Revolutionizing Electrospinning: A Review of Alternating Current and Pulsed Voltage Techniques for Nanofiber Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
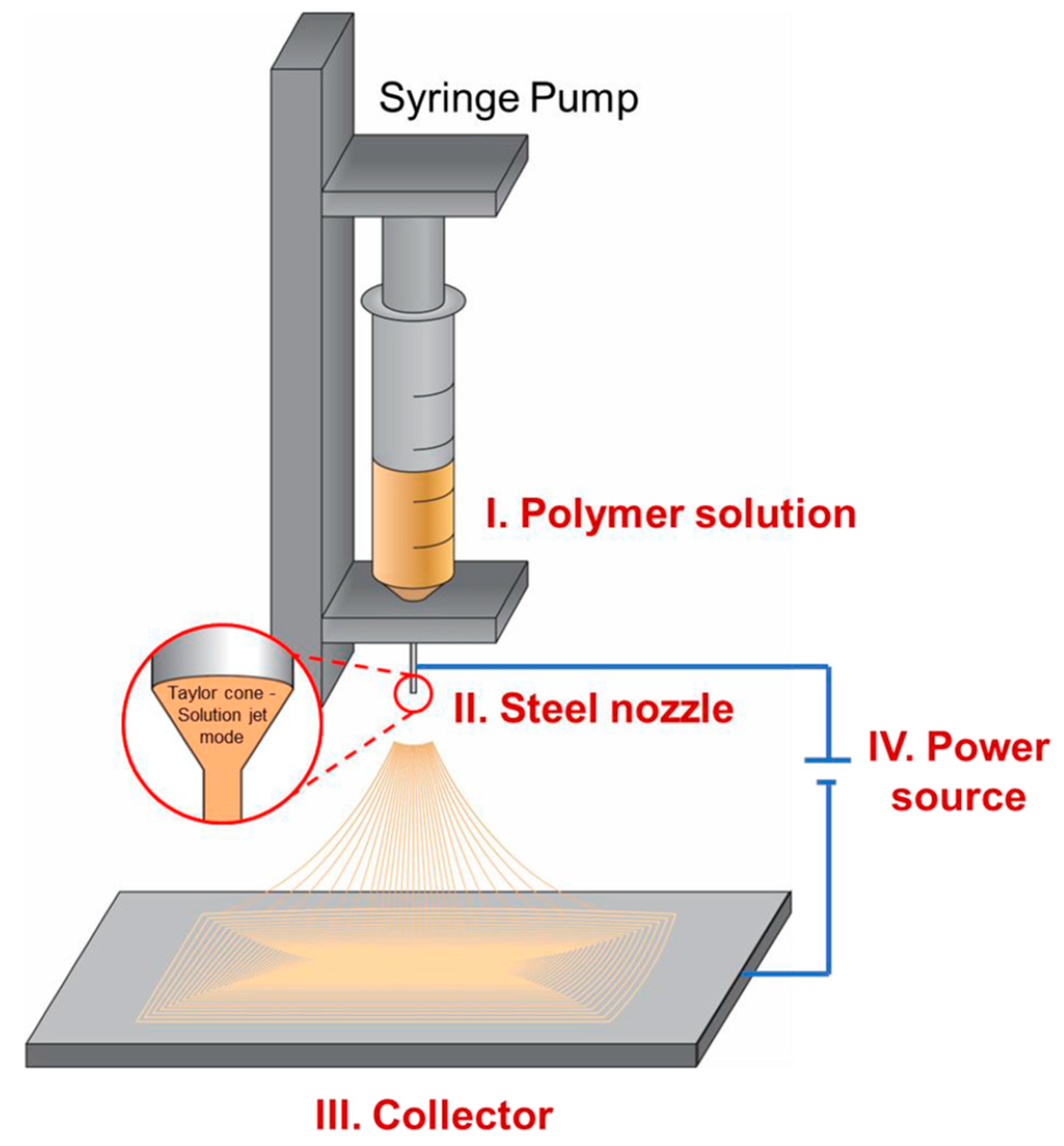
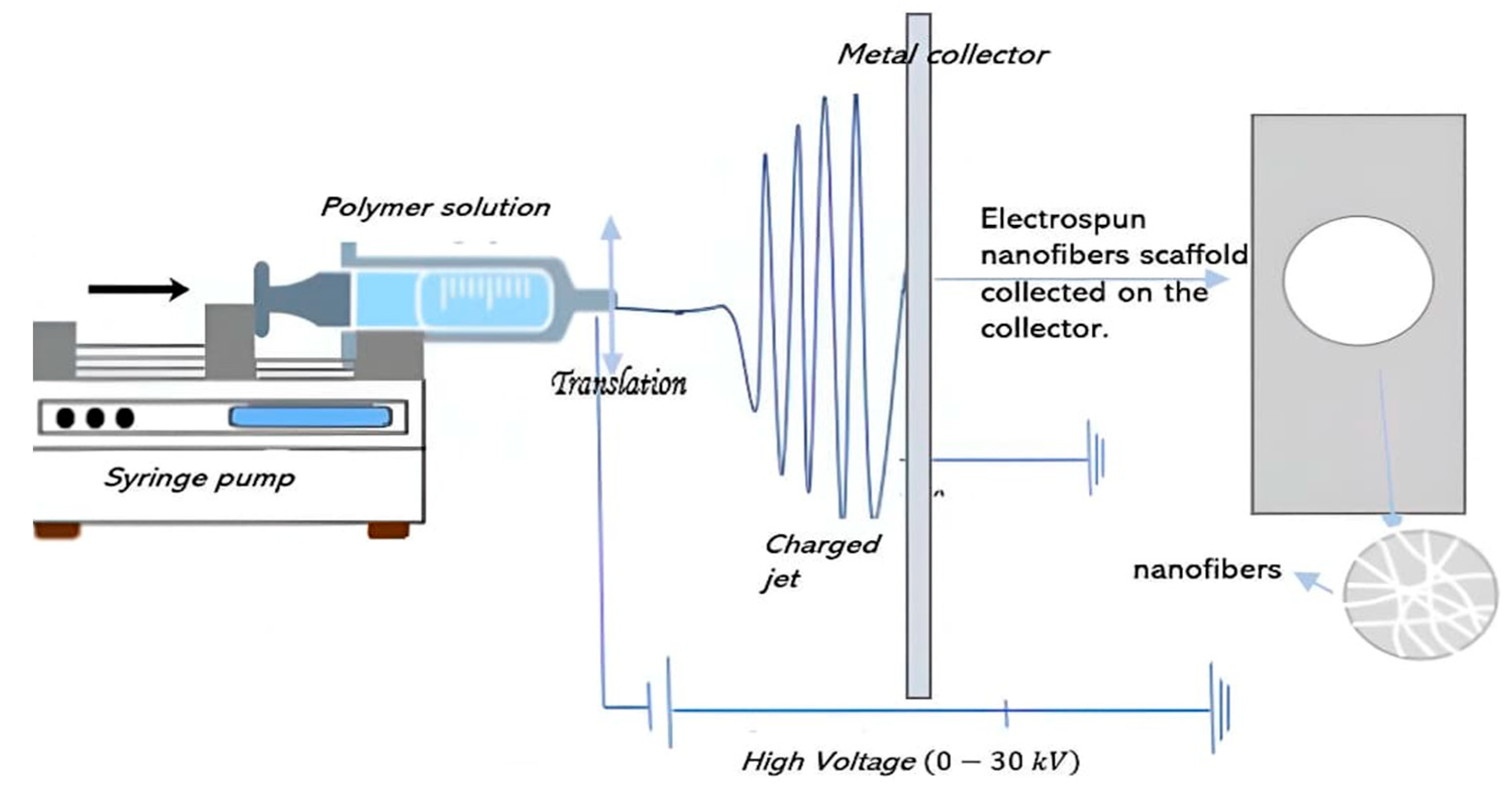
2. Fundamentals of Electrospinning
2.1. Principles of Electrospinning
2.2. Limitations of Conventional DC Electrospinning
3. Charge Generation and Transport in Electrospinning
3.1. Mechanisms of Charge Generation
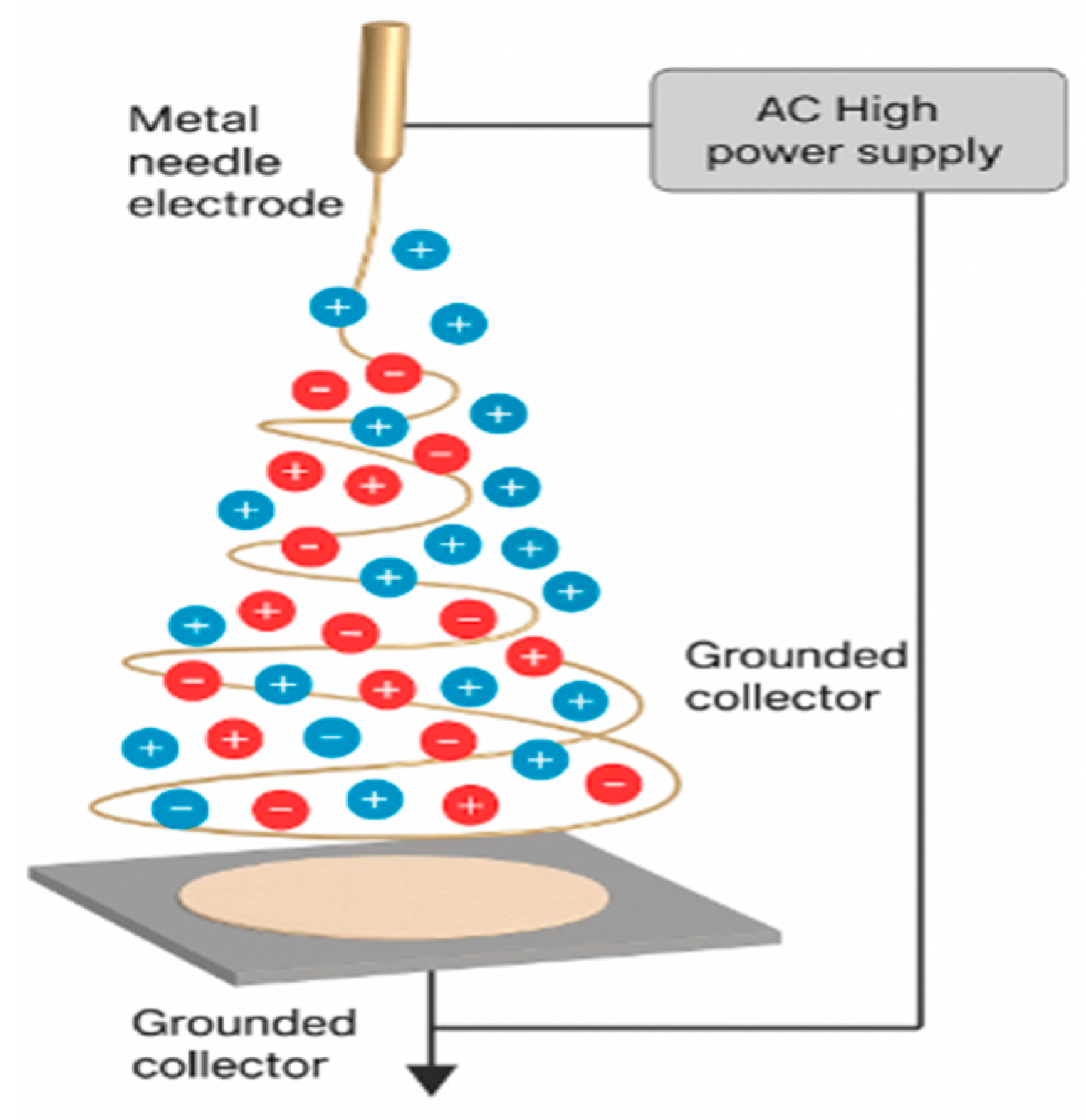
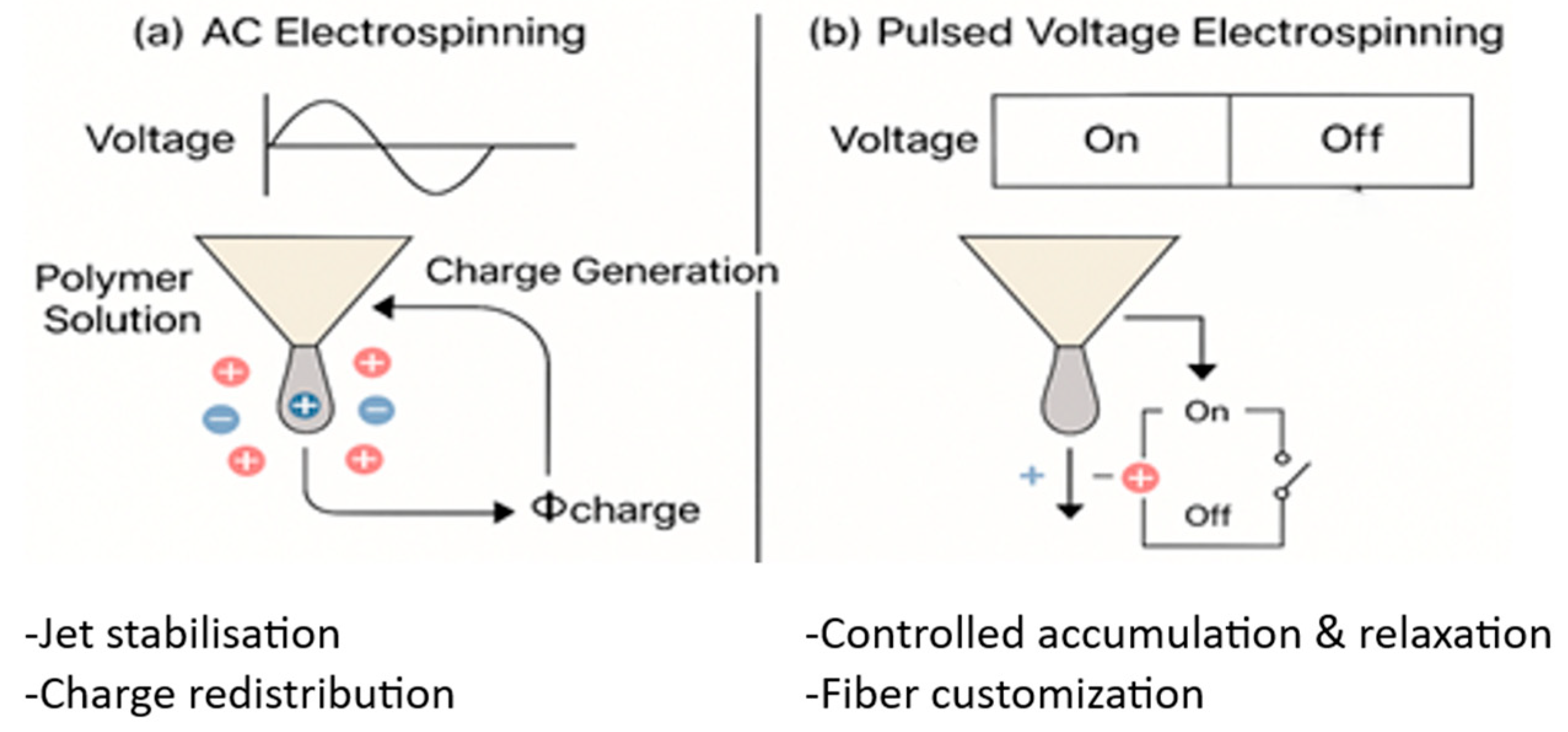
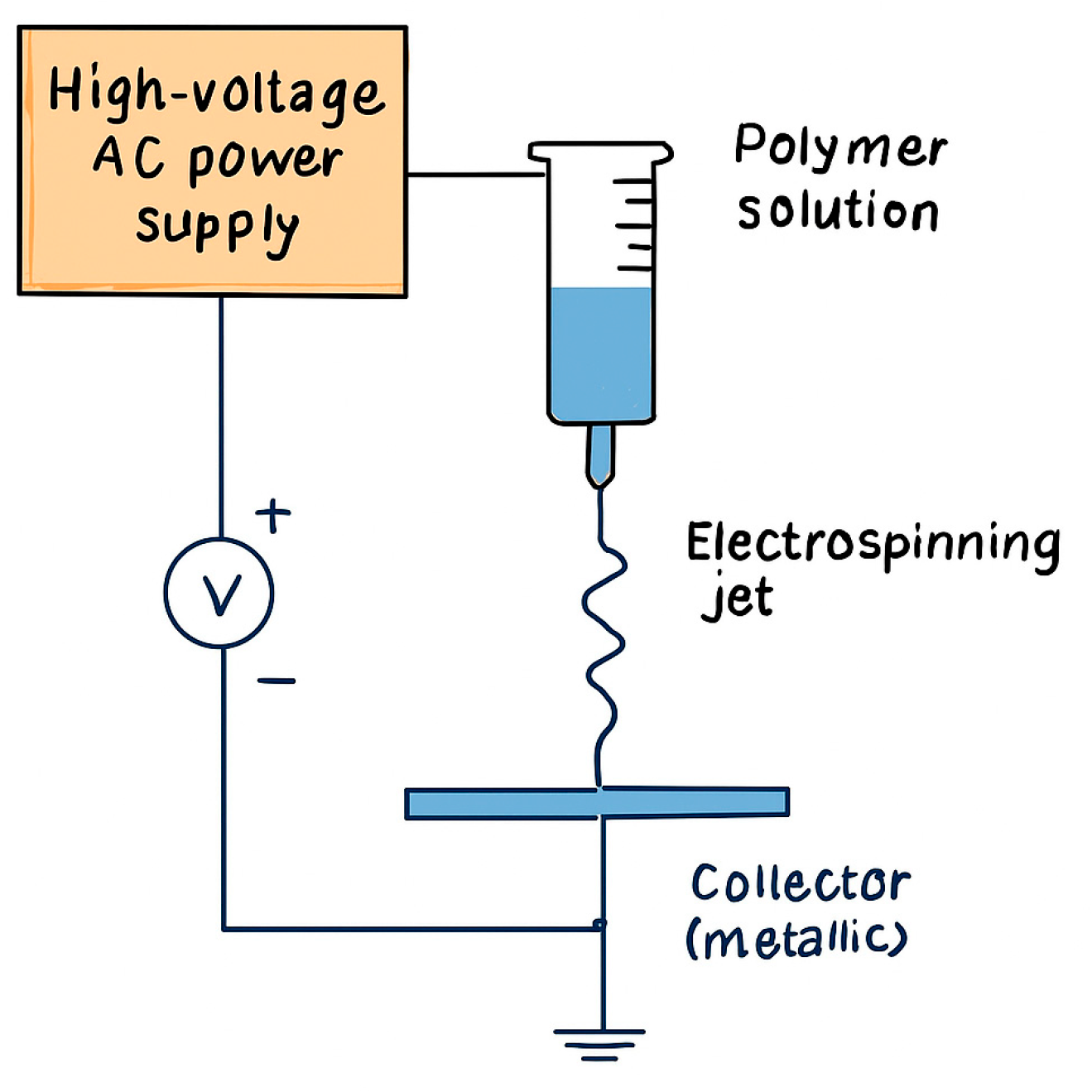
3.2. Charge Behavior in AC Electrospinning
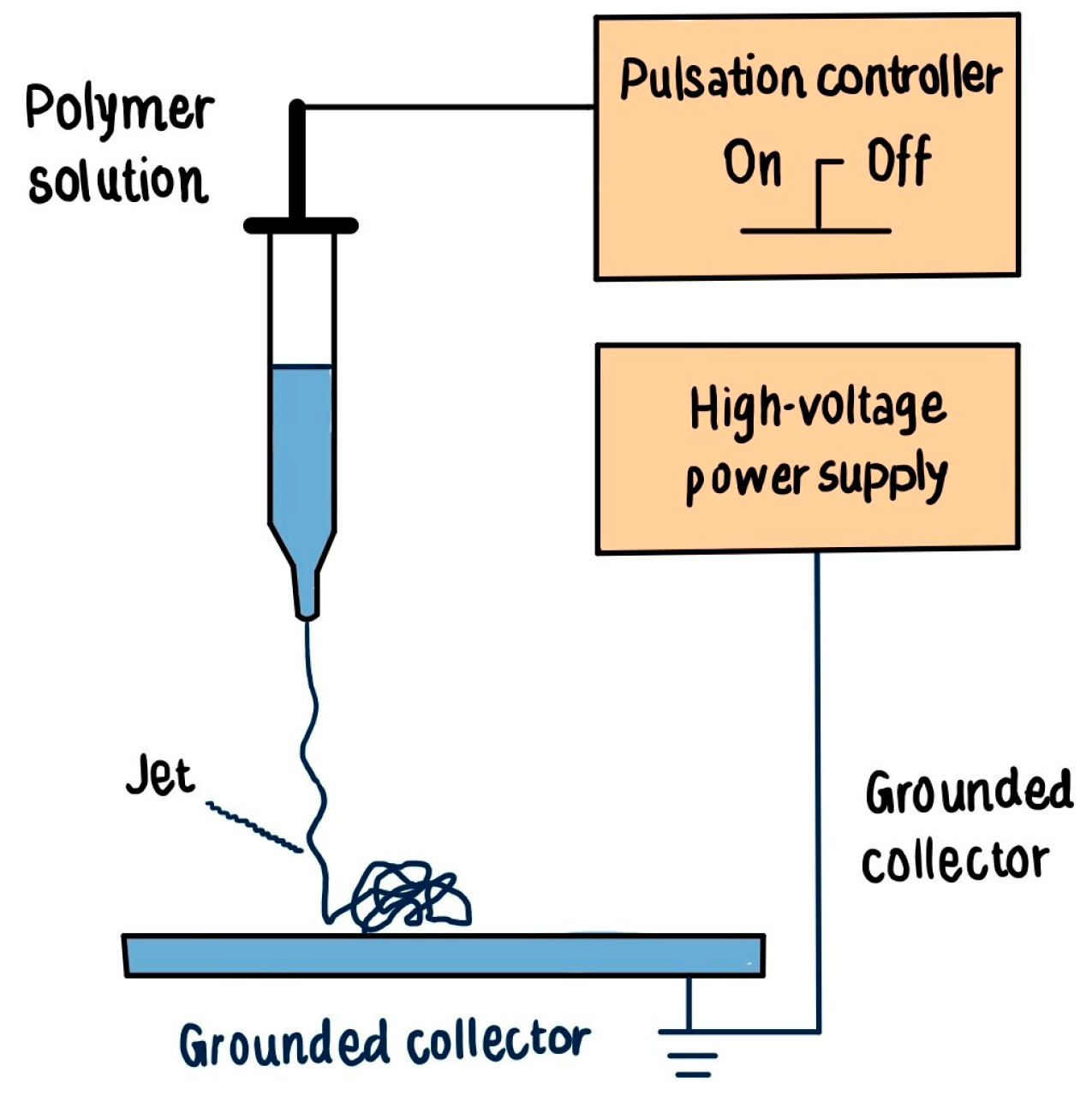
3.3. Charge Dynamics in Pulsed Voltage Electrospinning
4. Innovations in Electrospinning: AC and Pulsed Voltage Techniques
4.1. AC Electrospinning Mechanisms and Advantages
4.2. Pulsed Voltage Electrospinning: Controlled Precision
4.3. Factors Influencing Fiber Morphology
4.4. Comparative Advantages and Application Outlook
5. Quantitative Performance Metrics and Efficiency Analysis
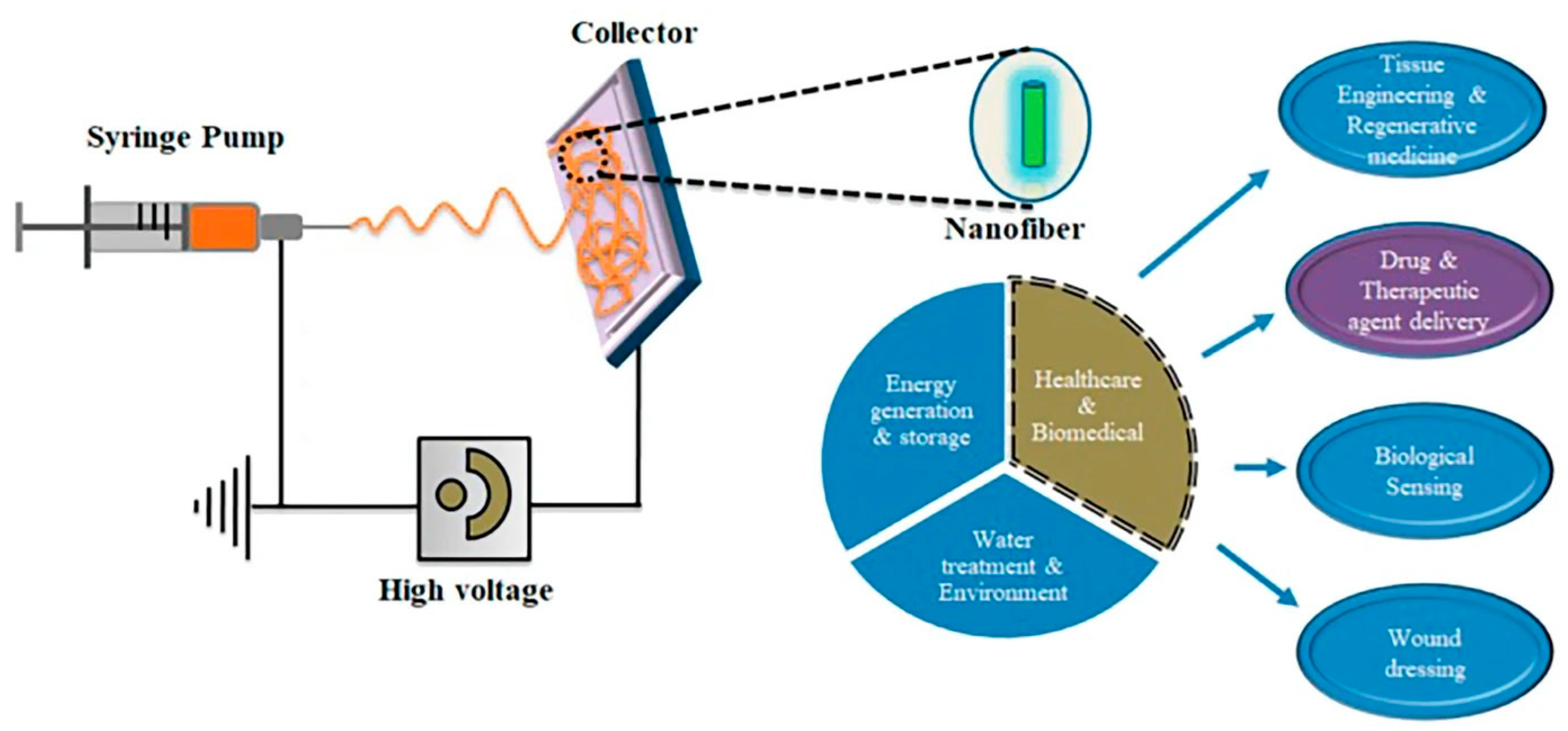
6. Applications of AC and Pulsed Voltage Electrospun Nanofibers
6.1. Biomedical Applications
6.2. Filtration and Protective Materials
6.3. Sensors and Wearables
6.4. Energy Storage and Conversion
6.5. Environmental and Agricultural Uses
7. Challenges, Limitations, and Future Outlook
7.1. Technical Challenges
7.2. Material Compatibility and Process Stability
7.3. Standardization and Modeling Gaps
7.4. Future Outlook
- AI-assisted process control: Integrating machine learning with real-time imaging and sensor data to dynamically tune pulse/AC parameters for defect-free fiber production.
- Scalable multi-nozzle systems: Designing multi-spinneret AC or PV platforms with synchronized control to maintain throughput without compromising fiber uniformity.
- Green solvents and biopolymers: Developing material systems that are compatible with non-toxic, environmentally friendly solvents under AC and PV conditions.
- Hybrid techniques: Combining AC or pulsed fields with magnetic, acoustic, or thermal fields to improve jet guidance, fiber alignment, or functionalization [53].
