Abstract
pH is a critical parameter requiring precise monitoring across scientific, industrial, and biological domains. Fluorescent pH probes offer a powerful alternative to traditional methods (e.g., electrodes, indicators), overcoming limitations in miniaturization, long-term stability, and electromagnetic interference. By utilizing photophysical mechanisms—including intramolecular charge transfer (ICT), photoinduced electron transfer (PET), and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)—these probes enable high-sensitivity, reusable, and biocompatible sensing. This review systematically details recent advances, categorizing probes by operational pH range: strongly acidic (0–3), weakly acidic (3–7), strongly alkaline (>12), weakly alkaline (7–11), near-neutral (6–8), and wide-dynamic range. Innovations such as ratiometric detection, organelle-specific targeting (lysosomes, mitochondria), smartphone colorimetry, and dual-analyte response (e.g., pH + Al3+/CN−) are highlighted. Applications span real-time cellular imaging (HeLa cells, zebrafish, mice), food quality assessment, environmental monitoring, and industrial diagnostics (e.g., concrete pH). Persistent challenges include extreme-pH sensing (notably alkalinity), photobleaching, dye leakage, and environmental resilience. Future research should prioritize broadening functional pH ranges, enhancing probe stability, and developing wide-range sensing strategies to advance deployment in commercial and industrial online monitoring platforms.
1. Introduction
pH, defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration, is a critical parameter governing chemical, biological, and physical processes [1]. In chemistry, pH influences reaction rates and equilibrium; environmental pH monitoring helps assess water quality or soil health. Accurate pH measurement is indispensable across diverse fields, including industrial production, agricultural science, environmental monitoring, and fundamental chemical research [2,3]. Furthermore, pH serves as a vital physiological indicator within the human body, influencing numerous cellular functions [4,5,6]. It plays a vital role as enzyme activity, protein structure, and cellular functions are highly dependent on specific pH ranges; minor deviations in blood pH (around 7.4) can lead to diseases. Consequently, reliable and precise methods for determining pH are essential.
Common techniques for pH assessment include pH indicators [7,8,9], pH test strips [10,11], and glass electrode pH meters [11,12,13,14,15]. Indicators and test strips rely on color changes of organic compounds in response to acidity/alkalinity [7], offering simplicity but suffering from inherent subjectivity in visual interpretation, limited accuracy, and non-reusability [8,9]. Glass electrode pH meters, utilizing a galvanic cell formed by a glass indicator electrode and a reference electrode (e.g., saturated calomel) [11,12], measure electromotive force to provide a direct pH readout [13,14]. While this method offers high accuracy, speed, and robustness against factors like sample color, turbidity, oxidants, reductants, and salinity [16,17,18,19,20,21], it faces significant challenges. These include susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, signal drift over time, difficulties in miniaturization, and limitations for long-term, online monitoring applications [17,18].
Fluorescent pH probes present a compelling alternative technology. These probes utilize molecules whose fluorescent properties (intensity, wavelength, lifetime) change predictably in response to pH variations, often through mechanisms like fluorescence quenching or enhancement. This approach offers distinct advantages over traditional methods, including reusability [22], miniaturization potential [23,24,25], lack of requirement for electrical components [26,27], intrinsic immunity to electromagnetic interference [27,28], and environmental friendliness [24,29]. These characteristics make fluorescent probes particularly suitable for applications demanding long-term, online monitoring and analysis in challenging environments.
Over the past few decades, significant progress has been made in the design and synthesis of fluorescent sensors, with their mechanisms being extensively studied. Key phenomena mainly include intramolecular charge transfer (ICT), photoinduced electron transfer (PET), and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)[30].
- (a)
- Intramolecular Charge Transfer (ICT)
In fluorescent systems featuring donor (D) and acceptor (A) moieties, photoexcitation induces intramolecular electron migration from groups D to A, resulting in excited-state charge separation. This process triggers significant dipole moment reorganization, leading to reduced emission photon energy and thereby generating the characteristic Stokes shift phenomena [31].
When the analyte specifically binds to the D moiety, its electron-donating capability may be attenuated through steric hindrance or electron cloud shielding effects. This elevates the highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO) energy, inducing a blue shift in the absorption spectrum and a decrease in the molar extinction coefficient [32]. Conversely, if the analyte interacts with the acceptor (A) moiety to strengthen its electron-withdrawing character, the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy decreases via extended conjugation or polarization, causing a red shift in the absorption spectrum and an increase in the molar extinction coefficient. ICT-based fluorescent ratio sensors effectively eliminate background interference using dual-wavelength emission intensity ratios or displacement-type spectral responses, making them particularly well suited for real-time dynamic monitoring in complex systems.
- (b)
- Photoinduced Electron Transfer (PET)
From the perspective of molecular orbital theory, the PET process can be elucidated through frontier molecular orbital (FMO) theory [33]. Upon photoexcitation, when an electron in the fluorophore’s HOMO undergoes transition to the LUMO, PET occurs if the recognition unit’s HOMO energy level lies between those of the fluorophore’s HOMO and LUMO. This energetic alignment enables electron transfer from the recognition unit to the fluorophore’s HOMO, thereby creating a non-radiative decay pathway. Since the LUMO electron cannot return to its original HOMO through a radiative transition, fluorescent emission is effectively quenched. Upon specific binding with the target analyte, the recognition unit’s oxidation potential increases substantially, causing its HOMO energy level to drop below that of the fluorophore’s HOMO. This modified energy alignment disrupts the PET pathway, consequently restoring fluorescence emission [34].
- (c)
- Fluorescent Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET)
FRET is a fluorescent response mechanism based on energy transfer, which fundamentally involves two distinct fluorophores: the donor fluorophore (D) and the acceptor fluorophore (A). When the donor fluorophore (D) is excited, it emits fluorescence, while the ground-state acceptor fluorophore (A) becomes excited through energy transfer and subsequently emits fluorescence. FRET is a distance-dependent photophysical phenomenon that requires the following conditions:
Spectral overlap: The emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore (D) must sufficiently overlap with the excitation spectrum of the acceptor fluorophore (A) to enable efficient energy transfer.
Distance proximity: The donor (D) and acceptor (A) must be within close proximity (typically < 10 nm or 100 Å) for resonance energy transfer to occur [35].
Orientation factor: The relative dipole–dipole alignment between D and A must be favorable to achieve optimal energy transfer efficiency.
FRET-based fluorescent probes typically exhibit large Stokes shifts, making this mechanism particularly suitable for designing ratiometric fluorescent sensors.
Precise pH monitoring across extreme and complex environments—from highly corrosive industrial settings to intricate biological systems—is crucial for advancing chemical, biomedical, and industrial applications. Fluorescent probes have emerged as indispensable tools in this pursuit, offering exceptional sensitivity, high spatiotemporal resolution, and non-invasiveness. Significant progress has been made in probe design, leveraging sophisticated photophysical mechanisms such as ICT, PET, and FRET. This enables the development of tailored sensors for specific ranges: extreme acidity (pH 0–3), strong alkalinity (pH > 12), weak acidity (pH 3–7), weak alkalinity (pH 7–11), near-neutrality (pH 6–8), and broad dynamic ranges. Modern probes incorporate advanced features like ratiometric detection (for internal referencing and improved accuracy), enhanced selectivity, biocompatibility, and subcellular targeting (e.g., to lysosomes, mitochondria). Applications extend far beyond solution testing, encompassing real-time imaging in living cells, tissues, and whole organisms, as well as monitoring food freshness, concrete integrity, and environmental samples. This review systematically details recent advancements in pH-responsive fluorescent probes, covering fundamental design principles, underlying mechanisms, critical performance metrics (sensitivity, range, response time, stability), and diverse applications. It aims to provide a comprehensive resource to guide future innovation in this dynamic field.
2. Acidic Fluorescent Probes
2.1. Strongly Acidic Fluorescent Probes
Strongly acidic conditions refer to solutions with very low pH values, typically ranging between 0 and 3, characterized by extremely high hydrogen ion (H+) concentrations and exhibiting strong acidic properties [36]. For example, human gastric juice maintains a pH of approximately 1 to 3, which aids in food digestion. The low pH environment of gastric acid can kill most of the ingested pathogens, which is an important non-specific immune barrier. Similarly, the electrolyte in lead-acid batteries, primarily composed of sulfuric acid solution, typically maintains a pH between 1 and 2, playing a critical role in the battery’s normal operation [37]. Additionally, in various industrial sectors such as metal processing, electroplating, and chemical production, strongly acidic wastewater with a pH of 1 to 3 is often generated [38]. These highly corrosive substances also possess certain toxicity, posing significant potential hazards to both human health and the ecological environment [39,40,41].
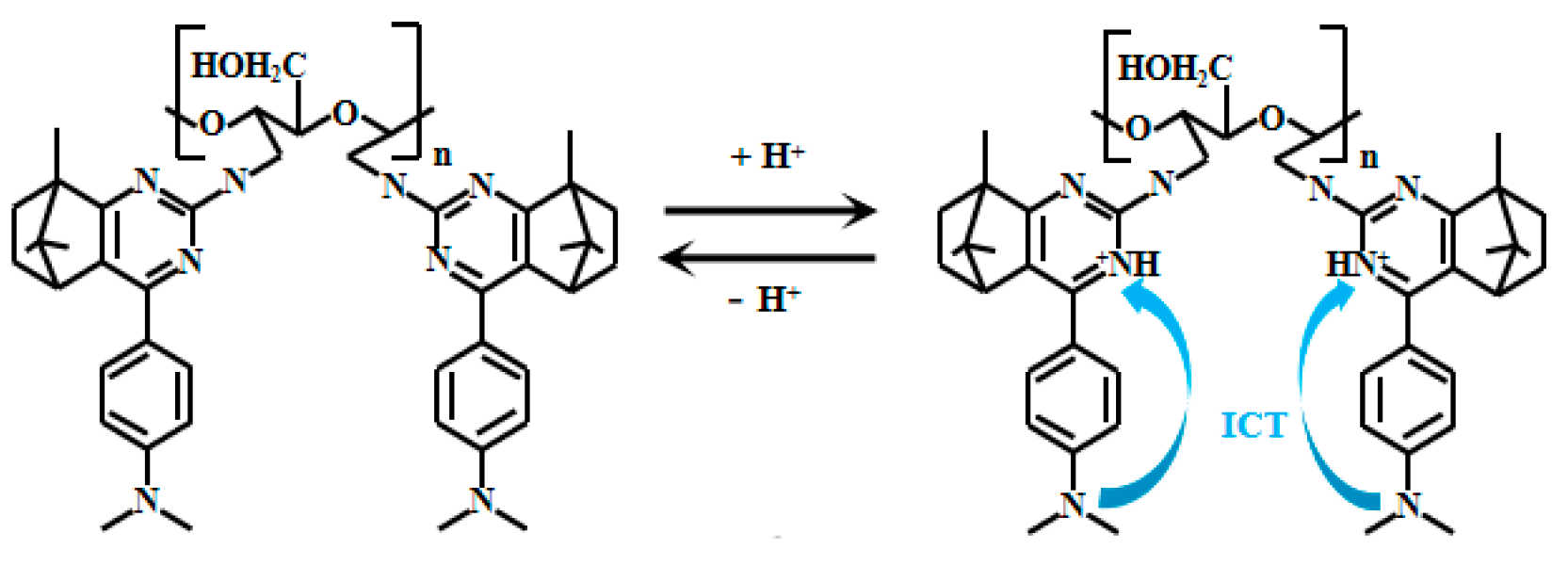
Camphor-based compounds have garnered considerable attention due to their unique rigid structure, which effectively restricts molecular vibrational relaxation and significantly reduces energy loss during collisions. Benefiting from these properties, camphor-based compounds exhibit excellent optical performance, offering broad potential for applications in fluorescent materials. Jie et al. [42] conducted in-depth research on the optical characteristics of camphor-based compounds and ingeniously reacted camphor derivatives with dialdehyde cellulose to successfully design and synthesize an innovative cellulose-based ratiometric fluorescent Probe 1 (Figure 1). They also fabricated a fluorescent hydrogel using cellulose as the matrix and applied it in practical scenarios. Under strongly acidic conditions, the nitrogen atom on the pyrimidine ring undergoes protonation. This protonation significantly enhances the ICT process from the dimethylamino group to the pyrimidine, enabling the probe to demonstrate outstanding fluorescent properties under varying pH conditions. When the pH of the solution gradually decreases from 6.86 to 1.04, the fluorescent intensity at 416 nm gradually decreases, accompanied by the appearance and rapid enhancement of a new peak at 486 nm. Meanwhile, the fluorescence intensity ratio (I486nm/I416nm) significantly changed, increasing from 0.34 to 1.94. Especially, a good linear relationship can be established between pH (in the range of 1.04–2.35) and the fluorescent intensity ratio I486/I416. In addition, the pKa value obtained by calculating the fluorescent intensity ratio as a function of pH variation is 1.57. Moreover, this probe showed almost no response to various metal ions, demonstrating excellent selectivity and accurate target recognition. When tested with samples such as white vinegar, apple cider vinegar, rice vinegar, and lemon juice, the results obtained using this probe closely matched those measured with a commercial PHS-3C pH meter, further validating its reliability and accuracy in practical applications.
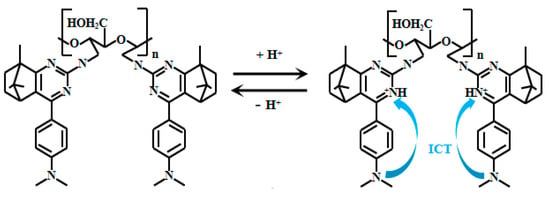
Figure 1.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 1.
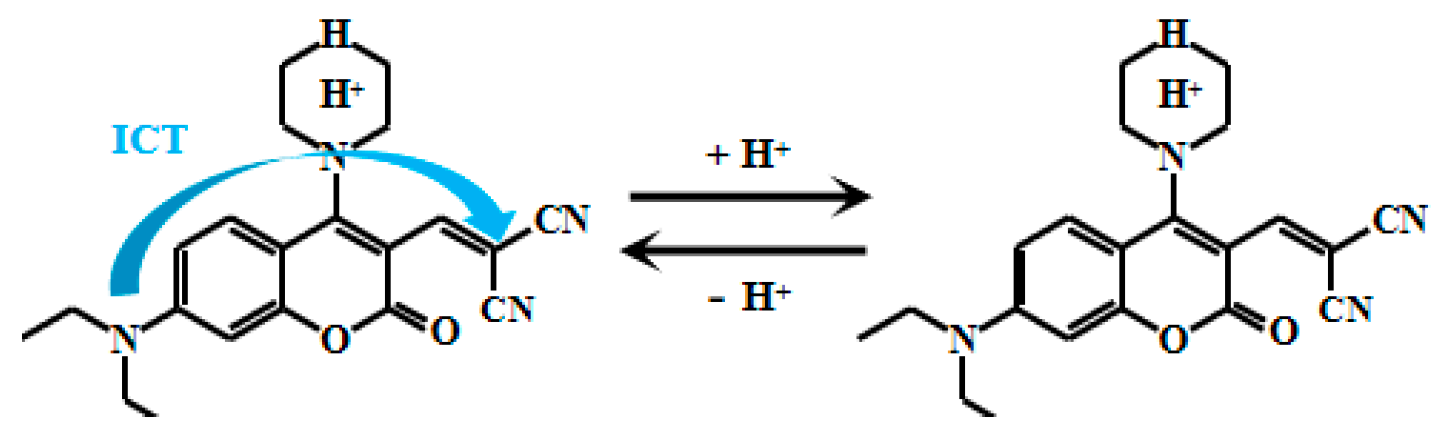
Xu et al. [43] designed a novel fluorescent Probe 2 (Figure 2) by coupling a coumarin fluorophore with a pyrimidine moiety for the detection of extremely low pH values. Under strongly acidic conditions, the nitrogen atoms on both the pyrimidine ring and diethylamino group undergo sequential protonation. This cascade protonation process induces PET from the pyrimidine to the coumarin moiety, resulting in significant fluorescent quenching of the probe. The relationship between fluorescent intensity and pH value based on Probe 2 shows an “S”-shaped calibration curve, and their quantitative relationship can be described by an equilibrium function as follows:
where Ia = 5540 and Ib = 0 represent the fluorescent intensity of the probe in acidic and conjugated base forms, respectively. According to the formula in the literature, its pKa value is 2.1. In summary, the linear regression relationship between log [(5540 − I)/I] and pH value is Y = −1.16pH + 2.17, R2 = 0.9909. Notably, rigorous cellular experiments confirmed the probe’s outstanding performance in imaging strongly acidic intracellular environments of bacteria, enabling in-depth investigation of bacterial acid environments and related physiological processes.
