Abstract
The rapid growth of the Industrial Revolution (IR) 4.0 has prompted the Malaysian Education Institution to transform the current education system into the future education system 4.0. The impact of IR 4.0 has opened a new paradigm for the Malaysian Educational Institution to ensure that all lecturers are capable of using information and communication technologies (ICT) in teaching and learning. However, there is a challenge in identifying appropriate digital learning platforms and tools to engage students in learning at their own pace. In this paper, we aimed to investigate the demand for digital learning platforms and tools according to the needs of students in Polytechnic Malaysia. The study was conducted randomly among 320 students from various fields of study in selected polytechnics. The analysis method used in this study was a quantitative method using questionnaires as an instrument. The results of our study indicated that e-learning platforms were the highest demand students’ preferred compared to other learning platforms and tools. Hence, the implications of this study could be useful as a guideline to assist Malaysian Polytechnic lecturers in strengthening the practice of using digital learning and develop digital proficiency for enabling education 4.0 in the future.
1. Introduction
Malaysia is one of the Industrial Revolution (IR) 4.0 nations involved in globalization, changing in technology-driven for economic growth. It empowers digital technology with the aid of interconnection through the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, virtual and augmented reality, artificial intelligence, and other IT paradigms that trigger most industries [1]. This positive impact provides an opportunity for many industries to increase productivity and strategy not only in the manufacturing sectors but also in the Malaysian education sector as well. Correspondingly, the impact of it towards the education paradigm has led to future education 4.0 by considering the benefits to the new vision in learning skills and knowledge trends [2]. Students have to be trained, mentored, and facilitated in a different pedagogical approach to correspondence with new possibilities.
Digital learning is an instructional practice in any educational activity that uses technology to improve the learning experience of the students. It makes use of a wide range of technology-enhanced educational strategies that ultimately helps students. Not only is digital learning a highly advanced form of technology, but it allows students much flexibility for them to study at any time at their convenience without thinking about their schedules. This advantage has made digital learning hugely popular not only among engineering students but also triggers among social science students as well. As for the engineering field, engineering education has redesigned the role of their education practice to ensure the content and concept of education 4.0 can be sustained to aligned with the industry 4.0 [3]. This involves blended learning, flipped learning, personalized learning, and other techniques that rely on small or large-scale digital platforms and tools. Hence, it can improve the students’ engagement in the subjects they are interested in and can share their learning experiences with peers. Therefore, Malaysia polytechnic must provide education trends to ensure that technology, values, and modern industry are integrated, and yet at the same time, the lecturers should be equipped enough to fulfill the level of expertise to produce high-quality skilled graduates.
The motivation for this study was based on the discussion by [4], who stated that polytechnic lecturers are still inexperienced in education technology and have difficulty in fully utilizing information and communication technologies (ICT) in teaching. Therefore, the findings of this study can be used for polytechnic lecturers to strengthen their digital ICT proficiency practice based on the needs of future education 4.0 introduced by [5]. By this, the polytechnic lecturers need to make an informed decision about digital learning platforms and tools that could meet the students’ interests. Thus, the objective of our paper was to highlight the level of student demand towards the use of digital learning platforms and tools for lecturers strengthens the digital proficiency practice in Polytechnic Malaysia. Figure 1 showed the proposed theoretical framework of this study.
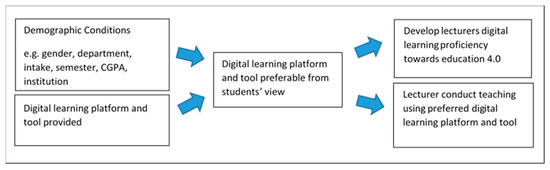
Figure 1.
Proposed theoretical framework.
The structure of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents related works of the previous studies. Section 3 presents the materials and methods used and limitation for the research. Research findings and analysis of this study is detailed and justified in Section 4. Section 5 presents the discussion of this study. Finally, future directions and conclusions are pointed out in Section 6 and Section 7 respectively.
