Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Post-Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from an Experimental Animal Model and Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Study
2.2. Clinical Case-Control Study
2.2.1. Participants
2.2.2. Controls
2.2.3. Variables
2.3. Platelet Poor Plasma Preparation
2.4. EVs Quantification
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
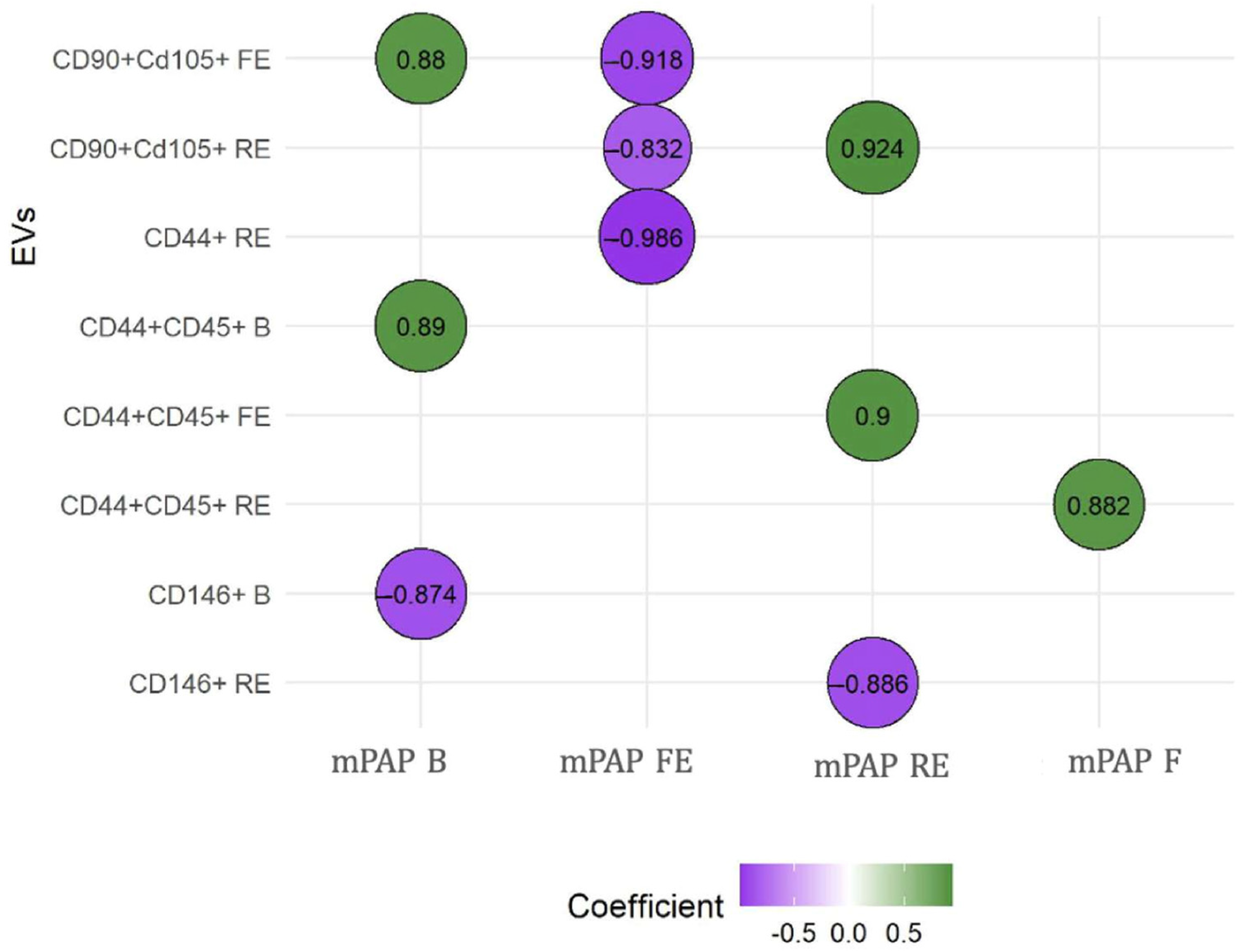
3.1. Experimental Study
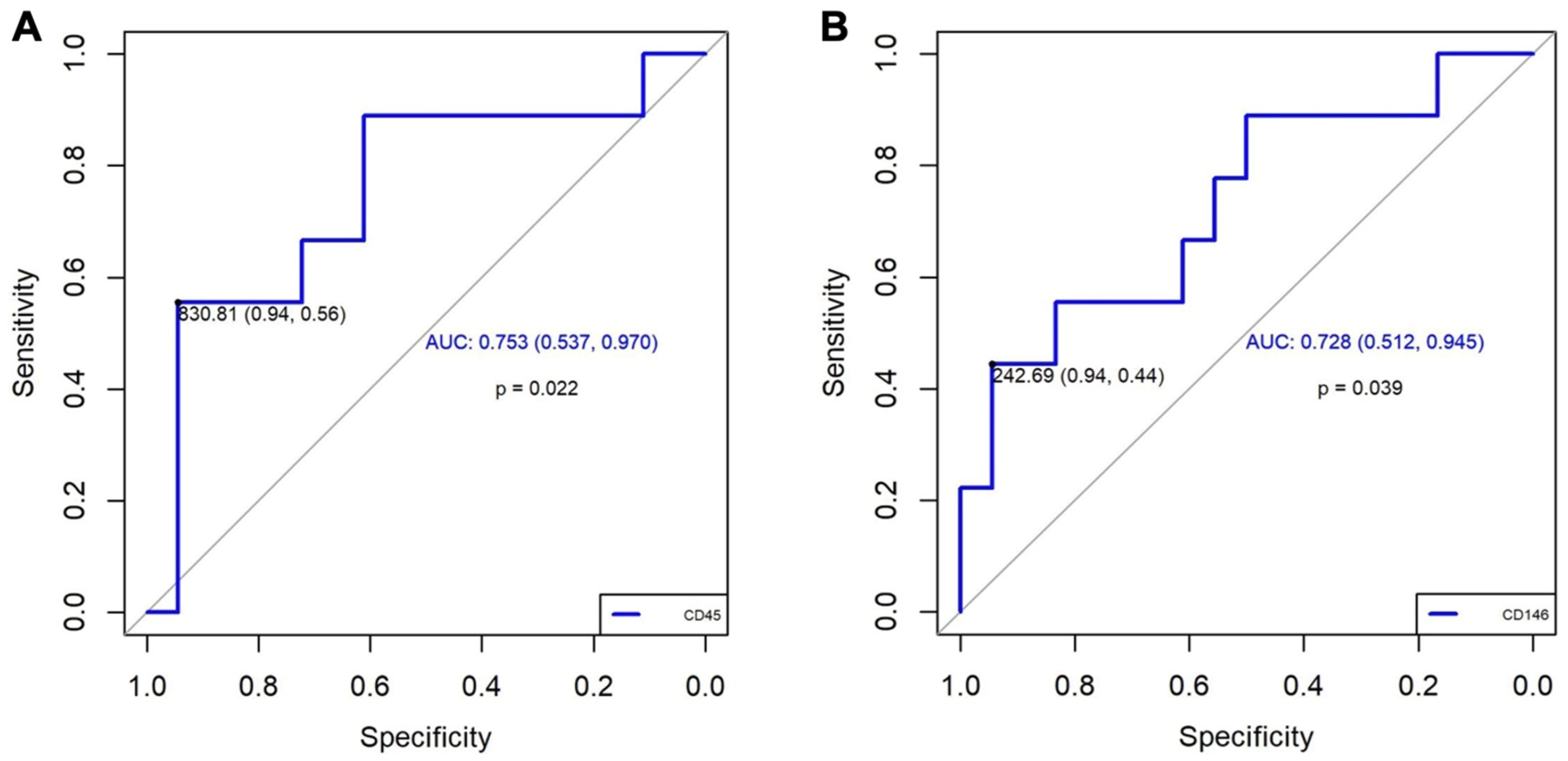
3.2. Clinical Case-Control Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| α-SMA | α-smooth muscle actin |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| B | Baseline |
| CCL2 | Chemotactic protein-1 |
| CTEPH | Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension |
| EEVs | Extracellular vesicles of endothelial origin |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| F | Final |
| FE | First embolization |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| JAF | Janus Kinase |
| LEVs | Extracellular vesicles of leukocyte-derived |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κB |
| NLRP3 | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptor protein 3 |
| NPV | Negative predictive value |
| PAP | Pulmonary arterial pressure |
| PE | Pulmonary embolism |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PPV | Positive predictive value |
| Q-Q plots | Normal probability plots |
| RV | Right ventricular |
| S1P | Sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| STAT | Signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TF | Tissue factor |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: Developed by the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Endorsed by the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT) and the European Reference Network on Rare Respiratory Diseases (ERN-LUNG). Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tura-Ceide, O.; Smolders, V.F.E.D.; Aventin, N.; Morén, C.; Guitart-Mampel, M.; Blanco, I.; Piccari, L.; Osorio, J.; Rodríguez, C.; Rigol, M.; et al. Derivation and Characterisation of Endothelial Cells from Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medrek, S.; Safdar, Z. Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Risk Factors and Mechanisms. Methodist. Debakey Cardiovasc. J. 2016, 12, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Jin, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress on the Pathogenesis of CTEPH. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, M.; de Perrot, M.; Jaïs, X.; Jenkins, D.P.; Lang, I.M.; Matsubara, H.; Meijboom, L.J.; Quarck, R.; Simonneau, G.; Wiedenroth, C.B.; et al. Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Realising the Potential of Multimodal Management. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, J.; Henriksen, H.H.; Marin de Mas, I.; Johansson, P.I. An Explorative Metabolomic Analysis of the Endothelium in Pulmonary Hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, W.R.; Kim, N.H. Microvascular Disease in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: The Story Continues. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1121–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.E.; Pepke-Zaba, J. Is Distal Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Treatable with PAH Targeted Drugs? Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 34, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humbert, M.; Morrell, N.W.; Archer, S.L.; Stenmark, K.R.; MacLean, M.R.; Lang, I.M.; Christman, B.W.; Weir, E.K.; Eickelberg, O.; Voelkel, N.F.; et al. Cellular and Molecular Pathobiology of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, S13–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, P.P.; Zhou, R.L.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, S.Y. Pathological Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Review. Aging Dis. 2020, 11, 1623–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, K.; Smolders, V.F.E.D.; Tura-Ceide, O.; Wouter Jukema, J.; Quax, P.H.A.; Goumans, M.J. Endothelial Dysfunction in Pulmonary Hypertension: Cause or Consequence? Biomedicines 2021, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabile, N.; Guignabert, C.; Montani, D.; Yeghiazarians, Y.; Boulanger, C.M.; Humbert, M. Cellular Microparticles in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R.; Dorai, T. Microvesicles and Exosomes in Pulmonary Hypertension. Vessel. Plus 2020, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfranca, A.; Iñiguez, M.A.; Fresno, M.; Redondo, J.M. Prostanoid Signal Transduction and Gene Expression in the Endothelium: Role in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 70, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hinsbergh, V.W.M. The Endothelium: Vascular Control of Haemostasis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 95, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiel, E.; Vallet, B.; Ten Cate, H. The Endothelium in Intensive Care. Crit. Care Clin. 2005, 21, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Xue, G. Major Physiological Signaling Pathways in the Regulation of Cell Proliferation and Survival. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 249. [Google Scholar]
- Browder, T.; Folkman, J.; Pirie-Shepherd, S. The Hemostatic System as a Regulator of Angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 1521–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccioni, G.; Sblendorio, V. Atherosclerosis: From Biology to Pharmacological Treatment. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2012, 9, 305. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.M.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. The Role of Microvesicles and Its Active Molecules in Regulating Cellular Biology. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7894–7904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Hascall, V.C.; Markwald, R.R.; Ghatak, S. Interactions between Hyaluronan and Its Receptors (CD44, RHAMM) Regulate the Activities of Inflammation and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.H.; Liang, J.P.; Zhu, C.J.; Lian, Y.J. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Therapy for Pulmonary Hypertension: A Comprehensive Review of Preclinical Studies. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Pan, P. Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Transfer in Lung Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, J.M.; Pereira, M.; Wen, S.; Dooner, M.S.; Del Tatto, M.; Papa, E.; Goldberg, L.R.; Baird, G.L.; Ventetuolo, C.E.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. Exosomes Induce and Reverse Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension in Mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Mitsialis, S.A.; Aslam, M.; Vitali, S.H.; Vergadi, E.; Konstantinou, G.; Sdrimas, K.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Kourembanas, S. Exosomes Mediate the Cytoprotective Action of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2012, 126, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Hui, H.; Cai, T.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, X. CD146 Coordinates Brain Endothelial Cell–Pericyte Communication for Blood–Brain Barrier Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7622–E7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano, E.M.M.; Rodríguez, B.G.; Lunar, I.G.; Arnau, D.P.; Sánchez-López, V.; Álvarez, A.G.; Candelera, R.O. Microvesicles and Inflammatory Markers in an Animal Model of Chronic Postcapillary Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 20, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Liante, V.; Sánchez-López, V.; Martínez-Sales, V.; Ramón-Nuñez, L.A.; Arellano-Orden, E.; Cano-Ruiz, A.; Rodríguez-Martorell, F.J.; Gao, L.; Otero-Candelera, R. Impact of Sample Processing on the Measurement of Circulating Microparticles: Storage and Centrifugation Parameters. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2016, 54, 1759–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, V.; Vila-Liante, V.; Arellano-Orden, E.; Eliás-Hernández, T.; Ramón-Nuñez, L.A.; Jara-Palomares, L.; Martínez-Sales, V.; Gao, L.; Otero-Candelera, R. High Correlation between 2 Flow Cytometry Platforms in the Microparticles Analysis Using a New Calibrated Beads Strategy. Transl. Res. 2015, 166, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguero, J.; Ishikawa, K.; Fish, K.M.; Hammoudi, N.; Hadri, L.; Garcia-Alvarez, A.; Ibanez, B.; Fuster, V.; Hajjar, R.J.; Leopold, J.A. Combination Proximal Pulmonary Artery Coiling and Distal Embolization Induces Chronic Elevations in Pulmonary Artery Pressure in Swine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, A.A.; Mihailova, A.M.; Cherepanov, D.E.; Chefu, S.G.; Shilenko, L.A.; Vaulina, D.D.; Butskikh, M.G.; Chervaev, K.A.; Sidorova, E.E.; Ivkin, D.Y.; et al. The Use of Microencapsulated Autologous Thrombi for Modelling Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension in Rats. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 175, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpov, A.A.; Vaulina, D.D.; Smirnov, S.S.; Moiseeva, O.M.; Galagudza, M.M. Rodent Models of Pulmonary Embolism and Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vítková, V.; Živný, J.; Janota, J. Endothelial Cell-Derived Microvesicles: Potential Mediators and Biomarkers of Pathologic Processes. Biomark. Med. 2018, 12, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markiewicz, M.; Richard, E.; Marks, N.; Ludwicka-Bradley, A. Impact of Endothelial Microparticles on Coagulation, Inflammation, and Angiogenesis in Age-Related Vascular Diseases. J. Aging Res. 2013, 2013, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amabile, N.; Heiss, C.; Real, W.M.; Minasi, P.; McGlothlin, D.; Rame, E.J.; Grossman, W.; De Marco, T.; Yeghiazarians, Y. Circulating Endothelial Microparticle Levels Predict Hemodynamic Severity of Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.C.; Andriantsitohaina, R. Microparticles in Angiogenesis: Therapeutic Potential. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, G.; Rao, L.; Wei, Y.; Yue, H.; Yuan, T.; Yang, P.; Xiong, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Blockade of JAK2 Protects Mice against Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension by Repressing Pulmonary Arterial Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, A.A.; Mihailova, A.M.; Shilenko, L.A.; Vaulina, D.D.; Sidorova, E.E.; Akhmetova, A.A.; Docshin, P.M.; Krasichkov, A.S.; Sanarova, K.E.; Moiseeva, O.M.; et al. Inhibition of JAK1,2 Prevents Fibrotic Remodeling of Pulmonary Vascular Bed and Improves Outcomes in the Rat Model of Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Luo, F.; Wang, E.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, S.; Peng, J.; Liu, B. Magnolol Attenuates Right Ventricular Hypertrophy and Fibrosis in Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Arterial Hypertensive Rats Through Inhibition of the JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 755077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, R.P.; Highland, K.B.; McConnell, J.W.; Burger, C.D.; Roscigno, R.F.; Cravets, M.; McCaffrey, R.; Zisman, L.S.; Howard, L. A Phase 1b, Multi-Center, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Inhaled Seralutinib in Subjects with WHO Group 1 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. 2021. Available online: https://www.gossamerbio.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Poster-ATS21.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2025).