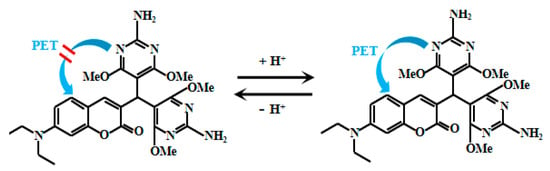
Figure 2.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 2.
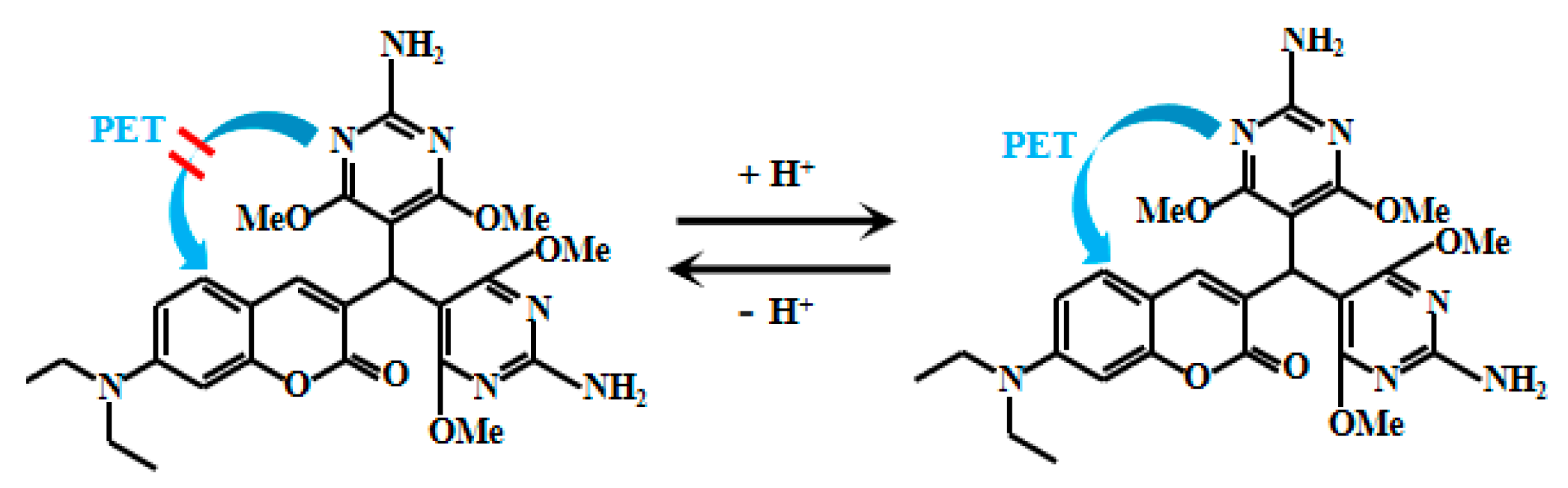
Li et al. [44] integrated dicyanoethylene and pH-sensitive morpholine groups into a coumarin fluorophore to design and synthesize an innovative fluorescent Probe 3 (Figure 3). Under highly acidic conditions, protonation of the oxygen atom in the morpholine group significantly enhances the ICT process from the lone electron pair on the diethylamino nitrogen atom to the malononitrile group, leading to a remarkable increase in the fluorescent intensity of the probe. N2H4 is a strong nucleophilic reagent that readily attacks electron-deficient sites. When the electron-deficient dicyanoyl group is conjugated to coumarin via a conjugated bond, the extended conjugation structure causes fluorescent spectra to shift toward the red end. However, when this conjugated structure is attacked by the nucleophilic reagent N2H4, the shortened conjugation structure leads to a significant blue-end shift in the fluorescent spectrum. Between pH 1.3 and 1.8, Probe 3 exhibits a strong linear correlation between fluorescent intensity and pH, enabling precise monitoring of pH variations within this range. Furthermore, owing to the reactive nature of the malononitrile group with N2H4, the probe can also perform ratiometric detection of N2H4. This multifunctionality enables the probe to not only monitor solution acidity but also quantitatively analyze specific chemical species, offering a powerful tool for both research and practical applications in chemical detection.
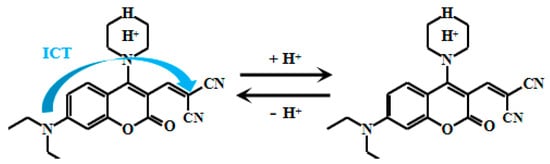
Figure 3.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 3.
2.2. Weakly Acidic Fluorescent Probes
A weakly acidic solution refers to one with a pH below the neutral value of 7, typically ranging between 3 and 7 [34]. Fruits like oranges and apples demonstrate weak acidity, their juices typically falling between pH 3.0–4.0 (orange) and pH 3.3–4.0 (apple). Another example is lactic acid, which generally maintains a pH between 4.0 and 4.6. Human sweat also displays weak acidity, with its pH fluctuating between 4.5 and 7.0. Within cells, the pH of lysosomes and endosomes is not constant either, varying between 4.5 and 6.8 [45]. Methanol poisoning causes metabolic acidosis through formic acid, multi-organ damage, and blood pH below 7.35 [46,47]. These weakly acidic environments play crucial physiological roles in organisms. For instance, the weakly acidic conditions in fruits help preserve their nutritional content, while intracellular weakly acidic environments are closely associated with processes such as substance degradation and transport [48,49]. Real-time quantification of weakly acidic pH ranges provides fundamental insights for studying pathophysiological mechanisms and disease etiology [50].
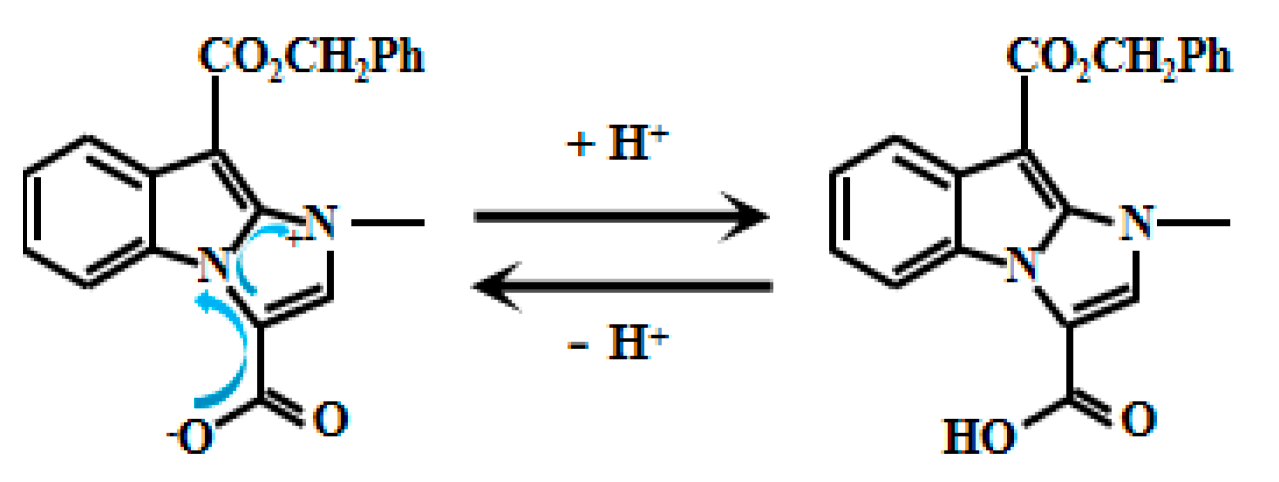
Based on imidazole and indole groups, Xu et al. [51] meticulously designed and synthesized a pH-responsive fluorescent Probe 4 (Figure 4). Deprotonation of the carboxyl group under low H+ conditions triggers electron transfer from carboxylate to imidazole, resulting in marked fluorescence enhancement. Further research revealed a clear linear correlation between the fluorescent intensity and pH values within the range of 3.2 to 4.4. This linear relationship indicates that the probe can sensitively and accurately reflect changes within this pH range, providing an effective means for pH detection. Notably, the probe demonstrated high-performance imaging within the acidic intracellular environment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This practical validation confirms its utility for real-time yeast fluorescence imaging. Beyond providing a powerful tool to study acidic compartments and associated physiological processes in yeast cells, this work establishes novel applications for fluorescent probes in bioimaging—highlighting significant scientific and translational potential.
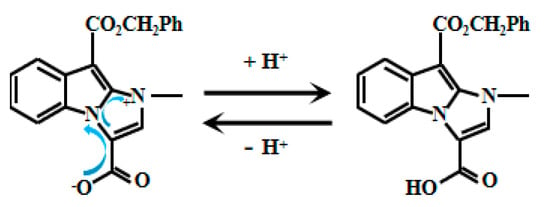
Figure 4.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 4.
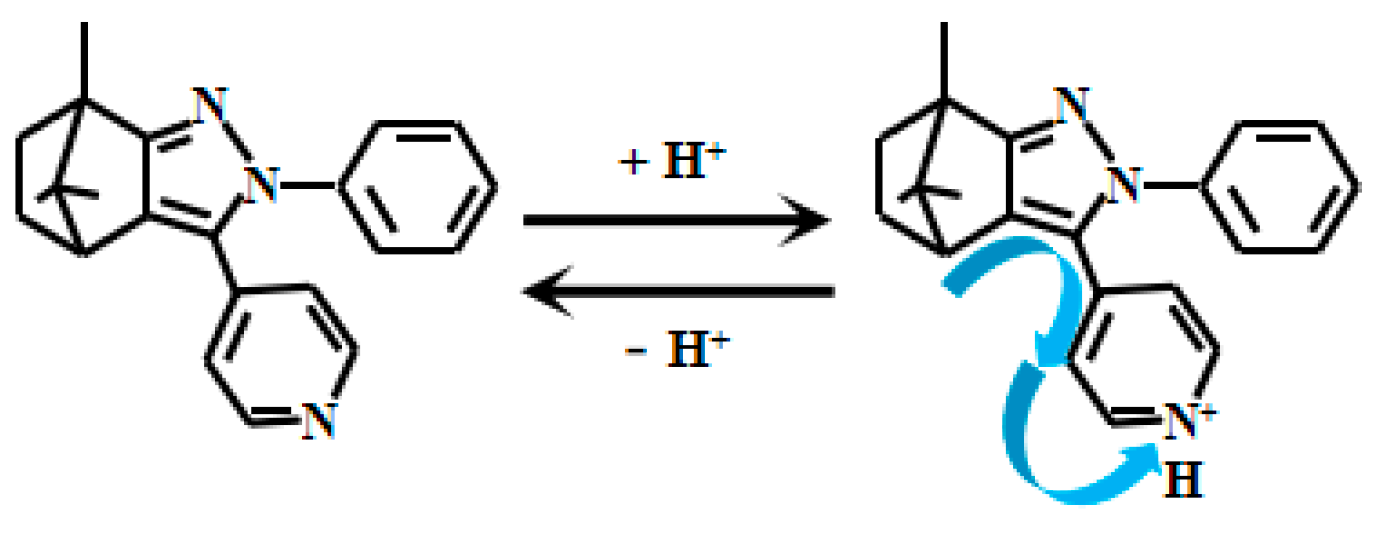
Li et al. [52] ingeniously designed and synthesized a D-π-A structured fluorescent Probe 5 (Figure 5) using camphor-based compounds, pyrazole, and pyridine groups as building blocks. Under weakly acidic conditions, the nitrogen atom on the pyridine group undergoes protonation, inducing electron transfer toward the pyridine moiety and thereby generating the ICT effect. When increasing the acidity from 8.0 to 1.0, the fluorescent intensity of the Probe 5 decreased significantly at 487 nm, while it showed an opposite trend at 585 nm. Experimental results revealed a strong linear correlation between the fluorescent intensity ratio (F585nm/F487nm) of the probe and pH values within the range of 3.0 to 5.5, demonstrating its high sensitivity in weakly acidic pH monitoring.
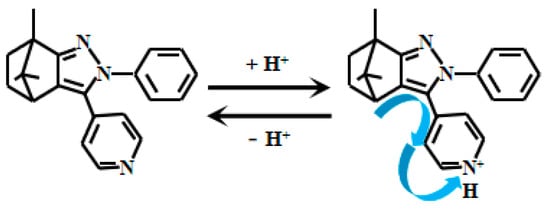
Figure 5.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 5.
More importantly, fluorescent imaging studies confirmed that the probe exhibits low cytotoxicity and excellent biocompatibility. This makes it particularly suitable for monitoring pH variations in intracellular environments and living organisms such as zebrafish. This probe serves as a highly promising tool for in-depth research into pH-related physiological and pathological processes in biological systems. Its potential applications in biomedical research could significantly advance our understanding of acid-base balance regulation in living organisms, broadening the scientific perspective on pH-dependent mechanisms.
Feng et al. [53] successfully synthesized a novel fluorescent Probe 6 (Figure 6) by reacting a rhodamine derivative with norbornene. This probe exhibits unique optical properties in solutions with pH values ranging from 7.0 to 3.5, where its fluorescent color gradually shifts from red to green. At 480 nm, the fluorescent intensity gradually decreased, and at 582 nm, the fluorescent intensity gradually increased. Within pH 3.9–5.3, this ratio (I580nm/I480nm) exhibits excellent linear correlation with pH, enabling precise detection of pH variations. A defining feature of this probe is its morpholine moiety—a lysosome-targeting group—enabling specific biomedical applications. Leveraging this design, the probe achieves ratiometric pH detection within intracellular lysosomes. These organelles depend critically on acidic microenvironments for physiological function, making the probe a powerful tool to investigate lysosomal pH regulation and its implications in disease pathogenesis. This capability provides novel insights into cellular pathophysiology while advancing diagnostic and therapeutic development.
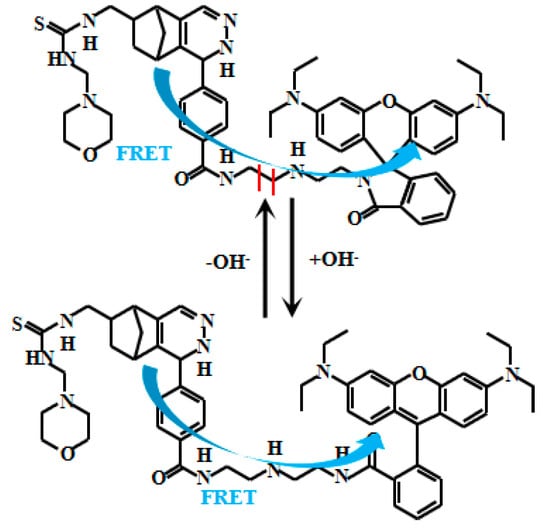
Figure 6.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 6.