2. Related Works
2.1. Advantage of Education 4.0 for Malaysia Education
The existence of IR 4.0 continues to change the world, and even Malaysia education also faces the challenge of preparing students to meet the demands of the IR 4.0 industry. Through the IR 4.0 revolution, the method of approach in teaching and learning is known as education 4.0, has changed to a new era of the learning system. This 4.0 education has characteristics that shape students for self-learning, critical thinking, digital capabilities, and problem-solving ability [6,7,8]. According to [9], education 4.0 is a new learning system that enables students to develop lifelong learning and skills. It provides the notion of teaching and learning innovation and uses ICT in its processes. Moreover, Hussin [2] also stated it enables self-directed and more flexible learning regardless of time and place through accessible ICT platforms and tools everywhere. Therefore, the learning process can become more affordable and faster because students can learn in mobility through blended and virtual learning with the BYOD (bring your own device) approach. As well as ICT supported, students are also fully empowered to determine how they learn and independently able to improve the educational learning process based on their needs and achievements [10].
2.2. Digital Learning Platform and Tool
Anttila [11] stated that digital learning is a digital tool for obtaining digital teaching materials to carry out online or offline learning activities over wired or wireless networks. With the advancement of information technology and related technologies, digital learning can be leveraged by lecturers to create innovative features to provide students with systematic knowledge and teaching materials. In the IR 4.0 era, digital learning has increased its field to support the various industries in Malaysia. According to [12] the sufficient knowledge or digital learning of the industrial operations before the employment or during the work may motivate the learners positively. In addition, digital learning can develop learners’ self-motivation and professionalism for quality improvement [13]. In [14], it described that digital learning could be accessed to online learning and adapt to digital instructional that makes use of technology devices such as smartphone and tablet. Therefore, learning can be done via an online or web-based model where students can study independently [15]. As to support education 4.0, there are various digital learning tools and platforms that could engage and motivate students to study. The choice of digital learning is essential in determining a sustainable learning lifestyle [16]. Table 1 shows several platforms and tools of digital learning that possibly facilitate communication between lecturers and students.

Table 1.
Digital learning platforms and tools [17].
As seen in Table 2, there are several related studies of digital learning platforms and tools commonly applied for Malaysian education polytechnic—the chosen of the platform and tools based on the students’ awareness and experience in class.

Table 2.
Related studies of digital learning platforms and tools.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data Collection
In this study, a sample of 320 students was obtained from 180 (56.3%) females and 140 (43.8%) males from 7 departments in 11 Malaysian polytechnics. We surveyed students from the Department of Commerce (JP), Department of Tourism and Hospitality (JPH), Department of Design and Visual Communication (JRKV), Department of Information and Communication Technology (JTMK), Department of Electrical (JKE), Civil Engineering Department (JKA), Department of Mechanical (JKM), and Department of Aircraft Maintenance (JPP). The questionnaire was selectively distributed to the lecturers for the students in the classroom to answer online based using a self-administered approach [36].
This study was designed using quantitative methods through open and closed questions. A set of questionnaires was developed and consisted of two sections for collecting data. Students are required to fill in demographic data in Section A as shown in Table 3. As for Part B (Table 4), questions related to digital learning platforms and tools based on students’ personal experiences in Polytechnic Malaysia. Question items are designed based on Table 2 as they are the basis of the research presented in this paper.

Table 3.
Demographic items.

Table 4.
Survey items for Section B.
3.2. Limitations
There were some challenges in our research when collecting data, as we found that the number of participants did not reach the target of representing the entire Malaysian Polytechnic Institution. Therefore, we have identified some limitations to this fact; (1) the selection of lecturers to assist in the research during the dissemination of the questionnaire could influence the number of students participating in answering the survey and therefore, only students who are taught by them can respond to the given survey; (2) we stated digital learning platforms and tools in the general interest, which refer only to the personal experiences of students at Polytechnic Malaysia. However, our study has achieved the aim by demonstrating the demand for appropriate digital learning platforms and tools among students for lecturers to strengthen the digital ICT practices towards education 4.0 in Polytechnic Malaysia.
4. Results
In this study, we have selected the group of students that represent 11 Polytechnic Malaysia from seven departments based on the current cohort of study (some of the courses not be offered at the same polytechnics). The respondents’ distribution of all departments were presented in Figure 2. It shows that the percentage of respondents from JTMK students is considerably highest with 63% whereas JKE students 16%, JP students 9%, JKA students 4%, JPH and JRKV students 2% respectively and JPP students 1%. From the results, we have found there is a gap in the number of participants for each departments, as such we have discussed in Section 3.2.
