Abstract
Introduction: Life expectancy varies across geographical and political landscapes for a multitude of reasons. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus responsible for the 2020 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and pandemic, is present in 215 countries, and is described as a pathogen that is most deadly to individuals 65 years and older. However, it is unclear if the majority of COVID-19-related deaths are targeting individuals above or below life expectancy. Methods: Through seven months of the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic, an association between life expectancy and COVID-19 related deaths was assessed. The reported age of those suffering from COVID-19-related deaths was evaluated across eight countries (United States, Germany, Italy, Hungary, Poland, South Africa, Sweden, and Switzerland), and placed into binary categories depending on whether or not the death occurred above or below the country’s life expectancy. Results: Given this dataset, it was observed that there was a greater proportion of COVID related deaths above life expectancy (M = 64.58%, SD = 6.46) as opposed to below life expectancy (M = 35.41%, SD = 6.46), as these differences were significant (95%CI [18.518, 42.881], p < 0.001). In contrast, an insignificant trend was observed when examining the relationship between deaths above life expectancy and Gini index (Pearson correlation coefficient r= −0.62, n = 8, p = 0.09). The disparity, or percent difference in death occurring above versus below life expectancy was greatest in the countries with life expectancies of 80+ (Sweden, Switzerland, Germany). Conclusions: Considering life expectancy may be an appropriate approach for reporting COVID-19 related deaths, as well as planning responses to localized COVID-19 outbreaks, prioritizing drug treatment, and assessing ICU capacity.
Introduction
Since the turn of the century, coronavirus outbreaks have become the norm. In 2004, the first outbreak featured severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus-1 (CoV-1). Not too long after (i.e., 2012), Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) emerged onto the scene [1]. Eight years later (i.e., 2020), the latest outbreak features severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which afflicts both pulmonary and extrapulmonary systems [2]. SARS-CoV-2 is the cause of the 2020 coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19), which was first identified in Wuhan, China, and is now present in 215 countries [3]. Through economic hardship, estimated infection rates, health risks, and fatalities [4,5,6], SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for a great deal of harm via the most recent global pandemic, and it has forced society to re-imagine life expectancy.
Life expectancy is the expected age which the average individual of a given population reaches before being deceased. While pandemics including bubonic plague, Spanish flu and the HIV/AIDS have long plagued the human population [7,8,9], the recent COVID-19 pandemic features a novel coronavirus that is controversial because of its impact on older individuals, which may not have necessarily achieved life expectancy. In 1900, U.S. life expectancy was 48 years of age [10], at the same time, infectious diseases such as influenza, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and enteritis and diarrhea causing-parasites are thought to have caused 31% of all U.S. deaths—a century ago [11]. Since 1900, life expectancy has increased, as life expectancies in South Africa, U.S., and Sweden are now ~60, ~70, and~80 years, respectively. While many factors may explain life expectancy increase, wealth inequality may also play a role, as it has dramatically increased since the late 20th century [12], and may affect a country’s ability or inability to assuage the outcome of infectious diseases.
To determine if COVID-19-related deaths are associated with life expectancy, deaths in-cidences above and below life expectancy were assessed across eight countries. COVID-19 related deaths were then placed into binary categories (i.e., ‘deaths above life expectancy’, and ‘deaths below life expec-tancy’). While controlling for regional life expectancy, the aim of this survey was to uncover if the majority of COVID related deaths occur above or below life expectancy. It is hypothesized that disparity in those deaths occurring above life expec-tancy will vary across political borders, perhaps due to wealth inequality.