Hong et al. [54] meticulously designed and synthesized a novel polymeric pH fluorescent Probe 7 (Figure 7), using rhodamine B, hydrazine hydrate, and acrylamide as starting materials. Under acidic conditions, the rhodamine B moiety in the probe undergoes a ring-opening reaction, while the oxygen atom on the lactam group becomes protonated. This triggers the transfer of lone electron pairs from the nitrogen atom of the diethylamine group to the lactam unit, resulting in the ICT effect. As the pH decreases, the fluorescent peak intensity at 585 nm progressively increases, emitting bright orange-red fluorescence. A highly linear correlation between pH and fluorescent intensity at 585 nm was observed within the pH range of 5.0 to 6.0. Under weakly acidic conditions (pH 5.0), the probe demonstrated minimal interference from various metal ions, highlighting its exceptional selectivity for accurate pH detection. Additionally, the probe exhibits outstanding water solubility and membrane permeability, enabling rapid cellular uptake under weakly acidic conditions. Capitalizing on these advantages, the probe has been successfully applied in fluorescent imaging studies of pH dynamics in live TM3 cells. This advance not only delivers an effective tool for tracking intracellular pH dynamics but also enables deeper investigation of cellular pH homeostasis and associated pathophysiological processes, providing critical support for cell biology research and disease diagnostics/therapeutics development.
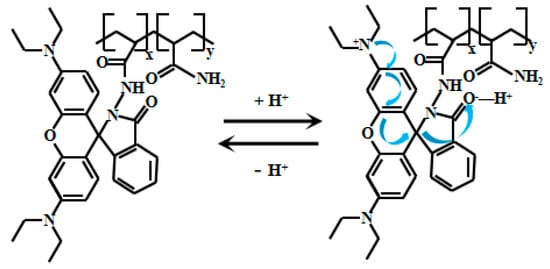
Figure 7.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 7.
2.3. Wide-Range Acidic Fluorescent Probes
Song et al. [55] successfully prepared novel Fe-doped carbon dots (Fe-CDs, Probe 8) using a metal-based deep eutectic solvent (MDES). The fluorescent intensity of Fe-CDs exhibited a significant decrease as the pH varied from 2 to 7, with nearly complete fluorescent quenching observed at pH 7. Notably, the fluorescent intensity demonstrated an excellent linear relationship within the pH range of 2–7. Furthermore, Fe-CDs displayed remarkable stability, excellent water solubility, and specific responsiveness to NO2−, enabling their successful application in nitrite detection in food and aqueous environments.
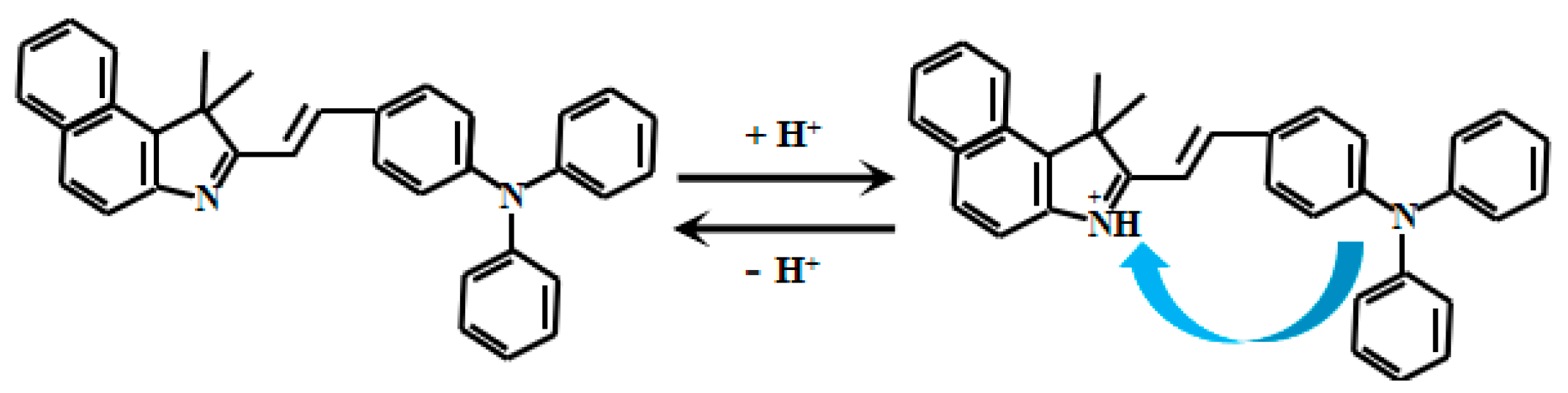
Liu et al. [56] designed a D-π-A structured fluorescent Probe 9 (Figure 8) using triphenylamine as the electron donor and benzindole as the electron acceptor. Under acidic conditions, protonation of the nitrogen atom on the indole moiety induced electron transfer from triphenylamine to indole, generating the ICT effect. As the pH of the probe solution decreased from 7.4 to 2.1, the fluorescent intensity of the probe gradually quenched, demonstrating its sensitive pH responsiveness with good linearity in the pH range of 2.1–7.4. Filter paper impregnated with Probe 9 showed distinct color changes visible to the naked eye. This probe has been successfully applied for pH detection in biological systems, including zebrafish and onion tissues, providing a powerful tool for investigating acid-base balance in living organisms.
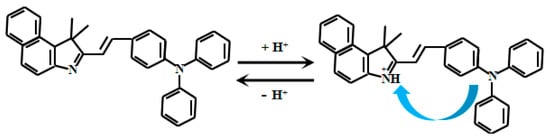
Figure 8.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 9.
Huang et al. [57] successfully synthesized nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon quantum dots (N,S-CQDs, Probe 10) using inexpensive raw materials such as salicylic acid and thiourea as carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur sources, respectively, through a one-step hydrothermal method. These N,S-CQDs exhibit extremely high sensitivity to pH, with the fluorescent intensity at 409 nm showing a highly linear correlation with pH values within the range of 2.01 to 5.11. The synthesized N,S-CQDs possess notable advantages, including strong fluorescence, excellent anti-interference capability, high photostability, and a high quantum yield.
3. Alkaline Fluorescent Probes
3.1. Strongly Alkaline Fluorescent Probes
Strong alkalinity refers to solutions with a pH typically above 12. These solutions contain a high concentration of hydroxide ions (OH−), exhibiting strong corrosiveness and reactivity. Common strong bases such as sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and potassium hydroxide (KOH) are widely used in various industrial fields due to their significant chemical properties. In the paper industry, strong alkalis are employed for pulp bleaching and treatment; in the textile industry, they assist in fiber processing and dyeing; in soap manufacturing, they serve as key raw materials; and in petroleum refining, they play a crucial role in impurity removal and chemical conversion. Additionally, concrete, a common construction material, typically maintains an alkaline internal environment with a pH often exceeding 12 [58]. This alkalinity promotes the formation of a dense passive film on the surface of steel reinforcement. Acting as a protective barrier, this film effectively isolates the steel from corrosive external substances, preventing corrosion and ensuring the structural stability and durability of concrete [59]. This characteristic is vital for the long-term safety of infrastructure such as buildings and bridges, as steel corrosion can weaken structural integrity and even lead to safety hazards [27].
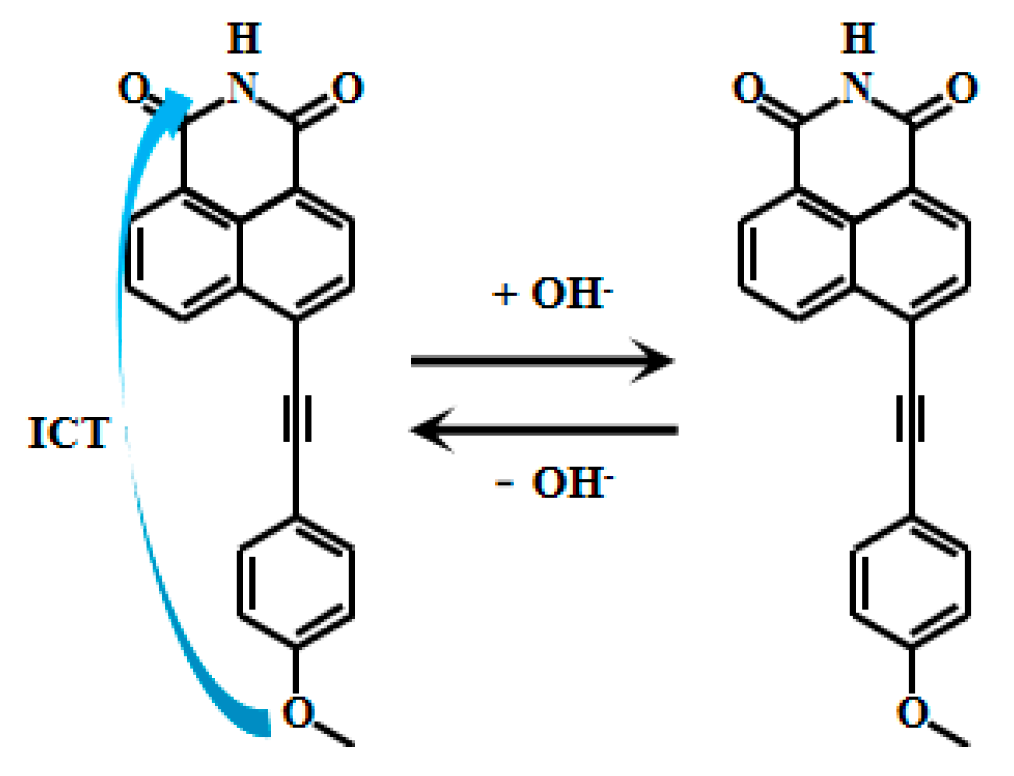
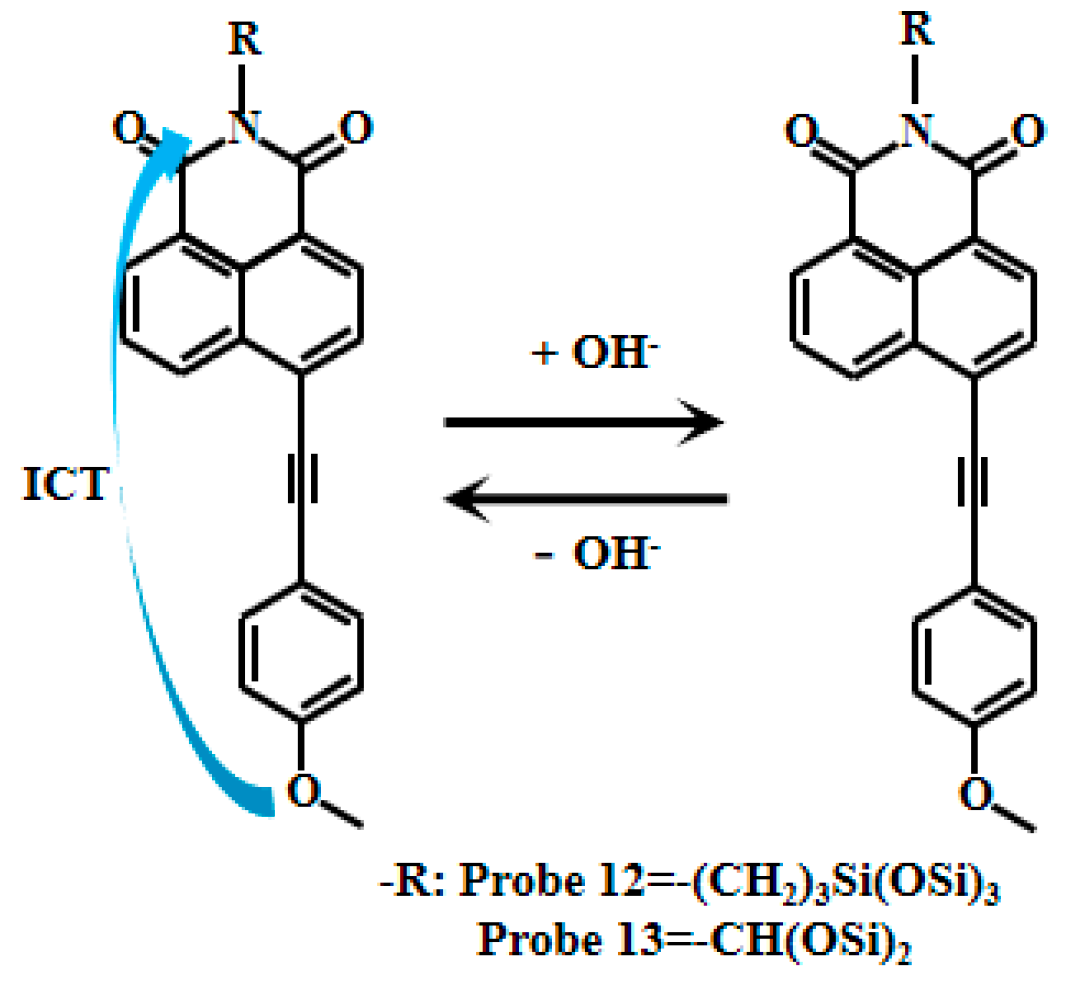
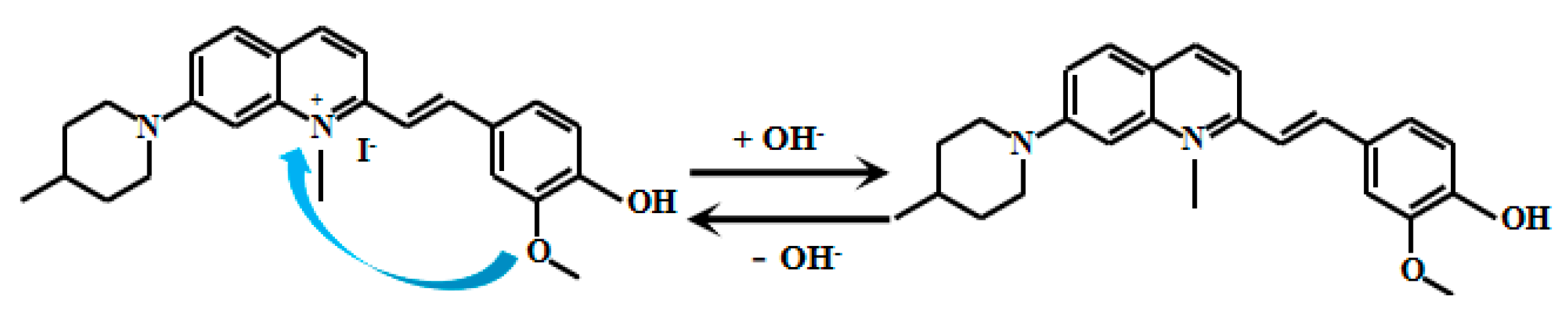
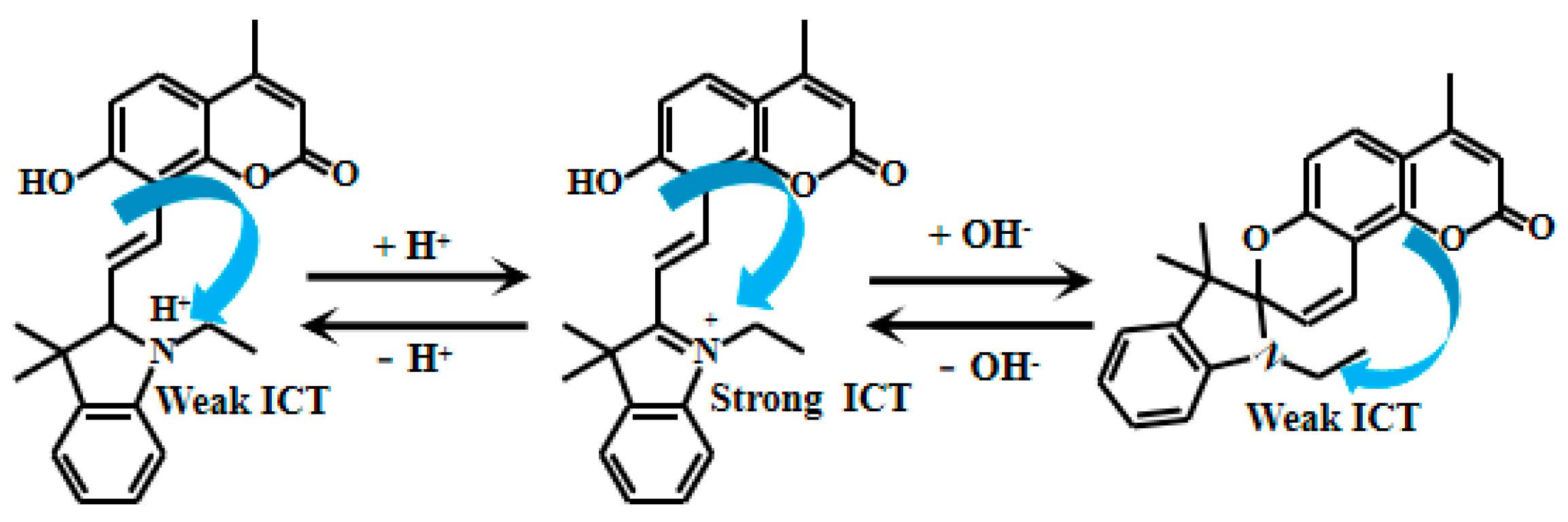
Tariq et al. [60,61] encapsulated naphthalimide-based fluorescent Probe 11 (Figure 9) within a cross-linked polyvinyl alcohol-glutaraldehyde matrix to produce thin films with well-defined physicochemical and photophysical properties. By adjusting the glutaraldehyde ratio, they obtained sensing films with varying mesh densities, which were further developed into photoelectric diodes. These films exhibited a linear relationship between fluorescent intensity and pH within ranges of 10.5–13.5 and 10.5–12.5, respectively. They also demonstrated reversible and reliable responses to pH changes and were successfully applied in measuring the pH of concrete pore solutions. Xu [62] also developed the naphthalimide-based fluorescent Probes 12 and 13 (Figure 10) that respond to strong alkaline pH by encapsulating silica fluorescent nanoparticles in PVA/SiO2 sol-gel membranes with an accuracy of ±0.1 pH units, and demonstrate good accuracy in measuring the pH of actual concrete pore solutions. Naphthalimide-based fluorescent dyes operate through an intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) mechanism, where photoexcitation induces electron transfer from the methoxy group to the naphthalimide moiety, generating fluorescence. Under alkaline conditions (pH >12), deprotonation of the naphthalimide group reduces its ICT efficiency, leading to decreased fluorescence intensity.
