Abstract
The phase transformation of fayalite from copper slag during oxidation roasting was systematically studied in this work with an analysis using X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometer, scanning electronic microscope, and energy dispersive spectrometer. The results show that the oxidation of fayalite occurs at ≥300 °C. Fayalite is first oxidized into amorphous Fe3O4 and SiO2 during oxidation roasting. The former then converts into Fe2O3 while the latter converts into cristobalite solid solution with increasing temperature. Meanwhile, the specific saturation magnetization of roasted products increases from 9.43 emu/g at 300 °C to 20.66 emu/g at 700 °C, and then decreases to 7.31 emu/g at 1100 °C. The migration of iron in fayalite is prior to that of silicon during oxidation roasting. Therefore, the thickness of the iron oxide layer on the particle surface steadily increases with roasting temperature, from about 1.0 μm at 800 °C to about 5.0 μm at 1100 °C. This study has guiding significance for the iron grain growth in copper slag during the oxidation-reduction roasting process.
1. Introduction
The demand for metal copper worldwide has steadily increased in recent decades, and may reach about 28.5 million tons in 2030 [1]. However, more than 80% of metal copper is produced from copper concentrate (e.g., chalcopyrite (CuFeS2), bornite (Cu5FeS4) and chalcocite (Cu2S)) by pyrometallurgy, in which the main products are metal copper and copper slag. According to the statistics, the production of copper slag is 2.0–3.0 times that of metal copper, meaning that about 40 million tons of copper slag is generated annually in the world [2,3,4]. The large-scale disposal of copper slag still focuses on the raw material of cement, the output of which has been decreasing year by year. Other applications of copper slag are not realized due to the immaturity of resource utilization technology and the difficulty of comprehensive recovery of valuable metals. The treatment of stockpiling not only occupies a large amount of land, but also causes pollution in the surrounding environment for the presence of Zn, Pb, Cu, et al. Therefore, the utilization of copper slag has become particularly urgent.
Considering that fayalite and magnetite are the main minerals, iron extraction becomes one of the research directions for the resource utilization of copper slag. The magnetite in copper slag can be selectively enriched by grinding, followed by magnetic separation. However, the obtained concentrate has low iron content and low iron recovery, and the presence of Zn hinders the utilization of concentrate as a raw material for ironmaking [5]. If the temperature of melting copper slag further increases, the iron in the copper slag can be reduced into liquid iron in a reducing atmosphere [6]. Meanwhile, the silicon is removed as slag by reacting with calcium oxide. However, high-energy consumption hinders its industrialized application. Through reduction roasting, the fayalite and magnetite in copper slag can be reduced into metallic iron, while Zn and Pb are enriched in the dust. After that, the metallic iron is enriched by magnetic separation. Large amounts of additives, such as calcium salts and sodium salts, should be added during reduction roasting to increase the iron grain size in reduced products [7,8,9]. This method has the drawback of generating a large amount of magnetic tailing because of the unrecyclable additives. Thus, attention should also be paid to the subsequent treatment of slag or tailing when realizing the high value utilization of copper slag for recovering valuable metals.
The authors proposed a new method for iron extraction from copper slag using additive-free activation roasting-magnetic separation and realizing the near-zero waste discharge from CS. The obtained concentrate is a raw material for electric furnace steelmaking and tailing for cement production [10]. The core of this method is iron oxide migration during oxidation roasting and metallic iron aggregation during the subsequent reduction roasting, resulting in the growth of iron grain without additives. Ultimately, the metallic iron can be efficiently recovered through magnetic separation. However, there has been a lack of systematic research on the oxidation behavior of fayalite in copper slag. Gaballah et al. [11] focused on the oxidation kinetics of fayalite during roasting in air, and found that hematite whiskers were formed on the particle surface in the roasted products. Gyurov et al. [12] studied the isothermal oxidation kinetics of copper slag in synthetic air for converting fayalite into ferrous and silicate phases suitable for resources to be recovered. Li et al. [13] tried to convert the fayalite in copper slag to magnetite and free silica through roasting in vapor, and the separation between iron oxide and silica was realized by alkaline leaching.
