Predicting Adsorption Performance Based on the Properties of Activated Carbon: A Case Study of Shenqi Fuzheng System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Adsorption Method
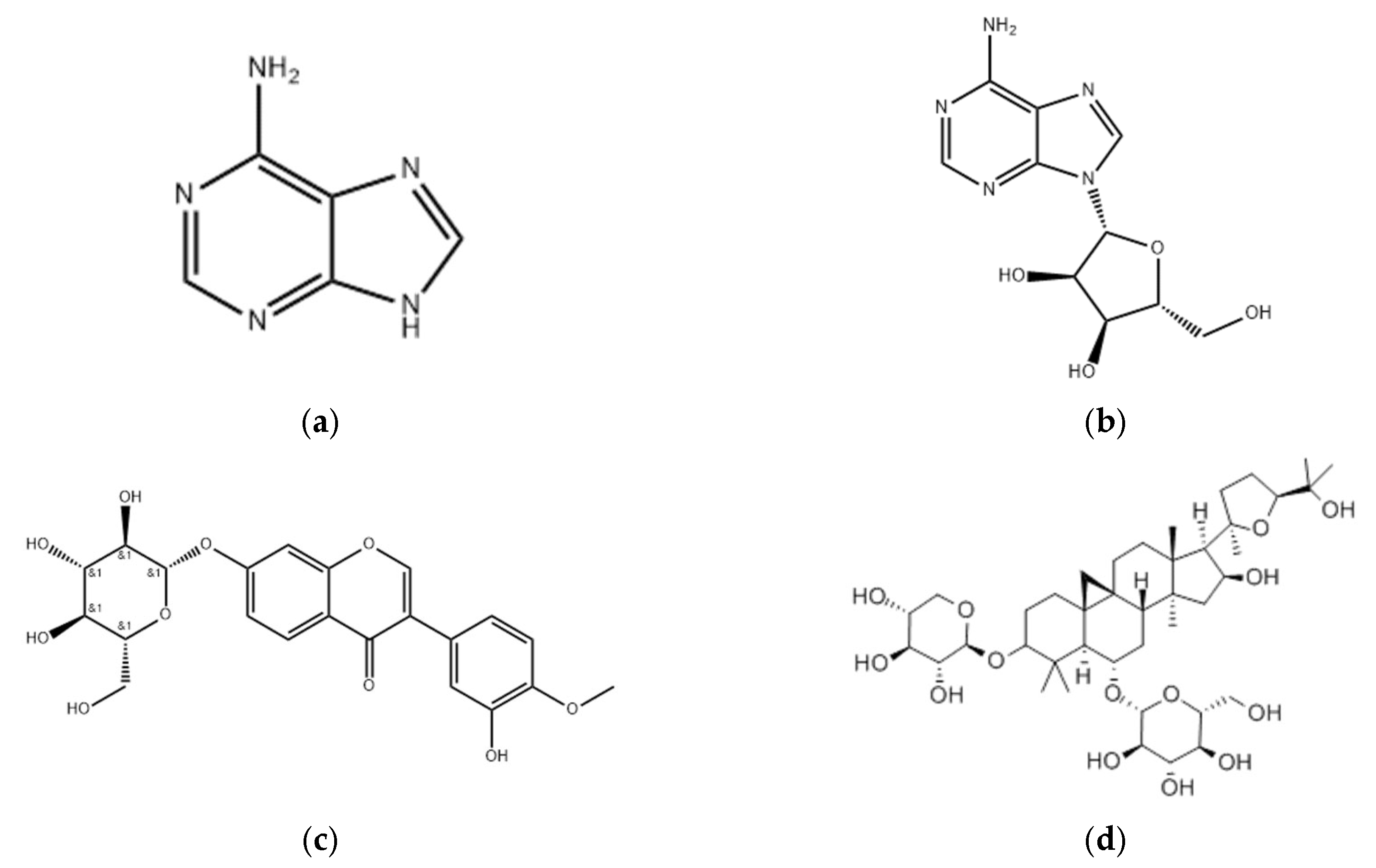
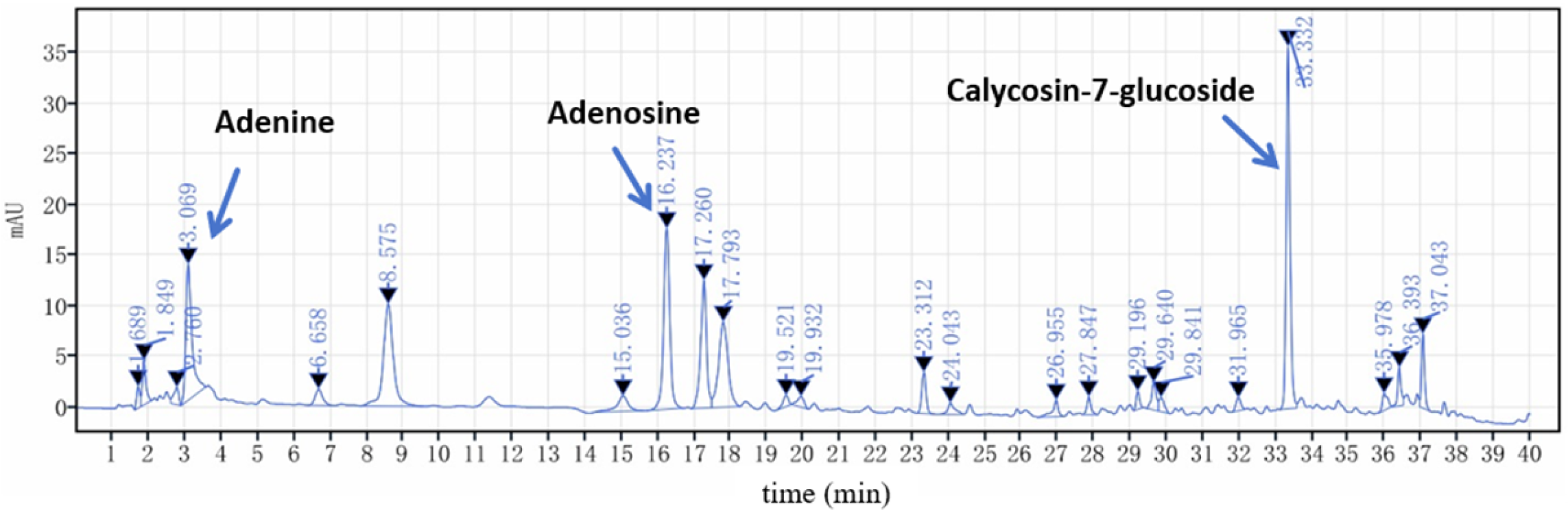
2.2.2. Determination of the Contents of Adenine, Adenosine, and Calycosin-7-glucoside by HPLC
Preparation of Reference Solution
Preparation of Test Solution
Chromatography Conditions
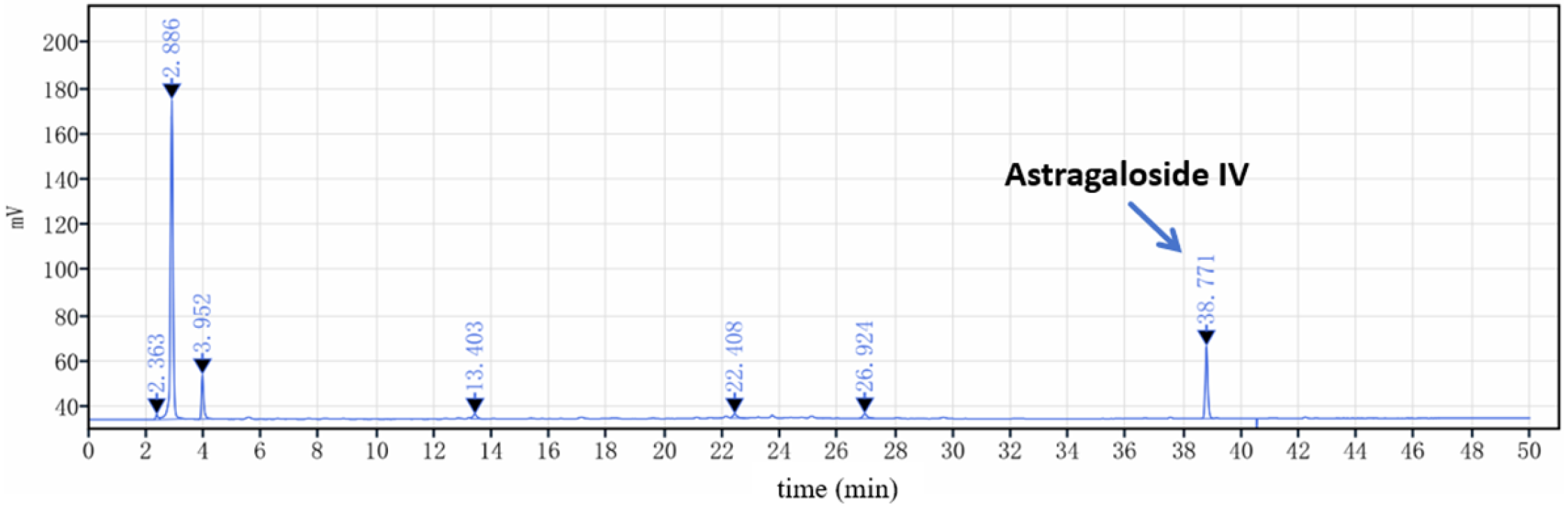
2.2.3. Determination of the Content of Astragaloside IV by HPLC
Preparation of Reference Solution
Preparation of Test Solution
Chromatography Conditions
2.2.4. Characterization of Specific Surface Area and Pore Volume
2.2.5. FTIR Characterization
2.2.6. XPS Characterization
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Determination of Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity
2.3.2. Linear Regression Modeling
2.3.3. Modeling Validation
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Activated Carbon Characterization Methods
3.1.1. Equilibrium Adsorption Capacity of Batches A1–A5
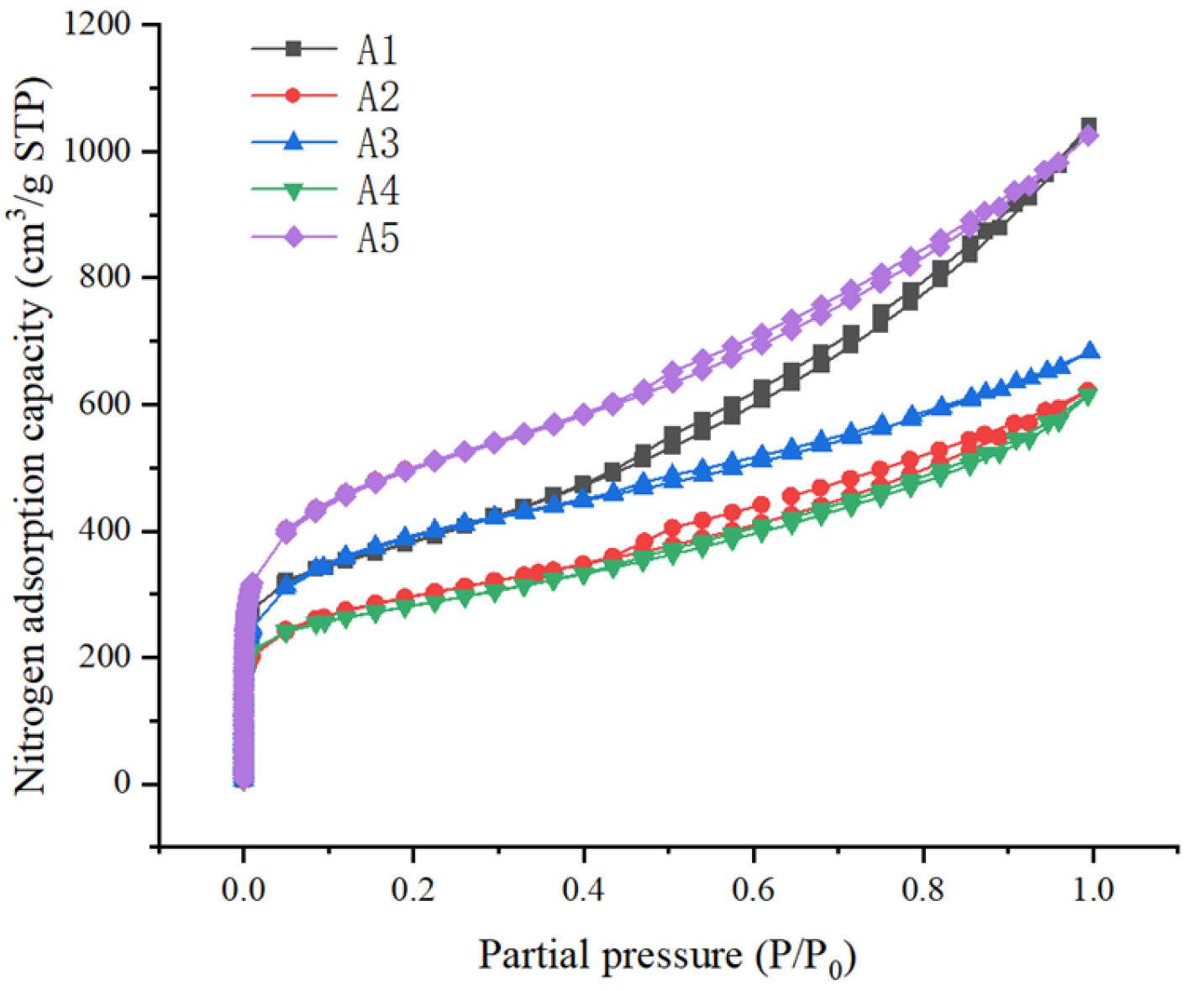
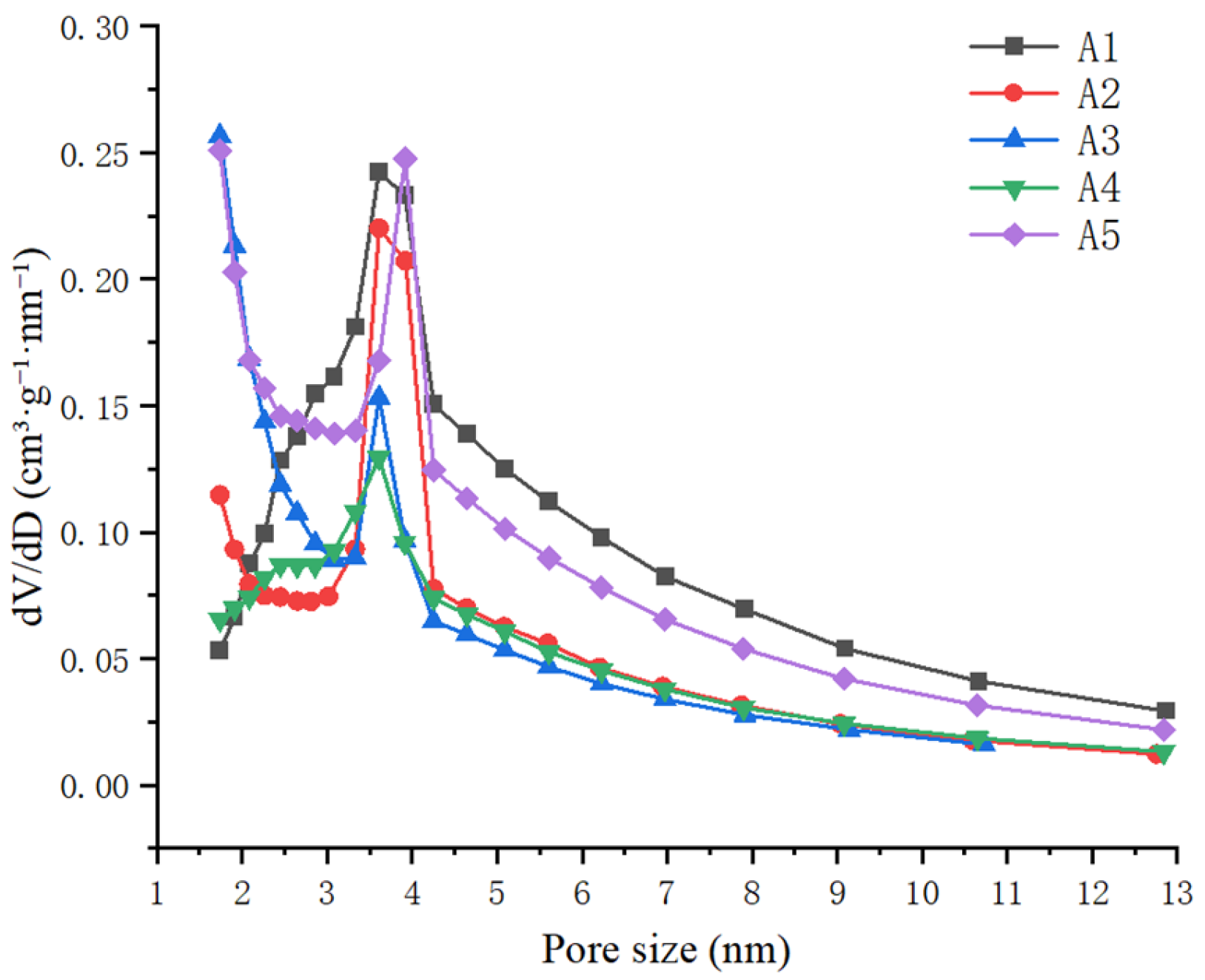
3.1.2. Results of Specific Surface Area and Pore Volume Characterization
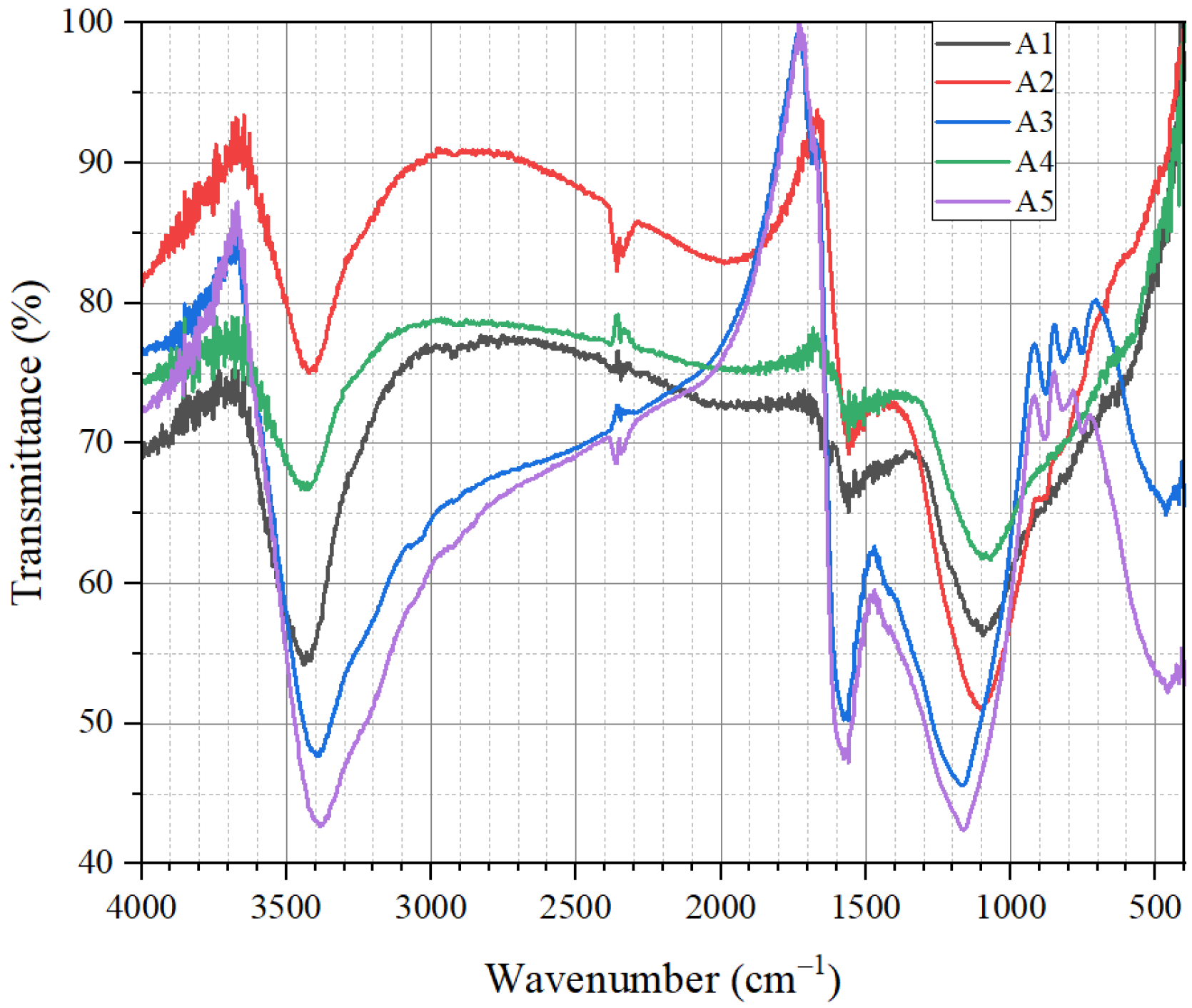
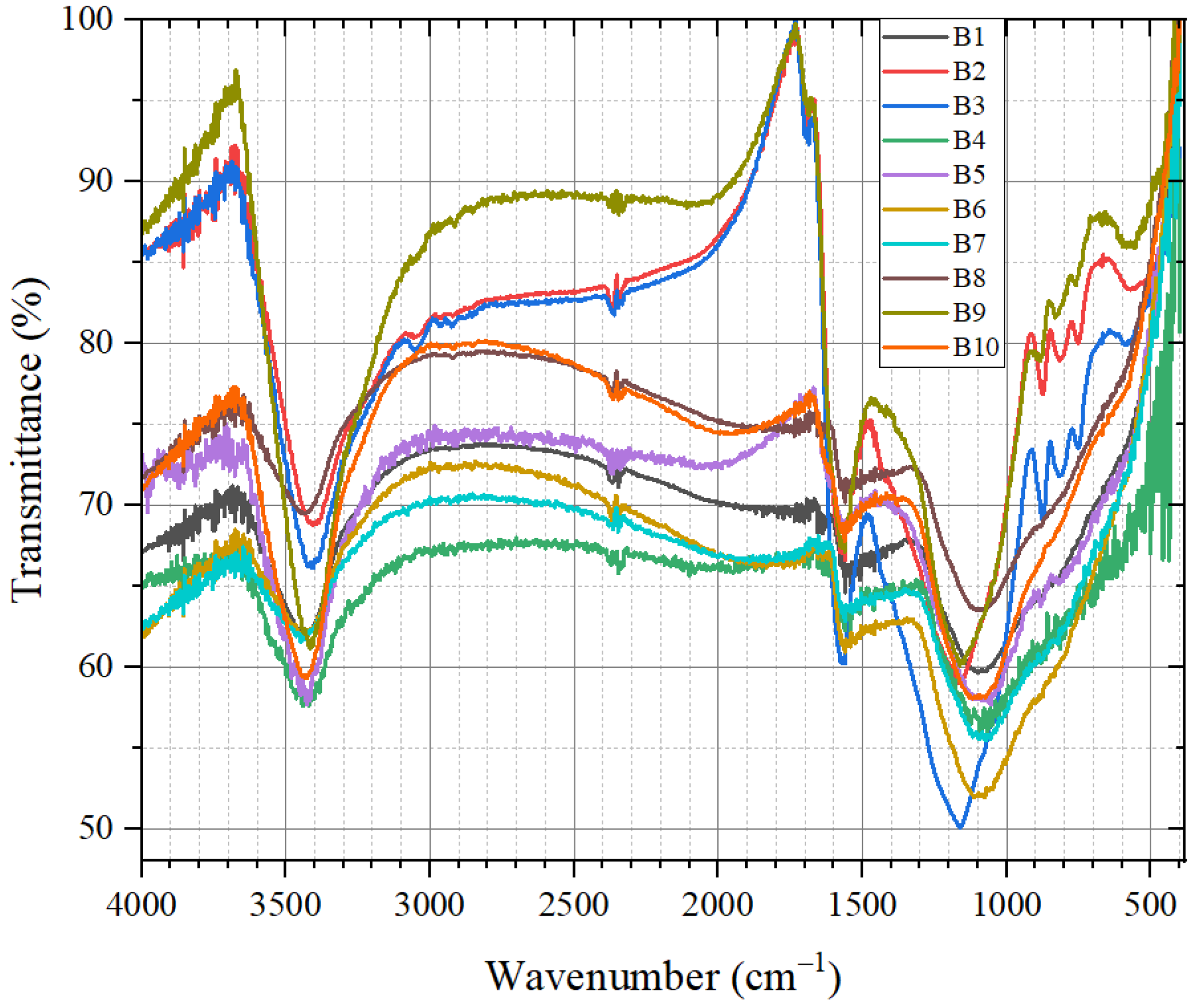
3.1.3. Results of Mid-Infrared Spectrum Characterization
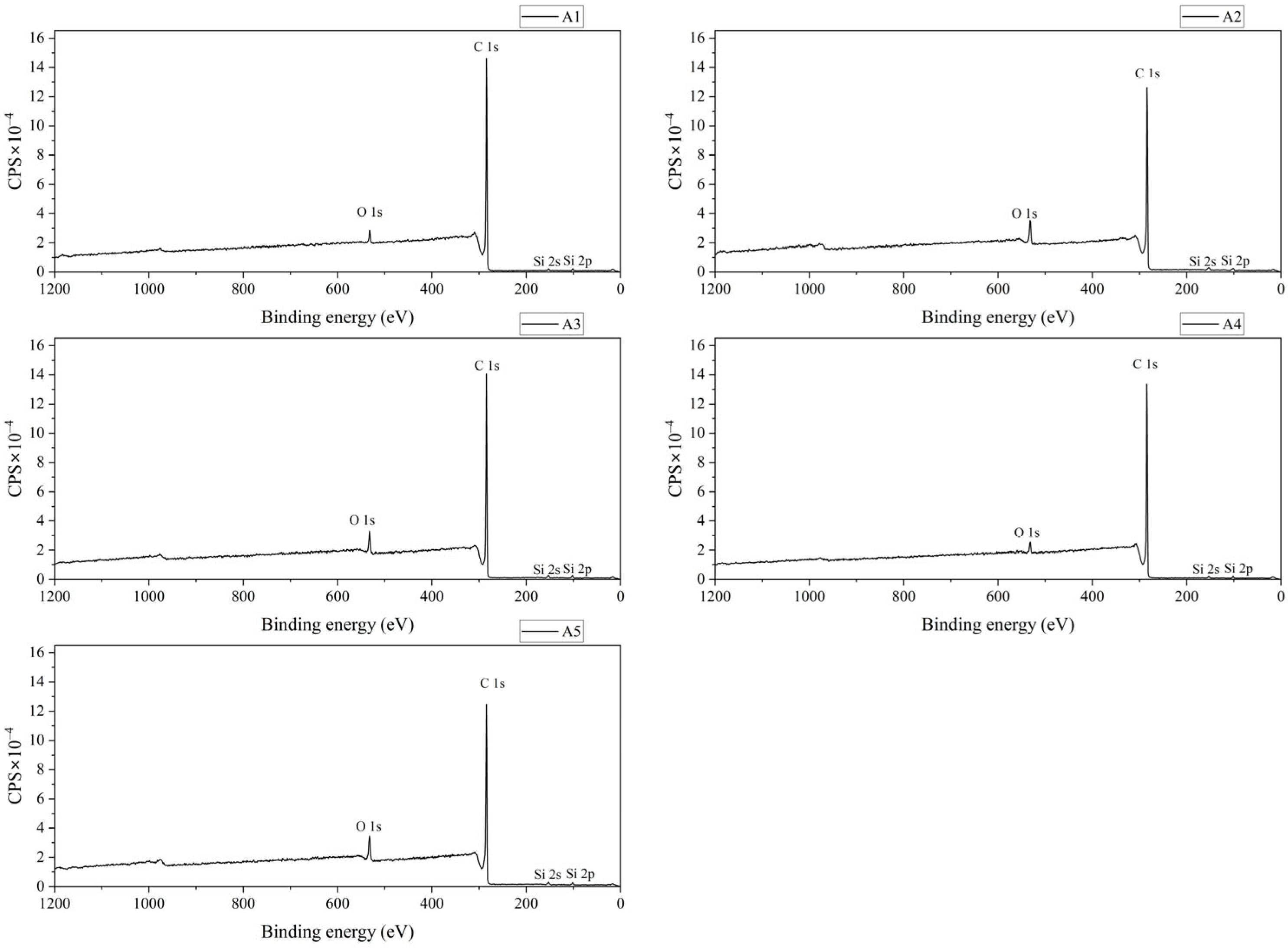
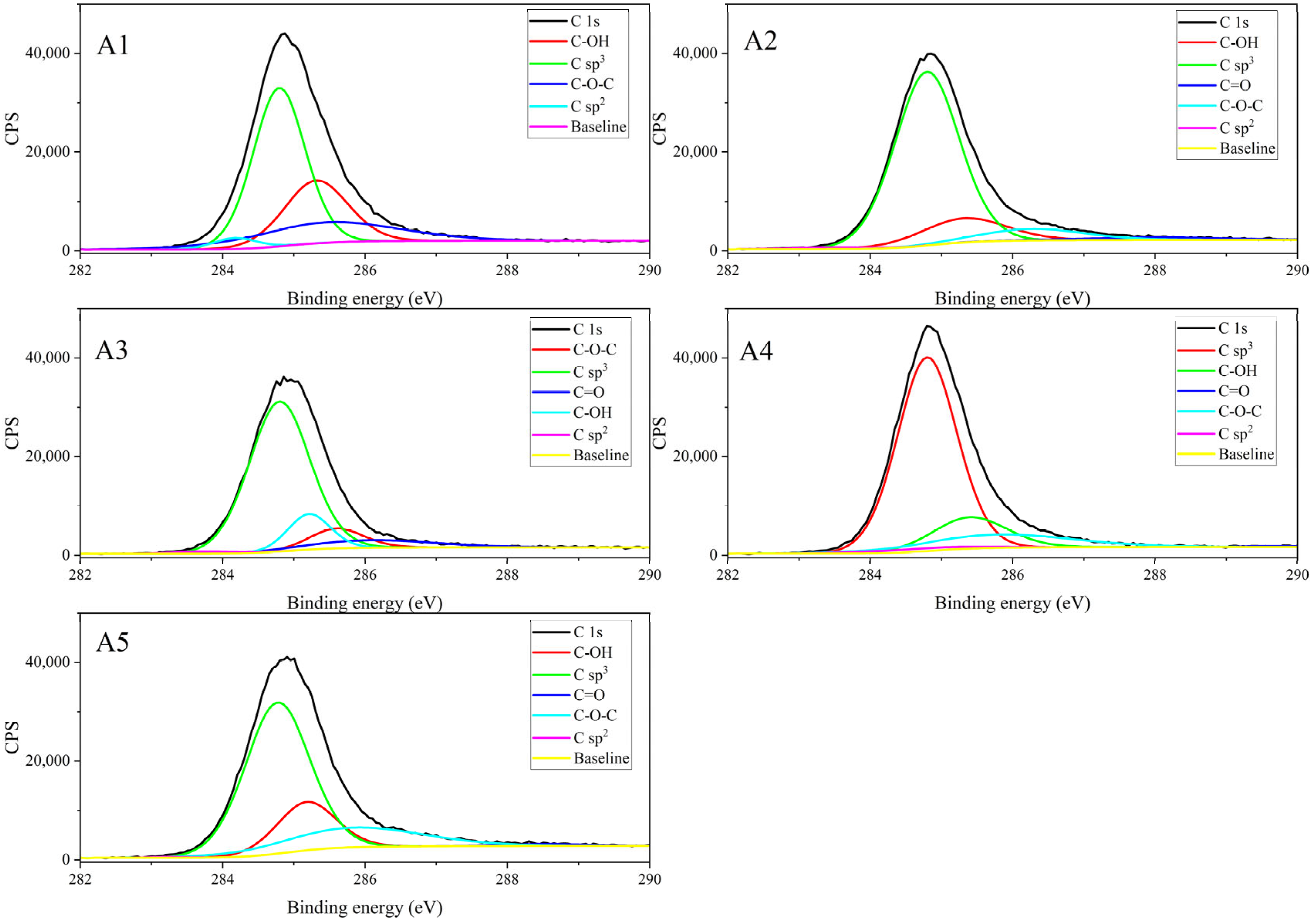
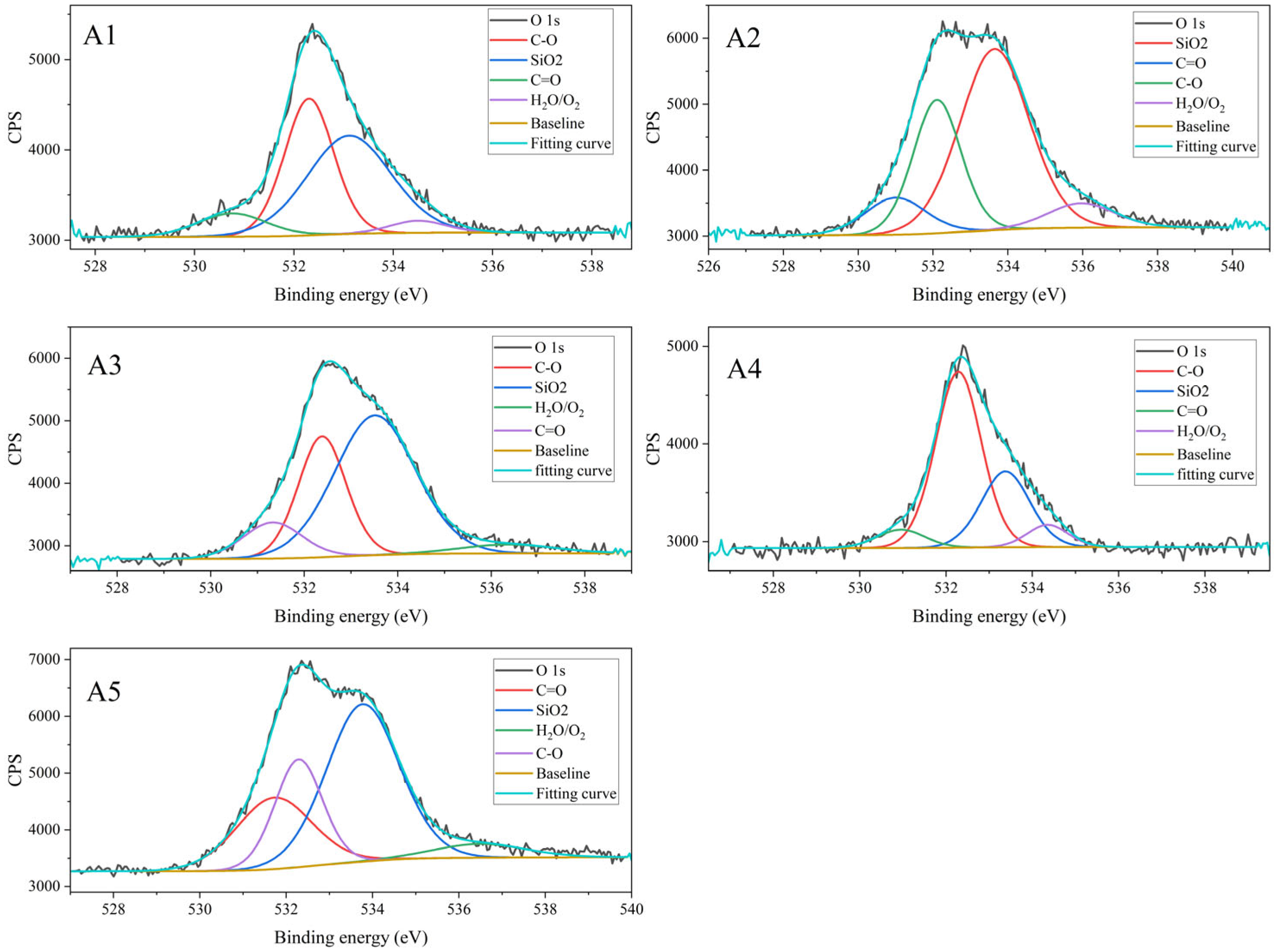
3.1.4. Results of XPS Characterization
3.1.5. Comparison of Characterization Methods
3.2. Mid-Infrared Spectrum Modeling
3.3. Modeling Validation
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Adsorption Mechanism
4.2. Methodological Value
4.3. The Shortcomings
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectrum |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| DSE | Diluted Shenqi Extract |
