Abstract
Next-generation recycling technologies must be urgently innovated to tackle huge volumes of spent batteries, photovoltaic panels or printed circuit boards (WPCBs). Current e-waste recycling industrial technology is dominated by traditional recycling technologies. Herein, ionic liquids (ILs), deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and promising oxidizing additives that can overcome some traditional recycling methods of metal ions from e-waste, used in our works from last year, are presented. The unique chemical environments of ILs and DESs, with the application of low-temperature extraction procedures, are important environmental aspects known as “Green Methods”. A closed-loop system for recycling zinc and manganese from the “black mass” (BM) of waste, Zn-MnO2 batteries, is presented. The leaching process achieves a high efficiency and distribution ratio using the composition of two solvents (Cyanex 272 + diethyl phosphite (DPh)) for Zn(II) extraction. High extraction efficiency with 100% zinc and manganese recovery is also achieved using DESs (cholinum chloride/lactic acid, 1:2, DES 1, and cholinum chloride/malonic acid, 1:1, DES 2). New, greener recycling approaches to metal extraction from the BM of spent Li-ion batteries are presented with ILs ([N8,8,8,1][Cl], (Aliquat 336), [P6,6,6,14][Cl], [P6,6,6,14][SCN] and [Benzet][TCM]) eight DESs, Cyanex 272 and D2EHPA. A high extraction efficiency of Li(I) (41–92 wt%) and Ni(II) (37–52 wt%) using (Cyanex 272 + DPh) is obtained. The recovery of Ni(II) and Cd(II) from the BM of spent Ni-Cd batteries is also demonstrated. The extraction efficiency of DES 1 and DES 2, contrary to ILs ([P6,6,6,14][Cl] and [P6,6,6,14][SCN]), is at the level of 30 wt% for Ni(II) and 100 wt% for Cd(II). In this mini-review, the option to use ILs, DESs and Cyanex 272 for the recovery of valuable metals from end-of-life WPCBs is presented. Next-generation recycling technologies, in contrast to the extraction of metals from acidic leachate preceded by thermal pre-treatment or from solid material only after thermal pre-treatment, have been developed with ILs and DESs using the ABS method, as well as Cyanex 272 (only after the thermal pre-treatment of WPCBs), with a process efficiency of 60–100 wt%. In this process, four new ILs are used: didecyldimethylammonium propionate, [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO], didecylmethylammonium hydrogen sulphate, [N10,10,1,H][HSO4], didecyldimethylammonium dihydrogen phosphate, [N10,10,1,1][H2PO4], and tetrabutylphosphonium dihydrogen phosphate, [P4,4,4,4][H2PO4]. The extraction of Cu(II), Ag(I) and other metals such as Al(III), Fe(II) and Zn(II) from solid WPCBs is demonstrated. Various additives are used during the extraction processes. The Analyst 800 atomic absorption spectrometer (FAAS) is used for the determination of metal content in the solid BM. The ICP-OES method is used for metal analysis. The obtained results describe the possible application of ILs and DESs as environmental media for upcycling spent electronic wastes.
1. Introduction
Current e-waste recycling industrial technology is dominated by traditional methods with high energy consumption in pyrometallurgical processes, using strong inorganic acids, such as H2SO4, HCl and HNO3, or some organic acids, such as citric acid or tartaric acid, in hydrometallurgical processes. A short review is presented on organic solvent leaching with different oxidizing additives and surfactants at low temperatures to extract valuable metals from the waste of different batteries and printed circuit boards (WPCBs).
The following solvents were used to recover Zn and Mn metals from the “black mass” (BM) of spent zinc batteries: trihexyltetradecylphosphonium chloride, [P6,6,6,14][Cl], (Cyphos IL 101), trihexyltetradecylphosphonium thiocyanate, [P6,6,6,14][SCN], bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinic acid, Cyanex 272, and bis-(2-ethylhexyl)phosphoric acid, D2EHPA. A flow chart of the best method of recovery for zinc and manganese has been presented [1]. A leaching efficiency of 100 wt% for Zn(II) was obtained through a combination of {Cyanex 272 + diethyl phosphite, (DPh)}, as well as 100 wt% for Zn(II) and Mn(II) using DESs (choline chloride, [N2OH,1,1,1][Cl], ChCl:lactic acid, 1:2, DES 1, and ChCl:malonic acid, 1:1, DES 2) with the addition of the didecyldimethylammonium chloride surfactant DDACl [1]. The electrochemical recovery of zinc from acidic aqueous solutions was described. For all the procedures, the O/A ratio, temperature, time of extraction, pH and selectivity and distribution ratios were presented [1].