The previous studies focus on the oxidation kinetics or separation between iron and silicon, ignoring the phase transformation and iron migration of fayalite during oxidation roasting. However, Liu et al. [14] studied the multiphase transformation of copper slag during oxidation roasting at 750–1050 °C with the analysis methods of X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The phase transformation of fayalite during oxidation roasting at a low temperature is still not clear, especially on the amorphous intermediate products, and there has also been a lack of systematic research on iron migration. New analysis methods of synchrotron-based X-ray imaging, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), and so on, have demonstrated great potential for studying phase growth [15,16]. Therefore, thermogravimetry (TG), XRD, XPS, and VSM were used to investigate the phase transformation of fayalite from copper slag in this work, while iron migration was studied using SEM and the energy dispersion spectrum (EDS).
2. Experimental
2.1. Raw Material
In order to study the phase transformation of fayalite during oxidation roasting, the copper slag was treated by magnetic separation to remove magnetite, and the obtained magnetic tailing (−200 mesh 91.56%) was the raw material in this work. There is 42.72% Fe, 35.55% SiO2, 1.56% Zn, 0.22% Pb, 1.15% Al2O3, 0.86% CaO, and 0.31% Cu in the fayalite from copper slag. The XRD pattern of fayalite from copper slag is shown in Figure 1, in which fayalite is the main mineral together with small amount of cristobalite. The presence of cristobalite may be caused by the smelting process of copper. The other minerals cannot be detected in the XRD pattern due to the low content or poor crystallinity. Therefore, the fayalite from copper slag treated by magnetic separation has good purity, and can be used to study the phase transformation of fayalite during oxidation roasting.
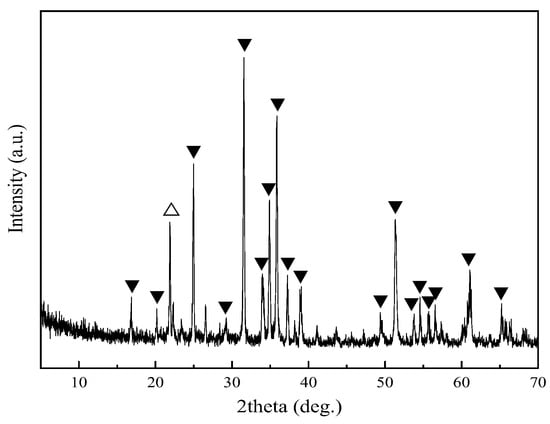
Figure 1.
XRD pattern of fayalite from copper slag. ▼—fayalite; △—cristobalite.
The SEM-EDS of fayalite from copper slag is shown in Figure 2. From the EDS analysis, the distribution of the Fe element was consistent with that of the Si element, meaning that fayalite is the main mineral. Furthermore, the independent silica particle with dark gray could be found in the fayalite from copper slag. This finding further confirms the presence of cristobalite in fayalite from copper slag, together with the phase analysis in Figure 1.
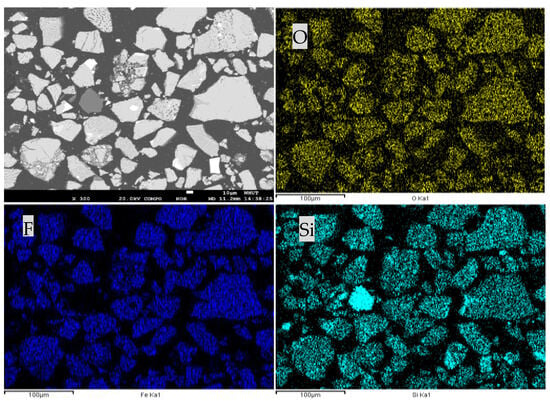
Figure 2.
SEM-EDS of fayalite from copper slag.
2.2. Procedures
A total of 5 g of fayalite from copper slag was evenly placed on a corundum crucible lid with 5 mm × 5 mm. Then, the corundum crucible lid was heated in a thermostatic muffle furnace (SX2-16-13A, Yingshan Dianlu Co., Ltd., Yingshan, Hubei, China) at a preset temperature for 60 min. Air with a velocity of 600 mL/min was introduced into the thermostatic muffle furnace to promote the oxidation of fayalite. After that, the corundum crucible lid was taken out of the thermostatic muffle furnace and cooled to room temperature. Ultimately, the roasted products of fayalite from copper slag were obtained and put into a sealed bag for the purposes of subsequent analysis.
