Abstract
This article presents a study on the development of amorphous aluminophosphate (Am-AlP) and silico-aluminophosphate (Am-SiAlP) materials for the removal of cadmium (Cd) from wastewater. Cadmium is a toxic heavy metal that poses significant environmental and health risks, and its removal from water sources is crucial. This study explores the synthesis of these materials, focusing on the impact of silicon content on their adsorption properties. The materials were characterized using various techniques, including FTIR, XRD, TGA, and BET analysis, which revealed that the incorporation of silicon increased the surface area and porosity of the adsorbents, enhancing their cadmium removal efficiency. The Am-SiAlP (7.5) sample, with a 7.5 mol% Si content, showed the highest adsorption capacity (52.63 mg g−1) and removal efficiency (93%). Kinetic studies revealed that over 90% of cadmium was removed within the first 30 min, indicating rapid adsorption capabilities. The adsorption process was found to follow a pseudo-second-order kinetic model, indicating chemisorption as the rate-limiting step. The Langmuir isotherm model best described the adsorption, suggesting monolayer adsorption of cadmium on the adsorbent surface. This study also investigated the effect of interfering ions, showing that while the presence of other ions slightly reduced the adsorption efficiency, the Am-SiAlP (7.5) material still performed well. This research concludes that Am-SiAlP materials, particularly Am-SiAlP (7.5), are promising adsorbents for cadmium removal due to their high efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental friendliness.
1. Introduction
Accelerated industrial growth and urbanization have precipitated severe environmental degradation, with heavy metal (HM) contamination emerging as a critical concern [1]. Defined by elevated atomic weights and densities (>5 g/cm3), HMs such as cadmium (Cd), arsenic (As), lead (Pb), mercury (Hg), and chromium (Cr) are non-biodegradable, persistent in ecosystems, and prone to bioaccumulation, posing substantial risks to human health and ecological stability [2]. While natural phenomena like volcanic eruptions contribute marginally to HM dispersion, anthropogenic activities—mining, metallurgical processes, industrial waste discharge, vehicular emissions, and intensive agriculture—are the predominant sources [3]. The pervasive accumulation of HMs in aquatic environments threatens biodiversity and necessitates urgent remediation strategies.
Cadmium, in particular, exhibits exceptional ecological toxicity due to its ionic mimicry of calcium, enabling substitution in mineral matrices via shared ionic radii and charge characteristics [4]. Its environmental persistence and mobility—amplified by runoff, irrigation, and sedimentation—facilitate bioaccumulation in the food chain, culminating in severe human pathologies such as itai-itai disease, renal dysfunction, bone demineralization, and carcinogenesis [5]. Regulatory bodies like the EU and WHO have established stringent thresholds for Cd in water systems (0.08–27 μg/L and 3 μg/L, respectively), reflecting the gravity of its environmental impact [6].
To mitigate HM pollution, technologies such as co-precipitation, ion exchange, membrane filtration, and adsorption have been advanced [7,8]. Adsorption, however, dominates due to its operational simplicity, cost-efficiency, and adaptability in adsorbent design (e.g., carbonaceous substances, biopolymers, zeolites, and metal–organic frameworks) [9,10]. Recent innovations include magnetic composites and functionalized aluminophosphates, which offer scalable and regenerative solutions for Cd sequestration [11,12].
Amorphous aluminophosphates (Am-AlP) and silico-aluminophosphates (Am-SiAlP) represent a sustainable class of porous adsorbents, synthesized without toxic surfactants or extreme conditions [13,14]. Their high surface area and tunable porosity enhance catalytic performance in organic syntheses (e.g., transesterification), yet their application in HM adsorption remains underexplored [15]. Metal doping (e.g., Fe3+ in Am FeAlP) modifies pore architecture and surface chemistry, improving Cd adsorption kinetics and capacity beyond crystalline analogs [16].
This study synthesizes and characterizes Am-AlP and Am-SiAlP materials, optimizing silicon content (Si/Al ratio) to assess their Cd removal efficiency. Experimental variables—contact time, temperature, and Si incorporation—were systematically evaluated to elucidate their effects on adsorption performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Aluminum nitrate nonahydrate, sodium silicate solution (SiO2~26.5%), 85 weight % phosphoric acid, 25% ammonium hydroxide solution, and cadmium nitrate tetrahydrate were all purchased from Sigma Aldrich, Dorset, UK.
2.2. Material Preparation
2.2.1. Am-AlP
Amorphous aluminophosphate (Am-AlP) was synthesized via a co-precipitation method adapted from the literature [13]. The protocol involved dissolving 20 g of aluminum nitrate nonahydrate in 400 mL of distilled water under magnetic stirring. Once fully dissolved, 3.61 mL of phosphoric acid was introduced to maintain a 1:1 Al:P molar ratio, followed by 10 min of continuous agitation. The pH was then adjusted to 7.0–7.5 by dropwise addition of ammonium hydroxide, triggering the formation of a dense white precipitate. This precipitate was aged in its mother liquor for 2 h, vacuum-filtered, and repeatedly rinsed with distilled water. The filtered solid was oven-dried at 60 °C for 6 h and subsequently calcined in a muffle furnace at 300 °C for 5 h to yield the final amorphous product.
2.2.2. Am-SiAlP
Amorphous silico-aluminophosphates (Am-SiAlP) were prepared using a procedure analogous to that employed for Am-AlP synthesis, with sodium silicate introduced as a silicon source before ammonium hydroxide addition. The silicon-to-aluminum molar ratios tested were 0.025:0.975, 0.05:0.95, 0.075:0.925, and 0.100:0.900. To create the Am-SiAlP (2.5) variant (0.025:0.975 ratio), 0.16 g of sodium silicate was mixed with 19.31 g of aluminum nitrate and 3.61 mL of phosphoric acid in 400 mL of distilled water. Five batches of adsorbent were produced, labeled as Am-SiAlP (xx), where “xx” represents the silicon content in mol percent. For example, a silicon-free sample (0:1 ratio) was termed Am-AlP, while the 0.025:0.975 ratio sample was labeled Am-SiAlP (2.5). All synthesized materials underwent calcination at 300 °C for 5 h to yield the final product.
2.3. Material Characterization
The surface functional groups of the synthesized Am-AlP and Am-SiAlP adsorbents were analyzed using Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy (PerkinElmer Spectrum 100, PerkinElmer, Shelton, CT, USA) to identify key chemical moieties. Powder X-ray Diffraction (PXRD) (PANalytical X’pert Pro, Cu Kα radiation, λ = 0.154056 nm) was employed to determine crystallinity, phase composition, and structural integrity. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) (TA Instruments Q500) assessed thermal stability by heating samples to 700 °C at 10 °C/min under nitrogen, monitoring mass loss associated with decomposition. Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area and porosity were quantified via nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms at 77 K using a Micromeritics TriStar II 3020 (Malvern Panalytical, Freat Malvaen, UK). Finally, Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) (Thermo Scientific iCAP 7400, Thermo Scientific, Cheshire, UK) precisely measured cadmium concentrations in aqueous solutions before and after adsorption experiments.
2.4. Evaluation of Effect of Silicate Concentration on Adsorption Performance
To assess the adsorption efficacy of each material, 50 mg of the adsorbent was introduced into 20 mL of a 100 ppm cadmium solution. The mixtures were continuously shaken for 6 h to maximize contact between the adsorbent and cadmium ions. Post adsorption, 1 mL aliquots were extracted from each sample, diluted tenfold, and analyzed via Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES) to quantify the residual cadmium ion concentration in the solution. The removal efficiency was determined from
The cadmium adsorption capacity was calculated from the following equation:
In Equations (1) and (2), and are the liquid-phase concentrations of cadmium initially and at equilibrium respectfully and both measured in mg L−1. is volume of synthetic wastewater solution (L) and is the mass of dry adsorbent used for the experiment in grams. Sample with the highest removal efficiency was used in the detailed adsorption study outlined below.
2.4.1. Isotherm Study
The Cd2+ adsorption isotherm for Am-SiAlP (7.5) was studied by adding 0.05 g of the adsorbent to 20 mL cadmium solutions with initial concentrations between 250 and 800 ppm in separate glass vials. Seven vials, each containing a different Cd2+ concentration, were placed in water baths maintained at controlled temperatures (room temperature, 30 °C, 40 °C, 50 °C, and 60 °C). A magnetic hotplate stirrer (Radleys) beneath the baths regulated the temperature while maintaining a constant stirring speed of 200 rpm. After 48 h, the samples were collected for concentration analysis.
2.4.2. Adsorption Kinetics
The adsorption kinetics of Cd2+ by Am-SiAlP (7.5) were studied using a constant biosorbent dosage. A precisely measured amount of the adsorbent was introduced into 300 mL of a 300 ppm cadmium solution, resulting in a dose of 2.5 g L−1. The mixture was stirred at 200 rpm on a Radleys hotplate at room temperature for 6 h. Aliquots (0.1 mL) were taken at specified time intervals for subsequent concentration analysis.
2.4.3. Effect of Background Ions
Different salts were added to a cadmium solution with a concentration of 100 ppm to study the effect of other ions on cadmium removal. The experimental conditions were as follows: salt concentrations of 0.1 mol L−1 (NaCl, NH4Cl, K2SO4, NaHCO3, and a blank); initial Cd(II) concentration of 100 ppm; shaking time of 3 days at 110 rpm; Am-SiAlP (7.5) dosage of 1.0 g L−1; and room temperature.
2.4.4. Influence of Other Metal Ions
A measurement of 0.1 g of the Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent particles was added to each of six vials containing 50 mL of solution, with equimolar concentrations (50 mg/L) of the following binary combinations of metal ions: Cd2+–Ca2+, Cd2+–Mg2+, Cd2+–Fe2+, Cd2+–Pb2+, and Cd2+–Zn2+. After a contact time of 24 h, the concentrations of the remaining metal ions were determined using inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analysis. The uptake of Cd2+ from each binary solution, denoted as , was compared with the uptake from a solution containing 50 mg L−1 of Cd2+ only.
