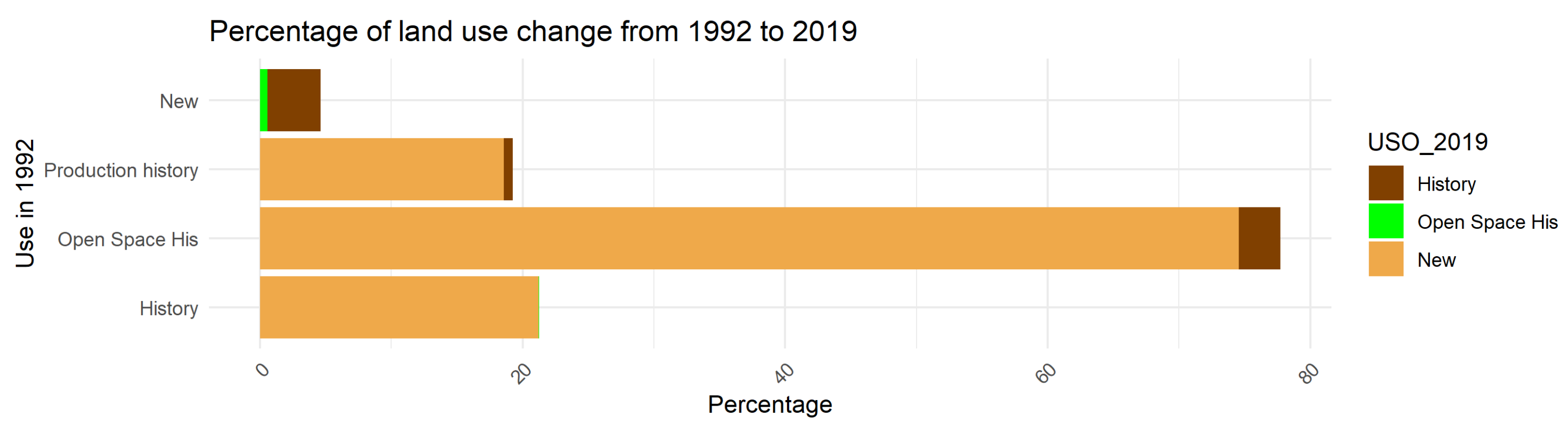Abstract
In line with UNESCO’s Historic Urban Landscape approach, this study highlights the need for integrative tools that connect heritage conservation with broader urban development dynamics, balancing preservation and growth. While several machine-learning models have been applied to analyse the drivers of urban change, there remains a need for comparative analyses that assess their strengths, limitations, and potential for combined applications tailored to specific contexts. This study aims to compare the predictive accuracy of three land-use change models (Random Forest, Logistic Regression, and Recursive Partitioning Regression Trees) in estimating the probability of land-use transitions, as well as their interpretative capacity to identify the main factors driving these changes. Using data from the Bellavista neighborhood in Tomé, Chile, the models were assessed through prediction and performance metrics, probability maps, and an analysis of key driving factors. The results underscore the potential of integrating predictive (Random Forest) and interpretative (Logistic Regression and Recursive Partitioning Regression Trees) approaches to support heritage planning. Specifically, the research demonstrates how these models can be effectively combined by leveraging their respective strengths: employing Random Forest for spatial simulations, Logistic Regression for identifying associative factors, and Recursive Partitioning Regression Trees for generating intuitive decision rules. Overall, the study shows that land-use change models constitute valuable tools for managing urban transformation in heritage urban areas of intermediate cities.
Keywords:
land use change; urban heritage; random forest; logistic regression; recursive partitioning regression trees; urban planning MSC:
91B72; 91
1. Introduction
Understanding urban transformation is a fundamental aspect of contemporary urban planning, given the interaction between physical changes in land use and the social, economic, and cultural dynamics that influence the identity of cities [1,2,3]. A deep understanding of these processes is essential for striking an appropriate balance between urban growth and the preservation of cultural identity [4,5]. In this context, the conservation of cultural heritage has become a significant challenge in areas with historical and industrial legacies, where pressures from urban development and real estate speculation threaten the loss of built heritage [6,7,8,9]. Heritage protection is part of the international commitments made by states, especially within the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with SDG 11 being the most notable, as it aims to promote inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable cities [10].
In this sense, those responsible for the conservation of historical heritage primarily rely on instruments such as protection, conservation, or development control zoning. These tools delineate areas of historical, landscape, or architectural value and impose restrictions on permitted uses [11]. They aim to balance the preservation of built heritage with the dynamics of urban transformation through incentives, regulations, and restrictions that guide land use [12]. However, their effectiveness depends on the institutional capacity to anticipate patterns of change and understand the factors influencing transformation [13,14].
Among the main risks to conservation are unplanned real estate expansion, pressure on areas of historical value, and morphological fragmentation of the urban fabric due to the opening of new road infrastructure or changes in permitted uses [15,16]. These processes are expressed spatially through changes in land use, which makes the analysis of these changes a tool for heritage planning [17]. In particular, planners require interpretable spatial evidence that allows them to prioritise driving factors associated with land transformation [18]. Recent studies have shown that heritage protection areas do not always guarantee morphological stability, as their impact depends on physical variables and the degree of regulatory compliance [19]. Notably, the opening of new roads is one of the most consistent drivers of change, increasing pressure on heritage environments and buffer zones [20,21].
To address these challenges, it is essential to have accessible and understandable tools for urban planners and decision-makers [4,5]. In recent years, various approaches have been developed to identify and quantify the drivers of urban transformation. These factors encompass biophysical, socioeconomic, institutional, and morphological dimensions, and their interactions shape both the magnitude and direction of territorial change processes. Additionally, quantitative methods have been incorporated to establish causal or associative relationships between explanatory variables and spatial transition patterns. Among these, traditional statistical approaches (such as logistic regression, principal component analysis, and geographically weighted regression) stand out for their ability to estimate the individual effects of each variable on territorial change [22,23]. Simultaneously, machine learning-based techniques, such as Random Forest, Support Vector Machines, and Neural Networks, have demonstrated high predictive performance in complex and nonlinear contexts [24,25].
However, most of these techniques have focused on urban expansion processes rather than changes within the existing urban heritage. Among the few that address intra-urban transformations, even fewer consider a detailed breakdown of land-use categories or the specific phenomena of change in historical urban contexts. Another limitation concerns the low interpretability of many machine learning models when compared with classical statistical methods. These problems restrict their efficiency in planning within urban heritage contexts, where understanding causal relationships at a detailed level and ensuring traceability of results are essential [26,27,28].
It is important to note that in this work, the term “interpretability” is used in the sense of intrinsic interpretability, understood as the model’s capacity to transparently show how the variables produce the result, without requiring external post-processing techniques [29,30]. From this perspective, our analysis compares logistic regression (), recursive partitioning (), and random forests () considering widely recognized criteria of structural interpretability—model transparency, variable-effect traceability, complexity, and communicability—thereby allowing for a rigorous evaluation of the degree of explainability inherent in each approach.
According to this definition, and are considered fully interpretable models: the former because they offer coefficients and marginal effects directly attributable to each predictor and the latter because they generate hierarchical partitioning rules that can be easily understood and communicated by a human analyst. In contrast, models are not considered intrinsically interpretable. However, the literature places them in an intermediate category between transparent and completely opaque models. Although their internal structure is difficult to inspect, they provide global measures of variable importance that allow for a partial understanding of their functioning [29,31,32,33].
The aim of this study is to address a persistent gap in the literature: the lack of methodological comparisons evaluating the interpretive utility of different models for tackling specific heritage planning and conservation problems. In historical urban contexts, where decisions must transparently justify why certain areas are more vulnerable to transformation than others, the interpretability of the model is as important as its accuracy. Therefore, this work not only compares the predictive capacity of three techniques (, , and ) but also critically examines how each translates territorial factors into actionable information for urban managers and conservationists. The purpose is to determine how the different forms of explanation offered by these models can support the identification of heritage risks, the evaluation of regulatory effectiveness, and the prioritization of interventions in historic urban environments.
