Abstract
The emergence of extensively drug-resistant (XDR) foodborne pathogens poses grave threats to food safety. This study characterizes the genome of an XDR Salmonella Kentucky isolate (Sal23C1) co-harboring cfr, mcr-1 and tet(A) from Shanghai chicken meat in 2022, which was the only isolate co-harboring these three key resistance genes among 502 screened Salmonella isolates. Genomic analysis revealed that the multidrug resistance gene cfr, which confers resistance to phenicols, lincosamides, oxazolidinones, pleuromutilins and streptogramin A, was identified within a Tn3-IS6-cfr-IS6 structure on the transferable plasmid p3Sal23C1 (32,387 bp), showing high similarity to the Citrobacter braakii plasmid pCE32-2 (99% coverage, 99.98% identity). Concurrently, the mcr-1 gene resided in a pap2-mcr-1 structure on the transferable IncI2 plasmid p2Sal23C1 (63,103 bp). Notably, both genes could be co-transferred to recipient bacteria via conjugative plasmids at frequencies of (1.15 ± 0.98) × 10−6. Furthermore, a novel ~79 kb multidrug resistance region (MRR) chromosomally inserted at the bcfH locus was identified, carrying fosA3, mph(A), rmtB, qnrS1 and blaCTX-M-55. Additionally, a novel Salmonella Genomic Island 1 variant (SGI1-KI) harbored aadA7, qacEΔ1, sul1 and the tet(A) variant. The acquisition of these antibiotic resistance genes in this isolate enhanced bacterial resistance to 21 antimicrobials, including resistance to the critical last-resort antibiotics tigecycline and colistin, which left virtually no treatment options for potential infections. Taken together, this is the first comprehensive genomic report of an XDR poultry-derived Salmonella Kentucky isolate co-harboring cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant. The mobility of these resistance genes, facilitated by IS6 elements and conjugative plasmids, underscores significant public health risks associated with such isolates in the food chain.
1. Introduction
Salmonella is a primary contributor to foodborne illness globally, affecting both developing and developed countries [1]. Annually, this pathogen is estimated to cause approximately 93.8 million human infections and 155,000 deaths worldwide, underscoring its status as a critical public health challenge [2]. Human salmonellosis typically results from consuming contaminated foods, with poultry, pork and eggs frequently implicated as major sources [2,3,4].
Antimicrobials are widely administered for therapeutic purposes in humans and within food animal production systems [5]. However, evidence indicates that antimicrobial use in food animals promotes the emergence of resistance in Salmonella strains transmitted through food [5,6]. Notably, previous research has consistently identified multidrug-resistant (MDR) isolates of Salmonella Kentucky (S. Kentucky) [7,8]. Recently, the trajectory of MDR development in significant bacterial pathogens, including Escherichia coli (E. coli), Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae), Acinetobacter baumannii, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, shows a progression towards extensively drug-resistant (XDR) profiles [9,10,11]. According to definitions established by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (US CDC) and the European CDC, XDR refers to isolates resistant to at least one agent in all but two or fewer antimicrobial categories [12]. The presence of XDR bacteria has become an emerging concern, with detections reported in multiple nations such as China, Bangladesh, Egypt, Italy and Pakistan in recent years [8,10,11,13,14,15].
Colistin and tigecycline are critical last-resort antibiotics for treating serious infections caused by XDR Gram-negative pathogens, particularly carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter [16,17]. However, escalating resistance to both agents in Enterobacteriaceae is now evident [16,18], creating a therapeutic crisis for invasive XDR infections. In Salmonella, antibiotic resistance typically develops through chromosomal mutations or via lateral genetic exchange mediated by mobile genetic elements (MGEs) like plasmids and transposons (Tns), which can sometimes originate from other bacteria [19]. Among known resistance determinants, the cfr, mcr-1 and tet(A) variant genes are particularly significant due to their ability to confer resistance to crucial last-resort agents, including colistin and tigecycline [15,16,20].
Functionally, the cfr gene encodes an rRNA methyltransferase conferring cross-resistance to five antimicrobial classes: streptogramin A, pleuromutilins, oxazolidinones, lincosamides and phenicols, while also reducing the efficacy of 16-membered macrolides [20]. Initially identified on the plasmid pSCFS1 in Staphylococcus sciuri, cfr has since disseminated widely via plasmids/MGEs across diverse Gram-positive and Gram-negative genera [21,22]. In parallel, mcr-1 encodes a phosphoethanolamine transferase mediating plasmid-borne colistin resistance. Since its 2015 discovery, mcr-1 has spread globally (>40 countries), with ten variants (mcr-1 to mcr-10) identified in diverse sources [23,24]. Its plasmid association facilitates inter-species spread. Detection is more common in animal-derived isolates than human clinical samples, likely reflecting exposure differences [24,25,26]. As far as we know, only one report describes chromosomal mcr-1 in S. Kentucky from chicken, and plasmid carriage in Salmonella remains unreported [27]. Distinctly, the tet(A) variant is an intrinsic efflux pump conferring tigecycline resistance in K. pneumoniae and Salmonella, often synergizing with ramA mutations [27,28]. It typically causes low-level resistance and is found on plasmids or chromosomally within SGI1, enabling both horizontal transfer and vertical inheritance.
Previous investigations identified retail food as a major reservoir of Salmonella in China, with most food-derived isolates exhibiting high antibiotic resistance [3,4]. To elucidate the mechanisms driving XDR in these isolates, we screened 502 Salmonella isolates from Shanghai food samples for key antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) (cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant). Notably, a food-associated isolate, Sal23C1, was found to exhibit an XDR profile co-harboring all three genes. This study provides an in-depth characterization of Sal23C1, including antimicrobial susceptibility profiling, the evaluation of the cfr and mcr-1 gene transfer potential, and molecular analysis via whole genome sequencing (WGS).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates
From January 2020 to January 2023, a total of 502 Salmonella isolates were collected from retail food samples from retail markets and supermarkets in Shanghai, China. The food types included pork (n = 170), poultry (n = 163), beef (n = 60), lamb (n = 40), shrimp (n = 15), roast meat (n = 12), freshwater fish (n = 9), steamed buns (n = 8), frozen dumplings (n = 6), sushi (n = 5), fried rice (n = 2), and cold vegetable dishes (n = 2). Salmonella isolation was performed using a modified adaptation of the ISO 6579-1:2017 protocol [29]. Briefly, each sample was aseptically collected, placed in a sterile bag, and transported to the laboratory under refrigeration (4–8 °C) within 8 h. For processing, 25 g of each sample was homogenized with 225 mL of buffered peptone water (Huankai, Guangzhou, China) and incubated at 37 ± 1 °C with shaking (160 rpm) for 4 h. Then, 1 mL of the pre-enrichment culture was transferred to 9 mL of tetrathionate broth (Huankai, China) and incubated at 42 °C. After enrichment, a loopful of culture was streaked onto xylose lysine tergitol 4 agar (XLT-4; Huankai, China). Presumptive Salmonella colonies were subcultured on CHROMagar™ Salmonella plates (CHROMagar, La Plaine St. Denis, France) and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Salmonella identification was initially based on key biochemical characteristics, including H2S production, anaerobic glucose fermentation without gas production, and urease negativity. Further confirmation was conducted using API 20E test strips (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France), a commercial identification system for Enterobacteriaceae. The verified isolates were subsequently subcultured on Luria–Bertani agar and genetically confirmed through PCR targeting the invA gene with specific primers (invA-F: CTTGATTGAAGCCGATGCCG; invA-R: TCATCGCACCGTCAAAGGAA). The identification of the serotype was performed through standardized biochemical assays and commercial antisera (Statens Serum Institute, København, Denmark) following manufacturer protocols [30].
