Abstract
Evidences demonstrated that timing of weaning influences long-term growth in full term infants. However, studies on preterm infants are still lacking, and the international guidelines are focused only on healthy full-term newborn, without consensus for preterms. We aimed at evaluating, in a cohort study, the consequences of different timing of weaning on auxological outcomes up to 12 months of corrected age in a population of neonates born with gestational age < 32 weeks or birth weight < 1500 g. We divided the enrolled neonates in two cohorts according to the timing of weaning: (i) Early Weaning: introduction of complementary food before 6 months of corrected age; (ii) Late Weaning: complementary food introduced after 6 months of corrected age. Growth parameters (weight, length, body mass index, and ponderal index) were measured at 12 months of life. The two groups were statistically comparable for baseline clinical characteristics, and differences on growth parameters were not reported between the two study groups. These results were confirmed in linear and binary logistic regression multivariate models. Timing of weaning is not related to growth of preterm newborns in the first 12 months of corrected age. Studies are needed to reach consensus for the appropriate nutritional approach for preterm babies after discharge.
Keywords:
weaning; nutrition; VLBW; body weight; length; body mass index; follow-up; complementary food; breastfeeding; infant formula; neonatology; microflora 1. Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), survival of preterm infants has significantly improved thanks to the advances in neonatal care [1]. With the improvement in neonatal survival, preterm birth rates are increasing.
One of the most important prematurity-related morbidity in survived infants is malnutrition, which is in turn associated with poorer growth [2]. It has been demonstrated that there are critical windows for nutritional intervention during the first months of life, which may influence long-term growth. [2,3,4,5,6,7]. Evidences for healthy, full term infants demonstrated that the timing of starting complementary feeding, known as weaning, influences growth outcomes [8]. The WHO defines weaning the period when the diet changes from complete breastfeeding to when the child is able to eat family food [9]. International nutritional guidelines recommend exclusive or predominant breastfeeding approximately for the first six months [10,11]. However, timing and modalities for the introduction of complementary food are still lacking in preterm infants [12]. International guidelines are focused mainly on healthy full-term newborn, without consensus for preterms and, consequently, with variable clinical attitude among physicians [10,11].
Studies on preterm infants recognized that the first weeks of life represent a crucial timeframe for nutritional intervention [2,3,5,13], while it is yet to be demonstrated if the timing of weaning may also be considered an additional critical window for long-term growth outcomes [10]. Studies on optimal timing of weaning in preterms are needed; we designed a cohort study to evaluate the consequences of weaning on auxological outcomes of infants, born very preterm, in the first 12 months of corrected age.
2. Materials and Methods
We enrolled all newborns with gestational age < 32 weeks or body birth weight < 1500 g, consecutively admitted in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) of Policlinico Umberto I, Sapienza University of Rome, from January 2015 to December 2019 and with a follow-up of 12 months. We excluded subjects with major congenital (intestinal and extra-intestinal) malformations, inborn errors of metabolism, born to mother with autoimmune diseases, congenital infection, transfer to other hospital or death within the first 72 h of life, or with incomplete clinical data, lost to follow-up, or that developed food intolerance in the first 12 months [14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
Researchers not involved in the clinical practice collected data in a specific data form, unaware of the study aims; a statistician blinded to the study aims performed data analysis. We prospectively recorded prenatal, perinatal, and postnatal data in a specific data form. All infants were monitored until discharge, transfer to other hospital, or death. Maternal age, gestational age, and body weight at birth, antenatal steroid administration, type of delivery, gender, twin pregnancies, 5-min Apgar score, pH on cord blood, and Clinical Risk Index for Babies (CRIB) II score were collected [21]. Morbidity was defined as the presence of at least one of the major prematurity-related complications, such as necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) Bell-Stage ≥ 2, intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), periventricular leukomalacia (PVL), sepsis proven by positive culture, retinopathy of prematurity (ROP), and bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) of at least moderate grade. Diagnosis of NEC, BPD, IVH, PVL, ROP, and sepsis were performed according to standard criteria by physicians caring for the babies and were blinded of the study aims [22,23,24,25,26]. Extrauterine growth restriction (EUGR) with longitudinal definition was defined as the loss of 1 standard deviation from birth to 36 weeks of PMA [27]. The age of 36 weeks of PMA represents a criteria for discharge. Data on PN and EN were daily collected. We also collected data regarding need of invasive or non-invasive mechanical ventilation.