The results show that urban transformation in heritage contexts follows complex and nonlinear spatial patterns, making models like particularly suitable for simulating scenarios and capturing highly complex interactions. In contrast, is the most appropriate model for identifying heritage risk zones, as it produces explicit rules and thresholds that are easily linked to zoning criteria. , for its part, is particularly useful for evaluating the effectiveness of regulatory instruments, as it allows for the quantification of the marginal effect of each variable and analyzes whether protected areas are fulfilling their intended purpose. Finally, the factor ranking provided by serves as a valuable tool for prioritizing interventions, clearly revealing which territorial elements most distinctly differentiate conservation and urban renewal processes.
The main contribution of this study is to provide distinct analytical tools that support heritage decision-making by linking spatial modeling with the specific needs of planners. In line with UNESCO’s Recommendation on Historic Urban Landscapes, the study prioritizes understanding the factors driving urban transformation, which facilitates the selection of the most appropriate model for each specific problem. This approach enables a more direct connection between analytical results and heritage management, optimizing risk identification, regulatory assessment, and intervention planning in historic urban environments.
The rest of the article is organized as follows: Section 2 characterizes the theoretical foundations of the models; Section 3 describes the proposed methodology; Section 4 presents the main findings, including the performance evaluation through cross-validation, the analysis of probability maps to examine spatial patterns, and the comparative interpretation of model outputs. This is followed by Section 5, which discusses the implications of the results, and Section 6, which summarizes the main conclusions and contributions of the study.
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Land Use Change Models
Land use change models are usually structured in two complementary phases: an explanatory phase, aimed at estimating the propensity for change based on factors, and a spatial simulation phase, which assigns these changes to the territory according to neighbourhood rules or spatial constraints [17,34]. The first phase generates continuous probability maps (0–1) that reflect the influence of driving factors [24,26,35]. The second phase seeks to reproduce spatial patterns based on probability maps and observed spatial dynamics [17,22,26].
This study focuses on the explanatory phase of modeling. To this end, we selected intrinsically interpretable models that can explicitly demonstrate how (and to what extent) each territorial variable contributes to both heritage conservation and transformation. In this approach, interpretability serves as a key analytical tool for heritage management and territorial planning. However, alongside its explanatory value, it is equally important to evaluate the predictive capacity of the models, as their accuracy in reproducing observed patterns supports the robustness and reliability of the conclusions regarding the driving factors.
The selected models fall within the explanatory phase of land-use change and offer complementary approaches for interpreting the factors driving territorial transformation. allows for the quantification of the direction and magnitude of each variable’s effect using coefficients and odds ratios, establishing itself as one of the most widely used methodologies for modeling territorial suitability in land-use change studies [35]. , for its part, incorporates measures of relative importance and captures nonlinear interactions between variables, making it possible to rank factors even in highly complex morphological and regulatory contexts [36]. Finally, generates hierarchical rules and critical thresholds that are easy to interpret, facilitating the communication of results and their translation into operational criteria for territorial management and planning [19,37].
In contrast, other approaches, such as CA-Markov, SLEUTH, or CLUE-S, were discarded because, although they effectively reproduce spatial patterns and prospective scenarios, they do not allow the change to be attributed to individual factors [17]. Similarly, artificial neural network (ANN) models are black boxes, whose interpretation depends on post hoc methods [38]. In this context, the models selected for their interpretability fulfil the study’s purpose of drawing useful conclusions for heritage conservation based on the factors that explain land use change.
2.1.1. Rpart Model
The Rpart (Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees) model is an implementation of the decision tree approach developed by [39] and has been widely used in classification and regression tasks involving spatial variables [40,41]. This technique performs a hierarchical partitioning of the dataset, segmenting it into internally homogeneous subgroups based on the values of the predictor variables [37]. Each partition generates a conditional rule of the form “if … then …”, which explicitly describes the combinations of variables under which land-use change occurs, thus providing a direct and easily transferable framework for land-use planning.
Its main strength lies in its high visual interpretability: the derived rules can be represented by tree diagrams that explicitly show the critical thresholds of the variables and the conditions under which land-use change occurs. Unlike linear models, it does not require assumptions of linearity or independence between predictors; however, it can produce excessively complex trees if an appropriate pruning process is not applied, which increases the risk of overfitting.
In the practice of heritage management, Rpart offers a significant communication advantage: it allows technical results to be translated into clear, understandable rules that planners can directly apply. For example, a rule such as “if the density exceeds 40 dwellings/ha and the distance to road axes is less than 200 m, the probability of development increases substantially” can be incorporated into planning instruments as criteria for defining buffer zones, development areas, or specific restrictions, facilitating their spatial representation and operational application on the ground.
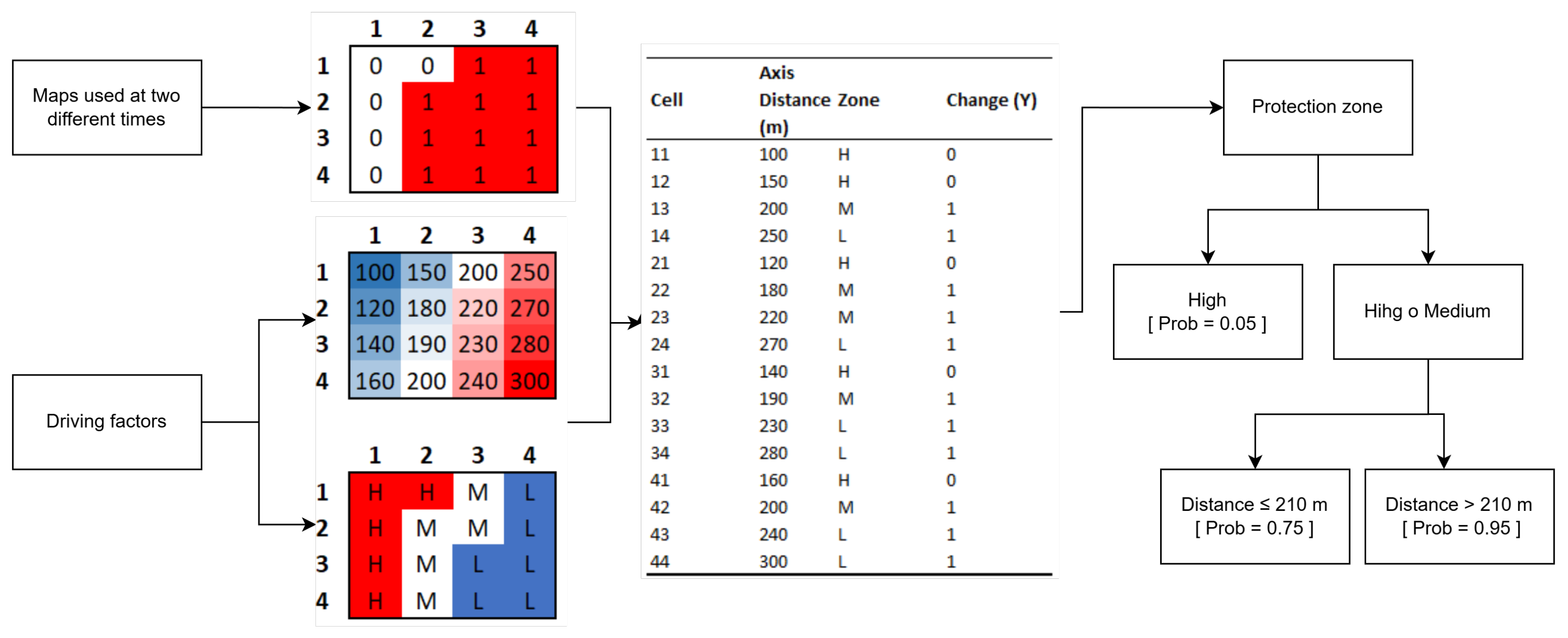
Figure 1 exemplifies the hierarchical classification logic of the Rpart model applied to a hypothetical case of a heritage neighborhood represented by a 4 × 4 grid. The left panel presents land-use change maps corresponding to two time periods, while the right panel displays the driving factors used as explanatory variables: the distance to the main road axis, which is numerical, and the heritage protection category (High, Medium, Low), which is qualitative. This configuration allows for the visualization of how the algorithm identifies thresholds and combinations of variables that structure the propensity for change in the study area.

