O3, NO2) and air temperature used multivariable DLNM analysis-adjusted wind speed, relative humidity, holiday, seasonality and time trends, and lag was set at 0–5 days [22]. The DLNM handled the time series data for nonlinear relationships and delayed effects. The Poisson regression managed the count data using a generalized linear model. The relative risk (RR) for asthma ERVs, related to the levels of ambient pollutants and the air temperature, were analyzed by a quasi-Poisson regression model with a linear function evaluating the exposure–response function. The maximum lag was set to 5 days for each variable. The natural cubic spline used for air temperature, relative humidity and wind speed had 4 equally spaced internal knots. We adjusted the seasonality and time trends using a natural cubic spline with seven degrees of freedom (df) for the calendar time. The factor variables of days of the week and holidays were adjusted. Thresholds were arranged as the median of air pollutants and minimum asthma ERV temperature (MAT) (26 °C). RRs of air pollutants were assessed as a 10-unit increase from the reference levels. The cold air temperature was 25% of the air temperature in research years (18.1 °C), and the RR of air temperature used ERVs at 18 °C compared with ERVs at 26 °C. The extremely cold air temperature was 1% of the air temperature in the research years (9.8 °C), and the RR of air temperature used ERVs at 10 °C compared with ERVs at the reference level of air temperature. The analysis was performed by the R package dlnm (R version 4.0.2) [22]. Poisson distribution-like schematic calculation of possible variables for the relative risk of ERVs was conducted. Poisson regression is a generalized linear model that assumes that the response variable Y and the logarithm of its expected value can be modeled by a linear combination of air pollutant parameters. The average asthma ERVs, air pollutants and meteorological factors each month are shown in a graph.

Table 1.
The asthma emergency room visits, air pollutants and meteorological factors in Longtan district over 4 years (2016–2019).

Table 2.
The correlation between air pollutants and climate factors.
We counted the numbers of asthma ERVs in pediatric (0–17 years old), adult (18–64 years old) and older asthma patients (>65 years old). According to sex, we also counted the numbers of asthma ERVs in male and female patients. The cold season was defined as November to April, and the warm season was defined as May to October.
3. Results
There were 1321 asthma ERVs in this study. The average age at the time of the asthma ERVs was 43.43 ± 29.44 years old. There were 679 males and 642 females in the four-year period. A total of 999 (75.62%) asthma ERVs were discharged after treatment, 296 (22.41%) asthma ERVs required hospitalization, 9 asthma ERVs were transferred to other hospitals, 19 asthma ERVs were discharged against medical advice and 1 asthma ERV resulted in death (Table 1). The maximum number of monthly asthma ERVs was 136 in February, and the minimum was 82 asthma ERVs in August. The (lowest) nadir mean air temperature was 15.03 °C in February and the peak was 29.37 °C in July. The peak of the mean PM2.5 was 26.97 ppm in April. The mean O3 values exhibited twin peaks of 37.89 ppb in April and 39.09 ppb in October (Figure 2).
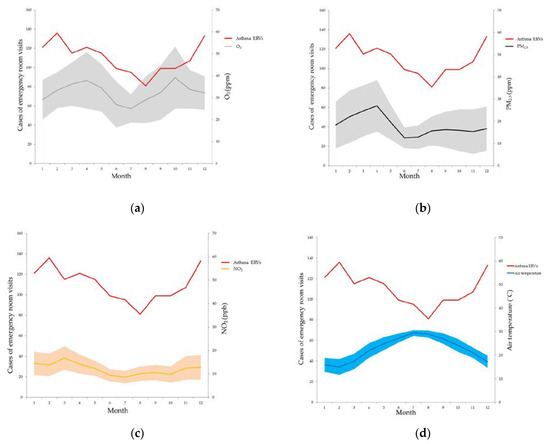
Figure 2.
The asthma emergency room visits, ozone (a), PM2.5 (b), NO2 (c) and air temperature (d) in different months over four years in the Longtan district of Taoyuan in Taiwan.
