Abstract
This article provides an overview of the use of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) applied to the treatment of water contaminated by pesticides. Given the global increase in the use of pesticides and the ineffectiveness of conventional treatment methods, EAOPs emerge as promising alternatives. They stand out for their efficiency in the degradation of organic compounds, minimal reliance on additional chemical reagents, and minimal generation of waste. The main methods addressed include anodic oxidation, photoelectro-oxidation, electro-Fenton and photoelectro-Fenton, which use hydroxyl radicals, a potent non-selective oxidant, to mineralize pollutants. A total of 165 studies were reviewed, with emphasis on the contributions of countries such as China, Spain, Brazil, and India. Factors such as electrode type, presence of catalysts, pH, and current density influence the effectiveness of treatments. Combined processes, especially those integrating UV light and renewable sources, have proven to be more efficient. Despite challenges related to electrode cost and durability, recent advances highlight the sustainability and scalability of EAOPs for the treatment of agricultural and industrial effluents contaminated with pesticides.
1. Introduction
Water pollution is a significant global concern, which directly affects its availability. The level of pollution of water resources has been progressive, and pesticides, in turn, assume a prominent role as contaminants. With their unbridled use, the presence of pesticides in water for human consumption has become a concern in both national and international contexts, fostering concern about the adverse effects on the environment and human health [1,2,3,4].
According to the report by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), entitled: “Statistical YearBook: World Food and Agriculture 2023” [5], there was a 62% increase in the use of pesticides between 2000 and 2021, with the Americas responsible for 50% of this use. In 2021, approximately 3.5 million tons of pesticides were used globally, with Brazil leading consumption (0.72 million tons), followed by the United States (0.46 million tons) and Indonesia (0.28 million tons). While essential to agricultural productivity, intensive pesticide use contributes to environmental contamination and the development of resistant pest species [6,7].
The main forms of contamination by pesticides come from the sanitation of storage containers, application equipment, pesticide factories, agro-industrial effluents, and drainage from intensive agriculture [8]. Even at trace levels, these compounds pose ecotoxicological risks due to their bioaccumulation in aquatic environments, which can generate chronic and toxic effects for living organisms [9].
Given the inefficiency of conventional treatment methods for pesticide removal, Advanced Oxidative Processes (AOPs) emerge as promising alternatives, standing out for their capacity to degrade and mineralize these organic compounds [10,11,12]. These methods are based on the in situ generation of hydroxyl radicals (·OH), capable of non-specific oxidation of a wide range of pollutants (E° = 2.8 V) [13].
Among AOPs, electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) stand out for their advantages, such as reduced need for chemical addition, rapid degradation of organic compounds, and minimal formation of harmful by-products [14]. However, their large-scale application still faces challenges, such as high operating costs and electrode degradation [15]. Research has been exploring strategies to overcome these limitations, including developing more efficient electrodes and integrating these processes with renewable energy sources [16].
In view of this scenario, the present study aims to present the main foundations of EAOPs and to carry out a systematic review of the literature from the last 10 years on the application of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes in pesticide degradation. The review seeks to map the main techniques used, the most studied types of pesticides, and recent advances in the improvement of these processes.
2. Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes (EAOPs)
EAOPs are being applied for the remediation of environmental pollution, especially focusing on the remediation of wastewater contaminated with pesticides and pharmaceuticals [17,18,19,20]. EAOPs consist of heterogeneous processes, where ·OH is generated on the surface of the electrode, and/or homogeneous processes, where ·OH is electrogenerated in situ.
These processes receive great attention from the scientific community in the treatment of wastewater due to their high performance in degrading organic substances, using relatively simple equipment, being an effective and ecological technology due to the absence or addition of low levels of non-toxic chemicals, and operating under ambient conditions of temperature and pressure, with ease of scaling up to industrial scale [17,18,19,20,21,22]. The main EAOPs are called anodic oxidation (AO), photo-electro-oxidation (PEO), electro-Fenton (EF), and photoelectro-Fenton (PEF).
2.1. Anodic Oxidation (AO)
Anodic oxidation, also called electro-oxidation, allows the oxidation of pollutants in two main ways: by direct or indirect electrolysis. Indirect electrolysis can, in turn, be reversible or irreversible, and the redox reagent involved is electrogenerated through an anodic or cathodic process [21]. Direct electrochemical oxidation occurs when there is direct transfer of electrons on the electrode surface, without the aid of other substances. The indirect form, on the other hand, is mediated by some electroactive species that act as intermediaries for the transport of electrons between the electrode and the organic compounds for their oxidation, which is possible at low potentials, i.e., before the onset potential for O2 evolution [17,18,19,20,21].