Figure 1.
Diagram of the Rpart model applied to a hypothetical heritage neighborhood. The left panel shows land use changes in two periods, while the right panel presents the explanatory factors (distance to the main road and heritage protection category). The diagram illustrates how the algorithm defines thresholds and combinations of variables that explain the propensity for change in the study area.
The model identifies both variables and determines, firstly, that the heritage protection zone is the factor with the greatest discriminating power. This initial threshold separates areas with high protection, where the probability of change is very low (≈0.05), from those with medium or low protection, which have a substantially higher propensity for transformation. Within this second group, the distance to the main axis emerges as a critical threshold—set at 210 m—that allows for distinguishing between sectors of intermediate risk (≈0.75) and areas with high risk (≈0.95). This hierarchical structure explicitly summarizes how combinations of territorial factors modulate the probability of change, offering a transparent interpretation that is directly applicable to heritage planning and management processes.
2.1.2. Random Forest Model
Random Forest (RF) is a non-parametric machine learning model that assembles multiple decision trees constructed from random subsets of data and variables [31]. Each tree generates a partial prediction, and the final probability of change corresponds to the average of these predictions, thereby reducing variance and improving model stability.
The main strength of lies in its ability to capture non-linear relationships and complex interactions between territorial factors without requiring statistical assumptions about the distribution of variables [36]. Furthermore, it incorporates importance metrics that prioritize change drivers, making it particularly useful in multifactorial urban systems. However, the model can overfit if the number of trees or the maximum depth is not properly regulated; this risk can be mitigated through cross-validation procedures, ensuring adequate generalizability [42].
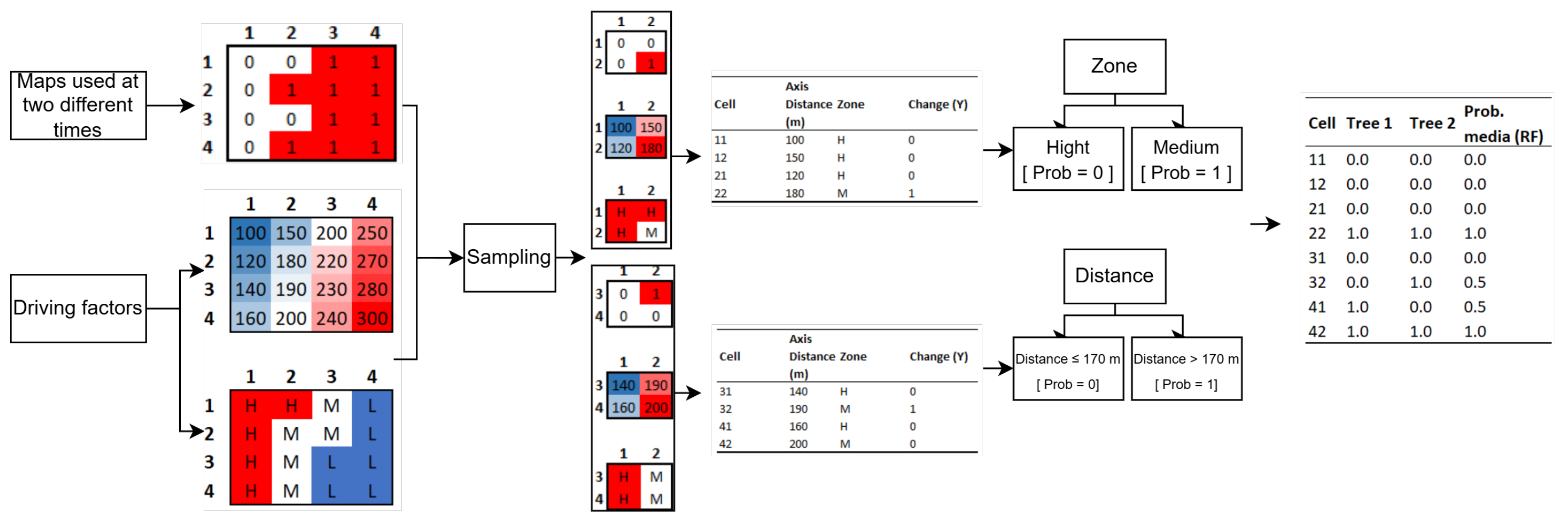
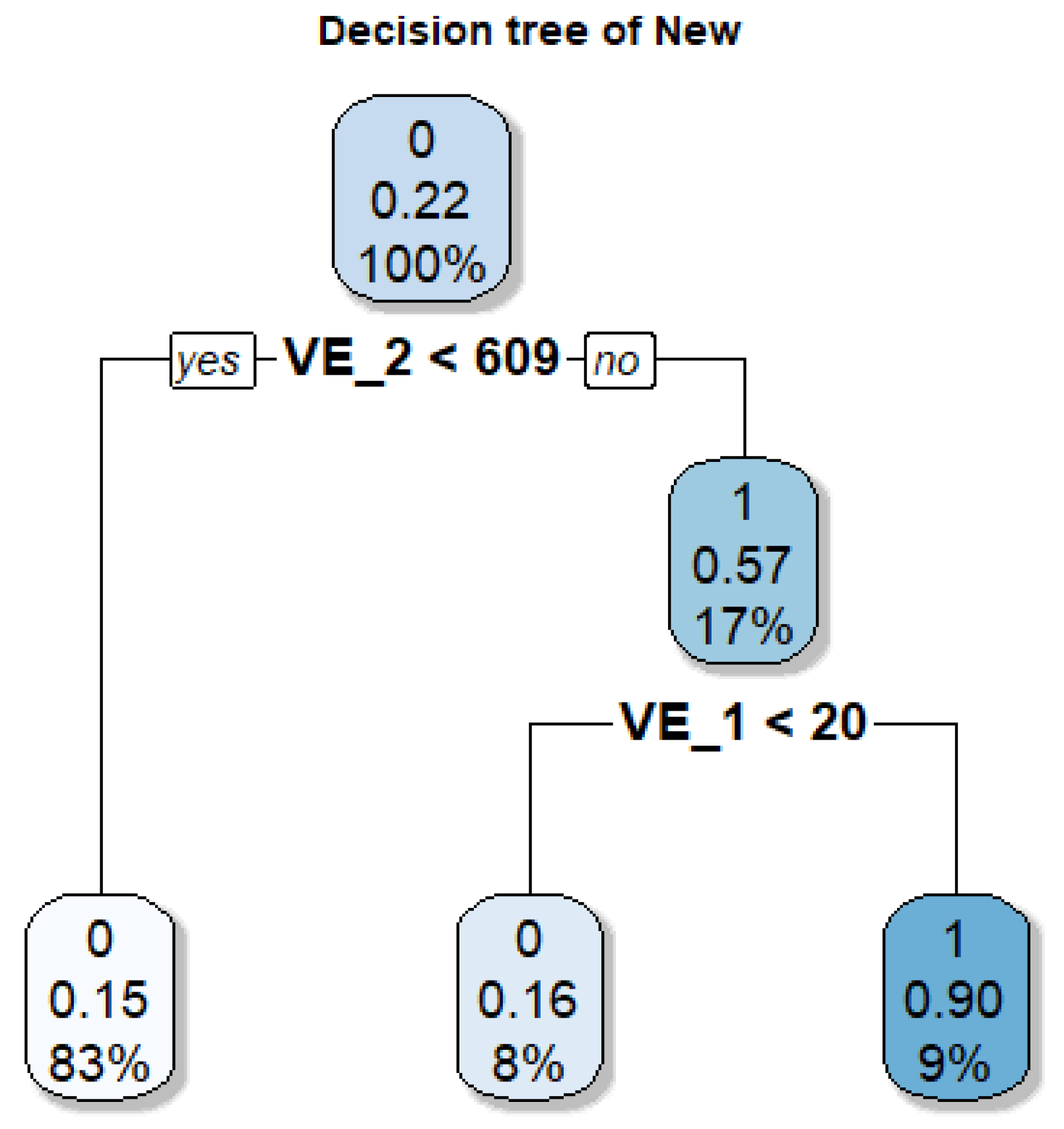
Figure 2 illustrates in a simplified way the logic of the RF model applied to the same 4 × 4 urban grid used in the previous example. In the example, each tree is trained with a different subset of explanatory variables. Tree 1 selects the Zone variable as the main criterion, separating highly protected areas (probability of change ≈ 0) from areas with medium protection (probability ≈ 1). Tree 2, on the other hand, prioritises the Distance variable, setting a threshold of 170 m that distinguishes areas close to the axis (probability ≈ 0) from those further away (probability ≈ 1). The final probability of the RF model results from the average of the individual predictions of the trees (right table), generating intermediate values in cases where the predictions disagree (e.g., cells 32 and 41 with probability ≈ 0.5).
