Research on Unwinding Mechanism Design and Tension Control Strategy for Winding Machines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Design of Constant Tension Unwinding Mechanism for Wire Winding Machines
2.1. Design Requirements
2.1.1. Parameter Requirements
2.1.2. Functional Requirements
2.2. Design Criteria
- (1)
- Functionality Criterion: The winding machine must execute core processes and accommodate wires of varying diameters to meet diverse production requirements.
- (2)
- Equal Strength Principle: Structural dimensions should ensure uniform load-bearing capacity across components, eliminating localized over/under-strength areas. This avoids the “weakest link” effect, promotes homogeneous stress distribution, optimizes material utilization, reduces weight, and lowers costs.
- (3)
- Reliability and Lifetime Criterion: Design must account for component failure modes through appropriate material selection and structural optimization. Redundant design elements should be incorporated to enhance fault tolerance.
- (4)
- Safety Criterion: Hazards must be minimized by reducing high-risk moving parts, implementing fixed guards, and installing interlocking devices.
- (5)
- Cost and Manufacturability: Technical solutions should balance economic feasibility while meeting functional and quality standards. Overly complex designs that increase production costs must be avoided.
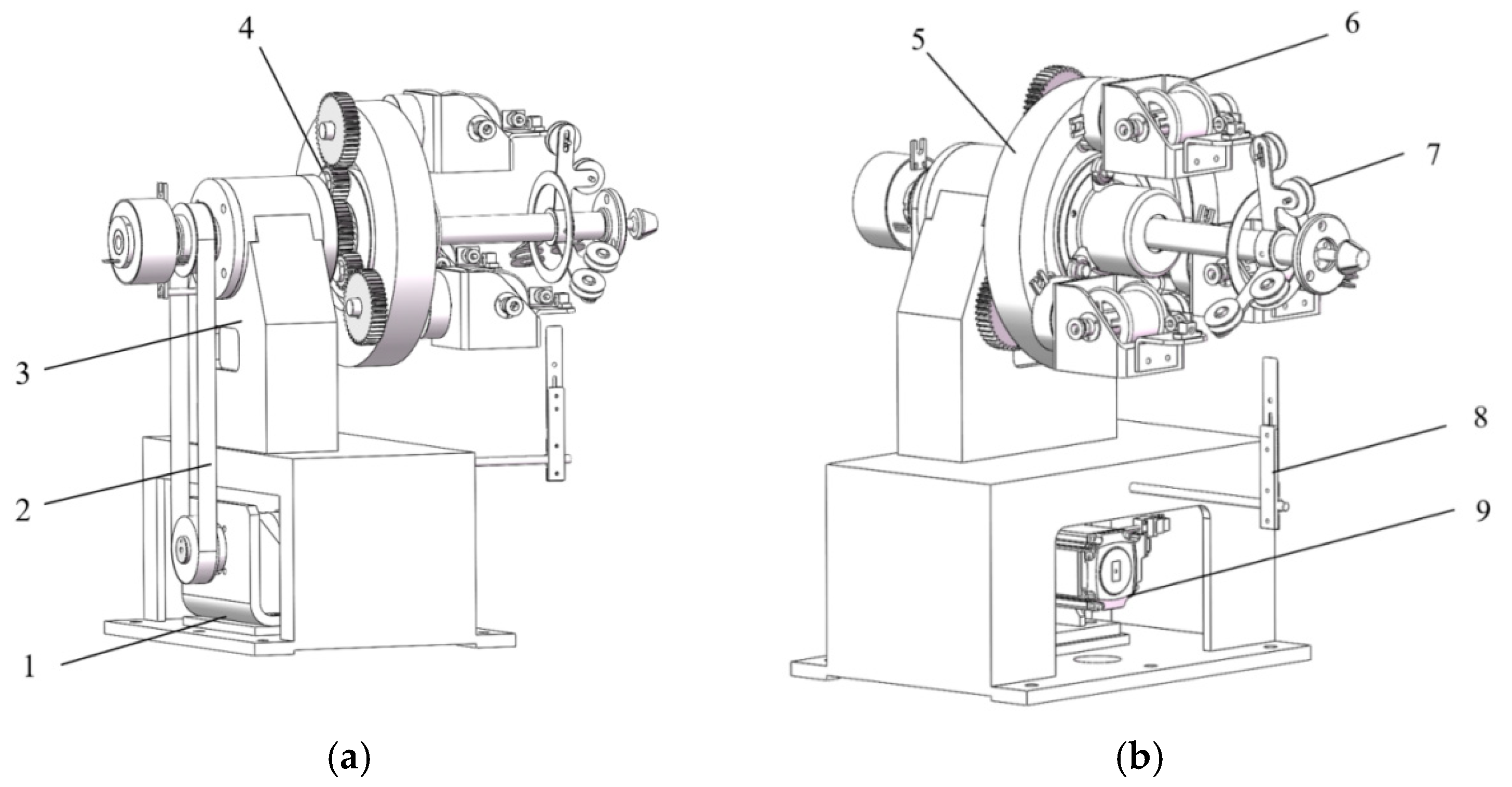
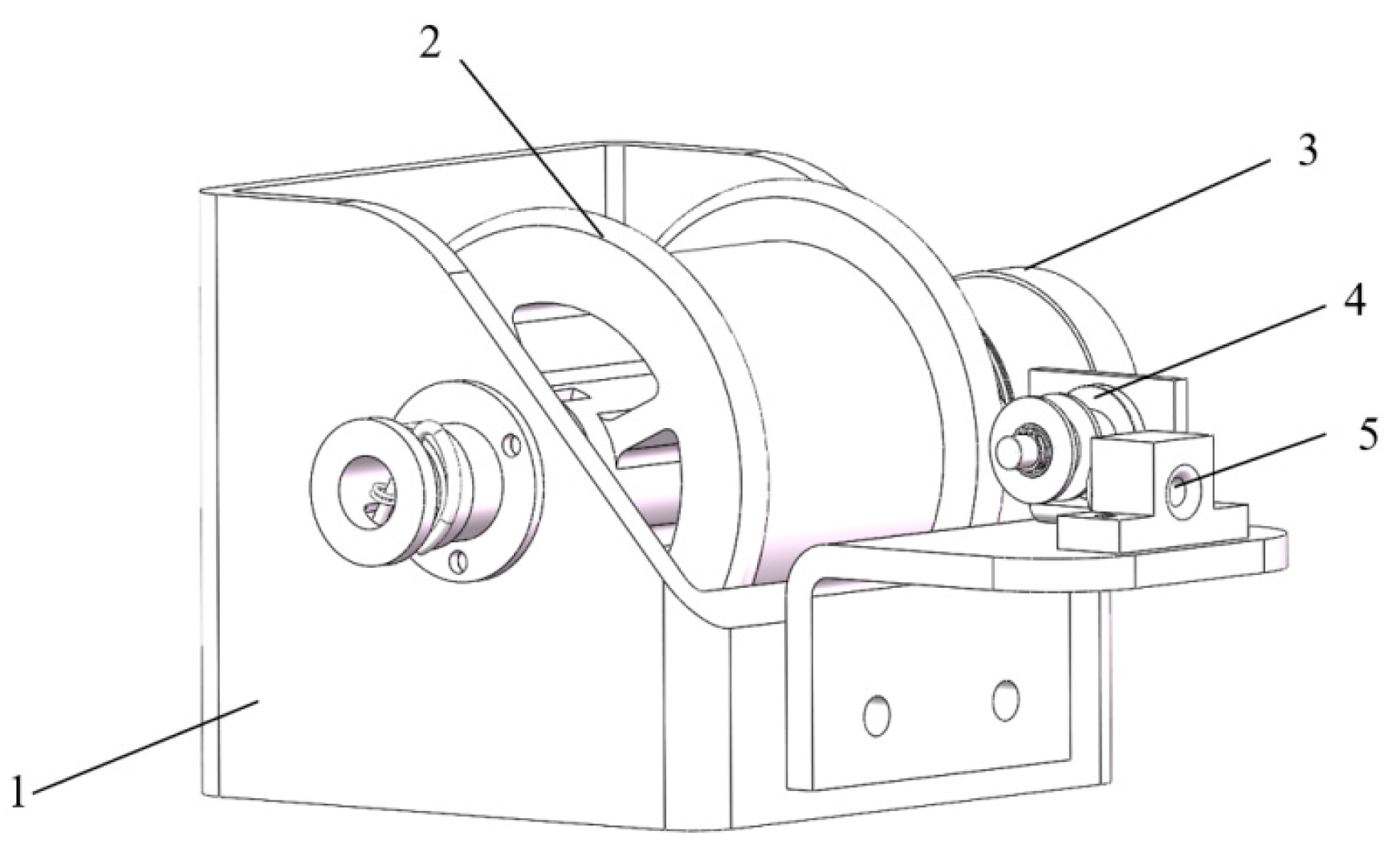
2.3. Structural Design
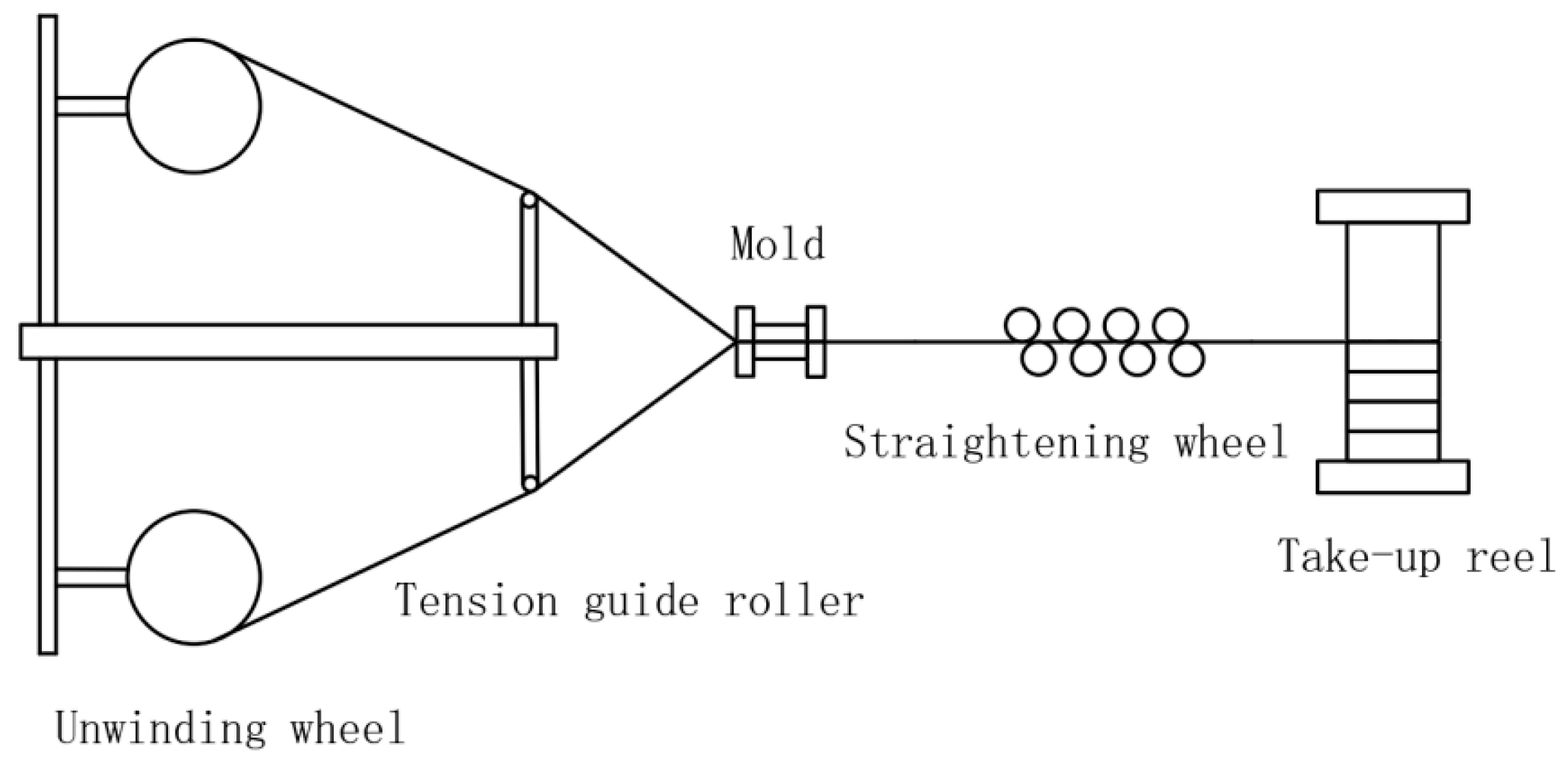
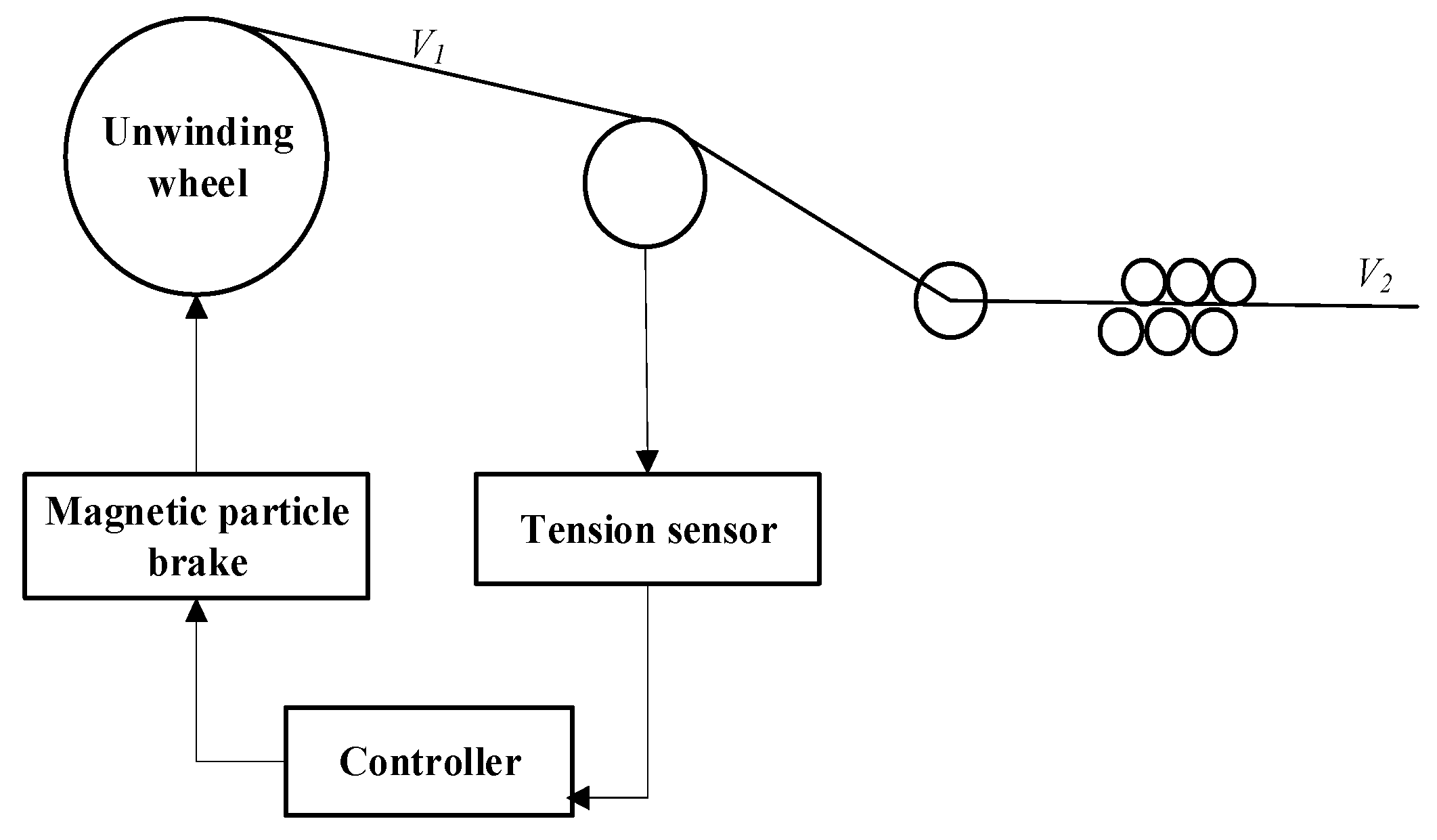