The efficiency of hydroxyl radical production and, consequently, the oxidation of organic compounds depends on the materials used as electrodes. Since the formation of ·OH is a heterogeneous process, in the case of using metal oxide electrodes, or oxide anodes (MOx), the conversion/combustion process begins with the discharge of water produced by adsorbed hydroxyl radicals (MOx(·OH)) (reaction (1)) [23].
MOx + H2O → MOx(·OH) + H+ + e
The interaction between the adsorbed hydroxyl radicals and the oxygen present can lead to the transition of these radicals from the adsorbed form to the oxide anode structure, promoting the formation of higher oxides (MOx+1), as illustrated in reaction (2).
MOx(·OH) → MOx+1 + H+ + e
Reactions (1) and (2) demonstrate the existence of two distinct states of active oxygen on the surface of oxide electrodes: physical adsorption of oxygen in the form of hydroxyl radical and chemical adsorption of oxygen as higher oxides [23,24]. When there are no oxidizable organic compounds, the adsorbed oxygen results in the formation of O2, which regenerates the electrode surface, as explained in reactions (3) and (4).
MOx(·OH) → ½ O2 + H+ + e + MOx
MOx+1 → ½ O2 + MOx
When oxidizable organic compounds are present, the dynamics of adsorbed oxygen change. Physically adsorbed oxygen MOx(·OH) tends to preferentially promote mineralization to CO2, according to reaction (5). On the other hand, chemically adsorbed oxygen in the form of higher oxides (MOx+1) favors selective oxidation of organic compounds, leading to the formation of oxidized organic species (RO), as shown in reaction (6) [23,24].
R + MOx(·OH) → CO2 + ZH+ + Ze + MOx
R + MOx+1 → RO + MOx
For the desired type of occurrence, it is essential to prioritize the form of oxygen adsorption on the electrode surface. If the concentration of adsorbed hydroxyl radicals is higher than that of higher oxides, complete oxidation of organic compounds tends to be the dominant pathway. However, if the concentration of oxides is higher, selective oxidation will probably predominate [20,23,24].
The mechanism is different in the case of a non-active anode, such as boron-doped diamond (BDD) [25]. Water oxidation leads to the formation of BDD(·OH). This compound is responsible for the oxidation of organic pollutants, initially generating by-products and then promoting their complete mineralization into CO2, which in turn regenerates the initial material (reactions (7)–(9)) [24,25].
BDD + H2O → BDD(·OH) + H+ + e
BDD(·OH) + RH → BDD + by-products
By-products + BDD(·OH) → BDD + CO2 + H2O + inorganic ions
During indirect oxidation, the anodic oxidation or cathodic reduction reaction (of water or species present in the medium) results in the formation of intermediate products or oxidizing agents such as ozone, hydrogen peroxide, and other active species on the electrode surface under the action of external current. The oxidizing agents generated interact with organic pollutants, promoting their oxidation and the subsequent formation of several intermediate compounds. While the initial oxidation reaction takes place on the electrode surface, the subsequent degradation of the pollutants occurs predominantly in the solution phase beyond the electrode surface [24,25].
2.2. Photo-Electro-Oxidation (PEO)
Photo-electro-oxidation has emerged as a promising technology for the removal of emerging contaminants in industrial and drinking water wastewater, especially when present in low concentrations, such as pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and dyes [26]. This process is based on the combination of the energy of photons incident on the surface of the electrodes with the electron flow generated by the potential difference in an electrochemical cell. For optimal efficiency, the electrode must have a photoactive surface, usually deposited on a conductive support, such as TiO2. During PEO, UV radiation activates a semiconductor, promoting charge separation: valence band (VB) electrons absorb photons and migrate to the conduction band (CB), leaving positive holes in the VB (TiO2 bandgap ~3.2 eV). This phenomenon generates reactive oxygen species, known as photon-ROS, while the polarization of the electrodes induces the discharge of water molecules on the anode surface, forming electron-ROS, such as ·OH [27]. The mechanisms involved in this process are like those of photohydrolysis and electrochemical oxidation (EO), enhancing the degradation of pollutants [26,27,28,29,30].