2.3. Analyses
An X-ray diffractometer (MAX–RB, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) was used to analyze the phase composition of fayalite and its roasted products, with the experiment parameters of 2 theta (degree) interval 10°–70°, scanning speed 5 °/min, and step size 0.02. Furthermore, the phase analysis was performed using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Thermo ESCALAB 250XI, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). A scanning electronic microscope (JXA–8230, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) together with an energy dispersive spectrometer (INCA X–Act, Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, UK) were selected to analyze the microstructure of fayalite and its roasted products. In order to increase the electrical conductivity of the samples, the fayalite or its roasted product was first fixed into the mixture of epoxy resin and triethanolamine, then polished using a metallographic sample polishing machine (MP-2B, Dongguan Zhongte Precision Instrument Co., Ltd., Dongguan, China) before being coated with C. A vibrating sample magnetometer (HH-20, Nanjing Nanda Instrument Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) was used to analyze the magnetic intensities of the roasted products of fayalite from copper slag. Wet sieving and an atomic absorption spectrometer (CONTRAA–700, Analytik Jena AG, Jena, Germany) were used to analyze the particle size and chemical composition of fayalite from copper slag. A thermal analyzer (SDTQ600, TA Instruments, New Castle, DE, USA) was used for the thermo-gravimetric (TG) analysis of fayalite from copper slag, with the experiment parameters of air velocity 100 mL/min, heating rate 10 K/min, and temperature interval 25 °C to 1100 °C.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermal Analysis of Fayalite
The TG curve of fayalite from copper slag was shown in Figure 3. When roasting temperature increases from 25 °C to 300 °C, the mass decreases by 0.37%, which is caused by the dehydration. After that, the mass steadily increases with roasting temperature, meaning the conversion of fayalite into iron oxide and silica through reaction with oxygen in air. By comparison, it can be seen that the increasing rate of mass in the temperature interval of 800 °C to 1040 °C is significantly higher than that in the temperature interval of 300 °C to 800 °C. Therefore, elevated temperature benefits the oxidation of fayalite from copper slag. The maximum increase in mass reaches 4.39% at the temperature of 1040 °C, meaning the full oxidation of fayalite from copper slag is realized. Therefore, fayalite can be easily oxidized into iron oxide and silica through oxidation roasting.
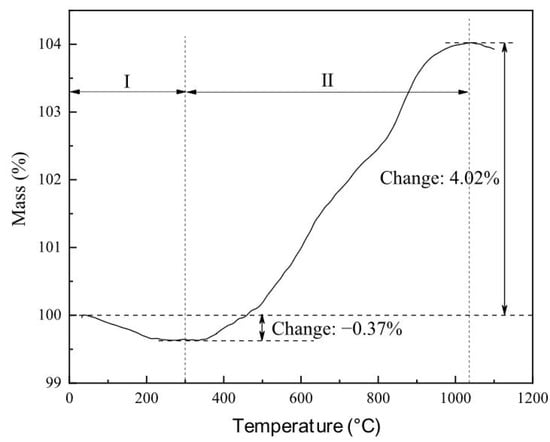
Figure 3.
TG curve of fayalite from copper slag. I—dehydration process; II—oxidation process.
3.2. Phase Transformation of Fayalite
In order to systematically study the phase transformation of fayalite, the fayalite from copper slag was treated by oxidation roasting from 300 °C to 1100 °C at intervals of 100 °C, and the phase composition of roasted products were shown in Figure 4. Compared with the XRD pattern of fayalite from copper slag shown in Figure 1, the XRD pattern of roasted product obtained at 300 °C has no significant change in the main minerals of fayalite and cristobalite. The diffraction peak intensity of fayalite decreases as the roasting temperature increases from 400 °C to 600 °C, while that of cristobalite increases due to its good crystallinity. When the roasting temperature reaches 700 °C, the diffraction peaks of hematite are detected, meaning fayalite is oxidized into hematite and silica. Only the diffraction peaks of hematite and cristobalite can be found in the XRD pattern of roasted product obtained at 800 °C, meaning the full decomposition of fayalite is realized. After that, the diffraction peak intensity of hematite and cristobalite increases with the roasting temperature. The change in the former is caused by the improving crystallinity, while that of the latter can be explained by the formation of cristobalite solid solution [17,18]. Furthermore, the diffraction peaks of magnetite are found in the roasted product obtained at 1000 °C and 1100 °C. During roasting at high temperature, the iron in fayalite migrates to the particle surface and forms a hematite layer (Section 3.4), which hinders any further reaction between oxygen and fayalite inside the particle. Thus, fayalite converts into magnetite and silica under low oxygen pressure.
