Profiling the Differential Distribution of Ginsenosides Across Ginseng Tissues Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.1.1. Raw Materials
2.1.2. Reagents and Consumables
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2.2. LC and MS Conditions
2.2.3. Ginsenoside Identification
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Composition and Retention Analysis of Ginsenosides
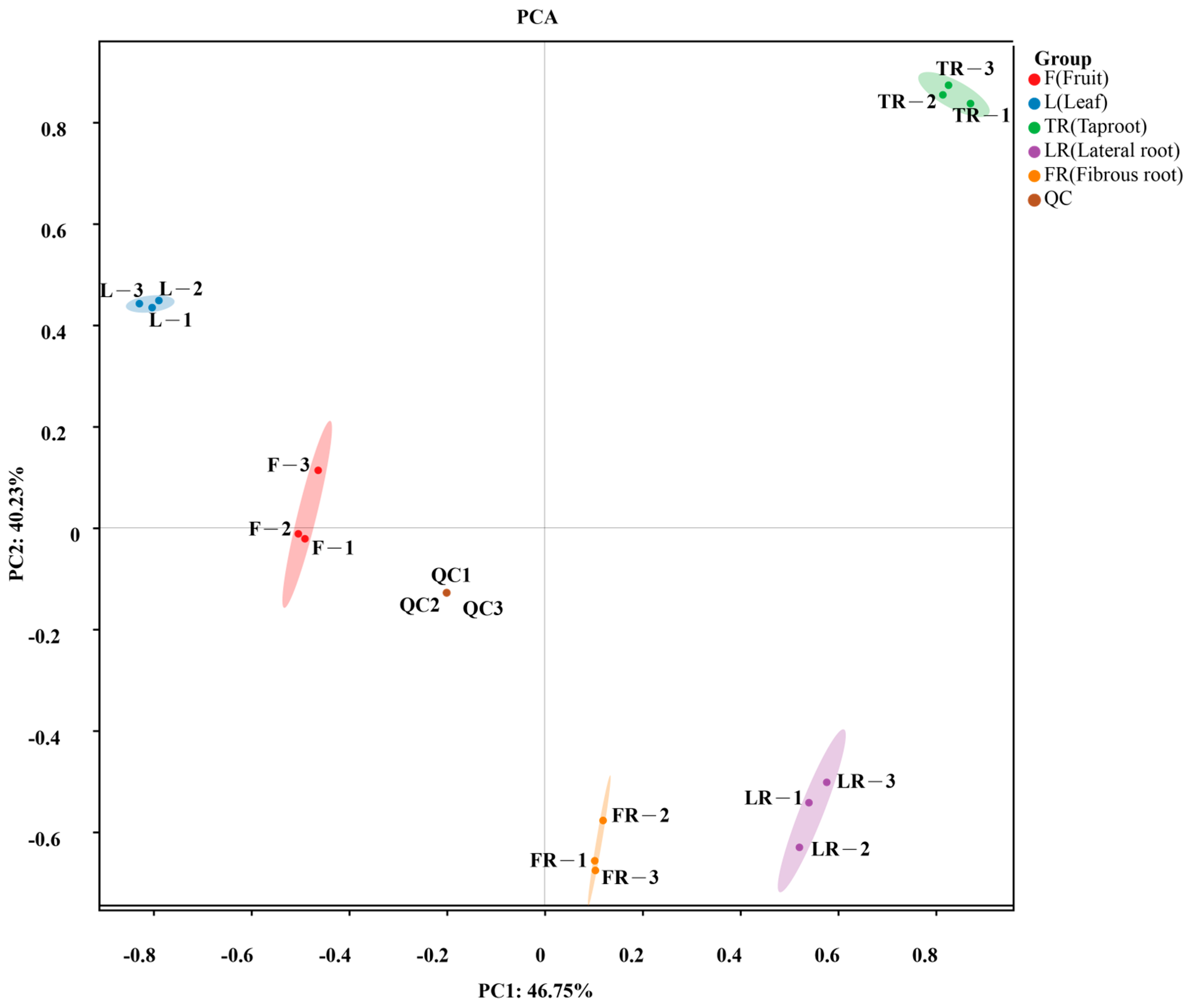
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Ginsenosides Across Tissues
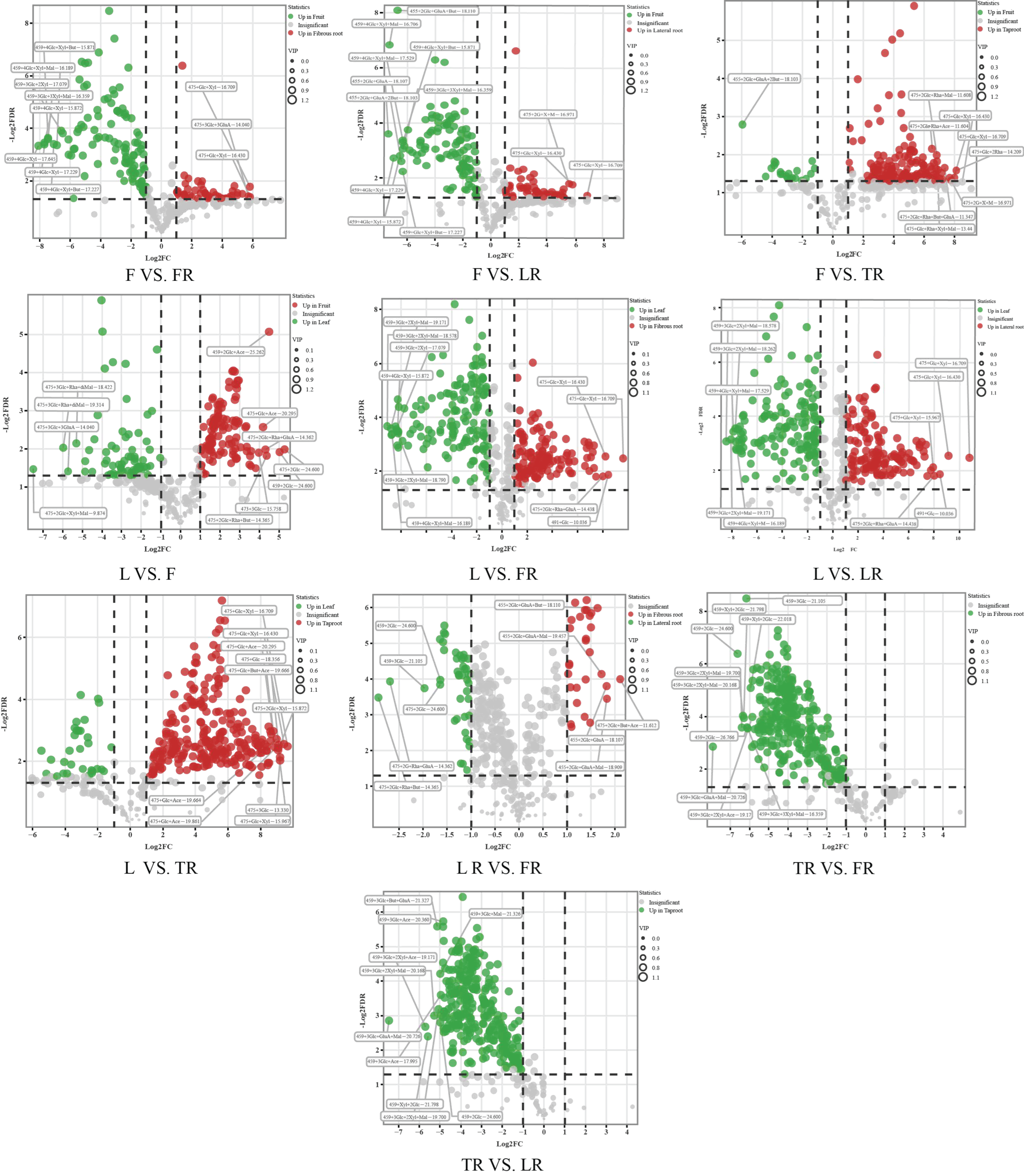
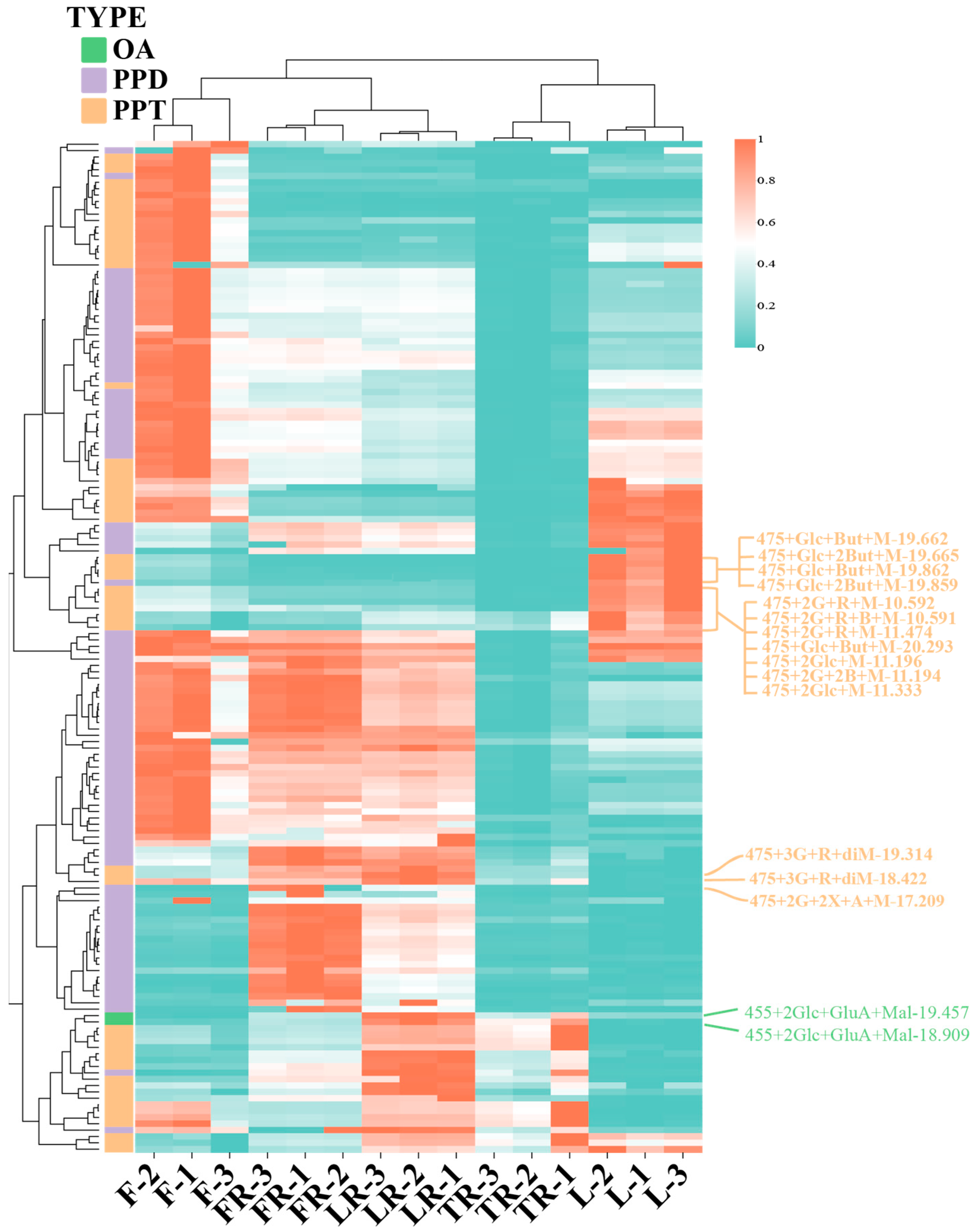
3.3. Analysis of Ginsenoside Content Differences in Different Ginseng Parts
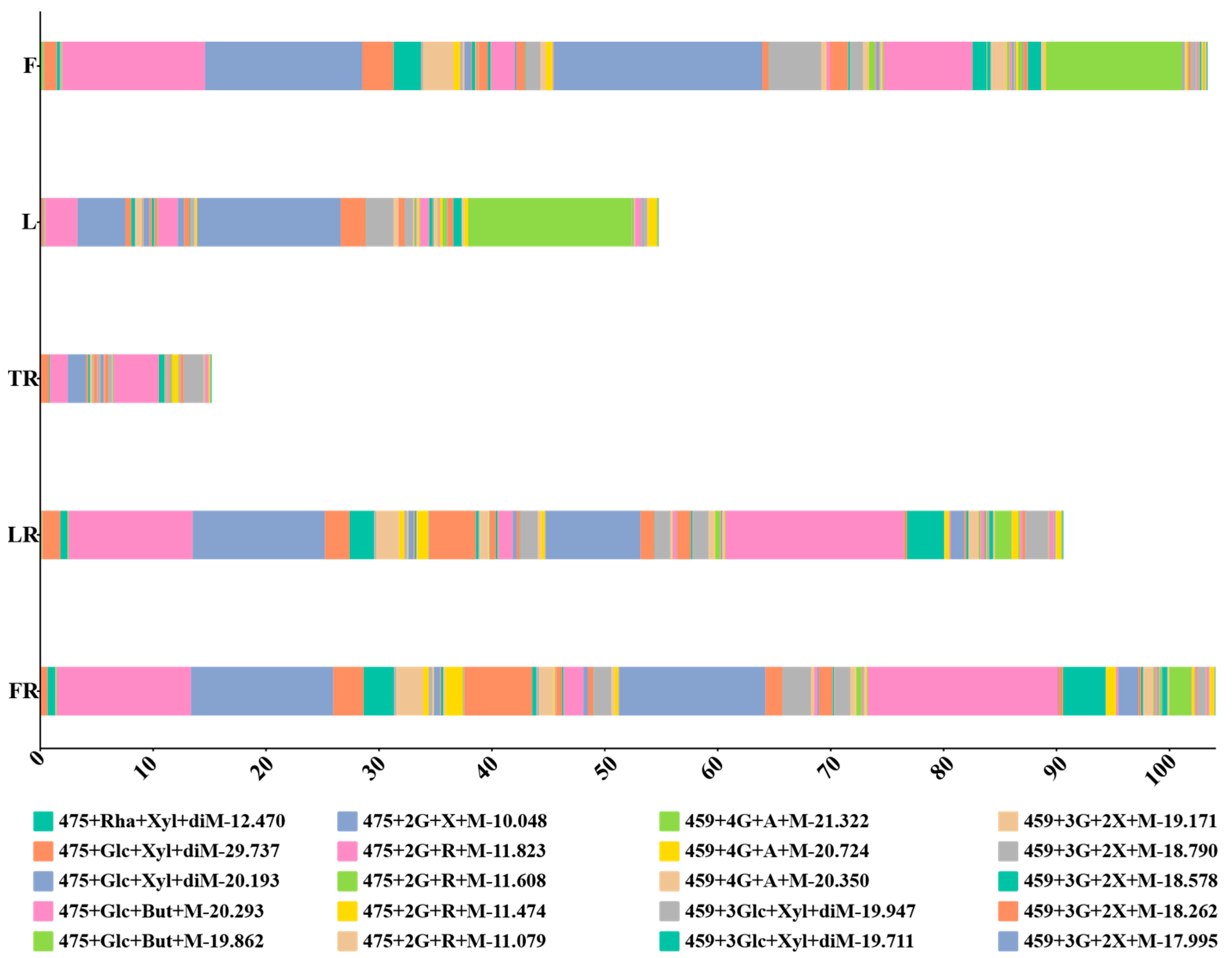
3.4. Analysis of Malonylated Ginsenoside Content Differences in Different Ginseng Parts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loo, S.; Kam, A.; Dutta, B.; Zhang, X.; Feng, N.; Sze, S.K.; Liu, C.F.; Wang, X.; Tam, J.P. Broad-Spectrum Ginsentides Are Principal Bioactives in Unraveling the Cure-All Effects of Ginseng. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2024, 14, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaz, M.; Rahman, N.U.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M.; Jaffar, H.Z.E.; Manea, R. Ginseng: A Dietary Supplement as Immune-Modulator in Various Diseases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 83, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.Y.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.J.; Yin, J.N.; Gao, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.G.; Li, H.J. Ginsenoside Rg5 Inhibits Human Osteosarcoma Cell Proliferation and Induces Cell Apoptosis through PI3K/Akt/mTORC1-Related LC3 Autophagy Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5040326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Xin, Y.; Cui, M.; Jiang, X.; Gu, L. Inhibitory