2.3. Combined Process: Electro-Fenton (EF) and Photo-Electro-Fenton (PEF)
Based on these principles, several variants of electrochemical processes have been explored to increase the efficiency of pollutant degradation. Among them, the combination with the Fenton reagent results in the processes called electro-Fenton and photo-electro-Fenton. These processes combine electrochemical action with other advanced oxidation mechanisms, enhancing the removal of contaminants and reducing the formation of undesirable by-products [10,11,12,31].
Fenton reagent consists of the reaction between hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and ferrous ions (Fe2+) in an acidic medium to produce ·OH. In this process, iron acts as a catalyst and H2O2 as an oxidizing agent, promoting the formation of ·OH and the continuous regeneration of Fe2+ through the cathodic reduction of Fe3+, ensuring the propagation of the Fenton cycle (reaction (10)). The ideal pH for this reaction is around 3, as higher values favor the precipitation of Fe3+ in the form of hydroxides, reducing the efficiency of the system [32,33].
Fe2+ + H2O2 → Fe3+ + ·OH + OH−
In the electro-Fenton (EF) process, ·OH production is intensified through the electrochemical generation of H2O2. In addition to the oxidation promoted by the homogeneous ·OH formed in the solution, reactions with heterogeneous ·OH on the electrode surface and with secondary oxidizing species, such as active chlorine, may also occur, depending on the experimental conditions [32]. The most used cathode materials for in situ H2O2 production are based on carbon (carbon nanotubes, graphite, lattice glassy carbon (RVC), carbon felt, or carbon sponge).
In the photo-Fenton process, UV light provides enough energy to activate the Fenton reaction, promoting the activation of iron and hydrogen peroxide. This process is more efficient, faster, and effective compared to conventional Fenton due to its high capacity to degrade organic pollutants, even with lower concentrations of ferrous ions. Furthermore, its application in a wider range of environmental conditions makes it a promising alternative for effluent treatment. The photo-Fenton system is a process that occurs in the presence of UV radiation; first the Fenton process reaction occurs, and then Fe3+ is photoreduced to Fe2+ according to reaction (11). Furthermore, direct photolysis of H2O2 also produces ·OH (reaction (12)) [32,33].
Fe3+ + H2O2 + hν → Fe2+ + ·OH + H+
H2O2 + hν → 2 ·OH
In photo-electro-Fenton (PEF), which uses UV light (e.g., 254 nm), and in solar photo-electro-Fenton (SPEF), ultraviolet radiation applied to the solution plays an additional role in the degradation of pollutants. This effect occurs due to the photolysis of Fe(III) complexes with organic compounds, such as carboxylic acids (reaction (13)), and the photoreduction of the [Fe(OH)]2+ species, resulting in the regeneration of Fe2+ and the additional production of ·OH (reaction (14)) [34,35].
Fe(OOCR)2+ + UV → Fe2+ + CO2 + R·
[Fe(OH)]2+ + UV → Fe2+ + ·OH
The combination of processes resulted in better results in relation to the degradation of organic compounds compared to the processes applied separately; that is, the synergistic effect is efficient [10,12,34,35]. As a major advantage, EAOPs use as inputs the energy required to perform electrolysis and that used by the UV radiation source, with the only reactants being electrons and photons.
3. Overview of Literature
A literature review was conducted, focusing on the application of EAOPs in treating effluents containing pesticides. A search was performed in the Scopus, SciELO, and Web of Science databases, using the following keywords: electrochemical, wastewater, effluent treatment, pesticide, herbicide, anodic oxidation, electro-oxidation, photo-electro-oxidation, electro-Fenton, and photo-electro-Fenton (The Boolean search strategy applied was as follows: (((“electrochemical”) AND (“pesticide” OR “herbicide”) AND (“wastewater” OR “effluent treatment”)) AND ((“anodic oxidation” OR “electro-oxidation”) OR (“photo-electro-oxidation” OR “photo-electro-catalysis”) OR (“electro-fenton” OR “electrofenton”) OR (“photoelectrofenton” OR “photo-electro-fenton” OR “photoelectro-fenton”))).
