Abstract
Efficient biomass harvesting remains one of the primary barriers to the commercial feasibility of large-scale microalgal production. This study investigates the effect of different culture media on the surface physicochemical properties of Tetradesmus sp., with emphasis on their role in natural aggregation. Cultures were grown for 30 days under controlled light and temperature conditions using Blue Green 11 (BG11), Tris–acetate–phosphate (TAP), and deionized water supplemented with Bayfolan® fertilizer. Surface hydrophobicity was assessed through microbial adhesion to solvents (MATS) and contact angle analysis, electrokinetic properties were evaluated by zeta potential measurements, and cell surface chemistry was characterized by attenuated total reflectance (ATR) sampling methodology for Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Across all treatments, Tetradesmus sp. exhibited inherent hydrophobicity, but Bayfolan® supplementation yielded the highest contact angle (49.0 ± 0.9°) and the least negative free energy of interaction (ΔGsws = −26.36 mJ·m−2), indicating a stronger tendency toward self-aggregation. Zeta potential values remained consistently negative (−10 to −14 mV), with no significant variation among media, suggesting that hydrophobic interactions rather than electrostatic forces govern aggregation. ATR-FTIR spectra confirmed the presence of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, with changes in peak intensities reflecting metabolic adjustments to media composition. These results demonstrate that low-cost Bayfolan® supplementation enhances surface hydrophobicity and aggregation, providing a sustainable strategy to facilitate biomass recovery and reduce harvesting costs in microalgal biorefineries.
Keywords:
Tetradesmus sp.; Bayfolan®; hydrophobicity; zeta potential; ATR-FTIR; biomass recovery; harvesting 1. Introduction
Microalgae are photosynthetic organisms that have gathered significant attention for their diverse biotechnological applications, encompassing biofuel production, bioremediation, and the synthesis of high-value products such as proteins, lipids, carotenoids, vitamins, and enzymes. These microscopic organisms are a renewable and environmentally sustainable source for raw material production, offering distinct advantages over traditional agricultural crops. These advantages include rapid growth rates, high photosynthetic efficiency, and the capacity to thrive in non-arable lands or even wastewater, thereby avoiding competition for valuable resources [1].
The economic viability of microalgae-based industries fundamentally depends on overcoming critical bottlenecks in their production. Among these, the efficient and cost-effective recovery of biomass from dilute cultures remains a significant challenge, often accounting for a substantial portion of the total production cost. A better understanding of microalgal cell surface physicochemical properties, such as hydrophobicity, zeta potential, and the nature of functional groups, is therefore of utmost importance for optimizing various biotechnological processes. These surface characteristics are fundamental for engineering efficient and sustainable downstream processes. The electrical properties of cell surfaces are influenced by the cell’s structure and extracellular products, which in turn are linked to its growth and metabolic state [1,2]. This establishes a clear causal relationship: the metabolic state of microalgae, shaped by cultivation conditions, directly dictates the composition and structure of the cell surface and secreted products like extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). These molecular-level changes then manifest as macroscopic surface properties, which ultimately govern the efficiency of critical processes such as biofouling control in photobioreactors, the design of attached growth systems, and particularly, the effectiveness of bioflocculation for biomass harvesting [3,4,5]. The processing of microalgae biomass consists of several steps: harvesting, dewatering, extraction, fractionation, and conversion [6,7]. These steps present several bottlenecks that affect the efficiency of the entire process; therefore, different approaches have been developed. Among the current harvesting processes, chemical flocculation, bioflocculation, gravitational sedimentation, filtration, electrocoagulation–flocculation, flotation, centrifugation, or a combination of all the above can be found [8,9].
BG-11 has high nitrogen availability in order to maximize the biomass/protein ratio, causing changes in its biochemical composition. However, TAP introduces organic carbon (acetate) and ammonium/nitrate, allowing for analysis of how mixotrophic metabolism modifies physicochemical properties (i.e., lipid accumulation, pigmentation, or floatability) [10,11,12].
Meanwhile, Bayfolan® Forte is a foliar liquid fertilizer formulated mainly for agriculture. It contains a mixture of macronutrients (N, P, and K) and micronutrients like Fe, Mn, Zn, Cu, and B; its low cost compared to synthetic media such as BG-11 and TAP makes it attractive for use in Latin America. Some studies have reported it to be useful for the massive production of biomass [13,14].
Scenedesmus dimorphus (recently reclassified as Tetradesmus dimorphus) has emerged as a robust model species for biomass production due to its high growth rates, substantial lipid accumulation, and adaptability to a wide range of cultivation conditions [15,16]. Its ability to thrive in defined media, agricultural effluents, and wastewater while maintaining high biomass productivity highlights its dual role as a feedstock for biofuels and as a tool for nutrient remediation [14,17,18]. Moreover, its favorable fatty acid profile, resilience to environmental fluctuations, and ease of cultivation at a large scale provide clear advantages over other microalgal species, justifying its continued study as a strategic organism for sustainable bioenergy and bioproducts [19,20,21].
Consequently, research has focused on manipulating the surface properties of Tetradesmus dimorphus by using different culture media, which directly contributes to enhancing biomass recovery. Therefore, the objective of the present study was to evaluate the effect of the three culture media mentioned above (TAP, BG11, and Bayfolan®) on physicochemical properties such as microbial adhesion to solvents (MATS), zeta potential, surface contact angle (ɵ), and surface free energy (ΔGswsTOT).