2.4.5. Regeneration and Reusability Study
For the regeneration experiment, the metal ion-loaded Am-SiAlP (7.5), obtained by filtration from the Am-SiAlP (7.5)/metal solution at room temperature (20 °C) following the adsorption process, was rinsed three times with distilled water to remove physically adsorbed metal ions. Subsequently, the washed Am-SiAlP (7.5) was introduced into 100 mL of eluent (0.1 mol/L HCl, NaOH, or EDTA). The mixture was then shaken for 6 h, after which magnetic separation was employed to recover the solid. The supernatant was subsequently collected and analyzed. The regeneration efficiency of the adsorbent ) and the corresponding metal recovery efficiency () were calculated as follows:
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The root mean square RSME was employed as a test statistic to analyze the data set to confirm the best fit model for the adsorption system. The calculated expression for can be written as follows:
where is the calculated amount of Cd2+ uptake on the adsorbent obtained by calculation from the different models and is the value determined from experiments, is the number of observations and is the number of parameters in the model. A smaller value of indicates a better fit of the model to the experimental date whilst a large value of indicates that the model is not fit for the model.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Samples
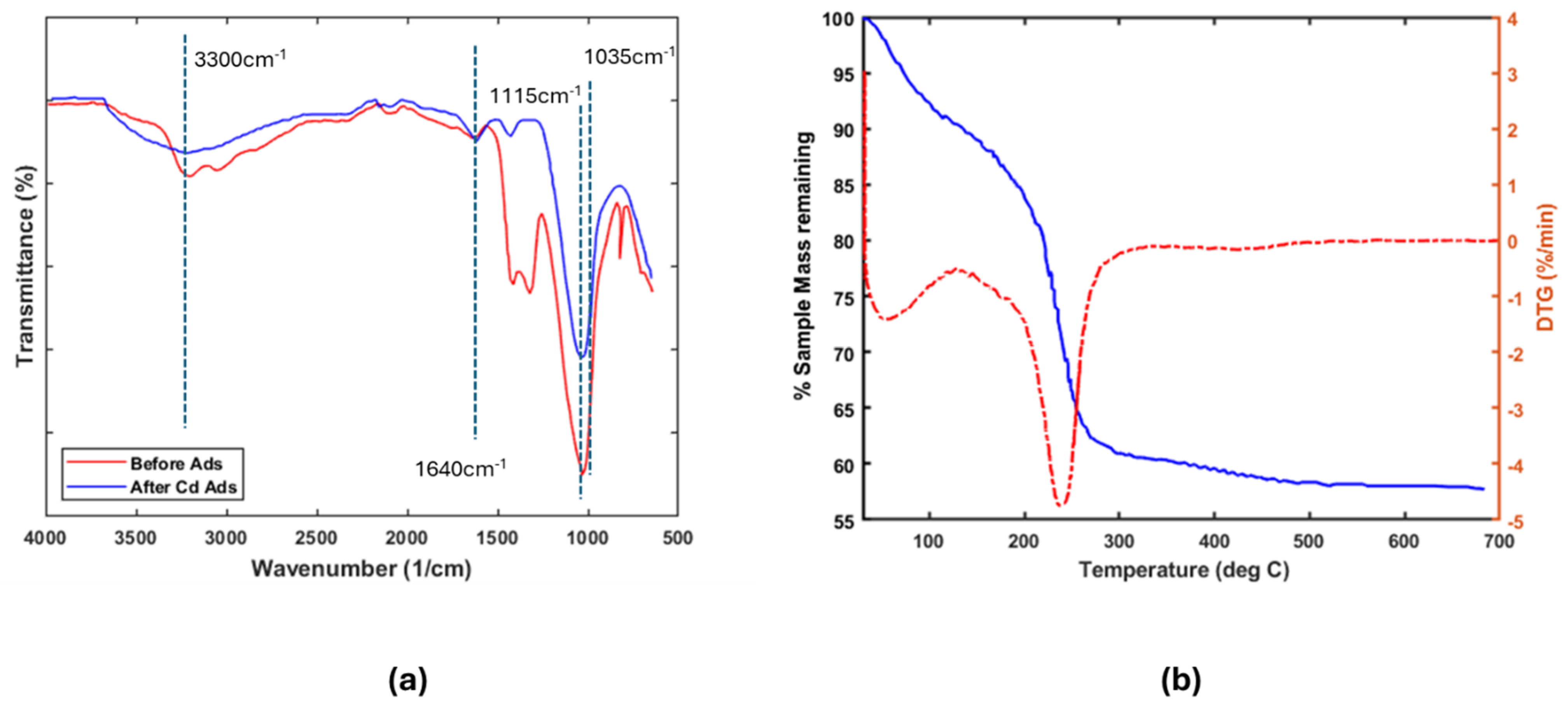
The FT-IR spectra of the materials (Figure 1) exhibit distinct absorption peaks associated with key functional groups. A broad band spanning 2700–3600 cm−1 corresponds to O–H stretching vibrations, signifying the presence of surface hydroxyl groups (Si–OH, Al–OH) and adsorbed water [17]. Additionally, prominent peaks near 1034–1047 cm−1 arise from Si–O stretching vibrations in the silicate tetrahedral framework, reflecting variations in network bonding configurations [18].
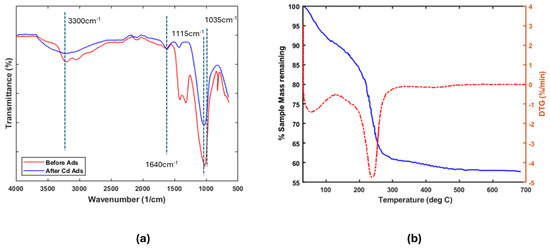
Figure 1.
(a) FTIR spectra of sample Am-SiAlP (7.5) before and after adsorption. (b) Thermo-gravimetric analysis of Am-SiAlP (7.5) obtained using a heating rate of 10 °C/min. The dashed line represents the derivative of the sample weight.
The FT-IR spectra in Figure 1a display characteristic absorption bands associated with different functional groups. The broad absorption region between 2700 and 3600 cm−1 arises from O–H stretching vibrations, confirming the presence of surface hydroxyl groups (Si–OH; Al–OH) and adsorbed moisture [17]. A sharp peak at 1115 cm−1 corresponds to asymmetric PO4 tetrahedral vibrations, characteristic of phosphate groups. Weak bands near 1640 cm−1 further indicate adsorbed water molecules [19]. Notably, the altered intensity and disappearance of specific peaks after adsorption reveal interactions between the functional groups, adsorbate, and water molecules. These spectral modifications suggest that adsorption modifies the material’s vibrational properties [20].
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed to evaluate the material’s thermal stability by measuring weight loss during controlled heating. The experiment, conducted under inert atmosphere up to 700 °C (Figure 1b), revealed three distinct thermal regimes. An initial 15% mass loss below 190 °C corresponds to physically adsorbed water evaporation. Subsequent decomposition between 190 and 280 °C suggests a thermal breakdown of labile functional groups and hydroxyl group condensation, releasing structural water molecules [7]. Above 280 °C, the constant mass indicates thermal stability, demonstrating the material’s structural integrity at elevated temperatures.
The synthesized materials’ surface characteristics were evaluated through nitrogen adsorption–desorption measurements using the BET method (Table 1). As established in the literature, surface properties such as specific area and porosity play a crucial role in governing adsorbent–adsorbate–solvent interfacial interactions [21]. Our measurements revealed consistently high BET surface areas (131–183 m2/g), aligning with previous reports by Hamza et al. [13]. A clear increasing trend in surface area was observed with silicon incorporation—pristine Am-AlP showed 121.5 m2/g, while silicon-substituted Am-SiAlP demonstrated a maximum surface area of 183 m2/g, highlighting the beneficial effect of silicon doping on textural properties.

Table 1.
BET surface area for various adsorbent materials with different silicon contents.
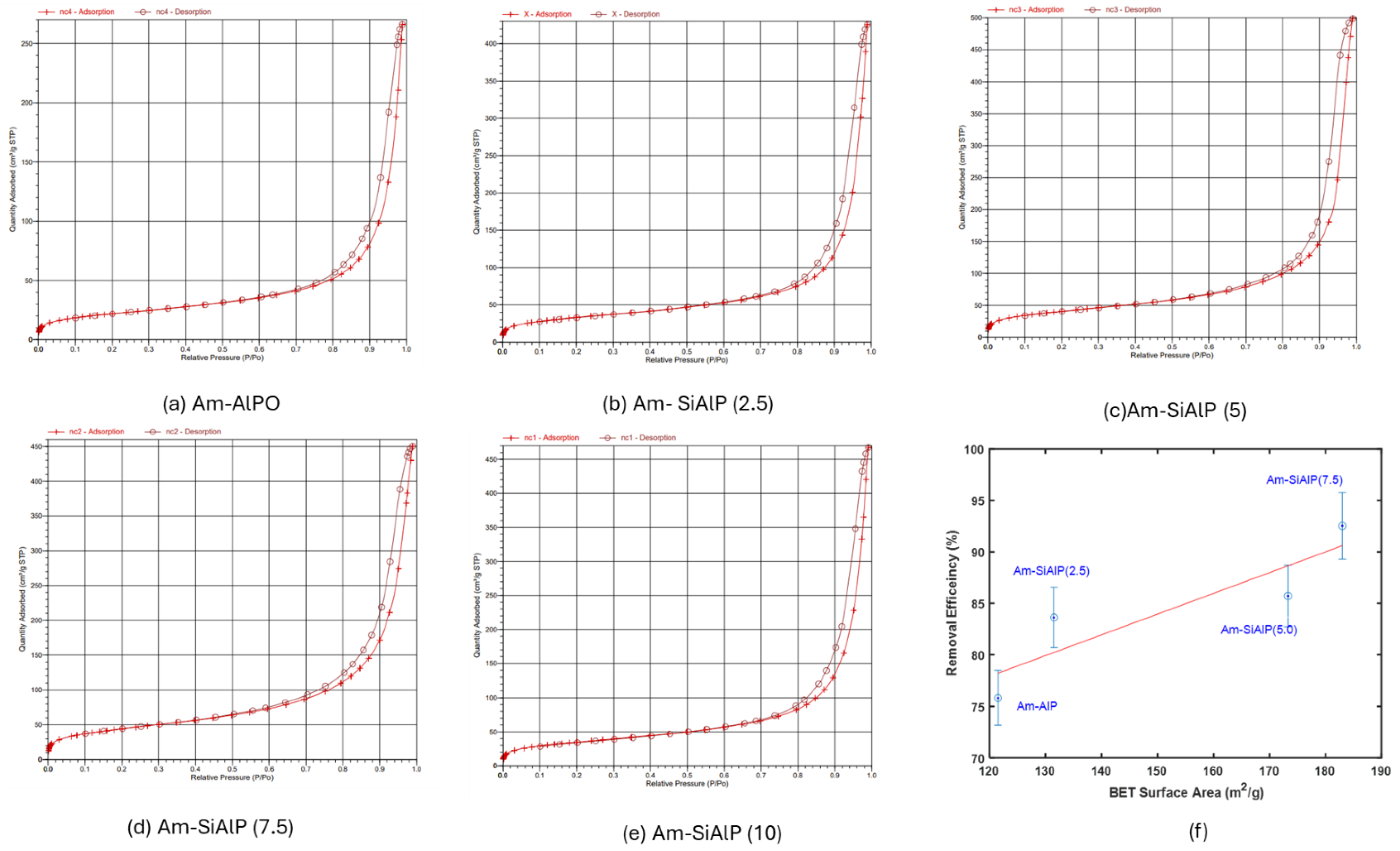
The BET isotherms for the five samples are presented in Figure 2. An H3 hysteresis loop is exhibited by the adsorption–desorption isotherms, which is indicative of flaky particles with slit-shaped, elongated, and narrow pores. This behavior is characterized as being typical of materials possessing both mesoporous and macroporous features [22].
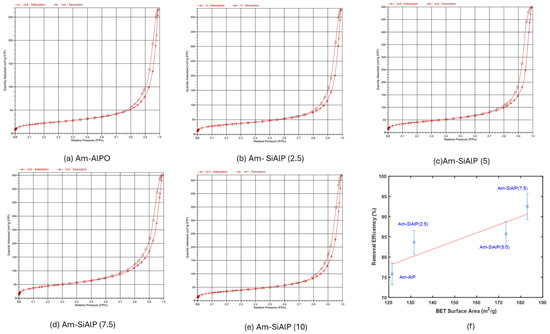
Figure 2.
(a–e) N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm of the adsorbent samples at 77 K. (f) Correlation between BET surface area and adsorption efficiency of the samples.
Overall, an increase in the BET surface area of the materials was observed with the molar percentage of silicon incorporated into the aluminophosphate (AlP) framework. However, when the Si content was increased beyond 7.5 mol% relative to the Al content, no further enhancement in the total surface area was achieved. In fact, pore blockage was caused by an increase to 10 mol% Si, leading to a reduction in the surface area for Am-SiAlPO (10). Notably, a similar trend was observed in the adsorption efficiency of the adsorbent materials, which will be discussed in detail in subsequent sections.
It was reported by Hamza et al. [13] that the pore structure is modified, the pore diameter is enhanced, and the total pore volume is increased by heteroatom incorporation in amorphous aluminophosphate. This effect was found to be particularly pronounced when the heteroatom or metal was trivalent or tetravalent, as opposed to bivalent metals. It is hypothesized that some degree of pore expansion is induced upon incorporation of Si into the aluminophosphate network to accommodate the heteroatom. The structural flexibility of amorphous aluminophosphate is highlighted by this behavior, which is comparable to the adaptability observed in zeolitic frameworks [23].