- Standardization initiatives: Establishing common metrics and test protocols to enable the reproducibility and industry certification of electrospun materials.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, S.; Fujihara, K.; Teo, W.E.; Yong, T.; Ma, Z.; Ramaseshan, R. Electrospun Nanofibers: Solving Global Issues. Mater. Today 2006, 9, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Electrospinning: A Fascinating Method for the Preparation of Ultrathin Fibers. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5670–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaengl, W.S.; Kuffel, E. High Voltage Engineering Fundamentals, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Stracqualursi, E.; Araneo, R.; Pozio, A.; Rinaldi, A.; Hein, L.A. Assessment of the Electrostatic Field Uniformity Within an Electrospinning Device. In Proceedings of the 24th EEEIC International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 8th I and CPS Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe, EEEIC/I and CPS Europe 2024, Rome, Italy, 17–20 June 2024; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, S.; Chetwani, N.; Hsueh-Chia, C. Alternating Current Electrospraying. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 9358–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cselko, R.; Pozman, R.A.; Szekely, L. Electrospinning with Non-DC Voltages. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference, EIC 2023, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 18–21 June 2023; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, S.; Abbas, Z.; Zhao, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, D. Nib-Assisted Coaxial Electrohydrodynamic Jet Printing for Nanowires Deposition. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.; Federici, J.; Imura, Y.; Catalani, L.H. Charge Generation, Charge Transport, and Residual Charge in the Electrospinning of Polymers: A Review of Issues and Complications. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 044701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessick, R.; Fenn, J.; Tepper, G. The Use of AC Potentials in Electrospraying and Electrospinning Processes. Polymer 2004, 45, 2981–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanishevsky, A. Electrospinning Using AC Electric Fields. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2025, e2400907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalous, T.; Pokorný, P.; Lukáš, D.; Sanetrník, F. Electric Wind Phenomena During AC Colectorless Electrospinning; Tanger Ltd.: Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sivan, M.; Madheswaran, D.; Valtera, J.; Kostakova, E.K.; Lukas, D. Alternating Current Electrospinning: The Impacts of Various High-Voltage Signal Shapes and Frequencies on the Spinnability and Productivity of Polycaprolactone Nanofibers. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Roh, S.; Nguyen, M.T.N.; Lee, J.S. Structural Control of Nanofibers According to Electrospinning Process Conditions and Their Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Xie, G.; Kang, J.; He, H.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y. Solution Electrospinning with a Pulsed Electric Field. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirek, A.; Korycka, P.; Grzeczkowicz, M.; Lewińska, D. Polymer Fibers Electrospun Using Pulsed Voltage. Mater. Des. 2019, 183, 108106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, G.; Stracqualursi, E.; Araneo, R.; Pozio, A.; Rinaldi, A.; Hein, L.A. 3D FEM Simulation of Electrospinning Machine for the Study of Full-Scale Electrostatic Field on the Electrohydrodynamic Process. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Environment and Electrical Engineering and 2023 IEEE Industrial and Commercial Power Systems Europe, EEEIC/I and CPS Europe 2023, Madrid, Spain, 6–9 June 2023; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Gao, L.; Xu, L. The Mechanism of Electrospinning Device. Mech. Eng. 2021, 43, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending Instability of Electrically Charged Liquid Jets of Polymer Solutions in Electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, G.; Dmitriev, R.I.; Tyagi, V.; Jenkins, J.; Rotaru, G.M.; Rottmar, M.; Rossi, R.M.; Toncelli, C.; Papkovsky, D.B.; Maniura-Weber, K.; et al. Steering Surface Topographies of Electrospun Fibers: Understanding the Mechanisms. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, P.; Kyu, T. Dynamics and Morphology Development in Electrospun Fibers Driven by Concentration Sweeps. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Wycisk, R.; Pintauro, P. Electrospun Composite Proton-Exchange and Anion-Exchange Membranes for Fuel Cells. Energies 2021, 14, 6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, M.G.; Wilkes, G.L.; Colby, R.H.; Long, T.E. Correlations of Solution Rheology with Electrospun Fiber Formation of Linear and Branched Polyesters. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Study on Relationship between Jet Instability and Formation of Beaded Fibers during Electrospinning. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro De Prá, M.A.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R.M.; Maraschin, M.; Veleirinho, B. Effect of Collector Design on the Morphological Properties of Polycaprolactone Electrospun Fibers. Mater. Lett. 2017, 193, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromager, B.; Marhuenda, E.; Louis, B.; Bakalara, N.; Cambedouzou, J.; Cornu, D. Recent Advances in Electrospun Fibers for Biological Applications. Macromol. 2023, 3, 569–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgie, J.R.P.; Leclinche, F.; Dréan, E.; Dolez, P.I. Electrospinning of High-Performance Nanofibres: State of the Art and Insights into the Path Forward. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Steckl, A.J. Coaxial Electrospinning Formation of Complex Polymer Fibers and Their Applications. Chempluschem 2019, 84, 1453–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.; Trendafilova, I. A Novel Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Electrospun Nanofibers and Its Application as a Self-Powered Nanosensor. In Nanosensors for Smart Cities; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 117–128. ISBN 9780128198704. [Google Scholar]
- Bazbouz, M.B.; Taylor, M.; Baker, D.; Ries, M.E.; Goswami, P. Dry-Jet Wet Electrospinning of Native Cellulose Microfibers with Macroporous Structures from Ionic Liquids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L. Electrospinning Jets and Polymer Nanofibers. Polymer 2008, 49, 2387–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulichikhin, V.G.; Skvortsov, I.Y.; Subbotin, A.V.; Kotomin, S.V.; Malkin, A.Y. A Novel Technique for Fiber Formation: Mechanotropic Spinning-Principle and Realization. Polymers 2018, 10, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, S.; Zhou, G.