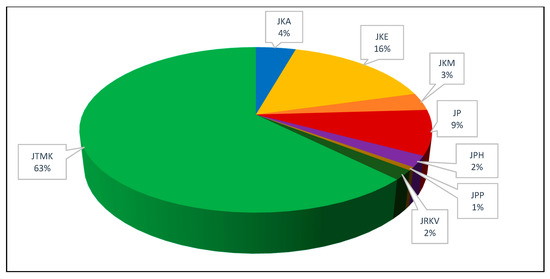
Figure 2.
Distribution of respondents by the department.
We performed a set of questionnaire to investigate the demand for digital learning platforms and tools according to the needs of students in Polytechnic Malaysia. As seen in Figure 3, we also have included traditional methods (chalk and blackboard) as control features in the questionnaire for comparative purposes. The data indicates that majority of the respondents have a high interest in the use of the curriculum information document online system (CIDOS, 25%) in classroom learning followed by mobile learning apps at 16%, chalk, and blackboard at 16%, augmented and virtual reality (AR and VR) apps at 14%, YouTube at 13%, gamified via Kahoot! and Quizizz and MOOC at 8%, respectively. The reason for this corresponds as students perceive CIDOS would be easier to access the materials related to the course taken by them.
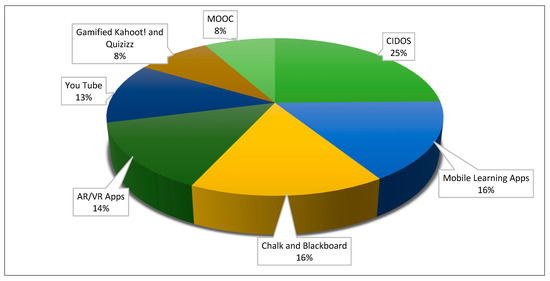
Figure 3.
Digital learning platforms and tools preferred by students.
Previously, we have mentioned some challenges in our research which might influence our results. Therefore, we tried to address this problem by grouping the respondents into two groups, namely engineering and non-engineering students. As such, we have selected four departments from JP, JPH, JRKV and JTMK to represent the non-engineering students whereas another four departments from JKE, JKA, JKM and JPP represent the engineering students. The results presented in Figure 4 shows that engineering students have a higher demand for traditional methods, with 29.1% compared to others. As for non-engineering students, the CIDOS learning platform is the highest demand in the classroom, with 27%. Interestingly, we realized that the use of traditional methods among the engineering students is higher compared to non-engineering students, as only students thought it could enhance their understanding in the classroom.
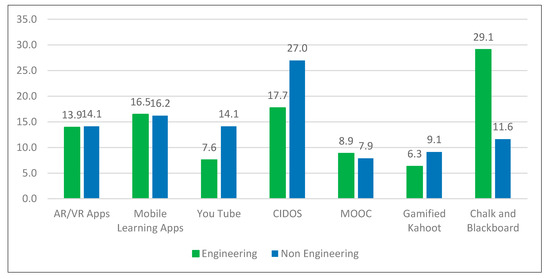
Figure 4.
Students’ demand for the use of digital learning platforms and tools by field of studies.
Additionally, in Figure 5, we found that female students have dominated the interest in learning to use CIDOS more than male students. However, male students dominate the use of mobile apps and gamified platforms through Kahoot! and Quizizz more than females. In addition, the results also reveal that both genders have the same demand for digital learning through YouTube.
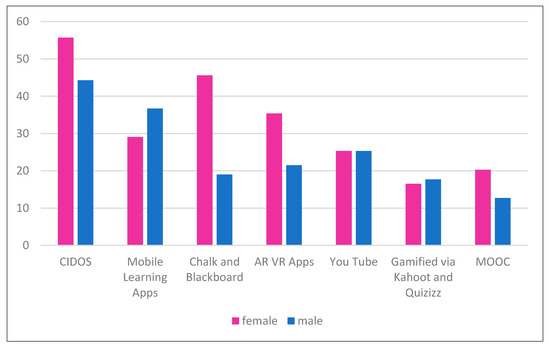
Figure 5.
Students’ demand for the use of digital learning platforms and tools by gender.
Predominantly, the use of appropriate digital learning platforms and tools as a medium to attract students to learn at their own pace can enable lecturers to teach better and develop digital proficiency towards education 4.0. Figure 6 shows the results to see how the use of preferred digital learning could impact students’ understanding of knowledge. From the results, 91% (291) students agreed that digital learning influenced their learning in the classroom whereas only 9% (29) said no. Therefore, the preferred digital learning platforms and tools from the students have shown the most positive impact to the understanding of learning.