2. Methodology
2.1. Microalgae Cultivation
The Tetradesmus sp. strain used in this study was acquired from the culture collection of Continental Algae-Ecology and Taxonomy Laboratory, Faculty of Science, National Autonomous University of Mexico (U.N.A.M.). Cultures were grown as follows: (a) using 1000 mL of sterilized BG11 medium, (b) in 1000 mL of TRIS acetate phosphate (TAP) medium (Phyto Technology Laboratories, Lenexa, KS, USA), and (c) in 1000 mL of sterilized deionized water enriched with 3 mL of Bayfolan® Forte from Bayer. All experiments were conducted in triplicate. Cultures were kept at room temperature (25 ± 1 °C) with a 12/12 h light/dark cycle at a photosynthetically active photon flux density (PPFD) of approximately 60.32 umol/s/m2 using white LEDs as a light source. Cell growth was determined by measuring optical density using a Cintra 303 UV-vis spectrophotometer (GBC, Sydney, NSW, Australia) at a wavelength of 750 nm (O.D. 750) and harvested at their stationary phase after 30 days.
2.2. Microbial Adhesion to Solvents Experiments (MATS)
The MATS test was conducted according to Xia et al. 2016 [20]. Cells were harvested by centrifugation and then resuspended in a 0.01 M potassium phosphate buffer at pH 6.8. The solution absorbance was adjusted to 0.4 at 600 nm (OD600) (A0). A volume of 0.4 mL of a selected solvent was added to a sample of 2.4 mL of cell suspension. Three solvents were used separately: chloroform, hexane, and acetone. Each suspension was vortexed for 30 s and settled for 20 min. The aqueous phase was removed, and its absorbance was measured at OD600 (A1), using a Cintra 303 UV-vis spectrophotometer (GBC, Sydney, NSW, Australia). Experiments were carried out in triplicate. The MATS percentage (p) was obtained according to Equation (1):
2.3. Zeta Potential Measurements
A total of 10 mL of algae culture was placed in a test chamber. The zeta potential was measured after harvesting using a Zetasizer Series Nano ZS ZEN 3600 (Malvern, UK). Each value was calculated as the average of at least three subsequent runs of the instrument, with each run consisting of 25 measurements.
2.4. Surface Contact Angle and Surface Free Energy
Contact angle determination was performed following the sessile drop technique [22]. The microalgal suspensions were harvested, washed twice, and resuspended in a saline solution (0.85% w/v NaCl) to obtain a final concentration of approximately 5.0 × 106 cells mL−1. The resulting algal lawns were obtained by filtering the previously washed suspensions using 0.45 μm nitrocellulose membrane filters. Contact angle measurements were performed in triplicate for each growth medium. Subscripts s and l refer to the solid surface and probe liquid, respectively. Water, glycol, and glycerol were used as probe liquids; therefore, their surface parameters were known (Table 1). In this approach, surface free energy is decomposed into a Lifshitz-van der Waals component () and a Lewis acid–base component (, which is split into a Lewis acid component ) and a Lewis base component (. Surface contact angle was measured for each medium and each probe liquid. Surface tension parameters and free energy of interactions were calculated following the Lifshitz-van Waals/acid–base method (the LW/AB method, Equation (2)) [23,24].

Table 1.
Surface energy parameters of the probe liquids (MJm−2) [25].
After contact angle measurements, the values of surface hydrophobicity of the studied algal suspensions were determined using the approach of van Oss [23], which allows the assessment of the absolute degree of hydrophobicity of any surface in comparison to its interaction with water. In this approach, when ΔGSWS TOT < 0, the interaction between the two entities is stronger than the interaction of each entity with water and the material is considered hydrophobic; on the contrary, when ΔGSWS TOT > 0, the material is considered hydrophilic, and it can be calculated according to Equation (3) [9]:
2.5. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR)
ATR-FTIR testing was used to identify the major functional groups in the raw and lyophilized microalgae. Spectra were collected on a Perkin–Elmer Spectrum Two instrument, coupled with a Diamond ATR accessory (DurasamplIR II, Smiths Detection, Warrington, UK), scanning over the wavenumber range of 4000–650 cm−1 at a resolution of 4 cm−1 and 14 scans. Processing of FTIR spectra was carried out with the Omnic 8.2 software.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The results shown are the averages of triplicates. An ANOVA was performed using the SPSS 18.0 package (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA), with a confidence level of 95%.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrophobicity Assessment
In the MATS experiments (Figure 1), Tetradesmus sp. cells consistently exhibited a tendency towards hydrophobicity across all tested media. The adhesion preference followed a clear order: chloroform > hexane > acetone (e.g., 59.33 > 44.66 > 41 for Bayfolan®). This indicates a strong affinity for acidic solvents (like chloroform) and a notable aversion to polar solvents (like acetone), regardless of the specific culture medium.
