Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Macroporous Adsorption Resins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. HPLC Analysis of SMYAD
2.4. Static Screening of Resins
2.5. Adsorption Kinetics on D101 Resin
2.6. Adsorption Isotherms and Heat of Adsorption
2.7. Optimization of Dynamic Adsorption and Desorption for D101 Resin
2.8. Determination of Elution Product by HPLC
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Static Adsorption and Desorption
3.2. Adsorption Kinetics of SMYAD on D101 Resin
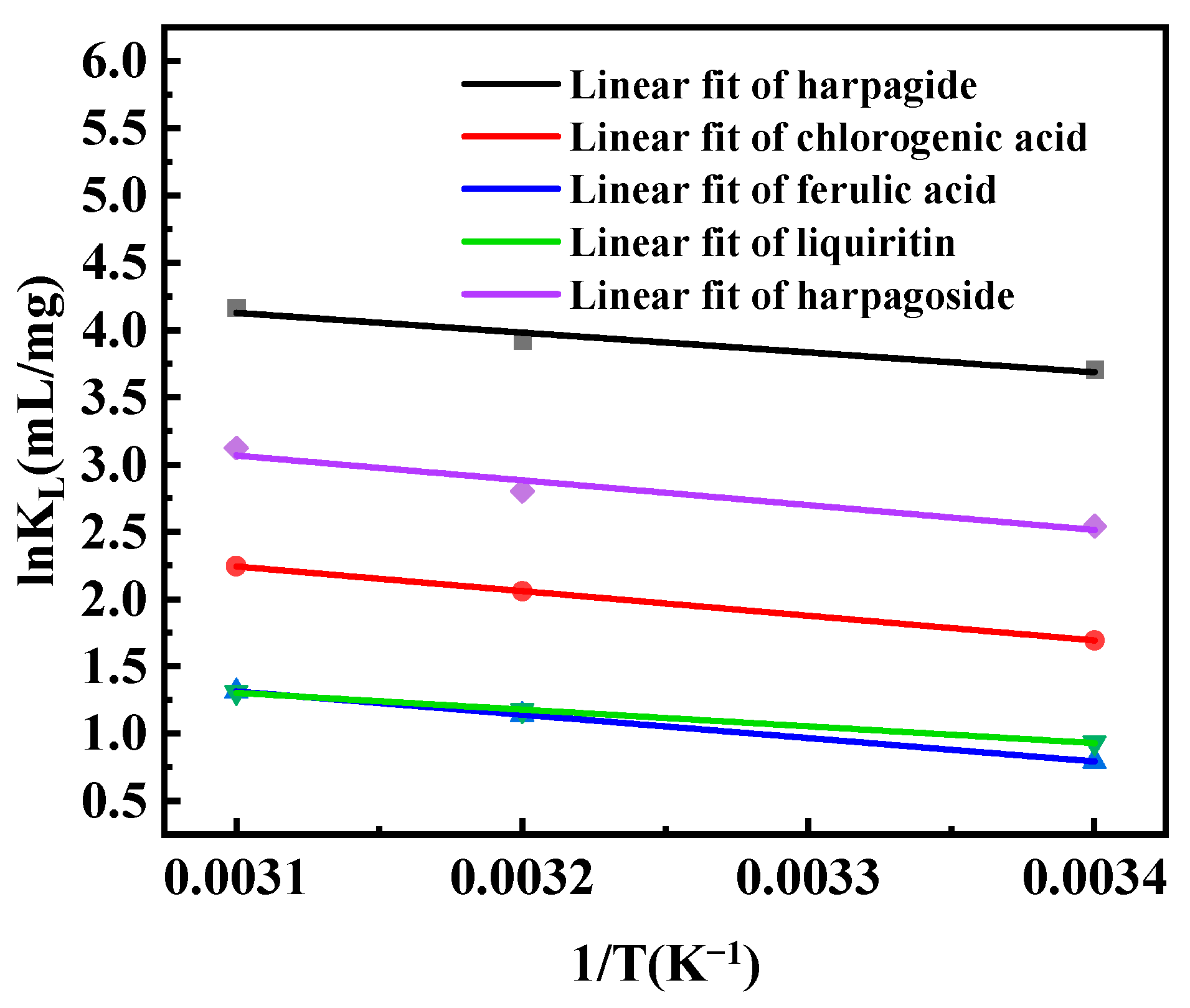
3.3. Adsorption Isotherms and Heat of Adsorption on D101 Resin
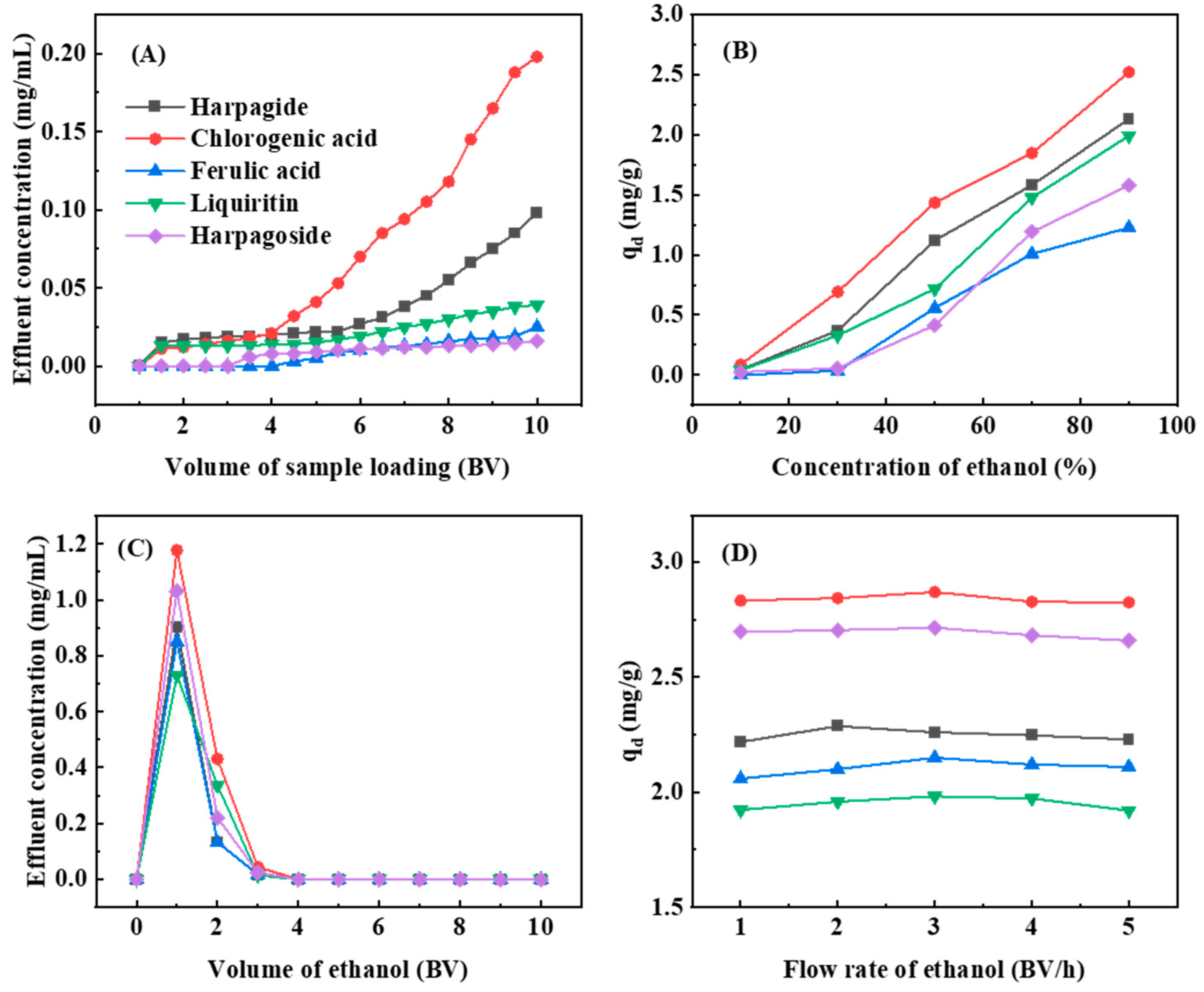
3.4. Dynamic Adsorption and Desorption of SMYAD on D101 Resin
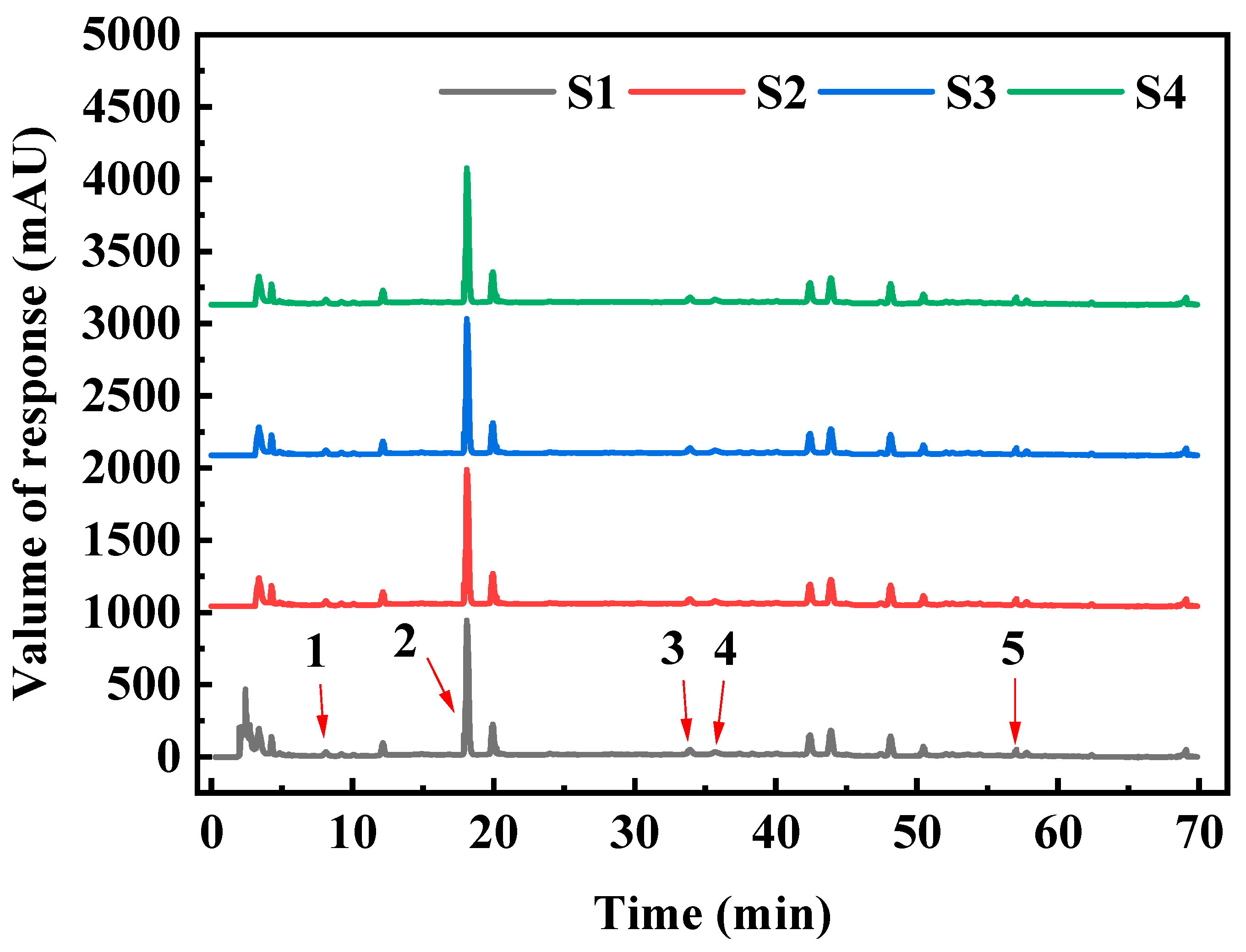
3.5. Evaluation of Purification Effect of D101 Resin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, J.; Xu, W.; Li, Z.; Gao, P.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Y.; Hu, J. Network pharmacology-based approach to research the effect and mechanism of Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction against thromboangiitis obliterans. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2218105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, A.-H.; He, L.-W.; Qiu, S.; Xue, J.-R.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.-J. Therapeutic Effect and Mechanism of Si-Miao-Yong-An-Tang on Thromboangiitis Obliterans Based on the Urine Metabolomics Approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 827733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Liang, G.; Miao, X.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Si-Miao-Yong-An Decoction alleviates thromboangiitis obliterans by regulating miR-548j-5p/IL-17A signaling pathway. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2024, 22, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chai, Y.; Li, W.; Guan, L.