- Frantz, R.P.; McLaughlin, V.V.; Sahay, S.; Escribano Subías, P.; Zolty, R.L.; Benza, R.L.; Channick, R.N.; Chin, K.M.; Hemnes, A.R.; Howard, L.S.; et al. Seralutinib in Adults with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (TORREY): A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fu, C.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Zhang, F.; Wei, Q. The Role of CD44 in Pathological Angiogenesis. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 13125–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, N.K.Y.; Lai, J.C.Y.; Birkenhead, D.; Shaw, A.S.; Johnson, P. CD45 Down-Regulates Lck-Mediated CD44 Signaling and Modulates Actin Rearrangement in T Cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7033–7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakao, S.; Hao, H.; Tanabe, N.; Kasahara, Y.; Kurosu, K.; Tatsumi, K. Endothelial-like Cells in Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Crosstalk with Myofibroblast-like Cells. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelillo-Scherrer, A. Leukocyte-Derived Microparticles in Vascular Homeostasis. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gąsecka, A.; Banaszkiewicz, M.; Nieuwland, R.; van der Pol, E.; Hajji, N.; Mutwil, H.; Rogula, S.; Rutkowska, W.; Pluta, K.; Eyileten, C.; et al. Article Prostacyclin Analogues Inhibit Platelet Reactivity, Extracellular Vesicle Release and Thrombus Formation in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firth, A.L.; Yao, W.; Ogawa, A.; Madani, M.M.; Lin, G.Y.; Yuan, J.X.J. Multipotent Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells Are Present in Endarterectomized Tissues from Patients with Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2010, 298, C1217–C1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.C.; Krause, D.S.; Deans, R.J.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.J.; Horwitz, E.M. Minimal Criteria for Defining Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy Position Statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