Details regarding the metal extraction behaviour of the BM of spent Li-ion batteries were presented using ILs ([N8,8,8,1][Cl], [P6,6,6,14][Cl], [P6,6,6,14][SCN] and [Benzet][TCM]), eight DESs and two popular organophosphorous-based acids, Cyanex 272 and D2EHPA [2]. Much better results were obtained, at 90–100 wt% recovery of Co(II), Ni(II) and Li(I), using DESs than those obtained with ILs. The extraction efficiency using [P6,6,6,14][SCN] or mixtures of two ILs showing synergistic effects at a low temperature, T = 303 K, was very low. The mixture of {[P4,4,4,14][Cl] + NaCl + H2O + BM} (ABS method—Aqueous Biphasic System), with the addition of H2O2 and DDACl, revealed a very low extraction efficiency for Co(II), at 39.6 wt%, and a successful 90.8 wt% efficiency for Li(I) at pH = 11. The results indicated promising extraction for Li(I) (41–92 wt%) and Ni(II) (37–52 wt%) using (Cyanex 272 + DPh). A complete flow chart for the selective recovery of Co(II), Li(I) and Ni(II) from the BM was presented [2]. Only DESs miscible with water, DES 2 and (ChCl:phenylacetic acid, 1:2) or (benzethonium chloride, [Benzet][Cl]: lactic acid, 1:2), showed better extraction efficiency and were proposed for the extraction of Co(II), Li(I) and Ni(II) with high extraction efficiency [2]. The use of Cyanex 272 and D2EHPA with different additives showed an extraction efficiency of Co (II), Li(I) and Ni(II) at a level of ca. 100 wt% [2]. In the following work, new DESs and bi-functional ILs were used for the leaching of valuable elements from spent Li-ion portable batteries (LiPBs) [3]. The leaching and separation process of Co(II), Ni(II), Cu(II), Li(I) and Mn(II) from the BM, obtained from LiPBs with different solvents, were presented [3]. The results of extraction with six DESs {DES 1, DES 2, ChCl + succinic acid (1:1), glutaric acid (1:1) and citric acid (1:1) as well as citric acid (2:1)} with different additives, such as DDACl, H2O2, trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA), sodium dichloroisocyanurate (NaDCC), pentapotassium bis(peroxymonosulphate) bis(sulphate) (PHM), (glycine + H2O2) or (glutaric acid + H2O2) were presented [3]. TCCA is well known as an inexpensive oxidant for the disinfection of swimming pools and is used in the processes of the extraction of metal ions.
The recovery of metals from the BM of waste Ni-Cd batteries was also under our investigations [4]. The extraction efficiency of DES 1 and DES 2 was much better than those observed for ILs [P6,6,6,14][Cl] and [P6,6,6,14][SCN]. The results under optimal conditions were 30 wt% for Ni(II) and 100 wt% for Cd(II) [4].
The leaching of copper and other metals from the spent printed circuit boards (WPCBs) with ILs, DESs and Cyanex 272 was presented using two different procedures: after the physical, mechanical and thermal pre-treatment at T = 1023 K for 7h and the leaching process with acids [5], or straight from the solid phase after the physical, mechanical and thermal pre-treatment at T = 1023 K for 7 h [6]. In the first method, the ILs, ABS method with ILs, Cyanex 272 and two DESs were investigated [5]. In the second method, two DESs, DES 2 and (ChCl + ethylene glycol, 1:2), and four ILs, didecyldimethylammonium propionate, [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO], didecylmethylammonium hydrogen sulphate [N10,10,1,H][HSO4], didecyldimethylammonium dihydrogen phosphate, [N10,10,1,1][H2PO4] and tetrabutylphosphonium dihydrogen phosphate, [P4,4,4,4][H2PO4], were used [6]. Various additives, such as DDACl, H2O2, TCCA, glycine or PHM, were added to ILs during leaching [6].
The use of tributylmethylammonium chloride, [N4,4,4,1][Cl] with TCCA was presented in the literature earlier with an extraction efficiency of 100% for Au, Pd, Cu, and Ag at low temperature, T = 298 K [7]. Glycine was also investigated earlier with sodium cyanide for the extraction of Au, Ag, Pd, Pt from WPCBs [8], as well as Cu(II) using the S:L = 1:100 with the addition of 10% of H2O2 at a temperature T = 303 K for 2 h at pH = 6–6.5 [9]. Glycine, as an amino acid, is known as the complexing agent of metals. The extraction efficiency of Cu(II) was 94% [9].
Nowadays, reviews discuss many current technologies for the secondary utilization of used Li-ion batteries and recycling of valuable metals [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. BM of Li-ion batteries contains highly precious metals, such as Co, Ni, Li and Mn, which are rare in nature. Therefore, the aims of current scientific developments are to recover valuable metals from the spent BM with preferable alternative methods using new solvents such as DESs and ILs [2,3,21]. An excellent overview of widely used ILs and the recent advances to extract metals from Li-ion batteries and their comparative assessment of performance and selectivity, minimum solute interaction and possible technological use is presented in [22] and the literature cited therein.