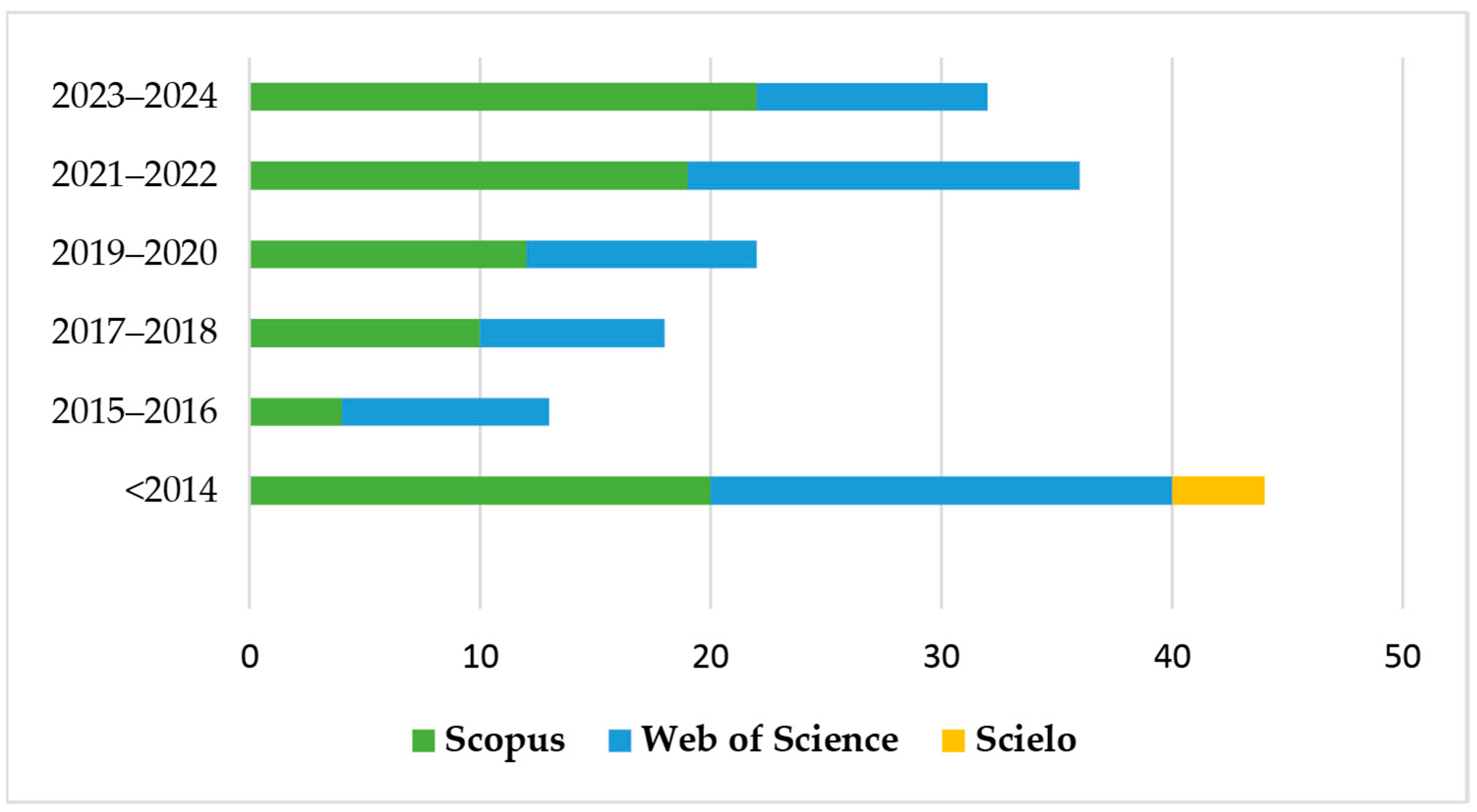
As a result, 165 documents were identified, covering both primary articles and review articles, with no temporal delimitation. The distribution of studies over the years can be seen in Figure 1, evidencing the evolution of scientific interest in the topic.
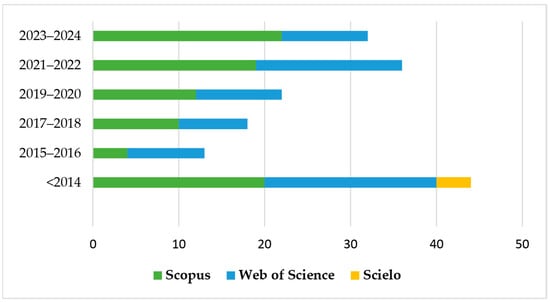
Figure 1.
Number of publications in Scopus, SciELO, and Web of Science databases reporting the application of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOP) in treating effluent-containing pesticides in the last 10 years.