At 52 weeks of postmenstrual age (PMA) and at 12 months of corrected age, nurses unaware of the study aims measured growth parameters (body weight, length, body mass index (BMI, weight/length2), and ponderal index (weight/length3)), as previously described [28]. Enteral and parenteral nutrition from hospital admission to discharge were administered as previously described [29,30]. At discharge, medical staff encouraged breastfeeding. Preterm formula was administered when breast milk was insufficient or not available up to 2500 g of body weight. Subsequently, at term, formula was introduced.
At discharge, parents and family pediatricians of babies were provided with a detailed set of written recommendations regarding modalities of introduction of complementary food, in accordance with European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) [10] and regarding the amounts of energy intakes that infants could have received per day [31]. Family pediatrician received further information by phone or videoconference if required. We summarized these recommendations in Table S1. In brief, we suggested to continue breastfeeding or formula along with the introduction of complementary food and to offer a variety of foods with different flavors and textures [10]. We recommended to introduce all variety of foods at the same time. We suggested to avoid delayed introduction of some foods to reduce possible allergy reactions. Amount of complementary food should be increased depending on child’s appetite. We recommended to start weaning from the 52 weeks of PMA and 9 months of corrected age only in the presence of the following of two criteria: (i) positive clinical judgment of family pediatrician to infants that attained motor skills (independently by growth and human milk alimentation) adequate to cope safely with solid foods and (ii) family deemed to be ready. In this way, we hypothesized a spontaneous distribution of the timing of weaning along the period between 52 weeks of PMA and 9 months of corrected age. During the follow-up visit, a researcher unaware of the study aims prospectively recorded time of complementary food introduction, and he kept in contact with the pediatrician to verify if parents respected the indication received regarding variety of foods, textures, frequency, and amounts of meals. The family pediatrician verified the compliance regarding recommendation received, including food texture, variety, frequency of meals, and caloric intake (Table S1). We reported data regarding compliance to our recommendations in a specific data form. We divided enrolled newborns in 2 groups according with the timing of weaning: (1) Early Weaning: introduction of complementary food before 6 months of corrected age and (2) Late Weaning: complementary food introduced after 6 months of corrected age. We excluded from analysis infants receiving complementary food before 52 weeks of PMA or after 9 months of corrected age.
Physician unaware of the study aims measured growth parameters (weight, length, BMI, and ponderal index) at 12 months of corrected age, and standardized growth parameters (weight z-score, length z-score, and BMI z-score) at 12 months were considered as primary outcome of the study.
Statistics
Statistical analysis was performed using Statistical Package for Social Science software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) version 25.0. We checked for normality using Shapiro−Wilk test. The mean and 95% confidence interval summarized continuous variables and number and percentage described categorial variables. We used χ2 test for categorical variable and t-test or Mann−Whitney for paired and unpaired variables.
Correlations were performed between growth parameters at 12 months (standardized and unstandardized) and timing of weaning by Pearson correlation.
We performed linear regression analysis separately for male and female infants, using as covariates maternal age, gestational age at birth, duration of breastfeeding, age of weaning, and, as dependent variable, standardized growth parameters at 12 months. We also evaluated in a binary regression analysis the influence of covariates (intrauterine growth restriction, born before 28 weeks of PMA, male sex, morbidity, EUGR, exclusive breastfeeding up to weaning, and group assignment) on growth impairment at 12 months of corrected age (defined as Z-Score parameters < −1 for body weight, length and BMI).
We considered the level of significance for statistical tests as 2-sided (p-value < 0.05).
3. Results
Of 255 eligible newborns, we enrolled 154 neonates at 12 months of corrected age (Figure 1). As shown in Table 1 and Table 2, the two groups of the study were similar for baseline clinical characteristics and morbidity rate.