Figure 2.
Simplified representation of the Random Forest model applied to the same 4 × 4 urban plan. Unlike Rpart, RF generates multiple trees using bagging, each trained with different combinations of variables (distance to the road axis and heritage protection category). The final predictions result from averaging the values of the trees, producing intermediate values in cells where their decisions differ.
2.1.3. Logistic Regression Model
Logistic Regression (LR) is a parametric statistical model that estimates the probability of occurrence of a binary event (in this case, the change or non-change in a land use class) based on a set of explanatory variables [43]. Its application in territorial studies has proven especially valuable, from urban sprawl [44] onto agricultural land to the multiclass analysis of complex spatial dynamics [45]. Using a logistic link function, the model transforms the linear combination of predictors into a bounded probability between 0 and 1, allowing its coefficients and odds ratios to be interpreted as direct measures of the direction and magnitude of each factor’s effect. Its main strength lies in its interpretive transparency: each variable can be explicitly linked to a quantifiable impact on the probability of territorial transformation [35]. However, LR has limitations associated with the assumptions of linearity between predictors and response, the independence between factors—which can be evaluated using Cramer’s V or the variance inflation factor (VIF)—and its lower performance in contexts where non-linear relationships or complex interactions predominate [46].
In the field of heritage planning, logistic regression is particularly valuable for evaluating the effectiveness of protected areas and for quantifying the influence of accessibility and urban morphology on land transformation. Its statistical foundation and fully interpretable structure facilitate the communication of results to decision-makers, providing solid empirical evidence for the formulation of conservation regulations and the definition of heritage zoning [15].
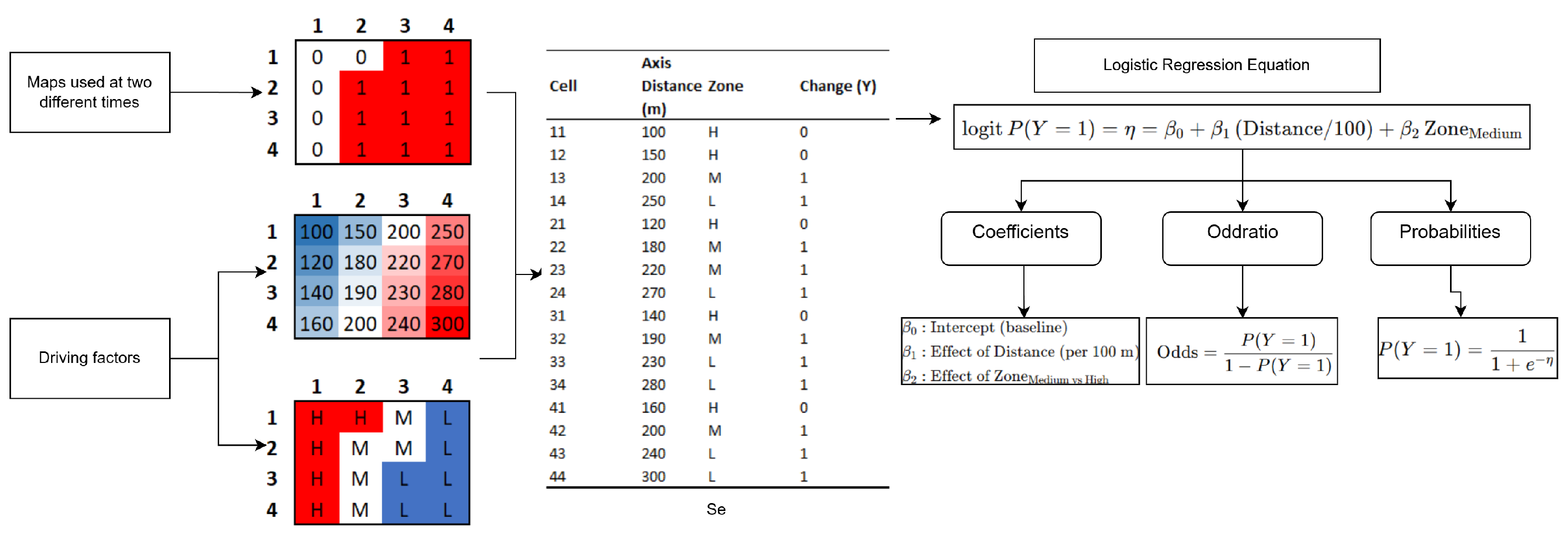
The Figure 3 illustrates the structure of the LR model used to estimate the influence of normative and morphological factors on the occurrence of land-use change. The coefficients () are interpreted through their exponential transformation (), which expresses the odds ratio, indicating both the magnitude and direction of each variable’s effect.

Figure 3.
Diagram of the model used to estimate the effect of regulatory and morphological factors on land use change. The coefficients are interpreted using their odds ratios, showing that a greater distance from the road axis and belonging to a medium protection zone significantly increase the probability of urban transformation.
3. Methodology
The present study adopts a comparative approach to evaluate the explanatory capacity and predictive accuracy of three widely used methods in spatial land-use change modeling: , , and . The methodological design is structured in three stages:
- Application of the models to an urban case study, followed by a quantitative comparison of prediction metrics as evaluation: model validation was performed using a five-fold stratified cross-validation (5-fold CV) scheme applied to the training set, which represented 80% of the total observations. In each iteration, the , , and models were retrained, calculating performance metrics such as accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, F1 score, balanced accuracy, and Kappa coefficient. The decision threshold was determined from the Youden index (J), obtained using the ROC curve [47], with the aim of maximizing both sensitivity and specificity. This procedure allowed for more robust estimates of each model’s predictive capacity, reducing the variance associated with a single data partitioning [48]. Subsequently, the model with the best average performance was retrained using the entire training set and evaluated on the remaining 20% (test set) to estimate its final performance and generalizability. Additionally, the assumption of spatial independence was assessed using Moran’s I applied to the residuals of the Logistic Regression model to detect potential spatial patterns not captured by the predictors.
- The analysis of the probability maps identifies areas most likely to experience land-use transition, based on the estimates from each model. In this stage, the probability maps obtained from each model are generated and compared, representing the spatial distribution of transformation risk. The analysis focuses on identifying consistent territorial patterns, contrasting differences in the locations of vulnerable areas, and evaluating the degree of coherence between the methods. The objective is to determine the extent to which these predictions provide useful and reliable information for decision-making in heritage urban planning, especially in identifying critical areas where interventions, regulations, or protective measures are needed.