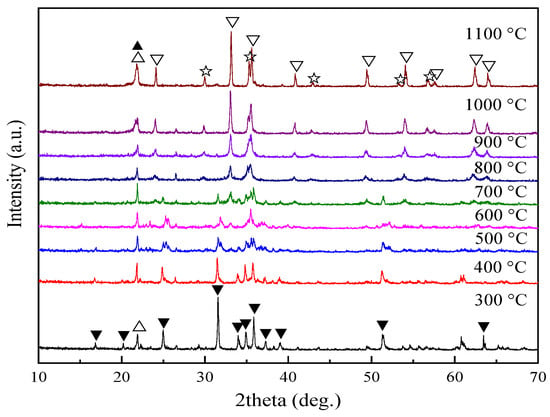
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of roasted products. ▼—fayalite; △—cristobalite; ▽—hematite; ☆—magnetite; ▲—cristobalite solid solution.
XPS was further used to analyze the phase composition of roasted products, and the results were shown in Figure 5. The high resolution of Fe 2p is shown in Figure 5a, in which the peaks located at 709.14 eV (Fe 2p3/2) and 722.25 eV (Fe 2p1/2) show the presence of Fe2SiO4, together with additional satellite peaks located at 715.45 eV [19]. The presence of Fe3O4 can be explained with the peaks located at 710.41 eV (Fe 2p3/2) and 724.01 eV (Fe 2p1/2), together with additional satellite peaks located at 718.6 eV [20]. The presence of Fe2O3 is due to the peaks located at 712.25 eV (Fe 2p3/2) and 726.03 eV (Fe 2p1/2), together with additional satellite peaks located at 718.72 eV [21,22]. Only fayalite and magnetite can be found in the roasted products obtained from 300 °C to 500 °C, and the peak intensity of magnetite increases with temperature. At a low temperature, fayalite can be oxidized into magnetite. When the roasting temperature reaches 600 °C to 700 °C, hematite can also be found apart from fayalite and magnetite, meaning magnetite is further oxidized into hematite. Only magnetite and hematite can be found in the roasted products obtained at ≥800 °C. The peak intensity of hematite increases with temperature, while that of magnetite decreases. That is, elevated temperature promotes the conversion of magnetite into hematite.
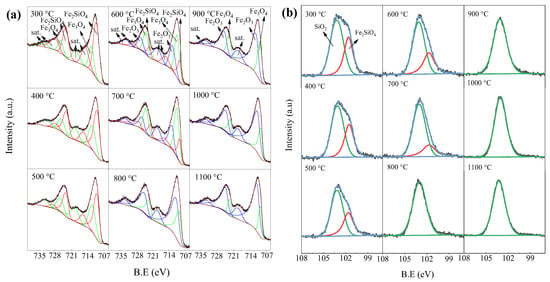
Figure 5.
XPS patterns of roasted products: (a) high resolution of Fe 2p; (b) high resolution of Si 2p.
The high resolution of Si 2p is shown in Figure 5b, in which the peaks located at 101.7 eV and 103.7 eV show the presence of Fe2SiO4 and SiO2, respectively [23,24]. Only fayalite and silica can be found in the roasted products obtained at 300 °C. The peak intensity of fayalite steadily decreases with roasting temperature, while that of silica increases. Therefore, elevated temperature benefits the decomposition of fayalite. There is no fayalite in the roasted products obtained at ≥800 °C, meaning the fayalite has been fully converted. It should be noted that magnetite and silica, which are not found in Figure 4, can be detected through XPS, as shown in Figure 5, verifying the presence of amorphous phases during the oxidation roasting of fayalite at a low temperature.