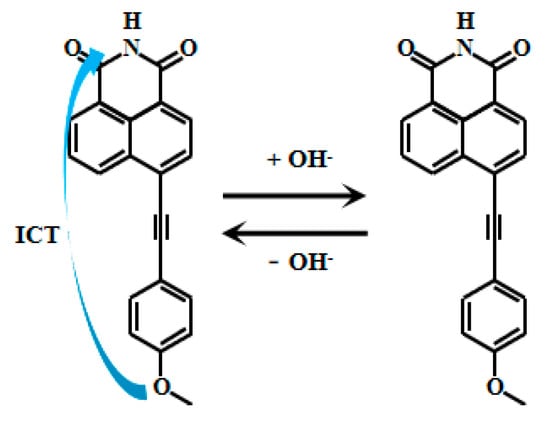
Figure 9.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 11.
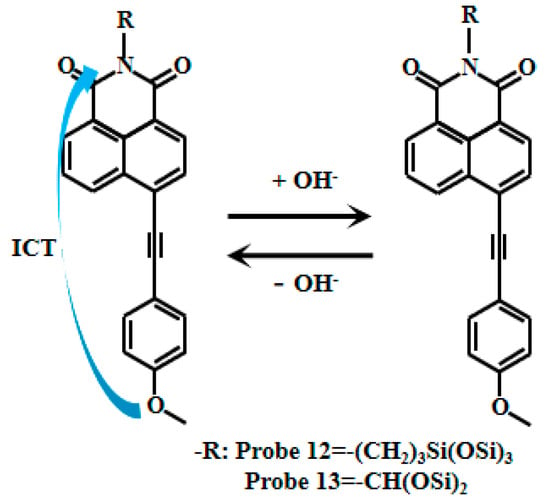
Figure 10.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 12 and Probe 13.
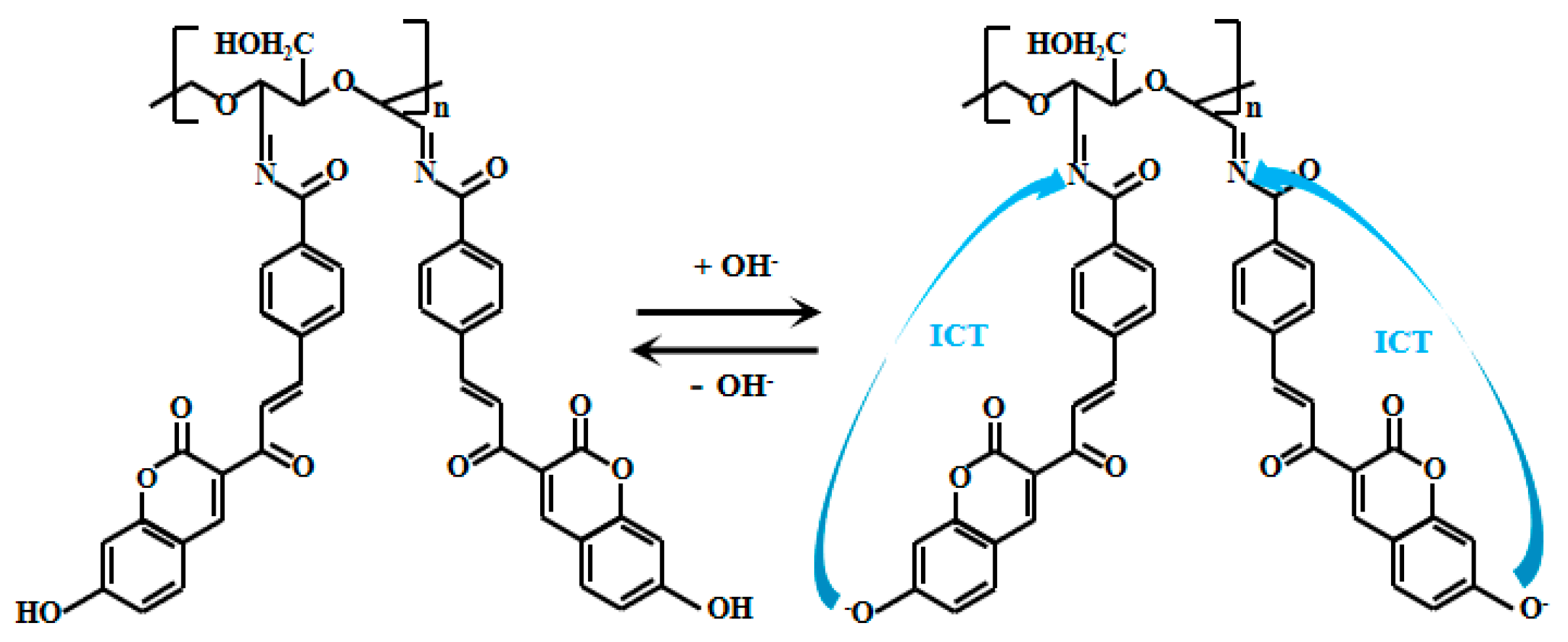
Huang et al. [63] grafted a coumarin derivative (HCB) onto dialdehyde cellulose (DAC) to prepare Probe 14 (Figure 11). In strongly alkaline solutions, the phenolic hydroxyl group on the coumarin undergoes deprotonation in the alkaline conditions, which enhances the ICT effect, thereby generating intense fluorescence. The Probe 14 solution at 577 nm gradually decreased as the pH increased from 7.5 to 14. Additionally, a new peak emerged at 459 nm, and its fluorescent intensity progressively increased with rising pH. Within the pH range of 9–13, the fluorescent intensity ratio (I459nm/I577nm) of the Probe 14 showed a positive correlation with pH, exhibiting a good linear relationship. Moreover, the Probe 14 demonstrated excellent selectivity for alkaline pH, strong anti-interference capability, and a fast response time (6 min), making it an effective fluorescent sensor for pH detection in the alkaline environments. Probe 14 was successfully applied for precise pH detection in environmental water samples and was further fabricated into pH test strips, which displayed distinct color changes under both sunlight and UV light. As pH increased, the test strips gradually darkened under sunlight, while the fluorescent color shifted from yellow to blue.
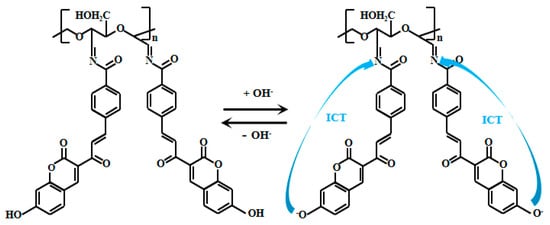
Figure 11.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 14.
3.2. Weakly Alkaline Fluorescent Probes
Weak alkalinity refers to solutions with a pH slightly above 7, typically ranging from 7 to 11. For example, sodium bicarbonate, commonly known as baking soda, dissolves in water to form a weakly alkaline solution with a pH of around 8.3. Additionally, soy milk is a common weakly alkaline beverage, with a pH usually between 7.4 and 7.9. In living organisms, the extracellular fluid maintains a weakly alkaline pH of approximately 7.4, which is crucial for sustaining normal cellular physiological functions. The cytoplasm also exhibits a near-neutral to weakly alkaline pH of about 7.2 [64], while mitochondria—the energy factories of cells—maintain an internal pH of around 8.0 [65]. This precise pH regulation plays a vital role in facilitating biochemical reactions and ensuring the proper functioning of cellular organelles [35]. For instance, the weakly alkaline environment within mitochondria helps maintain the activity of energy metabolism-related enzymes, thereby ensuring a stable supply of cellular energy [31]. Understanding these weakly alkaline pH ranges not only enhances our knowledge of the acid-base properties of everyday substances but also provides valuable insights into physiological mechanisms and pathological changes in living systems [66,67].
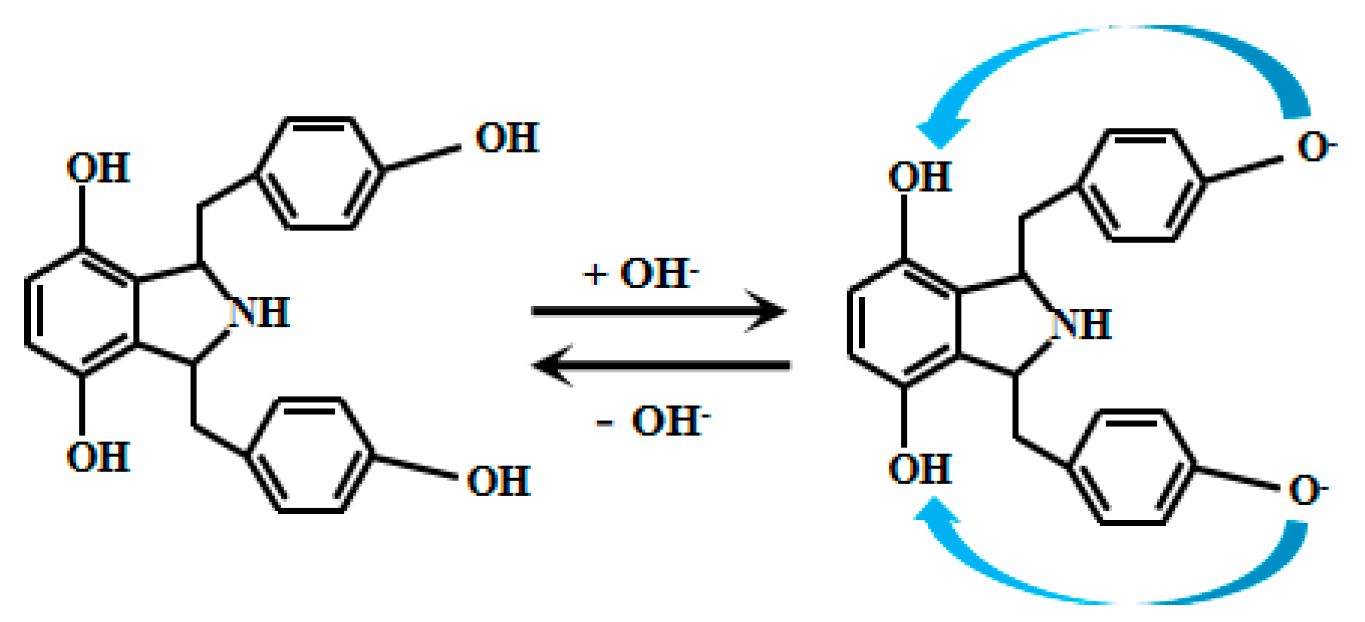
Kong et al. [68] ingeniously developed an innovative, simple, and efficient synthetic strategy to successfully prepare 14 derivatives of 1,3-bis(arylimino) isoindoline and a 2,3-bis(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl) benzene-1,4-diol. Detailed analysis of the fluorescence properties of these 14 compounds revealed that Probe 15 (Figure 12) exhibits distinct fluorescence characteristics under weakly alkaline conditions. Specifically, in this environment, the hydroxyl group on the phenol moiety of Probe 15 undergoes deprotonation, facilitating electron transfer to the amino group. This triggers the ICT effect, resulting in fluorescence emission. Further studies revealed that within the pH range of 7.00 to 9.30, the fluorescence intensity of Probe 15 increases significantly with rising pH, demonstrating an excellent linear correlation between fluorescence intensity and pH. This discovery not only highlights the potential of Probe 15 for fluorescence-based pH sensing but also provides important theoretical and experimental foundations for developing novel pH-responsive fluorescent probes.
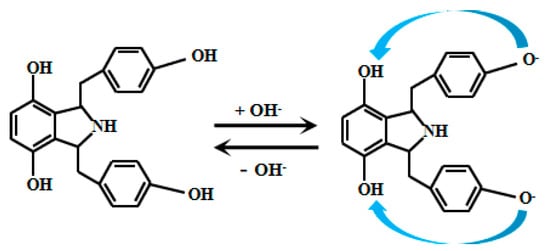
Figure 12.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 15.
Chen et al. [69] meticulously designed the ICT-based switchable fluorescent Probe 16 (Figure 13) for weakly alkaline environments. In acidic conditions, the methoxy group’s electrons in the Probe 14 transfer to the nitrogen atom on the quinoline moiety, resulting in fluorescent emission. However, under alkaline conditions, deprotonation of the phenolic hydroxyl group converts it into a quinoid structure.
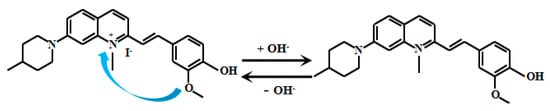
Figure 13.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 16.
The electron-withdrawing effect of the carbonyl group suppresses electron transfer from the methoxy group to the quinoline nitrogen, thereby quenching the fluorescence of Probe 16. When the solution pH decreases gradually from 11.00 to 6.00, Probe 16 exhibits significantly enhanced fluorescent intensity at 630 nm. Notably, within the pH range of 6.50–10.00, the fluorescent intensity demonstrates an excellent linear correlation with pH values, indicating its high sensitivity and accuracy for pH monitoring in this range. Cellular imaging experiments confirmed that Probe 16 possesses low cytotoxicity without interfering with normal cellular functions, along with remarkable photostability that maintains consistent fluorescent performance under prolonged illumination. Importantly, Probe 16 specifically targets mitochondria in various cell types, making it a powerful tool for mitochondrial research. Leveraging these advantages, Probe 16 successfully enables real-time monitoring of mitochondrial pH in HeLa cells, providing a new tool to study intracellular acid-base balance and its physiological/pathological implications.