The correlation between the textural properties and the adsorption efficiency of the different samples is illustrated in Figure 2f. As shown in Figure 2f, an increase in adsorption efficiency from approximately 76% to 93% was observed as the surface area of the samples was raised from 121.5 m2/g to 185 m2/g. This trend is aligned with findings in the literature; for instance, a similar increase in removal efficiency of Cr6+ with increasing surface area was observed by Campbell et al. [24] in various coffee-based activated carbons. The pore size distribution of the samples is provided in the supplemental information as Figure S1.
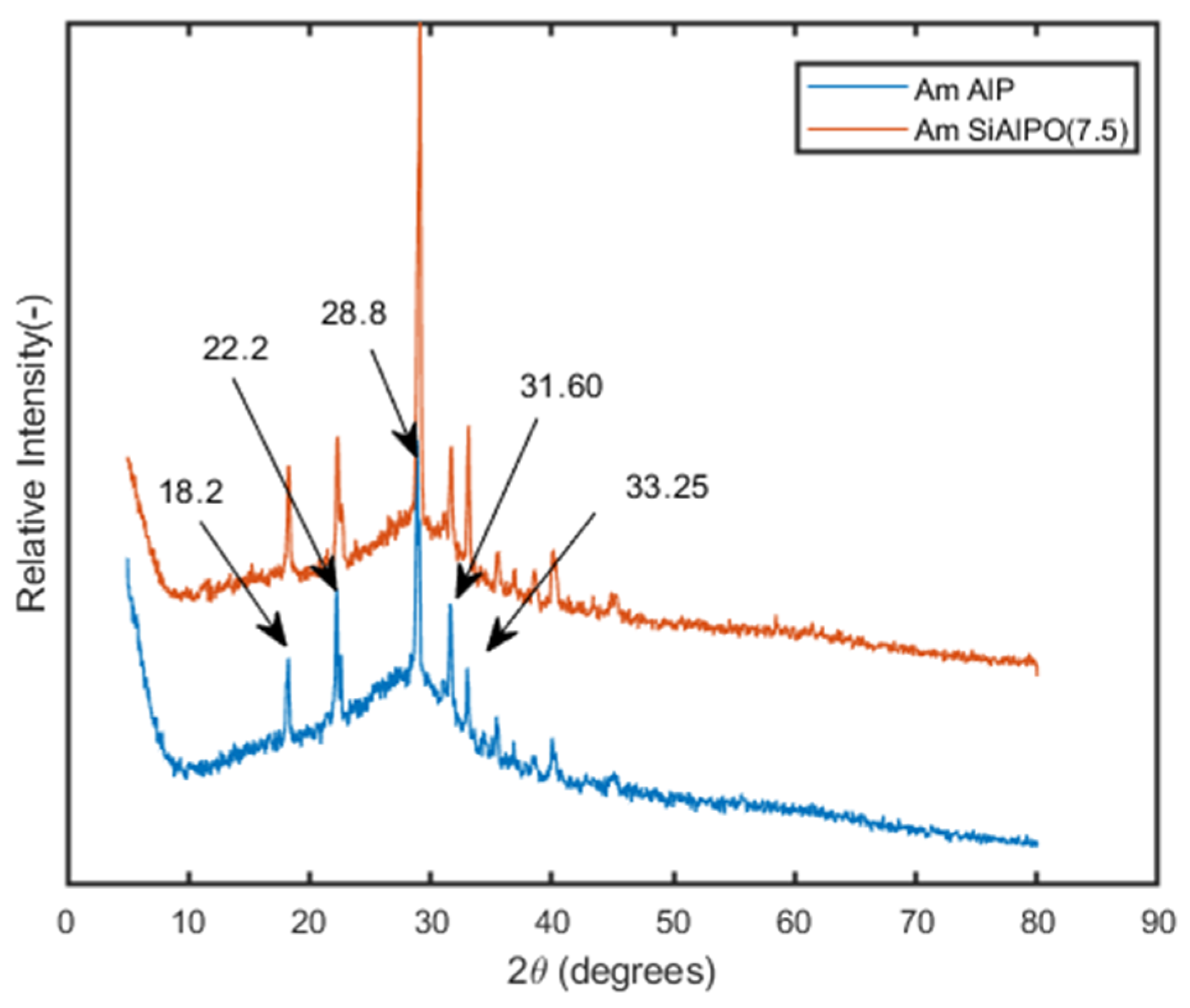
The PXRD profiles of Am-AlP and Am-SiAlP materials were recorded, and the corresponding patterns are presented in Figure 3.
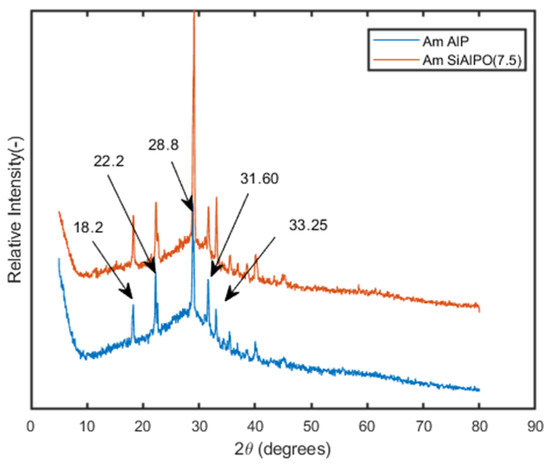
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of Am-AlP. and Am-SiAlPO (7.5) before and after adsorption of Cd2+ from wastewater sample.
These materials exhibit an amorphous nature and a low degree of crystallinity, as evidenced by a broad peak in the 2θ range of 20–40 degrees, which aligns with findings reported in the literature [20,25]. Additionally, peaks corresponding to the Berlinite phase were observed at 2θ values of 18.2, 22.2, 28.8, 31.3, 31.6, 33.25, 35.35, 36.7, 38.5, 39.0, 40.2, 44.25, and 46.0, consistent with previous studies [13].
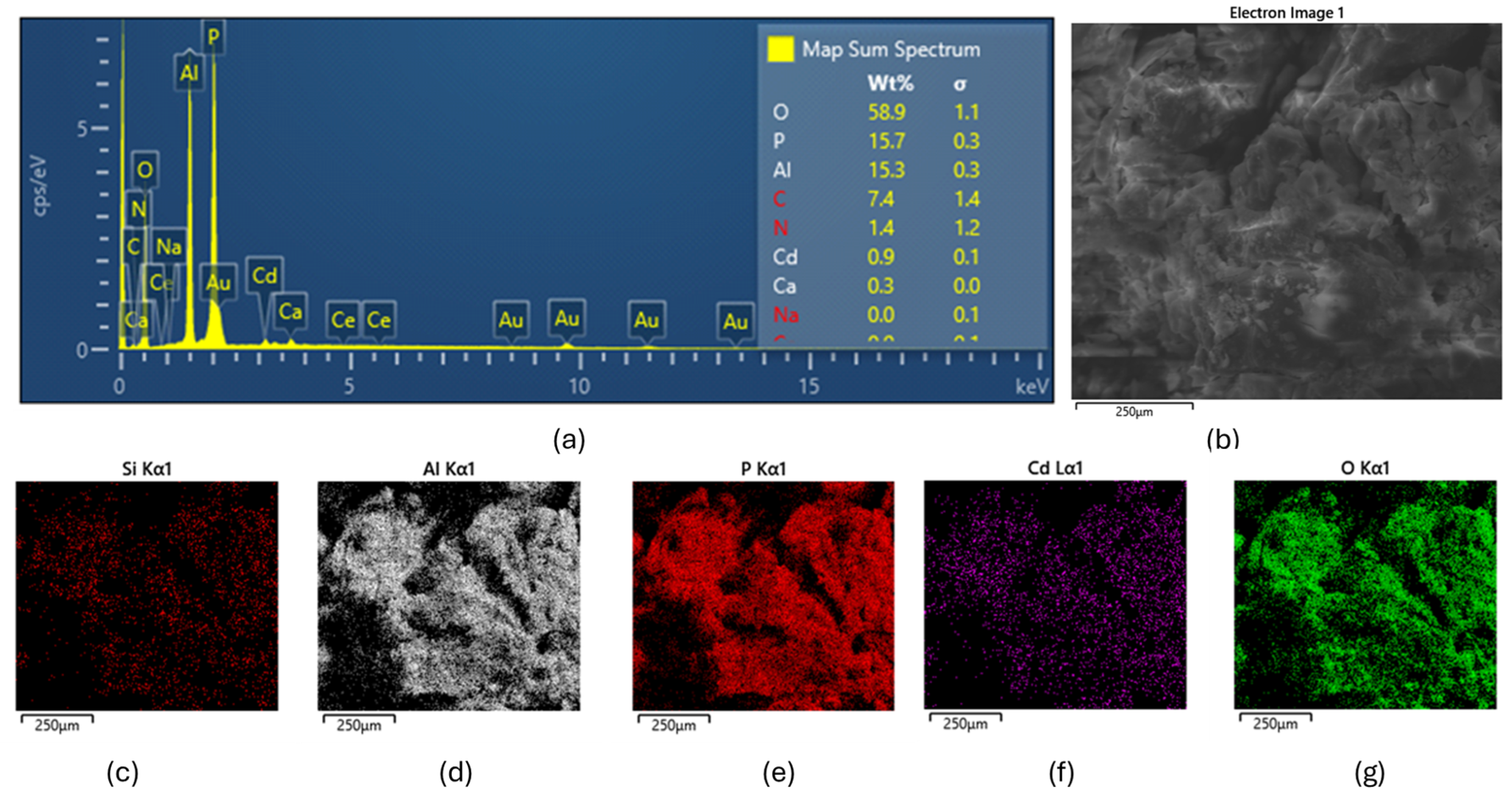
Figure 4 presents a comprehensive elemental analysis from the cadmium adsorption study. The EDAX map spectrum in Figure 4a reveals the presence of several elements on the adsorbent surface following Cd2+ adsorption, with spectral peaks corresponding to Si, Al, P, Ca, O, and, notably, Cd. The SEM image in Figure 4b depicts the morphological structure of the adsorbent post-adsorption, while the elemental mapping images (Figure 4c–g) illustrate the spatial distribution of Si, Al, P, Cd, and O across the surface.
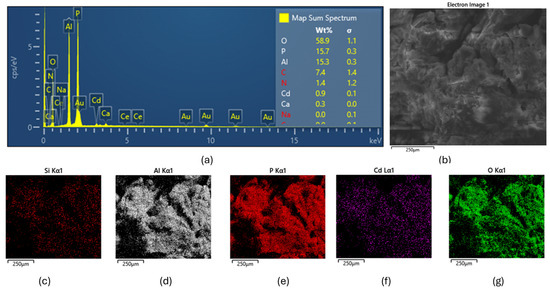
Figure 4.
Elemental and morphological characterization of the adsorbent following Cd2+ adsorption. (a) EDAX spectrum showing the presence of Si, Al, P, Ca, O, and Cd on the adsorbent surface; (b) SEM image illustrating the surface morphology post-adsorption; (c–g) elemental mapping images depicting the spatial distribution of (c) Si, (d) Al, (e) P, (f) Cd, and (g) O across the surface of the adsorbent.
The SiAlP material appears to be an aluminosilicate-based adsorbent modified with phosphorus. Similar materials have been studied by [26], who demonstrated that phosphorus-modified aluminosilicates can significantly enhance heavy metal removal via multiple mechanisms, including ion exchange, complexation, and precipitation. The elemental maps showing co-localization of Cd with Al and P suggest potential complexation mechanisms. This observation is consistent with the findings of [27], who reported that phosphorus-rich binding sites in modified adsorbents tend to form stable complexes with cadmium ions, thereby improving removal efficiency.
The successful adsorption of Cd2+ onto the adsorbent surface was further confirmed by SEM–EDX analysis. The map-sum spectrum of detected elements, shown in Figure 4, indicates that approximately 0.9% of Cd was present on the surface. This value is lower than that determined from batch adsorption experiments, which is expected, as only a fraction of the adsorbed cadmium resides on the surface, with the remainder likely located within the internal pores of the adsorbent. This observation is in agreement with the findings of [24], who reported a similar distribution pattern in hierarchical porous materials, where a significant portion of heavy metals is retained within internal pore structures.