The content of Fe-bearing minerals in roasted products was calculated according to Figure 5a, and the results were listed in Table 1. The content of fayalite steadily decreases with roasting temperature from 82.93% at 300 °C to 15.92% at 700 °C, and then reaches zero at ≥800 °C. The content of magnetite shows a trend of increasing first and then decreasing, from 17.07% at 300 °C to 50.79% at 700 °C, then to 19.21% at 1100 °C. There is no hematite in the roasted products obtained at ≤500 °C, but the content of hematite shows an increasing trend with temperature, from 31.78% at 600 °C to 80.79% at 1100 °C. Therefore, fayalite decomposes into magnetite during oxidation roasting at low temperature. Furthermore, magnetite is oxidized into hematite at a high temperature. The phase transformation of iron-bearing minerals during oxidation roasting of fayalite agrees with what was previously reported [14], but the decomposition of fayalite occurs at a low temperature.

Table 1.
The content of Fe-bearing minerals in roasted products.
3.3. Magnetic Transformation of Roasted Products
When fayalite, which has a moderate magnetic property, decomposes into ferromagnetic magnetite, its magnetic property will change significantly. Therefore, the roasted products of fayalite from copper slag were analyzed by VSM to investigate the magnetic transformation, and the results were shown in Figure 6. It seems that the magnetic hysteresis loop varies with the phase composition in roasted products. From Table 1, the main minerals are fayalite and magnetite in the roasted product obtained at 300 °C and 500 °C, while they are fayalite, magnetite and hematite in the roasted product obtained at 700 °C. When the roasting temperature reaches ≥900 °C, only magnetite and hematite can be found in the roasted products. In addition, the demagnetization of magnetite is different from that of fayalite and hematite, due to their specific magnetic property. Magnetite is a type of strong magnetic mineral, while fayalite and hematite are weak magnetic minerals. As shown in Figure 6f, the specific saturation magnetization of roasted products increases from 9.43 emu/g at 300 °C to 20.66 emu/g at 700 °C, and then decreases to 7.31 emu/g at 1100 °C. This variation can be explained by the content of magnetite roasted products, as listed in Table 1. The specific saturation magnetization of roasted products agrees well with the phase composition, as found in Figure 5. Therefore, these results further confirm the formation of amorphous magnetite during oxidation roasting of fayalite at a low temperature.
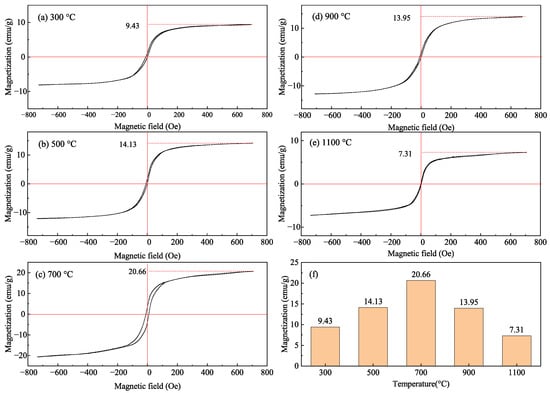
Figure 6.
The magnetic hysteresis loops (a–e) and specific saturation magnetization (f) of roasted products.
3.4. Microstructure Analysis of Roasted Products
The microstructure of roasted products was analyzed with SEM-EDS, and the results were shown in Figure 7 and Table 2. From the SEM images shown in Figure 7, there is no significant change in roasted products obtained at 400 °C and 600 °C. However, fayalite from copper slag was oxidized into iron oxide (magnetite and hematite) and silica at 300–600 °C, as found in Figure 5. That means the oxidation reaction only occurs on the particle surface, and the iron oxide layer is not formed. When the roasting temperature reaches 800 °C, a reaction layer with white color can be detected on the particle surface of fayalite from copper slag. The thickness of the reaction layer steadily increases with the roasting temperature, from about 1.0 μm at 800 °C to about 5.0 μm at 1100 °C.
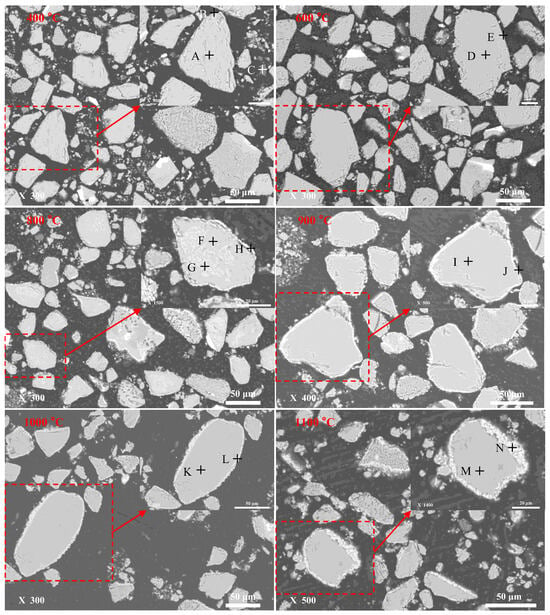
Figure 7.