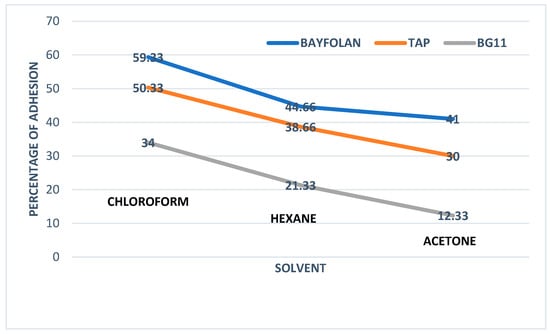
Figure 1.
Results from the MATS method obtained with the solvents: chloroform, hexane, and acetone.
Contact angle measurements further elucidated the hydrophobic nature of the algal surface. The largest water contact angle was observed for cells grown in Bayfolan® (49.0 ± 0.9°), followed by TAP (37.1 ± 1.8°) and BG11 (34.6 ± 3.9°). These values indicate that the Tetradesmus sp. surface generally prefers oil properties rather than water properties across all three culture media, with Bayfolan® significantly enhancing this preference (Table 2).

Table 2.
Surface contact angles for Tetradesmus sp. determined for each culture.
The total free energy of interaction (ΔGsws) provided a quantitative measure of hydrophobicity. All three culture media resulted in negative ΔGsws values, unequivocally confirming the hydrophobic nature of the cell surface. Notably, Bayfolan® exhibited the least negative ΔGsws value (−26.3574 MJm−2), which signifies a stronger cohesive force among the microalgae cells when grown in this medium. This implies that the microalgae are more prone to agglomeration in Bayfolan® compared to TAP (−132.8269 MJm−2) and BG11 (−273.9238 MJm−2). This observation aligns with the acid–base surface tension trend, where Bayfolan® < TAP < BG11 (107.32, 238.52, and 278.51, respectively). It is important to clarify that a less negative ΔGsws (i.e., a value closer to zero) indicates a less unfavorable interaction with water, which in turn means a stronger cohesive force between the cells themselves in an aqueous environment. This leads to increased hydrophobicity and a greater tendency for self-aggregation or agglomeration, a crucial characteristic for efficient biomass recovery (Table 3).

Table 3.
Surface physicochemical properties of Tetradesmus sp. determined for each culture medium.
The results from the MATS test with the three solvents show that microalgae have the highest affinity for acidic solvent, chloroform, regardless of culture media (Figure 1). All treatments exhibited a negative value of ΔGsws, suggesting surface hydrophobicity, consistent with the highest contact angle shown using water as a probe; thus, the cell surface has an affinity for oil properties (Table 2 and Table 3).
3.2. Hydrophobicity in Microalgae: A Comparative and Mechanistic Discussion
Microalgal hydrophobicity, typically quantified through methods like MATS or contact angle measurements, describes the cell surface’s relative affinity for non-polar substances over water. This property is a critical physicochemical characteristic that dictates cell–cell and cell–surface interactions [24]. The total free energy of interaction (ΔGsws) offers a quantitative metric for hydrophobicity, with negative values indicating a hydrophobic surface.
The hydrophobicity of microalgal cells is a result of a confluence of factors. The biochem-ical composition of the cell wall, including the relative proportions of lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, plays a significant role in determining surface hydrophobicity [26]. Furthermore, extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs), secreted by microalgal cells, can profoundly affect surface properties, including hydrophobicity. The quantity and chemical composition of EPSs are known to be modulated by various culture conditions, such as nutrient availability (e.g., nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon), pH levels, and other environmental stress factors [27]. For instance, nitrogen deprivation has been shown to induce cell wall thickening and alter its overall composition in some microalgae [28]. Similarly, acidic pH and moderate salinity can enhance EPS production in certain species, potentially contributing to changes in surface hydrophobicity [29]. The growth phase of microalgae also influences surface characteristics, with observed changes in lipid content and the concentration of hydroxyl functional groups as cells progress through their lifecycle.
The current study’s findings demonstrate that Tetradesmus sp. exhibits inherent hydrophobicity across all tested culture media, with Bayfolan® notably enhancing this characteristic. This observation aligns with the general understanding that microalgae surfaces can range from hydrophilic to slightly hydrophobic under natural pH conditions [30]. For context, Chlorella vulgaris is typically hydrophilic, whereas Anabaena variabilis is naturally hydrophobic [24]. Previous research on green microalgae has reported hydrophilic surface properties with contact angles ranging from 30° to 58° [24]. The contact angles measured for Tetradesmus sp. in BG11 (34.6°) and TAP (37.1°) fall within this established range, while the value for Bayfolan® (49.0°) pushes towards the higher, more hydrophobic end of this spectrum. A significant observation from the broader literature is that microalgae species known to form colonies often possess distinctly hydrophobic surfaces, a property crucial for facilitating flocculation [24]. The results for Tetradesmus sp., particularly when grown in Bayfolan®, suggest a heightened propensity for agglomeration, which is consistent with this general principle.
The enhanced hydrophobicity observed with Bayfolan® has direct implications for microalgae harvesting. Increased hydrophobicity directly promotes self-aggregation and bioflocculation [26]. When the total free energy of interaction (ΔGsws) is less negative (i.e., closer to zero), the cohesive forces between microalgae cells are stronger, which facilitates agglomeration and makes biomass recovery easier. This is because it becomes more challenging to exclude water between highly hydrophilic cells, thereby hindering their aggregation. Furthermore, hydrophobicity is a critical determinant for effective froth flotation, as it improves the adherence of cells to air bubbles. For naturally hydrophilic species like Chlorella vulgaris, external surfactants are used to increase hydrophobicity and improve flotation efficiency [30]. The findings for Tetradesmus sp. suggest that cultivating it in Bayfolan® could intrinsically improve its flotation characteristics, potentially reducing or eliminating the need for external chemical modifications during harvesting.