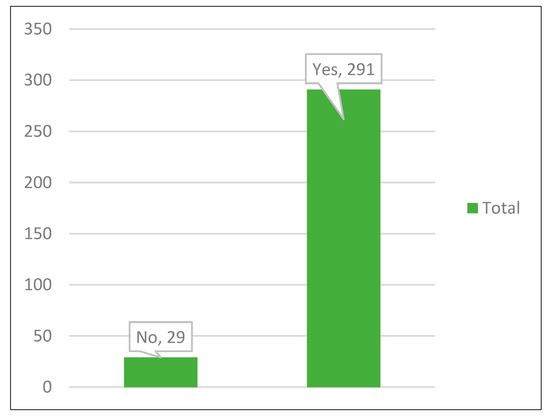
Figure 6.
Students’ response to the impact of digital learning.
5. Discussion
This paper aims to investigate the demand for digital learning platforms and tools according to the needs of students in Polytechnic Malaysia. Our study has revealed that e-learning platforms using CIDOS are the highest learning platforms in which students most preferred to be used in the classroom for learning purposes. The results are in line with other studies conducted from [37], which indicated that CIDOS is well received among students, which was supported in our study. However, we have found previous studies [38] that stated some of the lecturers were not convenient in using CIDOS due to the time and difficulties constraints. By these issues, our findings have proven that CIDOS mainly should be utilized in an extensive way and more efficient among lecturers to motivate the students to learn. In another way, by implementing this platform efficiently or use different platforms like google classroom, webinar or Coursera, lecturers can guide students to learn independently for moving towards the transformation of education 4.0.
Secondly, our study shows that digital learning using a mobile learning application platform has the potential to attract students for sustainable learning. A study from [39] showed that mobile learning is a useful learning tool for learning. Therefore, it can be concluded that learning to use mobile applications can provide lecturers the opportunity to explore and innovate useful software materials by filling the digital practice gap.
Thirdly, there are other digital learning platforms and tools that take into account, which possibly gives excitement in learning, such as AR and VR apps, YouTube, online gamification, and MOOC. Using an online gamified platform such as Kahoot and Quizziz, proved to increase the students’ interest, which is beneficial to lecturers utilized it in the classroom. However, our study has discovered that there is a lack of demand for learning through MOOC platforms among the students. We believe this circumstance has related to the challenges and issues discussed due to lifestyle, infrastructure, infostructure, and professional development [22]. Thus, perhaps by using MOOCs in individual courses of study, it would be able to give a promising response from students in the future [40].
Demand for digital learning platforms and tools among students in Polytechnic Malaysia remains high favored compared to traditional methods. Nevertheless, there are various potentials digital learning that lecturers can use to interest students; our results have revealed that engineering students are more likely to choose traditional methods through chalk and blackboard in class. We consider these barriers as learning in engineering fields would depend on the material support, curriculum, management decisions, and the readiness of lecturers to use the technologies [3]. Although there are a number of challenges faced by lecturers in the use of digital learning [41], the importance of technology towards education 4.0 is an opportunity for efficient future learning.
6. Future Directions
For future research, this study will collect more samples with detailed survey questions in order to support a personalized learning environment among students which may contribute to the field of learning analytics. We also like to explore the usage of digital learning platform and tools among lecturers in Malaysian educational institutions in order to share knowledge and support the education 4.0.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we present the demand for digital learning among students and a theoretical framework to help lecturers develop digital competencies to implement education 4.0 in the future. The use of appropriate digital learning platforms and tools can drive student engagement in learning in line with educational 4.0. Therefore, lecturers should prepare, adapt and enhance digital proficiency and ICT to meet the demands of students who want technology in their learning.