- Analysis of the explanatory capacity of each model, focusing on the interpretation of the driving variables. In this stage, a systematic examination is conducted of how each model represents the influence of the drivers of change. In the case of , the analysis focuses on the coefficients and odds ratios, which quantify the direction and magnitude of the effect of each territorial variable. For , the focus is on the hierarchical rules and critical thresholds that structure the decision tree, revealing specific combinations of normative and morphological conditions under which land transformation occurs. In the model, attention is paid to the relative importance of the variables, allowing for the prioritization of the factors that best distinguish between stable areas and sectors undergoing urban renewal processes. This comparative approach allows for contrasting the consistency between methods, identifying which factors exert the greatest influence on territorial transformation, and evaluating their relevance for the design of conservation and heritage zoning instruments. Overall, the analysis seeks to maximize the interpretability of the models and extract robust evidence to strengthen decision-making in land management.
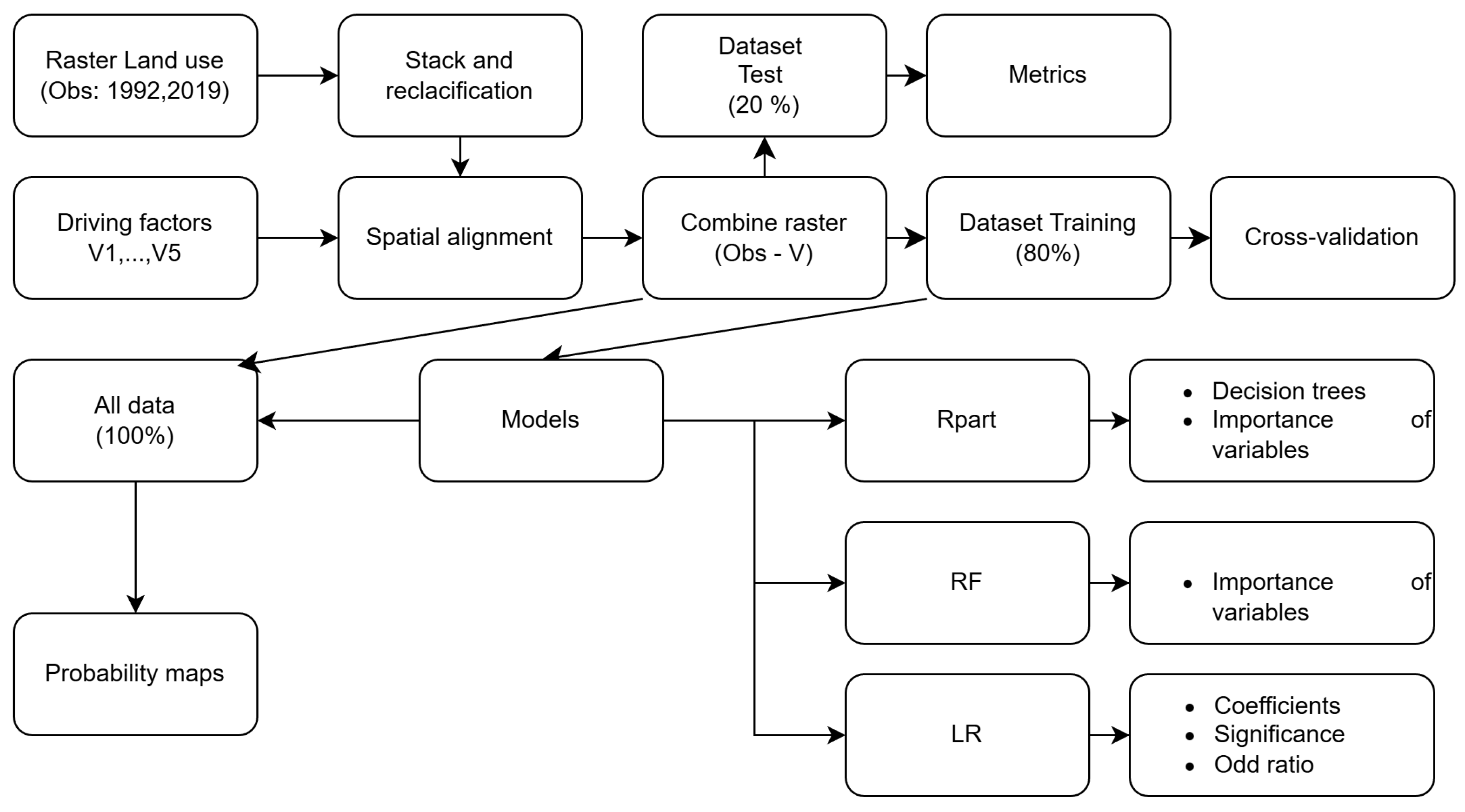
All processing and analysis were performed in R (v4.3.1) using RStudio, with the rpart [37], randomForest [49], lulcc [50], and pROC [51] packages for model fitting, evaluation, and visualization. Figure 4 illustrates the methodological flow of the land-use change modeling process. It begins with raster maps of observed land use from 1992 and 2019, which are stacked and reclassified along with the explanatory factors (: Distance to the Historic Network; : Distance to Beach; : Historic Conservation Zone; : Sectional Zone of the Coastal Border; : Historic Monument Zone).

Figure 4.
Proposed steps for analysis of driving factors in land-use change modeling through a comparative analysis, evaluating their predictive capacity and the interpretative potential of the determinant factors.
After spatial alignment, the layers are combined to generate the input dataset. This dataset is divided into 80% for training and 20% for testing. To evaluate model performance, a cross-validation scheme was applied to the training set. Subsequently, the metrics were estimated on the test set. This procedure allowed for the quantification of predictive capacity using widely accepted indicators in spatial modeling: overall accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, F1 score, balanced accuracy, and the Kappa coefficient. Together, these metrics facilitate the evaluation of both the model’s overall performance and its ability to accurately distinguish between stable areas and areas undergoing transformation. The applied models (, , and ) facilitate the generation of probability maps and the analysis of the importance of variables, coefficients, significance, and odds ratios associated with land-use changes. To be precise, a complete algorithm is formally presented and explained in Appendix A: Algorithm A1 (input, step 1 and step 2) and Algorithm A2 (step 3, step 4, step 5, step 6 and output).
3.1. Data
The study area corresponds to the Bellavista neighborhood, located in the city of Tomé, Chile. This urban enclave of industrial origin preserves a significant collection of heritage buildings linked to the former textile industry. The territory has undergone substantial transformations in its urban morphology, driven by deindustrialization, real estate pressure, and the reconfiguration of public spaces. Due to its high concentration of historically significant elements and the intensity of recent dynamics of change, Bellavista constitutes a representative case for analyzing land-use transition patterns in heritage urban contexts.