PM2.5 exposure had a positive relationship with asthma ERVs, with an RR of 1.166 (95% confidence interval (C.I.): 1.051–1.294) for a 10-unit increase with a 2-day lag. O3 exposure had a positive relationship with asthma ERVs, with an RR of 1.179 (95% C.I.: 1.034–1.345) for a 10-unit increase with a 1-day lag. The ambient temperature in cold weather (25%:18 °C) was compared with MAT of 26 °C (RR 1.214, 95% C.I.: 1.009–1.252) with a 1-day lag. NO2 exposure had no significant relationship with asthma ERVs, with an RR of 1.238 (95% C.I.: 0.881–1.74), for a 10-unit increase with a 1-day lag (Figure 3). The lag−response curve of incremental cumulative effects of air temperature showed a cumulative RR of 1.9 (95% C.I.: 1.035–3.488); a cumulative effect of PM2.5 of 1.125 (95% C.I.: 0.933–1.358); O3 of 1.027 (95% C.I.: 0.836–1.262) and NO2 of 0.776 (95% C.I.: 0.464–1.293) (Figure 4). The RR of PM2.5 in the differential age group was 1.195 (1.001–1.426) at a 2-day lag in pediatric asthma patients, 1.253 (95% C.I.: 1.037–1.515) at a 1-day lag in older asthma patients and 1.281 (95% C.I.: 1.087–1.509) at a 4-day lag in adult asthma patients. The extremely cold temperature (1%: 10 °C)) association was evident in elderly asthma patients, with an RR of 1.378 (95% C.I.: 1.049–1.811) compared with MAT at a 1-day lag and an RR of 1.193 (95% C.I.: 1.037–1.373) at a 1-day lag in male asthma patients, whereas no association was observed among children or females.
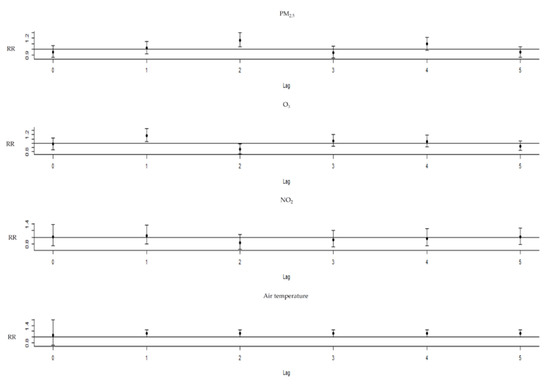
Figure 3.
The relative risks of PM2.5, ozone and NO2 with the thresholds increased every 10 units, and air temperature compared with the temperature of minimum asthma emergency room visits.
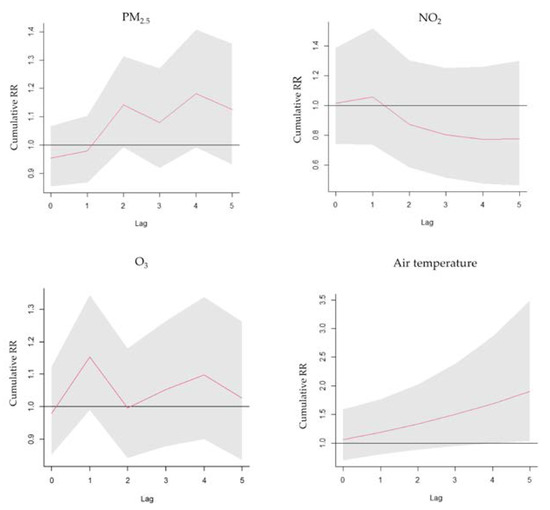
Figure 4.
Lag−response curve of the cumulative effects of PM2.5, O3, NO2 and air temperature.
The RR of PM2.5 was 1.231 (95% C.I.: 1.061–1.244) at a 2-day lag, and the RR of O3 was 1.33 (95% C.I.: 1.106–1.599) at a 1-day lag every 10-unit increase in female asthma patients. The RR of NO2 in the warm seasons was 2.308 (95% C.I.: 1.132–4.705) every 10 units, without lag. The RR of PM2.5 in the cold season was 1.2 (95% C.I.: 1.051–1.37) every 10 units, with increased lag at 2 days; the RR of O3 in cold seasons was 1.222 (95% C.I.: 1.007–1.484) every 10 units, with increased lag at 1 day and the RR of cold temperature (13 °C) compared with 18 °C in cold seasons was 1.129 (95% C.I.: 1.027–1.24) at a one-day lag.