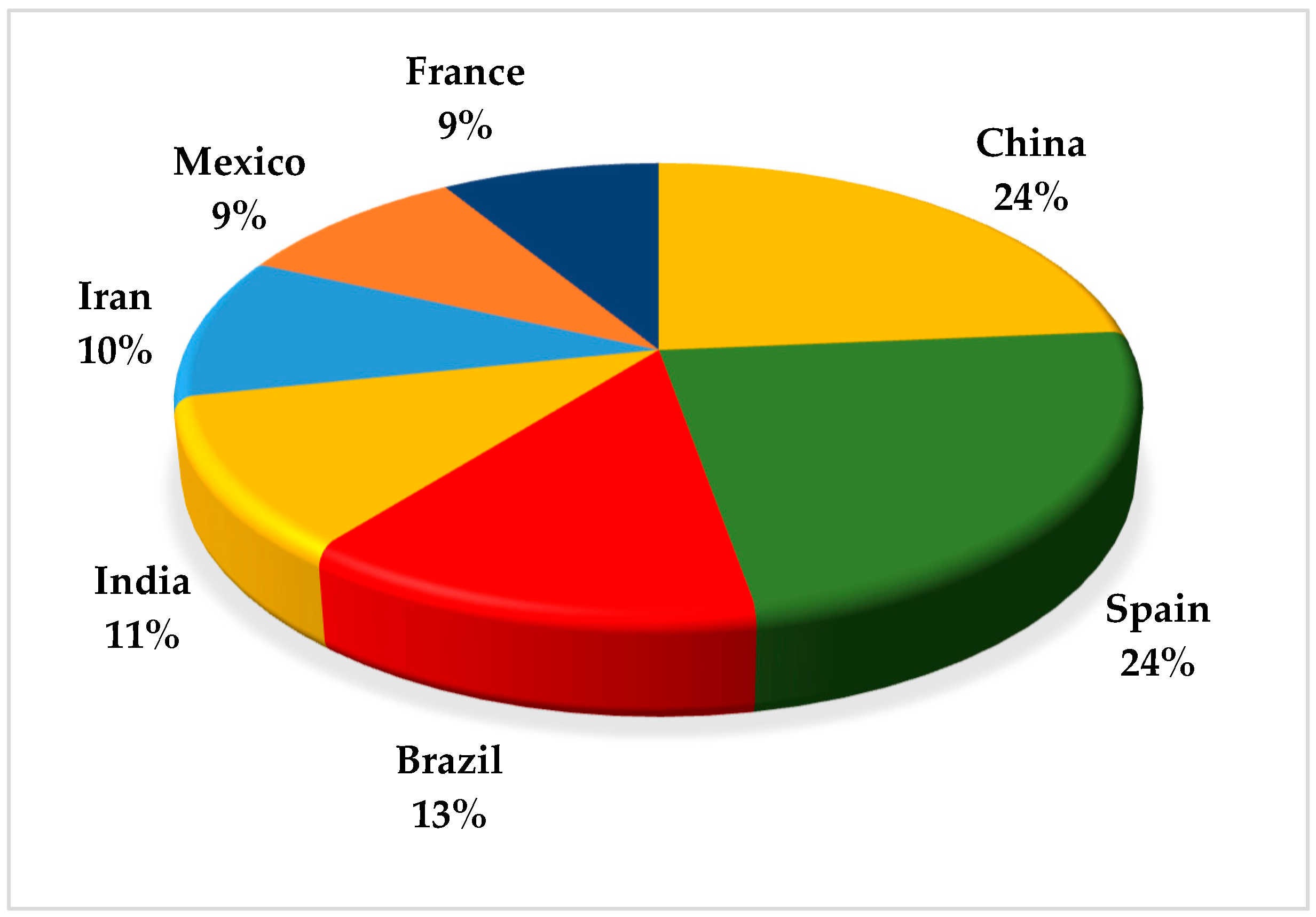
There has been an increase in publications focused on research on the application of EAOP in pesticide treatment in the last 10 years, with around 128 publications in this period (2014–2024). There was an increase of around 41% in the last three years (2021–2024) compared to the previous three years (2017–2020). Figure 2 shows the representation of the main countries that published the most on this topic in the last 10 years. Spain and China led the publications, followed by Brazil and India.
