Pore-Engineered Magnetic Biochar: Optimizing Pyrolysis and Fe3O4 Loading for Targeted Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon (CAH) Adsorption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of BC and Fe3O4@BC
2.2. Characterization of BC and Fe3O4@BC
2.3. Adsorption Performance of BC and Fe3O4@BC
2.4. BET Analysis and Calculation
2.5. Characterization of Competitive Adsorption Between MBC and Soil
3. Results
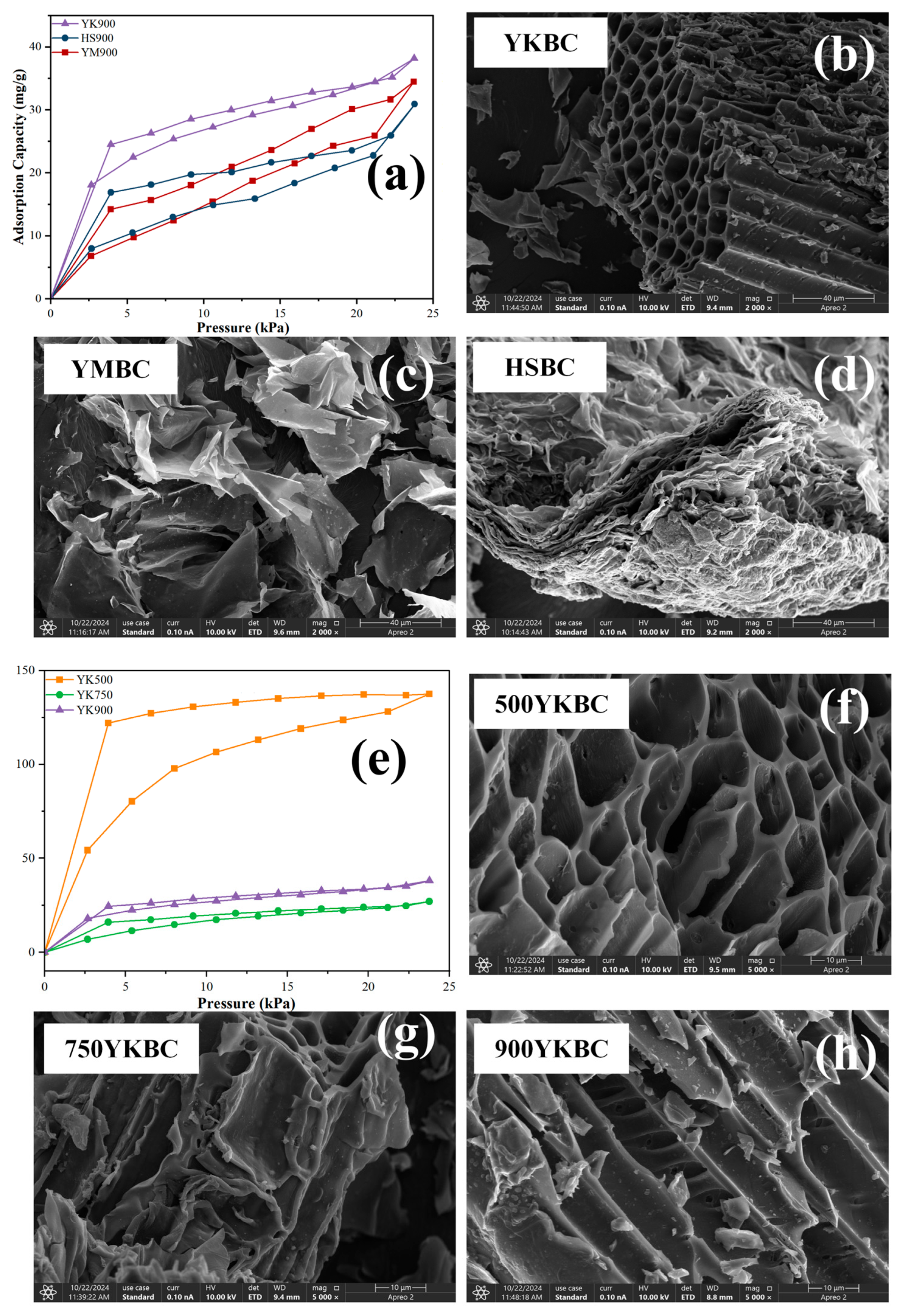
3.1. Optimization of Biochar Sources and Pyrolysis Temperatures for Enhanced TCM Adsorption
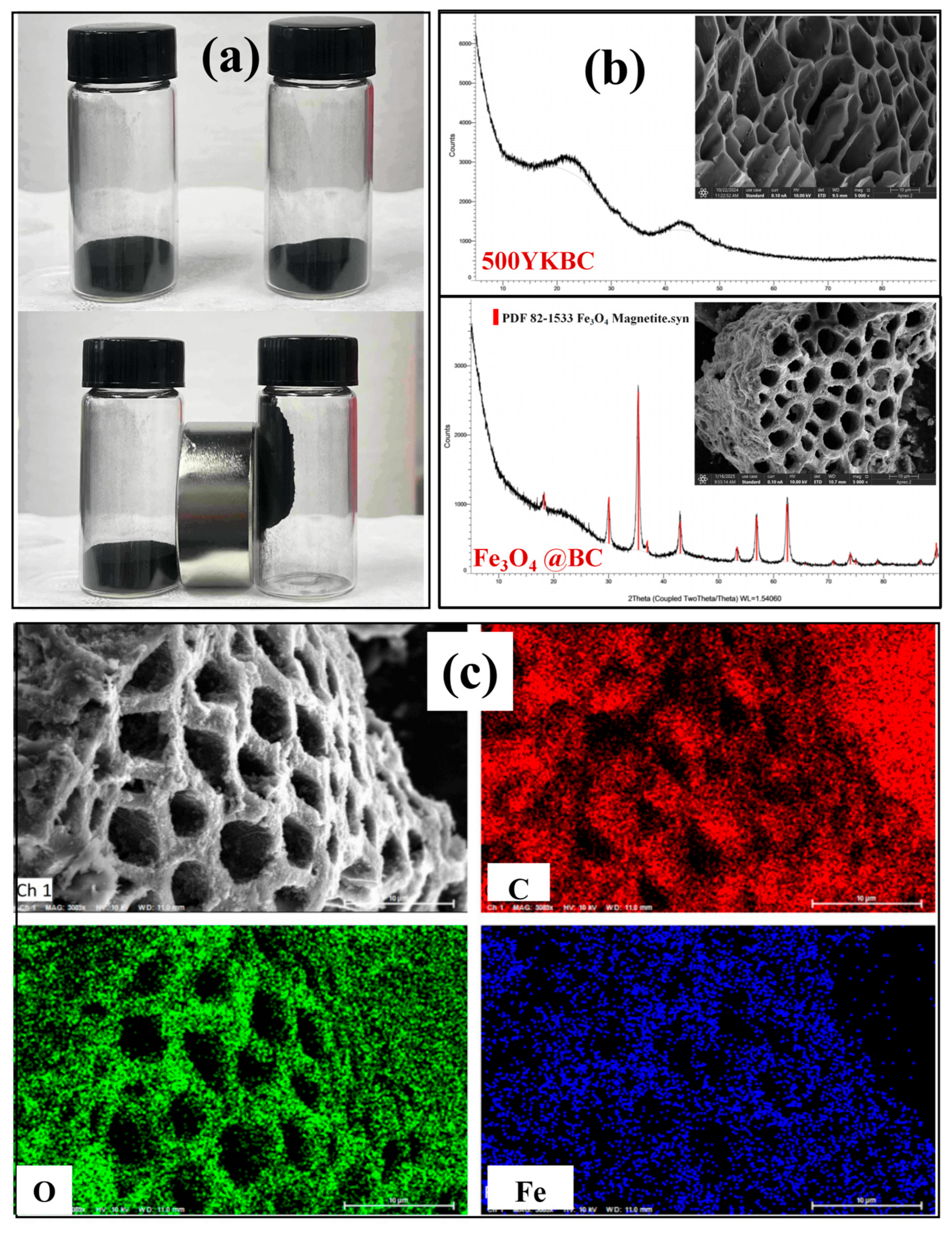
3.2. Validation of Fe3O4 Synthesis and Composite Characterization
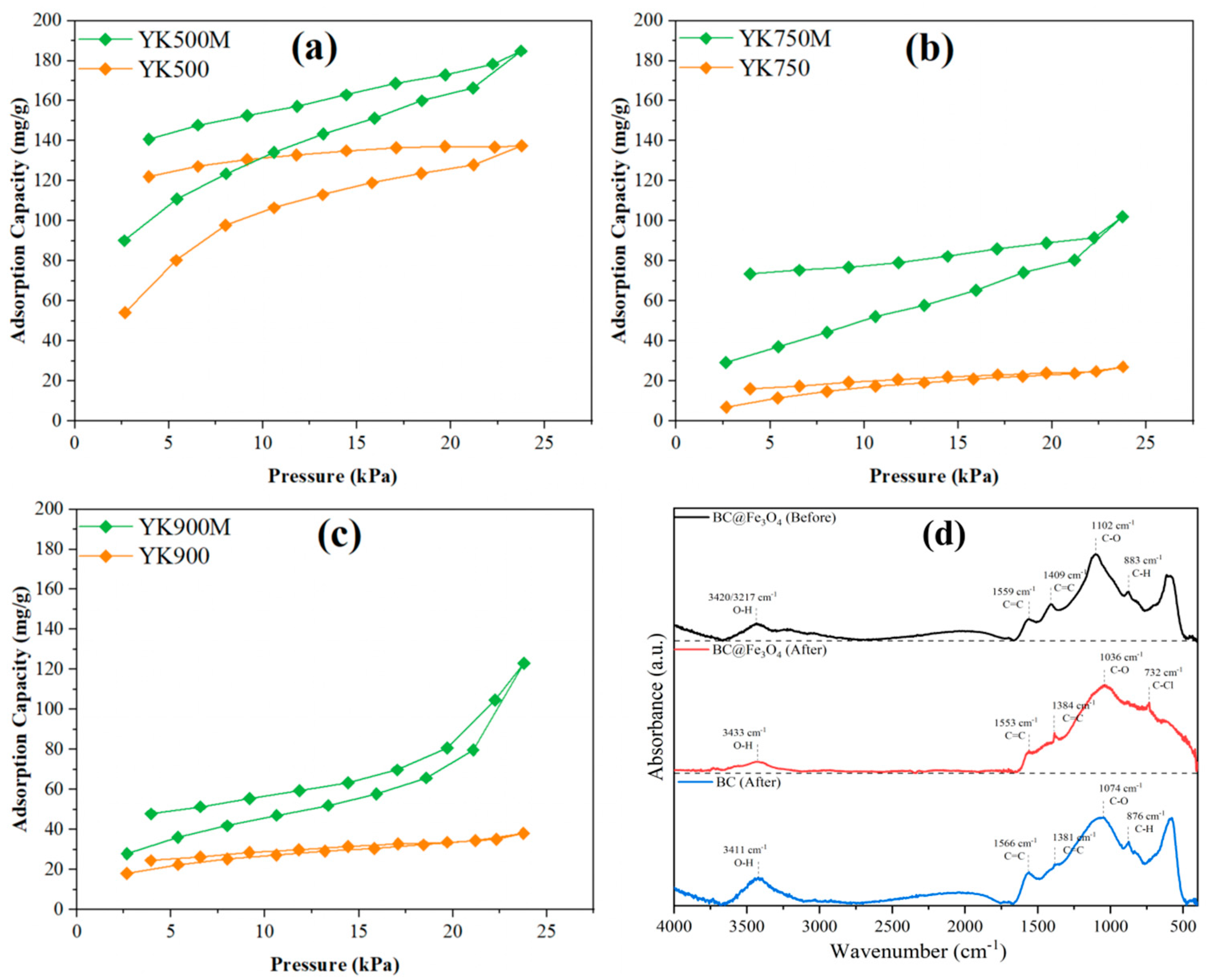
3.3. Enhanced TCM Adsorption Using Fe3O4 Loading and Mechanistic Insights
3.4. Influence of Fe3O4 Loading Ratios on Adsorption Performance of Typical CAHs
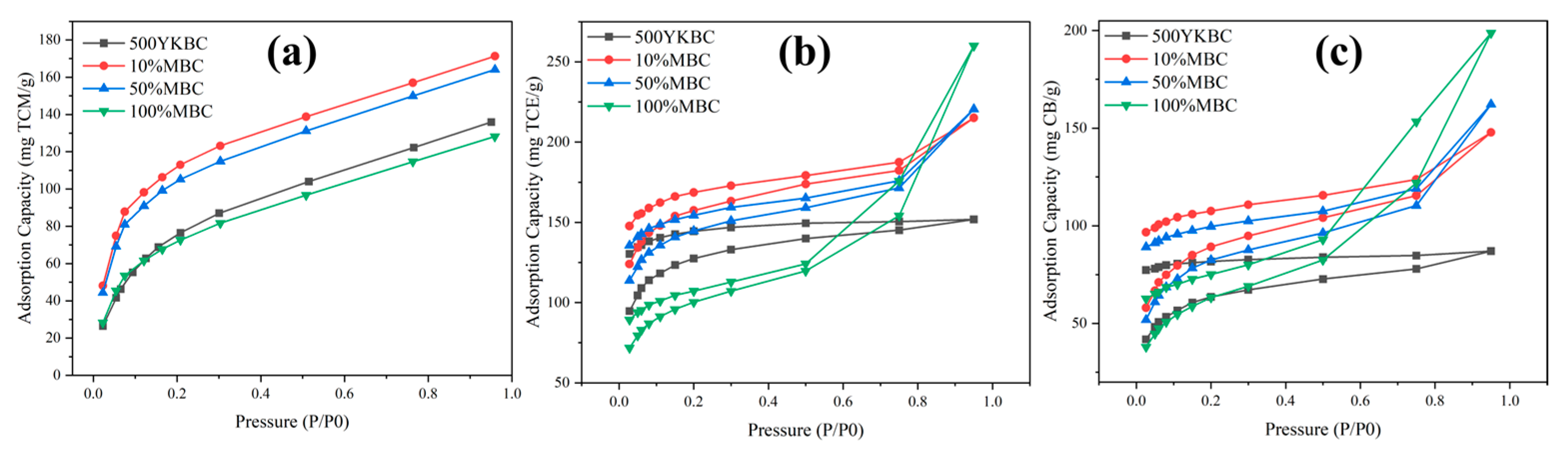
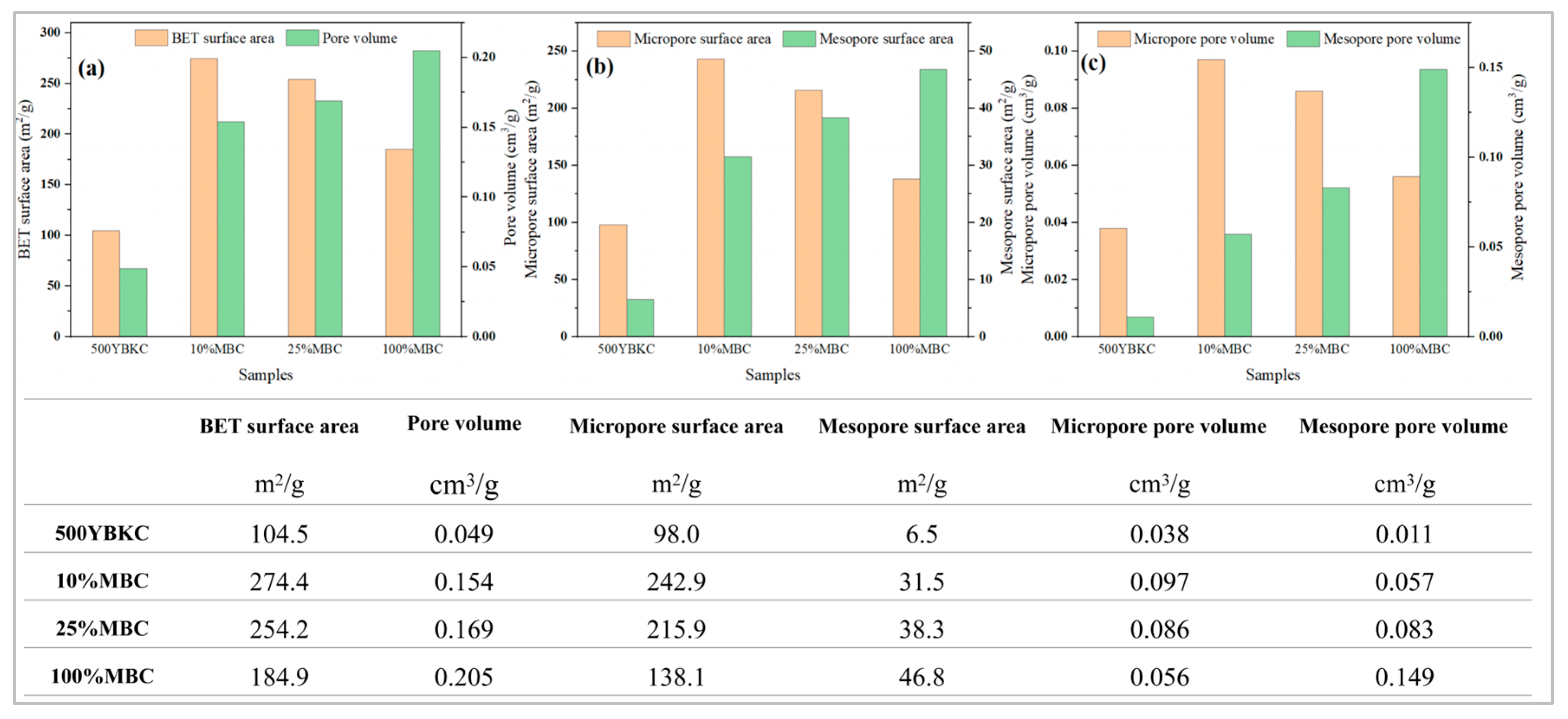
3.5. Comparative Pore Analysis of the Synthetic Materials
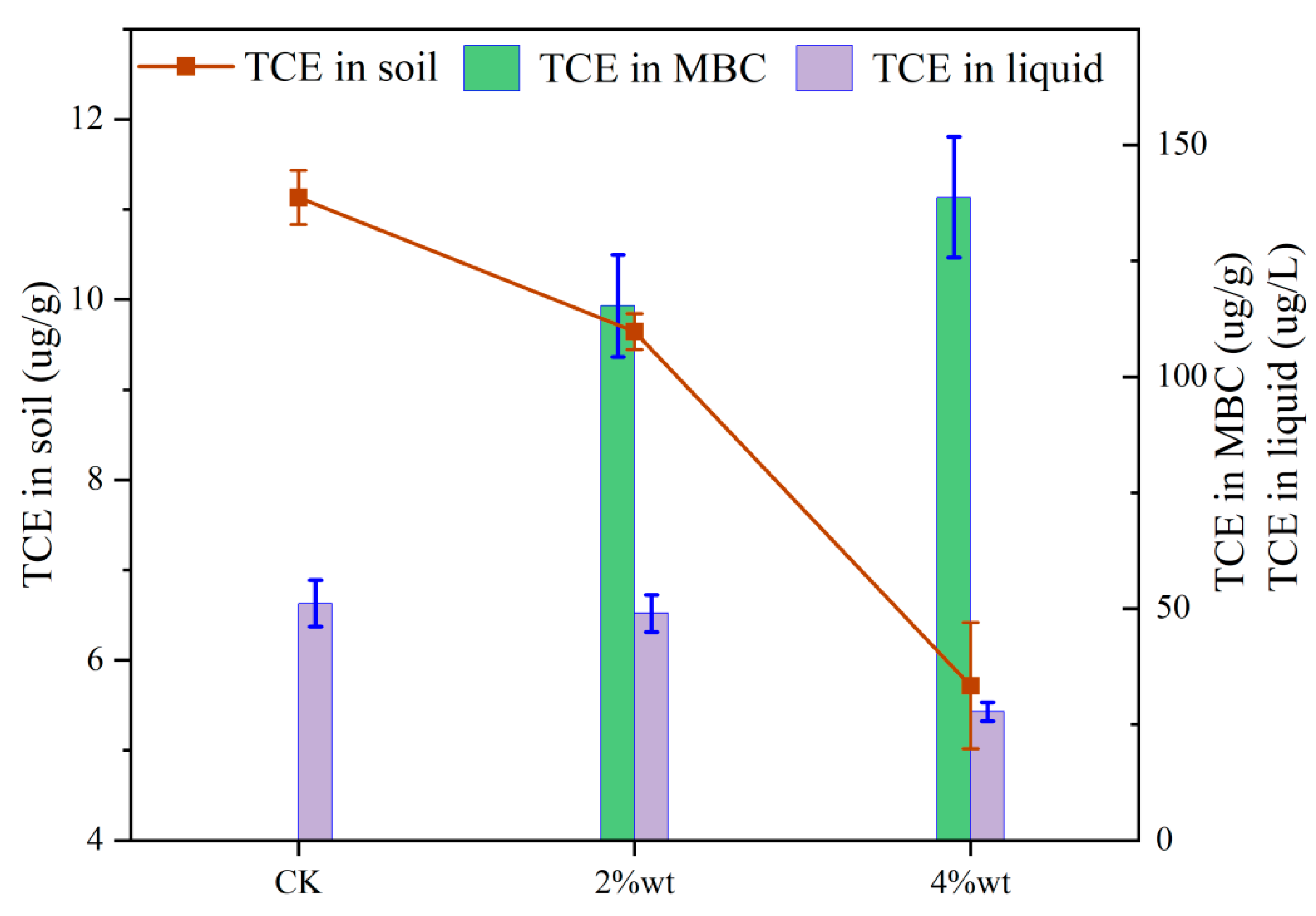
3.6. Competitive Adsorption Between MBC and Soil
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sassetto, G.; Presutti, M.; Lai, A.; Simonetti, G.; Lorini, L.; Papini, M.P.; Zeppilli, M. Field Test of a Bioelectrochemical Membrane-Less Reactor for Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon and Nitrate Removal from a Contaminated Groundwater. ChemPlusChem 2025, 90, e202400683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lei, L.; Gong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, G.; Guo, G. Strategies and Mechanisms for Improving Groundwater Remediation Efficiency of Chlorinated Ethenes by Controlling the Particle Size of Polyhydroxyalkanoate. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 496, 154038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L. Distribution Characteristics of Chlorinated Hydrocarbons in Contaminated Plots of Typical Organic Chemical Plants and Risk Assessment Based on Monte Carlo Simulation. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2024, 14, 98–111. [Google Scholar]
- GB36600-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Xiao, Z.; Jiang, W.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y. Bioremediation of Typical Chlorinated Hydrocarbons by Microbial Reductive Dechlorination and Its Key Players: A Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 202, 110925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Kang, Z.; Ni, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Cao, J.; Qian, L. Remediation of Trichloromethane-Contaminated Soil and Groundwater Using Microbial and Iron-Based Materials: A Review. Pedosphere 2025, 35, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-H.; Li, Z.-T.; Lai, C.-Y.; Zhao, H.-P. Enhancing Reductive Dechlorination of Trichloroethylene in Bioelectrochemical Systems with Conductive Materials. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Ye, M. Effects of Activated Carbon Properties on Chlorobenzene Adsorption and Adsorption Product Analysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, H.; Cao, W. Enhanced 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol Removal from Soil by Electrokinetic Remediation Coupled with Biochar in a Permeable Reactive Barrier. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abromaitis, V.; Racys, V.; van der Marel, P.; Meulepas, R.J.W. Biodegradation of Persistent Organics Can Overcome Adsorption–Desorption Hysteresis in Biological Activated Carbon Systems. Chemosphere 2016, 149, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Feng, Y.; Hu, M.; Lin, D.; Yang, K.; Wu, W. Highly Efficient Bioregeneration of High Temperature-Pyrolyzed Biochar after Trichloroethylene Adsorption through Biodegradation of Dehalococcoides. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.M.; Matturro, B.; Amanat, N.; Rossetti, S.; Petrangeli Papini, M. Coupled Adsorption and Biodegradation of Trichloroethylene on Biochar from Pine Wood Wastes: A Combined Approach for a Sustainable Bioremediation Strategy. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S. Biochar as an Electron Shuttle for Reductive Dechlorination of Pentachlorophenol by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.K.; Nayak, A. Cadmium Removal and Recovery from Aqueous Solutions by Novel Adsorbents Prepared from Orange Peel and Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 180, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, C.; Zeng, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, T.; Song, B.; Zhou, C. Abiotic Transformation of Chlorinated Organics at the Active Surface of Iron-Bearing Minerals in Soils and Sediments. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2024, 67, 2991–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, P.; Aulenta, F.; Rossetti, S.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Danko, A.S. Impact of Magnetite Nanoparticles on the Syntrophic Dechlorination of 1,2-Dichloroethane. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Wu, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, M. Co-Sorption/Co-Desorption Mechanism of the Mixed Chlorobenzenes by Fresh Bulk and Aged Residual Biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 429, 128349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, B.; Xian, J.; Tsang, E.P.; Cheng, W.; Fang, J.; Fang, Z. Magnetic Biochar for Environmental Remediation: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, C.S.; Guerreiro, M.C.; Gonçalves, M.; Oliveira, L.C.A.; Anastácio, A.S. Activated Carbon/Iron Oxide Composites for the Removal of Atrazine from Aqueous Medium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Tong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Tao, Y.; Dai, X.; et al. Applications of Functionalized Magnetic Biochar in Environmental Remediation: A Review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 434, 128841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.; Niu, L.; Zhang, H. Fe-Loaded Biochar Facilitates Simultaneous Bisphenol A Biodegradation and Efficient Nitrate Reduction: Physicochemical Properties and Biological Mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhong, C.; Sun, A.; He, K.; Liu, X.; Song, H.; Li, J. A Super Magnetic Porous Biochar Manufactured by Potassium Ferrate-Accelerated Hydrothermal Carbonization for Removal of Tetracycline. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Shen, X.-L.; Gao, L.-J.; Jin, X.; Li, Y.-M. Adsorption and Co-Adsorption of 2,4-Difluoroaniline and Copper (II) Using Nickel-Manganese Ferrite Magnetic Biochar Derived from Orange Peel. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, M.; Haderlein, S.B.; Kellerhals, T.; Luzi, S.; Zwank, L.; Angst, W.; Schwarzenbach, R.P. Mechanisms and Products of Surface-Mediated Reductive Dehalogenation of Carbon Tetrachloride by Fe(II) on Goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 2058–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amonette, J.E.; Workman, D.J.; Kennedy, D.W.; Fruchter, J.S.; Gorby, Y.A. Dechlorination of Carbon Tetrachloride by Fe(II) Associated with Goethite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4606–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrey, M.L.; Wilkin, R.T.; Ford, R.G.; Wilson, J.T. Nonbiological