Methods
Assessing reported COVID-19 deaths: above and below life expectancy
To determine if these deaths were occurring above or below life expectancy, data published by United States (Center for Disease Control), Germany (Robert Koch-Institut), Italy (Istituto Superiore di Sanità), Hungary (Tájékoztató oldal a koronavírusról), Poland (Polityka Zdrowotna), South Africa (Institute for Communicable Diseases), Sweden (Folkhälsomyndigheten), and Switzerland (Bundesamt für Gesundheit) were used for this study. Data from these government agencies were downloaded from Statista (https://www.statista.com/). These countries were chosen because they represent a broad life expectancy range of about 20 years (Table 1), and public datasets were available as mortality among age-classes, which is the nature of this study. Since life expectancy is usually assessed in a manner specific to a particular region or country, incidence of death was categorized as above life expectancy or below life expectancy (Table 1). The percent of deaths occurring above or below life expectancy were recorded for each country. Disparity (% difference) was taken by calculating percent difference in death occurring above and below expectancy. Comparison between countries was necessary to account for regional differences that may impact the death rate.

Table 1.
Eight countries were assessed for this study. Life expectancy ranges are provided courtesy of World Bank—worldbank.org.
Analysis
Among the eight countries (Figure 1), ‘all deaths above life expectancy’ percentages (n = 8) were compared to their ‘all deaths below life expectancy’ percentages (n = 8). The Shapiro-Wilks test was employed to assess normality in distribution. In addition, Levene’s test was used to assess equality in variance. Since a paired t-test is commonly used to determine differences between two variables from the same source, the use of this parametric test was justified for this study. Here, proportionate deaths above and below life expectancy were compared from countries. In addition, Wilcoxon rank sign exact test, was also employed to verify the findings. The top three countries with the greatest disparity were compared against countries with lower disparities using the Welch two sample t-test. To determine if wealth inequality was a good predictor of COVID related death (e.g., above life expectancy), the Gini index was used [13]. A correlation between Gini index and log percent death above life expectancy was tested with Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient.
Figure 1.
Provided here are 8 points that depict geographical reference of the 8 countries used in this study. Map was constructed using Maptive (www.maptive.com).
Results
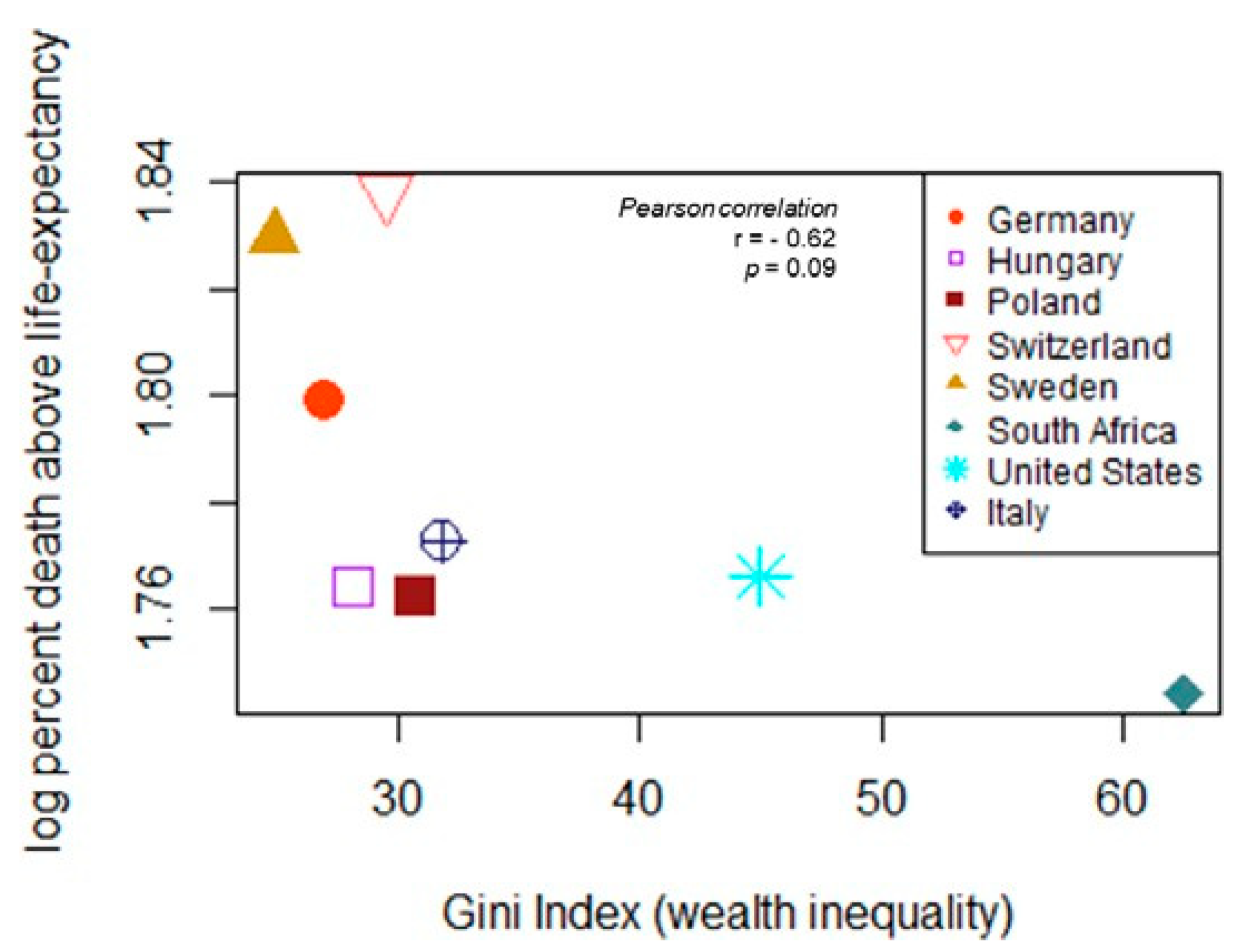
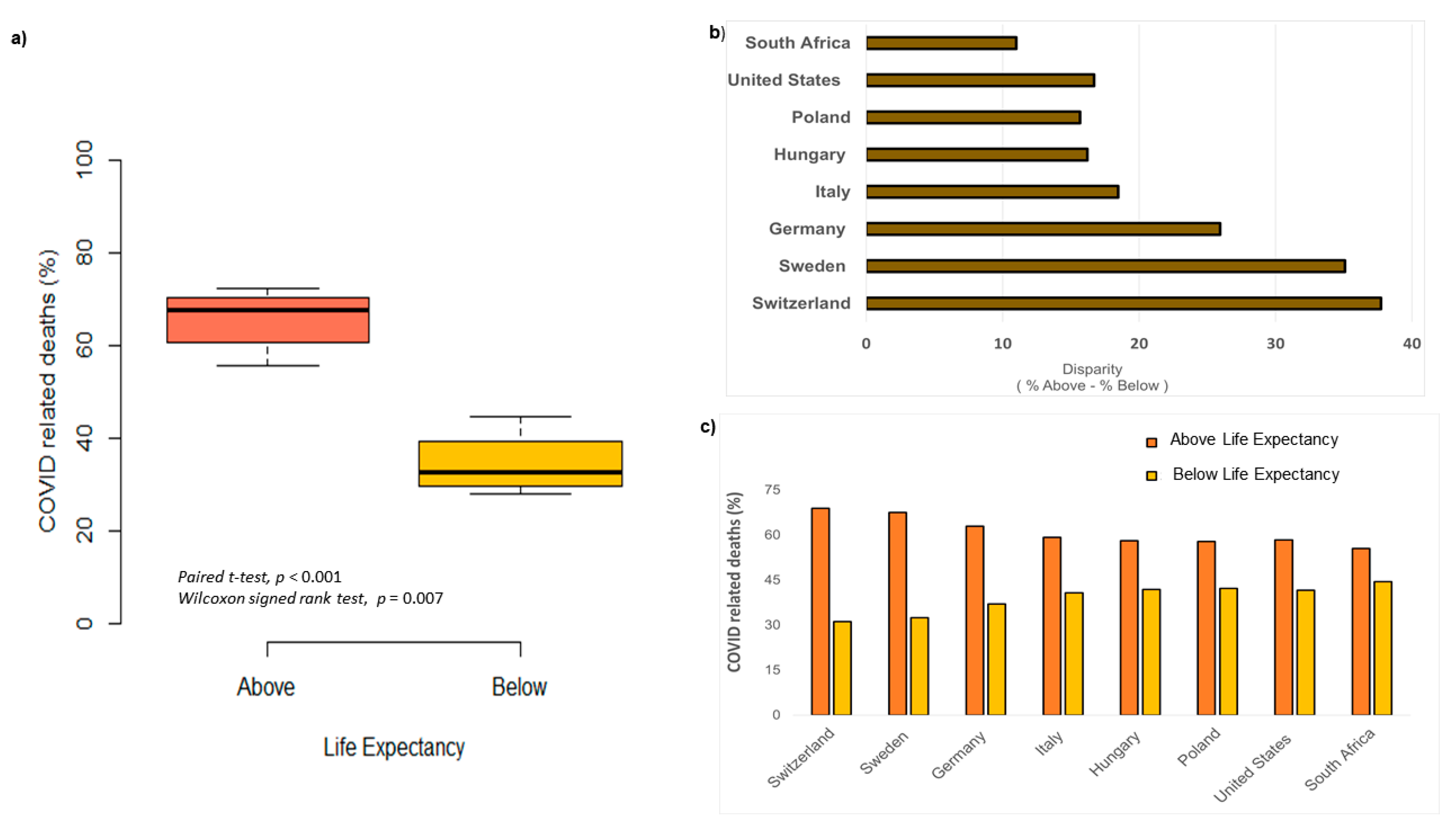
Wealth inequality was not a significant predictor of death above life expectancy (Figure 2, Pearson correlation coefficient r= −0.62, n = 8, p = 0.09). Given this dataset, the majority of COVID-19 related deaths occurred among individuals above life expectancy (death above life expectancy, M = 64.58%; versus death below life expectancy, M = 35.41%; Figure 