Abstract
This paper considers the exponential stabilization problem for a class of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with multiple time-varying delays, whose nonlinear terms satisfy the linear growth condition. The state feedback controller that relies on a positive parameter to be determined is constructed to deal with nonlinear terms. By tactfully introducing the Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional with an exponential function and selecting the applicable parameter to be determined, the implementable state feedback controller can be obtained to guarantee that the closed-loop system is exponentially stable. The proposed state feedback control scheme is finally applied to the control design of two-stage chemical reactor system, which illustrates the effectiveness of the control method.
1. Introduction
Time delay phenomena frequently exist in a large number of practical applications, such as information transfer processes, chemical reaction processes, communication networks and power supply networks, etc. Additionally, the appearance of a time delay is one of the important factors leading to performance deterioration and the instability of a system; hence, the stability analysis of dynamic systems with time delays has become an important theoretical and practical topic. During the past several decades, with the help of different controller design and analysis methods, a great deal of effort has been put into the stabilization problems of nonlinear time delay systems, especially for strict-feedback nonlinear time delay systems. By adopting fuzzy logic systems to identify the unknown nonlinear terms, Refs. [1,2,3] investigated the problems of adaptive fuzzy tracking control for strict-feedback nonlinear time delay systems with an output constraint or full-state constraints. Through introducing the radial basis function neural networks to approximate unknown nonlinear functions and designing the adaptive neural network controller, Refs. [4,5,6,7] considered the adaptive control problems of strict-feedback nonlinear time delay systems. In addition, Refs. [8,9,10,11], respectively, studied the robust adaptive control problems of strict-feedback nonlinear time delay systems with different system structures.
It can be seen from the above-mentioned literatures that almost all controllers are designed to make the closed-loop systems asymptotically stable or bounded. However, the control requirements of many practical systems are not only stable but also have a certain rate of convergence in some circumstances. Due to the fact that the exponential stability has this property, the exponential stabilization problems of nonlinear time delay systems have received much attention and have obtained a series of rich results. Oucheriah [12] addressed the robust exponential stabilization for a class of uncertain dynamic time delay systems with a bounded controller. Hua et al. [13] considered a class of interconnected time delay systems with general nonlinear interconnections and mismatched time delay functions, and a decentralized state feedback controller was systematically designed to ensure that the solutions of the closed-loop system were uniformly ultimately bounded and exponentially convergent towards a ball. Using the Razumikhin theorem, Dong et al. [14] provided the continuous state feedback controller design scheme and established the exponential stabilization criterion based on the solutions of the standard Riccati differential equation for nonlinear systems with uncertainties and time-varying delays. Applying some sufficient conditions in terms of linear matrix inequalities, the problem of the exponential stabilization of memristive neural networks with time delays was investigated in Wu and Zeng [15]. Benabdallah and Echi [16] dealt with the exponential stabilization control problem for a kind of nonlinear systems with a constant time delay. Taking into account the time-varying delays and nonlinear disturbances, Li et al. [17] solved the exponential stabilization for a class of switched time-varying systems, and time-dependent switching signals have been characterized by Metzler matrices such that the closed-loop system is globally exponentially stable. The exponential stabilization problems of memristive neural networks with time delays and different system structures were, respectively, investigated in [18,19,20,21].
Motivated by the above analysis, this paper will further consider the problem of exponential stabilization for a class of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with multiple time-varying delays. Firstly, we propose the state feedback control law, which depends on a determined positive parameter to compensate for nonlinear terms. Secondly, with the construction of the Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional that includes the exponential function and fully considers the influence of time-varying delays, by choosing the applicable parameter, the exponential stability of the closed-loop system is strictly verified via two different ways. Finally, a simulation example is provided to show the effectiveness of the proposed design strategy.
Notations: denotes the set of all non-negative real numbers, is the real n-dimensional space, stands for the unit matrix of the corresponding dimension, denotes the transpose, (or means the maximum (or minimum) eigenvalue of a symmetric matrix, stands for the Euclidean norm of a vector or the induced Euclidean norm of a matrix and represents the set of all -value continuous functions on endowed with the norm defined by for .
2. Problem Description
Consider the strict-feedback nonlinear system with multiple time-varying delays described by
where and are the system state and control input, respectively. For , , is the time-delayed system state, is the time-varying delay that satisfies , the nonlinear term satisfies the local Lipschitz condition and vanishes at zero, and the initial condition is with .