| BET | Brunauer–Emmett–Teller |
| BJH | Barrett–Joyner–Halenda |
| RSD | relative standard deviation |
References
- State Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; National Medical Products Administration: Beijing, China, 2025; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Tan, Q.; He, L.; Mao, Y.; He, J. Study on decolorization process of Compound Huanglian Injection. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2013, 44, 2386–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.J.; Sun, Y.; Liang, J.; Li, M.Q.; Li, X.L. Decolorization affects the structural characteristics and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Thesium chinense Turcz: Comparison of activated carbon and hydrogen peroxide decolorization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Xiao, W.; Sun, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, W. Impurity removal technology of Qihong Maitong Injection mixing liquid. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2013, 44, 696–700. [Google Scholar]
- Selenius, M.; Ruokolainen, J.; Riikonen, J.; Rantanen, J.; Nakki, S.; Lehto, V.P.; Hyttinen, M. Removing siloxanes and hydrogen sulfide from landfill gases with biochar and activated carbon filters. Waste Manag. 2023, 167, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Chen, X.; Ding, Y. Study on the capacity of adsorption of bacterial endotoxin in liquid by activated charcoal (for injection). Shanghai Med. Pharm. J. 2018, 39, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Z. Effect of Activated Carbon on the Bacterial Endotoxin Content of Dextran 40 API. Fine Chem. Intermed. 2024, 54, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Tang, S.W.; Xu, Y.Y.; Liu, F.M.; Li, M.M.; Zhi, X.L.; Ma, Y. Ultrasonic-assisted activated carbon separation removing bacterial endotoxin from salvia miltiorrhizae injection. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 103, 106781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, X.; Lü, S. Discussion on the correlation between sensitization of traditional Chinese medicine injections and production technology. Inf. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2012, 29, 52–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Shi, D.; Xue, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Prevention and treatment of pyrogens in the production of traditional Chinese medicine injections. Mod. Chin. Med. 2006, 8, 31–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Discussion on the generation and treatment of pyrogens in the production of traditional Chinese medicine injections. Heilongjiang Med. J. 2011, 24, 568–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, M. Potential risk analysis of application of activated charcoal in injection manufacture. Chin. J. New Drugs 2019, 28, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bläker, C.; Muthmann, J.; Pasel, C.; Bathen, D. Characterization of Activated Carbon Adsorbents—State of the Art and Novel Approaches. Chembioeng Rev. 2019, 6, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 12496.12-1999; Test Method for Wood Activated Carbon—Determination of Phenol Adsorption Value. Institute of Chemical Industry of Forest Products: Nanjing, China, 1999.
- GB/T 12496.10-1999; Test Method for Wood Activated Carbon—Determination of Methylene Blue Adsorption Value. Institute of Chemical Industry of Forest Products: Nanjing, China, 1999.
- GB/T 12496.8-2015; Test Method for Wood Activated Carbon—Determination of Iodine Adsorption Value. Institute of Chemical Industry of Forest Products: Nanjing, China, 2015.
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-C.; Chiang, P.-C.; Huang, C.-P. Effects of pore structure and temperature on VOC adsorption on activated carbon. Carbon 2001, 39, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzvetkov, G.; Mihaylova, S.; Stoitchkova, K.; Tzvetkov, P.; Spassov, T. Mechanochemical and chemical activation of lignocellulosic material to prepare powdered activated carbons for adsorption applications. Powder Technol. 