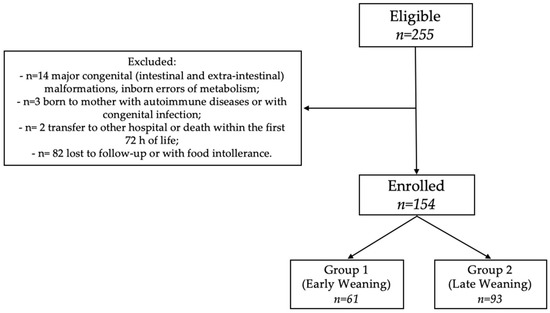
Figure 1.
Flow-chart.

Table 1.
Baseline clinical characteristics of the study population.

Table 2.
Morbidity rate of the study population.
Table 3 summarizes nutritional management of the newborns from birth. The rate of newborns receiving exclusive breast milk up to weaning were higher in group 1 compared to group 2 (Table 3). The mean age of weaning of total population was 6 months ± 1, and it appeared lower in group 1 (Table 3).

Table 3.
Nutritional management of the study population.
There were no differences for growth parameters (body weight, length, BMI, and ponderal index) at 52 weeks of PMA (Table S2). As shown in Table 4, the two groups did not show difference for growth parameters at 12 months of corrected age. To evaluate the influence of prematurity-related morbidity conditions on growth parameters, we separated all enrolled infants in two groups in relation to the presence of at least one prematurity-related morbidity conditions, and we found no statistical differences for growth parameters between the two subgroups at 52 weeks of PMA and 12 months of corrected age (Table S3).

Table 4.
Growth parameters at 12 months of corrected age.
We also observed no correlation between age of weaning and both unstandardized (body weight: r = 0.127, p = 0.118; length: r = 0.013, p = 0.873; BMI: r = 0.136, p = 0.091; ponderal index: r = 0.101, p = 0.212) and standardized (body weight: r = 0.153, p = 0.058; length: r = 0.056, p = 0.490; BMI: r = 0.143, p = 0.077) growth parameters at 12 months of corrected age.
Linear regression analysis, performed separately for male and female infants, showed that introduction of complementary food did not influence the standardized growth parameters at 12 months of corrected age (Table 5). Binary logistic regression model showed that early or late weaning did not influence growth parameters at 12 months of corrected age (Table 6).

Table 5.
Linear regression analysis to evaluate the influence of confounding variables on primary outcome.

Table 6.
Binary logistic regression analysis to evaluate the influence of confounding variables on primary outcome.
Compliance of the recommendations provided at discharge on weaning was very high in the two study groups. In particular, all the children received complementary food between 52 weeks of PMA and nine months of corrected age. No baby received during weaning foods different from suggested in variety, texture, and amounts. All children enrolled in both groups received complementary food and caloric intakes as recommended.
4. Discussion
We demonstrated that the timing of weaning did not influence growth of VLBW infants at 12 months corrected age. These results were confirmed also after adjusting for confounding variables in linear and binary multivariate models.
For healthy, full-term newborns, several randomized control trials have reported no effects of the timing of weaning on long-term growth [32,33,34]. Observational studies have evaluated the relation between the timing of introduction of solid foods and obesity [35,36]. Grote et al. [37], in a prospective cohort study, demonstrated an increase in standardized weight and length and a worse BMI at 24 months of life in children born at term receiving semisolid foods early in life (between 14 and 17 weeks after birth). A systematic review [38] concluded that, in full-term neonates, the introduction of solids prior to four months of age may result in an increased risk of childhood obesity, but there is little evidence of adverse weight status outcomes associated with introducing solids at 4–6 rather than at six months.