2.2. Polymerase Chain Reaction and DNA Sequencing of ARGs
Total genomic DNA from overnight cultures of Salmonella was isolated with the TIANamp Bacteria DNA Kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). In brief, bacterial cells from 1–2 mL of culture were pelleted by centrifugation (10,000 rpm, 2 min). The pellet was resuspended in 200 μL of Buffer GA, treated with 20 μL of Proteinase K and 220 μL of Buffer GB, mixed, and incubated at 70 °C for 10 min until lysate clarification. After adding 220 μL of ethanol, the mixture was transferred to a CB3 spin column and centrifuged (10,000 rpm, 30 s). The column was washed once with 500 μL of Buffer GD and twice with 600 μL of Buffer PW, with each wash step followed by a 30 s spin. After a final 2 min centrifugation and air-drying for 2–5 min, the DNA was eluted using 50–100 μL of Buffer TE. The DNA quality and concentration were determined via NanoDrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The detection of the ARGs cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant in the collected isolates was performed using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The primer sequences utilized were as follows: for the cfr gene, forward primer cfr-F: GTGAAGCTCTAGCCAACCGTC and reverse primer cfr-R: GCAGCGTCAATATCAATCCC; for the mcr-1 gene, forward primer mcr-1-F: GCAACCAAGCCTGATATGCG and reverse primer mcr-1-R: CGCTTAAAATACGCAGGCCC; and for the tet(A) variant gene, forward primer tet(A)-F: TCTGGTTCACTCGAACGACG and reverse primer tet(A)-R: AGCCCGTCAGGAAATTGAGG. Positive PCR amplicons were sent to Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) for sequencing confirmation. Isolates found to co-harbor all three ARGs (cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant) are referred to as CMT isolates.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of CMT Isolates
The Salmonella isolate Sal23C1 was identified as a CMT isolate, co-harboring the ARGs cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant. The antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Sal23C1 was performed using agar dilution and broth microdilution methods according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI; 2023) guidelines [31]. The agar dilution method was applied to the following antibiotics at the indicated concentration ranges: sulfisoxazole (16–2048 mg/L), trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole (0.5/9.5–16/304 mg/L), nalidixic acid (8–128 mg/L), ofloxacin (0.5–32 mg/L), ciprofloxacin (0.06–8 mg/L), ampicillin (4–128 mg/L), amoxicillin–clavulanic acid (4/2–128/64 mg/L), cefotaxime (1–64 mg/L), cefepime (1–64 mg/L), tetracycline (4–128 mg/L), chloramphenicol (8–128 mg/L), florfenicol (4–128 mg/L), streptomycin (8–512 mg/L), gentamicin (2–64 mg/L), amikacin (4–256 mg/L), kanamycin (8–256 mg/L), rifampin (4–128 mg/L), azithromycin (4–128 mg/L), fosfomycin (16–512 mg/L) and meropenem (0.06–16 mg/L). For tigecycline and colistin, the MICs were determined using the broth microdilution method. All the antibiotics used in this study were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA). The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined following CLSI (2023) standards [31], with Enterococcus faecalis 29,212 and E. coli 25,922 serving as quality control strains.
2.4. Whole Genome Sequencing and Analysis of the CMT Isolate
The raw sequence reads from the Salmonella isolate Sal23C1 were assembled de novo using the PacBio RS II Analysis system via the HGAP assembler. Leveraging the hierarchical strategy of HGAP along with PacBio long-read sequencing, this approach enabled the production of highly accurate and contiguous genome assemblies—essential for achieving complete genomic sequences. Genomic characterization was subsequently conducted using bioinformatic tools hosted by the Center for Genomic Epidemiology (https://www.genomicepidemiology.org/, accessed on 7 August 2025). Specifically, PlasmidFinder 2.1 (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/PlasmidFinder/, accessed on 7 August 2025) was used to identify plasmid replicons, ResFinder 4.1 (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/ResFinder/, accessed on 7 August 2025) was used to detect antimicrobial resistance genes, and MLST 2.0 (https://cge.food.dtu.dk/services/MLST/, accessed on 7 August 2025) was used to determine the multi-locus sequence type (MLST). The serotype was predicted using SeqSero2 v1.2.1 (http://www.denglab.info/SeqSero2) [32]. Insertion sequence (IS) elements were identified by querying the ISFinder database (https://isfinder.biotoul.fr/about.php, accessed on 7 August 2025).
2.5. Conjugation Transfer Assay
To assess the transferability of the cfr and mcr-1 genes from the Salmonella isolate Sal23C1, conjugation experiments were performed using rifampin-resistant E. coli J53 as the recipient strain and Sal23C1 as the donor. Selective conditions were established based on differential antibiotic susceptibility: Sal23C1 exhibited no growth on LB agar supplemented with 200 mg/L rifampin, while E. coli J53 failed to proliferate on plates containing 2 mg/L colistin plus 16 mg/L florfenicol. The donor and recipient cultures were separately incubated in LB broth with shaking (37 °C, 4–6 h). Subsequently, 1 mL aliquots were centrifuged, and the cell pellets were resuspended, mixed at a 1:1 ratio, and then spot-plated onto LB agar for overnight mating at 37 °C. Following overnight mating at 37 °C, the conjugation mixture underwent serial dilution in phosphate-buffered saline before plating onto triple-antibiotic selection plates (200 mg/L rifampin, 16 mg/L florfenicol, 2 mg/L colistin). The plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24–48 h. Putative transconjugants appearing as single colonies were PCR-verified to exclude false-positive candidates. We calculated the transfer frequency as the number of transconjugants per donor and express the conjugation efficiency as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments.