Effect of Ginsenoside Rg3 Combined with Cyclophosphamide on Growth and Angiogenesis of Ovarian Cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2007, 120, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, W.; Lin, Y. Pharmacological Effects of Natural Medicine Ginsenosides against Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 952332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Ruan, C.C.; Wang, L.J.; Sun, G.Z. The Effects of Dynamic Changes of Malonyl Ginsenosides on Evaluation and Quality Control of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 64, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wu, J.; Qu, C.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z. Isolation and identification of two new malonyl ginsenosides from Panax quinquefolius. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2023, 54, 6940–6945. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.S.; Wang, J.M.; Zhang, F.R.; Lei, F.J.; Wen, X.; Song, J.; Sun, G.Z.; Liu, Z. Ameliorative Effects of Malonyl Ginsenoside from Panax ginseng on Glucose-Lipid Metabolism and Insulin Resistance via IRS1/PI3K/Akt and AMPK Signaling Pathways in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 863–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D. Chemical Constituents of Malonyl Ginsenosides from Stems and Leaves of Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer and Their Protective Effects on Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.S.; Oh, M.H.; Lee, H.; Jung, J.T.; Jo, Y.H.; Pyo, M.K. Comparison of Malonyl Ginsenoside Contents in Parts of Korean Ginseng. Korean J. Pharmacogn. 2017, 48, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, S. Profiling and Multivariate Statistical Analysis of Panax ginseng Based on Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Qu, H.; Pan, H.