3.2. Adsorption of Cd from Aqueous Solution
3.2.1. Effect of Silicon Content on Removal Efficiency
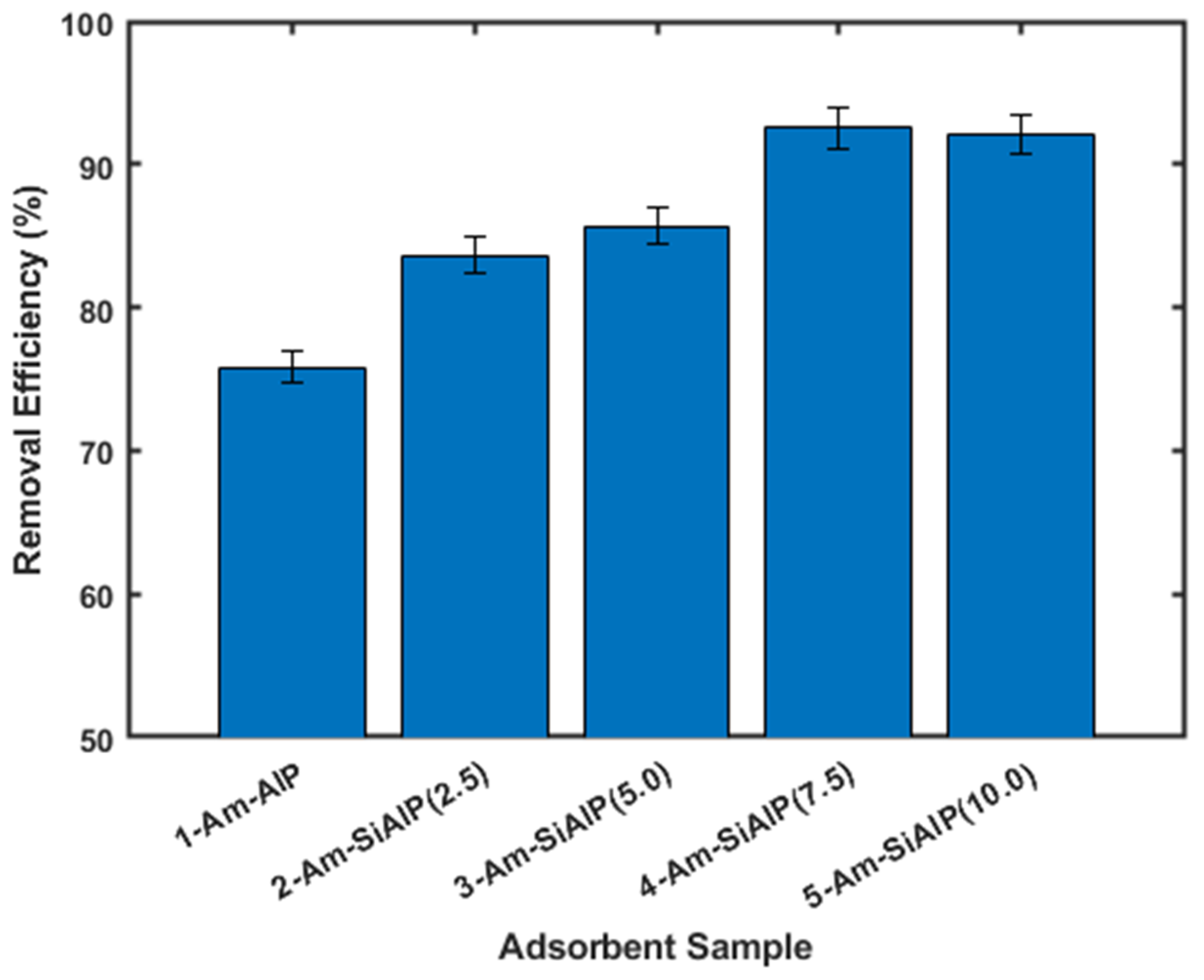
The adsorptive removal of Cd from wastewater was investigated using Am-AlP and Am-SiAlP materials as adsorbents, following the procedure outlined in the Experimental Section. As shown in Figure 5, all adsorbent materials studied in this work demonstrated activity towards Cd removal. Notably, the presence of silicon (Si) in the aluminophosphate (Am-AlP) significantly enhanced cadmium (Cd) removal efficiency. A clear trend emerged indicating that the percentage of Cd removal increased with higher molar ratios of Si in the aluminophosphate. For instance, the removal efficiency for samples without Si was approximately 76%, which improved to about 84% and 93% for samples with molar ratios of 2.5 and 7.5, respectively. The Am-SiAlP (7.5) sample exhibited the highest percentage of cadmium ion removal among all materials studied. However, increasing the molar ratio from 7.5 to 10 did not yield any further improvement in removal efficiency.
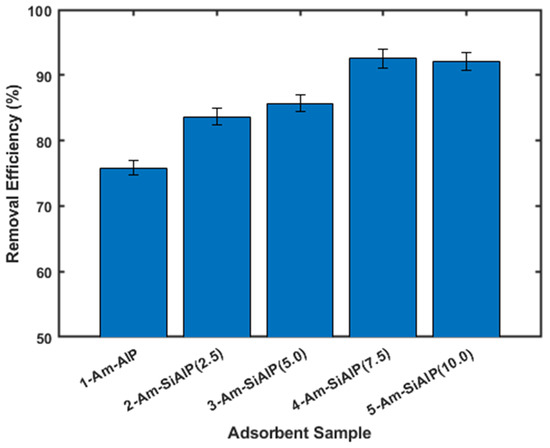
Figure 5.
Comparison of the different adsorbent materials. All experiments were conducted using cadmium solutions with initial concentration of 100 ppm and adsorbent dosage of 2.5 g L.
The increased affinity of Si-containing AlP can be attributed to the enhanced surface area and porosity of these materials. Generally, three major steps are involved in any adsorption process onto a solid adsorbent: (1) transport of the adsorbate/pollutant from the medium (in this case, Cd from an aqueous solution); (2) adsorption of the pollutant onto the solid surface; (3) transport of the pollutant within the adsorbent particle.
A higher surface area of the adsorbent improves the accessibility of Cd to the active sites, resulting in better interactions between heavy metal contaminants and these active sites [15,28]. Another benefit of incorporating Si into AlP is the potential formation of Brønsted acidic sites through the isomorphic substitution of Al by Si, a phenomenon also observed in zeolites and silicoaluminophosphates [29]. Additionally, the presence of surface silanol (Si–OH) groups in Am-SiAlP is weakly acidic, which enhances the interaction between the pollutant Cd and the adsorbent. The trends observed in this study align with other results reported in the literature [30]. The improvement in removal capacity could be attributed to changes in the surface structure of the adsorbent material upon the introduction of silicon.
3.2.2. Contact Time and Kinetics of Adsorption
Since Am-SiAlP (7.5) was identified as the most effective adsorbent in the previous set of experiments, this material was employed to investigate the effect of contact time between the adsorbent and the pollutant medium on the removal efficiency of Cd2+. The results are presented in Figure 6.
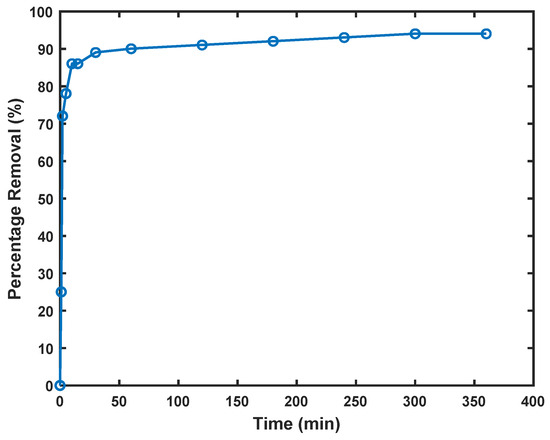
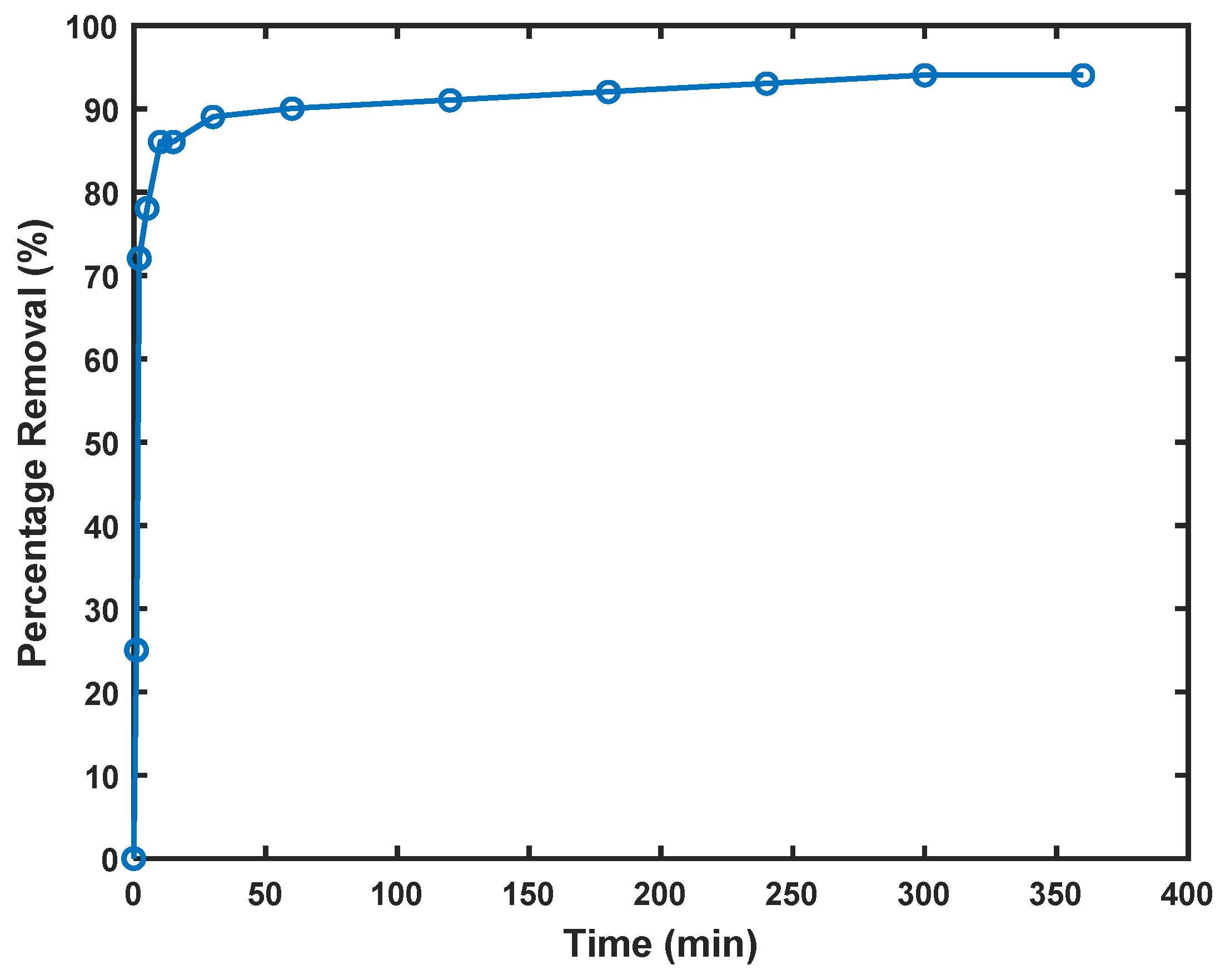
Figure 6.
Cd2+ removal as a function of contact time, dose 1.0 g/L; initial concentration of Cd2+ 0.89 mmol/L.