2.6. Phylogenetic Tree Analysis of the S. Kentucky Isolates and IncI2 Plasmids Harboring the mcr-1 Gene
To investigate the phylogenetic relationships among mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky isolates, we performed core genome phylogeny using the kSNP4.1 pipeline [33]. This analysis incorporated the study isolate Sal23C1 alongside fourteen S. Kentucky genomes acquired from public repositories (NCBI and Enterobase). In parallel, we constructed a comparative phylogeny for mcr-1-positive IncI2 plasmids, integrating one plasmid identified herein with fifteen publicly available NCBI plasmid sequences. All the resulting phylogenetic trees were visualized using the iTOL v6 platform (https://itol.embl.de, accessed on 7 August 2025). Detailed in Supplementary File S1 (‘Isolates and plasmids for phylogenetic analysis’) is a complete inventory of the bacterial isolates and plasmids employed for this study’s phylogenetic examination.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phenotypic Characteristics and Antibiotic Resistance Determinants of Isolate Sal23C1
The PCR screening of 502 Salmonella isolates from retail foods revealed varied prevalence of key resistance genes. The tet(A) variant was the most prevalent, detected in 124 isolates (24.7%), followed by mcr-1, which was present in 7 isolates (1.4%). The cfr gene was the rarest, identified in only one isolate (0.2%). Notably, a single isolate (0.2%), designated Sal23C1 and collected from retail chicken meat in Shanghai in 2022, was found to co-harbor all three genes—cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant. Serotyping and MLST analysis confirmed this isolate Sal23C1 as S. Kentucky ST198. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed that Sal23C1 exhibited simultaneous resistance to a broad spectrum of agents, including tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, nalidixic acid, cefepime, ampicillin, cefotaxime, amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, streptomycin, gentamicin, amikacin, kanamycin, chloramphenicol, florfenicol, azithromycin, fosfomycin, sulfisoxazole, rifampicin and trimethoprim–sulfamethoxazole. This profile meets XDR criteria according to contemporary ECDC/US CDC definitions [12]. Critically, this isolate Sal23C1 also exhibited resistance to the last-line agents colistin and tigecycline, while demonstrating susceptibility only to meropenem among all the tested antibiotics (Table 1).

Table 1.
Antimicrobial susceptibility, conjugation rate and whole genome analysis of isolate Sal23C1 collected in this study.
The assembly of the total reads resulted in four contigs with a total length of 5,079,104 bp and an N50 of 4,889,727, achieving a genome coverage of 250×. The WGS showed that the complete genome of Sal23C1 (GenBank PRJNA1303235) comprises one chromosome and three plasmid replicons, which include the chromosome (Sal23C1, 4,889,727 bp, GC 52.2%), IncI (p1Sal23C1, 93,887 bp), IncI2 (p2Sal23C1mcr, 63,103 bp) and one novel type (p3Sal23C1cfr, 32,387 bp). Genomic analysis identified 20 known ARGs (Table 1), consistent with the phenotypic resistance profile. These included genes conferring resistance to chloramphenicols (cfr, floR); colistin (mcr-1); beta-lactams (blaCTX-M-55, blaTEM-1B); rifamycin (arr-2); fluoroquinolones (qnrS1); aminoglycosides (rmtB, aac(3)-IId, aac(6′)-Iaa, aadA7, aadA17, aph(3′)-Ia); tetracyclines (tet(A) variant); folate pathway antagonists (sul1, dfrA14); lincosamides (lnu(F)); fosfomycins (fosA3); macrolides (mph(A)); and quaternary ammonium compounds (qacEdelta1). Additionally, three mutations in the Quinolone Resistance-Determining Region (QRDR) were identified in the chromosome: parC (S80I) and gyrA (D80N and S83F), known to confer quinolone resistance. This genetic basis fully explains the observed XDR phenotype.
Our findings demonstrated the presence of XDR profiles in the Salmonella isolate Sal23C1 collected from retail chicken meat, suggesting a potential animal origin transmitted via the food supply chain, which was aligned with reports of XDR Salmonella in animals and patients [34]. More importantly, colistin and tigecycline are regarded as antibiotics of last resort for treating serious clinical infections caused by XDR Gram-negative organisms, particularly carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and Acinetobacter isolates [16,17]. However, the emergence and spread of plasmid-mediated resistance genes like mcr (mediated resistance to colistin) or tet(A) variants (mediated resistance to tigecycline) significantly impair the therapeutic efficacy of these agents [15,16]. Critically, the co-occurrence of cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant in Sal23C1, marking the first report of these specific genes together in Salmonella, directly compromises both colistin and tigecycline. This leaves tigecycline and colistin ineffective, leaving meropenem as the sole tested effective agent for treating potential invasive infections caused by such isolates, creating a critical therapeutic crisis. In addition, the cfr gene provides cross-resistance to multiple classes (streptogramin A, pleuromutilins, oxazolidinones, lincosamides, phenicols) [20]. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) are key β-lactam resistance mechanisms; the co-existence of blaCTX-M-55 (a CTX-M-15 variant with enhanced cephalosporin hydrolysis due to A80V) and blaTEM-1B in Sal23C1 significantly contributes to its β-lactam resistance [35]. The acquired fosA3 confers high-level fosfomycin resistance, previously seen in animal-source Salmonella and human gastroenteritis cases [36]. Furthermore, it was found that the Salmonella isolates exhibited resistance to nalidixic acid when they carried only the gyrA/parC mutations. Our research indicates that the presence of qnrS1 with gyrA/parC mutations enhances resistance to ciprofloxacin, which is observed in Salmonella (≥8 μg/mL) [35].
The emergence of the colistin–tigecycline-XDR S. Kentucky ST198 in retail chicken meat highlights the critical need for comprehensive intervention strategies within poultry production systems to curb the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance. The extensive arsenal of ARGs, such as mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant, grants strains like Sal23C1 their challenging resistance profile. Alarmingly, antibiotic candidates under development for WHO critical-priority pathogens show concerning cross-resistance rates with existing agents, particularly against such isolates [37]. This underscores the urgent need to elucidate the genomic characteristics of these strains and understand the mechanisms enabling such devastating resistance combinations. To address this threat, antibiotic stewardship programs must be rigorously implemented to reduce the non-therapeutic use of critically important antibiotics, including colistin and tigecycline, in animal husbandry. Restrictions on these agents could mitigate the selective pressure driving the acquisition and spread of resistance genes. Enhanced biosecurity measures are also essential to prevent the introduction and transmission of resistant pathogens within farms. These include strict sanitation protocols, controlled access to poultry houses, and the use of protective clothing and equipment to minimize cross-contamination. Vaccination programs against Salmonella and the use of probiotics or prebiotics to promote gut health may further reduce reliance on antibiotics. Furthermore, continuous surveillance of antimicrobial resistance in both animals and food products, coupled with whole genome sequencing, is vital to track resistance trends and identify emerging threats early. The integration of these strategies within a One Health framework is crucial to effectively combat the spread of XDR pathogens from poultry to humans through the food chain.