There is no consensus for the weaning program of babies born preterm [10], and only few studies have evaluated growth parameters in preterm infants in relation with age of introduction of solid food. [39,40]. A randomized clinical trial (RCT) [39] including neonates born preterm with a mean gestational age of 31 weeks demonstrated that a preterm weaning strategy with early introduction of semisolid food soon after 13 weeks had a significant positive effect on length scores at 12 months compared to the control group, in which semisolid food was introduced after 17 weeks of postnatal age [39]. No significant difference was observed on weight and BMI of enrolled infants. The preterm weaning strategy also recommended the use of solid foods with a higher energy density and protein content compared to the control group. Both groups studied by Marriot et al. [39] started complementary feeding earlier compared to the weaning strategy adopted in our study. The Early Weaning group in the aforementioned study received complementary feeding earlier (12–13 weeks) compared to our study design. Patients in the two groups of this RCT, differently from our study, received complementary feeding with a different nutritional intake. Thus, it is not possible to establish if these results depended on nutritional intake or on timing of introduction of complementary feeding.
Morgan et al. [40] described the effects of the timing of weaning (before or after 12 weeks of life) on growth outcomes of infants born preterm up to 18 months of life. The authors showed that early weaned infants remained significantly heavier than later weaned infants evaluated at nine months [40]. However, this difference was not found at 18 months post-term follow-up.
We observed that the rate of infants receiving exclusively breast milk at the time when weaning was started was higher in group 1 compared to group 2. These results can be considered a casual association secondary to different time of solid food introduction. In other words, late introduction of solid food increases the probability of the not exclusive use of breast milk.
Our study suggested that weaning does not influence growth in the first year of life. In preterm infants, short- and long-term outcomes are influenced mainly by the nutritional approach of the first weeks of life [2,3,5,6,13,41], especially PN, while timing of weaning as a marginal impact on growth on this vulnerable population. In preterm newborns, a critical window for nutritional intervention remains in the first month of life. This could be due to the critical phase of the first weeks of life of these critical newborns, a window which appears to be more important and vulnerable compared to the timing of weaning. In fact, preterm infants are born at a time when their organs are structurally and functionally immature, leading to alterations in key organs as a result of the altered physical and biochemical environment caused by preterm birth [42,43,44].
Despite the interesting results regarding this yet undefined topic for preterm neonates, our findings should be interpreted considering some limitations. Results may be related to the effects of random error, bias, or confounding factors. We adjusted results for confounding variables that could have influenced the outcome of the study. However, confounding variables still unknown or not considered in our statistical model may have influenced the results. This was not an RCT. However, to reduce drop out, for randomization of the timing of weaning should be taken into account the two criteria that we used in this study. In our policy, the timing of weaning was guided by the presence of adequate infants motor skills and family collaboration. The researcher involved in the study did not participate in the choice of time of weaning. Consequently, we observed a spontaneous distribution of timing of weaning between 52 weeks of PMA and nine months. This methodology represents a selection bias that should be considered for the generalizability of the results. We verified that the infants received the caloric intakes recommended for age [31]. All enrolled infants respected the recommendations regarding the energy intakes. No difference in compliance regarding this aspect was found between the two study groups. Thus, we hypothesize that energy intake was similar between the two study groups; however, the lack of information about individual energy intakes represent an important limitation of the study. Further trials are advocated to evaluate if energy intakes, derived from milk and complementary food, may have a significant impact on growth in infants born preterm. We adjusted results in multivariate analyses for neonatal variables that could have influenced the outcome. However, it is not feasible to select all the possible variables that could influence growth of children in the first year of life; thus, we focused on variables relating to the neonatal period that are the most important for long-term consequences in preterm infants. Prematurity-related morbidity conditions could influence growth parameters; however, in univariate and multivariate