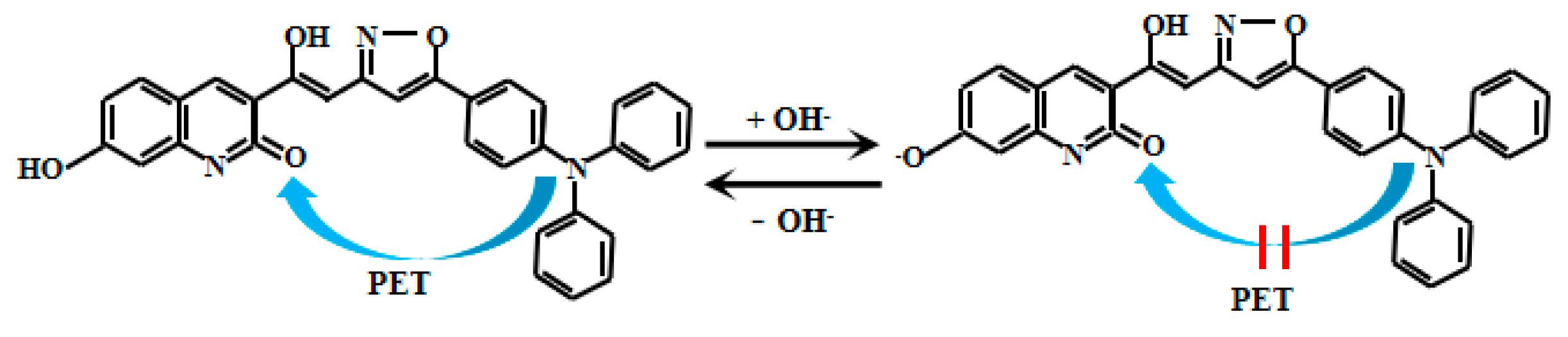
Liu et al. [70] skillfully developed a novel coumarin-based fluorescent Probe 17 (Figure 14) specifically designed for pH detection, as shown in Figure 10. In this probe, the lone electron pair on the nitrogen atom of the triphenylamine group effectively quenches coumarin fluorescence through the PET process. However, under weakly alkaline conditions, deprotonation of the hydroxyl group on coumarin inhibits the PET process from triphenylamine to coumarin, resulting in significant fluorescent enhancement of Probe 17. As the solution pH gradually increases, Probe 17 exhibits a distinct colorimetric response, transitioning from colorless to cyan-blue fluorescence. Particularly within the pH range of 6.50–9.98, the fluorescent intensity at 476 nm demonstrates an excellent linear correlation with pH values. Probe 17 demonstrates excellent performance not only in chemical analysis but also exhibits significant application potential in the field of biomedical imaging. Researchers have successfully utilized Probe 17 to image pH changes in live zebrafish, providing an intuitive and effective approach for studying the dynamic changes of acid-base balance within living organisms. Furthermore, Probe 17 has been successfully applied to real-time monitoring of the freshness of meat and shrimp. By detecting pH changes in these food products during storage, their freshness status can be tracked promptly, offering a new analytical pathway for food quality control and safety inspection.
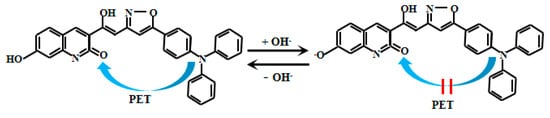
Figure 14.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 17.
3.3. Wide-Range Alkaline Fluorescent Probes
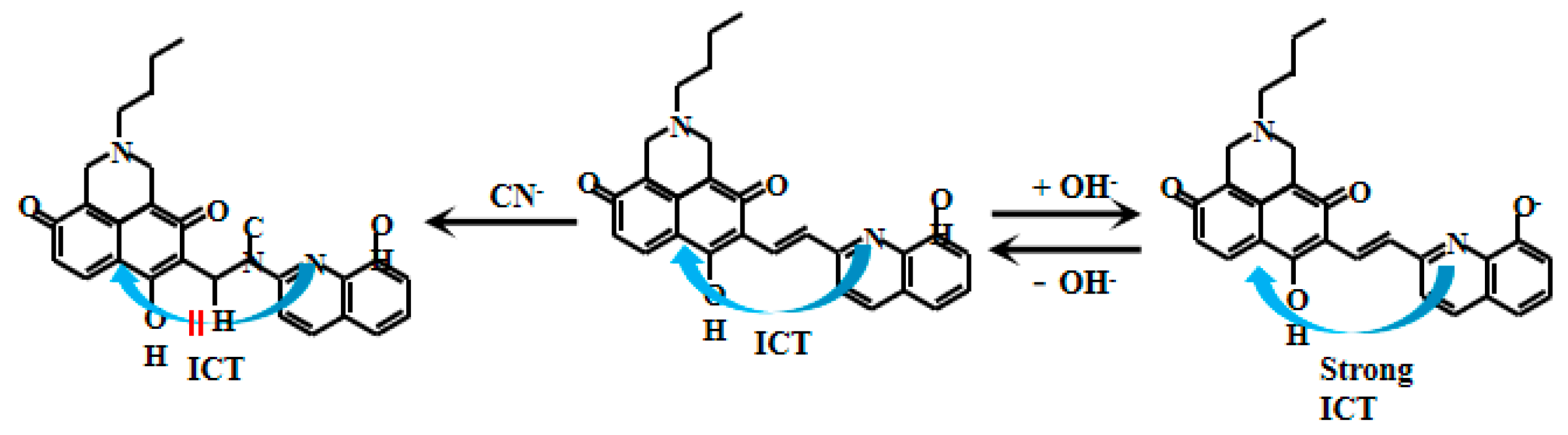
Zhang et al. [71] designed and synthesized a naphthalimide-based fluorescent Probe 18 (Figure 15). In this probe system, electron transfer from the 8-hydroxyquinoline moiety to the naphthalimide unit generates the ICT effect, enabling fluorescent emission. Under alkaline conditions (pH > 7.4), deprotonation of the hydroxyl group on 8-hydroxyquinoline produces an O− anion that significantly enhances the ICT effect, leading to a remarkable increase in fluorescent intensity. The probe exhibits a uniform and substantial fluorescent enhancement with increasing pH in alkaline environments. However, after the reaction between Probe 18 and CN−, the disruption of the conjugated system hinders intramolecular electron flow, resulting in the shutdown of the ICT effect and a reduction in the fluorescent intensity. Notably, a strong linear correlation exists between the fluorescent intensity and pH values within the range of 7.4–12.0, demonstrating the sensitivity and accuracy for pH monitoring in alkaline conditions for the Probe 18. Interestingly, the carbonyl group (C=O) can react with cyanide ions (CN−), disrupting the ICT-mediated electron transfer process and resulting in fluorescent quenching. Experimental observations showed gradual attenuation of the cyan fluorescent intensity with increasing CN− concentration. Complete fluorescent disappearance occurred at 40 µM CN−, confirming the specific response of the probe to cyanide. This dual functionality enables the probe to serve not only as an effective pH sensor but also as a fluorescent CN− detector, offering new analytical approaches for environmental monitoring, chemical analysis, and biomedical research applications.
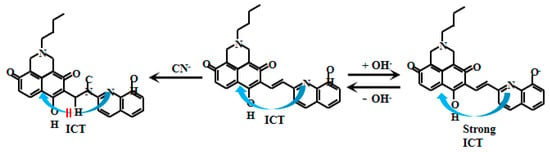
Figure 15.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 18.
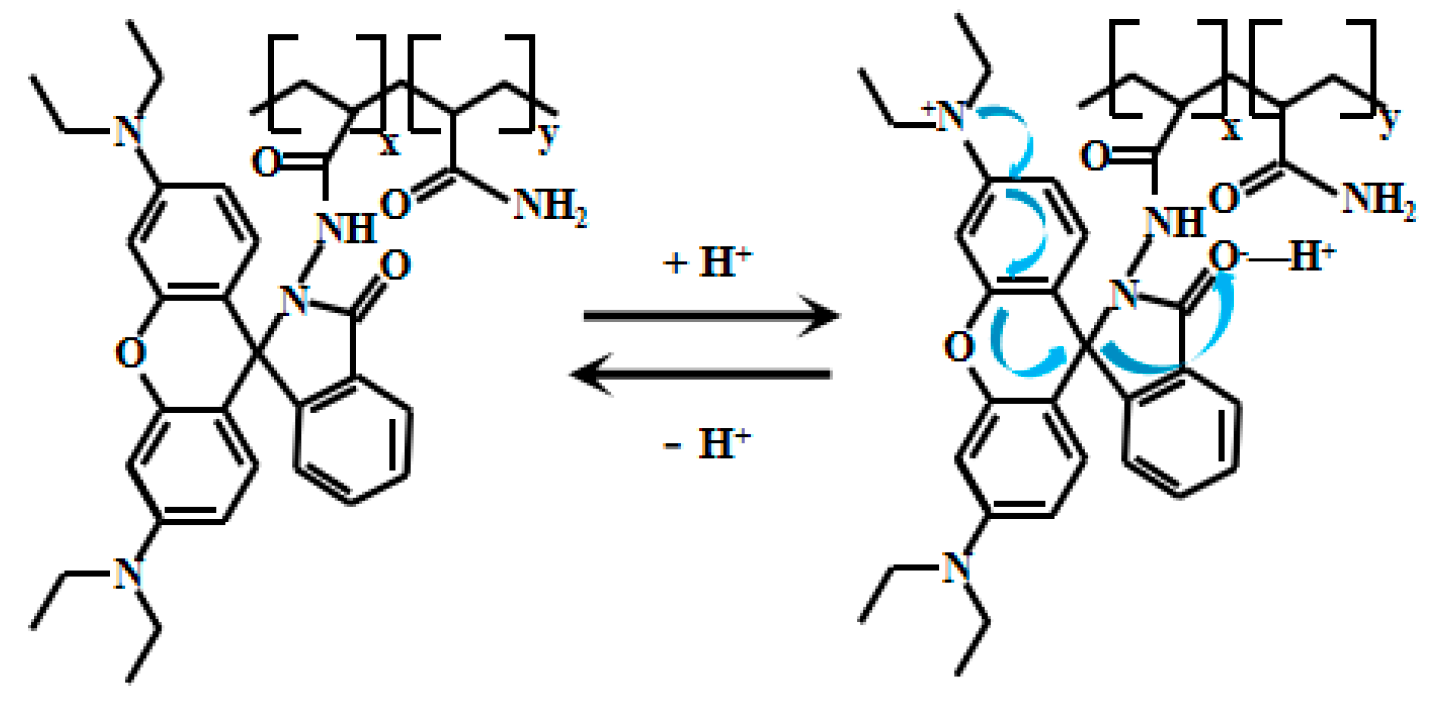
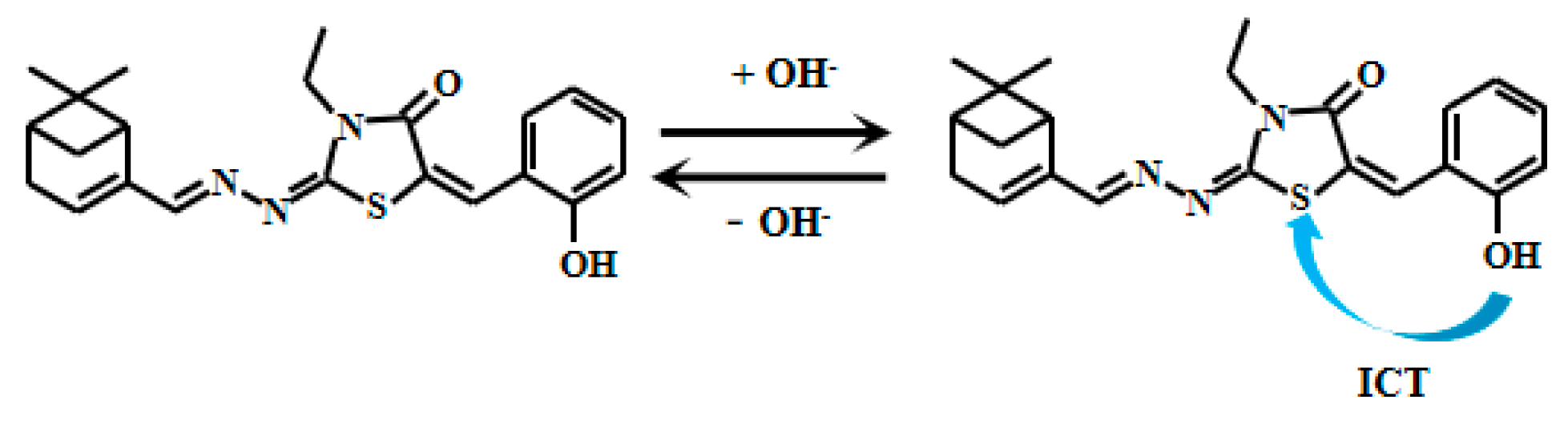
Xu et al. [72] designed and synthesized a novel myristaldehyde-based colorimetric fluorescent Probe 19 (Figure 16) for highly sensitive alkaline pH detection. Under alkaline conditions, deprotonation of the hydroxyl group in Probe 19 facilitates electron transfer from the hydroxyl to the thiazole moiety, thereby enhancing the ICT effect and resulting in significant fluorescent intensification. During pH elevation from 7.45 to 12.89, the probe demonstrates remarkable colorimetric changes, transitioning progressively from colorless to orange fluorescence. Across pH 8.45–11.21, the fluorescence intensity displays an excellent linear correlation with pH. The probe also displays good reversibility, allowing multiple detection cycles under varying pH conditions with reduced operational costs. Notably, Probe 19 has been successfully applied in biological imaging studies using live HeLa cells and zebrafish. In these experiments, the probe effectively tracked dynamic pH changes across cellular and organismal systems, serving as an intuitive imaging tool to study intracellular acid-base homeostasis and related physiological and pathological processes. These capabilities significantly broaden the probe’s utility in biomedical research.
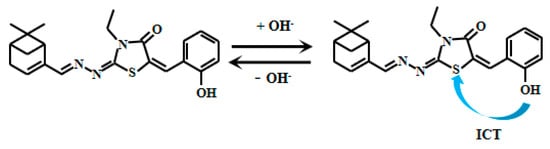
Figure 16.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 19.
4. Near-Neutral Fluorescent Probes
Near-neutral pH refers to solutions with pH values close to neutral, typically ranging from 6.0 to 8.0. While these solutions exhibit nearly neutral acid-base properties, they may show slight acidic or alkaline tendencies. A prime example is human blood, which maintains a tightly regulated pH between 7.35 and 7.45—slightly alkaline—a critical factor for normal physiological functions. Similarly, intracellular fluid maintains a near-neutral pH of 6.8–7.4, providing an optimal environment for biochemical reactions. In contrast, tumor cells exhibit a more acidic pH range of 5.5–7.0 [73]. This relatively lower pH likely reflects their metabolic characteristics and is closely associated with the formation and progression of the tumor microenvironment. Understanding pH dynamics across biological systems is scientifically and clinically valuable for elucidating physiological mechanisms, disease progression, and therapeutic approaches [74,75].