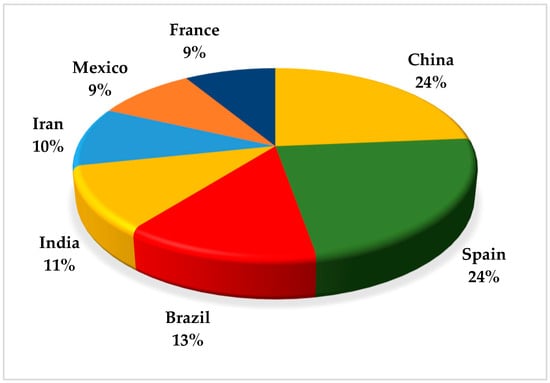
Figure 2.
Countries that published the most articles reporting on applying the advanced electrochemical oxidation processes (EAOP) in treating effluent-containing pesticides in the last 10 years.
Among the 128 published documents included in the analysis, 77% were primary articles, while 16% were reviewed articles. The main technical approaches described in the selected studies involve anodic oxidation, photo-electrocatalysis, electro-Fenton, and photo-electro-Fenton, demonstrating the diversity and complementarity of electrochemical processes applied in the treatment of compounds originating from pesticides. The articles selected for the construction of this overview, after full-text review and evaluation of methodological rigor, are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Selected literature references that applied electrochemical advanced oxidation processes (EAOPs) to degrade pesticides and the best results obtained.
4. Conclusions and Prospects
This overview of recent years shows progress and interest in the development and application of electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for the degradation of pesticides in aqueous matrices. The studies analyzed demonstrated that the efficiency of the processes depends on factors such as the type of electrode (e.g., BDD, Ti/RuO2, TiO2, and PbO2), the presence of catalytic agents, and the combination with UV radiation or peroxides, as well as the optimization of operational parameters (pH, current density, treatment time, etc.). Also noteworthy are innovative approaches such as the use of electrodes with specific morphological structures and processes mediated by gaseous oxidants, which combine high degradation efficiency with reduced energy consumption.
Due to the increasing environmental contamination caused by the indiscriminate use of pesticides and the inefficiency of conventional water treatment methods, such as flotation, coagulation, filtration, and decantation, EAOPs have emerged as sustainable, effective, and versatile technological alternatives. Furthermore, the phytotoxicological and ecotoxicological assessment of the treated effluents reinforces the environmental viability of EAOPs, indicating a reduction in residual toxicity and an increase in the biodegradability of the remaining compounds. In this context, these processes not only promote the mineralization of recalcitrant pesticides but also contribute to mitigating risks to human health and aquatic biodiversity. These findings support the role of EAOPs in circular economy and sustainable agriculture frameworks.
Thus, it is concluded that EAOPs represent a promising front in the treatment of effluents contaminated with pesticides, with potential for large-scale application and other persistent organic pollutants. The continuous improvement of materials, integration with renewable energy sources (solar-driven EAOPs [35]), and evaluation in real systems are strategic paths to consolidate their industrial applicability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.F.; methodology, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; validation, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; formal analysis, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; investigation, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; resources, J.C.F.; data curation, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; writing—review and editing, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; visualization, M.A.P.F., A.S.V. and J.C.F.; supervision, J.C.F.; project administration, J.C.F.; funding acquisition, J.C.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the São Paulo Research Foundation—FAPESP [grant numbers: 2016/22115-2; 2022/10999-4] and the Brazilian National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—CNPq [grant number: 402757/2016-5].