3.2. Phylogenetic Relationship of mcr-1-Positive S. Kentucky Isolates and IncI2 Plasmids
To investigate the global relatedness of the mcr-1-positive isolate identified in this study among other mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky strains, we performed phylogenetic analysis on 15 isolates (our isolate plus 14 mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky isolates sourced from NCBI and Enterobase). This analysis assessed clonal relationships (Figure 1A). Our findings indicate that mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky ST198 has been collected from various reservoirs, including humans, animals and food. These isolates grouped into distinct subclades I and II. Notably, within subclade II, isolates derived from humans, pork and poultry in countries such as Morocco, the UK, China and France clustered together, including the isolate from this study. The short branch lengths (scale bar < 0.1) observed among subclade II isolates suggest a close genetic link, despite their diverse geographical and source origins. Specifically, our isolate (Sal23C1) showed the closest phylogenetic affinity to two Chinese pork-derived isolates (Sal_P23040 and Sal_P23041) and a French clinical human isolate (traces-0lhyZjN). Consistent with their phylogenetic relatedness, all 15 mcr-1-positive isolates shared resistance determinants for sulfonamides (sul1) and quinolones (gyrA(S83F) and parC(S80I)), which were universally present (100%). Additionally, the tetracycline resistance gene tet(A) was detected in 14 isolates (93.3%), and blaTEM-1B in 12 isolates (80.0%). Importantly, blaCTX-M-55 and qnrS1 were uniquely identified in isolates originating from China. These results suggest the food chain as a potential transmission route for mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky within China.
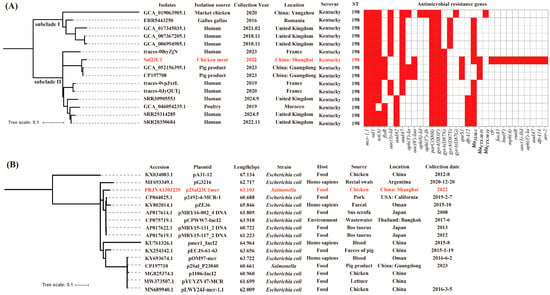
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic relationship of mcr-1-positive Salmonella Kentucky isolates and IncI2 plasmids. (A). Phylogenetic analysis of 15 mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky isolates. This analysis included 14 isolates sourced from NCBI and EnteroBase, plus the isolate sequenced in this study (Sal23C1, highlighted in red). The figure presents the basic isolate information and the presence of antimicrobial resistance genes (indicated in red). (B). Phylogenetic analysis of 16 IncI2 plasmids harboring the mcr-1 gene. This analysis included 15 plasmids sourced from NCBI, plus the plasmid sequenced in this study (p2Sal23C1mcr, highlighted in red).
Concurrently, phylogenetic analysis of 16 mcr-1-harboring IncI2 plasmids (Figure 1B) revealed considerable diversity and multiple branches among plasmids obtained from diverse sources (e.g., humans, food) in different countries (e.g., China, Thailand, Oman, Argentina). A significant observation was the close clustering of the plasmid p2492-4-MCR-1 (CP044025.1, 60,688 bp), originating from US pork, with the plasmid p2SalC1mcr identified in the current study.
Salmonella demonstrates broad host adaptability, capable of infecting a wide range of animal species, including mammals, birds and insects [38]. Consequently, these broad-host-range isolates can be disseminated via animal feces or through the food chain [38]. A phylogenomic comparison of the isolates characterized here with all the available mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky sequences from food, human and environmental sources confirmed their close relatedness, forming a distinct cluster alongside a human isolate from France. Furthermore, the minimal genetic divergence observed in the phylogenetic branches aligns with the consistent ST198 assignment. Although in vivo transmission experiments were not performed to definitively trace pathways, these results indicate phylogenetic proximity between chicken-derived and human S. Kentucky ST198 isolates. This supports the potential for chicken to act as a significant vector for mcr-1-positive S. Kentucky ST198 transmission. Enhanced surveillance efforts should therefore prioritize monitoring the IncI2 plasmid-mediated dissemination of mcr-1 within this lineage.
3.3. Molecular Characteristics of the Multidrug Resistance Region and Salmonella Genomic Island 1
Genomic analysis revealed a chromosome length of 4,889,727 bp and a GC content of 52.2% in the studied isolate. Of the 20 identified ARGs, eighteen resided within the multidrug resistance region (MRR) and the novel Salmonella Genomic Island 1 variant (designated SGI1-KI) on the chromosome, while only mcr-1 and cfr were located in plasmids. Notably, the insertion of the MRR disrupted the open reading frame (ORF) of the bcfH gene in this ST198 isolate Sal23C1, contrasting with the intact bcfH observed in ST314 clade reference genomes (e.g., GCF_002952975.1) (Figure 2A). Given that Sal23C1 was collected from chicken meat and that the role of the bovine colonization factor (bcf) fimbriae in avian intestinal colonization is minimal, the disruption of bcfH by the MRR insertion may confer a significant survival advantage through enhanced antibiotic resistance without substantially compromising fitness in its primary reservoir host [39,40].
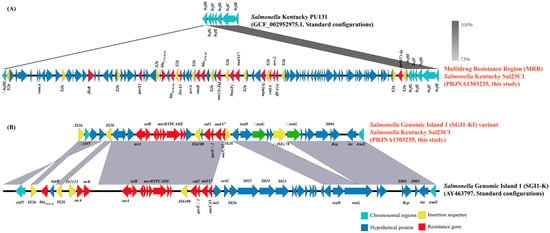
Figure 2.
Molecular characteristics of the multidrug resistance region and Salmonella Genomic Island 1. (A). Comparative analysis of the genetic structure of the multidrug resistance region (MRR) inserted within the bcfH gene in S. Kentucky ST198 isolate. Chromosomal genes are indicated in light blue, insertion sequences (IS) in yellow, and resistance genes in red. (B). Comparative analysis of the genetic structure of the Salmonella Genomic Island 1 (SGI1) variant inserted downstream of the trmE gene in S. Kentucky ST198 isolates, aligned against the reference SGI1 sequence (AY463797). Resistance genes are shown in red, and insertion sequences (IS) in yellow. Regions of sequence similarity identified by BLASTn are indicated by gray shading.
