Abstract
Introduction: The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection leads to immune activation, senescence and exhaustion of T cells. Co-stimulatory molecules play important roles in controlling these processes. The CD28 signaling triggers efficient T cell activation, while CD27 provides survival signals to CD28- T cells. Loss of these molecules was associated with senescent phenotype and resistance to checkpoint inhibitors. Romania has faced an HIV outbreak among people who inject drugs (PWID), most of them chronically infected with hepatitis C virus (HCV). HIV/HCV co-infection was associated with increased immune activation and rapid disease progression. Methods: We evaluated by flow cytometry the expression of CD27, CD28, CD38, HLA-DR, CD57 and PD-1 on CD4 and CD8 T cells from 34 subjected infected with HIV (22 PWID and 12 people who acquired HIV by sexual route – PWHS) and 18 HIV-negative individuals (controls). Results: We found that as compared to controls, HIV patients, regardless of infection route, have high percentages of intermediately differentiated (CD27+CD28-) and low percentages of less differentiated (CD27+CD28+) CD8 T cells. Significantly higher levels of CD8+CD27+CD28- T cells were found in PWHS than in PWID. A lower percentage of intermediately and highly differentiated (CD27- CD28-) CD8 T cells express CD57 in people living with HIV (PLWH) than in controls. Increased levels of less and intermediately differentiated CD4 and CD8 T cells expressing PD-1 were —identified in PLWH, especially in PWID; these directly correlated with HIV viral load and T cell activation and negatively correlated with CD4 counts. Conclusions: Our data show that induction of PD-1 on T cells expressing co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and/or CD28 might contribute to poor control of HIV infection and to immune activation.
Introduction
The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) research field has evolved significantly; efficient therapy and sensitive diagnostic kits contribute to increase life expectancy of people who live with HIV. In this context some new non-AIDS conditions have emerged that are linked to immune activation and inflammation. Chronic immune activation and inflammation contribute to an impaired immune response [1].
Continuous antigenic stimulation during chronic infections leads to immune exhaustion; this makes the immune system functionally impaired and thus unable to clear pathogens. Exhausted T cells are characterized by the expression of inhibitory receptors, such as Programmed Cell Death protein 1 (PD-1), Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), T-cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (Tim-3) and Lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (Lag-3) among others [2]. It was shown that PD-1 blockade can revert immune exhaustion in cancer patients; however, some patients showed resistance to immune checkpoint blockade, thus the attention was focused on finding markers of resistance [3]. Immune senescence was among the factors associated with resistance to checkpoint inhibitors; T cells lacking CD27 and CD28 or that express Tim-3 and CD57 were linked with resistance to checkpoint inhibitors [4].
CD28 is a co-stimulatory molecule expressed on both naïve and activated T cells that can deliver either pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory signals depending on the cell type: it favors the proliferation, differentiation and functions of conventional T cells and promotes the homeostasis and suppressor functions of regulatory T cells (Treg) [5].
The CD28- T cells were found to accumulate in aging, certain cancers, autoimmune diseases and some chronic infections, such as cytomegalovirus (CMV) and HIV infections [6].
Unlike CD28, the CD27 co-stimulatory molecule is expressed by resting T cells and its expression increases in response to activation. Studies on murine models lacking CD27 showed its impact to be low on naïve T cell activation but profound on memory T cells generation [7]. CD27 signaling was demonstrated to protect TCR/CD3 activated CD28- T cells from apoptosis by promoting cell division at the priming/infection site [8]. CD27 was found to play an important role in the replenishment of antigen specific CD4 T cells in HIV infected patients on combined antiretroviral therapy (cART) [9].
It was reported that loss of the co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 is associated with the induction of CD57 and acquisition of a senescent phenotype [10]. The HIV infection is characterized by accumulation of cells with senescent phenotypes; this seems to be driven by immune activation and persistent inflammation, to which other co-infections, such as those with HCV, hepatitis B virus (HBV), CMV, and Epstein-Barr virus, also contribute [11]. Chronic immune activation in HIV patients, that is driven by persistent antigenic stimulation, leads to immune exhaustion, a cellular status characterized by loss of the effector function and proliferative capacity [12]. The exhausted cells are phenotypically characterized by the expression of PD-1, an inhibitory receptor belonging to the CD28 family [2]. High levels of PD-1 were found on latently infected T cells in HIV. The administration of PD-1 inhibitors that have the ability to disrupt latency in patients on cART was part of the HIV-1 cure attempts [13].