4. Discussion
Our study suggested that the ozone and cold weather related to asthma ERVs are associated with PM2.5. Chemicals with oxidant-generating capabilities affect the human respiratory and immune systems [23]. Recent studies in cells and animal models have suggested several possible mechanisms, of which the most consistent observation is the direct effect of particulate components on the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the resulting oxidative stress and inflammatory responses [24,25].
Asthma exacerbation is defined as a worsening of shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, or chest tightness. If patients don’t receive effective treatment immediately, it will increase airflow resistance, causing an increase in breathing workload, gas exchange inefficiency and respiratory muscle fatigue and result in hypercapnic and hypoxemic respiratory failure. Acute asthma attacks are a significant public health problem and influence quality of life, affecting patients and families through causing absences from labor and school, frequent ERVs, hospitalizations and possible death [2,26].
PM carries metal components, and organic matter has the ability to generate oxygen free radicals, which can stimulate cells to produce ROS [27]. ROS-induced oxidative damage to lung cells may be the primary cause of damage due to PM exposure. PM2.5 may contain toxic substances from combustion, including acids, metals and nitrates. These ingredients can accumulate in the lungs and cause allergies with increased immunoglobin E and inflammation [28,29]. PM2.5 concentrations have been shown to be higher in cold weather [30], and our study also found the same trends. A previous study found that PM2.5 was related to asthma ERVs in Taipei [15]. Our study showed similar findings. The Longtan District had a higher altitude, from 150 m in the northwestern part to 230 m above sea level in the southeastern part, and is surrounded by mountains on the eastern, southern and western borders. The seasonal wind from the northeast carries the pollutants from mainland China, and the LinKou thermal power plant causes higher PM2.5 in the winter season. The mean daily PM2.5 concentration is at its highest in April due to residents worshiping their ancestors by burning incense and joss paper during the Qingming Festival on 5 April. The highway crosses the Longtan District with higher TRAPs. A lag of only one day in PM2.5 exposure was associated with acute asthma attacks in older asthma patients, which means that older asthma patients are more sensitive to PM2.5 changes and have weaker respiratory tract defenses than pediatric and adult asthma patients. Adult asthma patients carrying a heavy workload could initially go to the clinic and be sent to emergency departments, but symptoms would worsen after several days, and this would cause an even longer lag for asthma ERVs.
Ozone, a gas, is one of the most common air pollutants. It is most common in cities where there is heavy road traffic [14]. It is also more common in the spring and fall, when there is more sunlight due to higher attitude and low wind photochemical reaction from NO2. Ozone triggers asthma because it is very irritating to the lungs and airways. It is well-known that ozone concentration is directly related to asthma attacks, reducing lung function and causing ERVs to be required for medication treatment [31]. Acute ozone exposure in men causes sputum neutropenia in 30% of subjects, especially young children, women and those with persistent cardiorespiratory disease [32]. Exposure to O3 can promote airway infections and increase the risk of asthma attacks [33,34]. A similar finding was noted in our study. Inhaled ozone does not enter cells, but reacts with components of the airway-lining fluid in order to generate other ROSs and enhance local oxidative stress, inflammation and epithelial cell injury [35]. The mean concentration of ozone was five units higher than that in Taipei [12]. The potential reason was that several wafer manufacturing factories using ozone water for wafer washing were located in Longtan district. A past study found that daily O3 concentrations were associated with a higher risk of asthma in young adults. Women aged 40 to 64 years had the highest relative risk of ERVs, with an RR of 1.21 (95% CI 1.05–1.39) [16]. However, our study showed different findings, because as adult asthma patients need to work, they tend to go to the clinic rather than the emergency department for treatment. O3 was related to asthma ERVs in the female patients and in the cold seasons in our study.
Extreme temperatures are related to ERVs in the United States [36], and cold temperature-related respiratory ERVs in Taiwan are similar [37]. The link between extreme temperatures and asthma risk only occurs during ERVs and outpatient visits [16]. Cold temperatures in crowded environments may exacerbate transmission and lead to cross-infection [19]. Exposure to extreme temperatures may increase pulmonary vascular resistance and thrombosis, which can lead to symptoms. Additionally, people living in cold regions may have increased airway neutrophils, macrophages and airway inflammation [33]. This cold snap can exacerbate inflammation and lead to narrowing of the airways, which can lead to acute asthma attacks [38], but not in children [39] staying indoors of school or home most of the time. Our study showed that cold temperature was related to asthma ERVs compared with MAT and incremental cumulative effects of cold temperature. Our results showed that cold weather was related to respiratory disease in Taoyuan City. Short-term exposure to extremely cold temperatures was associated with asthma ERVs in males and elderly individuals; males worked outside, with more exposure to changes in weather, and elderly individuals had less protection against extreme cold temperature wear less clothes with insensitive to temperature change in outdoor activity.