Figure 6 illustrates the removal efficiency of Cd2+ by Am-SiAlP (7.5) over time, demonstrating a characteristic two-phase adsorption process. During the first 15 min of the adsorption process, 86% of cadmium was removed, with the rate slowing thereafter until equilibrium was attained within ~30 min. This distinctive kinetic profile can be explained through examination of recent literature on similar adsorption systems.
The rapid initial uptake observed in Figure 6 aligns with findings by [31], who studied porous clay-based materials with comparable composition to Am-SiAlP (7.5). Their research demonstrated similar rapid kinetics for Cd2+ removal, attributing this phenomenon to the high ion exchange capacity and accessible surface sites of silicon aluminum phosphate structures. This corroborates our observation that the swift adsorptive removal of cadmium ions can be attributed to the initial abundance of active sites available for adsorption.
The two-phase adsorption pattern evident in Figure 6 is consistent with mechanisms described by [32] in their study of functionalized clay adsorbents. They observed approximately 80% removal of Cd2+ within the first 20 min, followed by a slower approach to equilibrium—a pattern remarkably similar to our findings. The experimental data reveal that after ~30 min of contact time, surface adsorption sites reach saturation, and the dominant mechanism transitions to intra-particle diffusion of Cd2+ ions from the outer to inner regions of the adsorbent.
The high removal efficiency (>95% at equilibrium) demonstrated by Am-SiAlP (7.5) in Figure 6 compares favorably with other advanced adsorbents reported in the literature. Li et al. achieved similar removal efficiencies using zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron, but required longer contact times to reach comparable removal percentages [33]. Our kinetics data also align with the findings of [34], who demonstrated that materials with multiple active sites exhibit this characteristic rapid initial uptake followed by a diffusion-limited approach to equilibrium. The phosphoric acid-based materials studied by [35] similarly showed rapid adsorption kinetics, though with lower overall efficiency than our Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent. Ref. [36] similarly observed initial rapid adsorption phases followed by slower equilibrium approaches in their studies of metal ion removal, albeit using different adsorbent materials. Their mechanistic explanations regarding the transition from surface adsorption to intraparticle diffusion support our interpretation of the kinetic data presented in Figure 6.
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics Modeling
The kinetics of the adsorption process were evaluated through application of several kinetic models. The pseudo-first-order (6), pseudo-second-order (7), Elovich (8), and Modified Freundlich (9) models were employed to determine the relevant adsorption kinetic parameters [36]:
In Equation (8), is the equilibrium adsorption capacity (the maximum amount of adsorbate retained per unit mass of adsorbent) attained at a reference time point , the parameter is given as .
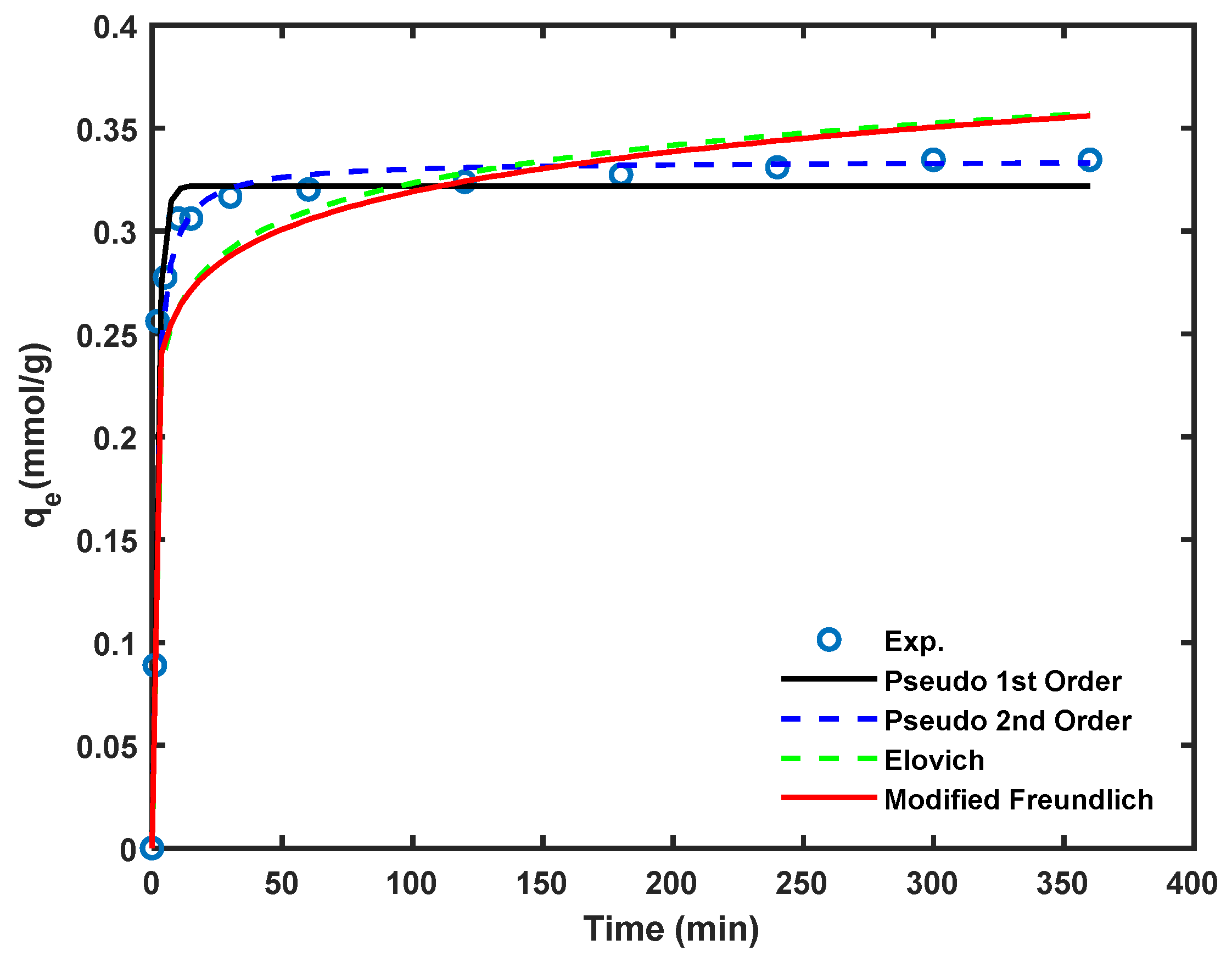
The Cd2+ removal efficiency of the Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent as a function of contact time is illustrated in Figure 7. The cadmium removal rate is highest during the initial stages, attributed to the greater availability of the adsorbent’s surface area for cadmium adsorption at the beginning of the process.
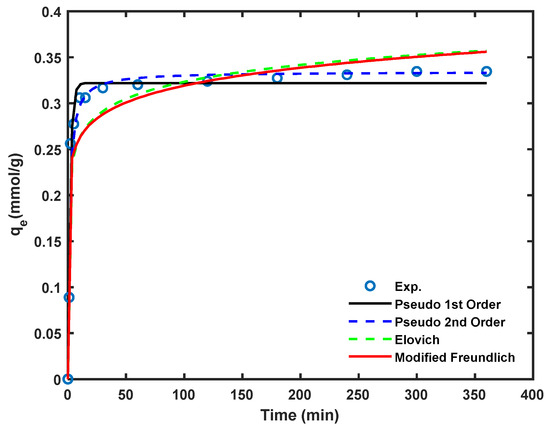
Figure 7.
Kinetics of the cadmium loading on Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent sample. All experiments were conducted using cadmium solutions with initial concentration of 100 ppm and adsorbent dosage of 2.5 g/L.
Non-linear regression on the kinetic data was performed on the date to obtain the kinetic model parameters using a bespoke code written in MATLAB version 2024a. The kinetic parameters are listed in Table 2. Comparison between the models was conducted using the Root Mean Sum Error. As can be seen, the pseudo second order model was the best among both models to describe kinetic experimental data because of the highest correlation coefficients (R2 > 0.990) and the least values of RMSE. The results indicated that the rate controlling step in Cd2+ removal was formation of chemi-sorptive bonds of between Cd2+ species and the adsorptive sites on the adsorbent surface which involves valence forces through sharing or exchanging electrons between adsorbent and adsorbate.

Table 2.
Kinetic parameters for the removal of cadmium.
3.4. Isotherm Analysis
The investigation of adsorption isotherms is essential for characterizing the equilibrium distribution of adsorbate molecules between the solid and liquid phases. In this study, the equilibrium data were analyzed using both Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. The Langmuir isotherm model is expressed mathematically as follows:
In Equation (10) qm and b are the Langmuir constants related to maximum monolayer adsorption capacity and energy of adsorption, respectively.
The Freundlich isotherm represents an empirical model frequently employed for characterizing adsorption phenomena. This model is mathematically expressed as follows:
where kf denotes Freundlich adsorption capacity parameter, and represents the adsorption intensity factor. Equation (12) represents the Sips isotherm models, respectively.
Non-linear regression of the different isotherm models to the experimental data obtained at room temperature using a custom MATLAB code are presented in Figure 8. The isotherm model parameters obtained for the non-regression fitting are presented in Table 3.
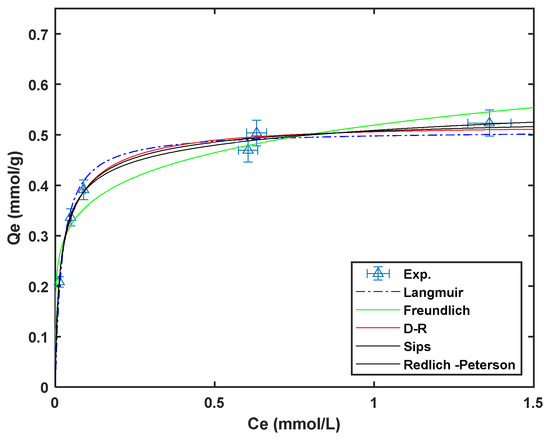
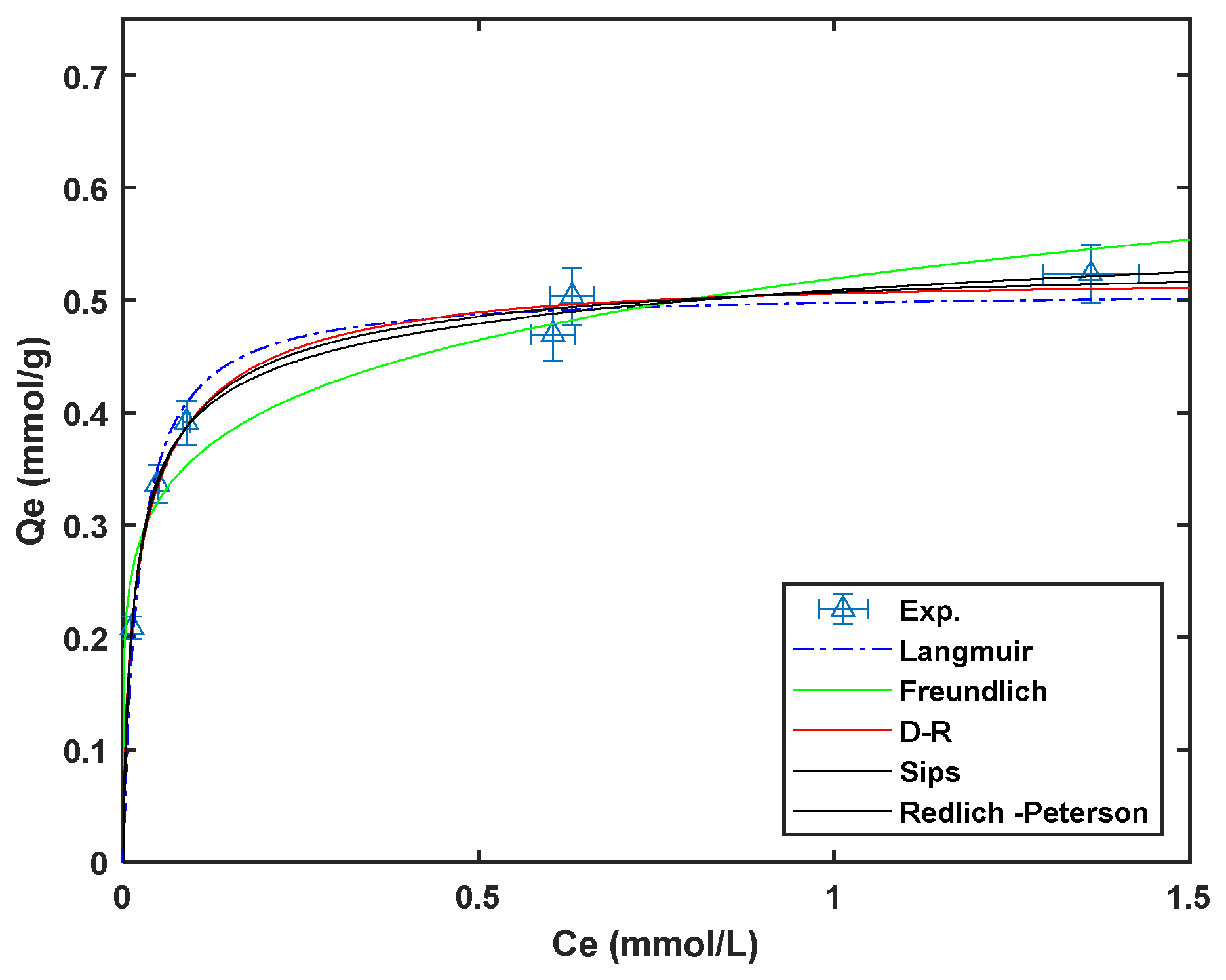
Figure 8.