SEM images of roasted products.

Table 2.
EDS analysis results of roasted products.
Combined with the EDS results listed in Table 2, there is no significant change in chemical composition from the positions of A–E. The main elements are Fe, O, and Si, together with a small amount of Zn, which exists in fayalite in the form of lattice substitution [25]. As the roasting temperature increases, the iron in fayalite migrates to the particle surface, because the main elements are Fe and O in the positions of J, L, and N. Meanwhile, the Fe content in positions of I, K, and M decreases. It should be noted that there is no Zn in the positions of J, L, and N, meaning that the Zn element does not migrate to the particle surface along with the Fe element during oxidation roasting. Therefore, elevated temperature promotes the decomposition of fayalite into iron oxide and silica, and the iron oxide can migrate to the particle surface.
3.5. Discussion of the Phase Transformation of Fayalite
According to the TG curve shown in Figure 3, fayalite from copper slag is stable during oxidation roasting at ≤350 °C. When the oxidation roasting temperature reaches 400 °C, fayalite decomposes into amorphous magnetite and silica, according to the XPS patterns shown in Figure 5 and the XRD patterns shown in Figure 4. Furthermore, the variation in the specific saturation magnetization of roasted products also confirms the formation of magnetite, as seen in Figure 6. The diffraction peaks of hematite are found in the roasted product obtained at 600 °C, as shown in Figure 4, meaning elevated temperature promotes the conversion of magnetite into hematite. The diffraction peak intensity of hematite steadily increases with roasting temperature. An iron oxide layer with thickness of about 1.0 μm is detected on the particle surface in the roasted product obtained at 800 °C, as shown in Figure 7, and its thickness increases with the roasting temperature to about 5.0 μm at 1100 °C. Therefore, the iron in fayalite can migrate to the particle surface during oxidation roasting at an elevated temperature. It should be noted that the diffraction peaks of cristobalite solid solution are found in the roasted product obtained at 1000 °C and 1100 °C, as shown in Figure 4, indicating the conversion of amorphous silica into cristobalite solid solution. Therefore, elevated temperature not only accelerates the decomposition of fayalite during oxidation roasting, but also promotes the migration of iron element in fayalite to the particle surface. In conclusion, fayalite decomposes first into amorphous silica and magnetite. The former converts into cristobalite solid solution as the oxidation temperature increases, while the latter converts into hematite. The iron oxide layer is formed on the particle surface of fayalite due to the iron migration, and its thickness steadily increases with the roasting temperature, from about 1.0 μm at 800 °C to about 5.0 μm at 1100 °C.
4. Conclusions
The phase transformation of fayalite from copper slag during oxidation roasting was systematically studied in this work, and the main findings were as follows:
- (1)
- During oxidation roasting, fayalite from copper slag first decomposes into amorphous magnetite and silica, then the former is oxidized into hematite while the latter converts into cristobalite solid solution as the temperature increases.
- (2)
- Elevated roasting temperature promotes the decomposition of fayalite into iron oxide and silica. Meanwhile, the iron oxide can migrate to the particle surface. The thickness of the iron oxide layer reaches about 5.0 μm in the roasted product obtained at 1100 °C.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.W.; Methodology: X.Z.; Software, Y.Z.; Validation, H.W. and Z.G.; Formal analysis, H.Z.; Investigation, H.Z. and X.W.; Resources, H.W.; Data curation, X.Z.; Writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; Writing—review and editing, Y.Z. and H.Z.; Visualization, Z.G.; Supervision, Z.G.; Project administration, H.W.; Funding acquisition, H.W. and X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially funded by the Scientific Research Foundation for High-level Talents of Anhui University of Science and Technology (2025yjrc0005; 2022yjrc25), Open Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Mineral Processing (BGRIMM-KJSKL-2024-08), and the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (GXXT-2022-083).