The control objective of this paper is to construct the state feedback controller such that the closed-loop system of system (1) with any initial condition is exponentially stable, i.e., there exists a pair of positive constants and N such that the solution of system (1) satisfies
To achieve this purpose, the following assumption is made for system (1).
Assumption 1.
For , there exist positive constants and such that
Remark 1.
The definition of exponential stability (2) for nonlinear time delay systems can be regarded as an extension of the definition of exponential stability for nonlinear systems without a time delay in Khalil [22]. In the case of the time-varying delay , inequality (2) will be changed into , which was used in Khalil [22].
Remark 2.
As illustrated in [12,14,15,16,17] and the related works, it can be seen that the linear growth condition in Assumption 1 is a natural condition often adopted to study the exponential stabilization problem of nonlinear time delay systems.
In what follows, the state feedback controller design and stability analysis of system (1) will be given.
3. Controller Design and Stability Analysis
Introduce the coordinate transformation
and the state feedback controller
where , is a positive parameter to be determined, stands for diagonal matrix and is selected such that is Hurwitz. With the help of (5) and (6), using the fact that , we obtain the transformed closed-loop system
Consider the Lyapunov function
where is a positive real number and is a positive definite symmetric matrix and satisfies . Applying (7) and (8), the derivative of is
Adopting the mean square inequality and (10), there is a positive constant such that
Then, the main result of this paper is illustrated in the following theorem.
Theorem 1.
Proof.
Remark 3.
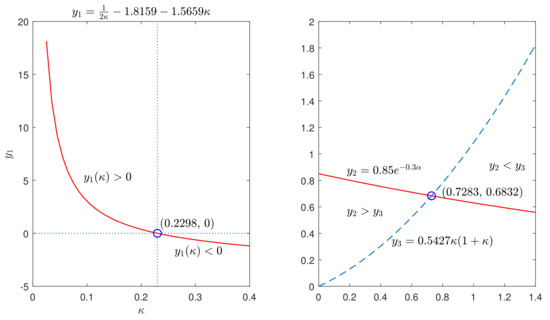
It should be pointed out that the positive parameter κ satisfying condition (12) always exists because tends to infinity and the remaining three terms are finite as κ tends to zero.
By selecting another Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional that is different from (13), we can draw another conclusion.
Theorem 2.
Proof.
Based on (20), (21) and the denseness of real numbers, (23) is changed into
where , and is a positive constant.
By virtue of (5), we further have
Hence, Theorem 2 is satisfied with and . □
Remark 4.
In this paper, the exponential stabilization problem for a class of strict-feedback nonlinear system (1) with multiple time-varying delays is investigated. By considering the Lyapunov–Krasovskii functional with exponential function (13) or (22), the exponential stability of the closed-loop systems can be proven.
On the basis of Theorem 2, it is possible to further deduce the following property on the exponential stabilization of system (1), which is summarized in Corollary 1.
Corollary 1.
Proof.
We know from Theorem 2 that the closed-loop system is exponentially stable if conditions (20) and (21) hold. Now, we can make condition (21) always true by suitably choosing the positive parameters and in the following way.
One can easily see that (21) is satisfied if and only if
Additionally, it is noted that tends to zero as tends to zero, which implies that there exists such that
Remark 5.
For Corollary 1, the positive parameter κ satisfying condition (20) can also be found. Since tends to infinity and the remaining two terms are finite in (20) as κ tends to zero, there always exists such that condition (20) holds. Hence, conditions (20) and (21) can be satisfied simultaneously by choosing and (27).
4. An Example
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed design scheme, let us consider the two-stage chemical reactor with delayed recycle streams [23,24] shown in Figure 1, which contains two well-mixed isothermal continuous stirred tank reactors 1 and 2. The mass balance equations are
where and are the compositions, and are the reactor volumes, F is the feed rate, and are the recycle flow rates, and are the reactor residence times, and are the reaction constants, and represent the uncertainties or disturbances and and are the time-varying delays.
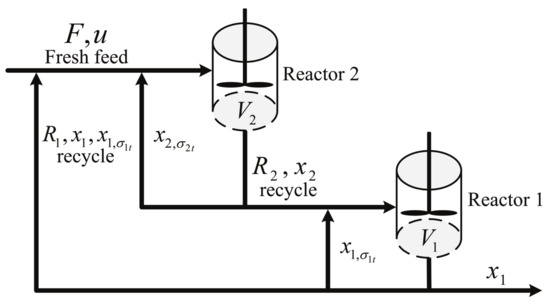
Figure 1.