Cadmium adsorption isotherms on Am-SiAlP (7.5) at 298 K (adsorbent dose: 1 g L−1, natural pH).

Table 3.
Summary of parameters of the different isotherm models for cadmium adsorption on the Am-SiAlP (7.5) at different temperatures.
The adsorption isotherms of Cd2+ on the Am-SiAlP (7.5) at 20, 40, and 60 °C were acquired at natural pH of cadmium solution. The adsorption capacities of cadmium (Cd2+) on the Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent, as presented in Table 3 of the article, were evaluated using Langmuir, Freundlich, and Sips isotherm models. The Langmuir model provided the best fit for the adsorption data, indicating that the process likely occurs through monolayer adsorption on homogeneous sites. The maximum adsorption capacity () of Am-SiAlP (7.5) was found to be 55.9 mg g−1 at 20 °C, 66.5 mg g−1 at 40 °C, and 103.2 mg g−1 at 60 °C, demonstrating a clear increase in adsorption capacity with temperature. This suggests that the adsorption process is endothermic, with higher temperatures favoring cadmium uptake. The Freundlich and Sips models also provided reasonable fits, but the Langmuir model’s higher correlation coefficients () confirmed its suitability for describing the adsorption behavior.
The results indicate that Am-SiAlP (7.5) has a high affinity for cadmium, with its adsorption capacity comparable to or exceeding that of many other adsorbents reported in the recent literature. For example, a study by [37] on polyethyleneimine-modified activated carbon reported a cadmium adsorption capacity of 103.18 mg/g, which is similar to the capacity of Am-SiAlP (7.5) at 60 °C. Another study by [38] on amino-functionalized silica gel showed a capacity of 49.52 mg g−1, which is lower than that of Am-SiAlP (7.5) at higher temperatures. Additionally, [39] investigated the removal of cadmium using anion exchange resins and highlighted the importance of surface functionalization in enhancing adsorption capacity, a principle that aligns with the findings of this study.
The high adsorption capacity of Am-SiAlP (7.5) can be attributed to its large surface area, porous structure, and the presence of silicon, which enhances surface functionality and active sites for cadmium binding. The temperature-dependent increase in adsorption capacity further suggests that the material could be highly effective in industrial applications where elevated temperatures are common. These results position Am-SiAlP (7.5) as a competitive adsorbent for cadmium removal, with potential for further optimization and application in real-world wastewater treatment scenarios. The data presented in Table 3 and Figure 8 show that the Langmuir model fit the cadmium removal best.
According to the Langmuir equation, the maximum uptake capacity of Cd2+ reached 52.63 mg g−1, when the initial concentration was 100 mg L−1, which are much higher than that of many of the previously reported adsorption materials shown in Table 4. The adsorption capacities of various adsorbents for cadmium (Cd2+) removal, as presented in Table 4 of the article, highlight the competitive performance of the developed amorphous silico-aluminophosphate (Am-SiAlP) material. The Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent demonstrated a maximum cadmium adsorption capacity of 52.63 mg g−1, which is significantly higher than many other reported adsorbents. For instance, resacetophenone-loaded silica gel and DHAQ-loaded silica gel showed much lower capacities of 7.01 mg g−1 and 7.89 mg g−1, respectively. Similarly, thiol-modified silica gel and GASG (a type of activated carbon) exhibited capacities of 10.43 mg g−1 and 6.09 mg g−1, respectively, which are considerably lower than that of Am-SiAlP (7.5).

Table 4.
Comparison of the adsorption capacities of the different adsorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions.
While some materials, such as amino-functionalized silica gel (49.52 mg g−1) and NTAA-LCM (143.4 mg g−1), showed comparable or higher adsorption capacities, the Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent stands out due to its cost-effectiveness, environmentally friendly synthesis, and high surface area. The AC/ZrO composite, with a capacity of 166.7 mg g−1, outperformed Am-SiAlP (7.5), but its synthesis and application may involve higher costs or more complex processes. Overall, the Am-SiAlP (7.5) material offers a balanced combination of high adsorption capacity, ease of synthesis, and environmental sustainability, making it a promising candidate for cadmium removal from wastewater. Its performance is competitive with many advanced adsorbents, and further optimization could enhance its applicability in real-world scenarios.
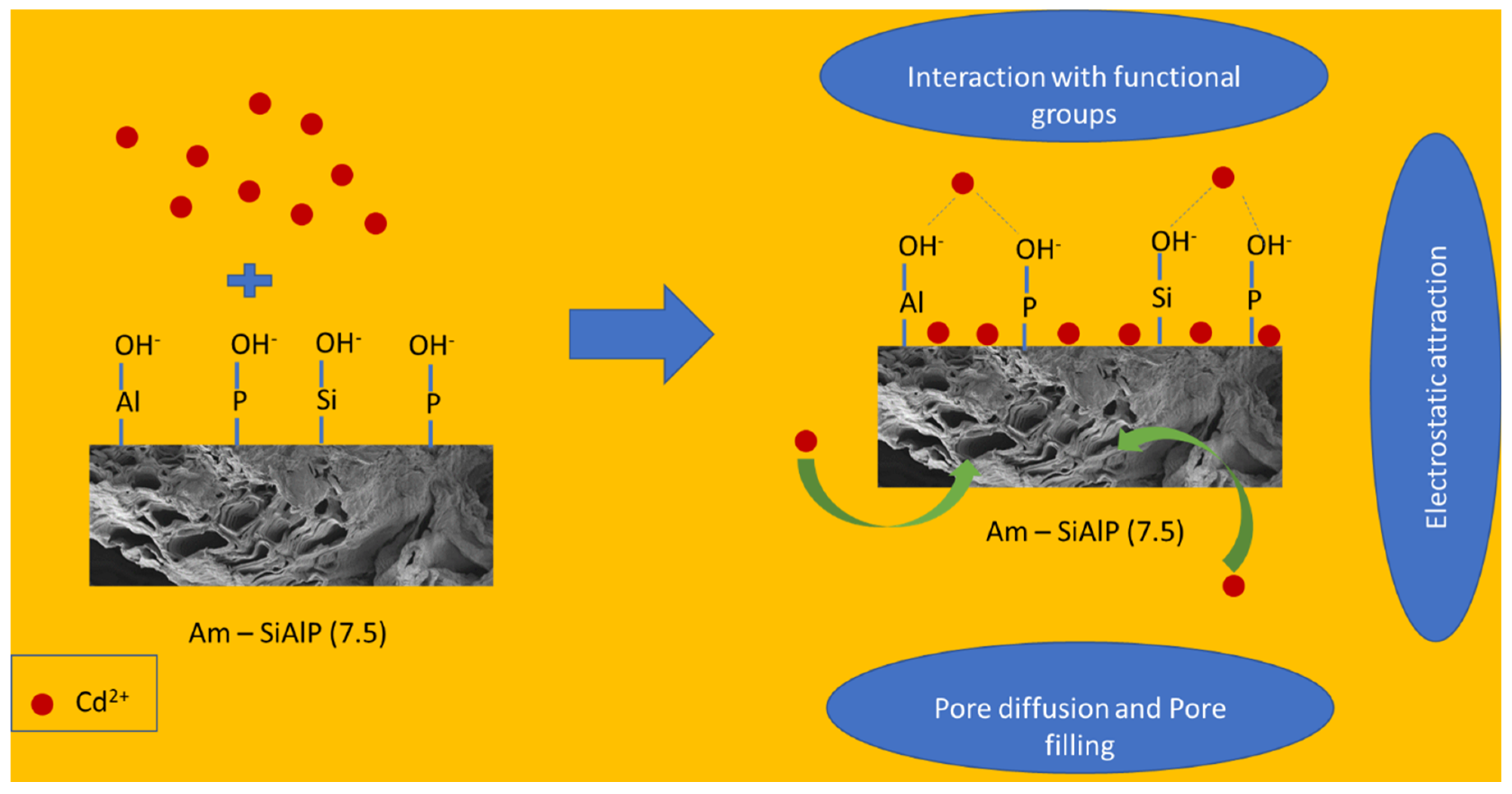
3.5. Mechanism of Removal of Cd2+ by Am-SiAlP Adsorbent
The role of active sites and active functional groups present on the surface (including the porous structure) of the adsorbent can be revealed by the changes in the FTIR peaks. Changes in the intensity or total disappearance of peaks can indicate the interaction between cadmium ions and the material surface. From the FTIR results, it is observed that the intensity of the following peaks has decreased: Peak at 710 cm−1, which corresponds to the asymmetric stretching of O-P-O; sharp peak around 1050 cm−1, which is related to Si-O-Si and Si-O-Al stretching vibrations; peak around 1400 cm−1, which is attributed to the vibrations of Si-O-Al or Si-O-P bonds, specifically the bending and stretching modes. Broad peaks from 2700 to 3500 cm−1 (bending modes of various hydroxyl groups). It is also noted that the peak around 820 cm−1 (Si-O-Si bending or Si-O-Al stretching) has completely disappeared. Based on these results and the XRD data, we believe the cadmium ions interact with these functional groups. The high surface area and porosity of the material facilitate the high dispersion of active sites throughout the network structure of silicoaluminophosphates.
A typical aluminophosphate structure consists of PO4 and AlO4 tetrahedral units that share corners through oxygen atoms. When a tetravalent Si atom incorporates into the AlPO4 framework via isomorphous substitution, the silicon atom replaces a phosphorus atom within the tetrahedral structure. This leads to a partial positive charge on the oxygen and a partial negative charge on the substituted Si atom, generating Brønsted acid sites. However, we believe that the abundant, highly dispersed, and varied hydroxyl groups (Al-OH, P-OH, and Si-OH) present on the surface act as binding sites for heavy metal cadmium, as reported elsewhere [44,45,46]. The weak chemical bonds between these hydroxyl groups are likely responsible for this interaction. We also examined the effect of pH on the performance of these adsorbent materials and observed better performance at higher pH (above 5), which is attributed to the significant deprotonation of these hydroxyl groups at higher pH. The proposed mechanism of removal of Cd2+ are summarized in Figure 9.