Removal of Cis-Dichloroethylene and 1,1-Dichloroethylene in Aquifer Sediment Containing Magnetite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Li, J.; Zhou, W.; An, J.; Tian, L.; Xiong, F.; Fei, W.; Feng, Y.; Ma, J. Abiotic Natural Attenuation of 1,2,3-Trichloropropane by Natural Magnetite under O2 Perturbation. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.; Cui, X.; Liu, M.; Qie, H.; Tang, Y.; Leng, W.; Luo, N.; Luo, H.; Lin, A.; Yang, W.; et al. Degradation of Trichloroethylene by Biochar Supported Nano Zero-Valent Iron (BC-nZVI): The Role of Specific Surface Area and Electrochemical Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, D.; Yan, J.; Qian, L.; Han, L.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Gu, M. Mechanistic Insights into Adsorptive and Oxidative Removal of Monochlorobenzene in Biochar-Supported Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron/Persulfate System. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U. Cadmium and Lead Remediation Using Magnetic Oak Wood and Oak Bark Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahira, A.; Nishida, S.; Fukunishi, K. Synthesis of Magnetic Activated Carbons for Removal of Environmental Endocrine Disrupter Using Magnetic Vector. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 114, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stanton, M.M.; Park, B.-W.; Vilela, D.; Bente, K.; Faivre, D.; Sitti, M.; Sánchez, S. Sem-Magnetotactic Bacteria Powered Biohybrids Target E. Coli Biofilms. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9968–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Li, H.; Wang, T.; Li, A.; Zhu, C.; Lu, G. Xrd-Engineering of Coordination Environment in Bioinspired Laccase-Mimicking Catalysts for Monitoring of Pesticide Poisoning. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makam, P.; Yamijala, S.S.R.K.C.; Bhadram, V.S.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Wong, B.M.; Gazit, E. FTIR-Single Amino Acid Bionanozyme for Environmental Remediation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, C.; Liang, Y.; Han, T.; Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, D.; Zhong, C. BET-Rational Construction of Defects in a Metal–Organic Framework for Highly Efficient Adsorption and Separation of Dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 289, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vopička, O.; Friess, K.; Hynek, V.; Sysel, P.; Zgažar, M.; Šípek, M.; Pilnáček, K.; Lanč, M.; Jansen, J.C.; Mason, C.R.; et al. Equilibrium and Transient Sorption of Vapours and Gases in the Polymer of Intrinsic Microporosity PIM-1. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 434, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glišić, I.; Ritsema van Eck, G.C.; Smook, L.A.; de Beer, S. Enhanced Vapor Sorption in Block and Random Copolymer Brushes. Soft Matter 2022, 18, 8398–8405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Gong, K.; Yue, F.; Han, X.; Wu, K.; Shao, P.; Fu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Oxygen- and Proton-Transporting Open Framework Ionomer for Medium-Temperature Fuel Cells. Science 2024, 385, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Wang, J. Adsorptive Removal of Pharmaceutical Pollutants by Defective Metal Organic Framework UiO-66: Insight into the Contribution of Defects. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Sun, M.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Microbial Community Dynamics in Groundwater of a Petrochemical Refinery: Influence of BTEX and Dichloroethane Contamination. Water 2024, 16, 3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Sheng, G.; Chiou, C.T.; Xing, B. Compositions and Sorptive Properties of Crop Residue-Derived Chars. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4649–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-Y.; Seo, Y.-D.; Kim, B.; Kim, I.Y.; Cha, D.K. Microbial Reduction of Nitrate in the Presence of Zero-Valent Iron and Biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H.; Hu, M. An Intensive Study on the Magnetic Effect of Mercapto-Functionalized Nano-Magnetic Fe3O4 Polymers and Their Adsorption Mechanism for the Removal of Hg(II) from Aqueous Solution. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 210, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, N.; Garg, V.K. Application of EDTA Modified Fe3O4/Sawdust Carbon Nanocomposites to Ameliorate Methylene Blue and Brilliant Green Dye Laden Water. Environ. Res. 2019, 172, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitu, A.; Chen, W.; Tadda, M.A.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, J. Enhanced Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment in a Biofilm Reactor Filled with Sponge/Ferrous Oxalate/Biochar Composite (Sponge-C2FeO4@NBC) Biocarriers: Performance and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 330, 138772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Fang, R.; Gul, I.; Aer, L.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Tang, L. Halohydrin Dehalogenase Immobilization in Magnetic Biochar for Sustainable Halocarbon Biodegradation and Biotransformation. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 27, 102759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Ren, B.; Hou, B.; Deng, X.; Deng, R.; Zhu, G.; Cheng, S. Adsorption of Sb(III) and Pb(II) in Wastewater by Magnetic γ-Fe2O3-Loaded Sludge Biochar: Performance and Mechanisms. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wei, X.; Sun, P.; Wan, J. Preparation, Characterization and Adsorption Performance of a Novel Anionic Starch Microsphere. Molecules 2010, 15, 2872–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, S.; Sharma, P.; Singh, S.P.; Nadda, A.K.; Sahoo, P.K.; Xia, C.; Sharma, S.; Ganguly, R.; Lam, S.S.; Kim, K.H. Engineered Biochar for the Effective Sorption and Remediation of Emerging Pollutants in the Environment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Dou, X.; Liu, Z.; Xie, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Pore-Engineered Magnetic Biochar: Optimizing Pyrolysis and Fe3O4 Loading for Targeted Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon (CAH) Adsorption. Separations 2025, 12, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12100260
Zhang F, Li Z, Dou X, Liu Z, Xie Y, Liu J, Zhang S. Pore-Engineered Magnetic Biochar: Optimizing Pyrolysis and Fe3O4 Loading for Targeted Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon (CAH) Adsorption. Separations. 2025; 12(10):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12100260
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Fengyuan, Zixuan Li, Xiaohan Dou, Zhengwei Liu, Yan Xie, Jingru Liu, and Shucai Zhang. 2025. "Pore-Engineered Magnetic Biochar: Optimizing Pyrolysis and Fe3O4 Loading for Targeted Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon (CAH) Adsorption" Separations 12, no. 10: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12100260
APA StyleZhang, F., Li, Z., Dou, X., Liu, Z., Xie, Y., Liu, J., & Zhang, S. (2025). Pore-Engineered Magnetic Biochar: Optimizing Pyrolysis and Fe3O4 Loading for Targeted Chlorinated Aliphatic Hydrocarbon (CAH) Adsorption. Separations, 12(10), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12100260