The HIV-1 epidemic in Romania is characterized by children infected with subtype F1 by parenteral route in late 1980s; current transmissions are mainly sexual. In the beginning of the 2010s a HIV-1 subepidemic among PWID was registered. The HIV-1 infected PWID were mainly men, HCV co-infected and were diagnosed with HIV-1 while being in detention (penitentiary). They were infected either with subtype F1 HIV-1 strains, which is the main subtype circulating among Romanian sexually infected patients, or with CRF14_BG strains, a recombinant form recently introduced in Romania and directly associated with injected drug use. The individuals infected with CRF14_BG HIV-1 strains had a more rapid disease progression: although they were recently infected, these patients had low CD4 counts (<200 cells/mm [3].) and CXCR4 tropism at baseline [14]. HCV genotype diversity was higher in Romanian PWID: genotypes 1, 3 and 4 were identified in this group as compared with HCV monoinfected patients who were exclusively infected with genotype 1. Moreover, regardless of the HIV-1 infecting subtype, PWID had significantly higher HCV viral loads than HCV mono-infected individuals, possibly due to a weaker immune response to HCV [15]. HCV-HIV coinfection in PWID was associated with poor evolution and higher mortality, probably caused by a weak CD4 recovery [16].
Based on these data, we hypothesize that HIV-HCV coinfection might induce a rapid loss of functional T cells in PWID as compared to those HIV mono-infected, people who acquired HIV by sexual route (PWHS). We aimed to evaluate the expression of CD27 and CD28 on CD4 and CD8 T cells from PWID as compared to those from sexually infected subjects and HIV negative individuals (controls) and to characterize the senescence and exhaustion levels of CD4 and CD8 T cell subpopulations expressing CD27 and/or CD28.
Methods
Study population
Thirty-four ART naïve HIV patients diagnosed between 2015 and 2017 were selected for this study based on convenience sampling strategy; 22 of them were PWID and 12 were PWHS. The selection criteria were HIV subtype (all of them were infected with HIV-1 subtype F1) and CD4 counts higher than 100 cells/µL. Eighteen controls that were HIV, HCV and HBV negative were included for comparison. Most of PWID were co-infected with HCV while only one of PWHS was also infected with HCV. The characteristics of the groups are presented in Table 1. The study was performed in accordance with Helsinki declaration and approved by the Bioethics Committee of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Prof. Dr. Matei Balș” (no. 7373/06.11.2015).

Table 1.
Characteristics of the study population.
Real time RT-PCR
Sera obtained by centrifugation of blood collected from HIV infected patients were used for HIV and HCV viral load (VL) measurements using commercial in vitro diagnostic kits on Cobas TaqMan core platform (Roche, Switzerland).
Flow cytometry
Fresh blood was collected on EDTA tubes to evaluate the activation level of CD4 and CD8 T cells and the expression of CD27, CD28, PD-1 and CD57. To evaluate the activation level, 75 µL whole blood were incubated with 12.5 µL of a cocktail of fluorescent linked antibodies, pulled each in equal amounts, targeting CD3-APC Cy7 (clone UCHT1), CD4-APC (clone RPA-T4), CD8-PE (clone SK1), HLA-DR-FITC (clone LN3), CD38-PerCP (clone HIT2) (BioLegend, USA). The exhaustion and senescence of CD4 and CD8 T cells expressing co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 were evaluated on 75 µL whole blood with 15 µL of a cocktail containing equal amounts of each fluorescent linked antibody targeting CD3-APC Cy7 (clone UCHT1), CD4-PerCP (clone RPA-T4) or CD8- PerCP (clone SK1), CD57-FITC (Clone HNK-1), CD27-APC (Clone M-T271), CD28-PE (clone CD28.2), PD-1-PE/Cy7 (Clone EH12.2H7) (BioLegend). The blood and antibody mixtures were incubated at room temperature in the dark for 15 minutes. The erythrocytes were consequently lysed by incubation with BD FACS Lysing Solution (BD Bioscience, USA) for 30 minutes at room temperature, followed by centrifugation and wash steps with phosphate buffer saline without calcium and magnesium (PBS, ThermoFisher). The cells were resuspended in 1% paraformaldehyde in PBS and collected on FACS Canto II (BD Bioscience). At least 20000 of lymphocytes were acquired for each sample. To evaluate the number of CD4 and CD8 T cells before acquisition 20 µL of CountBright absolute counting beads (ThermoFisher, USA) were added to the sample. The data were analyzed with FloJo 10.6.0 software (https://www.flowjo.com) and the gating strategy is presented in Figure 1.