3a), as these findings were significant on both parametric and non-parametric tests (paired t-test, 95%CI [18.518, 42.881], p < 0.001; Wilcoxon signed rank exact test, p = 0.007). Disparities were greatest in Switzerland, Sweden, and Germany (Figure 3b), showing that relative difference in deaths above life expectancy far exceeded deaths below life expectancy (Figure 3b). Interestingly, these same three countries have a life expectancy of 80 years or more. South Africa, United States, Poland, Italy and Hungary had more of a balance when considering deaths above versus below life expectancy. These five countries had disparities of less than 20% (Figure 3b), and were contrasted against countries with disparities of 20% or greater (Switzerland, Sweden, and Germany). Thus, an apriori contrast revealed significant differences between the two groupings (disparity above 20%, M = 32.91%; versus disparity below 20%, M = 15.61%; Welch Two Sample t-test, 95% CI [−30.848, −3.749], t(2.495) = −4.569, p = 0.028). The United States and South Africa were comparable in proportion of deaths below life expectancy (Figure 3c), but it is important to note that the United States has a life expectancy that outlasts South Africa by more than 10 years.

Figure 2.
An association between GINI index and COVID-related deaths above life expectancy. Trending toward significance, death above life expectancy was negatively correlated with wealth inequality (r= −0.62, p = 0.09), Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient.
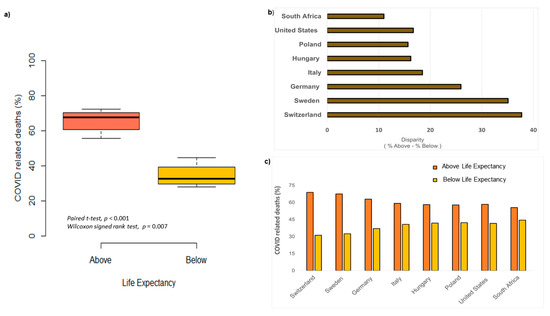
Figure 3.