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Zhang, J.; Bi, Q.; Guo, D. Characteristic Malonyl Ginsenosides from the Leaves of Panax Notoginseng as Potential Quality Markers for Adulteration Detection. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 4849–4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.; Li, R.; Ocholi, S.S.; Wang, H.; Cui, T.; Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Fu, Z.; Liu, E.; Wang, F.; et al. A Multi-Level Strategy Based on Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography-Q-Orbitrap-Mass Spectrometry Combined with PLS Regression Model and RT-Ensemble Pred Model to Intelligently Distinguish Different Geographical Locations of Huanglian Sample. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 262, 116864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W.; Guo, W.; Li, M.; Jia, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Study on Cold and Hot Properties of Chinese Materia Medica Using Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Combined with Network Pharmacology Analysis. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2025, 39, e70070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wei, F.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, G.; Ma, S.; Liu, B. Identification of Ophiocordyceps Sinensis and Its Artificially Cultured Ophiocordyceps Mycelia by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Orbitrap Fusion Mass Spectrometry and Chemometrics. Molecules 2018, 23, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, B.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tang, X.; Zhang, C.; Gao, Y. DIA-Based Serum Proteomics Revealed the Protective Effect of Modified Siwu Decoction against Hypobaric Hypoxia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Hou, W.; Wang, Y. Rapid Identification of Saponins in Panax Notoginseng Fruits by Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 50, 225–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ye, M.; Qiao, X.; Liu, C.; Miao, W.; Bo, T.; Tao, H.; Guo, D. A Strategy for Efficient Discovery of New Natural Compounds by Integrating Orthogonal Column Chromatography and Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analysis: Its Application in Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium and Panax notoginseng to Characterize 437 Potential New Ginsenosides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 739, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, S.; Piao, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Discrimination for Geographical Origin of Panax quinquefolius L. Using UPLC Q-Orbitrap MS-Based Metabolomics Approach. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 4843–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Piao, X. Dynamic Changes of Ginsenosides in Panax quinquefolium Fruit at Different Development Stages Measured Using UHPLC-Orbitrap MS. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Huang, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, C. Approaches to Establish Q-Markers for the Quality Standards of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2017, 7, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. Chemical Characteristics of Three Medicinal Plants of the Panax Genus Determined by HPLC-ELSD. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Han, X.; Li, D.; Liu, Z. Differences of malonyl ginsenosides and neutral ginsenosides in different parts of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng by high performance liquid chromatography and chemometric analysis. China Food Addit. 2024, 35, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, X.; Zhang, H.; Kang, J.P.; Yang, D.U.; Li, Y.; Pang, S.; Jin, Y.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, Y. Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng. Mol. Basel Switz. 2020, 25, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