2016, 299, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacañas, F.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. Adsorption of simple aromatic compounds on activated carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Tang, T.S.; Yu, W. Discussion on the Boehm titration method used in analysis of surface oxygen functional groups on activated carbon. Carbon Tech. 2011, 30, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanow, M.; Gärtner, T.; Sieber, V.; König, B. Activated carbon as catalyst support: Precursors, preparation, modification and characterization. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1188–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ou, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tang, Z.; Gong, X. The Effect of Activated Carbon Adsorption on Content of Four Indicative Constituents in Shenqi Fuzheng Diluent. Hans J. Med. Chem. 2024, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, W.; Gong, X.; Ye, T.; Qu, H.; Song, Y.; Hu, D.; Wang, G. Design space approach to optimize first ethanol precipitation process of Dangshen. Cshina J. Chin. Mater. Medica 2015, 40, 4411–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.F.; Yang, J.Y.; Cao, W.; Shao, J.Y.; Wang, G.X.; Qu, H.B.; Huang, W.H.; Gong, X.C. Critical process parameter identification of manufacturing processes of Astragali Radix extract with a weighted determination coefficient method. Chin. Herb. Med. 2020, 12, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Fan, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Ye, W. Chemical constituents of Shenqi Fuzheng Injection. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2011, 33, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C.; Ye, W. Chemical constituents of Shenqi Fuzheng Injection (II). Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2013, 35, 1494–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, S. Effective composition purification in Shenqi Fuzheng Prescription by different technologies. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2010, 32, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Ma, Y.; Bai, B.; Liu, D.; Zhou, Q. Identification of main ingredients of Shenqi Fuzheng Injection based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and its network pharmacology in treatment of triple negative breast cancer. Shanghai J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 58, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Batch No. | Manufacturers | Raw Material |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| A2 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| A3 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| A4 | Shanghai Xingchang Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir, some miscellaneous woods |
| A5 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| B1 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| B2 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| B3 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| B4 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| B5 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| B6 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| B7 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| B8 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| B9 | Shanghai Xingchang Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir, some miscellaneous woods |
| B10 | Shanghai Xingchang Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir, some miscellaneous woods |
| C1 | Shanghai Activated Carbon Plant Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir |
| C2 | Nanping Yuanli Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Nanping, China) | Sawdust of pine and Chinese fir |
| C3 | Shanghai Xingchang Activated Carbon Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) | Pine, Chinese fir, some miscellaneous woods |
| Ingredient | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | Average | Standard Deviation | RSD (%) | ANOVA p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calycosin-7-glucoside | 31.60 | 38.78 | 65.10 | 42.95 | 57.63 | 47.21 | 12.34 | 26.14 | <0.01 |
| Adenine | 17.85 | 17.07 | 9.280 | 16.63 | 11.05 | 14.38 | 3.505 | 24.38 | <0.01 |
| Adenosine | 18.23 | 24.87 | 28.64 | 19.97 | 30.85 | 24.51 | 4.847 | 19.78 | <0.01 |
| Astragaloside IV | 161.8 | 98.14 | 122.7 | 179.9 | 137.3 | 140.0 | 28.73 | 20.53 | <0.01 |
| Parameter | A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | Average | Standard Deviation | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBET (m2/g) | 1280 | 971.0 | 1278 | 916.0 | 1668 | 1223 | 269.2 | 22.01 |
| Total pore volume (cm3/g) | 1.613 | 0.9638 | 1.058 | 0.9537 | 1.589 | 1.236 | 0.3007 | 24.34 |
| Micropore porosity (cm3/g) | 0.1932 | 0.1738 | 0.2142 | 0.1921 | 0.2591 | 0.2065 | 0.02926 | 14.17 |
| Mesopore volume (cm3/g) | 1.279 | 0.7383 | 0.6914 | 0.7256 | 1.213 | 0.9294 | 0.2596 | 27.94 |
| Component | Atomic Relative Content (%) | Average | Standard Deviation | RSD (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | ||||
| O 1s | 2.42 | 5.8 | 5.09 | 2.32 | 6.15 | 4.36 | 1.66 | 38.05 |
| C 1s | 96.76 | 92.71 | 93.51 | 96.81 | 92.53 | 94.46 | 1.92 | 2.04 |
| Si 2p | 0.82 | 1.49 | 1.4 | 0.86 | 1.31 | 1.18 | 0.28 | 23.85 |
| Component | Relative Content (%) | Average | Standard Deviation | RSD (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | ||||
| C sp2/sp | 3.066 | 0.7829 | 1.289 | 1.986 | 0.2243 | 1.47 | 0.99 | 67.15 |
| C sp3 | 52.7 | 75.33 | 71.03 | 71.11 | 62.77 | 66.59 | 8.05 | 12.09 |
| C-OH | 25.46 | 13.69 | 11.81 | 14.22 | 18.32 | 16.70 | 4.87 | 29.15 |
