Abstract
Introduction: Co-infection of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) with syphilis is common and has significant clinical consequences. HIV infection can change the course and clinical manifestations of syphilis, resulting in atypical syphilis. A rare feature of this infection is malignant syphilis, which frequently resembles other skin lesions and poses a challenge in diagnosis. This report aims to describe a case of malignant syphilis in an HIV-positive patient. Case report: A 33-year-old man who has sex with men (MSM) came to the dermato-venereology outpatient clinic with chief complaints of ulcerative lesions on the face, trunk, arms, palms, and legs for the past two months. The patient complained of fever, chills, and decreased appetite two weeks prior to presentation. A dermatological examination showed numerous well-demarcated ulcerated plaques and nodules partially covered with crust. Reactive results were found on syphilis serologic tests with high titers. The test for HIV was reactive, with a CD4 cell count of 219 cells/mm3. The patient was then diagnosed with malignant syphilis and received treatment in the form of benzathine penicillin injection 2.4 million units once a week for three consecutive weeks. After treatment, the skin lesions and syphilis serologic titer improved. Conclusions: Secondary syphilis in patients with HIV infection may present as an atypical variant. As reported in this case, malignant syphilis should always be considered in the differential diagnosis when ulcerative and necrotic lesions are observed in individuals with HIV infection.
Introduction
There are six million new cases of syphilis in the world in individuals aged 15 to 49 years every year, and the numbers are increasing. [1] The reason for the enhancement of syphilis is multifactorial, including raising high-risk sexual behavior, reducing fear of infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and declining use of condoms in adults and adolescents. Syphilis is commonly found in the population of men who have sex with men (MSM). A man who has syphilis is also at high risk of acquiring HIV infectionin the future. Syphilis will increase the occurrence of HIV transmission by two to nine times compared to individuals without syphilis, and individuals with HIV infection also often present atypical clinical manifestations of syphilis, especially in infection with HIV type 1. [2]
Atypical manifestations of syphilis can be found at all stages, whether primary, secondary, or tertiary syphilis. In primary syphilis, atypical manifestations that can be found are the presence of multiple genital ulcers or accompanying ulcers in atypical locations. If left untreated, primary syphilis can develop into secondary syphilis, which indicates the spread of syphilis in the blood circulation and various body tissues. Atypical lesions can also be found at this stage, such as psoriasiform, lichen planus-like, vesicular, follicular, corymbiform, nodular, annular, pustular, frambesiform, and nodular-ulcerative or malignant syphilis (MS). MS, an uncommon atypical secondary syphilis, is often associated with HIV infection. The presence of necrotic and ulcerated lesions characterizes the disease. In addition, prodromal symptoms, such as fever, malaise, myalgias, headache, and weight changes, are often present in patients before skin lesions appear. [3]
Here we report a case of a 33-year-old MSM patient with HIV infection who was diagnosed with MS based on history, physical examination, laboratory, and histopathological examination. The purpose of this case report is to provide an overview of the existence of atypical forms of secondary syphilis, especially in individuals with HIV infection.
Case report
A 33-year-old man came to our dermato-venereology outpatient clinic with a chief complaint of ulcerative lesions on the face, trunk, arms, palms, and legs for the past two months. Two weeks prior, the patient had presented high fever, chills, and loss of appetite. He reported history of sexual intercourse with more than one male partner and had a history of being sexually assaulted when he was five years old.