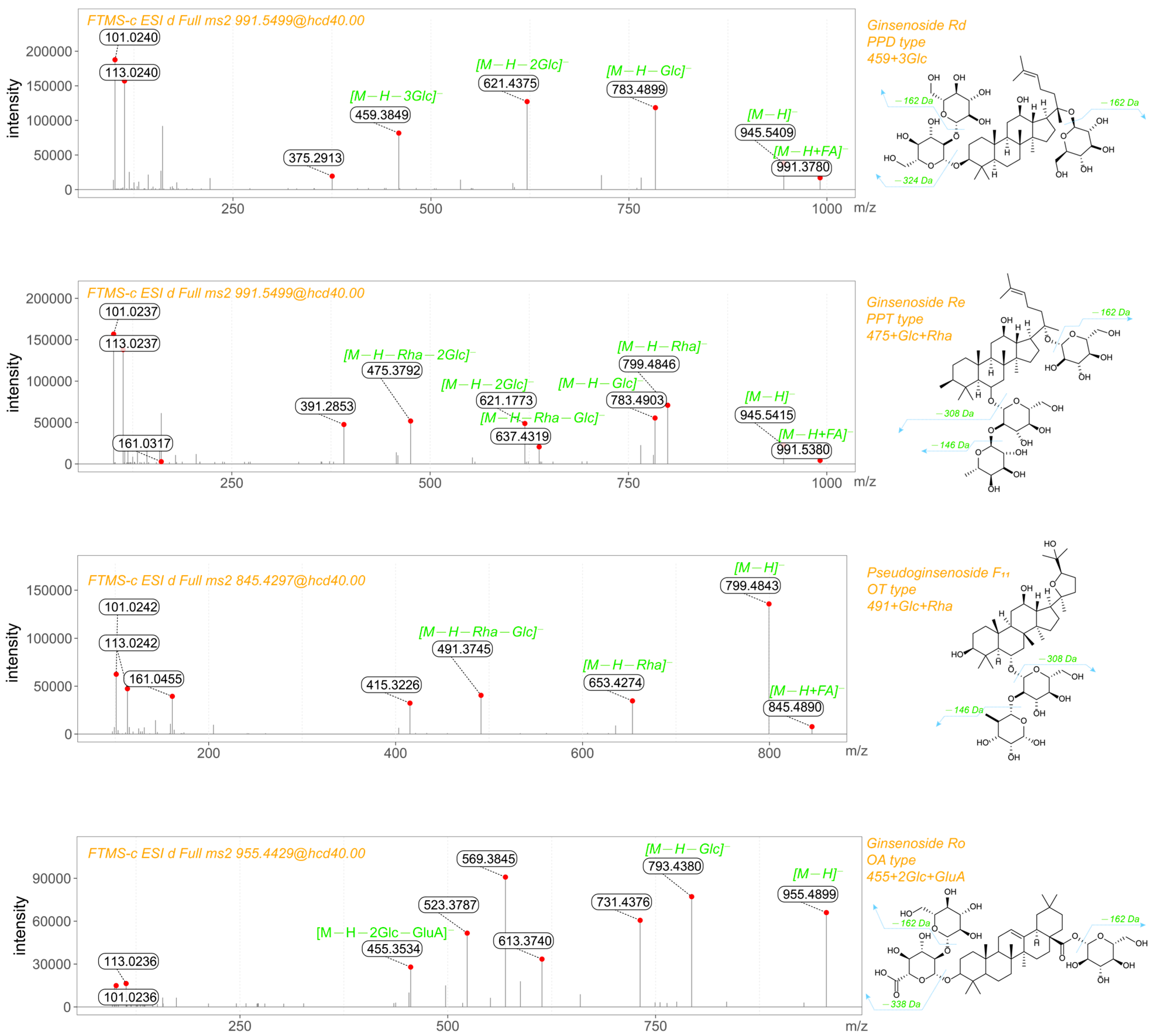
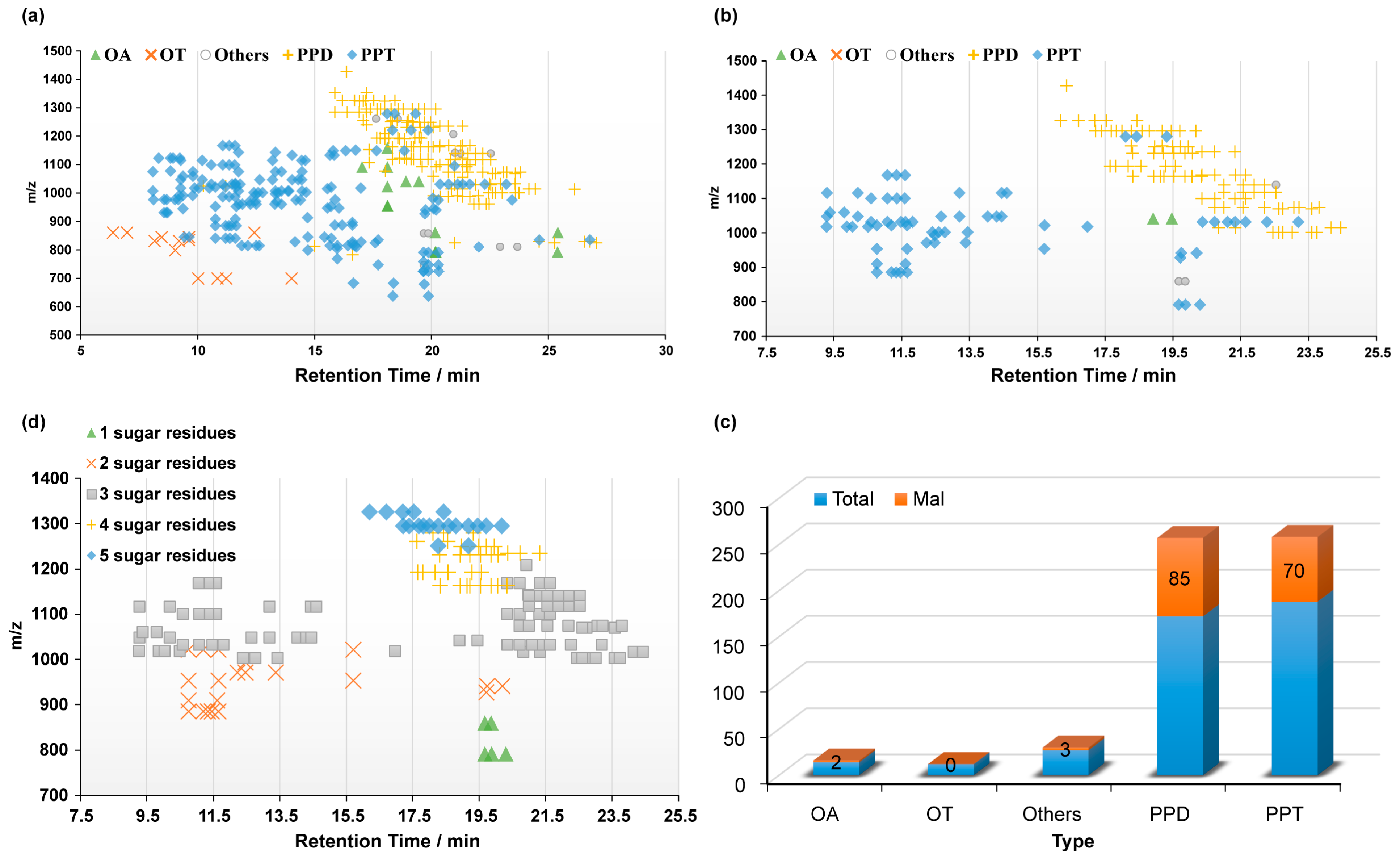
| Name | Identification | m/z | Retention Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 475+2Glc+Xyl-8.68 | Notoginsenoside R1 | 977.5327 | 8.68 |
| 475+2Glc-09.65 | Ginsenoside Rg1 | 845.4915 | 09.65 |
| 475+2Glc+Rha-09.79 | Ginsenoside Re | 991.5490 | 09.79 |
| 475+2Glc-14.75 | Ginsenoside Rf | 845.4911 | 14.75 |
| 475+Rha+Glc-16.67 | 20S-Ginsenoside Rg2 | 829.4976 | 16.67 |
| 475+Glc-16.71 | 20S-Ginsenoside Rh1 | 683.4385 | 16.71 |
| 475+Rha+Glc-17.04 | 20R-Ginsenoside Rg2 | 829.4982 | 17.04 |
| 475+Glc-17.24 | 20R-Ginsenoside Rh1 | 683.4398 | 17.24 |
| 459+4Glc-17.36 | Ginsenoside Rb1 | 1153.6023 | 17.36 |
| 459+3Glc+Xyl-18.07 | Ginsenoside Rc | 1123.5928 | 18.07 |
| 455+2Glc+GluA-18.15 | Ginsenoside Ro | 955.4921 | 18.15 |
| 459+3Glc+Xyl-18.69 | Ginsenoside Rb2 | 1123.5896 | 18.69 |
| 459+3Glc+Xyl-18.89 | Ginsenoside Rb3 | 1123.5886 | 18.89 |
| 459+3Glc-20.13 | Ginsenoside Rd | 991.5480 | 20.13 |
| 441+2Glc-23.07 | Ginsenoside Rg6 | 811.4873 | 23.07 |
| 457+Glc-23.62 | Ginsenoside Rk3 | 665.4291 | 23.62 |
| 457+Glc-24.16 | Ginsenoside Rh4 | 665.4294 | 24.16 |
| 459+2Glc-26.88 | 20S-Ginsenoside Rg3 | 829.4978 | 26.88 |
| 459+2Glc-27.41 | 20R-Ginsenoside Rg3 | 829.4971 | 27.41 |
| 459+2Glc+Ace-29.99 | 20S-Ginsenoside Rs3 | 871.5071 | 29.99 |
| 459+2Glc+Ace-30.28 | 20R-Ginsenoside Rs3 | 871.5085 | 30.28 |
| 441+2Glc-31.99 | Ginsenoside Rk1 | 811.4864 | 31.99 |
| 441+2Glc-32.46 | Ginsenoside Rg5 | 811.4879 | 32.46 |
| 459+Glc-32.96 | Ginsenoside Rh2 | 667.4450 | 32.96 |
| 459+4Glc+Xyl-15.85 | Notoginsenoside R4 | 1285.6000 | 15.85 |
| 459+4Glc+Xyl-17.22 | Ginsenoside Ra3 | 1285.6000 | 17.22 |