This study identified a chromosome-localized qnrS1 gene, differing from its typical location on IncHI2 plasmids [41]. This chromosomal integration likely promotes qnrS1′s stable persistence within the S. Kentucky isolate Sal23C1. Additionally, mutations in parC (S80I) and gyrA (S83F, D87N) were detected. As depicted in Figure 2A, blaCTX-M-55 was situated within an ~79 kb MRR positioned downstream of the bcfBCDEFG gene cluster. The MRR, flanked by IS26 elements integrated into bcfH, contained multiple ARGs with the following structure—IS26-IS26-floR-IS26-qnrS1-IS26-blaCTX-M-55-blaTEM-1-IS26-fosA3-IS26-rmtB-blaTEM-1-IS26-aac(3)-IId-IS26-lnu(F)-aadA17-IS26-mph(A)-IS26-cmlA-arrr-2-dfrA14-IS26-IS26-aph(3′)-Ia-IS26)—conferring resistance to multiple antimicrobials, including ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, cefepime, cefotaxime, amoxicillin–clavulanic acid, amikacin, azithromycin and fosfomycin.
The integration of the MRR into the bcfH locus, resulting in its disruption, may enhance S. Kentucky ST198 survival. Given that ARGs in Salmonella often emerge from selective pressures associated with antibiotic use in animal agriculture and veterinary medicine [42], the MRR-mediated antibiotic resistance likely provides a significant survival advantage in intensive antibiotic environments. Although the fim operon is the most highly expressed Salmonella fimbrial operon, bcf expression is specifically induced within the bovine ileum [43] and its role in avian intestinal colonization is minimal [44].
Analysis confirmed the presence of the SGI1-KI in this isolate and, upon comparison with the traditional SGI1-K structure (reference AY463797), identified it as a distinct variant (Figure 2B). SGI1-KI retained the genes accCA5, aadA7, qacEΔ1 and sul1 and the tet(A) variant, but lacked tnpR, the segment between S023 and resG, IS1133, strAB, and the blaTEM-1b genes [45]. The ST198 isolate Sal23C1 harbored a novel SGI1-K variant incorporating a mercury resistance module. Structural comparisons with the SGI1-K prototype confirmed specific deletions (tnpR, S023-resG segment, IS1133, strAB, blaTEM-1b) [45]. These alterations indicate rapid intraclonal evolution, differing from patterns in other isolates and potentially reflecting localized selection pressures. Previous reports describe SGI1-K in S. Kentucky ST198 as highly mosaic, with IS26-mediated gene acquisitions or losses generating extensive structural diversity [46]. This inherent genomic flexibility within SGI1-K likely confers adaptive advantages to this high-risk clone. The acquisition of extensive resistance determinants, particularly through large genomic insertions like the MRR that disrupt native genes (e.g., bcfH), can potentially impose a fitness cost on the bacterial host in the absence of antibiotic selection. However, the global dissemination and persistence of XDR S. Kentucky ST198 clones suggest that any such costs are effectively mitigated. The chromosomal integration of key resistance genes within stable genetic platforms (MRR, SGI1-KI) enhances their persistence compared to plasmid-borne genes, which may be lost more readily. Furthermore, the observed genomic rearrangements and deletions may themselves represent compensatory evolution that reduces the metabolic burden. The formidable survival advantage provided by multidrug resistance in environments with high antibiotic selective pressure appears to far outweigh any potential fitness defects, enabling the successful clonal expansion and spread of this high-risk lineage with minimal trade-offs.
3.4. Genomic Characteristics of cfr-Positive Plasmid p3Sal23C1cfr
The isolate Sal23C1 harbored three distinct replicons: an IncI plasmid (p1Sal23C1, 93,887 bp), an IncI2 plasmid (p2Sal23C1mcr, 63,103 bp) and a novel plasmid type (p3Sal23C1cfr, 32,387 bp) carrying the cfr gene. The cfr-positive plasmid, designated p3Sal23C1, had a total length of 32,387 bp and a GC content of 45.7% (Figure 3A). Comparative analysis revealed that p3Sal23C1 exhibits high similarity (96–100% query coverage; 99.9–100.0% nucleotide identity) to known cfr-carrying plasmids from Citrobacter braakii (CP138572.1), Salmonella (CP116020.1) and E. coli (KR779901.1, KP324830.1). The closest match was plasmid pCE32-2 (CP138572.1), with 99% coverage and 99.98% identity, although a 344 bp size difference was noted, and the orientation of the cfr gene was reversed in p3Sal23C1.
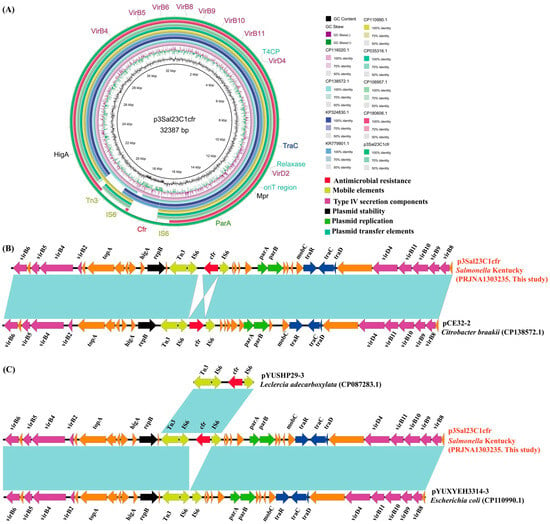
Figure 3.
Sequence alignment of plasmid p3Sal23C1cfr and the gene environment of the cfr gene. (A) Comparison of the circular plasmid sequence between plasmids p3Sal23C1cfr, KR779901.1, KP324830.1, CP106957.1, CP180606.1, CP110990.1, CP035316.1, CP138572.1 and CP116020.1 of Escherichia coli strains (n = 6), Citrobacter braakii strain (n = 1) and Salmonella strain (n = 1). (B) Linear comparison of the plasmid sequences of Salmonella p3Sal23C1cfr and Citrobacter braakii (CP138572.1) pCE32-2. (C) Linear comparison of the plasmid sequences between plasmids p3Sal23C1cfr (Salmonella), pYUSHP29-3 (Leclercia adecarboxylata, CP087283.1) and pYUXYEH3314-3 (Escherichia coli, CP110990.1). Open arrows indicate coding sequences.
Collinearity assessment indicated that p3Sal23C1 shares an identical plasmid backbone (95% coverage, 100.0% identity) with plasmid pYUXYEH3314-3 (CP110990.1) from E. coli. However, p3Sal23C1 contained an additional 1406 bp segment (Figure 3B). This region comprises the cfr-associated module. Blastn analysis demonstrated that the structure IS6-cfr-IS6-Tn3 within this module is consistent with that found in the plasmid pYUSHP29-3 (CP087283.1) from Leclercia adecarboxylata. Notably, IS6-like elements (IS15 family transposases) flank the cfr gene in the same orientation, suggesting the potential for mobilization via IS elements to form translocatable cfr-carrying units, thereby enabling the spread of linezolid resistance. The plasmid p3Sal23C1cfr encodes proteins associated with conjugative transfer functions (including traC, traD, traR, origin of transfer (oriT) region, a type IV secretion system (T4SS) cluster, and type IV coupling protein (T4CP) genes) alongside plasmid partitioning genes (parA and parB).