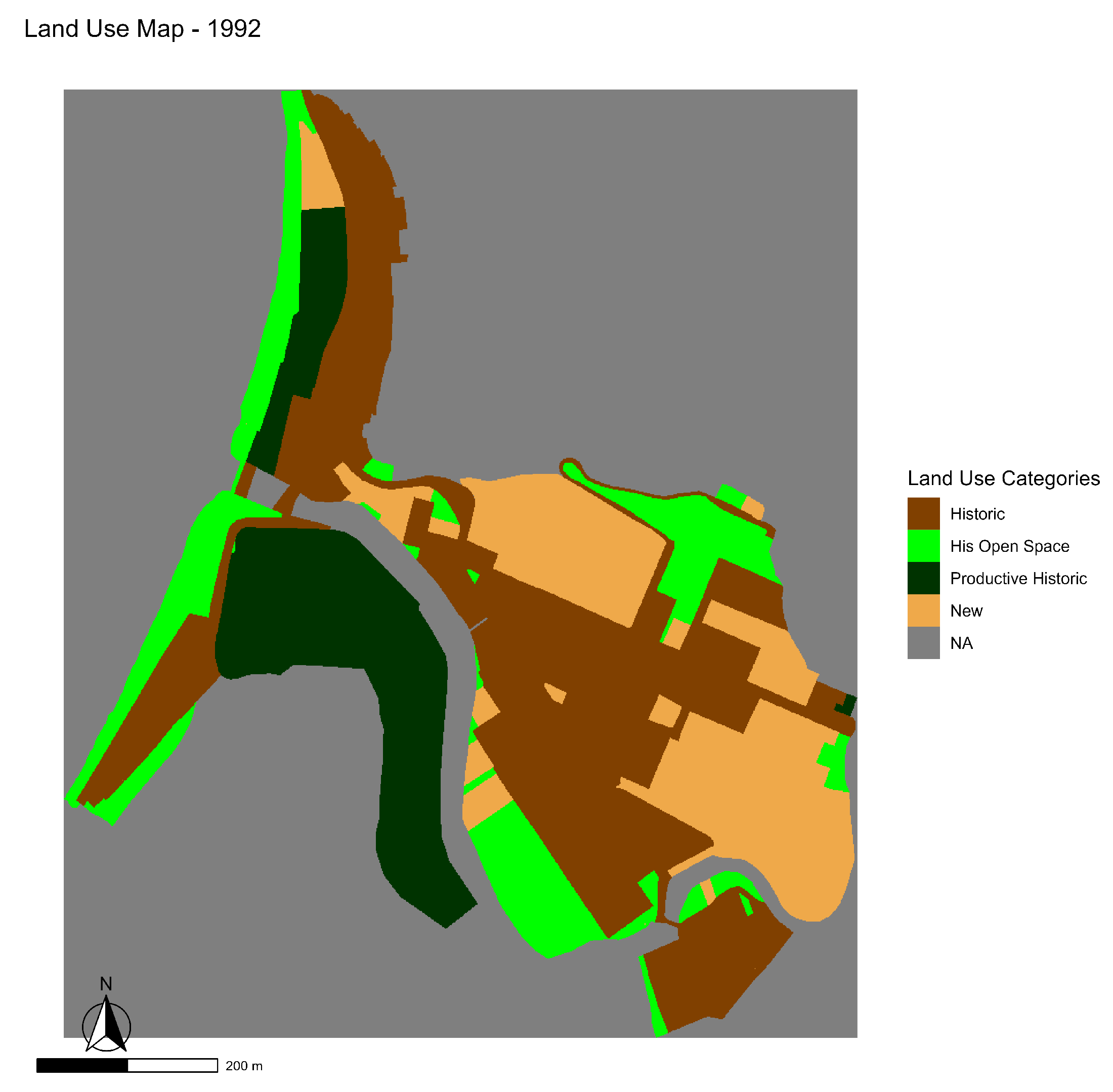
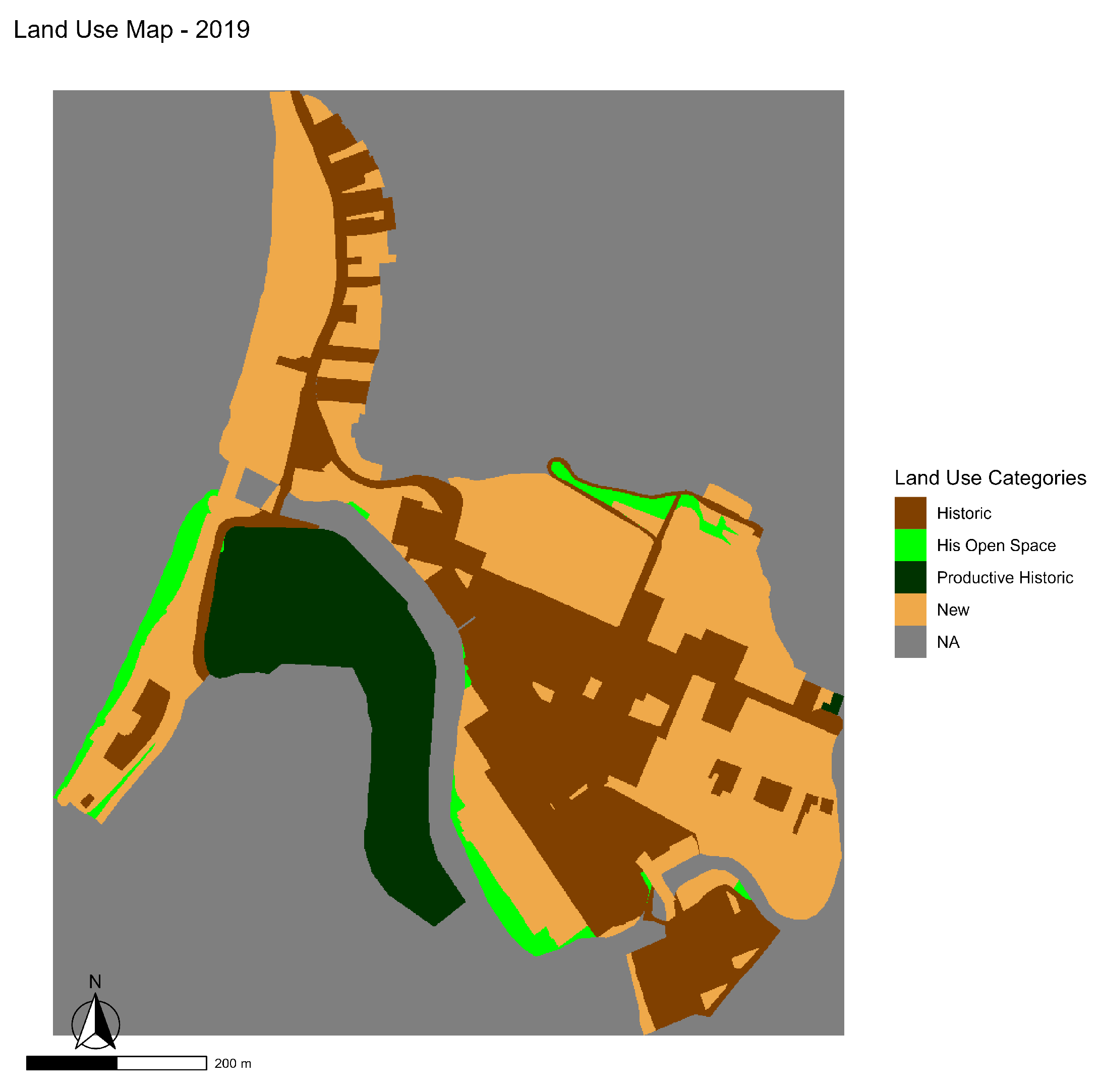
The data used in this study comes from the digitization and analysis of aerial orthophotos corresponding to the years 1992 (see Figure 5) and 2019 (see Figure 6), following the methodology previously documented in [52]. In this work, a cartographic database of land uses was developed through photointerpretation, complemented by cadastral information and field verifications. The unit of analysis corresponds to regular 1 × 1 m cells, on which a binary layer was built that distinguishes between change and no change in land use. For the purposes of this analysis, the original classes were reorganized into a simplified typology composed of five main categories:
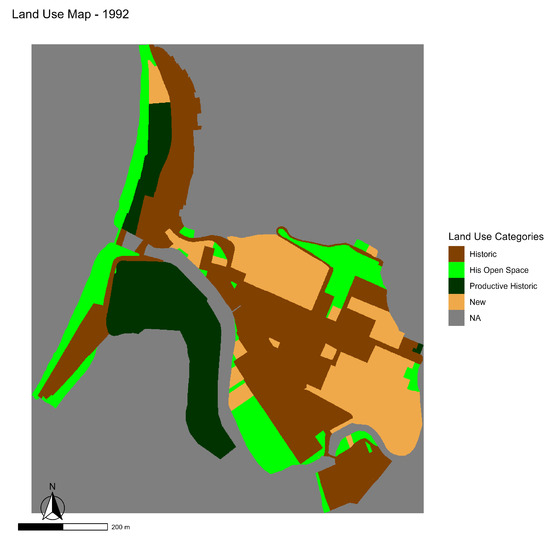
Figure 5.
Land use map of the Bellavista neighborhood in 1992.