| 459+3Glc+2Xyl-17.08 | Ginsenoside Ra2 | 1255.6000 | 17.08 |
| 459+Glc-31.69 | Ginsenoside compound K | 667.4437 | 31.69 |
| 475+Glc-18.44 | Ginsenoside F1 | 683.4371 | 18.44 |
| 441+2Glc-23.77 | Ginsenoside F4 | 811.4861 | 23.77 |
| 475+Xyl+Glc-16.51 | Ginsenoside F3 | 815.4820 | 16.51 |
| 459+2Glc-24.72 | Ginsenoside F2 | 829.4979 | 24.72 |
| 491+Rha+Glc-14.35 | Pesudoginsenoside F11 | 845.4914 | 14.35 |
| Group | Differential Ginsenoside Number |
|---|---|
| LR vs. FR | 72 |
| TR vs. FR | 301 |
| TR vs. LR | 306 |
| F vs. L | 187 |
| L vs. LR | 294 |
| L vs. FR | 294 |
| L vs. TR | 294 |
| F vs. FR | 165 |
| F vs. LR | 170 |
| F vs. TR | 172 |
| Place | Number of Tissue-Specific Malonyl Ginsenosides | Name | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fruits | 53 | 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+2But+diMal-20.599 | 459+3Glc+Xyl+diMal-18.949 | 475+Glc+Xyl+diMal-29.737 |
| 475+3Glc+Mal-12.660 | 475+Glc+Xyl+diMal-20.193 | 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+But+diMal-21.238 | ||
| 475+2Glc+Xyl+Mal-9.874 | 475+2Glc+Xyl+Mal-9.277 | 475+Glc+Rha+Xyl+Mal-12.404 | ||
| 475+Glc+Rha+Xyl+Mal-12.588 | 475+2Glc+Xyl+Mal-16.971 | 475+Glc+Rha+Xyl+Mal-13.443 | ||
| 475+2Glc+Xyl+Mal-10.048 | 475+3Glc+Mal-14.448 | 475+3Glc+But+Mal-14.444 | ||
| 475+2Glc+Xyl+Mal-10.5000 | 475+Glc+Rha+Xyl+Mal-12.773 | 475+3Glc+But+Mal-13.201 | ||
| 475+Glc+Rha+Xyl+Mal-12.773 | 475+3Glc+But+Mal-13.201 | 475+3Glc+Mal-13.203 | ||
| 475+2Glc+Rha+But+Mal-11.587 | 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+But+diMal-21.562 | 459+3Glc+Ace+Mal-21.563 | ||
| 459+3Glc+diMal-21.562 | 459+3Glc+diMal-22.532 | 459+3Glc+diMal-21.889 | ||
| 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+But+diMal-21.889 | 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+But+diMal-22.532 | 459+3Glc+diMal-22.188 | ||