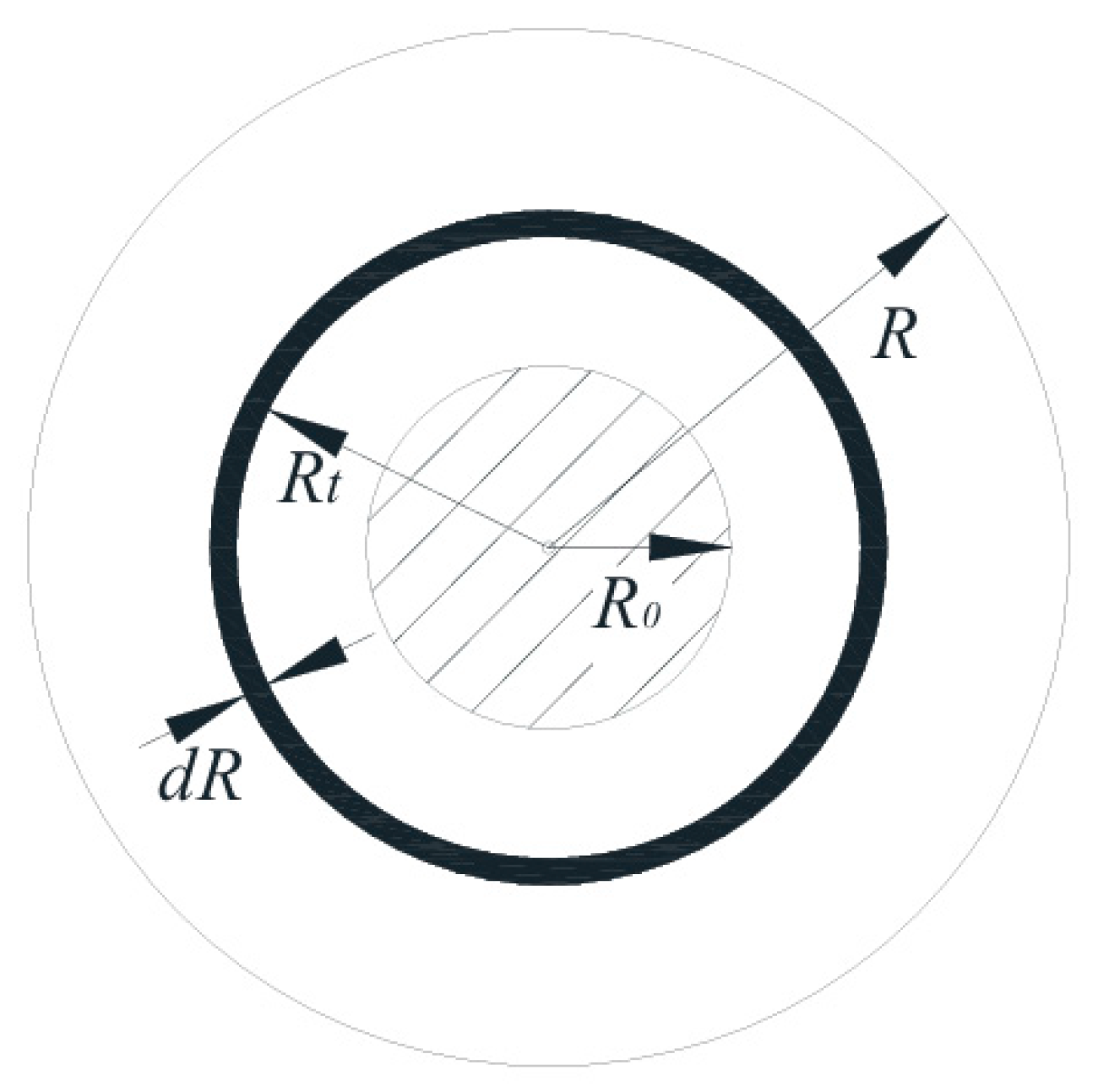
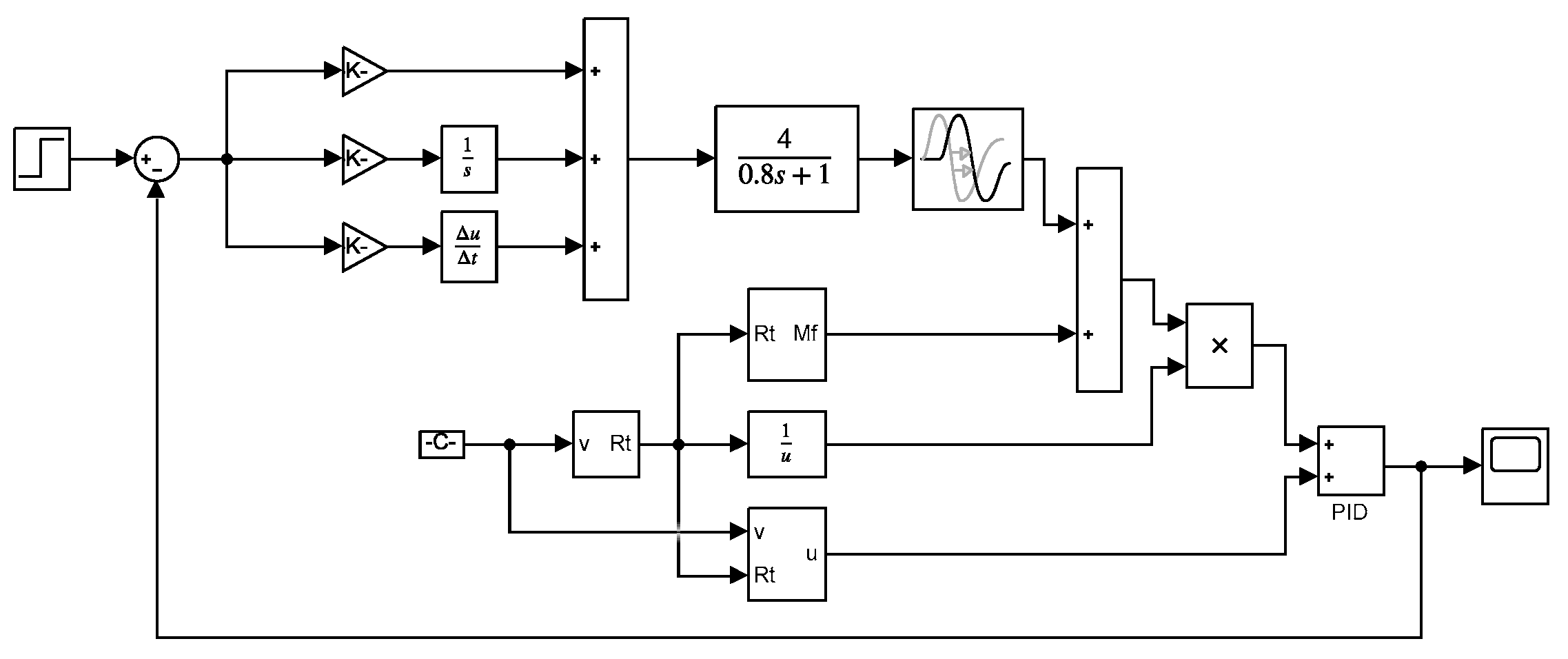
3. Unwind System Tension Control Model
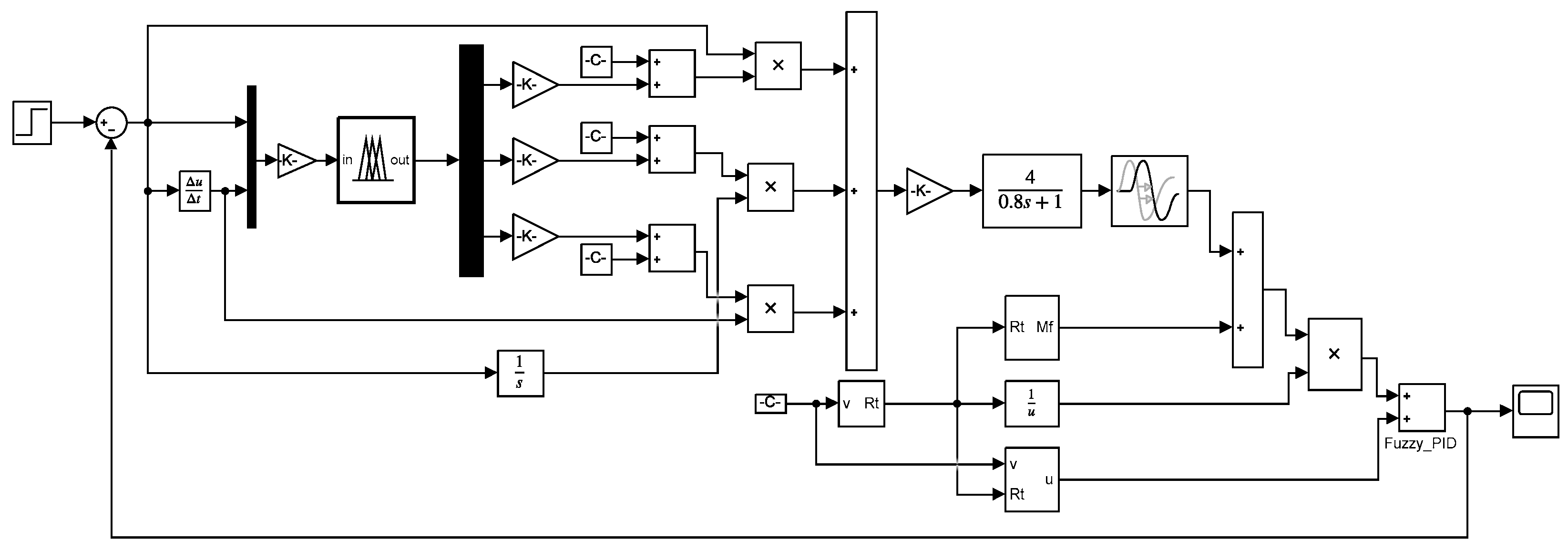
4. Fuzzy PID Control Strategy Design and Simulation Verification
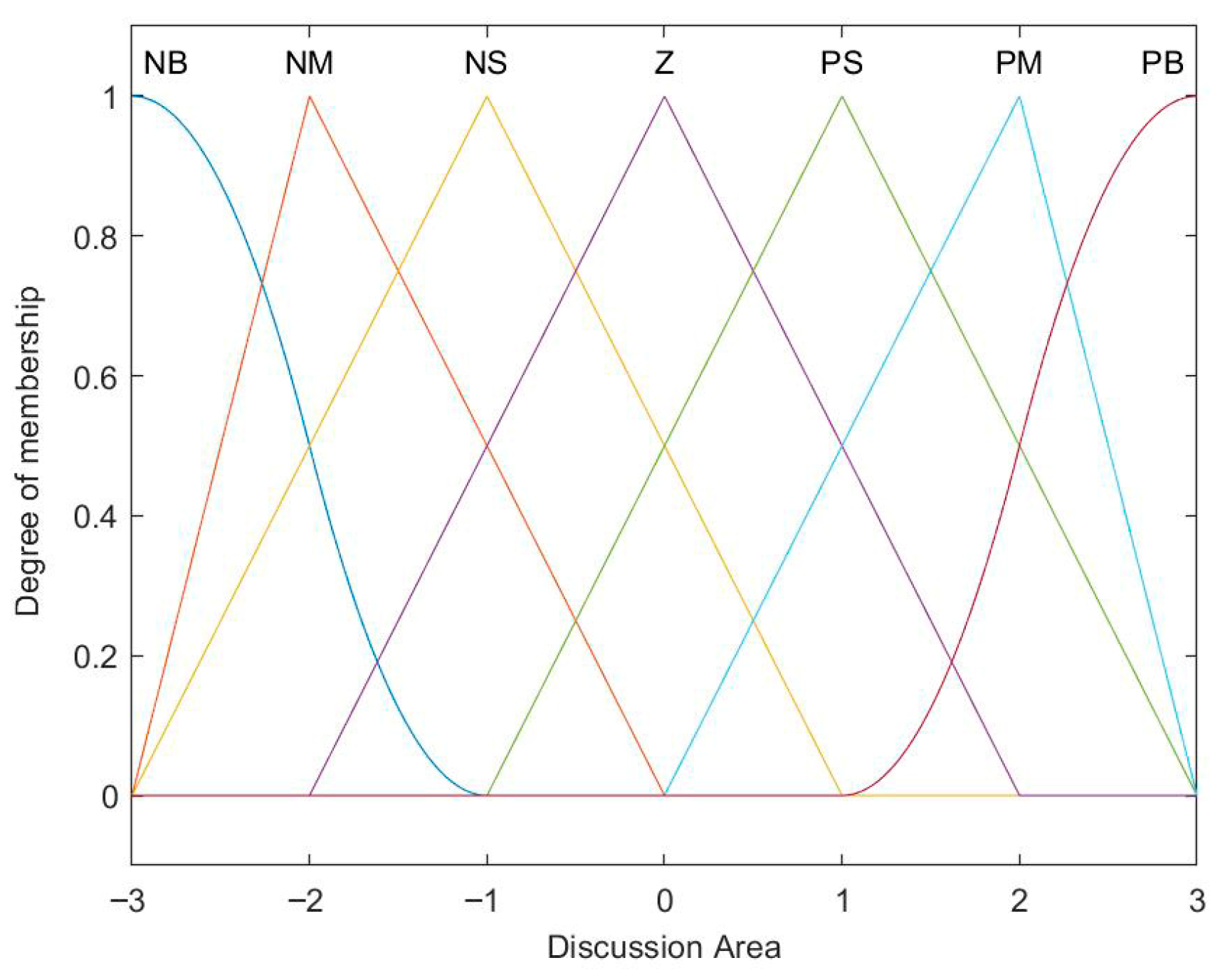
4.1. Design of Fuzzy PID Control Strategy
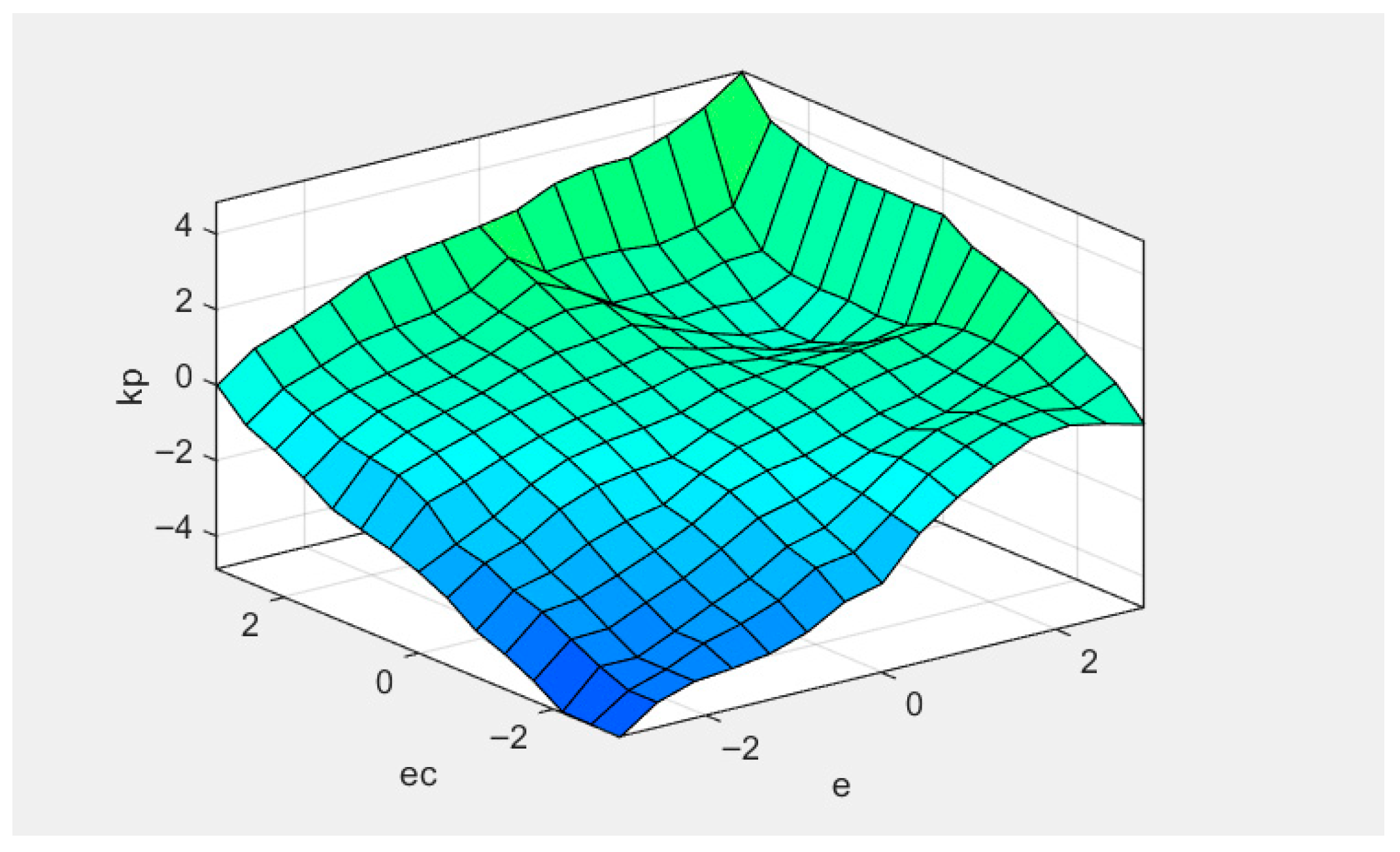
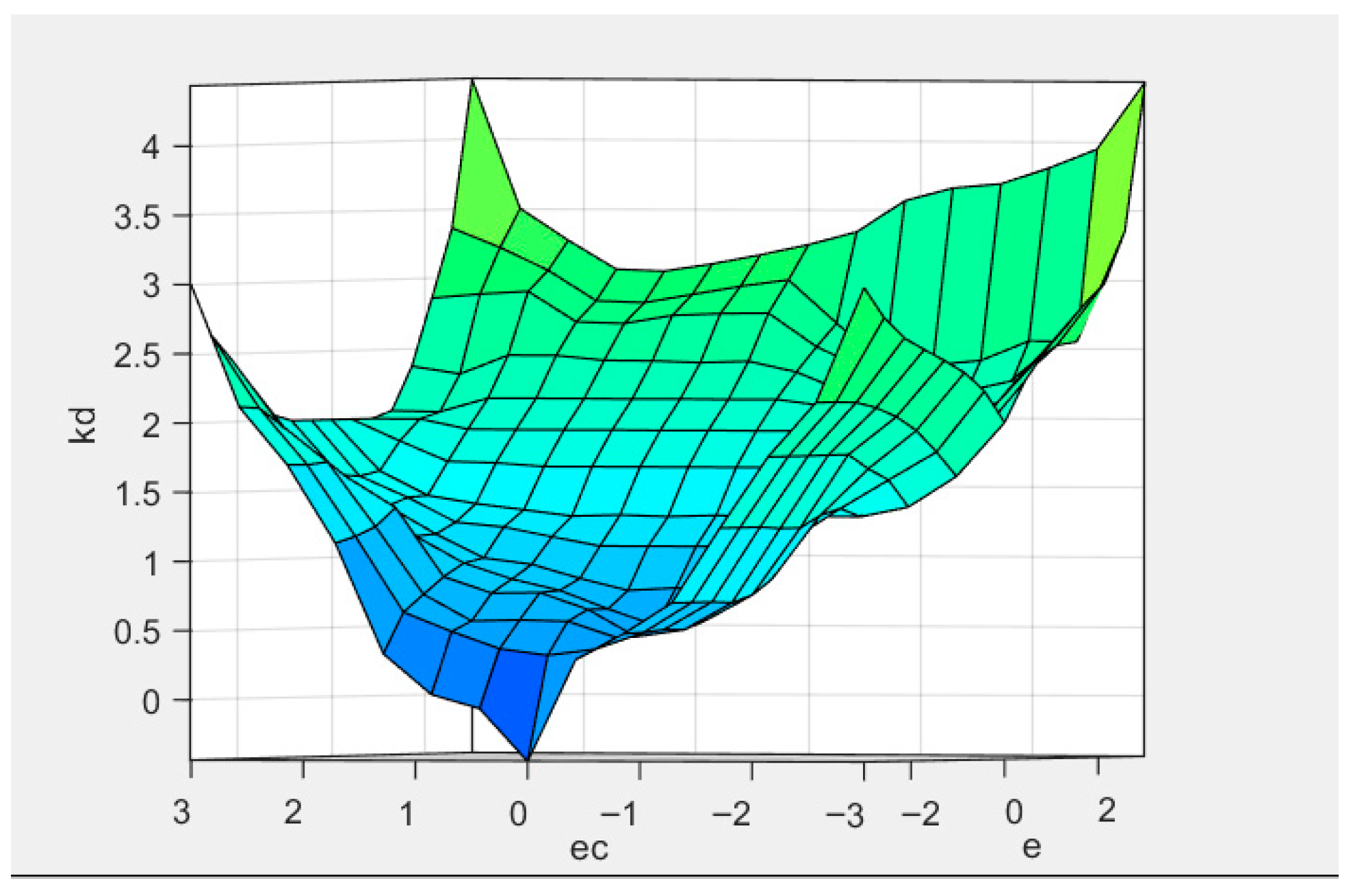
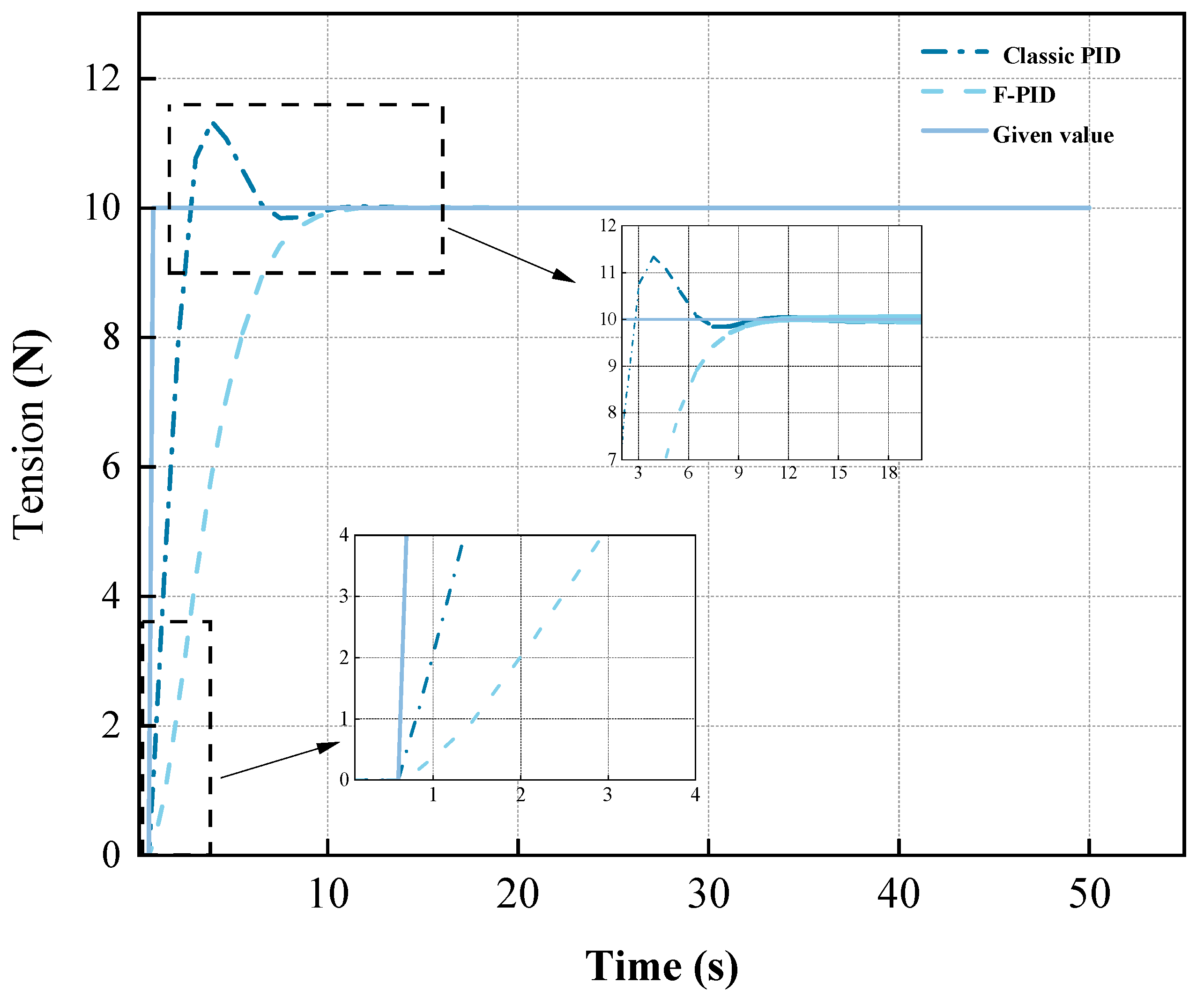
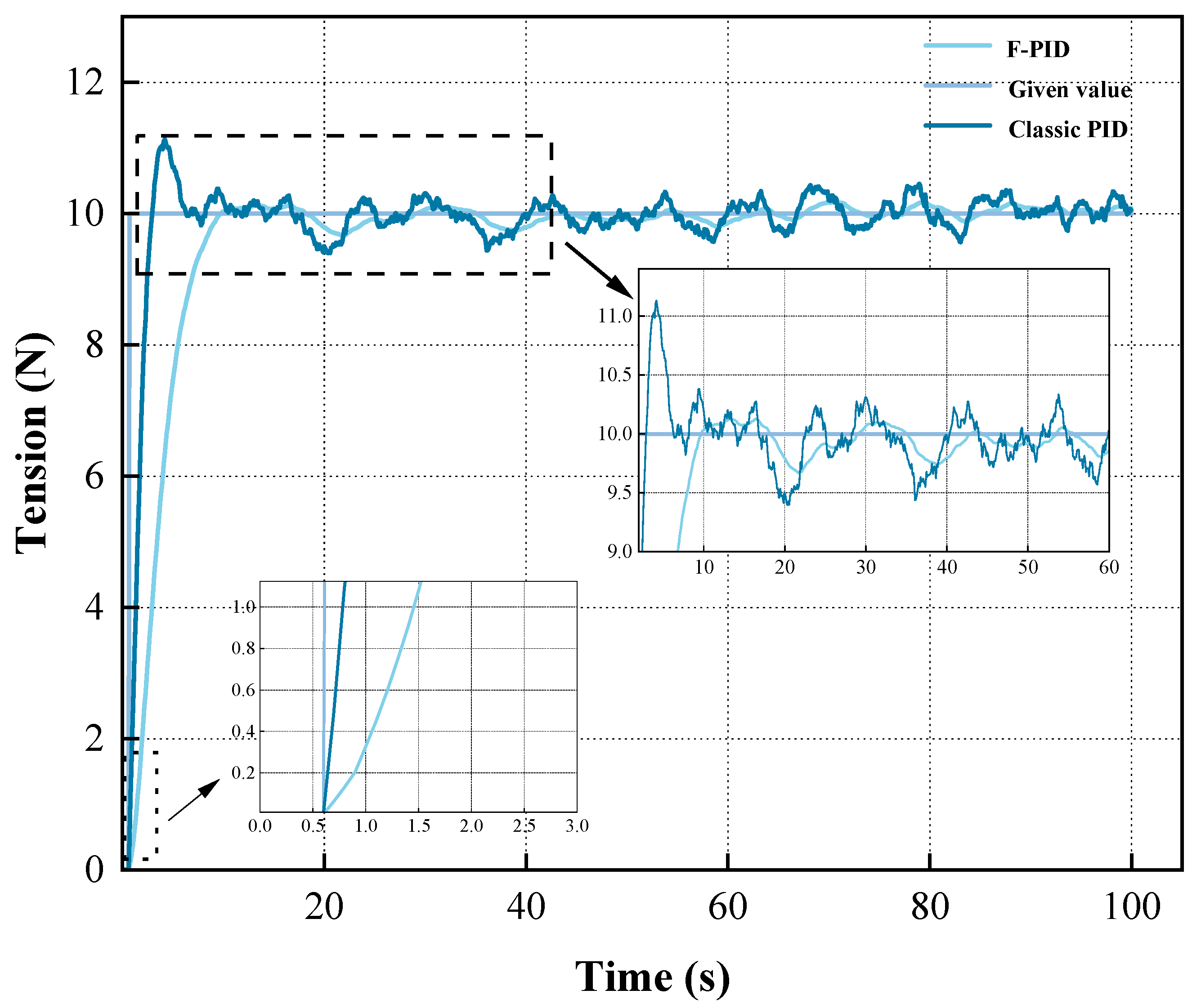
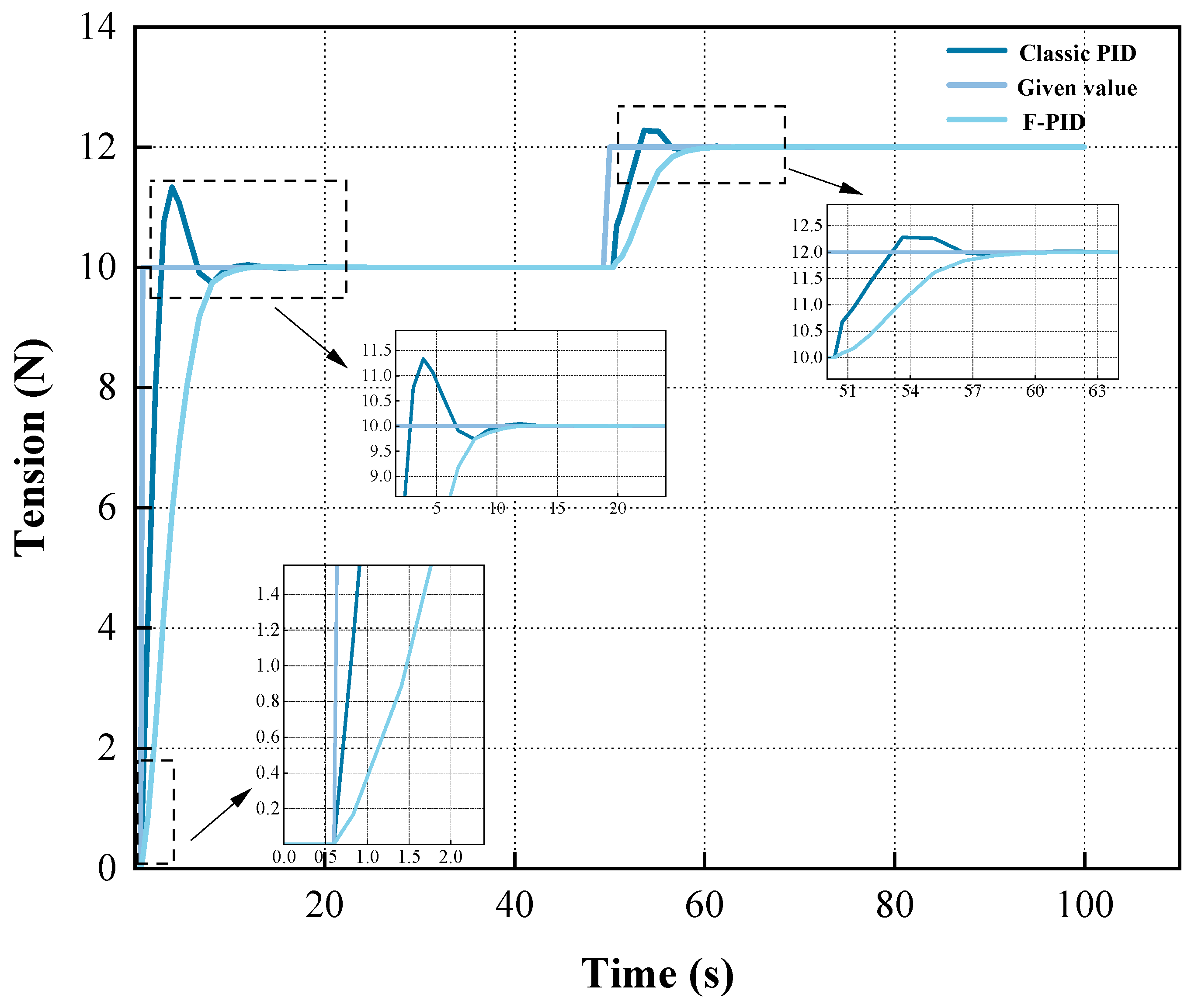
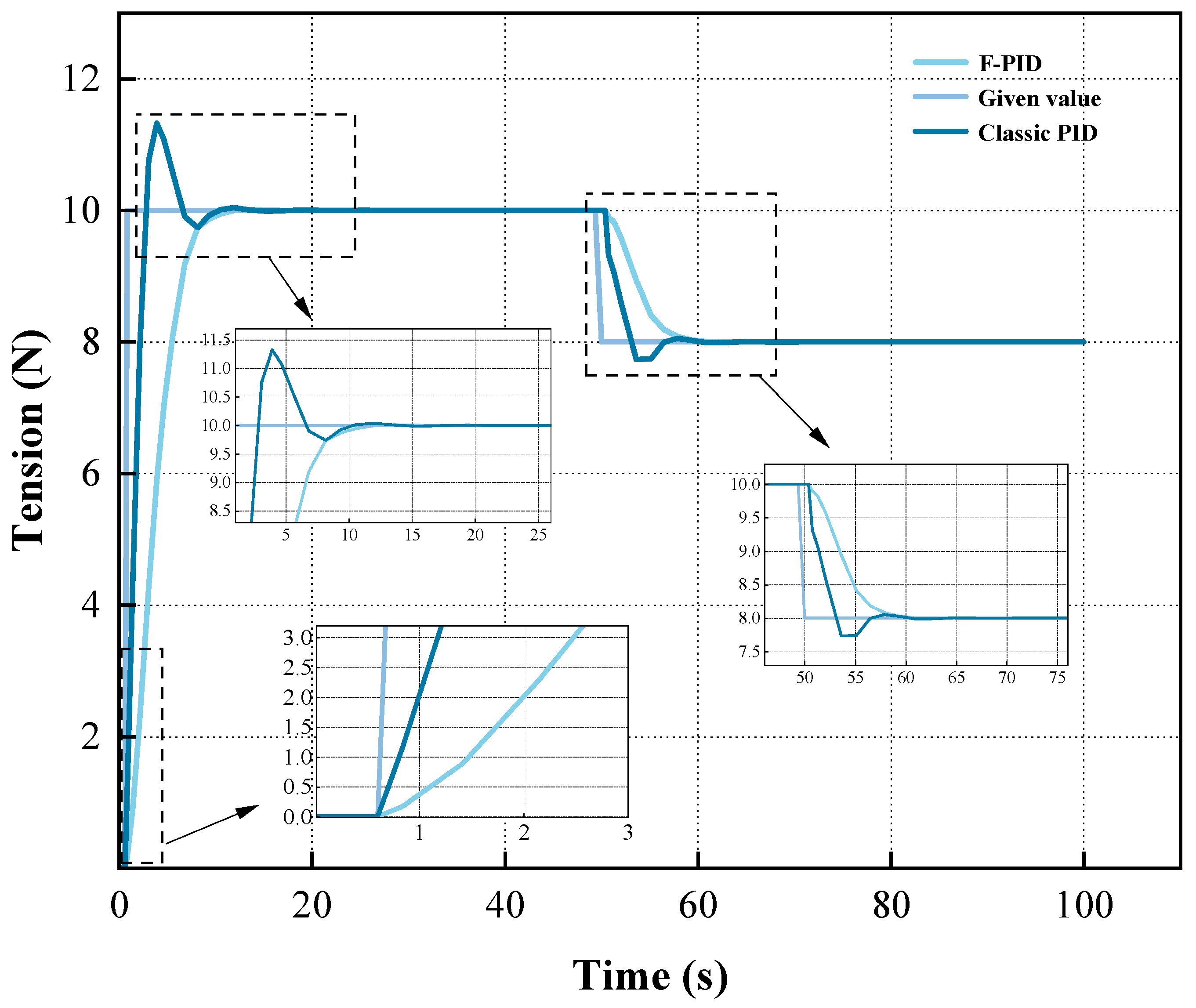
4.2. Simulation Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghate, M.; Pradhan, S.; Patel, M.; Bhavsar, D.; Vasava, K. Design and Fabrication of a Special Purpose Winding Machine for ELM Control Coils of JET. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 0602704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, I.B.; Zahra, N.G.; Farid, T. Modeling, Performance Analyzing, and Prototyping of Variable Reluctance Resolver with Toroidal Winding. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 4425–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Peng, Y.H.; Xu, H.J.; Xu, Z.-X. Achievement of automatic nylon rope winding control using adaptive decision-making algorithm. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 135, 1865–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Ma, H.W.; Wang, H.T. Research on speed regulation method of winding machine based on rectangular line mode. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 668, 12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.W.; Suo, H.F.; Ren, H.N. Design of Insulation Tape Tension Control System of Transformer Winding Machine Based on Fuzzy PID. Sensors 2021, 21, 6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Zhang, W.X.; Ding, X.L.; Zhang, M.; Wei, S.-H. Design and Analysis of a Novel Tension Control Method for Winding Machine. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Motomura, T. Robust Decentralized Tension Control in Hot Rolling. IFAC Pap. Line 2009, 42, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.S.; Cheng, M.Y.; Su, K.H. Wire tension control of an automatic motor winding machine—An iterative learning sliding mode control approach. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2018, 50, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Ding, J.; Sun, J. Study on High-Precision Tension Control Technology for a Cold-Rolling Pilot Mill with Hydraulic Tension. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.P.; Yan, F.G.; Wang, C. Research on the Simulation of Tension Control System of the Traction Wire Rope Cleaning and Detection Line of Pay-Off Unit. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 3485, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.Y.; Wang, D.Y.; Sun, M.; Fu, Z.; Yuan, B.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X. Optimizing Subway Train Operation with Hierarchical Adaptive Control Approach. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 138292–138302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.W.; Liu, S.; Liu, K. Design of an Optimal Fractional Order PID for Constant Tension Control System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 58933–58939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Chang, Y.S.; Lee, M.H. On the full stand modeling and tension control for the hot strip finishing mill with PID structure. KSME Int. J. 2004, 18, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, G.; Liu, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, K. Modeling of Accumulator in Roll-to-Roll Coating Equipment and Tension Control with Nonlinear PID. Polymers 2024, 16, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bai, J.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Z. Study of wire tension control system based on closed loop PID control in HS-WEDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 82, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zheng, C.G.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Dong, H.; Ke, Y. Fiber tension prediction and control methods in automated fiber placement. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 14888–14904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiffautt, C.; Sicard, P.; Bouscayrol, A. Tension control loop using a linear actuator based on the energetic macroscopic representation. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2004, 4, 2041–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, M.; He, Z. The application of PID controller with dead zone for yarn’s constant tension control system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 8th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 19–21 June 2013; pp. 