Life expectancy and COVID19-related death.
Discussion
COVID-19 differs from recent pandemics of the 21st century because it disproportionately targets individuals over 65 years of age [14]. While bats are the reservoir host of SARS related coronaviruses, SARS-CoV-2 shares a 96% sequence identity when comparing humans and bats [15]. As SARS-CoV-2 continues to disseminate throughout regions of the world, its genome is likely to diversify (i.e., founder effect), and may affect virulence and disease severity. Meanwhile, public health response, or lack thereof, may or may not be associated with wealth inequality 16.
While it is accepted that COVID-19 disproportionately harms older individuals, this description does not consider the impact of the disease vis-à-vis life expectancy. The aim here was to assess the occurrence of mortality above life expectancy. Given this dataset, the findings revealed that ~65% of COVID-19 deaths occurred above life expectancy (Figure 3A). In addition, deaths above life expectancy had an inverse correlation with Gini index (r= −0.62), perhaps suggesting that countries with less of a wealth gap have more individuals above life expectancy, which may lead to more COVID-19 related deaths in the above life expectancy category. As it relates to age distribution, less than 10 percent of the U.S population is estimated as above life expectancy [17], but yet this age class made up ~60 percent of COVID-related deaths.
Pandemics vary in targeted age class, but can they affect fitness?
Viruses can disproportionately affect certain age classes. SARS-CoV-2 can spread via emission of muco-salivary airborne droplets [18], leading to outcomes that can be exacerbated in confined settings [19]. The mode of transmission for SARS-CoV-2 may be most effective in densely populated areas [20]. In addition, COVID-19 is most severe among individuals 65 years and older [14]. This contrasts the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, which disproportionately targeted individuals below 65 years of age [21]. H1N1 is similar to SARS-CoV-2 in that it spreads via airborne droplets [22]. This differs from Ebola which spreads via direct contact [23], but parallel to H1N1, Ebola also targeted individuals under the age of 65 years, and is far more virulent than H1NI and COVID-19 [24,25]. The average age of Ebola pandemic deaths was 32 years of age [26].
Depending on the pandemic, and the virulent nature of the pathogen, the window of opportunity for infected host to reproduce may be small. This may elevate Darwin’s theory of natural selection (i.e., survival of the fittest), which requires there to be an advantage/disadvantage toward reproduction. Infectious diseases that target individuals before they have had an opportunity to reproduce can reduce population fitness. Average reproduction age varies across countries. In 1981, 20 percent of women in their early 30’s were childless in the U.S. In 2016, this figure rose to about 30 percent [17]. It may be the case that the untimeliness of a pandemic or virulent virus (i.e., Ebola) can disproportionately target younger age classes (i.e., <30 years of age) and may diminish fitness. As it relates to COVID-19, this virus targets individuals that are past peak age of reproduction, which may be indifferent to population fitness. Interestingly, difference in disease severity may exist between sexes, as elevated levels of estrogen have been reported to reduce disease severity and mortality in females [27].
Can variation in COVID-19 deaths be explained by regional differences?
Regional differences may also impact death rate. Countries in the northern hemisphere such as Sweden, Switzerland, Germany and the United States peaked in COVID-19 related deaths in April 2020, while in South Africa, COVID-19 related deaths peaked in late July 2020 [28]. Environmental factors associated within a particular region may also be used to explain disparities in COVID-19 related deaths. Regions with high concentrations of NO2 corresponded to 78% of COVID-19 deaths [6], and atmospheric CO2 was reported to be associated with infection rate [5]. This may suggest that air quality may be a factor in determining which populations are most at risk.