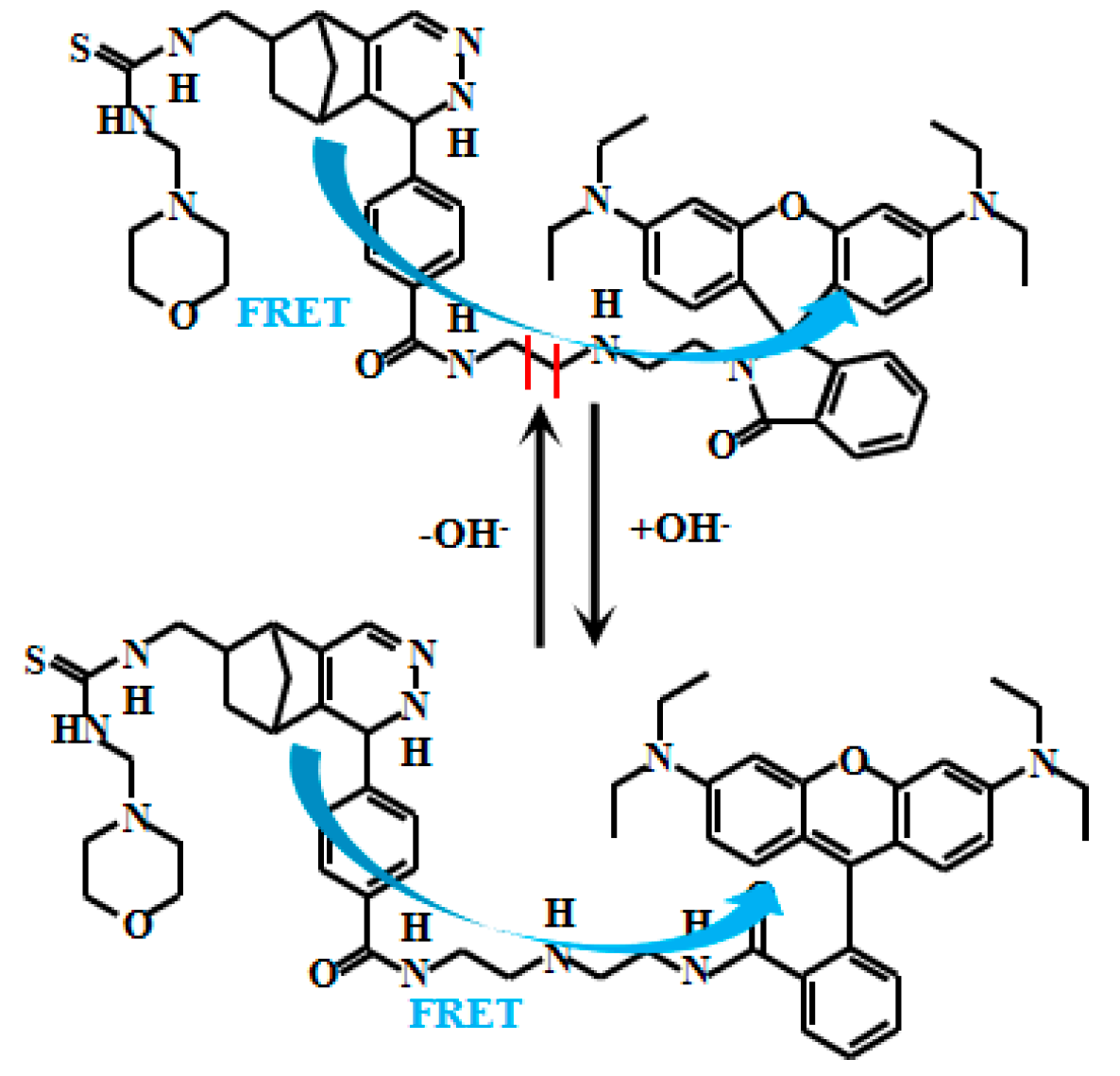
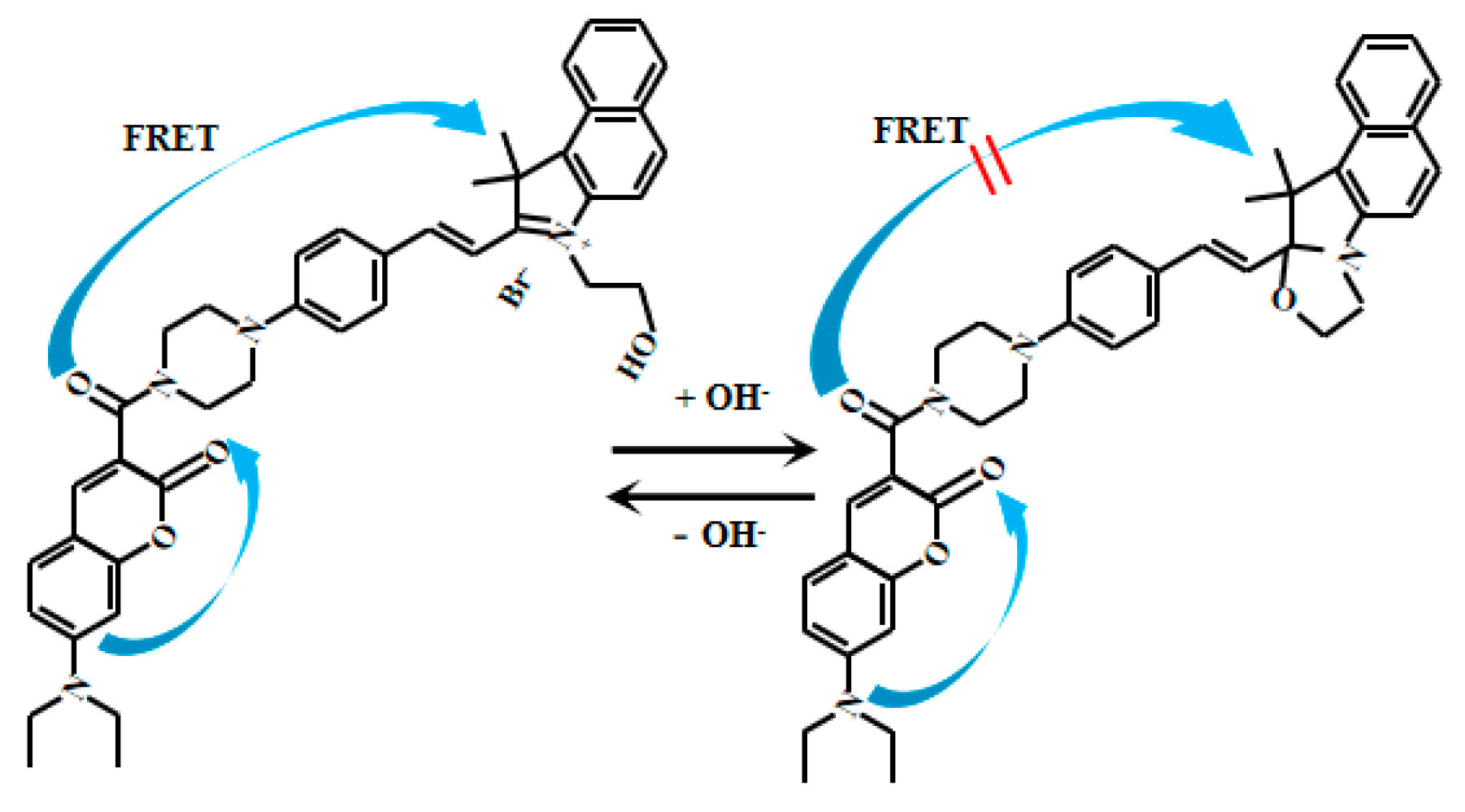
Yue et al. [66] developed an innovative ratiometric fluorescent Probe 20 (Figure 17) based on the FRET to detect pH changes from weakly acidic to weakly alkaline conditions. Under alkaline conditions, Probe 20 adopts a closed-loop conformation, inhibiting the FRET and allowing donor fluorescent emission. In acidic environments, however, it shifts to an open-loop state, where spectral overlap between the donor’s emission and the acceptor’s absorption enables the FRET, producing acceptor fluorescence. As the pH value increased from 6.0 to 9.0, the fluorescent intensity of Probe 20 at 608 nm gradually decreased while the fluorescent intensity at 485 nm increased. Probe 20 exhibits a robust response to pH fluctuations across 6.0–8.0. Within the narrower physiological range of 7.2–8.0, its fluorescence intensity ratio (I485nm/I608nm) displays a particularly strong linear correlation with pH. Furthermore, the probe enables real-time visualization of mitochondrial acidification in live cells, providing a powerful tool to study dynamic intracellular pH changes and associated physiological and pathological processes. This imaging capability allows direct observation of mitochondrial dynamics under varying pH conditions, advancing investigations into the interplay between mitochondrial function and cellular acid-base homeostasis. Collectively, these features offer novel mechanistic insights for cell biology and disease research.
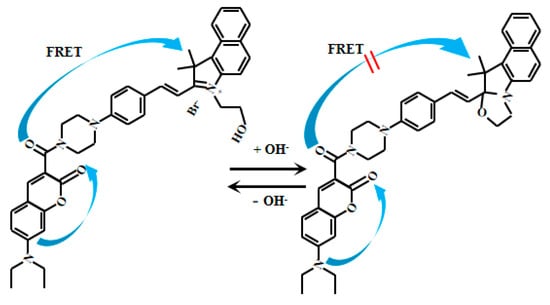
Figure 17.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 20.
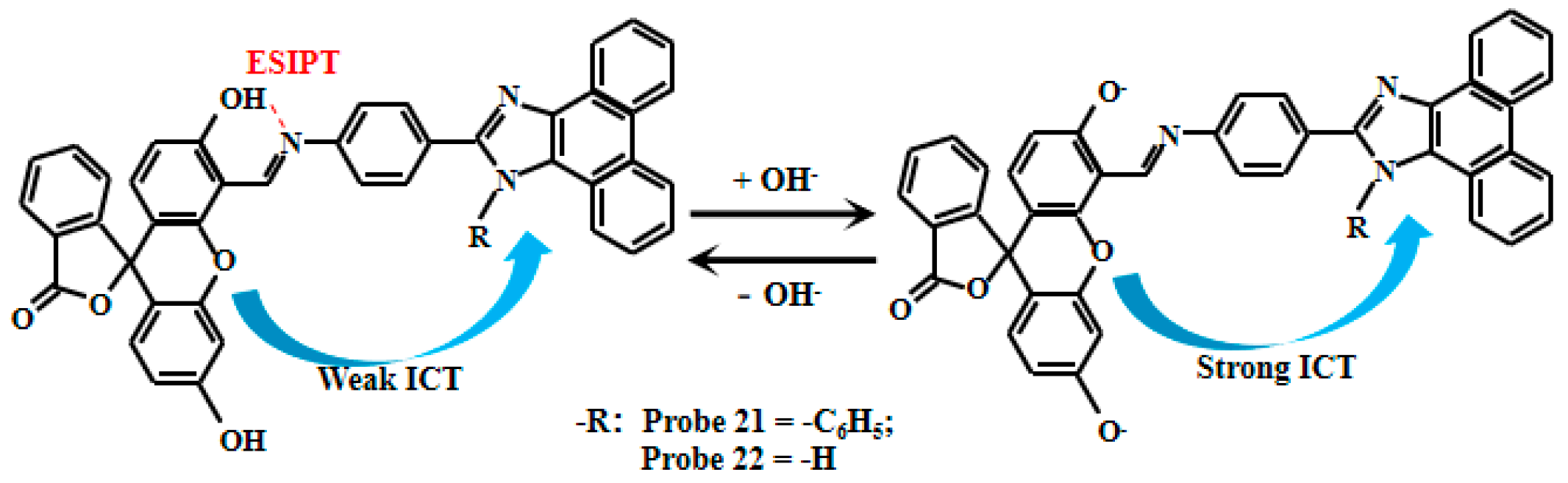
Du et al. [76] ingeniously designed and synthesized two novel pH fluorescent Probe 21 and Probe 22 (Figure 18), using phenanthroimidazole and fluorescein derivatives as building blocks. These probes exhibit dual response mechanisms: Firstly, under acidic conditions (pH 2–6), an intramolecular hydrogen bond forms between the hydroxyl hydrogen and nitrogen atoms, inducing the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) between enol and keto forms. Concurrently, the ICT effect occurs from the fluorescein to the phenanthroimidazole moiety, though the ESPT dominates the fluorescent mechanism at this stage. Secondly, in alkaline environments, deprotonation eliminates the ESIPT while enhancing the ICT effect, making ICT the predominant fluorescent mechanism. This dual-response system produces remarkable pH-dependent changes: the probe solution color transitions from pale yellow to bright yellow, demonstrating excellent colorimetric properties. Simultaneously, fluorescent intensity increases significantly with rising pH, showing highly linear correlations within specific ranges—Probe 21 exhibits linear response between pH 6.50–8.00, while Probe 22 operates effectively from pH 5.40–7.50. Probe 21 can complete the fluorescence enhancement within 1 min, while Probe 22 takes 20 min. The distinct transition points and dual-response mechanisms provide robust tools for monitoring pH variations in complex biological systems.
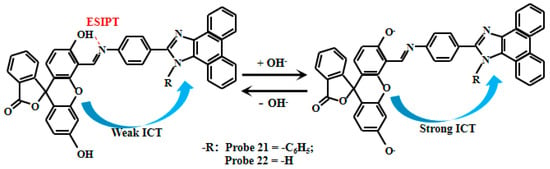
Figure 18.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 21 and Probe 22.
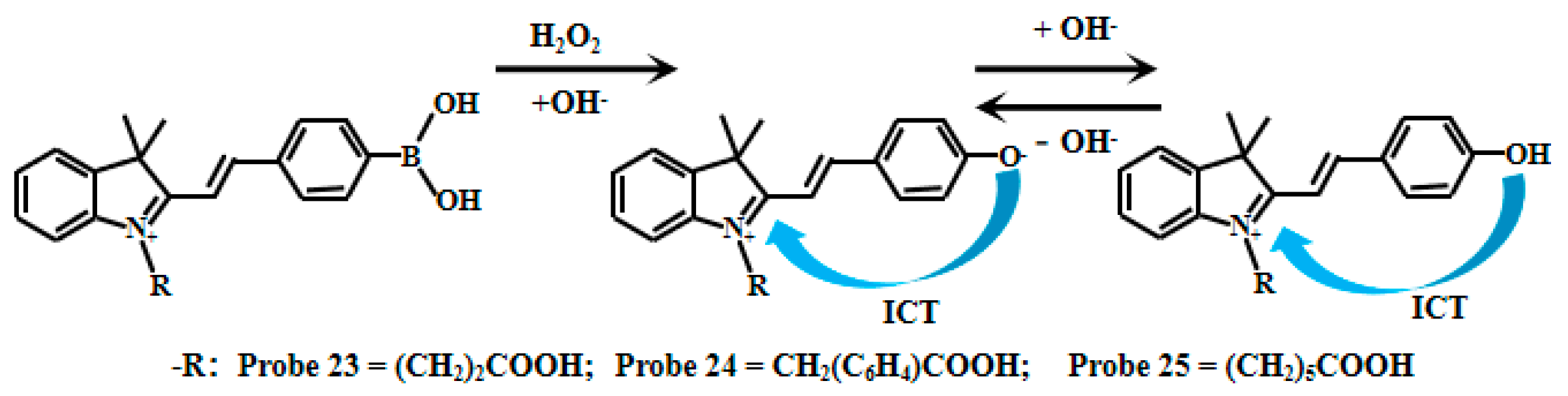
Han et al. [77] synthesized three pH-sensitive fluorescent Probes (23, 24, 25) through structural modification of hemicyanine derivatives (Figure 19). When the value of pH decreased from 9.0 to 4.0, the fluorescence intensity of Probes (23, 24, 25) showed fluorescence quenching at 560 nm, and a new emission peak appeared at 530 nm and gradually increased. These probes show pH-responsive fluorescence across pH 4.0–9.0. Their pKa values—determined from the ratiometric I530nm/I560nm vs. pH relationship—are 6.47 (Probe 23), 6.47 (Probe 24), and 6.40 (Probe 25). To achieve dual-responsive capability for both pH and H2O2 detection, the researchers incorporated a boronic acid moiety into the probe structure. This boronic acid group initially serves as a fluorescence quencher, while subsequent removal of the borate group by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) treatment restores the fluorescent signal. This innovative design enables simultaneous monitoring of pH changes and H2O2 levels in biological systems.