Harvesting is widely recognized as a major cost bottleneck in microalgae production, often accounting for 20–30% of the total production cost. By enhancing the natural agglomeration of Tetradesmus sp. through media manipulation (e.g., using Bayfolan®), the reliance on costly chemical flocculants or energy-intensive harvesting methods can be significantly reduced or even eliminated. This approach directly contributes to improving the economic feasibility and overall sustainability of microalgae cultivation. The specific components within Bayfolan® (e.g., its unique nutrient profile, trace elements, or plant-derived organic compounds) likely induce subtle yet impactful changes in the Tetradesmus sp. cell wall structure or extracellular polymeric substance (EPS) production. This metabolic shift could lead to the increased synthesis of hydrophobic cell wall components or the secretion of specific types of EPSs that enhance surface hydrophobicity. This research might prove that, through culture medium optimization, Bayfolan® exemplifies a “design-for-harvesting” approach. Instead of treating cultivation and harvesting as isolated steps, this integrated strategy offers a more sustainable biorefinery model, highlighting the practical significance of this work beyond mere surface property characterization. For Tetradesmus sp., modulating hydrophobicity through culture media changes appears to be a more effective strategy for promoting agglomeration than attempting to alter surface charge, a crucial species-specific characteristic [31].
3.3. Zeta Potential Determinations: A Comparative and Electrostatic Perspective
The zeta potential (ζ) is the electrostatic potential that exists at the shear plane of a particle; it is a measurement of the degree of repulsion between particles, and therefore, it has a relation to its environment [32,33]. Along with hydrophobicity and surface free energy, surface charge is another parameter associated with cell adhesion and, therefore, is essential for the application of effective harvesting [34]. Zeta potential measurements for Tetradesmus sp. consistently showed a negatively charged cell surface across all three culture media during the stationary phase, with values ranging from −10 mV to −14 mV. This negative charge is commonly attributed to the dissociation of carboxylic groups (-COOH) on the cell surface and the anionic characteristics of the cell wall due to the deprotonation of surface functional groups, which is typical for microalgae under physiological growth conditions (pH 4–8). Despite the variations in culture media, the study concluded that there was no statistically significant difference in zeta potential values among the three media. This suggests that for Tetradesmus sp. under these specific conditions, while a negative surface charge is present, its subtle variations across different culture media are not the primary mechanism driving the observed differences in agglomeration. Instead, the significant changes in hydrophobicity appear to be the dominant factor influencing aggregation behavior.
Table 3 summarizes the key physicochemical properties of Tetradesmus sp. across the tested culture media, providing a consolidated view of the experimental findings
A high magnitude of negative zeta potential typically indicates that algal cells are stably dispersed in the surrounding medium, thereby counteracting aggregation and making harvesting more challenging [25].
Several factors modulate the zeta potential of microalgae. Environmental pH is a primary determinant; microalgae cells generally exhibit a negative zeta potential at physiological pH values (typically between 4 and 8) due to the dissociation of carboxylic groups (-COOH) and the deprotonation of other surface functional groups on the cell wall. Decreasing the pH can lead to an increase in zeta potential, causing it to approach 0 mV at the isoelectric point (IEP), which is the pH at which the net surface charge is zero. The isoelectric point often correlates with maximum flocculation efficiency [35]. Conversely, at higher pH values, ionizable groups tend to lose protons, resulting in a more negative net surface charge [36]. The ionic strength and specific ion composition of the culture medium can also influence zeta potential by screening cell surface charges [37]. For instance, the type of nitrogen source or the presence of specific metal cations in the medium can affect the surface charge [38]. Furthermore, zeta potential values and their responses to environmental changes can vary significantly among different microalgae species [37]. For example, Anabaena variabilis exhibits a larger magnitude of negative zeta potential compared to Chlorella vulgaris at the same pH, which results in a more dispersed distribution of Anabaena variabilis cells in suspension [24].
In the present study, Tetradesmus sp. consistently maintained a negative zeta potential across all three tested culture media (BG11, TAP, and Bayfolan®), with values ranging from −10 mV to −14 mV. This range is typical for microalgae at physiological pH. For comparative purposes, Chlorella vulgaris also exhibits negative zeta potentials within its tested pH range [24]. A notable finding for Tetradesmus sp. was the non-significant difference in zeta potential values observed across the different culture media. This contrasts with studies on other microalgae species where pH or specific media components demonstrably alter zeta potential and influence flocculation efficiency [37]. This suggests a species-specific characteristic of Tetradesmus sp. or indicates that the tested media did not induce substantial changes in its surface charge under the experimental conditions.