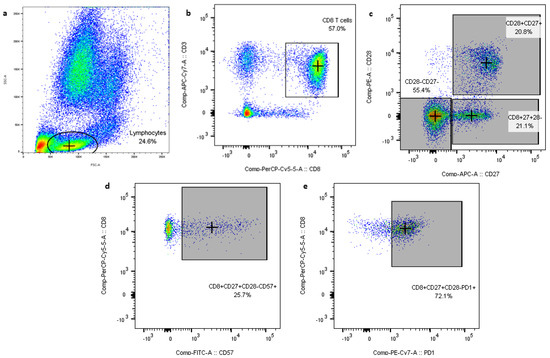
Figure 1.
Flow cytometry data gating strategy. Whole blood cells were stained with a mixture of antibodies as described in the Methods section and analyzed by flow cytometry. The gating strategy for analysis of T cell subpopulation: (a) Lymphocytes were gated based on forward and side scatter; (b) From lymphocytes gate CD4 and CD8 T cells were selected as CD3+ CD4+ or CD3+CD8+; (c) the expression of CD27 and CD28 was evaluated in CD4 or CD8 T cells gate, (d) CD4/CD8 T cell subsets defined based on the expressing CD27 and /or CD28 co-stimulatory molecules (Figure 1c) were evaluated for CD57 expression; (e) Expression of PD-1 was evaluated on T cells from each of the three gates defined in Figure 1c.
Statistical analysis
Data were statistically evaluated using IBM SPSS Statistics Data Editor v26 (IBM, USA) and plotted using GraphPad Prism 6 (https://www.graphpad.com/). The comparison of viral load between HIV groups was performed with the Mann Whitney test in GraphPad Prism 6. Spearman correlation test was used to identify association between T cell subsets and T cell activation, CD4 counts, VL, CD4/CD8 ratio, age and gender. To adjust for age and gender, multivariate general linear model with Bonferroni correction for multiple tests was used in the IBM SPSS Statistics Data Editor. The significance level was established at p values lower than 0.05.
Results
T cell progression to late differentiated stage in HIV groups
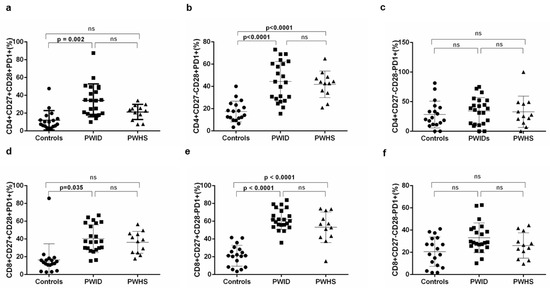
The HIV infection induces immune activation that leads to accumulation of terminally differentiated T cells, defined by loss of co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 and gain of CD57 [10]. In patients with HIV infection it was reported that CD4 T cells progress to late differentiated (CD27-CD28-), while CD8 T cells accumulate as CD27+CD28- [17]. Based on these data we evaluated the expression of co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 on CD4 (Figure 2a–c) and CD8 T cells (Figure 2d–f) from PWID and PWHS patients as compared to HIV negative controls. The statistical analysis showed that CD4 T cells expressing or not the co-stimulatory molecules CD28 and/or CD27 are comparable between HIV and control groups (Figure 2a–c). Regarding CD8 T cells, increased percentages of CD8+CD27+CD28- (Figure 2e) and reduced of CD8+CD27+CD28+ (Figure 1d) T cells were identified in both HIV groups as compared to controls; PWHS had the highest percentages of CD8+CD27+CD28- T cells. Moreover, only in the HIV group we found a direct correlation of CD8+CD27+CD28+ T cell percentages with CD4 counts (r=0.358; p=0.038) and with the CD4/CD8 ratio (r=0.739; p<0.001). We found no association of CD8+CD27+CD28+ T cell levels with age or gender, either in HIV individuals (r=0.193; p=0.274 and r=−0.233; p=0.185, respectively) or in control group (r=0.106; p=0.676 and r=−0.159; p=0.529, respectively). Moreover, the HCV status was positively associated with CD8+CD27-CD28- T cells (r=0.594, p<0.001) and negatively with CD8+CD27+CD28- T cells (r=−0.475, p=0.005).