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Jing, X. Electrospinning of Polymeric Nanofibers for Drug Delivery Applications. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak, A.; Grzeczkowicz, M.; Lewińska, D. The Effects of Pulsed Electrospinning Process Variables on the Size of Polymer Fibers Established with a 23 Factorial Design. Polymers 2024, 16, 2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Deevi, S.; Tepper, G. Biased AC Electrospinning of Aligned Polymer Nanofibers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, B.; Balogh, A.; Farkas, A.; Marosi, G.; Nagy, Z.K. Frequency and Waveform Dependence of Alternating Current Electrospinning and Their Uses for Drug Dissolution Enhancement. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 586, 119593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial Upscaling of Electrospinning and Applications of Polymer Nanofibers: A Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.V.; Jose, R.; Teng, T.H.; Chowdari, B.V.R.; Ramakrishna, S. Preparation and Electrochemical Studies of Electrospun TiO2 Nanofibers and Molten Salt Method Nanoparticles. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mori, A.; Fernández, M.P.; Blunn, G.; Tozzi, G.; Roldo, M. 3D Printing and Electrospinning of Composite Hydrogels for Cartilage and Bone Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2018, 10, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Burbery, N.J. Trends and Developments in the Manufacturing of Polymer Nanofibrils with the Electrospinning Technique. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 446–447, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Ghayour, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Nur, H.; Berto, F. Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Biomedical and Tissue Engineering Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Materials 2020, 13, 2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriar, S.M.S.; Mondal, J.; Hasan, M.N.; Revuri, V.; Lee, D.Y.; Lee, Y.K. Electrospinning Nanofibers for Therapeutics Delivery. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, B.; Milazzo, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Berrettini, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Qin, Z.; Buehler, M.J.; Danti, S. Electrospinning Piezoelectric Fibers for Biocompatible Devices. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e1901287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, N.Z.; Kenawy, M.Y.; Taha, N.A.; Abd El-Latif, M.M.; Ghareeb, D.A. Cellulose Acetate Nanofibers: Incorporating Hydroxyapatite (Ha), Ha/Berberine or Ha/Moghat Composites, as Scaffolds to Enhance in Vitro Osteoporotic Bone Regeneration. Polymers 2021, 13, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonino, C.A.; Efimenko, K.; Jeong, S.I.; Krebs, M.D.; Alsberg, E.; Khan, S.A. Three-Dimensional Electrospun Alginate Nanofiber Mats via Tailored Charge Repulsions. Small 2012, 8, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hao, M.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Ramakrishna, S. A Review on Recent Advances in Application of Electrospun Nanofiber Materials as Biosensors. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Foroughi, J.; Peng, S.; Baughman, R.H.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, C.H. Advanced Energy Harvesters and Energy Storage for Powering Wearable and Implantable Medical Devices. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2404492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Lou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chen, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhong, S.; Wang, H.; Wu, L. Carbon Nanofibers Derived from Carbonization of Electrospinning Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) as High Performance Anode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Porous Mater. 2023, 30, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Zhan, C.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R. Structural Design and Environmental Applications of Electrospun Nanofibers. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2020, 137, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wałach, W.; Oleszko-Torbus, N.; Utrata-Wesołek, A.; Bochenek, M.; Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Górecka, Ż.; Święszkowski, W.; Dworak, A. Processing of (Co)Poly(2-Oxazoline)s by Electrospinning and Extrusion from Melt and the Postprocessing Properties of the (Co)Polymers. Polymers 2020, 12, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, S.