Comorbidities may also play a role, as well as vary across regions. Specifically, comorbidities may increase the number of deaths occurring below life expectancy, especially when considering COVID-19 and HIV. In 1987, incidence of death from HIV was 38 years of age, on average in the U.S [29]. A quarter century later (i.e., 2013), mean HIV death increased to 50 years of age [29], but was still far below U.S life expectancy. While this may suggest that HIV infection may influence COVID deaths occurring below life expectancy, in Southeast Asia, where HIV transmission is still a concern, a significant correlation between COVID-19 and HIV comorbidities has yet been detected [30]. This may be explained by the expansion of antiretroviral therapy.
Different regions as well as variation in human hosts may also cause the virus to diversify according to a particular environment. SARS-CoV-2 may mutate and change according to characteristics of select regional hosts. SARs-CoV-2 type A and C may be less common in east Asia, when compared to type B [31]. In eastern Europe, strain B was also found to be relatively common [32]. Interestingly, it remains unclear which SARS-CoV-2 type (i.e., A, B, or C) is ancestral, and which two are derived [33]. This may be an important determinant as to how virus evolution may affect different regions. Small localized populations may experience bottleneck effects, enabling ‘Muller’s ratchet’ evolutionary hypothesis, which suggest a decrease in mean virus fitness, due to the accumulation of deleterious mutations, which is common among asexual reproducing organisms (i.e., viruses) [34].
Other factors explaining regional differences may include wealth and inequality (Figure 2). According to the Gini index, which measures wealth distribution; South Africa is one of the top 2 countries in wealth inequality, and the United States is in the top 40. All other countries used in this study were ranked between 121 and 152 [35].
Also, understanding the nutritional status of patients most at risk toward infectious diseases may be necessary for COVID-19 recovery, as supplementing select minerals, including zinc, iron, selenium and vitamins A through E, may provide nutritional intervention against infections, comorbidities, and COVID-19 [36].
Conclusions
The impact of COVID-19, including its targeted age range, may vary across space and time. This survey suggests that the majority of COVID-19 related deaths occur above life expectancy. Considering life expectancy may be appropriate for governmental agencies targeting individuals most at risk to COVID-19. It is encouraged that life expectancy be taken into account when planning responses to localized COVID-19 outbreaks, prioritizing drug treatment, and assessing ICU capacity.
Author Contributions
RJM conceived the idea, performed analysis, and wrote the manuscript.
Funding
Funding support provided by National Science Foundation Post-Doctoral Research Fellowship Biology Award #1907242.
Acknowledgments
Special thanks and acknowledgement to Logan W. Cole for taking time to read and provide helpful comments regarding manuscript content. Special thanks to James D. Bever, D. Christopher Rogers and Dhaval Vyas for good discussions. Also, special thanks to the wonderful comments from the editor and reviewer 1 & 2 at GERMS.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mann, R.; Perisetti, A.; Gajendran, M.; Gandhi, Z.; Umapathy, C.; Goyal, H. Clinical characteristics, diagnosis, and treatment of major coronavirus outbreaks. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 581521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.D.; Harris, C.; Cain, J.K.; Hummer, C.; Goyal, H.; Perisetti, A. Pulmonary and extra-pulmonary clinical manifestations of COVID-19. Front Med (Lausanne) 2020, 7, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mandhana, N.; Myo, M. Pandemic crushes garment industry, the developing world’s path out of poverty. Wall Str. J. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Coro, G. A global-scale ecological niche model to predict SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection rate. Ecol Modell 2020, 431, 109187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogen, Y. Assessing nitrogen dioxide (NO2) levels as a contributing factor to coronavirus (COVID-19) fatality. Sci Total Environ 2020, 726, 138605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvedy, C. The bubonic plague. Sci Am 1988, 258, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radusin, M. The Spanish flu—Part II: The second and third wave. Vojnosanit Pregl 2012, 69, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The Global HIV/AIDS pandemic, 2006. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2006, 55, 841–844. [Google Scholar]