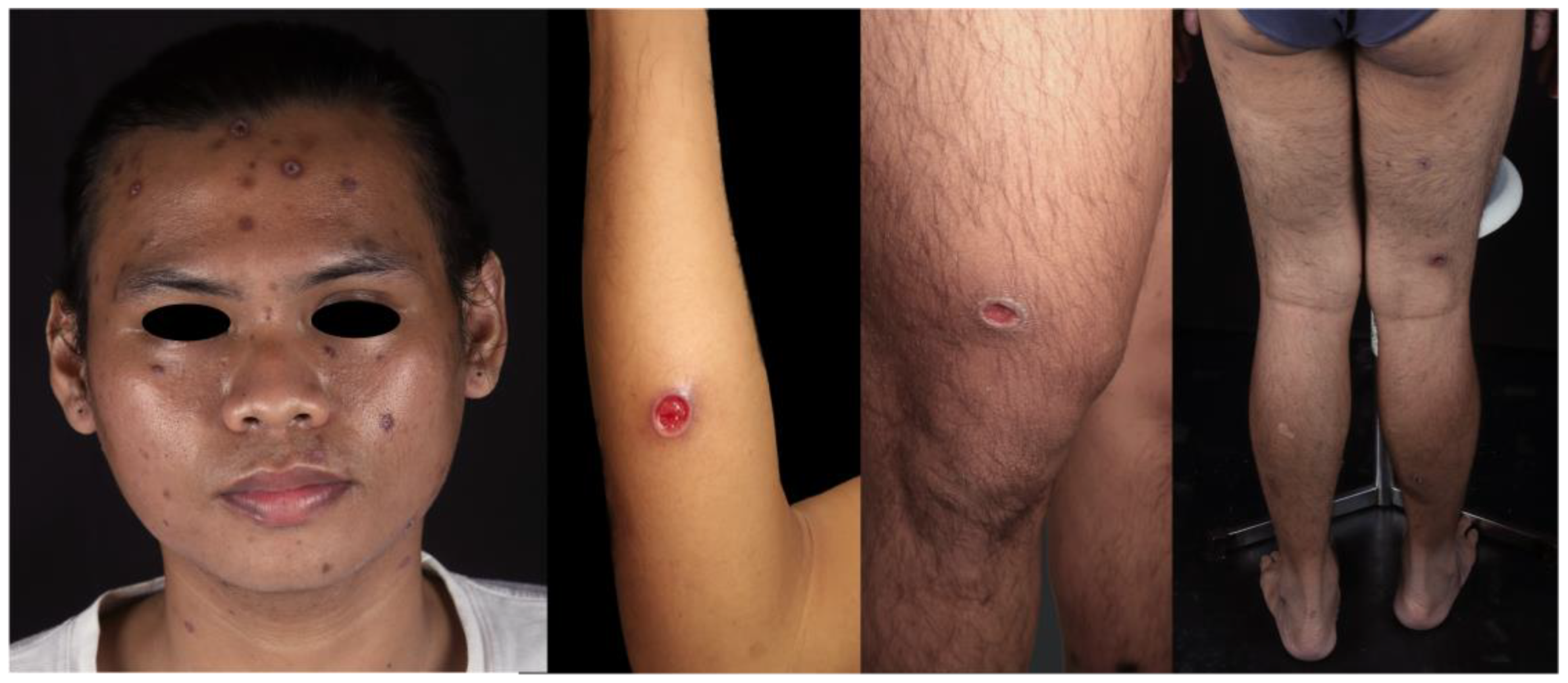
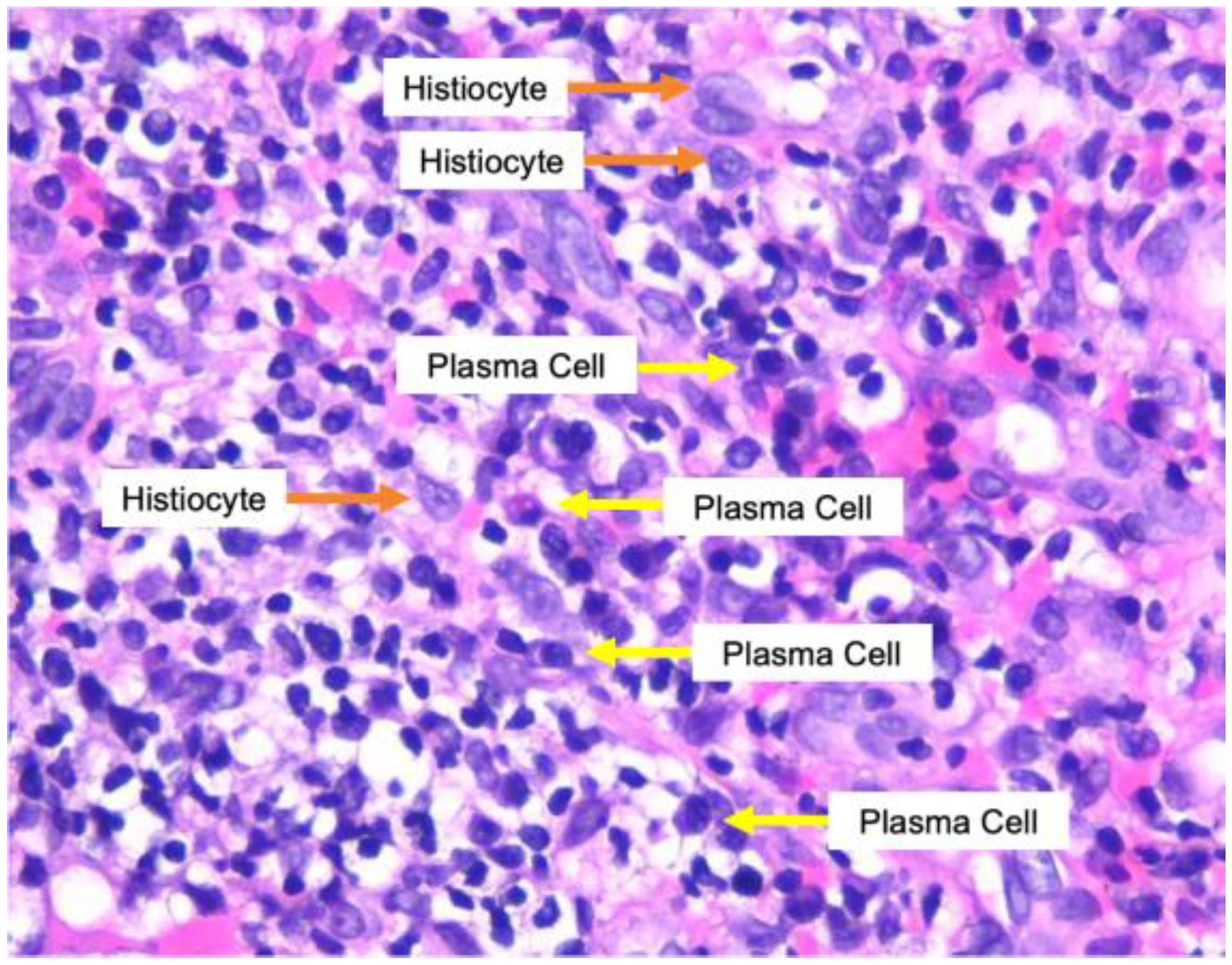
On the clinical examination, vital signs were within normal limits. The dermatology examination showed numerous well-demarcated ulcerated plaques and nodules, partially covered with crust (Figure 1). A skin biopsy was performed on an ulcerative lesion, and histological examination with hematoxylin-eosin staining showed infiltration of dense band-like inflammatory cells, with the domination of plasma cells, especially in perivascular and periadnexal fields. There were also lymphocytes, histiocytes, epithelioid cells, and neutrophils in a small amount (Figure 2). Laboratory examination revealed normal complete blood count, reactive Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) with titer 1:512, reactive Treponema pallidum Particle Hemagglutination (TPHA), and reactive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for HIV with CD4 count 219 cells/mm3.
Figure 1.
Skin lesions of MS showed numerous well-demarcated ulcerated plaques and nodules, partially covered with crust.
Figure 2.
Infiltration of dense band-like inflammatory cells consisting of plasma cells, histiocytes, lymphocytes, epithelioid cells, and neutrophils (hematoxylin-eosin staining).
Based on history, physical, and supporting examination, a diagnosis of malignant syphilis and HIV infection was established. The patient was treated with intramuscular injection of penicillin benzathine (2.4 million units) once a week for three consecutive weeks. He was also initiated on antiretroviral therapy (tenofovir, lamivudine, and efavirenz). The evaluation after six months revealed clinical improvement, and the titer of VDRL declined ≥ 4-fold (1:8).
Discussion