The multiple resistance gene cfr was first identified in a bovine Staphylococcus sciuri isolate from Germany in 2000, with the first human clinical case reported in an MRSA isolate from Colombia in 2005 [21,47]. Our study identifies a cfr-carrying Salmonella isolate originating from chicken meat in 2022. This finding also highlights foodborne Salmonella as a significant reservoir for the cfr gene. To our knowledge, this represents the first documented instance of a cfr-harboring plasmid within Salmonella derived from chicken meat. Although cfr was initially and remains predominantly detected in Gram-positive bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus capitis, its increasing identification in Gram-negative species is an alarming trend demanding vigilance [22,48,49].
3.5. Genomic Characteristics of mcr-1-Positive Plasmid p2Sal23C1mcr
The colistin resistance gene mcr-1 was identified on the IncI2 plasmid p2Sal23C1mcr. This plasmid measures 63,103 bp in length and has a GC content of 42.7%. The IncI2 plasmids from the S. Kentucky isolate p2Sal23C1mcr encode key components essential for conjugative transfer, including an oriT region, a T4SS cluster and T4CP genes. Comparative genomic analysis (Figure 4A) revealed significant similarity between p2Sal23C1mcr and known mcr-1-harboring IncI2 plasmids from E. coli (accessions: KX034083.1, MF693349.1, CP044025.1, KY802014.1, APO17614.1, CP075719.1, APO17622.1, APO17619.1, KU761326.1, KX254342.1, KY693674.1, MG825374.1, MW373507.1 and MN689940.1) and Salmonella (plasmid p2Sal_P23040), exhibiting 87–95% query coverage and 98.8–99.9% nucleotide identity. Among these, the plasmid pECJS-61-63 (KX254342.1) from E. coli showed the closest resemblance (95% coverage, 99.8% identity). Notably, the majority of these IncI2 plasmids solely carry the mcr-1 resistance gene. Consistent with typical mcr-1 organization, the gene’s coding sequence is invariably positioned immediately upstream of an open reading frame encoding a PAP2 family protein (Figure 4B). The analysis of specific plasmids (AP017614.1, AP017619.1, AP017622.1, CP075719.1, KX034083.1) detected the complete ISApl1 element downstream of the mcr-1 cassette.

Figure 4.
Comparative analysis of complete mcr-1-positive IncI2 plasmids. (A) Comparative visualization of 16 complete mcr-1-positive IncI2 plasmids using BRIG. The outermost ring depicts the plasmid AP017614.1 as the reference. Genes are color-coded by function. Horizontal transfer-associated genes are indicated: T4CP (blue) and T4SS clusters (green). The antimicrobial resistance gene mcr-1 is shown in red. (B) Comparison of the mcr-1 genetic context across all plasmids. All plasmids carry the pap2-mcr-1 unit. Notably, plasmids AP017614.1, AP017619.1, AP017622.1, CP075719.1 and KX034083.1 contain the transposon ISApl1 upstream of this unit, while the remainder lack ISApl1.
Research classifies the genetic environment of mcr-1 into four primary structural types [50]. The most prevalent configuration is Tn6330, a 2609 bp composite transposon containing the mcr-1 gene adjacent to a 765 bp ORF predicted to encode a PAP2 superfamily protein. Tn6330 is typically bounded by two copies of ISApl1, an IS30 family insertion sequence [51]. In contrast, the mcr-1-positive isolate examined here exhibited an mcr-1-pap2 structure lacking flanking ISApl1 elements. This absence points to potential recombination-mediated excision of ISApl1 from the mcr-1 locus during the isolate’s evolution. Such structural simplification aligns with prior findings suggesting that ISApl1 loss may enhance the stability and persistence of mcr-1 within plasmid vectors, thereby facilitating wider dissemination of this critical resistance determinant [52]. Consequently, a deeper understanding of mcr-1 transmission dynamics necessitates further investigation into its precise transposition mechanisms and evolutionary history.
3.6. Conjugation Transfer of Plasmids Carrying mcr-1 and cfr
Conjugation experiments were performed to evaluate the transferability of the plasmids p2Sal23C1mcr (carrying mcr-1) and p3Sal23C1cfr (carrying cfr) from the donor isolate. The resulting transconjugants grew normally on these selective plates. PCR analysis confirmed that these transconjugants harbored both the cfr and mcr-1 genes, indicating successful co-transfer of the respective plasmids from the donor to the E. coli J53 recipient. The conjugation frequency was (1.15 ± 0.98) × 10−6. This frequency range indicates that the plasmids are transferable at detectable and biologically relevant rates.
Genetic characterization revealed that both of the plasmids p2Sal23C1mcr and p3Sal23C1cfr harbored intact conjugative modules, including functional oriT, T4SS clusters, and T4CP genes. This finding is consistent with previous research [53], which demonstrated that such modules enable efficient horizontal plasmid transfer between bacterial strains. These conserved genetic elements provide a mechanistic basis for the observed experimental plasmid transfer.
Plasmids are primary vectors for the horizontal dissemination of resistance genes like cfr and mcr-1. The cfr gene has been identified on diverse plasmid types (e.g., pSCFS-like, pBS-like, pSS-like, p004-737×, pERGB, pMSA16), frequently co-harboring additional resistance determinants [22,48]. Similarly, mcr-1 is commonly associated with plasmids (IncX4, IncI2, IncHI2, IncA, IncI1, IncX1), which also often carry multiple resistance genes [3,16,24,25]. The presence of transferable multi-resistance plasmids harboring cfr and mcr-1 significantly expands the antibiotic resistance spectrum, intensifies co-selective pressures, and promotes the widespread dissemination of these critical resistance genes within foodborne Salmonella [3,54]. This poses a substantial threat to food safety and public health. Consistent with this pattern, our study confirmed the plasmid localization of cfr and mcr-1, underscoring the pivotal role of plasmids as vectors of resistance dissemination in Salmonella.