| 459+3Glc+Ace+Mal-22.192 | 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+But+diMal-22.190 | 459+3Glc+Ace+Mal-23.212 | ||
| 459+4Glc+Mal-19.561 | 459+2Glc+Rha+Mal-24.159 | 459+Glc+Rha+Xyl+But+diMal-21.002 | ||
| 459+Glc+2Xyl+2Ace+diMal-20.995 | 459+3Glc+Ace+Mal-20.999 | 459+3Glc+Mal-21.326 | ||
| 459+2Glc+Rha+Mal-21.330 | 475+3Glc+Mal-14.297 | 459+3Glc+Mal-23.191 | ||
| 459+2Glc+Xyl+Mal-23.018 | 459+3Glc+Mal-22.270 | 459+4Glc+Ace+Mal-21.322 | ||
| 459+3Glc+Mal-20.360 | 459+3Glc+Mal-21.633 | 459+3Glc+2But+Mal-21.633 | ||
| 459+3Glc+But+Mal-21.633 | 459+3Glc+But+Mal-21.324 | 459+3Glc+2But+Mal-21.328 | ||
| 459+2Glc+Rha+Mal-20.843 | 475+2Glc+Rha+But+Mal-11.079 | 475+2Glc+Rha+2But+Mal-11.078 | ||
| 475+2Glc+Rha+Mal-11.079 | ||||
| Leaves | 23 | 475+3Glc+Mal-14.037 | 475+3Glc+But+Mal-14.601 | 475+2Glc+Rha+Mal-11.608 |
| 475+2Glc+Rha+2But+Mal-11.349 | 475+2Glc+Rha+But+Mal-11.352 | 475+2Glc+Rha+2But+Mal-11.596 | ||
| 459+4Glc+Ace+Mal-20.724 | 459+3Glc+But+Mal-20.726 | 459+3Glc+Mal-20.726 | ||
| 459+3Glc+2But+Mal-20.728 | 459+3Glc+Ace+Mal-20.726 | 475+Glc+But+Mal-19.662 | ||
| 475+Glc+2But+Mal-19.665 | 475+Glc+But+Mal-19.862 | 475+Glc+2But+Mal-19.859 | ||
| 459+4Glc+Mal-19.275 | 475+2Glc+Rha+Mal-10.592 | 475+2Glc+Rha+But+Mal-10.591 | ||
| 475+2Glc+Rha+Mal-11.474 | 475+Glc+But+Mal-20.293 | 475+2Glc+Mal-11.196 | ||
| 475+2Glc+2But+Mal-11.194 | 475+2Glc+Mal-11.333 | |||
| Lateral roots | 9 | 455+2Glc+GluA+Mal-19.457 | 455+2Glc+GluA+Mal-18.909 | 475+3Glc+Mal-9.290 |
| 475+3Glc+But+Mal-9.289 | 475+2Glc+But+Mal-15.704 | 459+4Glc+Xyl+Mal-16.706 | ||
| 475+2Glc+2But+Mal-15.706 | 475+3Glc+Mal-10.199 | 475+3Glc+But+Mal-10.204 | ||
| Fibrous roots | 17 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-19.444, | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-17.995, | 459+4Glc+Xyl+Mal-18.429 |
| 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-19.444 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-18.262 | 459+4Glc+Mal-18.167 | ||
| 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-17.816 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-17.206 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-18.578 | ||
| 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-17.389 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-19.171 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-19.700 | ||
| 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-18.790 | 459+4Glc+Mal-17.799 | 459+4Glc+Xyl+Mal-16.189 | ||
| 459+3Glc+3Xyl+Mal-16.359 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-20.168 | 459+3Glc+2Xyl+Mal-17.675 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, H. Profiling the Differential Distribution of Ginsenosides Across Ginseng Tissues Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2025, 12, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12070170
Xu H, Li Z, Liu C, Wang Y, Qiao S, Zhang H. Profiling the Differential Distribution of Ginsenosides Across Ginseng Tissues Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Separations. 2025; 12(7):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12070170
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hang, Zheng Li, Chong Liu, Yukun Wang, Siwei Qiao, and Hao Zhang. 2025. "Profiling the Differential Distribution of Ginsenosides Across Ginseng Tissues Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Separations 12, no. 7: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12070170
APA StyleXu, H., Li, Z., Liu, C., Wang, Y., Qiao, S., & Zhang, H. (2025). Profiling the Differential Distribution of Ginsenosides Across Ginseng Tissues Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Separations, 12(7), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12070170