Mobile phones are devices operating worldwide, are expected to reach 18bn by 2025, and are a challenging waste stream. The use of [BMIM][HSO4], [HMIM][HSO4], [BMIM][Br], [BMIM][Cl] was presented for the extraction of Ag and Au from WPCB. High extraction efficiency was observed using 60% solutions of [BMIM][Br] or [BMIM][Cl] at a temperature of 333 K [23]. The recirculation of the valuable metallic elements from waste WPCB of mobile phones has been presented with ILs [BMIM][Cl], [EMIM][Cl], [BMIM][BF4] and [BMIM][PF6] with the addition of H2O2 [24]. The best extraction efficiency was obtained with [EMIM][Cl] and [BMIM][PF6] [24]. The use of ILs mainly with the [NTf2]− anion and organophosphorous acids with different additives was also presented for the extraction of metal ions from e-waste [25,26,27]. The use of ammonium IL [N1,1,8,H][HSO4] with the addition of H2O2 relieved the extraction of copper from the WPCB with a 20–30% extraction efficiency after the 1 h extraction in at a temperature of 343 K [28]. Much better extraction efficiency of copper (98%) from WPCB was presented with the following ILs, [BMIM][HSO4], [PS-MIM][HSO4], [CM-MIM][HSO4], [di-Ac-IM][HSO4], [C6(di-Ac-IM)[HSO4], with the addition of H2O2, after the primary pre-treatment with [BMIM][BF4] [29]. The extraction of Ag and Au from the WPCB after the leaching with HCl was developed with [BMIM][NTf2], [BMIM][PF6] and Cyphos 101 ([P6,6,6,14][Cl]) [30]. The extraction efficiency for Cu was around 90% and 99% using [BMIM][PF6] and Cyphos 101, respectively, at temperatures of 298 K, 323 K and 343 K with the rate of IL/solid phase = 1:1 [31].
The recycling of metals from the e-waste of batteries, printed circuit boards or photovoltaic panels is an emerging field due to its environmental and economic benefits. The goal is to analyse the different methods and process flow sheets and to find the best way to further reduce the cost and the mass and energy balances for further process improvements such as the minimization of acid consumption and to be more “green”.
2. Methods Used in the Leaching Processes with ILs and DESs
The BM sample of all batteries used was washed and analysed using A. Analyst 800 atomic absorption spectrometer, PerkinElmer, Inc., Shelton, Connecticut 06484-4794, U.S.A (FAAS, FAES techniques, pre-analysed for elemental composition by SEM/EDS), as was described in our published works [1,2,3,4,5,6] (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). The concentration was determined using ICP-OES method. All the chemicals were used as delivered without further purification [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The synthesis of ILs and DESs, as well as extraction and stripping procedures used for the different BMs, obtained from different batteries, was described in published works [1,2,3,4,5,6]. For example, for the leaching of metals from 1.5 g of BM, a mixture of 7.1 cm3 IL ([P6,6,6,14][SCN] or [P6,6,6,14][Cl]) or mixture of these two ILs showing the synergistic effect of the extraction and 4.5 cm3 H2O2 (30 wt% aqueous solution) and 8.0 cm3 of DDACl, (50% aqueous solution) was used [1]. The following mixtures {[P4,4,4,14][Cl], or [P8,8,8,8][Br], or [NBz,1,1,R][Cl] + NaCl + H2O + BM} were used in ABS method [1]. The selectivity of extraction was calculated from the concentration of metal ions in both phases [1]. The leaching of Li-ions batteries BM was proposed with 8 DESs with different additives (1.5 g of BM + 15 cm3 of DES + 15 cm3 of water + 2 cm3 of DDACl + 4.5 cm3 of H2O2) [2]. Extraction was conducted for 2h at T = 303 K, pH = 2.5–7 and O:A ratio 1:1 [2]. The extraction with ILs was similar: 1.5 g of BM + 11 g of IL ([P6,6,6,14][SCN]) or 15.5 g of trihexyl tetradecylphosphonium bis(2,4,4-trimethylpentyl)phosphinate, [P6,6,6,14][BTMPP] + 5 g of toluene + 4 cm3 of water + 8 cm3 of DDACl + 4.5 cm3 of H2O2) for 2–6 h at T = 313 K [2]. The leaching of LiPBs was provided with 5 DESs and 3 bi-functional ILs. A mixture of 10 g of BM + 15 g of DES + 10 cm3 of water + 8 cm3 of DDACl + 5 cm3 of H2O2 (or 8 g of TCCA in 22 cm3 of acetone, or 15 g of glycine) was stirred under reflux for 2 h, 3000 rpm at T = 333 K at pH = 3, and then the liquid phase was analysed for the metal ion content [3]. For the extraction procedure for the Ni-Cd batteries with ILs ([P6,6,6,14][SCN] and ([P6,6,6,14][Cl]), equal volumes of 15 cm3 of aqueous phase and 15 cm3 of organic phase with 1.5 g of the BM as for Li-ion batteries were used [4]. The mixtures were stirred for 30 min, 5000 rpm at T = 318 K [4]. Also, two DESs were used for the extraction of Ni, Cd-DES 1 and DES 2 [4]. The leaching procedure was similar to ILs—a mixture of 15 cm3 of DES, 1.5 g of the BM and 15 cm3 of water was used for 30 min, at T = 318 K at pH = 3 (ratio O:A = 1:1) [4].