Until now, the incidence of MS itself is not known with certainty, but it is reported that there is an increase in the number of cases in young HIV-positive male patients. [3] The cause of this type of disease manifestation is still unknown; an individual’s immune status may not affect the development because 80% of HIV-positive patients with MS are reported to have a CD4 count of more than 200 cells/mm3 and rarely have a history of opportunistic infections. [4] In this case, the patient had a CD4 of 219 cells/mm3. The existence of these findings can predict that individuals with acute HIV infection whose CD4 counts are still relatively high are a population at risk of developing MS.
Clinically, MS is characterized by papules, nodules, or plaques with necrosis in the center and may be covered with thick crusts. Occasionally, ulcers with firm edges and purulent discharge can be found without any inflammatory reaction around the lesion. The location is mainly on the trunk and extremities, but involvement of mucosa, palms, soles, and scalp are also reported. Fever and constitutional symptoms are common and appear before the skin lesions occur. [5] Histopathological examination can also help establish the diagnosis. The presence of plasma cells in the dermis, mixed with lymphocytes, histiocytes, and neutrophils, is the characteristic of syphilitic lesions. [6] Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining with Treponema pallidum monoclonal antibodies and silver staining, either by Warthin-Starry or Steiner staining, can also be used to detect spirochetes in tissue or skin lesions. [7] To help diagnose MS, Fisher et al. [8] created diagnostic criteria: appropriate clinical and histopathological features, the presence of high syphilis serological titers, the presence of a severe Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (JRH), and rapid resolution after administration of adequate therapy.