Zeta potential plays a crucial role in flocculation, as charge neutralization (bringing the zeta potential closer to 0 mV) typically promotes aggregation [25]. However, the results for Tetradesmus sp. suggest that while the cell surface is negatively charged, the degree of this charge (within the tested range) is not the primary factor driving differential agglomeration across the various culture media. This contrasts with the significant variations observed in hydrophobicity. This implies that for Tetradesmus sp., other mechanisms, such as bridging by extracellular polymers or enhanced van der Waals force of attraction, might be more influential for flocculation, especially in the context of media-induced changes.
While the current study’s zeta potential measurements were taken at the stationary phase, presumably at the culture’s natural pH, it would be valuable for future research to investigate the pH-dependent zeta potential curve for Tetradesmus sp. grown in each medium. The literature has consistently demonstrated that pH significantly affects the zeta potential and flocculation efficiency, often by enabling the system to reach an isoelectric point [35]. Exploring whether Tetradesmus sp. possesses an isoelectric point within a practical pH range, and if the culture medium influences this IEP or the steepness of the zeta potential curve, could reveal additional strategies for harvesting through pH adjustment, even if the native culture pH does not show large differences.
Table 4 provides a comparative overview of hydrophobicity and zeta potential for Tetradesmus sp. and other commonly studied microalgae species, offering a broader context for the present findings.
3.4. Functional Groups (ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy)
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is a rapid and non-destructive analytical technique widely employed to identify the major functional groups and biomolecules (such as lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates) present in microalgae biomass. The principle behind FTIR relies on the fact that each chemical bond within a molecule vibrates at specific frequencies. When the vibrational frequency of a bond matches that of the infrared radiation, absorption occurs. By analyzing the composition, shape, and intensity of these absorption bands at specific wavenumbers, valuable information about the molecular structure and functional groups can be obtained, enabling identification and even quantification [39].
Microalgal biomass typically exhibits characteristic absorption bands corresponding to various biomolecules and functional groups. Broad peaks observed around 3200 to 3350 cm−1 are due to O-H stretching vibrations from water, carbohydrates, and alcohols, as well as N-H stretching from proteins and amino acids. These hydroxyl and amine groups contribute significantly to the hydrophilic nature and overall surface charge of the cell wall [28]. Strong peaks around the region of 1630 to 1650 cm−1 are assigned to the H-O-H bending vibration of water and the amide band, corresponding to the C=O stretching vibrations in proteins. A strong peak around 1740 cm−1 is particularly characteristic of the C=O stretching in ester bonds of fatty acids, serving as a reliable indicator of lipid contents [39]. Bands in the 2800–3000 cm−1 region and at 1390–1455 cm−1 are related to C-H stretching and bending vibrations in hydrocarbons, suggesting the presence of lipids and proteins. The carbohydrate region typically displays prominent peaks around 1030–1050 cm−1, which are characteristic of C-O-C polysaccharides and C-O stretching, indicating the carbohydrate content, a primary structural component of microalgal cell walls. Beyond these, other functional groups, such as carboxyl, phosphate, and sulfate groups, are also present and contribute to the surface reactivity and charge of microalgae.
The ATR-FTIR spectra obtained for Tetradesmus sp. in this study revealed prominent peaks consistent with these typical microalgal functional groups. These included a strong O-H peak around 3294 cm−1, a H-O-H/protein peak at approximately 1635 cm−1, a carbohydrate peak around 1039 cm−1, and CH2/CH3 vibrations at ~1390 cm−1 and ~1455 cm−1. The composition of culture media, particularly the ratios of key nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, can significantly alter cell wall thickness and overall biochemical composition. For example, nitrogen deprivation has been shown to induce cell wall thickening and changes in the composition of structural polysaccharides [30]. Changes in the relative abundance or accessibility of these functional groups directly influence the macroscopic surface properties. An increase in hydrophobic components, such as lipids (indicated by stronger C-H bonds), would correlate with higher hydrophobicity. Conversely, the dissociation of carboxylic, hydroxyl, and amine groups contributes to the negative surface charge (zeta potential). Although the zeta potential differences observed in this study were not statistically significant, even subtle shifts in the balance of these charged groups, if not significant in bulk measurement, could still contribute to the overall surface behavior. If, for instance, Bayfolan®-grown cells exhibit a relative decrease in the intensity of peaks associated with hydrophilic groups (e.g., O-H, C-O-C) or a relative increase in peaks linked to hydrophobic groups (e.g., C-H from lipids) compared to cells grown in other media, this would provide a molecular explanation for the observed increase in hydrophobicity (Figure 2).
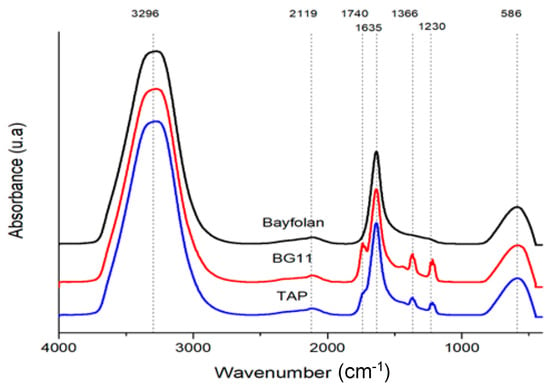
Figure 2.
ATR-FTIR results of raw microalgae in their respective culture media.