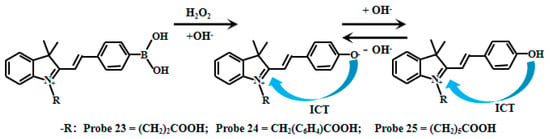
Figure 19.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 23, Probe 24, and Probe 25.
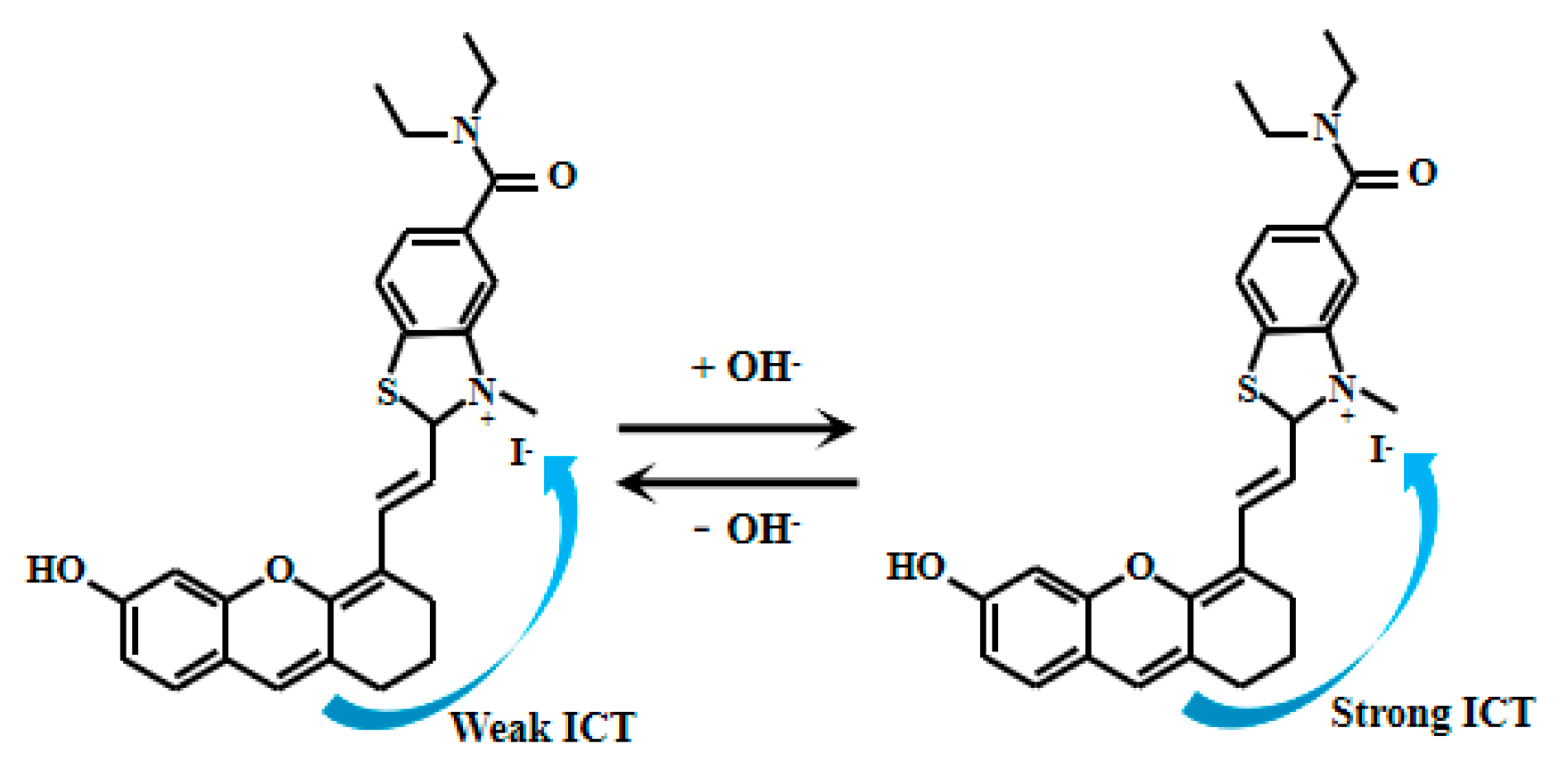
Li et al. [78] meticulously designed and synthesized a novel fluorescent Probe 26 (Figure 20), which consists of a benzothiazole group and an oxanthrene fluorophore, enabling the detection of solution pH and viscosity. In alkaline environments, the hydroxyl group on Probe 26 undergoes deprotonation, enhancing electron transfer from the oxanthrene fluorophore to the benzothiazole group and thereby intensifying the ICT effect. As the pH value increased from 4.0 to 11.0, the fluorescent intensity at 672 nm gradually decreased, while a peak gradually appeared at 715 nm and the fluorescent intensity gradually increased. Experimental results demonstrate that Probe 26 rapidly responds to pH changes in pure water, exhibiting excellent sensitivity and selectivity toward pH. Particularly within the pH range of 6.2 to 7.8, the fluorescence ratio of Probe 26 (I672nm/I715nm) and PH value display a satisfactory linear response, indicating its ability to accurately reflect variations in this pH interval. Probe 26 demonstrates significant potential for pH monitoring in complex environments, including real water samples, human serum, and food products. In food safety applications, it enables real-time assessment of meat freshness by tracking storage-induced pH changes. For environmental science, the probe facilitates water body pH measurements critical for evaluating ecological health. Its serum pH detection capability further supports biomedical diagnostics and disease research. Collectively, Probe 26’s robust performance and versatility establish it as a powerful tool for chemical analysis, environmental science, and biomedical research.
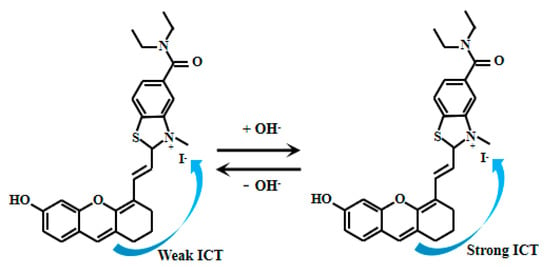
Figure 20.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 26.
5. Wide-Range pH Fluorescent Probes
Mei et al. [79] ingeniously introduced a charged methylindole group at the ortho-position of a hydroxycoumarin skeleton, designing and synthesizing a novel pH-sensitive Probe 27 (Figure 21). This probe exhibits unique fluorescent characteristics under different pH conditions. As the solution pH gradually increases from 2.00 to 6.65, the maximum fluorescent intensity of Probe 27 at 650 nm shows a progressive enhancement. When the pH further increases from 6.65 to 12.00, the fluorescent intensity at 650 nm gradually decreases while a new emission peak emerges at 465 nm with increasing intensity. Furthermore, the researchers evaluated various cations and anions, demonstrating that at pH 2.00, 6.65, and 12.00, these ions showed no significant impact on the fluorescent intensity of Probe 25. This indicates that Probe 27 possesses excellent anti-interference capability against ions and can accurately reflect pH variations even in complex ionic environments, providing a highly selective and sensitive tool for pH detection, particularly suitable for pH monitoring in systems with coexisting multiple ions.
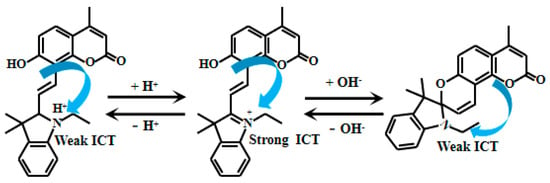
Figure 21.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 27.
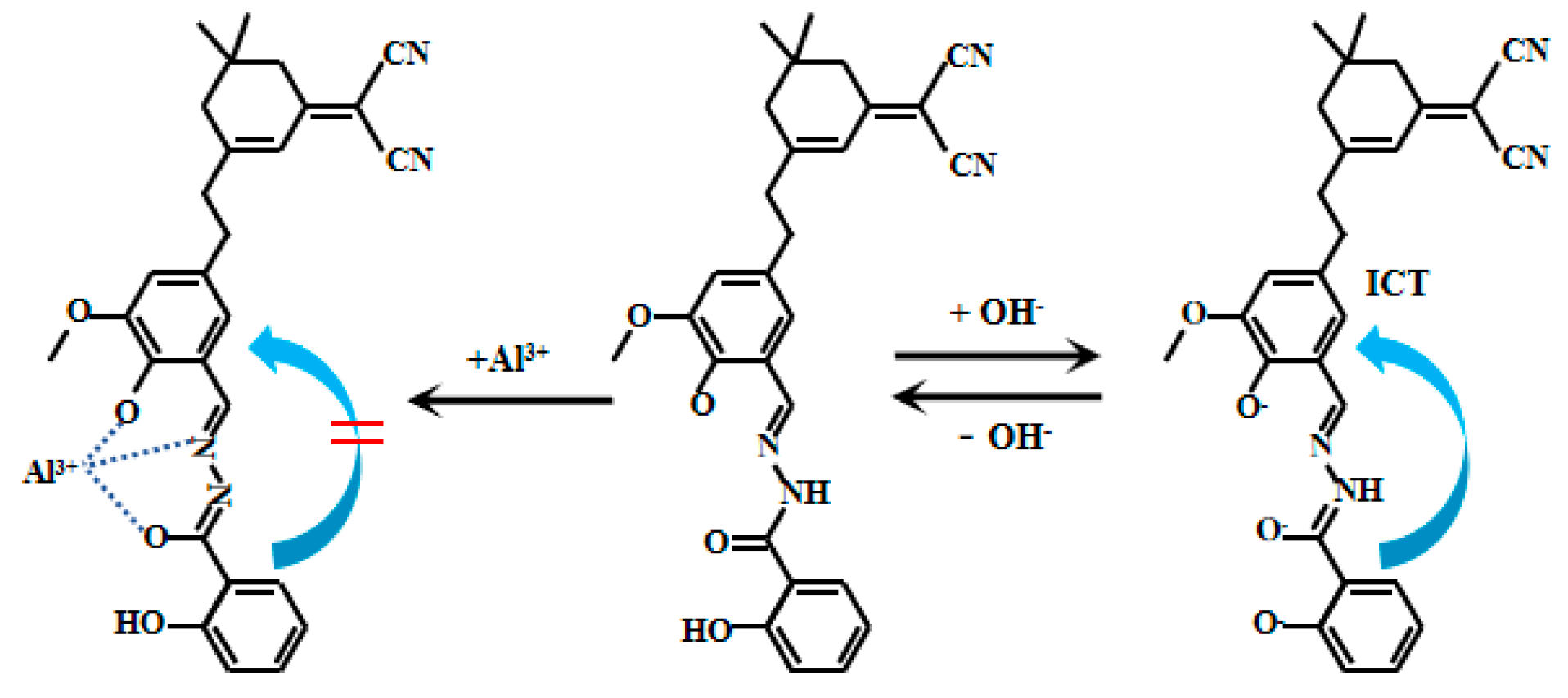
Liu et al. [80] designed and synthesized a bis-responsive near-infrared (NIR) Probe 28 (Figure 22) based on isophorone, which achieves highly selective and reversible detection of Al3+ (with significantly enhanced fluorescence) and pH (with significant color change), and exhibits excellent interference resistance. The fluorescent intensity of Probe 28 increased with increasing pH values within the range of 2.0–6.0. However, under conditions of pH (6.5–13.0), the fluorescence of Probe 28 shifted from 665 nm to 710 nm, accompanied by a decrease in fluorescent intensity. The colorimetric pH response, evident, is attributed to the ICT effects. The fluorescent ratio of Probe 28 (I710nm/I665nm) showed a good linear relationship with pH. Probe 28 has weak fluorescence, but its fluorescent intensity increases dramatically upon binding to Al3+. The probe exhibits significant color changes and a red shift in its fluorescence peak position in response to pH variations. Successfully applied for tracking Al3+ and detecting pH in vivo (in HeLa cells, zebrafish, and mice), the probe can also be monitored using smartphone colorimetry under different pH conditions, with corresponding Commission Internationale de l’Éclairage Color System (CIE color) charts generated. It responds rapidly to Al3+, with fluorescence stabilizing within 200 s.
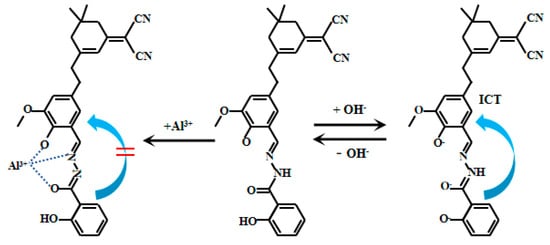
Figure 22.
Working mechanism of fluorescent Probe 28.
Table 1 summarizes key parameters of 26 pH-responsive fluorescent probes, detailing their core fluorophores, sensing mechanisms (predominantly ICT, PET, and FRET), pH response ranges (spanning pH 1.04–12.89), and diverse applications. These probes enable precise pH monitoring in contexts ranging from biomedical imaging (e.g., mitochondrial/lysosomal tracking in live cells) and food freshness assessment to environmental analysis and industrial diagnostics, as validated in peer-reviewed studies.

Table 1.
Parameters of 26 pH-responsive fluorescent probes.
6. Summary and Outlook
As a fundamental indicator of solution acidity/alkalinity, pH profoundly impacts scientific, industrial, and biological systems. Fluorescent pH probes offer significant application potential for long-term, online monitoring due to their inherent advantages. While substantial progress has been made in recent years, critical limitations persist. Current research exhibits a pronounced focus on near-neutral cellular environments, leaving extreme pH ranges—especially strong alkalinity (pH > 12)—relatively underexplored, thereby constraining broader utility. Furthermore, most probes operate within narrow pH windows, and achieving accurate, wide-range monitoring remains a significant challenge.
Practical implementation faces major technical hurdles: dye leakage compromises stability and accuracy; photobleaching limits long-term signal integrity; and insufficient robustness under harsh conditions undermines reliability. These factors collectively impede translation from laboratory validation to real-world deployment and commercialization.
7. Future Work
- (1)
- Probe enhancement strategies: Key strategies for advancing fluorescent probes include optimizing ICT efficiency through stronger electron donor/acceptor groups or nano-assemblies with signal amplification capabilities, and designing universal probes operable across broad pH ranges (e.g., pH 0–14) or specialized probes with ultra-high sensitivity at extreme values (e.g., pH > 13 or pH < 1).
- (2)
- Hysteresis characteristics of pH sensors: To enhance sensor reversibility and long-term stability, optimize sensing membrane design—including functional groups and cross-linking density—while analyzing OH− ion accumulation kinetics. Additionally, explore surface modification or buffering agents to minimize OH− retention and improve stability.
- (3)
- Stability: Structural modification of probe molecules (such as introducing large steric hindrance groups, oxidation/reduction resistant groups) or encapsulating them in stable carrier materials (such as silica and metal organic framework (MOFs)) to enhance their long-term photostability and chemical stability in specific harsh environments, such as strong acids/bases and highly reactive oxygen species.
- (4)
- Multi-functionality of sensors: In addition to pH detection, fluorescent sensors can also be used to detect other environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, and ion concentration. In the future, sensor design based on multifunctional fluorescent materials can be explored to achieve simultaneous detection of multiple parameters and improve the application value of sensors.
- (5)
- Mechanical performance of sensors: The deployment of fiber optic sensors in mechanically demanding environments necessitates enhanced durability—a currently understudied aspect. Future work must: (a) engineer organic–inorganic hybrid coatings with gradient modulus, optimizing interfacial binding energy through MD simulations to ensure structural integrity under extreme stress; and (b) develop multi-scale mechanical models quantifying deformation-induced optical signal drift, enabling rational anti-interference design.