Figure 1.
BM of Li-ion battery after powdering [2].
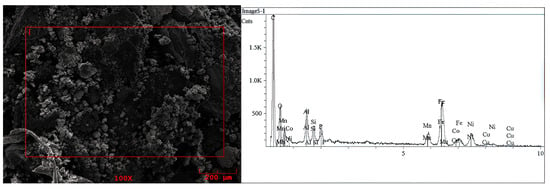
Figure 2.
SEM picture of the LiPBs BM solid sample and EDS spectrum of micro area marked on the image [3].
Two methods of acidic leaching were used: I (4M H2SO4 + 100 g/dm3 (NH2)2CS + 13 g/dm3 Fe2(SO4)3), and after two steps of leaching, II {5M HNO3 and (4M H2SO4 + 100 g/dm3 (NH2)2CS + 13 g/dm3 Fe2(SO4)3)} was used for the WPCB material after the thermal pre-treatment at a temperature T = 1023 K for 7 h [5]. The extraction of metal ions was performed using the acidic leachate [5] or from BM of WPCBs only after the thermal pre-treatment [6]. In the first work, the extraction was performed by using 4 cm of the liquid leachate phase of pH = 3–7, 5 cm3 of IL and 1 cm3 of H2O2 [5]. The [P6,6,6,14][Cyanex272] (from acidic leachate only), or [N10,10,1,1][D2EHPA], or [N10,10,1,1][Cyanex272],or [N10,10,1,1][SAL] was used in toluene (6.4 g of IL + 2.07 g of toluene). Mixture was stirred for 30 min at a temperature T = 303 K with A/O = 1:2 [5]. For the ABS method, 10 cm3 of the liquid leachate phase of pH = 3 + 2.2 g of NaCl + 8 g of IL ([P8,8,8,8][Br], or [P4,4,4,14][Cl]) + 1.5 cm3 H2O2 was used [5]. The mixture was stirred for 2 h at a temperature T = 303 K at pH = 7. The extraction was carried out for 2 h at a temperature T = 318 K [5]. Two DESs were used, DES 1 and DES 2, at temperature T = 333 K for 2 h at pH = 3–5. To 1.5 g of the BM after the thermal pre-treatment; 15 cm3 of DES + 8 cm3 of DDACl + 4 cm3 of H2O2 + 3 cm3 of water were mixed. The ratio is O:A = 1:1 v/v [5]. In the second work, 1.5 g of the BM of WPCBs only after the thermal pre-treatment was used with mixture of 15 cm3 of DES 1 or DES 2, 8 cm3 of DDACl, 4 cm3 of H2O2 and 3 cm3 of water as an extracting solution for 2 h, 3000 rpm at T = 333 K at pH = 5, O/A = 1:1 [6]. The following ILs were used with the addition of the oxidizing agent TCCA: [P4,4,4,4][Cl], [P4,4,4,14][Cl], [P8,8,8,8][[Br], [P6,6,6,14][Cl], [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO], [N10,10,1,H][HSO4], [N10,10,1,1][H2PO4], or [P4,4,4,4][H2PO4]. The mixture of 16 g of the IL + 1.5 g of the BM of WPCBs + 10 cm3 of H2O + 8 cm3 of DDACl + 4-12 g of TCCA (in 11–33 cm3 of acetone) for 2 h at 3000 rpm at T = 318 K, at pH = 2 was used for the extraction of metal ions. The O/A ratio = 2:1 for one-stage or two-stage extractions. The addition of glycine (4–12 g) and H2O2 (4 cm3) was also performed using the following ILs: [P4,4,4,4][Cl], [P8,8,8,8][Br], or [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO]. The extraction process was carried out for 2 h at 3000 rpm at T = 333 K, at pH = 6. Extraction with the addition of PHM (4–16 g) was also performed [6].
For all systems, the amount of solvents and additivities, temperature of the process pH and liquid/solid, as well as O/A ratios and the extraction efficiency and distribution ratios were described [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The utilization of new ILs/DESs with new additives may serve as a potential alternative to the acidic leaching methods.