Two-stage chemical reactor with delayed recycle streams.
Taking , , , , , , , , , , , and , system (28) is transformed into
It is clear that Assumption 1 is satisfied by , , , . Choosing , is thus Hurwitz. From which, we further obtain the positive definite symmetric matrix . By constructing the state feedback controller
and taking , , , , , , it is easy to deduce from (12) of Theorem 1 that
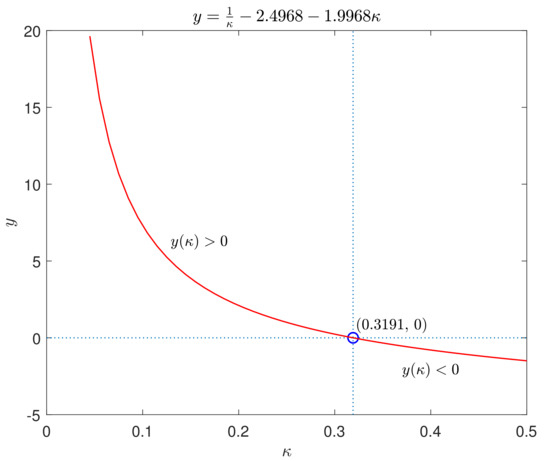
Figure 2.
The curve of .
In the simulation, selecting the initial data and , Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5, respectively, provide the responses of the closed-loop system (29) and (30) with different parameter values .
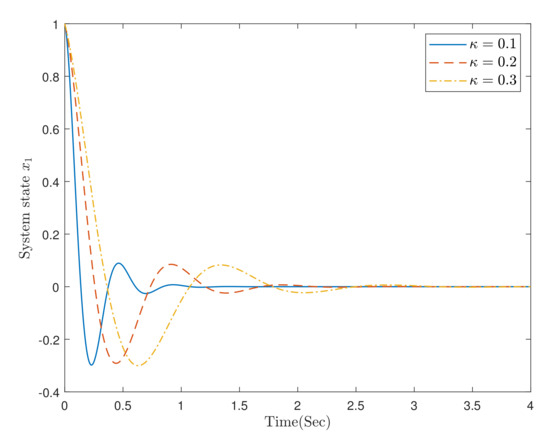
Figure 3.
The trajectories of system state .
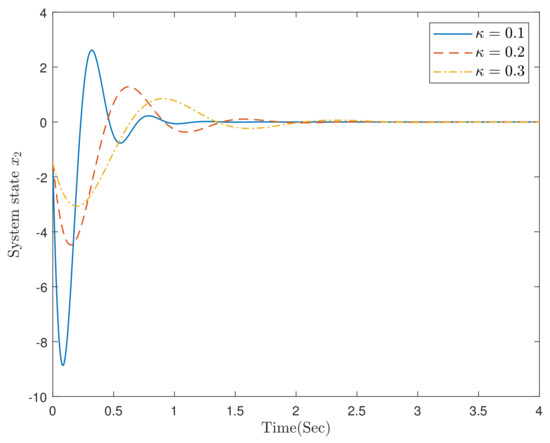
Figure 4.
The trajectories of system state .
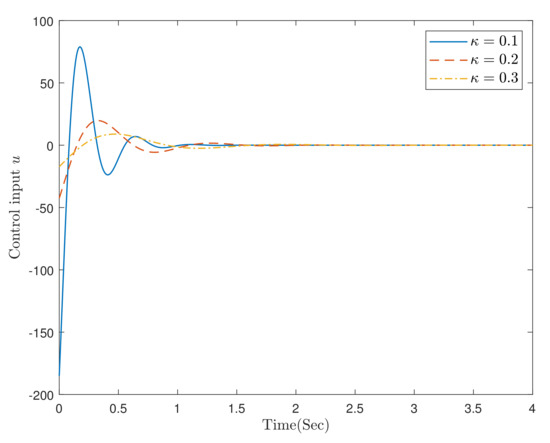
Figure 5.
The trajectories of control input u.