4. Conclusions
This study reports the first detection of a cfr-producing, colistin- and tigecycline-resistant and XDR S. Kentucky ST198 isolate from retail chicken meat, which is a highly concerning finding. Multiple acquired ARGs were identified in the MRR, SGI1-KI and plasmids within this isolate. Critically, the mcr-1 and cfr genes reside on transferable plasmids, facilitating their dissemination across bacterial species. The acquisition of these ARGs confers an XDR phenotype, enabling the pathogen to persist and spread under diverse antibiotic selection pressures, ultimately accelerating the selection of resistant isolates. The convergence of resistance to last-resort antibiotics, mediated by cfr, mcr-1 and the tet(A) variant, within this single, globally disseminated, high-risk clone (S. Kentucky ST198), facilitated by mobile genetic elements, represents an extreme public health threat. In light of these findings, it is imperative to implement comprehensive intervention strategies within poultry production systems to curb the dissemination of such high-risk resistant bacteria. Antibiotic stewardship programs that enforce the responsible use of antimicrobials—including restrictions on non-therapeutic applications and the prohibition of using critically important antibiotics for growth promotion—are essential to reduce the selective pressure for resistance development. Additionally, enhanced biosecurity measures should be adopted to prevent the introduction and spread of pathogens within farms. These include strict access control, sanitation protocols, effective waste management, and rodent and insect control. Integrated surveillance of antimicrobial resistance across the farm-to-fork continuum should be strengthened, coupled with periodic training of farmers and veterinarians on appropriate antibiotic use and infection prevention practices. Without such multidimensional interventions, the continued emergence and spread of pan-resistant pathogens in the food chain may become increasingly common, posing severe risks to public health.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/foods14173025/s1. File S1. Isolates and plasmids used for the phylogenetic analysis.
Author Contributions
Z.Z.: Methodology, investigation, and writing—original draft preparation. Z.M.: Review and editing. M.H.: Conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, and review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.32402259 and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant number 2023M742281).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article or supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zizza, A.; Fallucca, A.; Guido, M.; Restivo, V.; Roveta, M.; Trucchi, C. Foodborne infections and Salmonella: Current primary prevention tools and future perspectives. Vaccines 2024, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Kumar, S.; Jangid, H.; Dutta, J.; Shidiki, A. The rise of non-typhoidal Salmonella: An emerging global public health concern. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1524287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.; He, S.; Chang, J.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Shi, X. Characterization of novel mutations involved in the development of resistance to colistin in Salmonella isolates from retail pork in Shanghai, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2025, 430, 111027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; He, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, M.; Chang, J.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Shi, X. Contribution of Novel Substitutions in PmrAB to the Development of Resistance to Colistin in mcr-Negative Salmonella Isolates. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Odey, T.O.J.; Tanimowo, W.O.; Afolabi, K.O.; Jahid, I.K.; Reuben, R.C. Antimicrobial use and resistance in food animal production: Food safety and associated concerns in Sub-Saharan Africa. Int. Microbiol. 2024, 27, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Díez, J.; Moura, D.; Grispoldi, L.; Cenci-Goga, B.; Saraiva, S.; Silva, F.; Saraiva, C.; Ausina, J. Salmonella spp. in Domestic Ruminants, Evaluation of Antimicrobial Resistance Based on the One Health Approach—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Meng, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, Q.; Xu, C.; Kang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, F.; Jiao, X.; Pan, Z. Prevalence and transmission of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198 based on whole-genome sequence in an intensive laying hen farm in Jiangsu, China. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, J.; Lei, G.; Yang, Y.; Huang, W.; Leng, Y.; Miao, Y.; Li, M.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, Y. Emergence of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella Kentucky ST198 in Southwest China. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2025, 43, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, M.I.; El-banna, T.; Sonbol, F.; Elekhnawy, E. Arthrospira maxima and biosynthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles as antibacterials against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae and Acinetobacter baumannii: A review article. Microb. Cell Factories 2024, 23, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, M.A.; El-Aziz, A.M.A.; El-Sokkary, M.M.; Barwa, R. Characterization and genetic analysis of extensively drug-resistant hospital acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.S.R.; Hossain, H.; Rahman, M.N.; Rahman, A.; Ghosh, P.K.; Uddin, M.B.; Nazmul Hoque, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Rahman, M.M. Emergence of highly virulent multidrug and extensively drug resistant Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in buffalo subclinical mastitis cases. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.; Giske, C.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, K.; Saleem, S.; Jahan, S.; Nizamudin, S.; Arshad, F.; Huma, Z.-e.; Raza, S.M.; Mehmood, M.; Roman, M.; Haq, F.U. Molecular characterization of extensively drug resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi clinical isolates from Lahore, Pakistan. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 2987–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loconsole, D.; Sallustio, A.; Sacco, D.; Santantonio, M.; Casulli, D.; Gatti, D.; Accogli, M.; Parisi, A.; Zagaria, R.; Colella, V. Genomic surveillance of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae reveals a prolonged outbreak of extensively drug-resistant ST147 NDM-1 during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Apulia region (Southern Italy). J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 36, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Aziz, N.K.; Tartor, Y.H.; Gharieb, R.M.; Erfan, A.M.; Khalifa, E.; Said, M.A.; Ammar, A.M.; Samir, M. Extensive drug-resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from poultry and humans: Prevalence and molecular determinants behind the co-resistance to ciprofloxacin and tigecycline. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 738784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A.H.; Khare, K.; Saxena, P.; Debnath, P.; Mukhopadhyay, K.; Yadav, D. A review on colistin resistance: An antibiotic of last resort. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi, S.; Zekiy, A.O.; Krutova, M.; Gholami, M.; Kouhsari, E.; Sholeh, M.; Ghafouri, Z.; Maleki, F. Tigecycline antibacterial activity, clinical effectiveness, and mechanisms and epidemiology of resistance: Narrative review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korczak, L.; Majewski, P.; Iwaniuk, D.; Sacha, P.; Matulewicz, M.; Wieczorek, P.; Majewska, P.; Wieczorek, A.; Radziwon, P.; Tryniszewska, E. Molecular mechanisms of tigecycline-resistance among Enterobacterales. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1289396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, S.; Ricke, S.C.; Foley, S.L.; Han, J. The dynamics of the antimicrobial resistance mobilome of Salmonella enterica and related enteric bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 859854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, E.V.; Wu, K.J.; Tresco, B.I.; Syroegin, E.A.; Killeavy, E.E.; Balasanyants, S.M.; Svetlov, M.S.; Gregory, S.T.; Atkinson, G.C.; Myers, A.G. Structural basis of Cfr-mediated antimicrobial resistance and mechanisms to evade it. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Werckenthin, C.; Kehrenberg, C. Identification of a plasmid-borne chloramphenicol-florfenicol resistance gene in Staphylococcus sciuri. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 2530–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Zhang, W.; Du, X.