Data Availability Statement
The data present in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
To the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Finance Code 001 (M.A.P.F.). To PROPE-UNESP for the PIBIC-CNPq and to FAPESP—2024/08885-6 (A.S.V.).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EAOPs | electrochemical advanced oxidation processes |
| AOPs | advanced oxidative processes |
| ·OH | hydroxyl radicals |
| AO | anodic oxidation |
| PEO | photo-electro-oxidation |
| EF | electro-Fenton |
| PEF | photoelectro-Fenton |
| BDD | boron-doped diamond |
| CPC | compound parabolic collector |
| TOC | total organic carbon |
References
- Zhou, W.; Li, M.; Achal, V. A comprehensive review on environmental and human health impacts of chemical pesticide usage. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 11, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.H.; Lenzen, M.; McBratney, A.; Maggi, F. Risk of pesticide pollution at the global scale. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Amin, S.N.; Rahman, M.A.; Juraimi, A.S.; Uddin, M.K.; Brown, C.L.; Arshad, A. Chronic effects of organic pesticides on the aquatic environment and human health: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Maleski, A.L.A.; Balan-Lima, L.; Bernardo, J.T.G.; Hipolito, L.M.; Seni-Silva, A.C.; Batista-Filho, J.; Falcão, M.A.P.; Lima, C. Impact of pesticides on human health in the last six years in Brazil. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Statistical Yearbook 2023; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023; 384p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M.; Daniel Ruan, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Phung, D.T. Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.C.; Vilar, V.J.; Ferreira, A.C.; dos Santos, F.R.; Dezotti, M.; Sousa, M.A.; Gonçalves, C.; Boaventura, R.A.R.; Alpendurada, M.F. Treatment of a pesticide-containing wastewater using combined biological and solar-driven AOPs at pilot scale. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 209, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carra, I.; Santos-Juanes, L.; Fernández, F.G.A.; Malato, S.; Pérez, J.A.S. New approach to solar photo-Fenton operation. Raceway ponds as tertiary treatment technology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, J.C.; Loretti, G.H.; Tadayozzi, Y.S.; de Andrade, A.R. A phytotoxicity assessment of the efficiency 2,4-D degradation by different oxidative processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 266, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadayozzi, Y.S.; Santos, F.A.D.; Vicente, E.F.; Forti, J.C. Application of oxidative process to degrade paraquat present in the commercial herbicide. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2021, 56, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.E.; Tadayozzi, Y.S.; Putti, F.F.; Santos, F.A.; Forti, J.C. Degradation of commercial glyphosate-based herbicide via advanced oxidative processes in aqueous media and phytotoxicity evaluation using maize seeds. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 840, 156656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, A.; Deivayanai, V.C.; Kumar, P.S.; Rangasamy, G.; Hemavathy, R.V.; Harshana, T.; Gayathri, N.; Alagumalai, K. A detailed review on advanced oxidation process in treatment of wastewater: Mechanism, challenges and future outlook. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Qian, L.; Jing, Y.; Wei, K. Removal of triazole fungicides of 1H-1, 2, 4-triazole from pesticide tailwater by electrochemical oxidation using meso-flower PbO2 layer electrode. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2023, 12, 100367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahbub, P.; Duke, M. Scalability of advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) in industrial applications: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Q.; Sayed, M.; Khan, J.A.; Rehman, F.; Noreen, S.; Sohni, S.; Gul, I. Advanced oxidation/reduction processes (AO/RPs) for wastewater treatment, current challenges, and future perspectives: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 1863–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E. Recent development of electrochemical advanced oxidation of herbicides. A review on its application to wastewater treatment and soil remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 290, 125841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E. Fenton, photo-Fenton, electro-Fenton, and their combined treatments for the removal of insecticides from waters and soils. A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 284, 120290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E. Progress of homogeneous and heterogeneous electro-Fenton treatments of antibiotics in synthetic and real wastewaters. A critical review on the period 2017–2021. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, S.W.; Welter, J.B.; Albornoz, L.L.; Heberle, A.N.A.; Ferreira, J.Z.; Bernardes, A.M. Advanced electrochemical oxidation processes in the treatment of pharmaceutical containing water and wastewater: A review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Panizza, M. Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for wastewater treatment. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2018, 11, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Espinoza, J.D.; Nacheva, P.M. Degradation of pharmaceutical compounds in water by oxygenated electrochemical oxidation: Parametric optimization, kinetic studies and toxicity assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comninellis, C. Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Cerisola, G. Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6541–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E. Electro-Fenton, UVA photoelectro-Fenton and solar photoelectro-Fenton treatments of organics in waters using a boron-doped diamond anode: A review. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2014, 58, 239–255. Available online: https://www.scielo.org.mx/scielo.php?pid=S1870-249X2014000300002&script=sci_arttext&tlng=en (accessed on 7 July 2025). [CrossRef]