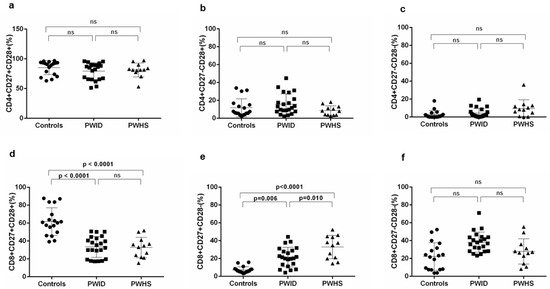
Figure 2.
Expression of CD27 and CD28 costimulatory molecules on CD4 and CD8 T cells in HIV infected patients and controls. CD4 T cells that express both CD27 and CD28 (a), lack just CD27 (b) or lack both costimulatory molecules (c) are presented for each enrolled subject. Percentages of CD8 T cells positive for CD27 and CD28 (d), those that express CD27 but lost CD28 expression (e) and CD8 T cells that lost both CD27 and CD28 expression (f) are presented for each investigated subject. Mean values and standard deviations for each group are presented. Statistical differences, evaluated in SPSS using age and sex as covariates with Bonferroni correction were included. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant, differences higher or equal to 0.05 were considered not significant and presented as not significant (ns).
T cell senescence in HIV infected patients
Loss of co-stimulatory molecules and expression of CD57 are associated with immunosenescence [10]. In chronic infections, CD57 expression was also identified on less differentiated cells; HIV specific CD27+CD8 T cells express CD57 and accumulation of these cells was suggested to contribute to failure of controlling HIV [18]. In this context we analyzed the expression of CD57 on CD4 (Figure 3 a-c) and CD8 T cells (Figure 3 d-f) that express or lost co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and/or CD28 in PWID and PWHS groups as compared to controls.
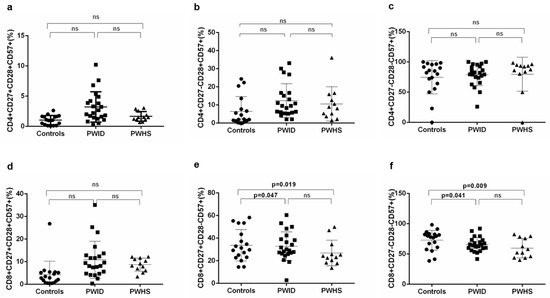
Figure 3.
Expression of CD57 on subpopulation of CD4 and CD8 T cells with or without co-stimulatory molecules. Percentages of CD57 positive CD4 T cell (a–c) and CD8 T cell subpopulations (d–f) expressing or lacking co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and/or CD28, are plotted for each investigated subject. Mean values and standard deviations for each group are presented. Statistical differences, evaluated in SPSS using age and sex as covariates with Bonferroni correction, were included. P values less than 0.05 were considered significant, differences higher or equal to 0.05 were considered not significant and presented as not significant (ns).
Our statistical analysis, that included gender and age as covariates, showed that HIV infected subjects as compared to controls had low percentages of intermediate and high differentiated CD8 T cells expressing CD57 (Figure 3e,f) and comparable levels of CD4 T cell subsets positive for CD57 (Figure 3a–c).
Activation of CD4 and CD8 T cells from HIV infected patients
Previous data reported increased activation of both CD4 and CD8 T cells in HIV positive subjects that persists at high levels even when the virus replication is kept under control with cART [11]. In our study, CD4 and CD8 T cell activation was higher in both PWID and PWHS groups than in the control group. However, when the data were statistically evaluated with ANCOVA, adjusting for age and gender, only CD8 T cell activation in PWID differed from controls (p<0.001).