While the current FTIR data qualitatively identifies major functional groups, a deeper analysis could involve quantifying the relative abundance of these groups (e.g., lipid-to-protein ratio and carbohydrate-to-protein ratio) across the different culture media. This quantitative comparison, using peak integration methods [39], would provide direct evidence of how each medium biochemically alters the cell wall, thereby establishing a stronger causal link between media composition, cell wall biochemistry, and the observed changes in hydrophobicity and zeta potential. For example, if Bayfolan® cultivation leads to a higher lipid-to-carbohydrate ratio, this would directly explain the increased hydrophobicity. Furthermore, FTIR, especially with quantitative analysis, can serve as a rapid and non-destructive diagnostic tool for optimizing culture media formulations. By monitoring changes in key functional group ratios, researchers can quickly assess the impact of different media on cell wall composition and predict subsequent surface properties relevant for harvesting. This approach can accelerate the development of media tailored for specific biotechnological outcomes.

Table 4.
Comparative overview of hydrophobicity and zeta potential in key microalgae species.
Table 4.
Comparative overview of hydrophobicity and zeta potential in key microalgae species.
| Microalgae Species | Hydrophobicity Characteristics | Zeta Potential Characteristics | Relevant Culture Conditions (If Applicable) | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetradesmus sp. | Inherent hydrophobicity; Bayfolan enhances (ΔGsws: −26.36 MJm−2); Water contact angles 34.6–49.0° | Consistently negative (−10 to −14 mV); non-significant difference across media | BG11, TAP, Bayfolan®; stationary phase | This study |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Naturally hydrophilic; hydrophobicity enhanced by cationic surfactants (e.g., C16TAB) | Consistently negative; magnitude smaller than Anabaena variabilis at same pH | Various pH, C16TAB addition | [26] |
| Anabaena variabilis | Naturally hydrophobic | Consistently negative; larger magnitude than Chlorella vulgaris at same pH | Various pH | [33] |
| Green microalgae (general) | Can be hydrophilic (CA 30–58°) or slightly hydrophobic | Generally negative at physiological pH (4–8) | Natural pH | [32] |
| Species forming colonies | Distinctly hydrophobic surfaces | Not specified | Not specified | [27] |
| Chlorella vulgaris | Moderate hydrophobic surfaces; contact angle and adhesion increase under certain pH/light regimes | Negative; magnitude becomes less negative under stress or adsorbate presence | Varied pH; light stress; presence of ionic/charged particles | [40] |
| Chlorella sorokiniana | Hydrophobicity influenced by biomass fraction; whole-cell biomass less hydrophobic than protein-rich fractions; surface tension lowers under certain pH | Negative zeta; magnitude influenced by fraction and pH | Semi-pilot scale; fractions of biomass; pH 7 and others | [33] |
| Tribonema sp., Scenedesmus sp. | Tribonema highly hydrophobic; Scenedesmus moderately hydrophobic when compared under same medium | Zeta potentials negative; differences in harvesting efficiency tied to hydrophobicity | Same current and shear conditions in electro-flotation | [36] |
4. Conclusions
The present study unequivocally demonstrates a significant influence of culture media on the surface physicochemical properties of Tetradesmus sp. Specifically, cultivation in Bayfolan® medium consistently resulted in higher hydrophobicity, evidenced by increased contact angle for water (49.0° ± 0.9) and a less negative total free energy of interaction (ΔGsws, −26.36 MJm−2). This indicates a stronger cohesive force among cells grown in Bayfolan®, which directly promotes easier agglomeration. While the zeta potential remained negative across all media, the observed differences were not statistically significant. This suggests that for Tetradesmus sp., under the specific growth conditions investigated, hydrophobicity is a more dominant factor influencing agglomeration behavior than subtle variations in surface charge. The ATR-FTIR data, revealing characteristic peaks for major macromolecules, provides a foundational understanding of the biochemical basis for these surface property changes.
These findings carry significant implications for the optimization of microalgae cultivation and harvesting. The ability to “engineer” microalgal surface properties in situ by manipulating culture media components represents a more sustainable and cost-effective approach compared to relying solely on post-harvest chemical treatments [40]. The observation that Bayfolan® promotes easier agglomeration directly addresses a major bottleneck in microalgae production: harvesting. This enhanced agglomeration can lead to reduced energy consumption and operational costs associated with dewatering processes, thereby enhancing the economic viability of microalgae cultivation.
This study provides compelling evidence that culture media significantly influenced the surface physicochemical properties of Tetradesmus sp., particularly its hydrophobicity. A key finding is that Bayfolan® medium consistently promotes significantly higher hydrophobicity, as indicated by increased contact angles and a less negative total free energy of interaction (ΔGsws). This directly correlates with enhanced agglomeration and a greater potential for easier biomass harvesting. The observed increase in hydrophobicity with Bayfolan® could be attributed to a shift in cellular metabolism induced by the medium’s specific nutrient profile or the presence of certain organic compounds. This might lead to an increased synthesis of hydrophobic components within the cell wall or the secretion of more hydrophobic extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs), a phenomenon observed in other microalgae under specific cultivation conditions [29]. While Tetradesmus sp. maintained a negative zeta potential across all tested media, the differences observed were not statistically significant. This suggests that for this specific species, under the experimental conditions, hydrophobicity is the more dominant factor influencing agglomeration behavior, rather than subtle variations in surface charge. The enhanced agglomeration observed with Bayfolan-grown Tetradesmus sp. has direct practical implications for harvesting. This increased hydrophobicity could significantly improve the efficiency of flotation techniques and reduce the need for chemical flocculants, thereby lowering operational costs and promoting a more sustainable biorefinery approach [40]. These findings offer valuable insights for optimizing Tetradesmus sp. cultivation and harvesting, aligning with the broader objective of achieving sustainable microalgae production.