2.1. Effects of the Extraction from Different Sources
To verify the effectiveness of the leaching, the extraction efficiency for the metal ion content was usually described as follows:
where g0/(g) is the initial metal content in BM, gE,Aq/(g) is the metal ion content in the aqueous phase, and gE,O/(g) is the metal ion content in the organic/DES phase after the extraction. The distribution ratio is as follows: [D = (content of metal ions after extraction/initial metal content in BM) × VAq (H2O + H2O2 + DDACl)/VIL or DES], where VAq or VIL or DES are the volumes of the measured probe [1]. The extraction efficiencies of metals from the BM or WPCB material after the thermal pre-treatment using ILs, mixtures of two ILs (synergistic effect) or ABS method were not as successful (E = 13–38%) as the extraction of metal ions from the aqueous solutions with the same methods (E = 60–99%) measured earlier [10].
The well-known organophosphorous-based acids were used as extraction solvents for different metals with good extractability and high extraction efficiency in many works [32]. In works presented here, a mixture of Cyanex 272 and DPh at low temperature T = 318 K, pH = 2.5, O/A = 1/1 was used with the addition of DDACl surfactant [1]. The extraction efficiency was satisfactory for zinc, EZn = 85.5–100 wt%, DZn = 0.9–1 at O/A = 1/1 at pH = 2.5 [1]. Extraction with DES 1 and DES 2 was also very successful for Zn(II), (EZn = 70–92 wt%) [1]. See the Patent Application in [33]. Zinc deposits of 95–100% purity were obtained during the potential controlled electrolyses [1]. The selective leaching performances of DESs miscible with water for the extraction of Co(II) (88.5 wt%), Li(I) (86.7 wt%) and Ni(II) (84.5 wt%) from the Li-ion batteries were shown [2]. DES at pH = 2.5 and DES (ChCl:phenylacetic acid, 1:2) for Co(II) (98.7 wt%) and for Li (I) (100 wt%) as well as DES (benzethonium chloride, [Benzet][Cl]:lactic acid, 1:2} for cobalt(II) (89.2 wt%) were presented [2]. The new proposed DES (ChCl/phenylacetic acid, 1:2) was very successful, with a leaching efficiency of 100 wt% of Li(I), DES:A = 1:1 [2]. The addition of Na2SO4 to Cyanex 272 revealed a Li(I) extraction efficiency of 92.0 wt%. The best results were obtained with D2EHPA (+ DDACl, H2O2 and Na2SO4) for all metals {Co(II), Li(I) and Ni(II)} at the level ca. 100 wt% [2].
The high extraction efficiency was obtained with DESs with different oxidizing additives and glycine in the solid–liquid extraction from the LiPBs BM [3]. DES 2 with the addition of (glycine + H2O2) or TCCA has shown good results. The extraction efficiency with DES 2 + glycine + H2O2 over Co(II), Ni(II), Li(I), Mn(II) was 60–65 wt% and for Cu(II) 75 wt%. DES 2, used as a new solvent with the addition of TCCA, induced an excellent extraction efficiency as large as 50–70 wt% for Co(II), Ni(II), Li(I), Mn(II) as well as 86 wt% for Cu(II) [3]. The results after the two-stage extraction and double stripping with (DES 2 + 15 g of glycine + H2O2) show the best 100 wt% extraction of all metals, except Cu(II) 75 wt% [3]. The extraction efficiency (E) of metal ions with DES 2 at T = 333 K, 2 h, at pH = 3 with different additives is presented in Table 1 and in Figure 3 and Figure 4. The results obtained with new bi-functional ILs, [N10,10,1,1][Cyanex272], [N10,10,1,1][D2EHPA] and [P6,6,6,14][Cyanex272]/toluene, were not so successful [3]. The results of the single-stage extraction for all metals were only at the level of 20–50 wt% [3].

Table 1.
The extraction efficiency (E) of metal ions extraction with DES 2 at T = 333 K, 2 h at pH = 3 [3].
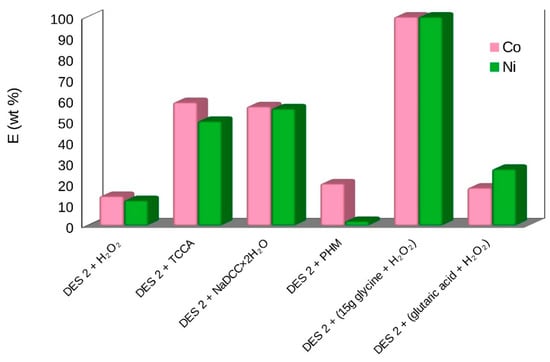
Figure 3.
The extraction efficiency (E) of cobalt and nickel extraction with DES 2 from BM of LiPBs battery at T = 333 K, 2 h, at pH = 3 with different additives [3].