5. Conclusions
This paper solves the exponential stabilization problem for a class of strict-feedback nonlinear systems (1) with multiple time-varying delays. By introducing two different Lyapunov–Krasovskii functionals (13) and (22) with an exponential function, two different proof approaches are provided to verify that the presented state feedback controller can guarantee that the closed-loop system is exponentially stable. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed control method.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K. and L.L.; methodology, L.L.; software, M.K. and L.L.; validation, M.K. and L.L.; formal analysis, M.K. and L.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K.; writing—review and editing, L.L.; supervision, L.L.; project administration, L.L.; funding acquisition, L.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China grant number 61773073, the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province grant number 2021MS313 and the Education Committee Project of Liaoning Province grant number LJ2019001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, H.Y.; Wang, L.J.; Du, H.P.; Boulkroune, A. Adaptive fuzzy backstepping tracking control for strict-feedback systems with input delay. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2017, 25, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Yuan, W.X.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.S.; Sun, Q. Adaptive fuzzy control of strict-feedback nonlinear time-delay systems with full-state constraints. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 20, 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.J.; Ma, M. Adaptive fuzzy tracking control for a class of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with time-varying input delay and full state constraints. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 3432–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Shi, P. Adaptive neural control for a class of perturbed strict-feedback nonlinear time-delay systems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Cybern. Part B Cybern. 2008, 38, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, W.S.; Yang, F.Z.; Li, J.; Zhu, Q. Global adaptive neural control for strict-feedback time-delay systems with predefined output accuracy. Inf. Sci. 2015, 301, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Li, L. Adaptive neural network tracking control for a class of switched strict-feedback nonlinear systems with input delay. Neurocomputing 2016, 173, 2121–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Yoo, S.J. Neural-networks-based adaptive quantized feedback tracking of uncertain nonlinear strict-feedback systems with unknown time delays. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 10691–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehardoli, H.; Eghtesad, M. Robust adaptive control of switched nonlinear systems in strict feedback form with unknown time delay. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 2015, 32, 761–779. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.C.; Xu, S.Y.; Li, Y.M.; Chen, W.M.; Chu, Y.M. Robust adaptive control of strict-feedback nonlinear systems with unmodelled dynamics and time-varying delays. Int. Control 2017, 90, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.S. Simple adaptive robust control schemes of uncertain strict-feedback nonlinear time-delay systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2017, 11, 2222–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, M.; Talebi, H.A.; Menhaj, M.B. Robust adaptive dynamic surface control of nonlinear time-varying systems in strict-feedback form. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 1432–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oucheriah, S. Exponential stabilization of a class of uncertain time-delay systems with bounded controllers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.C.; Wang, Q.G.; Guan, X.P. Exponential stabilization controller design for interconnected time delay systems. Automatica 2008, 44, 2600–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.L.; Wang, X.L.; Mei, S.W.; Li, W.X. Exponential stabilization of nonlinear uncertain systems with time-varying delay. J. Eng. Math. 2012, 77, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.L.; Zeng, Z.G. Exponential stabilization of memristive neural networks with time delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. 2012, 23, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Benabdallah, A.; Echi, N. Global exponential stabilization of a class of nonlinear time-delay systems. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 3857–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Sun, Y.G.; Meng, F.W.; Tian, Y.Z. Exponential stabilization of switched time-varying systems with delays and disturbances. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 324, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Fang, J.A.; Li, H.Y.; Duan, W.Y. Exponential stabilization of time-varying delayed complex-valued memristor-based neural networks via impulsive control. Asian J. Control 2018, 20, 2290–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Lewis, F.L.; Zeng, Z.G. Exponential stabilization of fuzzy memristive neural networks with hybrid unbounded time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Huang, T.W.; Zeng, Z.G.; Li, P. Exponential stabilization of inertial memristive neural networks with multiple time delays. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 51, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Huang, T.W.; Zeng, Z.G. Exponential stabilization of fuzzy memristive neural networks with multiple time delays via intermittent control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 3092–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Systems; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nguang, S.K. Robust stabilization of a class of time-delay nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2000, 45, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yin, S.; Zhang, L.X.; Yin, X.Y.; Yan, H.C. Improved results on asymptotic stabilization for stochastic nonlinear time-delay systems with application to a chemical reactor system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 47, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.H.; Xie, X.J. Finite-time stabilization of stochastic low-order nonlinear systemswith time-varying orders and FT-SISS inverse dynamics. Automatica 2021, 125, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.H.; Xie, X.J. Finite-time stabilization of output-constrained stochastic high-order nonlinear systems with high-order and low-order nonlinearities. Automatica 2022, 136, 110085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.L.; Deng, F.Q.; Sun, Y.; Shi, P. Fault estimation and fault-tolerant control for linear discrete time-varying stochastic systems. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 200201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.S.; Zhao, D.Y. Event-triggered fault detection for nonlinear discrete-time switched stochastic systems: A convex function method. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2021, 64, 200204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).