5. Recommendations for Future Research
The specific components within Bayfolan® (e.g., trace elements, organic compounds, or the unique nutrient ratios it establishes) likely act as a “stress factor” or provide a distinct nutritional profile. This subtly shifts the Tetradesmus sp. metabolism towards producing more hydrophobic cell wall components or secreting specific types of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs) that increase surface hydrophobicity. This is a crucial area for future research to identify the underlying mechanism. The results also underscore the importance of species-specific optimization in microalgae biotechnology. While some microalgae species may respond strongly to pH-induced charge neutralization for flocculation [35], Tetradesmus sp. appears to be more responsive to media-induced changes in hydrophobicity for agglomeration. This highlights that a “one-size-fits-all” harvesting strategy is generally not feasible across diverse microalgal strains. This research contributes to the broader concept of an “integrated biorefinery,” where upstream cultivation conditions need to be designed to facilitate downstream processing. By selecting a medium like Bayfolan®, the entire production chain from cultivation to harvesting can become more efficient and cost-effective, moving microalgae closer to commercial viability as a feedstock for various bioproducts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.A.-M.; Formal analysis, A.C.A.-M., A.M.M.-M., and U.P.-G.; Investigation, A.C.A.-M.; Methodology, A.C.A.-M. and U.P.-G.; Resources, A.M.M.-M.; Supervision, U.P.-G., N.V.G.-R., and L.A.-V.; Validation, U.P.-G., N.V.G.-R., A.M.M.-M., and L.A.-V.; Writing—original draft, A.C.A.-M.; Writing—review and editing, A.C.A.-M., U.P.-G., and A.M.M.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We are grateful for the support of the National Council of Science and Technology (CONACYT) for the scholarship granted (692130) to Ana Carolina Anzures-Mendoza to pursue a Doctorate in Engineering Sciences at Tecnológico Nacional de México, Campus Ciudad Madero. The authors are grateful for the support of Tamaulipas Council of Science and Technology (COTACYT) for publishing this work.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chew, K.W.; Yap, J.Y.; Show, P.L.; Suan, N.H.; Juan, J.C.; Ling, T.C.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Microalgae biorefinery: High value products perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, D.L.; Ralph, P.J. Microalgal bioremediation of emerging contaminants—Opportunities and challenges. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Baez, M.F.; Aguilera-Vazquez, L.; Rangel-Valdez, N.; Martinez-Salazar, A.L.; Zuñiga, C. Multi-Objective Optimization of Microalgae Metabolism: An Evolutive Algorithm Based on FBA. Metabolites 2022, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E.S.; Ejeromedoghene, O.; Okoye, C.O.; Ezeorba, T.P.C.; Nyaruaba, R.; Ikechukwu, C.K.; Oladipo, A.; Orege, J.I. Microalgae biorefinery: An integrated route for the sustainable production of high-value-added products. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 16, 100323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; Vecchi, V.; Barera, S.; Dall’oSto, L. Biomass from microalgae: The potential of domestication towards sus-tainable biofactories. Microb. Cell Factories 2018, 17, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muylaert, K.; Bastiaens, L.; Vandamme, D.; Gouveia, L. Harvesting of microalgae: Overview of process options and their strengths and drawbacks. In Microalgae-Based Biofuels and Bioproducts; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Danquah, M.K.; Gladman, B.; Moheimani, N.; Forde, G.M. Microalgal growth characteristics and subsequent influence on dewatering efficiency. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 151, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.C.; Gonçalves, A.L.; Simões, M. Microalgal/cyanobacterial biofilm formation on selected surfaces: The effects of surface physicochemical properties and culture media composition. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.L.; Ferreira, C.; Loureiro, J.A.; Pires, J.C.; Simões, M. Surface physicochemical properties of selected single and mixed cultures of microalgae and cyanobacteria and their relationship with sedimentation kinetics. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2015, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.A. Algal Culturing Techniques; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Maltsev, Y.; Kulikovskiy, M.; Maltseva, S. Nitrogen and phosphorus stress as a tool to induce lipid production in microalgae. Microb Cell Fact. 2023, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippka, R.; Deruelles, J.; Waterbury, J.B.; Herdman, M.; Stanier, R.Y. Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. Microbiology 1979, 111, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Bravo, S.G.; Castañeda-Chávez, M.R.; Aguilera-Vázquez, L.; Gallardo-Rivas, N.V.; Morales-Rodríguez, M.L.; Páramo-García, U. Cultivation of Scenedesmus dimorphus with Bayfolan® supplementation under different photoperiods: Biomass, lipid profile and wastewater treatment potential. Resources 2023, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegewald, E.; Wolf, M.; Keller, A.; Friedl, T.; Krienitz, L. ITS2 sequence–structure phylogeny in the Scenedesmaceae with special reference to Coelastrum, Tetradesmus and Desmodesmus. Phycologia 2019, 49, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laraib, N.; Hussain, A.; Javid, A.; Bukhari, S.M.; Ali, W.; Manzoor, M.; Jabeen, F. Mixotrophic Cultivation of Scenedesmus dimorphus for Enhancing Biomass Productivity and Lipid Yield. Iran J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Sci. 2021, 45, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, D.J.; Zhong, C.Q. Cultivating Scenedesmus dimorphus in lactic acid wastewater for cost-effective biodiesel production. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, J. Cultivation of Scenedesmus dimorphus for C/N/P removal and lipid production. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 18, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Microalgae for biodiesel production and other applications: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Hong-Ying, H.; Ke, G.; Ying-Xue, S. Growth and lipid accumulation of Scenedesmus obliquus in response to different nitrogen levels. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 5494–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Li, H.; Song, S. Cell surface characterization of some oleaginous green algae. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 2323–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, H.J.; Weerkamp, A.H.; van der Mei, H.C.; van Pelt, A.W.; de Jong, H.P.; Arends, J. Measurement of the surface free energy of bacterial cell surfaces and its relevance for adhesion. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1984, 48, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oss, C. Hydrophobicity of biosurfaces—Origin, quantitative determination and interaction energies. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 1995, 5, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, A.; Berberoglu, H. Physico-chemical surface properties of microalgae. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Yanpeng, L.; Zhou, S.; Xiangying, R.; Wenjun, Z.; Jun, L. Surface characteristics of microalgae and their effects on harvesting performance by air flotation. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 10, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Chou, A.; Chen, L.; Yan, H.; Zuo, Y.Y. Rapid Spectrophotometric Method for Determining Surface Free Energy of Microalgal Cells. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8751–8756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, G.; Delattre, C.; Dubessay, P.; Jubeau, S.; Vialleix, C.; Cadoret, J.-P.; Probert, I.; Michaud, P. What Is in Store for EPS Microalgae in the Next Decade? Molecules 2019, 24, 4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivakumar, S.; Serlini, N.; Esteves, S.M.; Miros, S.; Halim, R. Cell Walls of Lipid-Rich Microalgae: A Comprehensive Review on Characterisation, Ultrastructure, and Enzymatic Disruption. Fermentation 2024, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelaalincy, M.; Senthilkumar, N.; Karpagam, R.; Kumar, G.G.; Ashokkumar, B.; Varalakshmi, P. Enhanced Extracellular Polysaccharide Production and Self-Sustainable Electricity Generation for PAMFCs by Scenedesmus sp. SB1. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3754–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, S.; Wang, L.; Schenk, P.M. Effective harvesting of low surface-hydrophobicity microalgae by froth flotation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 159, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiak, W.; Krzemińska, I. Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) as Microalgal Bioproducts: A Review of Factors Affecting EPS Synthesis and Application in Flocculation Processes. Energies 2021, 14, 4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, S.; Yadav, K.K.; Sarkar, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Saha, P.; Haldar, S.; Karmakar, S.; Sen, T. Alteration of Zeta potential and membrane permeability in bacteria: A study with cationic agents. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafai, D.E.; Nemogová, I.; Dráber, P.; Cifra, M. Zeta potential for cell surface-nanoenvironment interaction assessment Zeta potential for cell surface—Nanoenvironment interaction assessment. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 2018, 20, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qi, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhan, X.; Stengel, D.B. Low energy harvesting of hydrophobic microalgae (Tribonema sp.) by electro-flotation without coagulation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 838, 155866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tao, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, B.; Tang, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Effective flocculation of target microalgae with self-flocculating microalgae induced by pH decrease. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 167, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Zhou, H.; Kapur, S.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y. Electrostatic charges on microalgae surface: Mechanism and applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesniewska, N.; Duval, J.F.L.; Caillet, C.; Razafitianamaharavo, A.; Pinheiro, J.P.; Bihannic, I.; Gley, R.; Le Cordier, H.; Vyas, V.; Pagnout, C.; et al. Physicochemical surface properties of Chlorella vulgaris: A multiscale assessment, from electrokinetic and proton uptake descriptors to intermolecular adhesion forces. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 5149–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciempiel, W.; Czemierska, M.; Szymańska-Chargot, M.; Zdunek, A.; Wiącek, D.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Krzemińska, I. Soluble Extracellular Polymeric Substances Produced by Parachlorella kessleri and Chlorella vulgaris: Biochemical Characterization and Assessment of Their Cadmium and Lead Sorption Abilities. Molecules 2022, 27, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayers, J.J.; Flynn, K.J.; Shields, R.J. Rapid determination of bulk microalgal biochemical composition by Fourier-Transform Infrared spectroscopy. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 148, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, D.; Charisis, A.; Theocharidou, A.; Ritzoulis, C.; Papapanagiotou, G.; Samara, C.; Chatzidoukas, C.; Kalogianni, E.P. Foaming Properties of Chlorella sorokiniana Microalgal Biomass. Colloids Interfaces 2024, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Yadav, P.; Sharma, H.; Gupta, R.K. Sustainable approaches in microalgal biomass harvesting: Current advances and future perspectives. Int. J. Agric. Biosci. 2024, III, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).