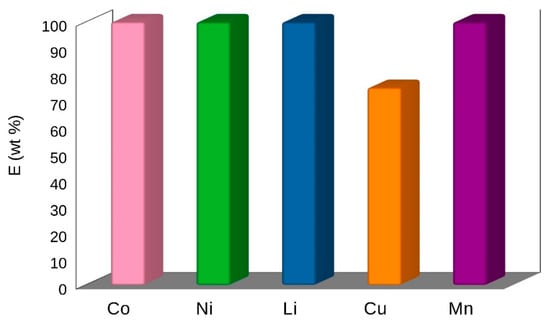
Figure 4.
The extraction efficiency (E) of metal ions extraction with DES 2 from BM of LiPBs battery at T = 333 K, 2 h, at pH = 3 with the addition of 15 g of glycine and H2O2 [3].
Furthermore, various leaching methods were systematically investigated for the extraction of metal ions from the BM of waste Ni-Cd batteries using ILs, the ABS method, two DESs and two organophosphorous acids [4]. The leaching efficiency reached 100 wt% over cadmium at a temperature of 318 K over 20 min using DES 1 and DES 2 [4]. The IL, [P6,6,6,14][Cl] was proposed for the extraction of Ni(II) from the aqueous phase after leaching BM with DES 1. The effective Ni/Cd separation was proved. The leaching of the solid BM with lL ([P6,6,6,14][Cl]) or with a mixture of two ILs ([P6,6,6,14][Cl], [P6,6,6,14][SCN]), or the ABS method showed the extraction efficiency of metals below 10–20 wt% [4]. Also, the extraction of metal ions from the BM with organophosphorous acids was only at the level of 20–30 wt% [4].
The relationship between the structure of bi-functional ILs, the ILs in the ABS method as well as the DESs and selective extraction efficiencies was investigated for the extraction of valuable metal ions from the BM of WPCBs after the thermal pre-treatment (T = 1023 K, 7 h) and two methods of acidic leaching [5]. The well-known ILs were selected for the extraction [P6,6,6,14][SCN], Aliquat 336, [P6,6,6,14][Cyanex272], [P4,4,4,14][Cl] (ABS method) and [P8,8,8,8][Br] (ABS method) [5]. The ABS method revealed the extraction efficiency of all metal ions from the liquid acidic leachate phase of 80–100 wt% at a temperature T = 303 K, after 30 min at pH = 3 [5]. The best extraction efficiency of Cu(II), Ag(I), Al(III), Zn(II) was obtained with [P6,6,6,14][Cyanex272]/toluene and was >60 wt% at a temperature T = 303 K after 30 min at pH = 7. The extraction efficiency of Ag(I) was EAg = 100 wt%, with distribution ratio D = 1 at a temperature T = 303 K for 30 min at pH = 3 using (Cyanex 272 + DPh) [5]. The results obtained with DES 2 showed lower extraction efficiencies from the solid material without acidic leaching: for Al(III), EAl = 67.3 wt%, ECu = 9.6 wt% and EAg = 14.2 wt% at pH = 5 [5].
The combination of the mechanical and thermal processes of cutting the WPCBs into small pieces, crushing in a hydraulic press and, finally, using the thermal pre-treatment at a temperature T = 1023 K for 7 h and leaching with DES 2 and DES {ChCl choline chloride + ethylene glycol, 1:2} as well as with four new ILs, such as didecyldimethylammonium propionate, [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO], didecylmethylammonium hydrogen sulphate [N10,10,1,H][HSO4], didecyldimethylammonium dihydrogen phosphate, [N10,10,1,1][H2PO4] and tetrabutylphosphonium dihydrogen phosphate, [P4,4,4,4][H2PO4], showed promise in enhancing the leaching efficiency of metals [6]. In the leaching process, the additives such as H2O2, TCCA, PHM or glycine in a single or two extraction stages were used [6]. Finally, the extraction efficiency of Ag(I) ions from the BM of the WPCB material was 100 wt% using the following ILs, [P4,4,4,4][Cl], [P4,4,4,14][Cl], [P8,8,8,8][Br], [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO] and [N10,10,1,1][H2PO4], with the addition of H2O2 or TCCA, or (glycine + H2O2) in a single or two extraction stages [6]. The best extraction efficiency of Cu(II), ECu = 68.9 wt% was with [P4,4,4,4][Cl] + TCCA (8 g, two extraction stages) and ECu = 50.1 wt% with [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO] + TCCA (8 g, two extraction stages) [6]. The best extraction efficiency of Zn(II) was EZn = 67.2–71.9 wt% with [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO] in a single or two extraction stages. The best extraction efficiency of Al(III), EAl = 81.2 wt% was with [P4,4,4,4][Cl] + TCCA (8 g, two extraction stages) and EAl = 52.5 wt% with [N10,10,1,1][C2H5COO] + TCCA (8 g, two extraction stages) [6].