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.W.; Zeng, S.K.; Zhao, J. Fully-digital tension control system with PID algorithm for winding ultra-fine enameled wires. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 892, 12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.W. Comparative study on control effect of permanent magnet synchronous motor based on Fuzzy PID control and BP neural network PID control. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1802, 32080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W. Research on integral separation control of warp tension based on fuzzy parameter optimization. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 3031–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.P. Design of yarn tension self-adaptive control system on warp knitting machine. J. Text. Inst. 2023, 115, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Guo, M.R.; Wang, J.G.; Gao, W. Warp yarn tension coupling models and fuzzy PID control for enhancing warp beam unwinding tension stability in sizing machines. J. Ind. Text. 2024, 2024, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Du, X.; Xu, G.; Wang, S. Tension Networked Control Strategy for Carbon Fiber Multilayer Diagonal Loom. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32280–32289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, C.; Lu, Q.; Chen, J.; Yan, J.; Yue, Q. Modelling and control of tension in a flexible pipe tensile armour manufacturing process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 3927–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, T. Constant Tension Control System of High-Voltage Coil Winding Machine Based on Smith Predictor-Optimized Active Disturbance Rejection Control Algorithm. Sensors 2023, 23, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delis, J.S. Design considerations, machinery and control options in coil winding. IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 1993, 9, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, X. On the Mechanical Analysis and Control for the Tension System of the Cylindrical Filament Winding. J. Text. Sci. Technol. 2016, 2, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.C.; Wang, K.X.; Xiong, L.; Zhao, J. Optimization of Bridge Crane Control System Using Fuzzy PID Control and Speed Control of Frequency Converter. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1802, 032007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, G.X.; Wang, L.C. Induction Heating Furnace Temperature Control Based on the Fuzzy PID. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 2024, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J. End Effector Control System of 6R Manipulator Based on Fuzzy PID. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 332–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunxiang, W.; Ruqing, Y.; Yongzhang, W.; Hua, L. Research on a precision tension control system with a magnetic particle clutch as the actuator. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2005, 27, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.J.; Yao, J.Y.; Deng, W.X. Adaptive RISE Control of Winding Tension with Active Disturbance Rejection. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 37, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Liu, S.; Wang, K.; Mei, X. Thermal Characteristics of Plastic Film Tension in Roll-to-Roll Gravure Printed Electronics. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Equipment Characteristics | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Payoff Wheel Specifications | mm |
| Equipment Weight | 500 kg |
| Electric Power Source | AC 380 V |
| Product Qualification Rate | 96% |
| Number of Revolutions Per Minute | 100–400 rpm |
| Traction Line Speed | 50–800 mm/min |
| Static | ≤80 decibel |
| Power | 0.75 kW |
| ec | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e | NB/Z/PS | NB/Z/NS | NB/Z/NB | NM/Z/NB | NS/Z/NB | NS/Z/NM | Z/Z/PS |
| NB/NM/PS | NB/NM/NS | NM/NS/NB | NS/NS/NM | NS/NS/NM | Z/Z/NS | PS/Z/Z | |
| NM/NB/Z | NM/NM/NS | NM/NS/NM | NS/NS/NM | Z/Z/NS | PS/PS/NS | PS/PS/Z | |
| NM/NB/Z | NM/NM/NS | NS/NS/NS | Z/Z/NS | PS/PS/NS | PM/PM/NS | PM/PB/Z | |
| NS/NS/Z | NS/NS/Z | Z/Z/Z | PS/PS/Z | PS/PS/Z | PM/PM/Z | PM/PB/Z | |
| NS/Z/PB | Z/Z/NS | PS/PS/PS | PM/PS/PS | NM/PS/PS | PM/PS/PS | PB/PM/PB | |
| Z/Z/PB | PS/Z/PM | PM/Z/PM | PM/Z/PM | PM/Z/PS | PM/Z/PS | PB/Z/PB | |
| Parameter Name | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Tension Ideal | 10 N |
| Wire Diameter | 0.1 mm |
| Wire Density | 8.3 g/cm3 |
| Diameter of Payoff Wheel | 70 mm |