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B.-T.; Wang, S. Magnetically Separable and Recyclable Lanthanum/Iron Co-Modified Attapulgite: A Sustainable Option to Efficiently Control Phosphate Loading. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 348, 131294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, I.Y.; Huang, R. Application of Different Waveforms of Pulsed Current in the Classical Electro-Cocatalytic Process for Effective Removal of Sulfamethoxazole: Oxidation Mechanisms. Catalysts 2024, 14, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinen, J.; Schavikin, J.; Osterberg, H.; Valoppi, F.; Nikolaev, D.; Laidmae, I.; Heinamaki, J.; Salmi, A.; Haeggstrom, E. The Role of Acoustic Streaming in Ultrasound-Enhanced Electrospinning—A FEM Simulation Study. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, IUS, Venice, Italy, 10–13 October 2022; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shabani, A.; Al, G.A.; Berri, N.; Castro-Dominguez, B.; Leese, H.S.; Martinez-Hernandez, U. Electrospinning Technology, Machine Learning, and Control Approaches: A Review. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 27, 2401353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Ding, Y.; Duan, Y.; Su, J.; Yin, Z.; Huang, Y.A. Large-Scale Direct-Writing of Aligned Nanofibers for Flexible Electronics. Small 2018, 14, e1703521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Optimal Range/Value | Effect on Electrospinning |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity | 0.1–2.0 Pa·s | Stable jet, smooth fibers prevents beads and clogging |
| Conductivity | 10–1000 µS/cm | Enhanced jet stretching, thinner fibers, and very high conductivity cause instability |
| Surface Tension | 20–40 mN/m | Facilitates jet initiation; balance needed to avoid beads |
| Temperature | 20–25 °C | Controls evaporation rate; influences fiber diameter and morphology |
| Relative Humidity | 30–50% | Affects fiber porosity and drying; high RH increases porosity |
| Parameter | DC Electrospinning | AC Electrospinning | Pulsed Voltage Electrospinning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Field Type | Constant | Alternating | Pulsed (intermittent) |