- Belver, C.; Bedia, J.; Peñas-Garzón, M.; Muelas-Ramos, V.; Gómez-Avilés, A.; Rodriguez, J.J. Structured photocatalysts for the removal of emerging contaminants under visible or solar light. In Visible Light Active Structured Photocatalysts for the Removal of Emerging Contaminants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 41–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Garcia-Segura, S. Recent progress of applied TiO2 photoelectrocatalysis for the degradation of organic pollutants in wastewaters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, W.; Su, R.; Luo, S.; Luo, Y. Photoelectrocatalytic oxidation of bisphenol A over mesh of TiO2/graphene/Cu2O. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 183, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplin, B.P. The prospect of electrochemical technologies advancing worldwide water treatment. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokoohi, R.; Poureshgh, Y.; Parastar, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Shabanloo, A.; Rahmani, Z.; Asl, F.B.; Tabar, M.V. Comparing the efficiency of UV/ZrO2 and UV/H2O2/ZrO2 photocatalytic processes in furfural removal from aqueous solution. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, J.C.; Robles, P.E.; Tadayozzi, Y.S.; Demori, M.A.; Santos, F.A.; Putti, F.F.; Vicente, E.F. Electrochemical processes used to degrade thiamethoxam in water and toxicity analyses in non-target organisms. Processes 2024, 12, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.H.; Dong, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, D.X.; Meng, D. A review on Fenton process for organic wastewater treatment based on optimization perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausi, M.; Savino, S.; Cangialosi, F.; Eramo, G.; Fornaro, A.; Quatraro, L.; Pinto, D.; D’Accolti, L. Pollutants abatement in aqueous solutions with geopolymer catalysts: A photo fenton case. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girón-Navarro, R.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Teutli-Sequeira, E.A.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Martínez-Cienfuegos, I.G.; Sánchez-Pozos, M.; Santoyo-Tepole, F. A solar photoFenton process with calcium peroxide from eggshell and ferrioxalate complexes for the degradation of the commercial herbicide 2,4-D in water. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 438, 114550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, A.; Tian, X.; Wen, Z.; Lv, H.; Li, D.; Li, J. Efficient mineralization of the antibiotic trimethoprim by solar assisted photoelectro-Fenton process driven by a photovoltaic cell. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 318, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelfi, D.R.; Brillas, E.; Gozzi, F.; Machulek, A., Jr.; de Oliveira, S.C.; Sirés, I. Influence of electrolysis conditions on the treatment of herbicide bentazon using artificial UVA radiation and sunlight. Identification of oxidation products. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.F.; Llanos, J.; Sáez, C.; López, C.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. On the design of a jet-aerated microfluidic flow-through reactor for wastewater treatment by electro-Fenton. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 208, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón, I.; Plakas, K.V.; Sirés, I.; Oller, I.; Maldonado, M.I.; Karabelas, A.J.; Malato, S. Optimization of electrocatalytic H2O2 production at pilot plant scale for solar-assisted water treatment. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 242, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, F.L.; Sáez, C.; Cañizares, P.; Rodrigo, M.A. Improving photolytic treatments with electrochemical technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 235, 116229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraleda, I.; Oturan, N.; Saez, C.; Llanos, J.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Oturan, M.A. A comparison between flow-through cathode and mixed tank cells for the electro-Fenton process with conductive diamond anode. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Costa, A.J.; Kronka, M.S.; Cordeiro-Junior, P.J.; Fortunato, G.V.; dos Santos, A.J.; Lanza, M.R. Treatment of Tebuthiuron in synthetic and real wastewater using electrochemical flow-by reactor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 882, 114978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, J.R.; González, T.; Correia, S. BDD electrochemical oxidation of neonicotinoid pesticides in natural surface waters. Operational, kinetic and energetic aspects. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 298, 113538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, I.C.C.; Oriol, R.; Ye, Z.; Martínez-Huitle, C.A.; Cabot, P.L.; Brillas, E.; Sirés, I. Photoelectro-Fenton treatment of pesticide triclopyr at neutral pH using Fe(III)–EDDS under UVA light or sunlight. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 23833–23848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.L.; Boujelbane, F.; Bui, H.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Bui, X.T.; Nguyen, D.N.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Phan, H.A.; Duong, H.T.G.; Bui, H.M. Pesticide production wastewater treatment by Electro-Fenton using Taguchi experimental design. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 3155–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezgui, S.; Díez, A.M.; Monser, L.; Adhoum, N.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.Á. Magnetic TiO2/Fe3O4-chitosan beads: A highly efficient and reusable catalyst for photo-electro-fenton process. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.R.; González, T.; Correia, S.E.; Núñez, M.M. Emerging contaminants decontamination of WWTP effluents by BDD anodic oxidation: A way towards its regeneration. Water 2023, 15, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.M.; Mena, I.F.; Saez, C.; Motheo, A.J.; Rodrigo, M.A. Treatment of organics in wastewater using electrogenerated gaseous oxidants. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2024, 63, 6512–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).