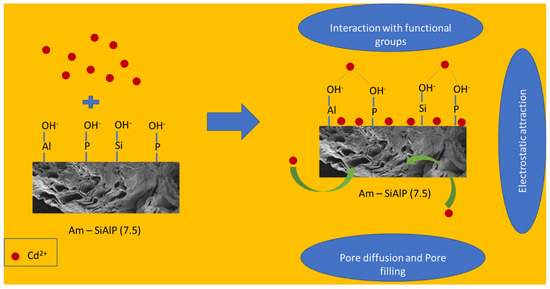
Figure 9.
Mechanism of Cd2+ by Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent.
3.6. Influence of Background Ions on Cd2+ Removal
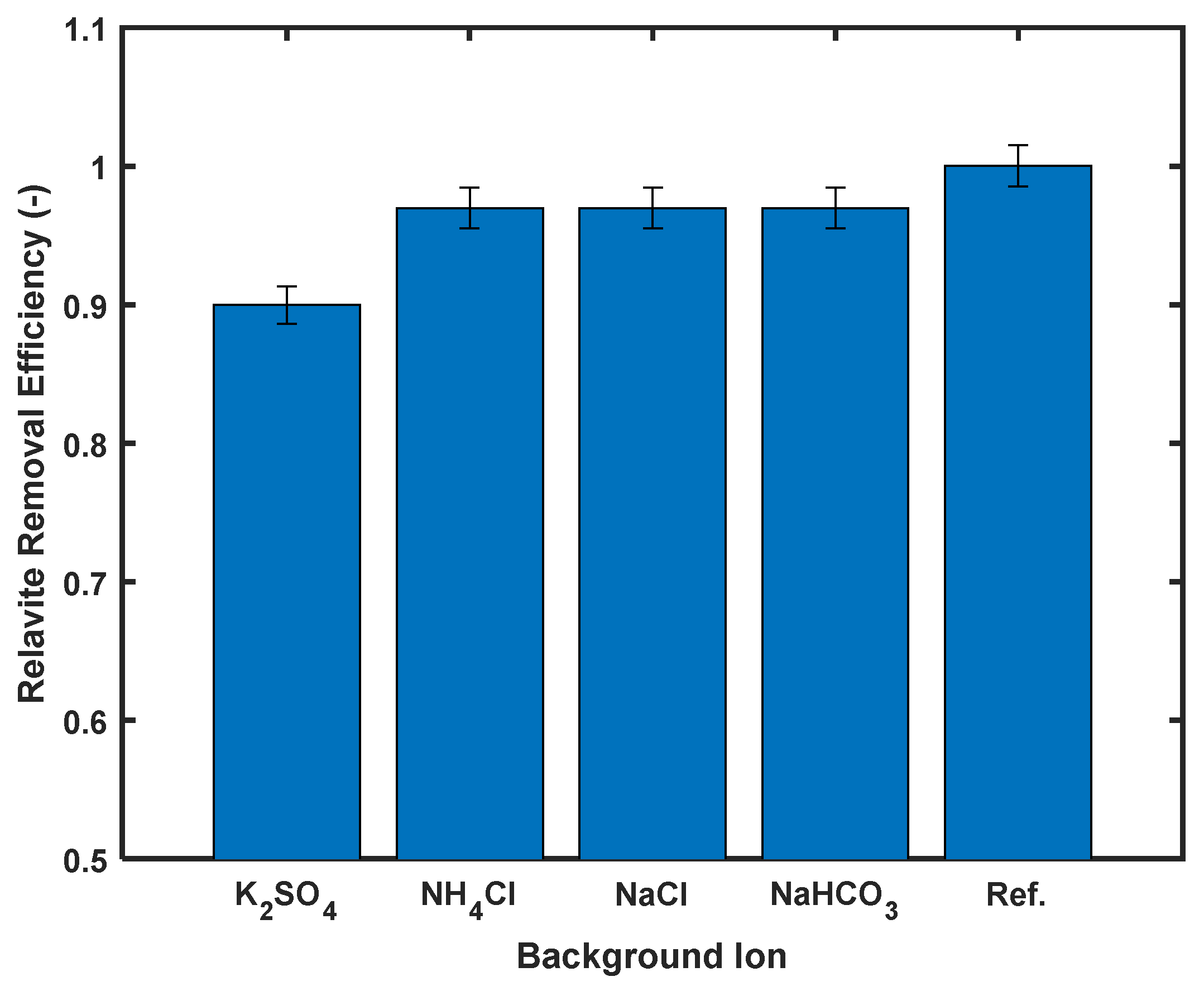
The interfering ion study was conducted to assess the effect of competing ions on Cd2+ adsorption. As illustrated in Figure 10, all tested ions exhibited inhibitory effects, with K2SO4 showing the most pronounced impact—decreasing adsorption efficiency from 93.8% to 83% (a >10% reduction). The remaining three ions caused a consistent 3.8% reduction in performance.
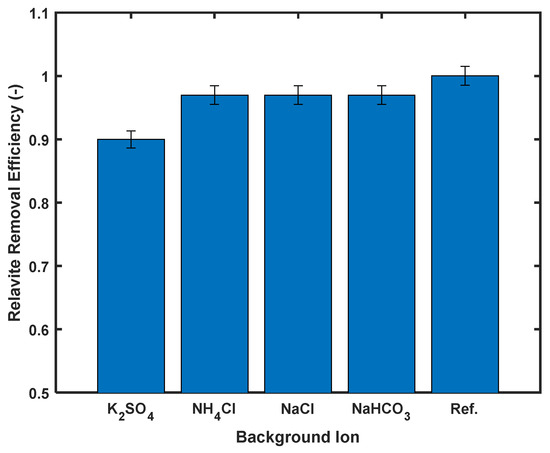
Figure 10.
Percentage removal caused by interfering ions, with initial concentration of 100 ppm and adsorbent dosage of 1.0 g/L.
While some studies suggest chloride ions may enhance cadmium removal through Cd2+–Cl− complexation [39], our observations agree with El-Hefnawy et al. [47], who documented reduced cadmium adsorption in sulfate- and chloride-containing systems. This suppression effect was explained by competitive binding between Na+ (from dissolved salts) and Cd2+ for active adsorption sites.
Despite the observed 10% reduction in removal efficiency, the performance of the silicoaluminophosphate adsorbent remains competitive.
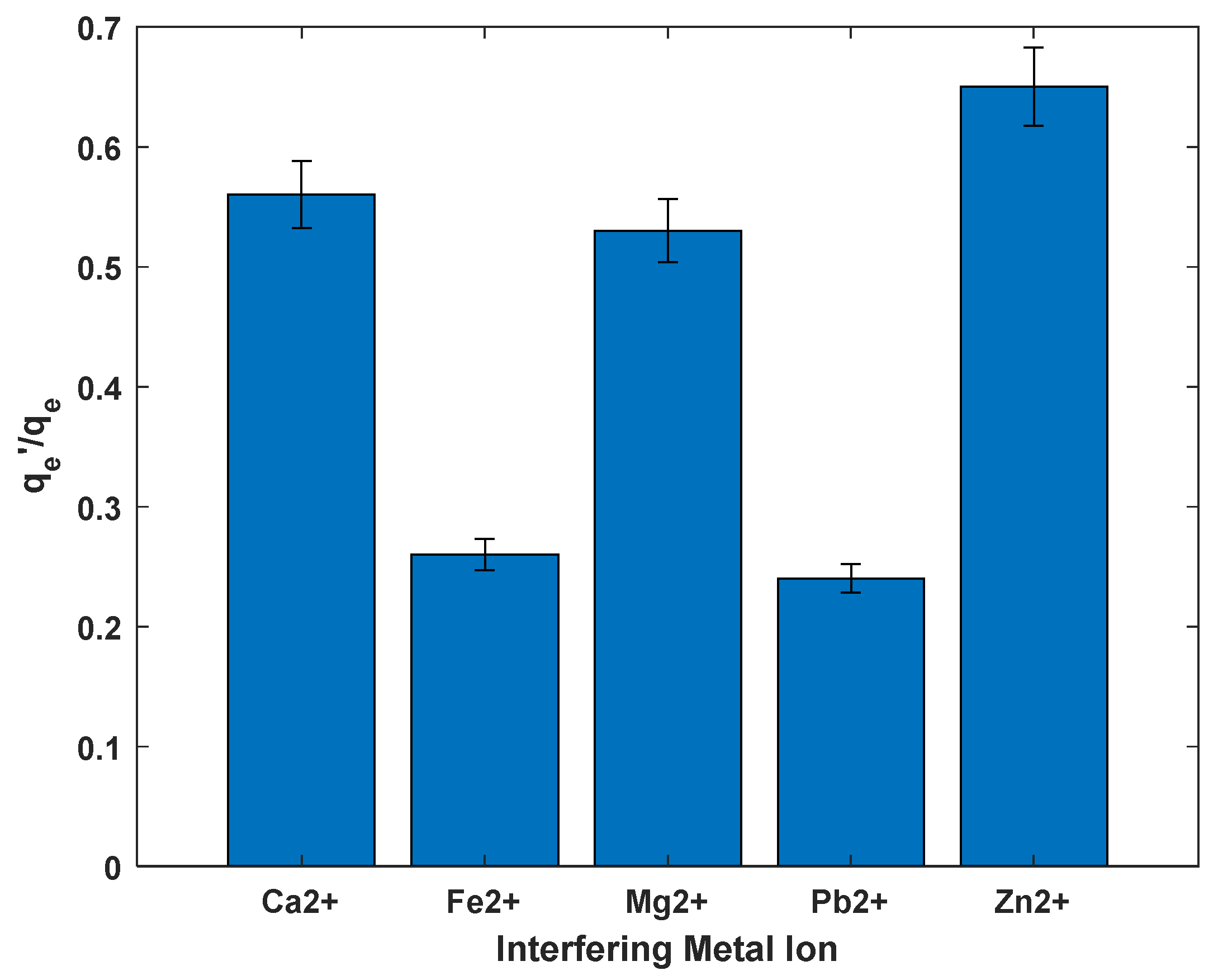
3.7. Effect of Presence of Other Metal Ions
The presence of competing metal ions in aqueous solutions significantly influences the adsorption efficiency of cadmium (Cd2+), as demonstrated by the ratios in the bar graph presented in Figure 11. These ratios compare cadmium uptake in the presence of other metal ions to uptake in a single-metal solution, with lower values indicating greater interference. The data show that Zn2+ has the least impact on cadmium adsorption, with a ratio of approximately 0.65. This minimal interference can be attributed to the chemical similarity between Zn2+ and Cd2+, particularly in terms of ionic radius and hydration behavior, which results in weaker competition for adsorption sites. Similar trends were observed by Han et al. (2013), who reported efficient cadmium removal even in the presence of co-contaminants when using biochar as an adsorbent [48]. Zhou (2024) reported inhibitory the effect of both zinc and lead on the removal of cadmium ions which concurs with the observations of this study [49].
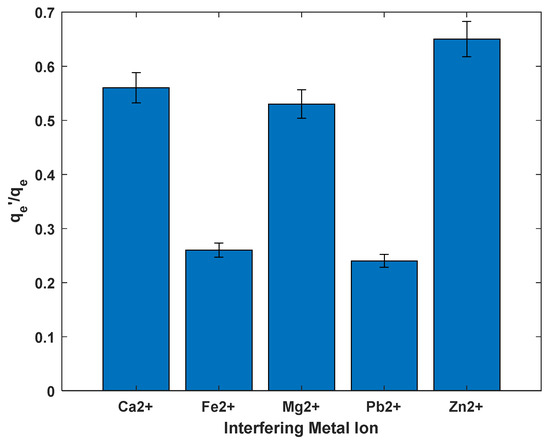
Figure 11.
Effect of presence of other ions on removal of Cd2+ from solution.
In contrast, Fe2+ and Pb2+ exhibit strong interference, with ratios around 0.27 and 0.25, respectively. These metal ions likely have higher binding affinities to the adsorbent, allowing them to effectively compete with and displace Cd2+ from active sites. This observation aligns with the findings of [50], who noted that transition metals such as Fe2+ often outcompete cadmium due to their strong interaction with functional groups on adsorbent surfaces.