| Typical Fiber Yield | 2–4 g/h | Up to 23.6 g/h | Moderate (pulse-dependent) |
| Fiber Morphology Control | Moderate | High (alignment, porosity) | Very high (diameter, porosity) |
| Bead Formation | Common | Reduced | Greatly reduced |
| Jet Stability | Low | High | High |
| Collector Requirement | Conductive | Collectorless possible | Conductive or time-synced |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate | High | High |
| Application Suitability | General purpose | Biomedical, textiles, filtration | Drug delivery, sensors, precision use |
| Fiber Alignment | Poor to moderate | Excellent | Good to excellent |
| Diameter Variability | High | Low | Very low |
| Scalability | High (allows multiple jets) | Moderate (limited by pulse rate and jet re-initiation time) | Moderate (limited by single-jet setup and inter-jet interference in multi-needle systems) |
| System Complexity | Higher (requires waveform generators and high frequency AC power supplies) | Moderate (requires pulse generator and switching circuit | Low(simple HV power supply, widely available) |
| Application Suitability | Filtration, aligned fiber mats, large scale scaffolds | Drug delivery, segmented fibers | Biomedical scaffolds, drug delivery, filtration membranes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Saif, Y.; Cselkó, R. Revolutionizing Electrospinning: A Review of Alternating Current and Pulsed Voltage Techniques for Nanofiber Production. Processes 2025, 13, 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072048
Al Saif Y, Cselkó R. Revolutionizing Electrospinning: A Review of Alternating Current and Pulsed Voltage Techniques for Nanofiber Production. Processes. 2025; 13(7):2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072048
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Saif, Yasir, and Richárd Cselkó. 2025. "Revolutionizing Electrospinning: A Review of Alternating Current and Pulsed Voltage Techniques for Nanofiber Production" Processes 13, no. 7: 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072048
APA StyleAl Saif, Y., & Cselkó, R. (2025). Revolutionizing Electrospinning: A Review of Alternating Current and Pulsed Voltage Techniques for Nanofiber Production. Processes, 13(7), 2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13072048