- Preston, S.H. American longevity: Past, present, and future. Cent. Policy Res. 1996, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gorina, Y.; Hoyert, D.; Lentzner, H.; Goulding, M. Trends in causes of death among older persons in the United States. Aging Trends 2005, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucman, G. Global wealth inequality. Annu Rev Econ 2019, 11, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerman, R.I.; Yitzhaki, S. A note on the calculation and interpretation of the Gini index. Econ Lett 1984, 15, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antiga, L. Coronaviruses and immunosuppressed patients: The facts during the third epidemic. Liver Transpl 2020, 26, 832–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, Z. Poverty, wealth inequality and health among older adults in rural Cambodia. Soc Sci Med 2008, 66, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Administration for Community Living. 2019 profile of older Americans. 2020. Available online: https://acl.gov/sites/default/files/Aging%20and%20Disability%20in%20America/2019ProfileOlderAmericans508.pdf (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Borak, J. Airborne transmission of COVID-19. Occup Med (Lond) 2020, 70, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J.; et al. Characteristics of household transmission of COVID-19. Clin Infect Dis 2020, 71, 1943–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, A.; Mukherjee, A.; Sarkar, K. Impact of population density on COVID-19 infected and mortality rate in India. Model Earth Syst Environ. 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, F.S.; Iuliano, A.D.; Reed, C.; et al. Estimated global mortality associated with the first 12 months of 2009 pandemic influenza A H1N1 virus circulation: A modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis 2012, 12, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliabadi, A.A.; Rogak, S.N.; Bartlett, K.H.; Green, S.I. Preventing airborne disease transmission: Review of methods for ventilation design in health care facilities. Adv Prev Med 2011, 2011, 124064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowell, G.; Nishiura, H. Transmission dynamics and control of Ebola virus disease (EVD): A review. BMC Med 2014, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.C. Similarity is not enough: Tipping points of Ebola Zaire mortalities. Physica A: Stat Mech Appl 2015, 427, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S.; Scott, D.; Hall, C.M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: A rapid assessment of COVID-19. J Sustain Tour 2020, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Duan, H.J.; Chen, H.Y.; et al. Age and Ebola viral load correlate with mortality and survival time in 288 Ebola virus disease patients. Int J Infect Dis 2016, 42, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopel, J.; Perisetti, A.; Roghani, A.; Aziz, M.; Gajendran, M.; Goyal, H. Racial and gender-based differences in COVID-19. Front Public Health 2020, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Economist. Tracking COVID-19 Excess Deaths Across Countries. 2020. Available online: https://www.economist.com/graphic- detail/coronavirus-excess-deaths-tracker (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Center for Disease Control, National Vital Statistics System. U.S. Mortality Data Files, 1987–2013. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data_access/vitalstatsonline.htm (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Ejaz, H.; Alsrhani, A.; Zafar, A.; et al. COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients. J Infect Public Health 2020, 13, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, P.; Forster, L.; Renfrew, C.; Forster, M. Phylogenetic network analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2020, 117, 9241–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surleac, M.; Banica, L.; Casangiu, C.; et al. Molecular epidemiology analysis of SARS-CoV-2 strains circulating in Romania during the first months of the pandemic. Life (Basel) 2020, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavian, C.; Pond, S.K.; Marini, S.; et al. Sampling bias and incorrect rooting make phylogenetic network tracing of SARS-COV-2 infections unreliable. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2020, 117, 12522–12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brufsky, A.; Lotze, M.T. Ratcheting down the virulence of SARS-CoV-2 in the COVID-19 pandemic. J Med Virol 2020, 92, 2379–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The world Factbook. Country Comparisons: Gini Index Coefficient—Distribution of Family Income. 2020. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/gini- index-coefficient-distribution-of-family-income/country- comparison (accessed on 1 August 2020).
- Junaid, K.; Ejaz, H.; Abdalla, A.E.; et al. Effective immune functions of micronutrients against SARS-CoV-2. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© GERMS 2025.