In this case, the patient had experienced a high fever, chills, and decreased appetite. After this condition improved, ulcerative lesions appeared in some areas of his body. The patient’s clinical picture is consistent with the existing literature regarding MS. Histopathological examination revealed infiltration of inflammatory cells consisting of plasma cells, lymphocytes, histiocytes, epithelioid cells, and neutrophils. This finding is also in accordance with the existing literature regarding histopathological examination of syphilis. However, IHC examinations are not currently available in our center. The patient also had a high VDRL titer (1:512), so it fits the criteria needed to establish a diagnosis of MS. For the last diagnostic criteria, the patient had no symptoms of severe JRH after adequate therapy. However, several studies have reported that there are patients with MS who do not develop JRH symptoms, and the absence of this reaction is not considered a reason to exclude the diagnosis of MS. [9]
Until now, there are no specific recommendations for the treatment of MS. The usual treatment regimen is the same as for late latent syphilis, using intramuscular injections of benzathine penicillin 2.4 million units once per week for three consecutive weeks. It was reported that as many as 80% of patients with MS treated with penicillin had rapid improvement of their skin lesions after receiving adequate therapy. [4] In this case, the patient received injections of penicillin benzathine three times, once weekly, for three consecutive weeks. The ulcer improved only after one week following the first injection. One month after the third injection, all the lesions had dried up and presented with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation; no new lesions were found.
After adequate therapy, patients with syphilis should be followed up at 3, 6, 9, 12, and 24 months by observing the titer of non-treponemal tests. A four-fold decrease from the initial titer indicates successful therapy for syphilis. [10] In our case, there was a decrease in the VDRL titer from 1:512 to 1:8 or more than a four-fold decline after six months; after 24 months, the VDRL test became negative.
Conclusions
Secondary syphilis in patients with HIV infection patients may occur in atypical forms. As demonstrated in our case, MS should always be considered in the differential diagnosis when ulcerative and necrotic lesions are found in individuals with HIV infection. This paper reports the case of a 33-year-old HIV-positive MSM diagnosed with MS. The diagnosis was established by history, physical, and supporting examination. Treatment using the injection of penicillin benzathine 2.4 million units once a week for three consecutive weeks gave an adequate response for skin lesions and the titer of VDRL.
Author Contributions
A.A. contributed to the initial draft of the manuscript. A.A., Y.E.I., and S.R.P. contributed to the clinical care of patient. A.A. and S.R.P. contributed to manuscript review and the final approval. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
None to declare.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors—none to declare.
Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and the associated images.
References
- Kojima, N.; Klausner, J.D. An update on the global epidemiology of syphilis. Curr Epidemiol Rep. 2018, 5, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeganeh, N.; Watts, H.D.; Camarca, M.; et al. Syphilis in HIV-infected mothers and infants: Results from the NICHD/HPTN 040 study. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2015, 34, e52–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivars Lleó, M.; Clavo Escribano, P.; Menéndez Prieto, B. [Atypical cutaneous manifestations in syphilis]. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2016, 107, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wibisono, O.; Idrus, I.; Djawad, K. Malignant syphilis: A systematic review of the case reports published in 2014-2018. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl Ed). 2021, S1578-2190(21)00174-8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortigosa, Y.M.; Bendazzoli, P.S.; Barbosa, A.M.; Ortigosa, L.C. Early malignant syphilis. An Bras Dermatol. 2016, 91, 148–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, M.; Fujii, Y.; Ozaki, K.; et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-positive secondary syphilis mimicking cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Diagn Pathol. 2015, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, M.P.; High, W.A.; Molberg, K.H. Secondary syphilis: A histologic and immunohistochemical evaluation. J Cutan Pathol. 2004, 31, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, D.A.; Chang, L.W.; Tuffanelli, D.L. Lues malignant. Presentation of a case and a review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1969, 99, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djawad, K. Malignant syphilis as an initial presentation of HIV infection: A case report. Int J Dermatol Venereol. 2021, 4, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipple, C.; Taylor, G.P. Syphilis testing, typing, and treatment follow-up: A new era for an old disease. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015, 28, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2023.