Author Contributions
Formal analysis, P.M.; methodology, O.K. and N.T.N.; validation, O.K.; writing—review and editing, S.D.A.B., and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) under Research University Grant Vot-20H04, Malaysia Research University Network (MRUN) Vot 4L876, and the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) Vot 5F073 supported under the Ministry of Education Malaysia. The work is partially supported by the SPEV project (ID: 2103-2020), Faculty of Informatics and Management, University of Hradec Kralove. We are also grateful for the support of Ph.D. students Jan Hruska and Michal Dobrovolny in consultations regarding application aspects from Hradec Kralove University, Czech Republic. The APC was funded by the SPEV project 2020/2103, Faculty of Informatics and Management, University of Hradec Kralove.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Maskuriy, R.; Selamat, A.; Ali, K.N.; Maresova, P.; Krejcar, O. Industry 4.0 for the Construction Industry—How Ready Is the Industry? Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussin, A.A. Education 4.0 Made Simple: Ideas For Teaching. Int. J. Educ. Lit. Stud. 2018, 6, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogoş, R.I.; Bodea, C.N.; Dascălu, I.; Safonkina, O.; Lazarou, E.; Trifan, E.L.; Nemoianu, I.V. Technology Enhanced Learning for Industry 4.0 Engineering Education. Rev. Roum. Sci. Tech. Ser. Electrotech. Energy 2018, 63, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Sirajuddin, P.T.S.; Mohamed, A.H. The Effectiveness of Training: Equipping and Enhancing ICT Knowledge and Skills among Polytechnic Lecturers in Producing Quality Highly Skilled Graduates. Adv. J. Tech. Vocat. Educ. 2017, 1, 1–05. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, P. Education 4.0, the Future of Learning Will Be Dramatically Different, in School and Throughout Life. 2017. Available online: http://www.thegeniusworks.com/2017/01/future-education-young-everyone-taught-together (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Sarah, D. Member Stories: Moving Towards Education 4.0. 2019. Available online: https://www.jisc.ac.uk/blog/member-stories-towards-higher-education-40-15-jan-2019 (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Puncreobutr, V. Education 4.0: New Challenge of Learning. St. Theresa J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2016, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Aberšek, B. Evolution of Competences For New Era or Education 4.0. In Proceedings of the XXV Conference of Czech Educational Research Association (CERA/ČAPV), Czech Budejovice, Czech Republic, 14–16 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sinlarat, P. Education 4.0 is More than Education. In Annual Academic Seminar of the Teacher’s Council on the Topic of Research of the Learning Innovation and Sustainable Educational Management; The Secretariat Office of Teacher’s Council: Bangkok, Thailand, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Deaconu, A.; Dedu, E.M.; Igret, R.S.; Radu, C. The Use of Information and Communications Technology in Vocational Education and Training—Premise of Sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, M.; Välimäki, M.; Hätönen, H.; Luukkaala, T.; Kaila, M. Use of web-based patient education sessions on psychiatric wards. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2012, 81, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharasudan, A.; Kot, S. A Scoping Review on Digital English and Education 4.0 for Industry 4.0. Soc. Sci. 2018, 7, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Liu, K.-S. A Study of the Effects of Digital Learning on Learning Motivation and Learning Outcome. Eur. J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2017, 13, 3553–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, R.; Jalil, Z.A.; M.Gunawan, M.F. Community College Students’ Perception Towards Digital Learning In Malaysia. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 195, 1798–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, N.A.A.; Hussein, N.; Aluwi, A.H. Satisfaction on Blended Learning in a Public Higher Education Institution: What Factors Matter? Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 211, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starcic, A.I.; Terlević, M.; Lin, L.; Lebenicnik, M. Designing Learning for Sustainable Development: Digital Practices as Boundary Crossers and Predictors of Sustainable Lifestyles. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A. 11 Digital Education Tools for Teachers and Students. 2018. Available online: https://elearningindustry.com/digital-education-tools-teachers-students (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Ismail, N.; Ayub, A.F.M.; Yunus, A.S.M.; Ab Jalil, H. Utilising CIDOS LMS in Technical Higher Education: The Influence of Compatibility Roles on Consistency of Use. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2017, 23, 7783–7787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, H. The Definition of Mobile Learning. 2018. Available online: https://www.teachthought.com/the-future-of-learning/a-definition-for-mobile-learning (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Padmanathan, Y.; Jogulu, L.N. Mobile Learning Readiness among Malaysian Polytechnic Students. J. Inf. Syst. Technol. Manag. 2018, 3, 113–125. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.-F.; Hwang, G.-J.; Sung, H.-Y. Trends and research issues of mobile learning studies in physical education: A review of academic journal publications. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2018, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaari, R.; Ismail, Y.; Kok, R.A. Introduction to Massive Open Online Course (MOOC): The Issues and Challenges Using MOOC as A Teaching and Learning Method in Malaysian Polytechnic. Adv. J. Tech. Vocat. Educ. 2018, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmon, S.J.; Major, C.H. Wherefore Art Thou MOOC: Defining Massive Open Online Courses. Online Learn. 2017, 21, 195–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.I.; Shamsudin, S. Video Lecture Styles in MOOCs by Malaysian Polytechnics. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Education and Multimedia Technology—ICEMT 2019, Nagoya, Japan, 22–25 July 2019; pp. 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.A.; Al-Samarraie, H. MOOCs in the Malaysian higher education institutions: The instructors’ perspectives. Ref. Libr. 2018, 59, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathil, N.F.; Osman, S.Z.M.; Jamaludin, R. An Analysis of Using Online Video Lecture on Learning Outcome: The Mediating Role of Student Interaction and Student Engagement. J. Educ. e-Learn. Res. 2016, 3, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmad, S. Video-Based Learning—The New Pitch and Resolution of Learning. 2015. Available online: https://elearningindustry.com/video-based-learning-new-pitch-resolution-learning (accessed on 27 March 2020).