The activation of both CD4 and CD8 T cells was positively associated with HIV VL (r=0.431, p=0.012; and r=0.384 p=0.027, respectively) and negatively with CD4 counts (r=−0.544, p=0.001; and r=−0.395 p=0.023, respectively) and CD4/CD8 ratios (r= −0.489, p=0.004; and r= −0.348 p=0.047, respectively). No correlation between CD4 or CD8 T cells activation and CD4 counts was identified in the control group. Both in HIV and control groups, we have identified negative correlations between CD4 or CD8 T cells activation and CD4 and CD8 T cells expressing co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 (Table 2) and positive correlation with CD4 and CD8 T cell subpopulations expressing exhaustion and senescence markers (Table 2).

Table 2.
Correlation of CD4 (A) and CD8 (B) T cell activation with exhaustion and senescence in HIV infected patients and control groups.
Discussion
HIV infection is associated with systemic inflammation and chronic immune activation that lead to exhaustion and senescence of both CD4 and CD8 T lymphocytes; these dysfunctions persist despite efficient viral suppression under treatment [1]. The co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 are mainly expressed by naïve and central memory cells, while transition to effector and terminally differentiated cells is associated with loss of these molecules. The HIV infection was associated with altered T cell differentiation, with high percentages of effector and memory T cell subpopulations and decrease in naïve T cells [17].
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the expression of co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28 on CD4 and CD8 T cells in PWID as compared to PWHS and to characterize the senescence and exhaustion levels in CD27+/- CD28+/- T cell subpopulations.
Most of the HIV F1 subtype infected PWID in Romania had a good immunologic status and no HIV/AIDS symptoms at diagnosis. For some of these patients this observation was documented either by laboratory tests (some of them had a negative serology test in the last 2 years) and by phylogenetic analysis [14,15]. In contrast, the patients that acquired HIV by sexual route are mostly diagnosed as late presenters with low CD4 counts and in an advanced disease stage. Moreover, some of the PWID were infected with a different strain of HIV (CRF14_BG) than that circulating in PWHS (subtype F1) and most of them were also HCV co-infected [14]. Because of these distinct characteristics of Romanian PWID and PWHS, the selection of appropriate groups with similar characteristics for comparison of immune profiles was challenging. For this study we selected 34 patients (22 PWID and 12 PWHS) infected with HIV subtype F1, with similar CD4 counts and VL (Table 1). In the PWID group most of the subjects were HIV/HCV co-infected, while in PWHS only one subject had HCV. The gender and age distribution among HIV groups and control group was significantly different, therefore in the statistical analysis age and gender were used as covariates.
Our data show that HIV infected subjects, either by sexual route or injecting drug use, have similar levels of CD4+ T cells differentiation (CD27+/- and CD28+/-) with the control group. Reduced percentages of CD8+CD27+CD28+ and increased of CD8+CD27+CD28- were found in HIV groups as compared to controls, while the percentages of CD8+CD27-CD28- were comparable among groups. Our data partially agree with previous data showing that HIV infection induces accumulation of CD28-CD27+ CD8 T cell subsets while CD4 T cell subsets progress to late differentiated (CD27-CD28-) [17]. The difference regarding CD4 T cells between this study and ours is that they looked at CD27 and CD28 expression on T cell subsets while we analyzed the total CD4 T cell population. They found that especially differentiated cells (central memory, effector memory and terminally differentiated effectors, TEMRA) lost CD27 and CD28, while for naïve T cells, which comprise most of the CD4 T cells, they have not found a significant difference to controls.
We found that less differentiated T cell (CD27+CD28+) levels are directly correlated with CD4 counts and negatively with T cell activation while high differentiation (CD27-CD28-) is in direct correlation with T cell activation (Table 2), suggesting that T cell activation in response to HIV might trigger T cell differentiation and CD4 destruction. PWID had the highest levels of both CD4 and CD8 T cell activation, although it was not significantly higher than in PWHS (Table 1) suggesting that additional factors might contribute to cell activation. The HCV co-infection of PWID might also impact T cells differentiation to late phenotypes, since HCV contributes to immune activation in HIV infected patients [16]. Our results showed a positive association between HCV status and CD8+CD27-CD28- T cell levels, supporting the involvement of HCV co-infection in T cell differentiation in HIV infected patients.