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y. Mechanism of Simiao Decoction in the treatment of atherosclerosis based on network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking. Medicine 2023, 102, e35109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Yan, Z.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, J. Novel treatment from a botanical formulation Si-Miao-Yong-an decoction inhibits vasa vasorum angiogenesis and stabilizes atherosclerosis plaques via the Wnt1/β-catenin signalling pathway. Pharm. Biol. 2023, 61, 1364–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.-H.; Yang, M.-F.; Xu, X.-R.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Q.-Y.; Li, H.; Wang, S.-Q.; Lou, L.-X.; Wu, A.-M.; et al. Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Seven Major Compounds in Normal and Atherosclerosis Mice after Oral Administration of Simiao Yong’an Decoction. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2022, 2022, 4604601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.-B.; Song, K.; Huang, W.-J.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Bai, Y.-Q.; Guo, K.-T.; Yang, R.-B.; Lou, W.-J.; Xia, C.-H.; et al. Si-Miao-Yong-An (SMYA) Decoction May Protect the Renal Function Through Regulating the Autophagy-Mediated Degradation of Ubiquitinated Protein in an Atherosclerosis Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, A.; Xie, Y.; Ouyang, H.; Lu, B.; Jia, W.; Xu, H.; Ji, L. Si-Miao-Yong-An Decoction for Diabetic Retinopathy: A Combined Network Pharmacological and In Vivo Approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 763163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zong, Y.; Feng, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Y. Exploring the potential mechanism of Simiao Yongan decoction in the treatment of diabetic peripheral vascular disease based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. Medicine 2023, 102, e36762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, X.; Su, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, R.; Jiao, W.; Luo, H.; Tian, Y.; Tang, J.; Li, X.; et al. Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction preserves cardiac function and regulates GLC/AMPK/NF-κB and GLC/PPARα/PGC-1α pathways in diabetic mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, S.-s.; Sun, H.-j.; Liu, J.-x.; Gao, Y.; Bai, D.; Zhu, L.-l.; Zhao, H.-y.; Zeng, H.; Ma, Y.-l. Simiao Yong’an decoction ameliorates murine collagen-induced arthritis by modulating neutrophil activities: An in vitro and in vivo study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 305, 116119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, H.; Su, C.; Zeng, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, Q.; Han, J.; et al. Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction ameliorates cardiac function through restoring the equilibrium of SOD and NOX2 in heart failure mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chi, S.; Wang, W.; Su, L.; Liu, B. Simultaneous Determination of Seven Components in Rat Plasma by the UPLC-MS/MS Method and Application of Pharmacokinetic Studies to SimiaoYong’an Decoction. Molecules 2017, 22, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; He, R.; Gao, J.; Chen, C.; Dai, H.; Cao, Z.; Lan, L.; Sun, G.; et al. Thorough evaluation of the Chinese medicine preparations and intermediates using high performance liquid chromatography fingerprints and ultraviolet quantum fingerprints along with antioxidant activity: Shuanghuanglian oral solution as an example. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1705, 464196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Yiyang, C.; Lixia, M.; Yue, J.; Jun, C.; Jie, D.; Yifan, M.; Jingjing, Z.; Guojun, Y. Study on the Fingerprints and Quality Evaluation of Angelica Sinensis Radix by HPLC Coupled With Chemometrics Based on Traditional Decoction Process of ACPTCM. Dose-Response 2020, 18, 