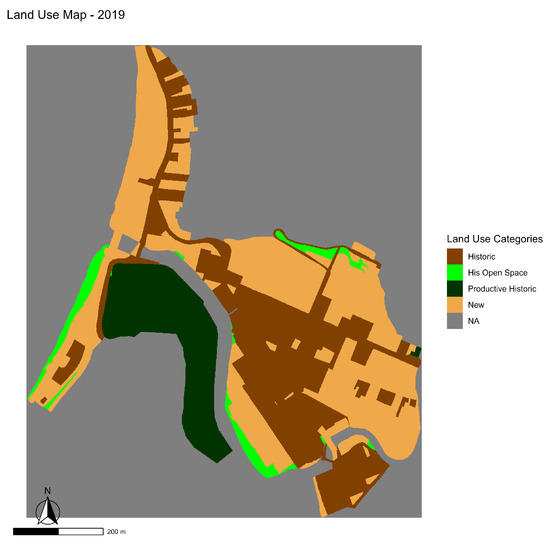
Figure 6.
Land use map of the Bellavista neighborhood in 2019.
For the analysis, four land use categories were distinguished. First, the Historical class encompasses residential, commercial, amenity, and circulation uses established before 1992, which form the neighborhood’s heritage base. Second, open spaces of historical origin (such as beaches, courtyards, and green areas) were identified; despite their informal nature, they play a structuring role in the urban configuration. Third, the “Historical Productive” class was defined, comprising industrial uses that are either disused or undergoing conversion, traditionally linked to the local economy. Finally, all uses emerging after 1992 (including new housing, recent commercial development, informal settlements, and coastal retaining structures) were grouped into the “New” category. The complete correspondence between the original uses and their reclassification is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Reclassification of land-use categories.
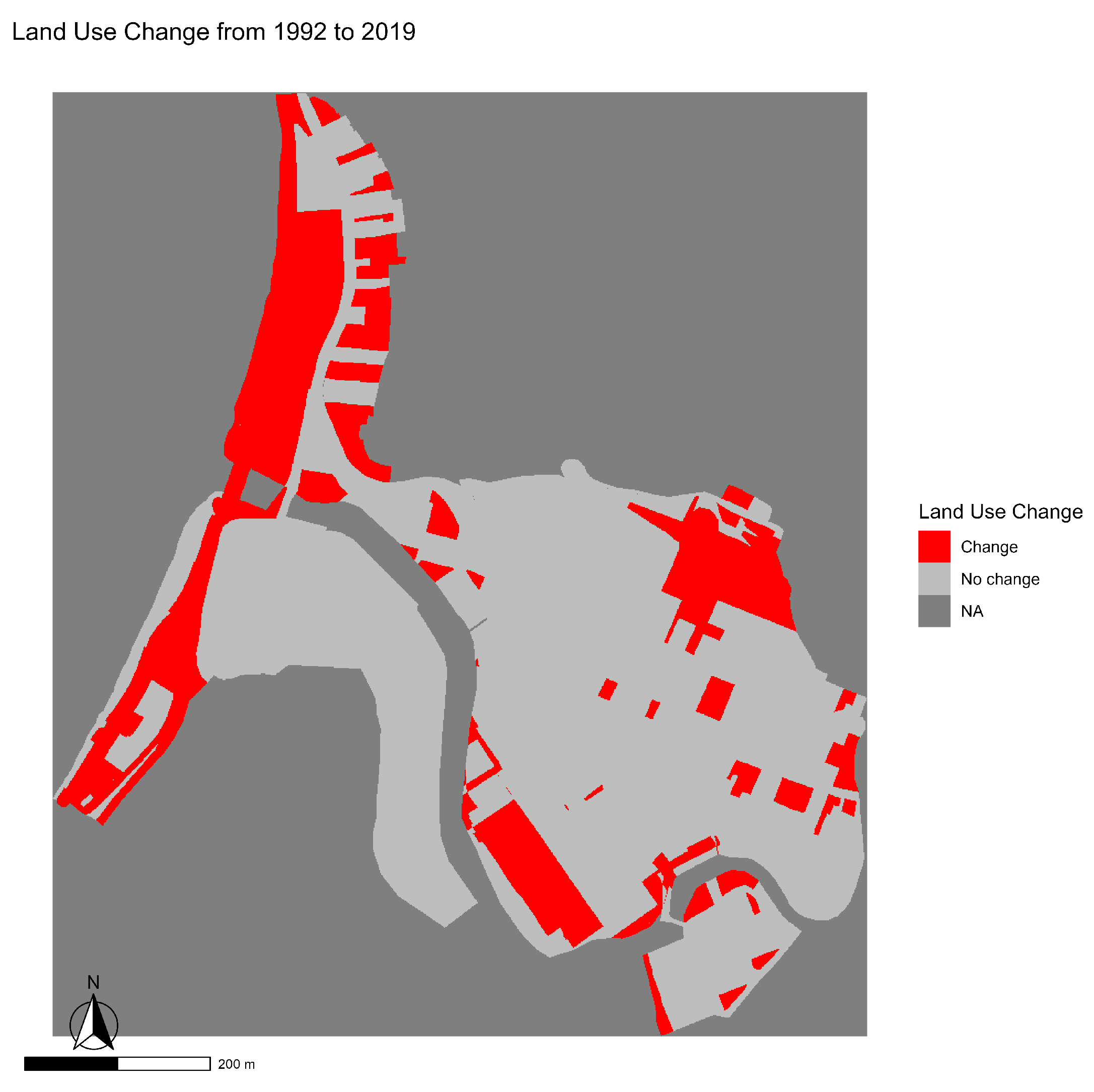
Figure 7 illustrates the spatial evolution of land use in the Bellavista neighborhood between 1992 and 2019, as well as the precise locations of the cells that underwent transformations during this period. A significant expansion of the areas classified as “new use” is evident, concentrated mainly in sectors previously occupied by industrial buildings or historic open spaces. This dynamic reflects a reurbanization process that has altered the original structure of the heritage fabric, moving towards greater densification and increasing functional diversification of the territory.
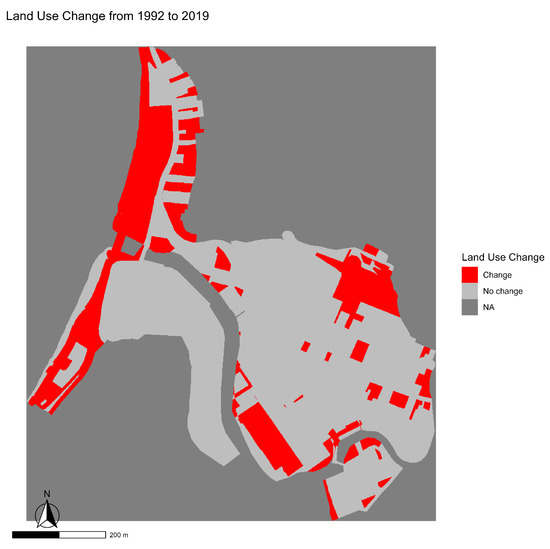
Figure 7.
Map showing the change in land use in the Bellavista neighborhood from 1992 to 2019.