Loss of CD28 and induction of CD57 expression are associated with immune aging. Increased percentages of T cells CD28-CD57+, as a consequence of persistent antigenic stimulation, were identified in different conditions such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and chronic infections [6]. Although it was suggested that loss of CD28 is associated with gain of CD57, CD28+CD57+ and CD28-CD57-CD8 T cells were identified in peripheral blood of healthy individuals and it was communicated that CD57 expression, irrespective of CD28, is linked to low proliferative potential of the CD8 T cells [20]. In HIV infection CD4 T cells expressing CD57 were also reported to be proliferation incompetent even when exposed to strong stimuli [21]. Our results indicate that the CD57 molecule is expressed on a higher percentage of CD4+ CD28+ CD27+/- and of CD8+CD27+CD28+ T cells from HIV infected patients than in the controls group, suggesting their low proliferative potential. However, the differences were not statistically significant. Moreover, we found that the levels of these T cells expressing CD57 and co-stimulatory molecules directly correlate with T cell activation (Table 2) suggesting that they might be prone to activation induced cell death. Our data showing that HIV patients, regardless of infection route, express lower percentages of intermediate and high differentiated CD8 T cells positive for CD57 than controls are in agreement with a previous report that identified lower levels of CD28-CD8+ T cells expressing CD57 in recently infected HIV patients. The authors suggested that these deficiencies are linked to higher odds of mortality and that early ART initiation might correct these defects [22].
Another molecule associated with low proliferative potential is the co-inhibitory molecule PD-1 that is up-regulated on activated T cells; interaction with its receptors inhibits cellular proliferation and function and is thus associated with cell exhaustion [2].
A great challenge for HIV cure is the elimination of virus reservoirs in latently infected cells, mainly memory CD4 T cells that express the co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and CD28. Activation of latently infected cells using several latency reversal agents, such as histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, gave limited results, [23]. suggesting the need of additional immune activation signals for efficient response. Attention was focused on PD-1 inhibitors, since HIV infected memory T cells with high expression of PD-1 have higher proviral DNA than the cells with low PD-1 [13]. Our data show that a high percentage of T cells expressing co-stimulatory molecules are positive for PD-1 in HIV infected patients, regardless of the infection route. The CD4 T cell subpopulations expressing PD-1 were in direct correlation with HIV viremia and T cell activation and in negative correlation with CD4 counts, suggesting that PD-1 expression might be induced in response to HIV and might contribute to disease progression. However, the studies with PD-1 blockers gave contradictory results: some data suggests that PD-1 blockade alone is not sufficient to activate the latent reservoir [24].
It was demonstrated that interaction of PD-1 on naïve CD4 T cells with its ligand might induce differentiation of these cells to Treg [25]. that might contribute to a deficient T cell response to HIV. This might explain the correlation we found between CD27+CD28+PD-1+ T cells and HIV viral load and CD4 counts. However, additional data are necessary to establish if the induction of PD-1 on less or intermediate differentiated T cells is a consequence of cell activation, a protection signal to limit over-activation or a cell exhaustion marker that might reflect the inability to control HIV.
Conclusions
Our data show that regardless of the HIV infection route, PD-1 is induced on both CD4 and CD8 T cells that express co-stimulatory molecules CD27 and/or CD28 and it is associated with viral load, T cell activation and CD4 depletion. Understanding the role of PD-1 induction on young T cells versus terminally differentiated cells is to be determined and it might contribute to the development of proper strategies for HIV treatment.
Author Contributions
L.B.—study design, sample processing, data acquisition, data analysis, statistical analysis, manuscript writing; O.V.—sample processing, data acquisition, data analysis, manuscript writing; R.J.—clinical sampling, manuscript writing; A.A.—clinical sampling, manuscript writing; I.N.—virological analysis, manuscript writing; E.N.—virological analysis, manuscript writing; D.O.—study design, data analysis, manuscript writing and review; S.P.—study design, data analysis, manuscript writing and review; All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was supported by Young Research Team project HIV-ID project 260/2015 (UEFISCDI) and POSCCE program CRCBABI project (642/2014).
Conflicts of Interest
None to declare.
Ethics Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki declaration, the informed consent of the participants was obtained. The study protocol was evaluated and approved by the Bioethics Committee of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases “Matei Bals” (no. 7373/06.11.2015) before participant enrolment.