| Spacing Inside the Wire Bobbin Wheel | 50 mm |
| Wire Bobbin Quality | 0.3 kg |
| Packing Factor | 0.785 |
| Weight of a Coil of Wire | 1.016 kg |
| Control Methods | Pre-Mutation Stabilization Time | Stabilization Time After Mutation | Pre-Mutational Overshoot | The Amount of Overshoot After Mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-12 N PID | 13.57 s | 63.10 s | 13% | 2.25% |
| 10-12 N F-PID | 10.53 s | 61.22 s | 0 | 0 |
| 10-8 N PID | 13.56 s | 64.74 s | 13% | 16.5% |
| 10-8 N F-PID | 10.52 s | 60.96 s | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, P.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pu, J. Research on Unwinding Mechanism Design and Tension Control Strategy for Winding Machines. Processes 2025, 13, 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082612
Han P, Wang W, Li Z, Zhang W, Pu J. Research on Unwinding Mechanism Design and Tension Control Strategy for Winding Machines. Processes. 2025; 13(8):2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082612
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Panxiang, Wei Wang, Zhihui Li, Weiliang Zhang, and Jialong Pu. 2025. "Research on Unwinding Mechanism Design and Tension Control Strategy for Winding Machines" Processes 13, no. 8: 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082612
APA StyleHan, P., Wang, W., Li, Z., Zhang, W., & Pu, J. (2025). Research on Unwinding Mechanism Design and Tension Control Strategy for Winding Machines. Processes, 13(8), 2612. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13082612