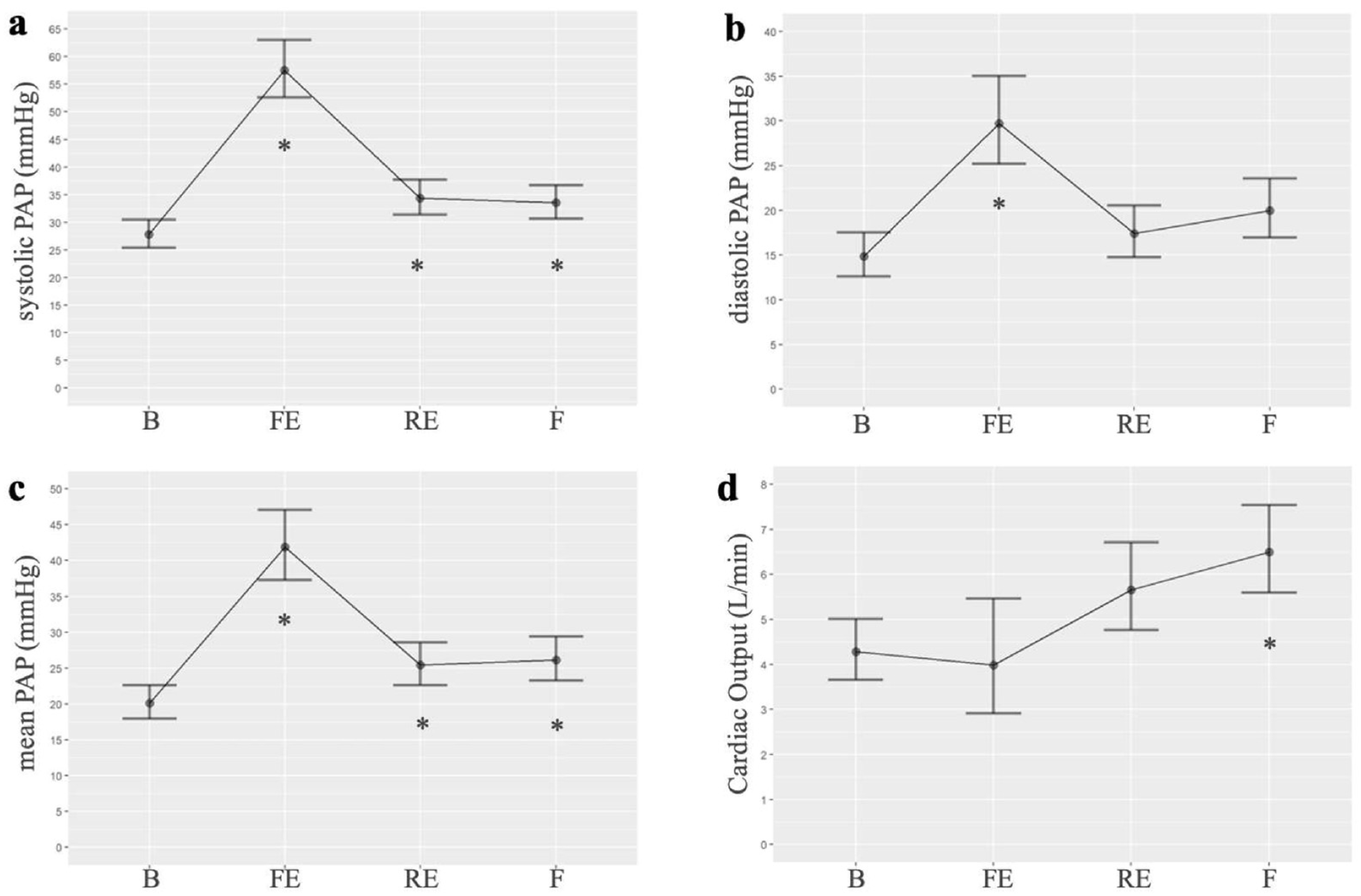
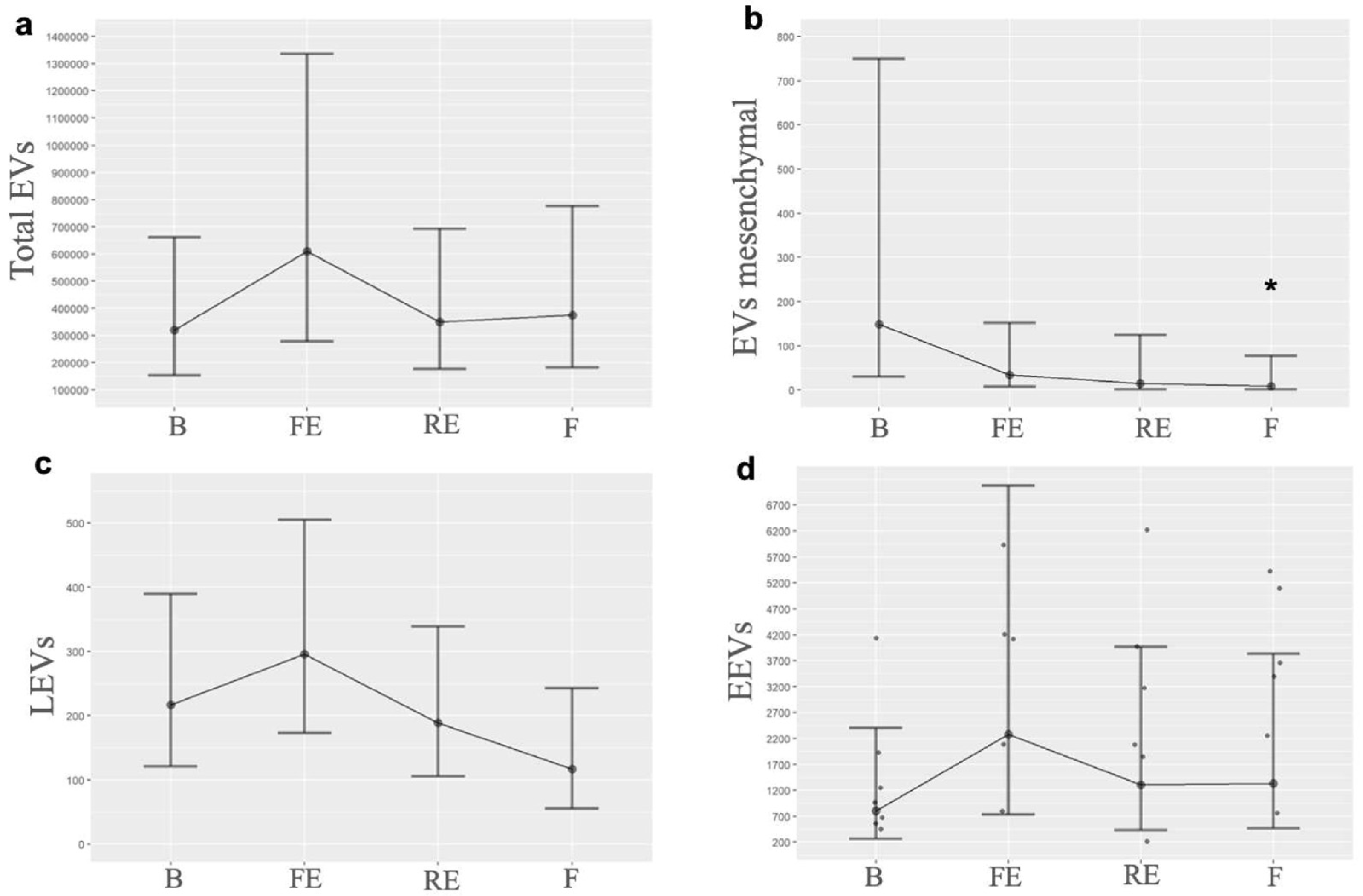
| EVs/Time | B | FE | RE | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total EVs | 319,748.0 (118,608.0) | 610,245.7 (244,310.6) | 350,841.1 (121,874.2) | 375,911.3 (139,032.1) |
| Consistent with mesenchymal-origin, mean (SE) | 149.33 (25.3) | 34.28 (4.9) | 15.14 (4.4) | 8.34 (2.68) |
| LEVs, mean (SE) | 217.30 (4.8) | 295.81 (5.5) | 189.17 (4.2) | 116.88 (4.09) |
| EEVs, mean (SE) | 802.12 (62.9) | 2274.57 (190.7) | 1307.6 (104.8) | 1335.11 (96.8) |
| Variables | Cases (n = 9) | Controls (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (SD) | 55.6 (±20.2) | 58 (±18) |
| Sex female, n (%) | 5 (55.6) | 10 (55.6) |
| BMI, mean (SD) | 29 (±6.1) | 30.5 (±5.3) |
| Arterial hypertension, n (%) | 1 (11.1) | 1 (5.5) |
| OSA, n (%) | 2 (22.2) | 0 |
| Bronchial asthma, n (%) | 1 (11.1) | 0 |
| Cancer, n (%) | 1 (11.1) | 6 (33.3) |
| Psychiatric disease, n (%) | 0 | 2 (11) |
| VTE provoked, n (%) | 5 (55.5) | 12 (66.7) |
| Quantification of Extracellular Vesicles | ||
| CD45+ (P25-75) | 875,1986 (504,8326–1033,7861) | 474,7100 (378,7331–639,4884) * |
| CD146+ (P25-75) | 198,1521 (90,9730–1317,2157) | 85,8275 (50,2293–159,3167) * |
| CD45+ (95% CI) | CD146+ (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|
| Odds ratio | 21.25 (1.91–236.00) | 13.60 (1.22–151.04) |
| Sensitivity, % | 94 (84–105) | 94 (84–105) |
| Specificity, % | 56 (23–88) | 44 (12–77) |
| Positive predictive value, % | 83 (53–103) | 80 (45–115) |
| Negative predictive value, % | 81 (64–98) | 77 (60–95) |