References
- Deeks, S.G. HIV infection, inflammation, immunosenescence, and aging. Annu Rev Med. 2011, 62, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jenkins, R.W.; Sullivan, R.J. Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2019, 20, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.; Gross, S.; Kirchberger, M.C.; Erdmann, M.; Schuler, G.; Heinzerling, L. Senescence markers: Predictive for response to checkpoint inhibitors. Int J Cancer. 2019, 144, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esensten, J.H.; Helou, Y.A.; Chopra, G.; Weiss, A.; Bluestone, J.A. CD28 costimulation: From mechanism to therapy. Immunity. 2016, 44, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.P.; Effros, R.B. T cell replicative senescence in human aging. Curr Pharm Des. 2013, 19, 1680–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, J.; Gravestein, L.A.; Tesselaar, K.; van Lier, R.A.; Schumacher, T.N.; Borst, J. CD27 is required for generation and long-term maintenance of T cell immunity. Nat Immunol. 2000, 1, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, J.; Xiao, Y.; Borst, J. CD27 promotes survival of activated T cells and complements CD28 in generation and establishment of the effector T cell pool. J Exp Med. 2003, 198, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riou, C.; Tanko, R.F.; Soares, A.P.; et al. Restoration of CD4+ responses to copathogens in HIV-infected individuals on antiretroviral therapy is dependent on T cell memory phenotype. J Immunol. 2015, 195, 2273–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Jamieson, B.D.; Hultin, L.E.; Hultin, P.M.; Effros, R.B.; Detels, R. Premature aging of T cells is associated with faster HIV-1 disease progression. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2009, 50, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zicari, S.; Sessa, L.; Cotugno, N.; et al. Immune activation, inflammation, and non-AIDS co-morbidities in HIV-infected patients under long-term ART. Viruses. 2019, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaitan, A.; Unutmaz, D. Revisiting immune exhaustion during HIV infection. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2011, 8, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromentin, R.; DaFonseca, S.; Costiniuk, C.T.; et al. PD-1 blockade potentiates HIV latency reversal ex vivo in CD4+T cells from ART-suppressed individuals. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, I.; Paraschiv, S.; Paraskevis, D.; et al. Recent HIV-1 outbreak among intravenous drug users in Romania: Evidence for cocirculation of CRF14_BG and subtype F1 strains. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2015, 31, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraschiv, S.; Banica, L.; Nicolae, I.; et al. Epidemic dispersion of HIV and HCV in a population of co-infected Romanian injecting drug users. PLoS ONE. 2017, 12, e0185866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Pol, S. Natural history and predictors of severity of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) co-infection. J Hepatol. 2006, 44 (Suppl. S1), S28–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojumdar, K.; Vajpayee, M.; Chauhan, N.K.; Singh, A.; Singh, R.; Kurapati, S. Altered T cell differentiation associated with loss of CD27 and CD28 in HIV infected Indian individuals. Cytometry B Clin Cytom. 2012, 82, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoji, A.; Connolly, N.C.; Buchanan, W.G.; Rinaldo, C.R., Jr. CD27 and CD57 expression reveals atypical differentiation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific memory CD8+ T cells. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007, 14, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, C.L.; Kaufmann, D.E.; Kiepiela, P.; et al. PD-1 expression on HIV-specific T cells is associated with T-cell exhaustion and disease progression. Nature. 2006, 443, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenchley, J.M.; Karandikar, N.J.; Betts, M.R.; et al. Expression of CD57 defines replicative senescence and antigen-induced apoptotic death of CD8+ T cells. Blood. 2003, 101, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, B.E.; Blyveis, N.; Fontenot, A.P.; Wilson, C.C. Functional and phenotypic characterization of CD57+CD4+ T cells and their association with HIV-1-induced T cell dysfunction. J Immunol. 2005, 175, 8415–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.A.; Sinclair, E.; Jain, V.; et al. Low proportions of CD28- CD8+ T cells expressing CD57 can be reversed by early ART initiation and predict mortality in treated HIV infection. J Infect Dis. 2014, 210, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson McManamy, M.E.; Hakre, S.; Verdin, E.M.; Margolis, D.M. Therapy for latent HIV-1 infection: The role of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2014, 23, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, J.K.; Cyktor, J.C.; Fyne, E.; Campellone, S.; Mason, S.W.; Mellors, J.W. Blockade of the PD-1 axis alone is not sufficient to activate HIV-1 virion production from CD4+ T cells of individuals on suppressive ART. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0211112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, L.M.; Salinas, V.H.; Brown, K.E.; et al. PD-L1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory T cells. J Exp Med. 2009, 206, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© GERMS 2021.