- (6)
- Frontier biomedical applications: Engineer a theranostic probe by merging the detection function of this sensor with photodynamic therapy (PDT) or photothermal therapy (PTT) capabilities, enabling concurrent diagnosis and treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F.; methodology, W.X. and Z.M.; validation, Q.T., Y.C., Q.J. and L.F.; formal analysis, Q.T., Y.C. and Q.J.; resources, L.F.; data curation, W.X. and Z.M.; writing—original draft preparation, W.X., Z.M., Q.T., Y.C., Q.J. and L.F.; writing—review and editing, L.F.; supervision, L.F.; project administration, L.F.; funding acquisition, L.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support to complete this study was provided by the Shandong Excellent Youth Science Foundation Program (No. 2023HWYQ-100), the Guangxi Science and Technology Program (No. Guike AA23026007), and the Taishan Scholars Program. The findings and opinions expressed in this paper are those of the authors only and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data will be made available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
References
- Hussain, K.; Lone, S.M.; Masoodi, K.Z.; Balkhi, S.M. Chapter 6-pH (negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration). In Techniques for Biochemical Analysis; Hussain, K., Lone, S.M., Masoodi, K.Z., Balkhi, S.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, M.; Lyana, S.; Ramli, N.; Zolkefli, N.; Mustapha, N.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Maeda, T. Survivability of Alcaligenaceae and Chromatiaceae as palm oil mill effluent pollution bioindicators under fluctuations of temperature, pH and total suspended solid. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 132, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarazona, J.V. Pollution, water. In Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 4th ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2024; pp. 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Ren, W.X.; Li, K.; Seo, J.; Sharma, A.; Yu, X.; Kim, J.S. Fluorescent bioimaging of pH: From design to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2076–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, L.; Aodeng, G.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. Research progress of organic small probes sensitive to tumor microenvironment. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1322, 140617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, A.; Won, M.; Kim, S.; Verwilst, P.; Maiti, M.; Yang, Z.; Qu, J.; Bhuniya, S.; Kim, J.S. A two-photon fluorescent probe records the intracellular pH through ‘OR’ logic operation via internal calibration. Sens. Actuators B. Chem. 2018, 268, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Xu, F.; Yu, J. Natural anthocyanin-based wearable colorimetric pH indicator with high color fastness. Dye. Pigment. 2025, 239, 112789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Li, G.; Shen, J.; Dai, R.; Li, X.; Liu, Z.; Jia, F. A CRISPR/Cas12a biosensor for portable and accessible detection of Salmonella typhimurium via multi-indicator pH millidisc colorimetry and smartphone imaging platform. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 286, 117611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscusi, G.; Lamberti, E.; Angilè, F.; Di Stasio, L.; Gerardi, C.; Giovinazzo, G.; Vigliotta, G.; Gorrasi, G. Smart pH-sensitive indicators based on rice starch/pectin/alginate loading Lambrusco pomace extract and curcumin to track the freshness of pink shrimps. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 291, 139085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, M.; Ahmadi, E.; Mohamadnia, Z. Stimuli-responsive fluorescent polymer nanoparticles: Versatile applications in rapid colorimetric and fluorometric detection of cyanide in blood plasma, pH sensing, paper-based sensors, and intelligent artworks. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2024, 452, 115552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wockenfus, A.M.; Koch, C.D.; Conlon, P.M.; Sorensen, L.D.; Cambern, K.L.; Chihak, A.J.; Zmolek, J.A.; Petersen, A.E.; Burns, B.E.; Lieske, J.C.; et al. Discordance between urine pH measured by dipstick and pH meter: Implications for methotrexate administration protocols. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 152–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantray, J.A.; Mansoor, S.; Wani, R.F.C.; Nissa, N.U. Chapter 3-pH meter: Its use and calibration. In Basic Life Science Methods; Tantray, J.A., Mansoor, S., Wani, R.F.C., Nissa, N.U., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsahi, A.; Ahmadi-hamedani, M.; Khodadi, M. Comparative evaluation of urinary dipstick and pH-meter for cattle urine pH measurement. Heliyon 2020, 6, 03316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, X.-H. Focusing on the process diagnosis of anaerobic fermentation by a novel sensor system combining microbial fuel cell, gas flow meter and pH meter. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 13658–13664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, H.; Asaka, T.; Iwami, K.; Umeda, N.; Yamamoto, C.; Hara, Y.; Masuda, A. Non-Destructive Measurement of Acetic Acid and Its Distribution in a Photovoltaic Module during Damp Heat Testing Using pH-Sensitive Fluorescent Dye Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriksunov, L.B.; Macdonald, D.D. Development of glass pH sensors for use at temperatures of 200–250 °C. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 22, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Chou, J. Preparation and characteristics of ruthenium dioxide for pH array sensors with real-time measurement system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 128, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, K.G.; Tarlov, M.J.; Cline, J.P. Sputtered thin-film pH electrodes of platinum, palladium, ruthenium, and iridium oxides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1995, 28, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yao, S.; Madou, M. A long-term stable iridium oxide pH electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2002, 81, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Cao, H.; Deb, S.; Chiao, M.; Chiao, J.C. A flexible pH sensor based on the iridium oxide sensing film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 169, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Hu, R.; Huang, R.; Lin, C. In Situ Measurement of Cl− Concentrations and pH at the Reinforcing Steel/Concrete Interface by Combination Sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Kazemzadeh, A. Optical pH Sensor Based On Chemical Modification of Polymer Film. Microchem. J. 1999, 63, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbar, A.; Kumar, R.; Dhawan, V.; Ranjan, N.; Sharma, A. Additive Manufacturing of Polymers for Tissue Engineering: Fundamentals, Applications, and Future Advancements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Schäferling, M.; Ondrus, V. The Art of Fluorescence Imaging with Chemical Sensors: The Next Decade 2012–2022. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.R.; Modi, C.D.; Singh, S.; Mori, D.D.; Soniwala, M.M.; Prajapati, B.G. Recent Advances in Additive Manufacturing of Polycaprolactone-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Regen. Eng. Transl. Med. 2024, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäferling, M. The Art of Fluorescence Imaging with Chemical Sensors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3532–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Bao, Y. Review of fiber optic sensors for corrosion monitoring in reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 120, 104029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, R.; Liu, Z.; Pereira, L.; Yang, C.; Sui, Q.; Marques, C. Optical fiber sensing for marine environment and marine structural health monitoring: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 140, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinlou, R.; Dargahi, M.; Vanashi, A.K. Alkaline range pH sensor based on chitosan hydrogel: A novel approach to pH sensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, W.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shi, L.; Zhang, C.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Polarity, pH and HClO triple-response fluorescent probe and its application in inflammation models. J. Mol. Liq. 2025, 422, 126953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, L.; Wang, C.; Zeng, J.; Xu, Y.; Xie, W.; Lu, X. Sulfonium perchlorate based near-infrared fluorescent probe targeting lysosome for pH imaging in living cells and tumor-bearing mice. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 329, 125558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Y.; Liu, Y.T.; Yao, S.Y.; Zhao, K.Y.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zou, Y.L.; Zhao, L.X. A multifunctional near-infrared fluorescent probe with a large Stokes shift for monitoring of Al3+ and pH in biological vivo and its smartphone application. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeur, B.; Leray, I. Design principles of fluorescent molecular sensors for cation recognition. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2000, 205, 3–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xiao, J.; Tang, D.; Zhou, L.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Z. Visualizing and tracking pH fluctuation in living systems and real food samples with a novel dual-site modulated reversible ratiometric fluorescent probe. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1331, 141647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Shen, Z.; Meng, Z.; Gong, S.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. A novel carbazole-pyrimidine-based dual mode fluorescent probe for detection of acidic and basic pH in biological systems. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 330, 125709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalupczok, S.; Kurzweil, P.; Hartmann, H.; Schell, C. The Redox Chemistry of Ruthenium Dioxide: A Cyclic Voltammetry Study—Review and Revision. Int. J. Electrochem. 2018, 2018, 1273768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, L.T.; Yusuff, A.S.; Aderibigbe, T.A. Assessment of natural groundwater physico-chemical properties in major industrial and residential locations of Lagos metropolis. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johan, P.D.; Ahmed, O.H.; Omar, L.; Hasbullah, N.A. Phosphorus Transformation in Soils Following Co-Application of Charcoal and Wood Ash. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.A.; Chimenti, M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.F.; Ahmed, O.H.; Omar, L.; Jalloh, M.B.; Kwan, Y.M.; Musah, A.A.; Chowdhury, A.J.K. Improving pH buffering capacity of an acid soil to regulate nutrient retention and mitigate water pollution using Calciprill and sodium silicate. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 319, 100491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, R.; Nwangburuka, C.; Oboirien, B. Origins, roles and fate of organic acids in soils: A review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 108, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, M.Z.; Xin, L.M.; Fei, Z.; Fa, W.S.; Long, W.Z.; Qin, Y.Y. Pyrimidin-2-amine derivative-grafted cellulose ratiometric fluorescent probe for pH detection in extremely acidic media. Cellulose 2021, 28, 10441–10455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Bi, F.-Z.; Miao, J.-Y.; Zhao, B.-X. A new fluorescent pH probe for extremely acidic conditions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 820, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T.; Ran, X.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, H.; Shu, W. A new fluorescent probe for detection of hydrazine and extremely acidic pH in different modes. Tetrahedron 2024, 159, 134007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Chen, S.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Ma, H. Lysosomal pH Rise during Heat Shock Monitored by a Lysosome-Targeting Near-Infrared Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10916–10920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Methanol poisoning with bilateral basal ganglia necrosis and hemorrhage without visual impairment: A case report. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2025, 93, e235–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangjou, A.; Moqadas, M.; Mohsenian, L.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Alshehery, S.; Ali, M.A.; Dehbozorgi, F.; Yadav, K.K.; Khorami, M.; et al. Awareness raising and dealing with methanol poisoning based on effective strategies. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Z. A pH-responsive NIR fluorescent probe for precise cancer phototheranostics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 440, 137877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwada, A.; Taoka, N.; Chijimi, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Shigematsu, K.; Miura, M.; Suzuki, T. Weakly acidic pH-responsive liposomal content release induced by histidine-modified agents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, L.; An, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jin, L.; Ai, T.; Dai, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Yang, X.-F. Learning from drugs: An edaravone-inspired design of a coumarin-based fluorescent probe for dual-channel imaging of hydroxyl radicals and pH in complex biosystems. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 441, 137946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Duan, R.; Liu, H.; Xia, C.; Duan, G.; Ge, Y. Preparation of a novel pH-responsive fluorescent probe based on an imidazo [1,2-a]indole fluorophore and its application in detecting extremely low pH in saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Meng, Z.; Gong, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. Development of a novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for real-time monitoring of acidic pH and its applications in food samples and biosystem. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 111169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Li, Z.; Zhai, P.; Ying, M.; Xu, Z.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Dong, B.; Yong, K.-T.; Xu, G. In-situ construction of fluorescent probes for lysosomes imaging and lysosomal pH ratiometric detection based on bioorthogonal fluorescence. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Liu, A.; Xu, Y.; Xu, D. Synthesis and properties of three novel rhodamine-based fluorescent sensors for Hg2+. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, L. A new fluorescent probe based on metallic deep eutectic solvent for visual detection of nitrite and pH in food and water environment. Food Chem. 2023, 398, 133935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, A.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, A.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Colorimetric/spectral dual-mode analysis of sensitive fluorescent probe based on 2,3,3-trimethyl-3H-benzo[e]indole detection of acid pH. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 124, 105792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaghaghazardi, M.; Kashanian, S.; Nazari, M.; Omidfar, K.; Joseph, Y.; Rahimi, P. Nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon quantum dots fluorescence quenching assay for detection of mercury (II). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 293, 122448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimer, C.; Yu, S.; Ghandehari, M. Probing pH Levels in Civil Engineering Materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2009, 21, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.H.; François, R. Influence of long-term corrosion in chloride environment on mechanical behaviour of RC beam. Eng. Struct. 2013, 48, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Baydoun, J.; Remy, C.; Ghasemi, R.; Lefevre, J.P.; Mongin, C.; Dauzères, A.; Leray, I. Fluorescent molecular probe based optical fiber sensor dedicated to pH measurement of concrete. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Ghasemi, R.; Lefevre, J.P.; Mongin, C.; Dauzères, A.; Leray, I. Ratiometric fiber optic fluorescent pH sensor for hydroxide diffusion measurements in concrete. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 405, 135297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Fan, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, J. Development of optical fiber sensors for high-alkaline pH monitoring based on silica fluorescent nanoparticles. Measurement 2025, 253, 117803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Qian, C.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. A novel ratiometric fluorescent sensor from modified coumarin-grafted cellulose for precise pH detection in strongly alkaline conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 130066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flinck, M.; Kramer, S.H.; Pedersen, S.F. Roles of pH in control of cell proliferation. Acta Physiol. 2018, 223, 13068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, H. Mitochondria-immobilized near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent pH probe to evaluate cellular mitophagy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11409–11416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Zhai, S.; Wei, B.; Zhao, B.; Lin, Z. A ratiometric fluorescent probe based on FRET mechanism for pH and its cell imaging. Dye. Pigment. 2025, 233, 112544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Xie, Z.; Hu, J. pH-Activated NIR fluorescent probe for sensitive mitochondrial viscosity detection. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2025, 23, 3314–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Y. Synthesis and Optical Properties of 1,3-Bis(Arylimino) isoindoline-4,7-diols. Tetrahedron 2023, 144, 133546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, B.; Liu, F.; Miao, J.; Zhao, B.; Lin, Z. A quinoline-salt-based fluorescent probe for precise monitoring of pH changes on mitochondria and water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 373, 132732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tian, X.; Gong, S.; Meng, Z.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. A novel coumarin-derived fluorescent probe for real-time detection of pH in living zebrafish and actual food samples. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1299, 137141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. A naphthalimide-based bifunctional fluorescent probe for detecting CN− and alkaline pH and its application in food samples and living cells imaging. Microchem. J. 2024, 206, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Gong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. A myrtenal-based colorimetric and fluorescent probe for reversibly monitoring alkaline pH and bioimaging in living cells and zebrafish. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 430, 113962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawa, T.; Hazra, A.; Barma, A.; Pal, K.; Karmakar, P.; Roy, P. 4-Methyl-2,6-diformylphenol based biocompatible chemosensors for pH: Discrimination between normal cells and cancer cells. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15501–15513. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Lang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Bai, R.; Zhang, S.; Xi, J.; Han, C.; Zhang, X. A novel aggregation-induced emission fluorescent probe for sensitive detection of pH changes in seafood freshness monitoring. Tetrahedron 2025, 181, 134700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; Ai, Y.; Liang, Q. A dual-response fluorescent probe Rh-O-QL for simultaneous monitoring of NAD(P)H and pH during mitochondrial autophagy. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 7799–7802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhao, H.; Peng, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, M.; Cui, Y.; Sun, G. A novel phenanthroline [9,10-d] imidazole-based fluorescent sensor for Hg2+ with “turn-on” fluorescence response. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 439, 114604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Sun, L.; Ma, X.; Qiao, H.; Sun, S.; Yang, J.; Chai, X.; Wu, Z.; et al. The development of logic gate-based fluorescent probes that respond to intracellular hydrogen peroxide and pH in tandem. Talanta 2024, 270, 125526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Dong, P.; Sun, S.; Zhai, S.; Zhao, B.; Lin, Z. A near-infrared fluorescent probe for simultaneous detection of pH and viscosity. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 318, 124486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, H.; Gu, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, K. A tri-response colorimetric-fluorescent probe for pH and lysosomal imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 370, 132425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yao, S.; Zhao, K.; Cui, H.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Zou, Y.; Zhao, L. A novel dual-responsive NIR fluorescent probe based on isophorone: Real-time detection of Al3+ in vivo and colorimetric sensing of pH through smartphone. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).