Moderate interference was observed in the presence of Ca2+ and Mg2+, with ratios around 0.55 and 0.52. These alkaline-earth metals, while present in many natural waters, tend to compete less effectively for adsorption sites due to their larger hydrated radii and lower binding energies. It has been previously reported that Ca2+ and Mg2+ can reduce cadmium adsorption, although their interference is generally less pronounced compared to transition metals, due to their relatively weak interaction with oxide surfaces [51].
Overall, these results emphasize the importance of accounting for background ions in water treatment processes. The nature and concentration of co-existing metal ions can significantly impact cadmium removal efficiency, highlighting the need for tailored adsorbent selection and process optimization in multi-contaminant systems.
3.8. Regeneration and Recovery Study
The adsorption–desorption cycles of Cd2+ were conducted three times using different eluents: 0.1 mol/L NaOH, HCl, and 0.1 mol/L EDTA. The regeneration efficiency of the Am-SiAlP (7.5) adsorbent exceeded 95% for both NaOH and EDTA after three cycles. However, the efficiency of HCl was notably lower at 59%. The loss of adsorbent could be attributed to the solubility of aluminum phosphate, a component of the adsorbent, in HCl. Regarding Cd2+ recovery efficiency, NaOH was outperformed by both EDTA and HCl, which each achieved over 90% recovery after three cycles.
3.9. Limitation of Studies Future Work Suggestions
Future research should focus on expanding the practical applicability and scalability of amorphous aluminophosphate (Am-AlP) and silico-aluminophosphate (Am-SiAlP) materials for wastewater treatment. One key area is testing these adsorbents in real-world wastewater samples, which often contain complex matrices of ions and organic compounds, to evaluate their performance under more realistic conditions. Furthermore, studies should evaluate the long-term stability and durability of these materials under varying environmental conditions, such as different pH levels, temperatures, and exposure to other contaminants, to ensure their robustness in practical applications [47]. Finally, research should explore the scalability of the synthesis process and conduct pilot-scale testing to assess the feasibility of using these materials in large-scale wastewater treatment systems.
4. Conclusions
The remarkable cadmium (Cd) removal capacity of amorphous aluminophosphate and silicoaluminophosphate adsorbents has been demonstrated in this study. The design strategy was based on the controlled variation of silicon (Si) content within the aluminophosphate framework, with the aim of enhancing surface and porous properties of the adsorbent.
The influence of Si content on physico-chemical properties and adsorption kinetics was investigated using aqueous Cd2+ solutions. The observed variations in Cd removal efficiency were found to be strongly dependent on surface area, porosity, and Si content. The adsorption process was determined to follow pseudo-second-order kinetics and was best described by the Langmuir isotherm model.
Among the tested formulations, Am-SiAlP (7.5) was identified as the most effective adsorbent, with a maximum removal capacity of 52.63 mg/g being achieved. These eco-friendly and cost-effective adsorbent materials have been shown to possess significant potential for heavy metal removal applications. Future investigations will be focused on evaluating the performance of the selected Am-SiAlP in continuous systems for Cd2+ and other contaminant removal.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations12050128/s1, Figure S1: Pore size distribution plots of the different adsorbent samples.
Author Contributions
H.A.: Conception Supervision, writing, O.J.: investigation, writing; C.M.: conception; writing; data analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agasti, N. Decontamination of heavy metal ions from water by composites prepared from waste. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Rozbu, M.R.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Nuzhat, S.; Rafa, N.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ong, H.C.; Mofijur, M. Heavy metal toxicity, sources, and remediation techniques for contaminated water and soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 25, 102114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubier, A.; Wilkin, R.T.; Pichler, T. Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl. Geochem. 2019, 108, 104388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Tu, Y.; Yu, E.; Xing, D. Cadmium accumulation and migration of 3 peppers varieties in yellow and limestone soils under geochemical anomaly. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2006/118/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 December 2006 on the Protection of Groundwater Against Pollution and Deterioration; European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qasem, N.A.A.; Mohammed, R.H.; Lawal, D.U. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: A comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water 2021, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Sun, Z.; Han, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, W.; Xu, C. Enhanced coagulation coupled with heavy metal capturing for heavy metals removal from coal gasification brine and a novel mathematical model. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 40, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervine, M.; Mangwandi, C. Evaluation of magnetic teawaste-based biochar particles for removal of cadmium from aqueous solutions. Particuology 2025, 99, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Annath, H.; Chen, H.; Mangwandi, C. Upcycling tea waste particles into magnetic adsorbent materials for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Particuology 2023, 80, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeogh, M.; Annath, H.; Mangwandi, C. Turning teawaste particles into magnetic bio-sorbents particles for arsenic removal from wastewater: Isotherm and kinetic studies. Particuology 2024, 87, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zou, H.; Liu, Q. Effects of Phosphate and Silicate Combined Application on Cadmium Form Changes in Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.; Nagaraju, N. Amorphous metal-aluminophosphate catalysts for aldol condensation of n-heptanal and benzaldehyde to jasminaldehyde. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayasankar, A.V.; Nagaraju, N. Preparation and characterisation of amorphous mesoporous aluminophosphate and metal aluminophosphate as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for transesterification reaction. C. R. Chim. 2011, 14, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annath, H.; Viswambaram Aloor, V.; Narasimhaiah, N. Understanding the role of acid sites of Zinc Aluminophosphate catalysts in eco-friendly synthesis of carbamates. Iran. J. Catal. 2021, 11, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Annath, H.; Manayil, J.C.; Thompson, J.; Marr, A.C.; Raja, R. Contrasting structure-property relationships in amorphous, hierarchical and microporous aluminophosphate catalysts for Claisen-Schmidt condensation reactions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 627, 118376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Gandhimathi, R. Removal of heavy metal ions from municipal solid waste leachate using coal fly ash as an adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, E.; Afsin, B. An investigation of Cu(II) adsorption by raw and acid-activated bentonite: A combined potentiometric, thermodynamic, XRD, IR, DTA study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 151, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.-J.; Jiang, S.-K.; Chao, X.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, M.-L.; Sun, S.-P. Removing miscellaneous heavy metals by all-in-one ion exchange-nanofiltration membrane. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiyeola, O.O.; Annath, H.; Mangwandi, C. Synthesis and evaluation of a new CeO2@starch nanocomposite particles for efficient removal of toxic Cr(VI) ions. Energy Nexus 2023, 12, 100244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Cadmium in Drinking-Water; World Health Organisation (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mangwandi, C.; Suhaimi, S.N.A.; Liu, J.T.; Dhenge, R.M.; Albadarin, A.B. Design, production and characterisation of granular adsorbent material for arsenic removal from contaminated wastewater. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 110, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghojavand, S.; Dib, E.; Mintova, S. Flexibility in zeolites: Origin, limits, and evaluation. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 12430–12446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.; Xiao, B.; Mangwandi, C. Production of activated carbon from spent coffee grounds (SCG) for removal of hexavalent chromium from synthetic wastewater solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glocheux, Y.; Albadarin, A.B.; Mangwandi, C.; Stewart, E.; Walker, G.M. Production of porous aluminium and iron sulphated oxyhydroxides using industrial grade coagulants for optimised arsenic removal from groundwater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 25, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Pittman, C.U. Activated carbons and low cost adsorbents for remediation of tri- and hexavalent chromium from water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 762–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhao, G.; Chen, C.; Chai, Z.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T.; Wang, X. Metal–organic framework-based materials: Superior adsorbents for the capture of toxic and radioactive metal ions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 2322–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Adil, M.; Yusof, A.M.; Kamaruzzaman, Y.B.; Ansary, R.H. Removal of Heavy Metal Ions with Acid Activated Carbons Derived from Oil Palm and Coconut Shells. Materials 2014, 7, 3634–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annath, H.; Chapman, S.; Donnelly, G.F.; Marr, P.C.; Marr, A.C.; Raja, R. Heterogenized Ionic-Liquid Metal-Oxide Hybrids: Enhanced Catalytic Activity in the Liquid-Phase Beckmann Rearrangement. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 16797–16805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Osman, A.I.; Mangwandi, C.; Rooney, D. Upcycling food waste digestate for energy and heavy metal remediation applications. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. X 2019, 3, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lin, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wen, X.; Luo, H. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution by modified attapulgite clay. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4994–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Wang, C.; Zhou, G.; Hua, C.; Cao, Y.; Song, Z. Novel environmental-friendly nano-composite magnetic attapulgite functionalized by chitosan and EDTA for cadmium (II) removal. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 153286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P. Zeolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron: New findings on simultaneous adsorption of Cd(II), Pb(II), and As(III) in aqueous solution and soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sdiri, A.; Higashi, T. Simultaneous removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by natural limestones. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Min, T.K.; Azizli, K.; Sufian, S.; Ullah, H.; Man, Z. Effective removal of methylene blue from water using phosphoric acid based geopolymers: Synthesis, characterizations and adsorption studies. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 61410–61420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, B.M.W.P.K.; Williams, R.A. Tea waste as a low cost adsorbent for the removal of Cu and Pb from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Gao, H.; Luo, X.; Su, T.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Z. Polyethyleneimine modified activated carbon for adsorption of Cd(II) in aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Yousefi, Y.; Rafati, A.A. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of several heavy metal ions on amino-functionalized silica nano hollow sphere and silica gel. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 85, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszałek, M.; Knapik, E.; Piotrowski, M.; Chruszcz-Lipska, K. Removal of cadmium from phosphoric acid in the presence of chloride ions using commercially available anion exchange resins. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 118, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.; Singh, A.K. Silica gel functionalized with resacetophenone: Synthesis of a new chelating matrix and its application as metal ion collector for their flame atomic absorption spectrometric determination. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 454, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, M.; Rostamian, R.; Rafati, A.A. Chemically modified silica gel with thiol group as an adsorbent for retention of some toxic soft metal ions from water and industrial effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.A.; Wood, J.; Rosenberg, E. Polymer Structure and Metal Ion Selectivity in Silica Polyamine Composites Modified with Sodium Chloroacetate and Nitriloacetic Acid (NTA) Anhydride. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6765–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Lin, X.; Wu, X.; Xie, Z. Solid phase extraction of lead (II), copper (II), cadmium (II) and nickel (II) using gallic acid-modified silica gel prior to determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 2008, 74, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Ai, S. Efficient removal of cadmium ions from water by adsorption on a magnetic carbon aerogel. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 5149–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amro, A.N.; Abhary, M.K.; Shaikh, M.M.; Ali, S. Removal of Lead and Cadmium Ions from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption on a Low-Cost Phragmites Biomass. Processes 2019, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, G.; Chen, H.; Hu, X.; Niu, Z.; Ma, S. Functionalized metal–organic framework as a new platform for efficient and selective removal of cadmium(ii) from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15292–15298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hefnawy, M.E.; Selim, E.M.; Assaad, F.F.; Ismail, A.I. The Effect of Chloride and Sulfate Ions on the Adsorption of Cd2+ on Clay and Sandy Loam Egyptian Soils. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 806252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liang, C.-F.; Li, T.-Q.; Wang, K.; Huang, H.-G.; Yang, X.-E. Simultaneous removal of cadmium and sulfamethoxazole from aqueous solution by rice straw biochar. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2013, 14, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L. Improving the removal performance of cadmium from wastewater by phosphate-modified sludge biochar: A mineral dissolution-precipitation perspective. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, Z.; Karim, A.; Karam, A.; Khalloufi, S. Adsorption of Heavy Metals: Mechanisms, Kinetics, and Applications of Various Adsorbents in Wastewater Remediation—A Review. Waste 2023, 1, 775–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, C.E.; Zachara, J.M.; Resch, C.T. Cadmium adsorption on iron oxides in the presence of alkaline-earth elements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1991, 25, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).