| Positive probability ratio, % | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Negative probability ratio, % | 0.47 | 0.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Zambrano, E.; Sánchez-López, V.; Gómez-Rodríguez, B.; García-Lunar, I.; Pereda-Arnau, D.; Jara-Palomares, L.; Elías-Hernández, T.; García-Álvarez, A.; Otero-Candelera, R. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Post-Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from an Experimental Animal Model and Patients. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061499
Mendoza-Zambrano E, Sánchez-López V, Gómez-Rodríguez B, García-Lunar I, Pereda-Arnau D, Jara-Palomares L, Elías-Hernández T, García-Álvarez A, Otero-Candelera R. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Post-Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from an Experimental Animal Model and Patients. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061499
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Zambrano, Elva, Verónica Sánchez-López, Belén Gómez-Rodríguez, Inés García-Lunar, Daniel Pereda-Arnau, Luis Jara-Palomares, Teresa Elías-Hernández, Ana García-Álvarez, and Remedios Otero-Candelera. 2025. "Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Post-Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from an Experimental Animal Model and Patients" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061499
APA StyleMendoza-Zambrano, E., Sánchez-López, V., Gómez-Rodríguez, B., García-Lunar, I., Pereda-Arnau, D., Jara-Palomares, L., Elías-Hernández, T., García-Álvarez, A., & Otero-Candelera, R. (2025). Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Post-Embolic Pulmonary Hypertension: Data from an Experimental Animal Model and Patients. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061499