- Saidin, N.F.; Halim, N.D.A.; Yahaya, N. A Review of Research on Augmented Reality in Education: Advantages and Applications. Int. Educ. Stud. 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesim, M.; Ozarslan, Y. Augmented Reality in Education: Current Technologies and the Potential for Education. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 47, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçayır, M.; Akçayır, G. Advantages and challenges associated with augmented reality for education: A systematic review of the literature. Educ. Res. Rev. 2017, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, A.A.; Adnan, A.H.M.; Mustafa Kamal, N.N.; Mohd, K.M.A.; Ahmad, M.K. Education 4.0 Immersive Learning with Spherical Videos (360°) and Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences. In Proceedings of the International Invention, Innovative & Creative (InIIC) Conference, Palace of Golden Horses, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2–3 November 2019; MNNF Publisher: Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia, 2019; pp. 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad, S.N.M.; Sazali, N.S.S.; Salleh, M.A.M. Gamification Approach in Education to Increase Learning Engagement. Int. J. Humanit. Arts Soc. Sci. 2018, 4, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Jaafar, R.; Ismail, N.H. Gamification in Programming: Does Gamification Increase Student’s Motivation? Adv. J. Tech. Vocat. Educ. 2018, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, R.A.; Ahmad, S.; Hashim, U.R. The effectiveness of gamification technique for higher education students engagement in polytechnic Muadzam Shah Pahang, Malaysia. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2018, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, I.; Sen, S. The effects of gamification on students’ academic achievement: A meta-analysis study. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2019, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Lavrakas, P. Self-Administered Questionnaire. In Encyclopedia of Survey Research Methods; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 804–805. [Google Scholar]
- Romli, R. Implementation of Cidos (E-Learning) Among Diploma in Accountancy Students in Politeknik Sultan Abdul Halim Mu’adzam Shah, Jitra, Kedah. In National Innovation and Invention Competition Through Exhibition (iCompEx); Unit Penyelidikan, Inovasi dan Komersilan POLIMAS: Kedah, Malaysia, 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamad, S.N.M.; Salam, S. and Bakar, N. Lecturers’ Perceptions and Attitudes Towards the Usage of Online Learning at Polytechnic. Int. J. Sci. Commer. Humanit. 2014, 2, 2012–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Safie, A.; Wahid, S.Z. and Idris, N. Evaluating Student Perception Towards Application of Mobile Learning. In e-Proceeding National Innovation and Invention Competition Through Exhibition (iCompEx); Unit Penyelidikan, Inovasi dan Komersilan POLIMAS: Kedah, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sanmugam, A.T.; Ibrahim, L. Exploring Engineering Students’ Views on Learning English for TVET using MOOC. Adv. J. Tech. Vocat. Educ. 2018, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.A.; Adnan, A.H.M.; Azamri, N.M.; Idris, K.B.; Norafand, N.N.; Ishak, N.I. Education 4.0 Technologies for English Language Teaching and Learning in the Malaysian Context. In Proceedings of the International Invention, Innovative & Creative (InIIC) Conference, Palace of Golden Horses, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2–3 November 2019; MNNF Publisher: Negeri Sembilan, Malaysia, 2019. ISBN 978-967-17324-4-1. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).