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions privacy. The data presented in this study are derived from a confidential project and can be obtained at the request of the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Elshkaki, A.; Graedel, T.E.; Ciacci, L.; Reck, B.K. Copper demand, supply, and associated energy use to 2050. Glob. Environ. Change 2016, 39, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Cao, S.; Li, Q.; Lu, X.; Liu, Z. Co-treatment of copper smelting slag and gypsum residue for valuable metals and sulfur recovery. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 183, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, T.C.; Singh, P.; Nikoloski, A.N. The potential for copper slag waste as a resource for a circular economy: A review—Part I. Miner. Eng. 2022, 180, 107474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G. Effective separation and recovery of valuable metals from copper slag: A comprehensive review. Environ. Res. 2025, 283, 122145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.Y.; Guo, Z.Q.; Pan, J.; Zhu, D.Q.; Yang, C.C.; Xue, Y.X.; Li, S.W.; Wang, D.Z. Comprehensive review on metallurgical recycling and cleaning of copper slag. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 168, 105366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Yan, D.; Xu, H. A new technology for copper slag reduction to get molten iron and copper matte. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2015, 22, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, L.; Shen, L. Growth behavior of iron grains during reduction roasting of fayalite. J. Sustain. Metall. 2024, 10, 2521–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pan, J.; Zhu, D.; Guo, Z.; Xu, J.; Chou, J. A novel process to upgrade the copper slag by direct reduction-magnetic separation with the addition of Na2CO3 and CaO. Powder Technol. 2019, 347, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.; Zhang, L.; Fu, W.; Wang, S.; Yin, W.; Chen, H. Mechanistic study on calcium ion diffusion into fayalite: A step toward sustainable management of copper slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, L. Iron extraction from copper slag by additive-free activation roasting–magnetic separation. Miner. Eng. 2024, 217, 108956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, I.; Elraghy, S.; Gleitzer, C. Oxidation kinetics of fayalite and growth of hematite whiskers. J. Mater. Sci. 1978, 13, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurov, S.; Kostova, Y.; Klitcheva, G.; Ilinkina, A. Thermal decomposition of pyrometallurgical copper slag by oxidation in synthetic air. Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. Study on mechanism of oxidation modification of copper slag. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 3223–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Multiphase transformation during process of copper slag calcination. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 44, 3159–3165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Du, W.; Cipicccia, S.; Bodey, A.; Rau, C.; Mi, J. Synchrotron X-ray operando study and multiphysics modelling of the solidification dynamics of intermetallic phases under electromagnetic pulses. Acta Mater. 2024, 265, 119593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Wan, M.; Yao, Z.; Hu, M. Heteroatom-doped carbon-based catalysts synthesized through a “Cook-Off” process for oxygen reduction reaction. Processes 2024, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, N.; Takahashi, H.; Ishida, S.; Horiie, F.; Wakamatsu, M. Mechanistic study of solid-state reaction between kaolinite and ferrous oxide at high temperatures. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 2000, 108, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, S. Separation of silicon and iron in copper slag by carbothermic reduction-alkaline leaching process. J. Cent. South Univ. 2020, 27, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Kim, Y.; Bae, S. Advances in Fe-modified lignocellulosic biochar: Impact of iron species and characteristics on wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 395, 130332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassandoost, R.; Pouran, S.R.; Khataee, A.; Orooji, Y.; Joo, S.W. Hierarchically structured ternary heterojunctions based on Ce3+/Ce4+ modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles anchored onto graphene oxide sheets as magnetic visible-light-active photocatalysts for decontamination of oxytetracycline. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 376, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, L.; He, J.; Cui, H. Ethyl mercaptan removal from gas streams using regenerable Co/Fe modified hexaniobate nanotubes. Colloid Surf. A 2022, 651, 129732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, C.; Dai, Q.; Su, C. Facile synthesis and lithium storage properties of engineered ultrafine porous Fe2SiO4/C composites. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 807, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Fan, X.; Hu, W.; Luo, F.; Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Li, Y. Formation mechanism and enhanced magnetic properties of Fe–Si/Fe2SiO4 soft magnetic composites transformed from Fe-6.5 wt%Si/α-Fe2O3 core-shell composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 152803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Peng, B.; Chai, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, H.; et al. Formation mechanism of zinc–doped fayalite (Fe2−xZnxSiO4) slag during copper smelting. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).