1559325820951730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chang, Q.; Lan, L.; Guo, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, Q. Reliability evaluation of traditional Chinese medicine fingerprints combined with qualitative and quantitative analysis and antioxidant activity to comprehensively evaluate the quality of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 21660–21671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Lan, L.; Gong, D.; Guo, Y.; Sun, G. Evaluation of quality consistency of herbal preparations using five-wavelength fusion HPLC fingerprint combined with ATR-FT-IR spectral quantized fingerprint: Belamcandae rhizoma antiviral injection as an example. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 214, 114733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Shi, R.; He, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y. Efficient purification of flavonoids from bamboo shoot residues of Phyllostachys edulis by macroporous resin and their hypoglycemic activity. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Guo, Q.-S.; Wang, G.-S. Preparative Separation and Purification of the Total Flavonoids in Scorzonera austriaca with Macroporous Resins. Molecules 2016, 21, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Li, M.-M.; Wang, W.-J.; Zheng, G.-D.; Yin, Z.-P.; Chen, J.-G.; Zhang, Q.-F. Separation and purification of anthocyanins from Roselle by macroporous resins. LWT 2022, 161, 113371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, W.; Gao, R.; Guo, Y. Optimized isolation and purification of Shaoyao Gancao decoction using macroporous resin. J. Chromatogr. B 2024, 1244, 124251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lin, S.; Li, Q.; Tong, Y.; Wang, P. Purification of Crocin-I from Gardenia Yellow by Macroporous Resin Columns In-Series and Its Antidepressant-Like Effect. J. Chem. 2022, 2022, 7651553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, J.; Ren, X.; Wang, Y. Extraction, purification and properties of water-soluble polysaccharides from mushroom Lepista nuda. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Su, J.; Chu, X.; Zhang, X.; Kan, Q.; Liu, R.; Fu, X. Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Total Flavonoids from Acanthopanax senticosus on Macroporous Adsorption Resins. Molecules 2021, 26, 4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, B.; Ma, C.; Lou, Z.; Wang, H. Adsorption/desorption behavior and purification process optimization of theaflavins on macroporous resin. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 7160–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Qin, L.; Wang, G.; Li, P.; Yu, A.; Liu, A.; Sun, R. Separation and Purification of Two Saponins from Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis by a Macroporous Resin. Molecules 2022, 27, 6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, W.; Li, Y.; et al. Study on the kinetic model, thermodynamic and physicochemical properties of Glycyrrhiza polysaccharide by ultrasonic assisted extraction. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 51, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Intriago, L.A.; Gorozabel-Mendoza, M.L.; Córdova Mosquera, A.; Delgado-Demera, M.H.; Duarte, M.M.M.B.; Rodríguez-Díaz, J.M. Kinetics, equilibrium, and thermodynamics of the blue 19 dye adsorption process using residual biomass attained from rice cultivation. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2020, 12, 3843–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasilewska, M.; Deryło-Marczewska, A. Adsorption of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on Alginate-Carbon Composites—Equilibrium and Kinetics. Materials 2022, 15, 6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arim, A.L.; Guzzo, G.; Quina, M.J.; Gando-Ferreira, L.M. Single and binary sorption of Cr(III) and Ni(II) onto modified pine bark. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 28039–28049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidescu, C.-M.; Ardelean, R.; Popa, A. New polymeric adsorbent materials used for removal of phenolic derivatives from wastewaters. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.A.; Alam, J.; Shukla, A.K.; Ali, F.A.A.; Alhoshan, M. Sustainable removal of phenol from wastewater using a biopolymer hydrogel adsorbent comprising crosslinked chitosan and κ-carrageenan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 251, 126340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubra, K.T.; Salman, M.S.; Hasan, M.N. Enhanced toxic dye removal from wastewater using biodegradable polymeric natural adsorbent. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaku, A.Z. Removal of manganese from wastewater using Moringa stenopetala plant parts as an adsorbent material. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stofela, S.K.F.; de Almeida Neto, A.F.; Gimenes, M.L.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of toluene into commercial organoclay in liquid phase: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 93, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Huo, X.; Xu, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, L. Separation of Flavonoids and Purification of Chlorogenic Acid from Bamboo Leaves Extraction Residues by Combination of Macroporous Resin and High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Molecules 2023, 28, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Lin, L. Adsorption and desorption characteristics of adlay bran free phenolics on macroporous resins. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
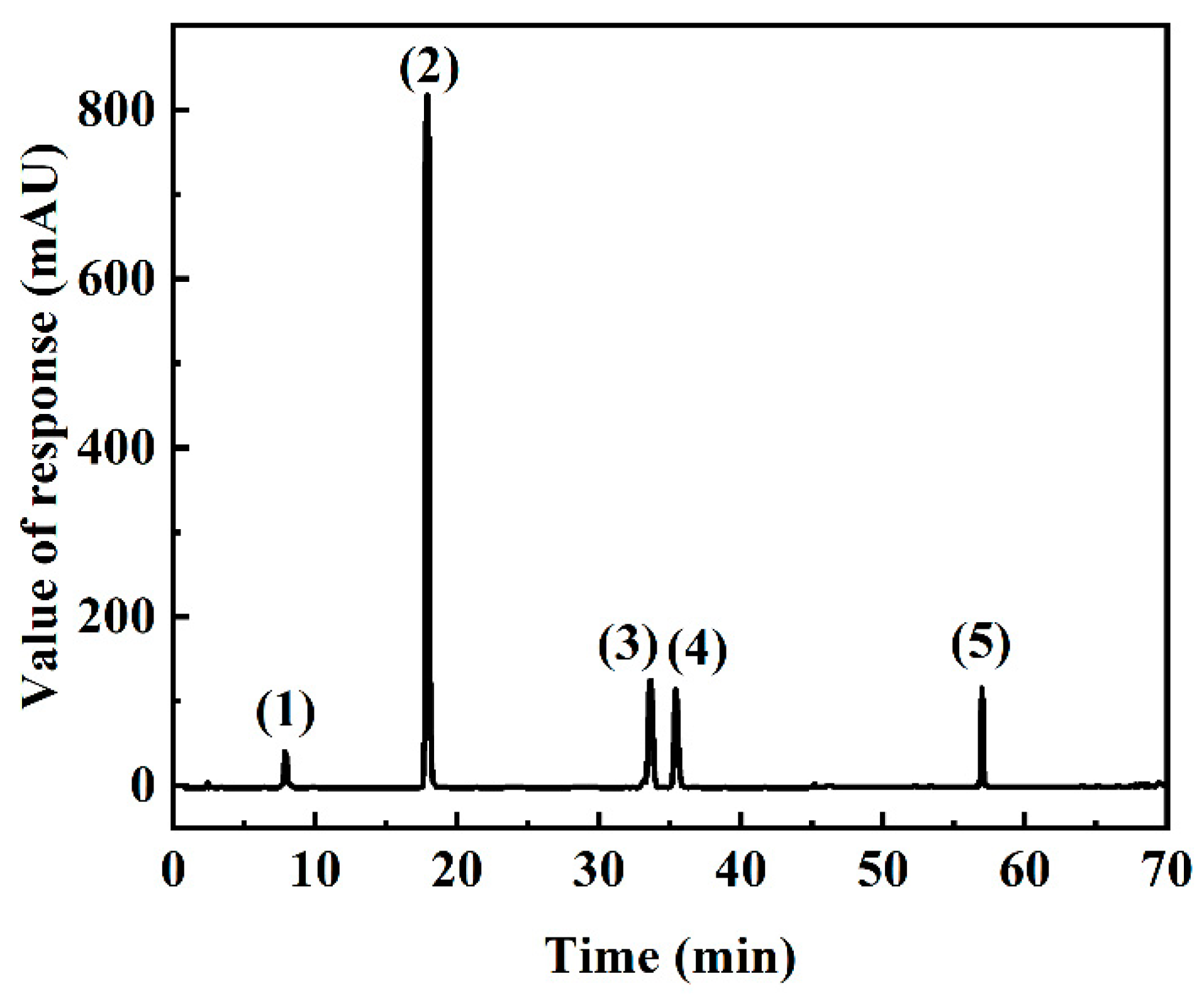
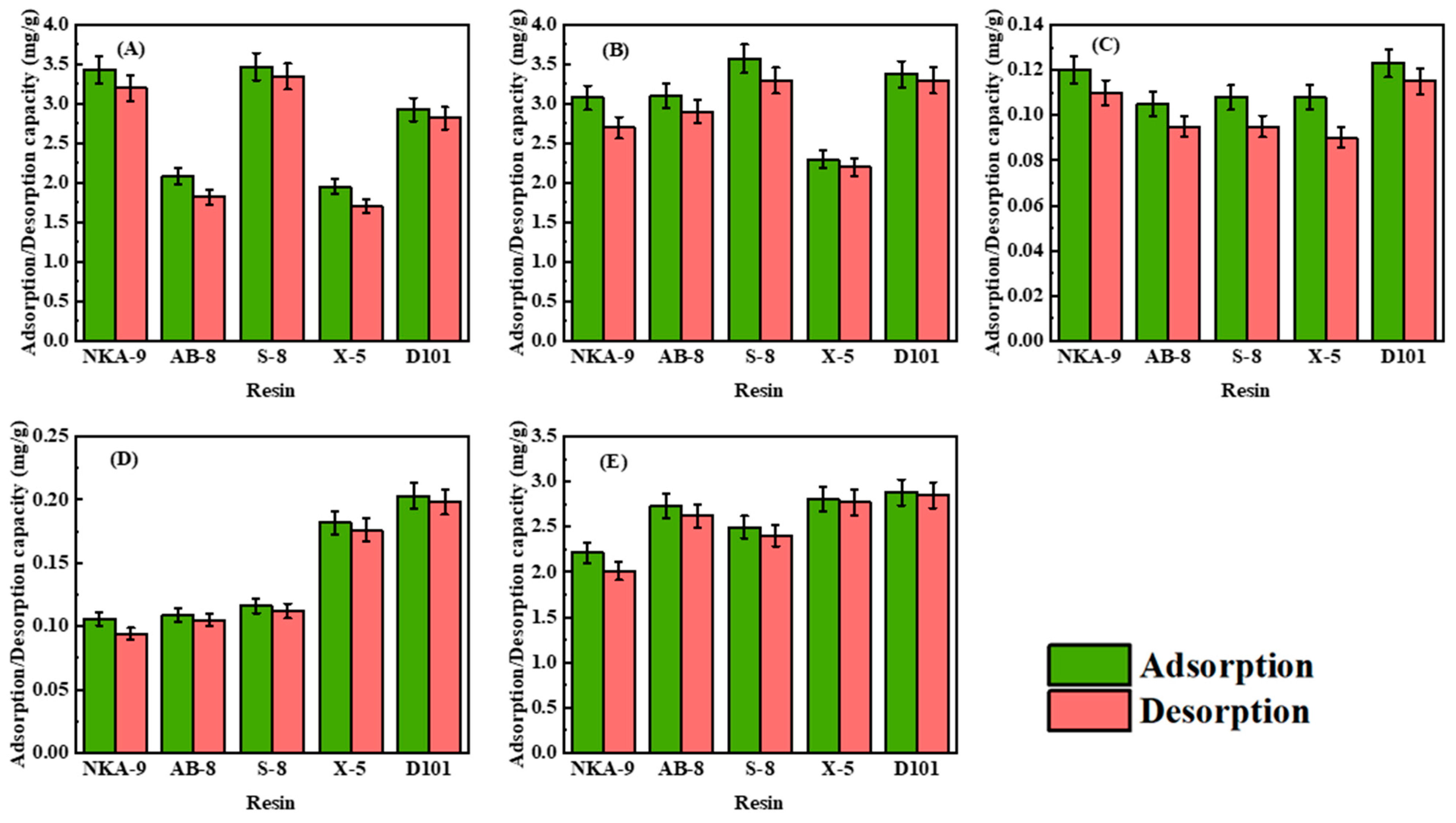
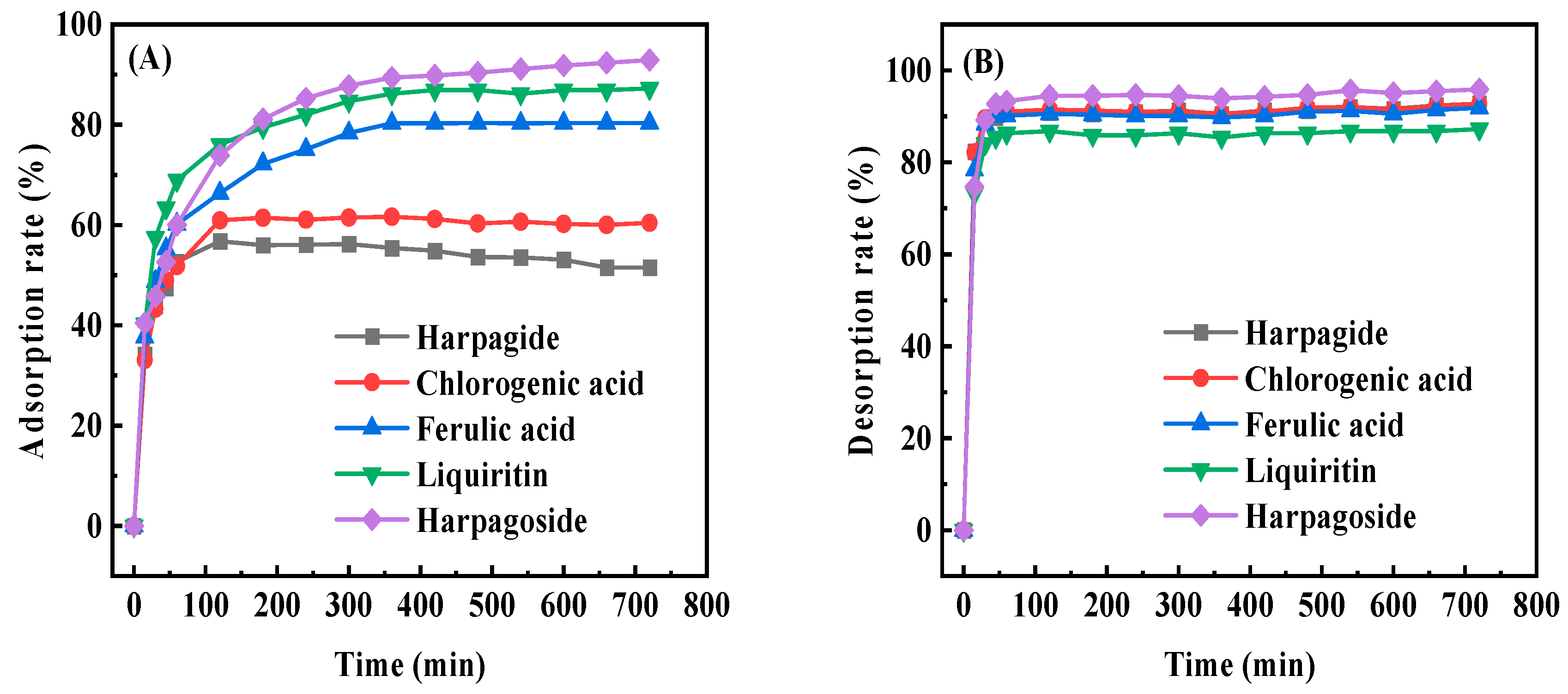

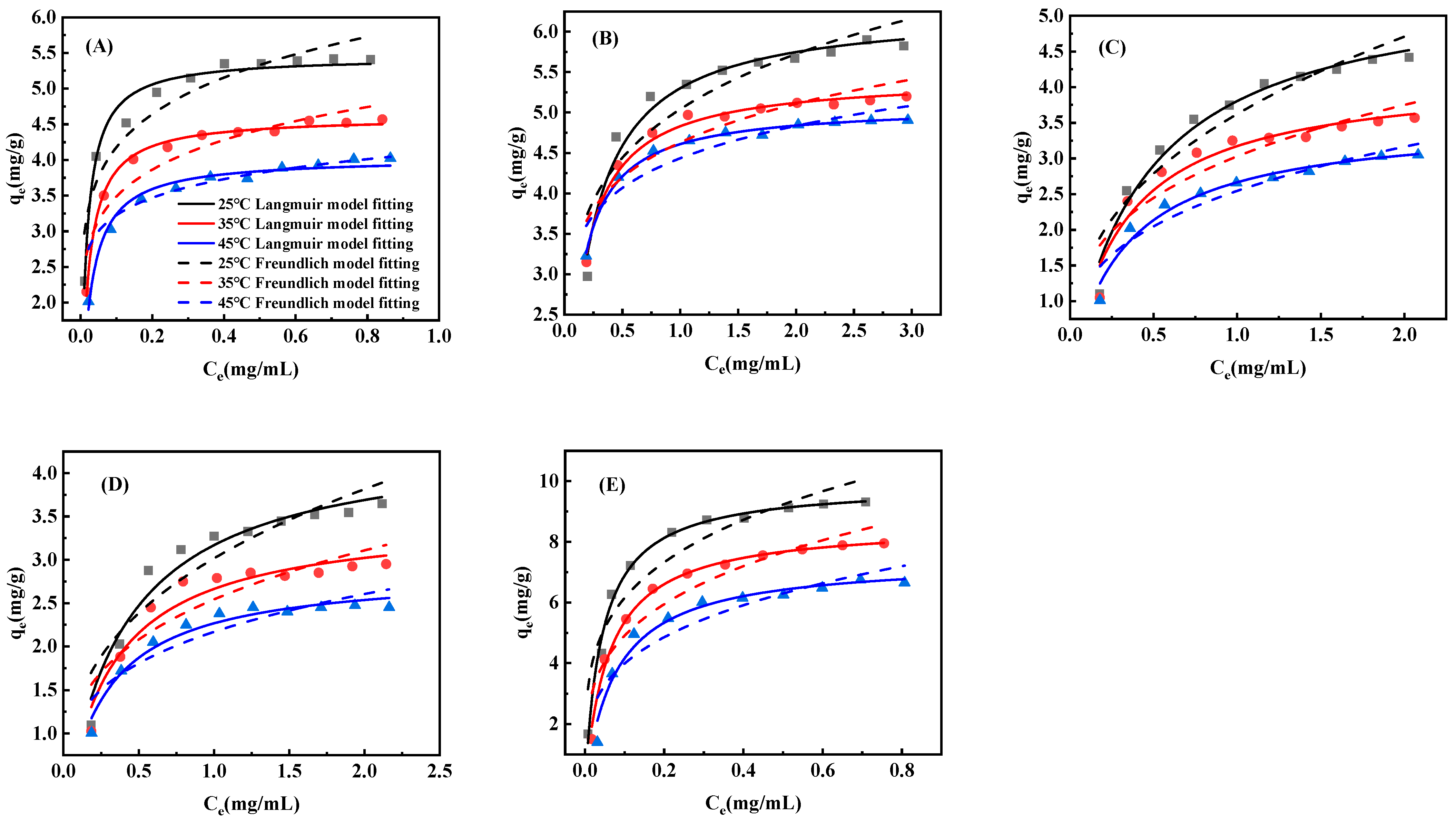
| Resin | Polarity | Diameter (mm) | Surface Area (m2/g) | Average Pore Size (Å) |
| NKA-9 | Polar | 0.3–1.25 | 250–290 | 155–165 |