models, we found no association between morbidity and growth at 12 months corrected age. Also, growth parameters at the beginning of weaning could influence the results at 12 months. We did not analyze data on growth at the beginning of weaning for each patient but at 52 weeks of PMA for all enrolled children. Despite that this could have an influence on our primary outcome, data recorded at 52 weeks of PMA did not show differences between the two study groups. To limit selection bias, neonatologists evaluating eligibility used objective inclusion criteria (such as gestational age and birth weight), unaware of the study aims, and data for the statistical analysis were collected by researchers not involved in the eligibility assessment and clinical practice, unaware of the study outcomes and design. We discussed and defined a protocol for the collection, measurement, and interpretation of data before starting the study. Besides, a blinded statistician performed the data analysis. Additional limitation of the study is the lack of information regarding strategy, quality, and quantity of complementary feeding and follow-up limited at 12 months of life.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our data demonstrated that the timing of weaning did not influence growth in the first year of life. The strategy of weaning, including the quality and quantity of semisolid food introduction, together with the timing might influence long-term growth outcomes. Thus, further well designed RCTs establishing the optimal timing and strategy of weaning for infants born preterm are advocated.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/children8121085/s1, Table S1. Practical guidance for weaning between 3 to 12 months of corrected age. Table S2. Growth parameters at 52 weeks of postmenstrual age. Table S3. Growth parameters in relation to the presence of morbidity conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, G.B. and G.T.; methodology, G.B., M.G.C. and G.T.; software, G.B. and G.T.; validation, G.B., M.G.C. and G.T.; formal analysis, G.B. and G.T.; investigation, G.B., M.G.C., F.P., M.D.C., C.P., E.O., R.P., G.D., L.D., D.R., S.O. and G.T.; data curation, G.B., M.G.C., F.P., C.P., E.O., R.P., G.D., L.D., D.R., S.O. and G.T.; writing—original draft preparation, G.B., M.G.C. and G.T.; writing—review and editing, G.B., M.G.C., F.P., M.D.C., S.O. and G.T.; visualization, G.T.; supervision, G.T.; project administration, G.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, Ethics Committee of Policlinico Umberto I Hospital, Sapienza University of Rome (5089, 13 September 2018).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed written consent was obtained by the parents of each enrolled newborn.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon reasonable request. All data relevant to the study are included in the article. Access to raw data would be provided upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. Survive and Thrive: Transforming Care for Every Small and Sick Newborn 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241515887 (accessed on 12 August 2019).
- Kumar, R.K.; Singhal, A.; Vaidya, U.; Banerjee, S.; Anwar, F.; Rao, S. Optimizing Nutrition in Preterm Low Birth Weight Infants-Consensus Summary. Front. Nutr. 2017, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrin, G.; Boscarino, G.; Gasparini, C.; Di Chiara, M.; Faccioli, F.; Onestà, E.; Parisi, P.; Spalice, A.; De Nardo, M.C.; Dito, L.; et al. Energy-Enhanced Parenteral Nutrition and Neurodevelopment of Preterm Newborns: A Cohort Study. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joosten, K.; Embleton, N.; Yan, W.; Senterre, T.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition: Energy. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2309–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; De Nardo, M.C.; Boscarino, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Cellitti, R.; Ciccarelli, S.; Gasparini, C.; Parisi, P.; Urna, M.; Ronchi, B.; et al. Early Protein Intake Influences Neonatal Brain Measurements in Preterms: An Observational Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscarino, G.; Conti, M.G.; Gasparini, C.; Onestà, E.; Faccioli, F.; Dito, L.; Regoli, D.; Spalice, A.; Parisi, P.; Terrin, G. Neonatal Hyperglycemia Related to Parenteral Nutrition Affects Long-Term Neurodevelopment in Preterm Newborn: A Prospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni Canani, R.; Passariello, A.; Buccigrossi, V.; Terrin, G.; Guarino, A. The Nutritional Modulation of the Evolving Intestine. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42, S197–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletzko, B.; Brands, B.; Grote, V.; Kirchberg, F.F.; Prell, C.; Rzehak, P.; Uhl, O.; Weber, M. For the Early Nutrition Programming Project Long-Term Health Impact of Early Nutrition: The Power of Programming. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization Guiding Principles for Complementary Feeding of the Breastfed Child. Available online: https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/752 (accessed on 15 September 2019).