2.2. Reaction Mechanism
The reaction mechanism between metal ions such as Li or Co extracted from the BM of LiBs batteries was discussed in many works [34,35,36]. The leaching process typically involves the formation of a soluble in the water anion [CoCl4]2− [36]. The mechanism of the interactions of metal ions in the solution is explained as an “ion exchange” and/or “ion pairing” interactions of metal ions transforming from the aqueous (Aq) to the organic phase (O) [37]:
2 Me+(Aq) + [Cl]−(Aq) + [COO]−(O) = MeCl(Aq) + Me[COO](O)
This reaction is possible after the process of the extraction of Me from the BM.
Generally, the driving forces for recycling and separations of metal technologies are described in many studies [14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Unfortunately, usually, there is not a complete list of metals discussed in the published papers, such as Fe, Al, Cu, Mn, Li, Co, Ni. The most important problem is to separate Co and Ni discussed in many works from 20 years for Li-ion batteries [38]. An interesting analysis of the hydrometallurgical Li-ion battery recycling was presented to understand the possible connections between different flow sheets, process parameters and the environmental impacts of the processes [39]. However, the first leaching of the BM of Li-ion batteries was usually proposed with H2SO4 [39]. Based on our investigations on the different kinds of batteries or WPCB materials, the selective leaching/extraction systems for valuable metal recycling may be considered for future technologies.
3. Conclusions
To conclude, all these results from leaching and extraction studies may provide rapid optimization parameters, such as the type of DES, or IL, or the oxidizing additives, volume ratio, extraction time, pH of the process, etc., to maximize the extraction efficiency for different metal ions from different materials. The processes presented in our works may be used for the recovery of metal ions from e-waste in future industrial applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.D.; methodology, U.D. and A.W.; formal analysis, A.W. and Z.D.; writing—original draft writing—review and editing, U.D.; visualization, U.D.; supervision, U.D.; project administration, U.D.; funding acquisition, U.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the ŁUKASIEWICZ Research Network—Industrial Chemistry Research Institute, Rydygiera 8, 01-793 Warsaw, Poland. (Decision No. 841325, 2024).
Data Availability Statement
Datasets from this study are available from the respective authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Łukomska, A.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Kolasa, D.; Luchcińska, S.; Lach, J.; Wróbel, K.; Domańska, U. Recovery of zinc and manganese from ”black mass” of waste Zn-MnO2 alkaline batteries by solvent extraction technique with ionic liquids, DESs and organophosphorous-based acids. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukomska, A.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Kolasa, D.; Luchcińska, S.; Domańska, U. Separation of cobalt, lithium and nickel from the ”black mass” of waste Li-ion batteries by ionic liquids, DESs and organophosphorous-based acids extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 343, 117694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, U.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Kolasa, D.; Wróbel, K.; Lach, J. Recovery of metals from the “Black Mass” of waste portable Li-Ion batteries with choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents and bi-functional ionic liquids by solvent extraction. Molecules 2024, 29, 3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukomska, A.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Kolasa, D.; Lach, J.; Wróbel, K.; Domańska, U. New method for recovery of nickel and cadmium from the “black mass” of spent Ni-Cd batteries by solvent extraction. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 357, 119087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukomska, A.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Lach, J.; Wróbel, K.; Kolasa, D.; Domańska, U. Recovery of metals from electronic waste—Printed circuit boards by ionic liquids, DESs and organophosphorous-based acid extraction. Molecules 2022, 27, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, U.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z. Recovery of strategic metals from waste printed circuit boards with deep eutectic solvents and ionic liquids. Processes 2024, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Sun, Y.; Rui, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, M.; Wei, L.; Lu, C.; Zhao, J.; et al. Study of the “Oxidation-Complexation” coordination composite ionic liquid system for dissolving precious metal. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Oraby, E.; Eksteen, J. Extraction of precious metals from waste printed circuit boards using cyanide-free alkaline glycine solution in the presence of an oxidant. Miner. Eng. 2022, 181, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yi, X.; Wang, R.; Huang, J.; Chen, M.; Sun, Z.; Sun, S.; Shu, J. Copper extraction from waste printed circuit boards by glycine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 253, 117463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukomska, A.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z.; Domańska, U. Liquid-liquid extraction of cobalt(II) and zinc(II) from aqueous solutions using novel ionic liquids as an extractants. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 307, 112955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho Jr, B.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Cobalt recovery from Li-Ion battery recycling: A critical review. Metals 2021, 11, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Cheali, P.; Xia, X. Progress, challenges, and prospects of spent lithium-ion batteries recycling: A. review. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 89, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, A.M.; Gabbay de Souza, R. Review of life cycle assessment on lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) recycling. Next Sustain. 