-D.; Krüger, H.; Feßler, A.T.; Ma, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, Y. Mobile oxazolidinone resistance genes in Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 34, e0018820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.-X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, N.H.; Al-Kadmy, I.M.; Taha, B.M.; Hussein, J.D. Mobilized colistin resistance (mcr) genes from 1 to 10: A comprehensive review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Shen, Y.-B.; Yang, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Shen, J. Plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance genes: Mcr. Trends Microbiol. 2024, 32, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mmatli, M.; Mbelle, N.M.; Osei Sekyere, J. Global epidemiology, genetic environment, risk factors and therapeutic prospects of mcr genes: A current and emerging update. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 941358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Ji, R.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Lu, M.-J.; Wu, H.; Mei, C.-Y.; Li, Q.-C.; Jiao, X. Colistin-and tigecycline-resistant CTX-M-14-producing Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198 from retail chicken meat, China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 59, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Sheng, Z.; Hao, M.; Jiang, J.; Ye, M.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Guo, Q.; Wang, M. RamA upregulates multidrug resistance efflux pumps AcrAB and OqxAB in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2021, 57, 106251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Suo, J.; Dai, J.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Su, L.; Cao, M.; Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Cui, S.; et al. Prevalence, antibiotic susceptibility and genomic analysis of Salmonella from retail meats in Shaanxi, China. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 403, 110305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Z.; He, S.; Hu, M.; Cui, Y.; Tai, C.; Shi, X. High Prevalence of Multidrug-resistant Salmonella from Retail Meat in Shanghai and the Molecular Characterization of blaNDM-9-carrying Plasmid. J. Future Foods, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Lubbers, B.; Diaz-Campos, D.; Schwarz, S. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. In Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI supplement VET01S; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Berwyn, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Den Bakker, H.C.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Dinsmore, B.A.; Lane, C.; Lauer, A.; Fields, P.I.; Deng, X. SeqSero2: Rapid and improved Salmonella serotype determination using whole-genome sequencing data. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e01746-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.G.; Nisbet, J. Building phylogenetic trees from genome sequences With kSNP4. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, msad235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisola Bello, A.; Olamilekan Adesola, R.; Idris, I.; Yawson Scott, G.; Alfa, S.; Akinfemi Ajibade, F. Combatting extensively drug-resistant Salmonella: A global perspective on outbreaks, impacts, and control strategies. Pathog. Glob. Health 2024, 118, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jiao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Poultry production as the main reservoir of ciprofloxacin-and tigecycline-resistant extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky ST198. 2-2 causing human infections in China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e0094423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yi, S.; Xu, X.; Zheng, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, X. Prevalence and Characteristics of Plasmid-Mediated Fosfomycin Resistance Gene fosA3 among Salmonella Enteritidis Isolates from Retail Chickens and Children with Gastroenteritis in China. Pathogens 2024, 13, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Bush, K.; Harbarth, S.; Paul, M.; Rex, J.H.; Tacconelli, E.; Thwaites, G.E. Critical analysis of antibacterial agents in clinical development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, B.; Mawad, A.M.; Saleh, M.; Kelley, W.G.; Harrington, P.J.; Lovestad, C.W.; Amezcua, J.; Sarhan, M.M.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Ramadan, H. Salmonellosis: An overview of epidemiology, pathogenesis, and innovative approaches to mitigate the antimicrobial resistant infections. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, P.; Paxman, J.J.; Wang, G.; Hor, L.; Hong, Y.; Verderosa, A.D.; Whitten, A.E.; Panjikar, S.; Santos-Martin, C.F.; Martin, J.L. Salmonella enterica BcfH is a trimeric thioredoxin-like bifunctional enzyme with both thiol oxidase and disulfide isomerase activities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2021, 35, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeboer, N.A.; Frye, J.G.; McClelland, M.; Jones, B.D. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium requires the Lpf, Pef, and Tafi fimbriae for biofilm formation on HEp-2 tissue culture cells and chicken intestinal epithelium. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 3156–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, M.; Duan, X.; Xie, L.; Yang, C.; Xu, L.; Fu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Cai, R. Emergence of chromosomally located blaCTX-M-14b and qnrS1 in Salmonella enterica serotype Kentucky ST198 in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazari Moghadam, M.; Rahimi, E.; Shakerian, A.; Momtaz, H. Prevalence of Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis isolated from poultry meat: Virulence and antimicrobial-resistant genes. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, A.D.; Raffatellu, M.; Winter, S.; Weening, E.H.; Kingsley, R.A.; Droleskey, R.; Zhang, S.; Figueiredo, J.; Khare, S.; Nunes, J. The use of flow cytometry to detect expression of subunits encoded by 11 Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium fimbrial operons. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 48, 1357–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.J.; Bowen, A.J.; Hulme, S.D.; Buckley, A.M.; Deacon, V.L.; Thomson, N.R.; Barrow, P.A.; Morgan, E.; Jones, M.A.; Watson, M. Analysis of the role of 13 major fimbrial subunits in colonisation of the chicken intestines by Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis reveals a role for a novel locus. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidian, M.; Holt, K.E.; Hall, R.M. The complete sequence of Salmonella genomic island SGI1-K. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.M. Salmonella genomic islands and antibiotic resistance in Salmonella enterica. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, S.M.; Xiong, L.; Arias, C.A.; Villegas, M.V.; Lolans, K.; Quinn, J.; Mankin, A.S. Acquisition of a natural resistance gene renders a clinical strain of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus resistant to the synthetic antibiotic linezolid. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, J.; Cai, J.; Ma, T.; Xie, N.; Fan, R.; Zhai, W.; Feßler, A.T.; Sun, C. Spreading of cfr-carrying plasmids among staphylococci from humans and animals. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02461-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R.; Cai, J. An 11-year linezolid-resistant Staphylococcus capitis clone dissemination with a similar cfr-carrying plasmid in China. Iscience 2022, 25, 105644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xie, M.; Chen, K.; Dong, N.; Lin, D.; Chan, E.W.-C.; Chen, S. Genetic basis of chromosomally-encoded mcr-1 gene. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snesrud, E.; McGann, P.; Chandler, M. The birth and demise of the IS Apl1-mcr-1-IS Apl1 composite transposon: The vehicle for transferable colistin resistance. MBio 2018, 9, e02381-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snesrud, E.; He, S.; Chandler, M.; Dekker, J.P.; Hickman, A.B.; McGann, P.; Dyda, F. A model for transposition of the colistin resistance gene mcr-1 by IS Apl1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6973–6976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xie, Y.; Liu, M.; Tai, C.; Sun, J.; Deng, Z.; Ou, H.Y. oriTfinder: A web-based tool for the identification of origin of transfers in DNA sequences of bacterial mobile genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W229–W234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Guan, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Pan, D.; Tang, B. Emergence of plasmid harbouring the cfr gene in porcine Salmonella. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2023, 62, 106833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).