| C-O-C | 18.78 | 7.98 | 8.364 | 12.36 | 17.69 | 13.03 | 4.53 | 34.74 |
| C=O | 0 | 2.213 | 7.51 | 0.3245 | 1.002 | 2.21 | 2.76 | 124.7 |
| Component | Relative Content (%) | Average | Standard Deviation | RSD (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | A4 | A5 | ||||
| C-O | 38.93 | 28.03 | 28.8 | 59.54 | 22.12 | 35.48 | 13.19 | 37.16 |
| C=O | 9.242 | 9.821 | 10.64 | 6.487 | 23.21 | 11.88 | 5.83 | 49.11 |
| SiO2 | 47.98 | 54.99 | 56.34 | 27.25 | 49.24 | 47.16 | 10.46 | 22.18 |
| H2O/O2 | 3.853 | 7.162 | 4.257 | 6.723 | 5.438 | 5.49 | 1.31 | 23.79 |
| Parameter | Calycosin-7-glucoside | Adenine | Adenosine | Astragaloside IV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 19.85 | 20.89 | 15.86 | 19.28 |
| B2 | 64.19 | 17.39 | 34.34 | 28.35 |
| B3 | 72.79 | 14.67 | 35.89 | 51.00 |
| B4 | 31.60 | 16.10 | 28.17 | 48.78 |
| B5 | 47.43 | 16.56 | 34.34 | 132.8 |
| B6 | 24.92 | 14.83 | 12.18 | 35.11 |
| B7 | 23.55 | 15.32 | 20.73 | 66.28 |
| B8 | 28.07 | 21.79 | 23.28 | 66.61 |
| B9 | 67.18 | 20.00 | 30.41 | 182.3 |
| B10 | 35.75 | 19.78 | 22.56 | 161.4 |
| Average | 41.53 | 17.73 | 25.78 | 79.20 |
| Standard deviation | 18.9 | 2.52 | 7.76 | 55.2 |
| RSD (%) | 45.5 | 14.2 | 30.1 | 69.7 |
| Items | Calycosin-7-glucoside | Adenine | Adenosine | Astragaloside IV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partial Regression Coefficient | p Value | Partial Regression Coefficient | p Value | Partial Regression Coefficient | p Value | Partial Regression Coefficient | p Value | |
| Constant | 26.15 | / | −11.91 | / | 0.86 | / | −41.52 | / |
| 1560 | / | / | 0.45 | <0.0001 | 0.47 | 0.0081 | / | / |
| 1560 + | −1.66 | <0.0001 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| 2325 + | / | / | / | / | −2.02 | <0.0001 | / | / |
| 3050 + | / | / | / | / | / | / | 8.72 | 0.0008 |
| 3442 + | / | / | / | / | / | / | −10.04 | <0.0001 |
| R2 | 0.8512 | 0.7600 | 0.8548 | 0.7677 | ||||