- Fewtrell, M.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fidler Mis, N.; Hojsak, I.; Hulst, J.M.; Indrio, F.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Complementary Feeding: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidelman, A.I. Breastfeeding and the Use of Human Milk: An Analysis of the American Academy of Pediatrics 2012 Breastfeeding Policy Statement. Breastfeed. Med. 2012, 7, 323–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.E.; Giannì, M.L.; Di Mauro, A.; Mosca, F.; Laforgia, N. Complementary Feeding in Preterm Infants: Where Do We Stand? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormack, B.E.; Harding, J.E.; Miller, S.P.; Bloomfield, F.H. The Influence of Early Nutrition on Brain Growth and Neurodevelopment in Extremely Preterm Babies: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passariello, A. Diarrhea in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. WJG 2010, 16, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passariello, A.; Terrin, G.; Cecere, G.; Micillo, M.; Marco, G.; Di Costanzo, M.; Cosenza, L.; Leone, L.; Nocerino, R.; Berni Canani, R. Randomised Clinical Trial: Efficacy of a New Synbiotic Formulation Containing Lactobacillus Paracasei B21060 plus Arabinogalactan and Xilooligosaccharides in Children with Acute Diarrhoea. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2012, 35, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocerino, R.; Paparo, L.; Terrin, G.; Pezzella, V.; Amoroso, A.; Cosenza, L.; Cecere, G.; De Marco, G.; Micillo, M.; Albano, F.; et al. Cow’s Milk and Rice Fermented with Lactobacillus Paracasei CBA L74 Prevent Infectious Diseases in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia, G.; Cascioli, C.F.; Ciccimarra, F.; Terrin, G.; Cucchiara, S. A Case of Protein-Losing Enteropathy Caused by Intestinal Lymphangiectasia in a Preterm Infant. Pediatrics 2001, 107, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canani, R.B.; Terrin, G. Recent Progress in Congenital Diarrheal Disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2011, 13, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.R.; van Karnebeek, C.D.M. Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2019, 162, 449–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, F.; Conti, M.G.; Boscarino, G.; Pannucci, C.; Dito, L.; Regoli, D.; Di Chiara, M.; Battaglia, G.; Prota, R.; Cinicola, B.; et al. Atopic Manifestations in Children Born Preterm: A Long-Term Observational Study. Children 2021, 8, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, G.; Tucker, J.; Tarnow-Mordi, W. CRIB II: An Update of the Clinical Risk Index for Babies Score. Lancet 2003, 361, 1789–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, R.; Terrin, G.; Palone, F.; Laudadio, I.; Cucchiara, S.; Boscarino, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Stronati, L. Fecal High-Mobility Group Box 1 as a Marker of Early Stage of Necrotizing Enterocolitis in Preterm Neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 672131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, M.G.; Angelidou, A.; Diray-Arce, J.; Smolen, K.K.; Lasky-Su, J.; De Curtis, M.; Levy, O. Immunometabolic Approaches to Prevent, Detect, and Treat Neonatal Sepsis. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 87, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Boscarino, G.; Metrangolo, V.; Faccioli, F.; Onestà, E.; Giancotti, A.; Di Donato, V.; Cardilli, V.; De Curtis, M. Morbidity Associated with Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Preterm Newborns: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2021, 47, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Ahmed, I.; Silveyra, P. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: An Update on Experimental Therapeutics. Eur. Med. J. (Chelmsf) 2019, 4, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Terrin, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Boscarino, G.; Versacci, P.; Di Donato, V.; Giancotti, A.; Pacelli, E.; Faccioli, F.; Onestà, E.; Corso, C.; et al. Echocardiography-Guided Management of Preterms with Patent Ductus Arteriosus Influences the Outcome: A Cohort Study. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 582735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peila, C.; Spada, E.; Giuliani, F.; Maiocco, G.; Raia, M.; Cresi, F.; Bertino, E.; Coscia, A. Extrauterine Growth Restriction: Definitions and Predictability of Outcomes in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants or Preterm Neonates. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; Coscia, A.; Boscarino, G.; Faccioli, F.; Di Chiara, M.; Greco, C.; Onestà, E.; Oliva, S.; Aloi, M.; Dito, L.; et al. Long-Term Effects on Growth of an Energy-Enhanced Parenteral Nutrition in Preterm Newborn: A Quasi-Experimental Study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrin, G.; Boscarino, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Iacobelli, S.; Faccioli, F.; Greco, C.; Onestà, E.; Sabatini, G.; Pietravalle, A.; Oliva, S.; et al. Nutritional Intake Influences Zinc Levels in Preterm Newborns: An Observational Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boscarino, G.; Conti, M.G.; De Luca, F.; Di Chiara, M.; Deli, G.; Bianchi, M.; Favata, P.; Cardilli, V.; Di Nardo, G.; Parisi, P.; et al. Intravenous Lipid Emulsions Affect Respiratory Outcome in Preterm Newborn: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA. Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA) Scientific Opinion on Nutrient Requirements and Dietary Intakes of Infants and Young Children in the European Union. EFS2 2013, 11, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsdottir, O.H.; Thorsdottir, I.; Hibberd, P.L.; Fewtrell, M.S.; Wells, J.C.; Palsson, G.I.; Lucas, A.; Gunnlaugsson, G.; Kleinman, R.E. Timing of the Introduction of Complementary Foods in Infancy: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Pediatrics 2012, 130, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, J.C.; Jonsdottir, O.H.; Hibberd, P.L.; Fewtrell, M.S.; Thorsdottir, I.; Eaton, S.; Lucas, A.; Gunnlaugsson, G.; Kleinman, R.E. Randomized Controlled Trial of 4 Compared with 6 Mo of Exclusive Breastfeeding in Iceland: Differences in Breast-Milk Intake by Stable-Isotope Probe. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, R.J.; Brown, K.H.; Canahuati, J.; Rivera, L.L.; Dewey, K.G. Effects of Age of Introduction of Complementary Foods on Infant Breast Milk Intake, Total Energy Intake, and Growth: A Randomised Intervention Study in Honduras. Lancet 1994, 344, 288–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schack-Nielsen, L.; Sørensen, T.I.; Mortensen, E.L.; Michaelsen, K.F. Late Introduction of Complementary Feeding, rather than Duration of Breastfeeding, May Protect against Adult Overweight. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, A.C.; Forsyth, J.S.; Greene, S.A.; Irvine, L.; Hau, C.; Howie, P.W. Relation of Infant Diet to Childhood Health: Seven Year Follow up of Cohort of Children in Dundee Infant Feeding Study. BMJ 1998, 316, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grote, V.; Schiess, S.A.; Closa-Monasterolo, R.; Escribano, J.; Giovannini, M.; Scaglioni, S.; Stolarczyk, A.; Gruszfeld, D.; Hoyos, J.; Poncelet, P.; et al. The Introduction of Solid Food and Growth in the First 2 y of Life in Formula-Fed Children: Analysis of Data from a European Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 1785S–1793S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daniels, L.; Mallan, K.M.; Fildes, A.; Wilson, J. The Timing of Solid Introduction in an ‘Obesogenic’ Environment: A Narrative Review of the Evidence and Methodological Issues. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2015, 39, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marriott, L.D.; Foote, K.D.; Bishop, J.A.; Kimber, A.C.; Morgan, J.B. Weaning Preterm Infants: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Arch Dis. Child. Fetal. Neonatal. Ed. 2003, 88, F302–F307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morgan, J.B. Does Weaning Influence Growth and Health up to 18 Months? Arch. Dis. Child. 2004, 89, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscarino, G.; Di Chiara, M.; Cellitti, R.; De Nardo, M.C.; Conti, M.G.; Parisi, P.; Spalice, A.; Di Mario, C.; Ronchi, B.; Russo, A.; et al. Effects of Early Energy Intake on Neonatal Cerebral Growth of Preterm Newborn: An Observational Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, J.; Benders, M.; Cachia, A.; Lazeyras, F.; Ha-Vinh Leuchter, R.; Sizonenko, S.V.; Borradori-Tolsa, C.; Mangin, J.F.; Hüppi, P.S. Mapping the Early Cortical Folding Process in the Preterm Newborn Brain. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bensley, J.G.; Moore, L.; De Matteo, R.; Harding, R.; Black, M.J. Impact of Preterm Birth on the Developing Myocardium of the Neonate. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 83, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, J.J. Brain Injury in Premature Infants: A Complex Amalgam of Destructive and Developmental Disturbances. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).