2024, 3, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobó, Z.; Dinh, T.; Kulcsár, T. A review on recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 6362–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zheng, H.; Tang, K.; Xi, P.; Li, M.; Wei, L.; Guan, Q. A Comprehensive review of Lithium-Ion Battery (LiB) recycling technologies and industrial market trend insights. Recycling 2024, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.-Q.; Nie, C.-C.; Li, X.-G.; Shi, S.-X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhu, X.-N.; Wang, Z. Review on comprehensive recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries: A full component utilization process for green and sustainable production. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, A.; Bhuyan, A.; Padhy, R.K.; Mangla, S.K.; Roopak, R. Drivers of lithium-ion batteries recycling industry toward circular economy in industry 4.0. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 179, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, B.K.; Zhang, B.; Tran, P.T.M.; Zhang, J.; Balasubramanian, R. Recycling of spent lithium-ion batteries for a sustainable future: Recent advancements. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 5552–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhoi, N.K. Advancements in E-waste recycling technologies: A comprehensive overview of strategies and mechatronics integration for future development. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 42, e01182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik, E. Innovative approaches to tin recovery from low-grade secondary resources: A focus on (bio)hydrometallurgical and solvometallurgical methods. Materials 2025, 18, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Dong, T.; Sha, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Selective extraction of lithium from spent lithium batteries by functional ionic liquid. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 7022–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Jaiswal, R.V.; Baiju, C.; Gardas, R.L. An emerging trend of ionic liquids in the separation of critical metals from spent lithium and nickel based batteries. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 400, 124594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejos-Michea, C.; Barrueto, Y.; Jimenez, Y.P. Life cycle analysis of the ionic liquid leaching process of valuable metals from electronic wastes. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yan, J.; Tariq, S.M.; Duan, C.; Zhao, Y. Comparative investigation on copper leaching efficiency from waste mobile phones using various types of ionic liquids. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanossova, M. Solvent Extraction of metallic species in ionic liquids: An overview of s-, p- and d-element. J. Chem. Techn. Metallurgy 2021, 56, 443–466. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, N.; Passos, H.; Billard, I.; Papaiconomou, N.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Recovery of metals from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) using unconventional solvents based on ionic liquids. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 859–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, E.; Barmak, K.; Westa, A.C.; Park, A.-H.A. Advancements in the treatment and processing of electronic waste with sustainability: A review of metal extraction and recovery technologies. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 919–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wstawski, S.Z.; Emmons-Burzyńska, M.; Rzelewska-Piekut, M.; Skrzypczak, A.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Studies on copper(II) leaching from e-waste with hydrogen sulfate ionic liquids: Effect of hydrogen peroxide. Hydrometallurgy 2021, 205, 105730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.-J.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.-T.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.-X.; Yang, B. Copper leaching from waste printed circuit boards using typical acidic ionic liquids recovery of e-wastes’ surplus value. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masilela, M.; Ndlovu, S. Extraction of Ag and Au from Chloride Electronic Waste Leach Solutions Using Ionic Liquids. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 102810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Fray, D.J. Recovery of high purity precious metals from printed circuit boards. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1152–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; He, F.; Zhao, J.; Sui, N.; Xu, L.; Liu, H. Extraction and separation of cobalt (II), copper (II) and manganese (II) by Cyanex 272, PC-88A and their mixtures. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 93, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domańska, U.; Wiśniewska, A.; Dąbrowski, Z. Recovery Method of Zinc and Manganese from ‘‘Black Mass” of Zinc Batteries Waste Using the Extraction Method with Eutectic Mixture, Ionic Liquids and Organphosphorous Acids. Polish Patent PL 243042, 22 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Xu, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X. Electrochemical behavior and electrodeposition of cobalt from choline chloride-urea deep eutectic solvent. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 295, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, N.; Binnemans, K.; Riaño, S. Solvometallurgical recovery of cobalt from lithium-ion battery cathode materials using deep-eutectic solvents. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, G.; Lu, Q.; Hua, M.; Li, H.; Ni, X.; Wu, P.; Zhu, W. Engineering a tandem leaching system for the highly selective recycling of valuable metals from spent Li-ion batteries. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudesocque, S.; Mohamadou, A.; Dupont, L.; Martinez, A.; Dechamps, L. Use of dicyanamide ionic liquids for extraction of metal ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 107894–107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janiszewska, M.; Markiewicz, A.; Regel-Rosocka, M. Hydrometallurgical separation of Co(II) from Ni(II) from model and real solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinne, M.; Aromaa-Stubb, R.; Elomaa, H.; Porvali, A.; Lundström, M. Evaluation of hydrometallurgical black mass recycling with simulation-based life cycle assessment. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2024, 29, 1582–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).