| Ingredient | Metrics | C1 | C2 | C3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calycosin-7-glucoside | Predicted value (mg/g) | 61.90 | 29.73 | 30.04 |
| Experimental values (mg/g) | 62.65 | 30.11 | 31.00 | |
| Relative error (%) | 1.19 | 1.28 | 3.09 | |
| Adenine | Predicted value (mg/g) | 20.07 | 16.90 | 20.46 |
| Experimental values (mg/g) | 22.10 | 16.56 | 20.17 | |
| Relative error (%) | 9.17 | 2.05 | 1.43 | |
| Adenosine | Predicted value (mg/g) | 31.20 | 17.63 | 24.90 |
| Experimental values (mg/g) | 31.63 | 17.20 | 25.25 | |
| Relative error (%) | 1.34 | 2.48 | 1.41 | |
| Astragaloside IV | Predicted value (mg/g) | 88.63 | 157.1 | 169.4 |
| Experimental values (mg/g) | 90.40 | 163.7 | 177.1 | |
| Relative error (%) | 1.96 | 4.02 | 4.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Z.; Chen, B.; Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Gong, X. Predicting Adsorption Performance Based on the Properties of Activated Carbon: A Case Study of Shenqi Fuzheng System. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080279
Tang Z, Chen B, Huang W, Liu X, Wang X, Gong X. Predicting Adsorption Performance Based on the Properties of Activated Carbon: A Case Study of Shenqi Fuzheng System. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(8):279. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080279
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Zhilong, Bo Chen, Wenhua Huang, Xuehua Liu, Xinyu Wang, and Xingchu Gong. 2025. "Predicting Adsorption Performance Based on the Properties of Activated Carbon: A Case Study of Shenqi Fuzheng System" Chemosensors 13, no. 8: 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080279
APA StyleTang, Z., Chen, B., Huang, W., Liu, X., Wang, X., & Gong, X. (2025). Predicting Adsorption Performance Based on the Properties of Activated Carbon: A Case Study of Shenqi Fuzheng System. Chemosensors, 13(8), 279. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13080279