NO2 was mainly from motor vehicle emissions and was not related to asthma ERVs in the four-year period. The potential reason was O3 formation through photochemical reactions with NO2 and volatile organic compounds at high altitudes [40], which resulted in lower mean daily NO2 (12.11 ppm) than that in Taipei (19.83 ppm) [12]. Although we found that NO2 was related to asthma ERVs in the warm season, the potential reason was that NO2 transferred to O3, resulting in higher O3 concentrations in the warm season.
We used asthma ERVs of a single regional hospital, urban air pollution and climate data to analyze the association by distributed lag nonlinear time series models. The results demonstrated the harmful effects of short-term exposure to PM2.5, ozone and cold temperature on asthma ERVs and discussed the different effects of sex and age.
There were some limitations to our study. First, the daily detailed treatments for asthma were not collected in our study; this may have been related to asthma attacks lasting for days, which may have caused negative effects due to the delay. Second, infection, seasonal change, smoking and in-kitchen smoking were significantly related to acute asthma symptoms and ERVs [26]. Smoking history and second-hand smoke exposure were not checked, which may have increased the number of acute asthma attacks. There was a 13.1% adult smoking population, and approximately 27.1% self-reported second-hand smoke exposure in a smoke survey conducted in 2020 in Taiwan [41]. This needs to be adjusted in future studies. Third, regarding the state of air pollution monitoring by the government, we used the data collected nearest to the hospital rather than to the residence places of the patients who had ERVs, which may overestimate the effect of air pollutants or air temperature. Although Taoyuan Armed Forces General Hospital is a larger hospital in southern Taoyuan that services the nearby residents, the air pollutants near the residence places of the asthma patients need to be checked to increase accuracy in further studies. Fourth, the cumulative effects of PM2.5 and O3 showed increasing trends, and the cumulative effect over time needs to be evaluated in the future. Fifth, the special terrain of Longtan District and the seasonal winds in Taiwan resulted in increased asthma ERVs, and different areas in Taiwan may have different levels of air pollution. A past study showed that air pollution was related to ERVs of respiratory disease and upper respiratory tract infections in the basin terrain of the Taipei area [42,43]. The relationship between air pollutants and asthma attacks must be studied in other areas with different terrains in the future.
5. Conclusions
This study showed positive relationships between short-term air pollutants of fine PM, ozone, climate factors of cold temperature exposure and acute asthma exacerbation. Since the mean fine PM and ozone concentrations have decreased in recent years due to the increased control over the quality of air in Taiwan, adverse effect concentrations have not yet been achieved, according to WHO air pollution guideline values [44], in recent years. The air pollution caused by the development of the semiconductor industry is worth noting. More aggressive policies for environmental pollutant control and asthma attack prevention are needed. This research could play an important role in improving public health policies to accommodate air pollution and low temperatures, which are associated with health risks.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-A.C.; data curation, C.-C.H. and Y.-H.C. (Yin-Han Chang); funding acquisition, Y.-H.C. (Yu-Hsuan Chen); investigation, S.-Y.Y., C.-C.H., Y.-Y.L. and Y.-H.C.; methodology, C.-A.C.; project administration, S.-Y.Y.; resources, C.-G.C., C.-C.H. and Y.-Y.L.; software, C.-A.C.; supervision, C.-A.C.; validation, S.-Y.Y., Y.-Y.L. and Y.-H.C. (Yin-Han Chang); writing—original draft, C.-G.C.; writing—review and editing, Y.-H.C. (Yu-Hsuan Chen) and C.-A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of TSGH (TSGHIRB No: C202105149 and 7 September 2021 approval).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived, as this was a retrospective study and chart review does not require informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank TYAFGH_E_111054, TYAFGH_E_112042 and CHGH110-(N)07 for their support in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Global Asthma Network. Global Asthma Report 2018. 2018. Available online: http://globalasthmareport.org/burden/burden.php (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Park, H.W.; Tantisira, K.G. Genetic signatures of asthma exacerbation. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2017, 9, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Adeloye, D.; Salim, H.; Dos Santos, J.P.; Campbell, H.; Sheikh, A.; Rudan, I. Global, regional, and national prevalence of asthma in 2019: A systematic analysis and modelling study. J. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 04052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gushue, C.; Miller, R.; Sheikh, S.; Allen, E.D.; Tobias, J.D.; Hayes, D., Jr.; Tumin, D. Gaps in health insurance coverage and emergency department use among children with asthma. J. Asthma 2019, 56, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.C.; Lin, C.C.; Yang, S.Y.; Chen, H.J.; Li, T.C.; Lin, J.G. Time Trend Analysis of the Prevalence and Incidence of Diagnosed Asthma and Traditional Chinese Medicine Use among Adults in Taiwan from 2000 to 2011: A Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health Interview Survey in Taiwan in 2017. 2021. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=364&pid=13636, (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Population Health and Welfare Quality Indicators Report in 2017. 2019. Available online: https://www.mohw.gov.tw/cp-3232-18296-1.html (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- World Health Organization. Outdoor air Pollution a Leading Environmental Cause of Cancer Deaths. Available online: https://www.iarc.who.int/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/pr221_E.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Vidale, S.; Campana, C. Ambient air pollution and cardiovascular diseases: From bench to bedside. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2018, 25, 818–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkovich, S.M.; Goodman, D.; Roa, C.; Crocker, M.E.; Gianella, G.E.; Kirenga, B.J.; Wise, R.A.; Checkley, W. The health and social implications of household air pollution and respiratory diseases. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2019, 29, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, C.A., III; Coleman, N.; Pond, Z.A.; Burnett, R.T. Fine particulate air pollution and human mortality: 25+ years of cohort studies. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 108924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.G.; Chen, Y.-H.; Yen, S.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Chou, K.-R.; Cheng, C.-A. Air Pollution Exposure and the Relative Risk of Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Taipei. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-K.; Sung, H.-J. Particulate-Matter Related Respiratory Diseases. Tuberc. Respir. Dis. 2020, 83, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manisalidis, I.; Stavropoulou, E.; Stavropoulos, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Environmental and Health Impacts of Air Pollution: A Review. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-C.; Chang, J.-W.; Lee, C.-L.; Huang, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-P.; Liu, C.-T.; Jean, S.-S.; Huang, S.-K.; Hsu, C.-W. Differential time-lag effects of ambient PM2.5 and PM2.5-PAHs on asthma emergency department visits. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 43117–43124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafirah, Y.; Lin, Y.K.; Andhikaputra, G.; Deng, L.W.; Sung, F.C.; Wang, Y.C. Mortality and morbidity of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease associated with ambient environment in metropolitans in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinasi, L.H.; Kenyon, C.C.; Hubbard, R.A.; Zhao, Y.; Maltenfort, M.; Melly, S.J.; Moore, K.; Forrest, C.B.; Roux, A.V.D.; de Roos, A.J. Associations between high ambient temperatures and asthma exacerbation among children in Philadelphia, PA: A time series analysis. Occup. Environ. Med. 2022, 79, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.C.Y.; Li, A.M.; Chan, E.Y.Y.; Goggins, W.B. The short-term association between asthma hospitalisationshospitalizations, ambient temperature, other meteorological factors and air pollutants in Hong Kong: A time-series study. Thorax 2016, 71, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, L.; Huo, X. Temperature drop and the risk of asthma:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 22535–22546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.longtan.tycg.gov.tw/home.jsp?id=7&parentpath=0,1 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Taiwanese Environmental Protection Administration. The Air Pollution Data; Taiwanese Environmental Protection Administration: Taoyuan, Taiwan, 2022. Available online: https://airtw.epa.gov.tw/CHT/Query/His_Data.aspx (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Gasparrini, A. Distributed Lag Linear and Non-Linear Models in R: The Package dlnm. J Stat Softw. 2011, 43, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-H.; Song, S.-H.; Guo, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Peng, L.; Fu, Z.-R. Long-term exposure to PM2.5 lowers influenza virus resistance via down-regulatingby downregulatingating pulmonary macrophage Kdm6a and mediates histones modification in IL-6 and IFN- promoter regions. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Wang, G.; Ho, K.F.; Han, J.; Dai, W.; Wu, C.; Cao, C.; Liu, L. In- vitro oxidative potential and inflammatory response of ambient PM2.5 in a rural region of Northwest China: Association with chemical compositions and source contribution. Environ. Res. 2022, 205, 112466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Kou, X.; Xie, L.; Cheng, F.; Geng, H. Effects of ambient PM2.5 on pathological injury, inflammation, oxidative stress, metabolic enzyme activity, and expression of c-fos and c-jun in lungs of rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 20167–20176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negash, M.; Tsegabrhan, H.; Meles, T.; Tadesse, D.B.; Gidey, G.; Berhane, Y.; Berhanu, K.; Haylemaryam, T. Determinants of Acute Asthma Attack among adult asthmatic patients visiting hospitals of Tigray, Ethiopia, 2019: Case control study. Asthma Res. Pract. 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, A.C.; Hebert, V.Y.; Cormier, S.A.; Subramanian, B.; Reed, J.R.; Backes, W.L.; Dugas, T.R. Particulate matter containing environmentally persistent free radicals induces AhR-dependent cytokine and reactive oxygen species production in human bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.G.; Morishita, M.; Keeler, G.J.; Harkema, J.R. Divergent effects of urban particulate air pollution on allergic airway responses in experimental asthma: A comparison of field exposure studies. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, C.; Ji, G.; Liu, H.; Shao, W.; Zhang, C.; Gu, A.; Zhao, P. Effect of exposure to ambient PM2.5 pollution on the risk of respiratory tract diseases: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Biomed. Res. 2017, 31, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Sun, M. Characteristics of PM2.5 and PM10 Spatio-Temporal Distribution and Influencing Meteorological Conditions in Beijing. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, M.; Balmes, J.R. Outdoor air pollution and asthma. Lancet 2014, 383, 1581–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.K.; Zhang, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Chung, K.F. Mechanistic impact of outdoor air pollution on asthma and allergic diseases. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmage, S.C.; Perret, J.L.; Custovic, A. Epidemiology of Asthma in Children and Adults. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Lin, X. Ozone Exposure and Asthma Attack in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 830897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, S.; Chung, K.F.; Adcock, I.M. Transcriptional Effects of Ozone and Impact on Airway Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Weinberger, K.R.; Nori-Sarma, A.; Spangler, K.R.; Sun, Y.; Dominici, F.; Wellenius, G.A. Ambient heat and risks of emergency department visits among adults in the United States: Time stratified case crossover study. BMJ 2021, 375, e065653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-K.; Chuang, C.-Y.; Li, M.-H.; Chou, C.-H.; Liao, C.-H.; Sung, F.-C. Associating Emergency room visits with first and prolonged extreme temperature event in Taiwan: A population-based cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 416, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, C.; Hu, W.; Turner, L.R.; Su, H.; Tong, S. Extreme temperatures and emergency department admissions for childhood asthma in Brisbane, Australia. Occup. Environ. Med. 2013, 70, 730–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, T.; Tokuda, Y.; Ohde, S.; Ishimatsu, S.; Nakamura, T.; Birrer, R.B. The relationship of short-term air pollution and weather to ED visits for asthma in Japan. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2009, 27, 153–159. (In Tokyo) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.L.; Wong, W.H.S.; Lau, Y.L. Association between air pollution and asthma admission among children in Hong Kong. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2006, 36, 1138–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Survey Results of Taiwanese Smoking Behavior. 2021. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=1718&pid=9913 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Lai, L.-W.; Lin, C.-Y. Influence of the Geographic Channel Effect on PM2.5 Concentrations over the Taipei Basin in Relation to Continental High-Pressure Systems during Winter. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-K.; Chang, C.-K.; Chang, S.-C.; Chen, P.-S.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.-C. Temperature, nitrogen dioxide, circulating respiratory viruses and acute upper respiratory infections among children in Taipei, Taiwan: A population-based study. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Air Pollution Guideline Values. 2022. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/345329/9789240034228-eng.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2022).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).