| S-8 | Polar | 0.3–1.25 | 100–120 | 280–300 |
| AB-8 | Weak-polar | 0.3–1.25 | 480–520 | 130–140 |
| X-5 | Non-polar | 0.3–1.25 | 500–600 | 290–300 |
| D101 | Non-polar | 0.3–1.25 | 550–600 | 90–110 |
| Time (Min) | A (%) | B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 95 |
| 3 | 5 | 95 |
| 18 | 11 | 89 |
| 45 | 20 | 80 |
| 55 | 33 | 67 |
| 60 | 50 | 50 |
| 70 | 100 | 0 |
| Components | C0 (mg/mL) | qe,ecp (mg/g) | PFO Parameters | PSO Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min− 1) | qe,1 (mg/g) | R2 | K2 () | qe,2 (mg/g) | R2 | |||
| Harpagide | 0.198 | 2.702 | 0.00288 | 1.211 | 0.989 | 0.0110 | 2.726 | 0.997 |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.943 | 3.416 | 0.00590 | 1.518 | 0.969 | 0.00881 | 3.548 | 0.998 |
| Ferulic acid | 0.234 | 0.129 | 0.00199 | 1.274 | 0.983 | 0.308 | 0.144 | 0.996 |
| Liquiritin | 0.117 | 0.204 | 0.00477 | 1.363 | 0.976 | 0.157 | 0.268 | 0.995 |
| Harpagoside | 0.202 | 3.031 | 0.00226 | 1.707 | 0.987 | 0.00906 | 3.096 | 0.999 |
| Langmuir Equation | Freundlich Equation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Components | Temperature (°C) | KL (mL/mg) | qm (mg/g) | R2 | KF[(mg/g) (mL/mg)1/n] | 1/n | R2 |
| Harpagide | 25 | 40.75 | 5.45 | 0.98 | 5.92 | 0.15 | 0.89 |
| 35 | 50.48 | 4.61 | 0.99 | 4.90 | 0.14 | 0.88 | |
| 45 | 64.58 | 4.03 | 0.98 | 4.11 | 0.10 | 0.87 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 25 | 5.44 | 6.28 | 0.97 | 5.04 | 0.18 | 0.83 |
| 35 | 7.83 | 5.45 | 0.99 | 4.63 | 0.14 | 0.84 | |
| 45 | 9.94 | 5.09 | 0.99 | 4.43 | 0.12 | 0.87 | |
| Ferulic acid | 25 | 2.21 | 5.53 | 0.97 | 3.62 | 0.38 | 0.89 |
| 35 | 3.13 | 4.19 | 0.94 | 3.03 | 0.31 | 0.83 | |
| 45 | 3.72 | 3.55 | 0.97 | 2.55 | 0.31 | 0.89 | |
| Liquiritin | 25 | 2.54 | 4.42 | 0.96 | 3.02 | 0.34 | 0.86 |
| 35 | 3.23 | 3.49 | 0.94 | 2.54 | 0.29 | 0.81 | |
| 45 | 3.70 | 2.88 | 0.96 | 2.17 | 0.26 | 0.84 | |
| Harpagoside | 25 | 12.70 | 9.91 | 0.99 | 10.99 | 0.25 | 0.90 |
| 35 | 16.48 | 8.60 | 0.99 | 9.27 | 0.28 | 0.89 | |
| 45 | 22.72 | 7.43 | 0.97 | 7.67 | 0.28 | 0.85 | |
| Purity (%) | Reserved Rate (%) | RSD | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | RSD | |||
| Harpagide | 0.82 | 4.94 | 0.04 | 80.32 | 0.02 |
| 5.31 | 82.71 | ||||
| 5.42 | 83.78 | ||||
| Chlorogenic acid | 2.48 | 10.98 | 0.05 | 81.33 | 0.03 |
| 11.30 | 82.72 | ||||
| 11.73 | 83.77 | ||||
| Ferulic acid | 0.76 | 3.82 | 0.06 | 70.74 | 0.03 |
| 4.07 | 71.43 | ||||
| 4.77 | 79.62 | ||||
| Liquiritin | 1.03 | 6.94 | 0.03 | 76.33 | 0.05 |
| 7.25 | 85.13 | ||||
| 7.31 | 86.26 | ||||
| Harpagoside | 1.17 | 7.95 | 0.03 | 78.73 | 0.02 |
| 8.03 | 79.32 | ||||
| 8.12 | 80.61 | ||||
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 1 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 |
| S2 | 0.999 | 1 | 0.998 | 0.999 |
| S3 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1 | 0.998 |
| S4 | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.998 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, W.; Liu, E.; Luo, Y.; Niu, Y.; Guo, Y. Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Macroporous Adsorption Resins. Separations 2025, 12, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040084
Jiao W, Liu E, Luo Y, Niu Y, Guo Y. Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Macroporous Adsorption Resins. Separations. 2025; 12(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040084
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Wei, Erhu Liu, Yao Luo, Yanxin Niu, and Yongxue Guo. 2025. "Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Macroporous Adsorption Resins" Separations 12, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040084
APA StyleJiao, W., Liu, E., Luo, Y., Niu, Y., & Guo, Y. (2025). Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics of Simiao Yong’an Decoction on Macroporous Adsorption Resins. Separations, 12(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12040084