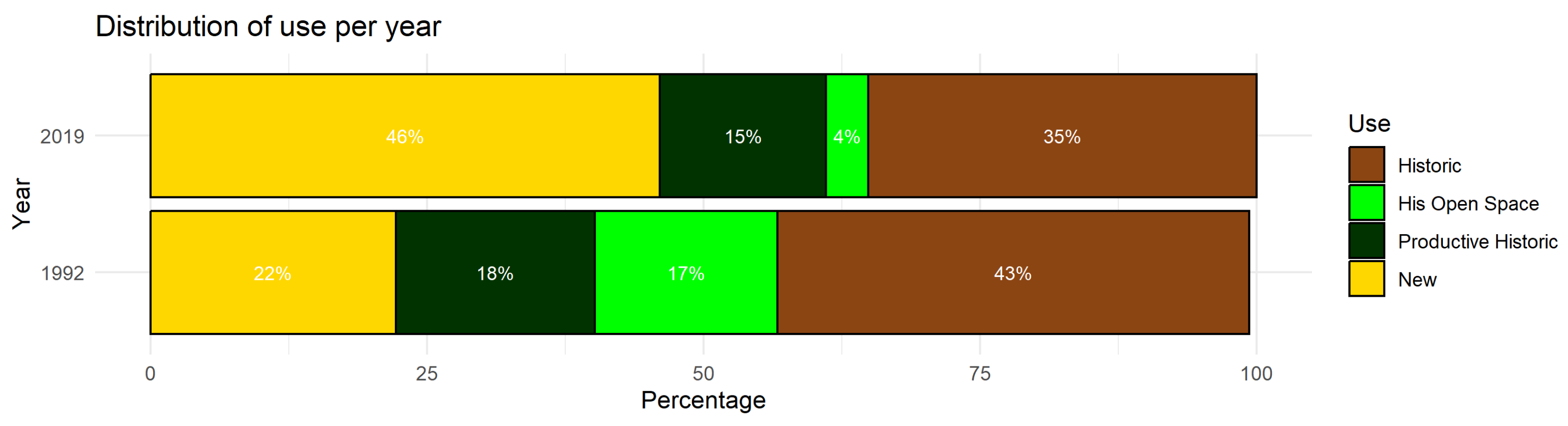
Figure 8 reinforces this trend by showing, in percentage terms, a 24% increase in the area classified as “new use” between 1992 and 2019, accompanied by a significant reduction in areas designated for historical productive uses. This redistribution of land use suggests a reconfiguration of the urban landscape, where the obsolescence of industrial land has progressively led to its conversion to residential or mixed uses.

Figure 8.
Percentage distribution of land use by category between 1992 and 2019 in the study area.
Figure 9 allows us to disaggregate the destination of the original urban land, revealing the proportion of each use category recorded in 1992 that was absorbed by new functions in 2019. It can be observed that a considerable portion of the land classified as “Historical Productive” land and “Historical Open Space” was transformed into recent residential or urban areas, highlighting the high vulnerability of industrial heritage to the pressures of urban development.
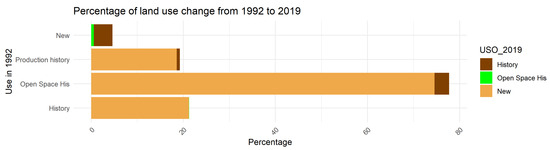
Figure 9.
Percentage of land use change between 1992 and 2019 according to the category of origin.
3.2. Driving Variables
The explanatory variables used in this study are based on the methodological proposal developed by [52], which aims to model urban dynamics in heritage territories, such as the Bellavista neighborhood of Tomé. This area has been the scene of various heritage activation processes and conflicts surrounding land use and the symbolic value of space, especially since the deindustrialization of the textile complex [53,54,55].
Based on this background and the territorial approach adopted, five driving variables of change have been incorporated, selected for their relevance in the literature and their ability to capture the factors that influence the urban transitions observed in the study area:
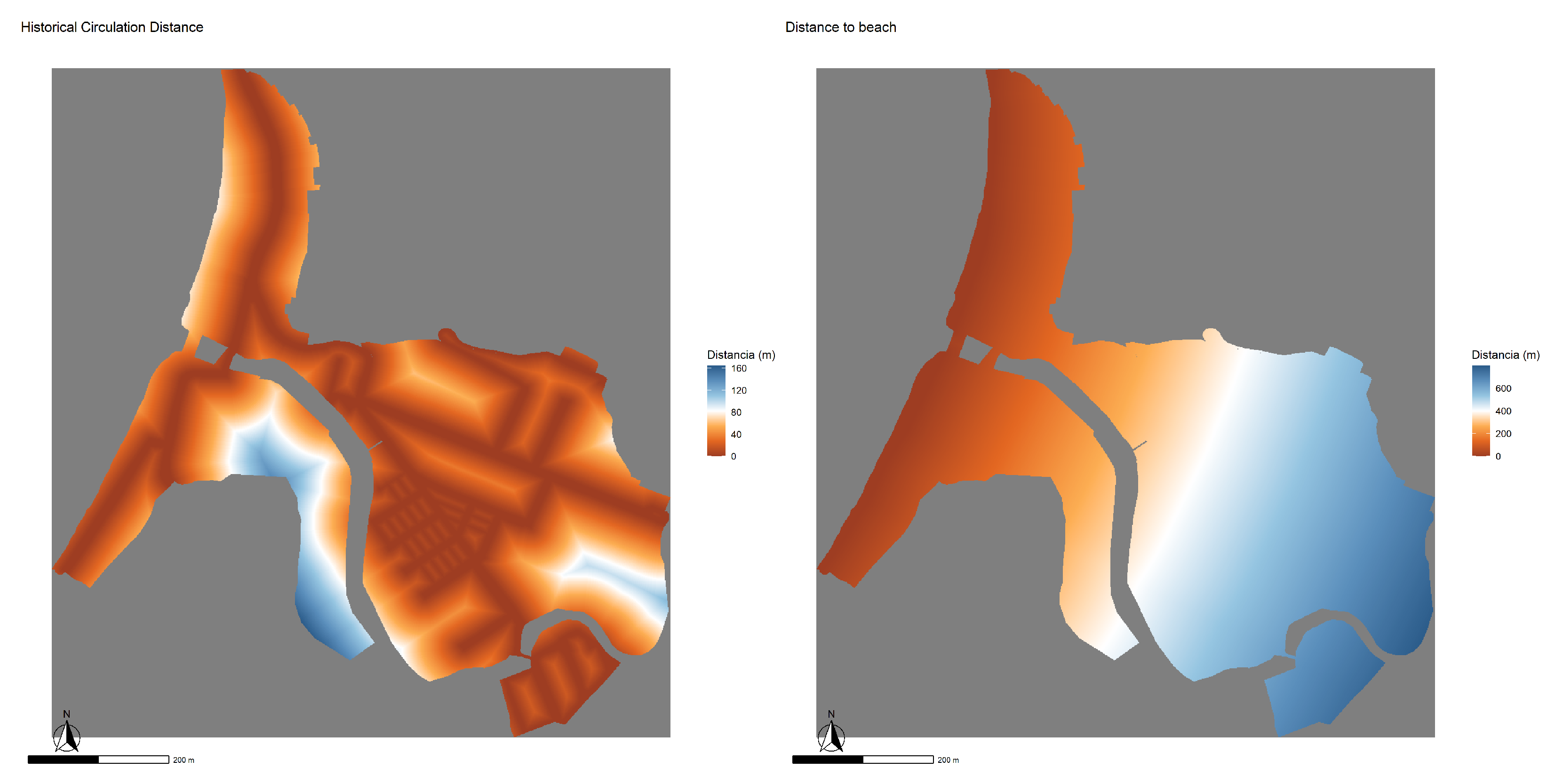
Continuous variables (Figure 10):
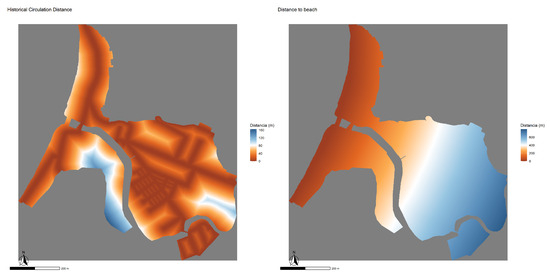
Figure 10.
(Left) Distance to the historic road network. (Right) Distance to the beach.
- Distance to the “Historical Traffic Network”. Defined as the Euclidean distance between each cell of the model and the foundational road layout of the Bellavista sector. This structured network, inherited from the original industrial design, plays a central role in the current urban configuration and has been identified as a key axis in the functional transformation processes of the neighborhood [52].
- Distance to the beach. It corresponds to the Euclidean distance from each cell to the coastline, an area of high real estate appreciation and subject to social disputes over its public use. As [54] warns, the seafront has been the scene of tensions between tourism, residential, and conservation interests, which directly impact the local dynamics of territorial transformation.
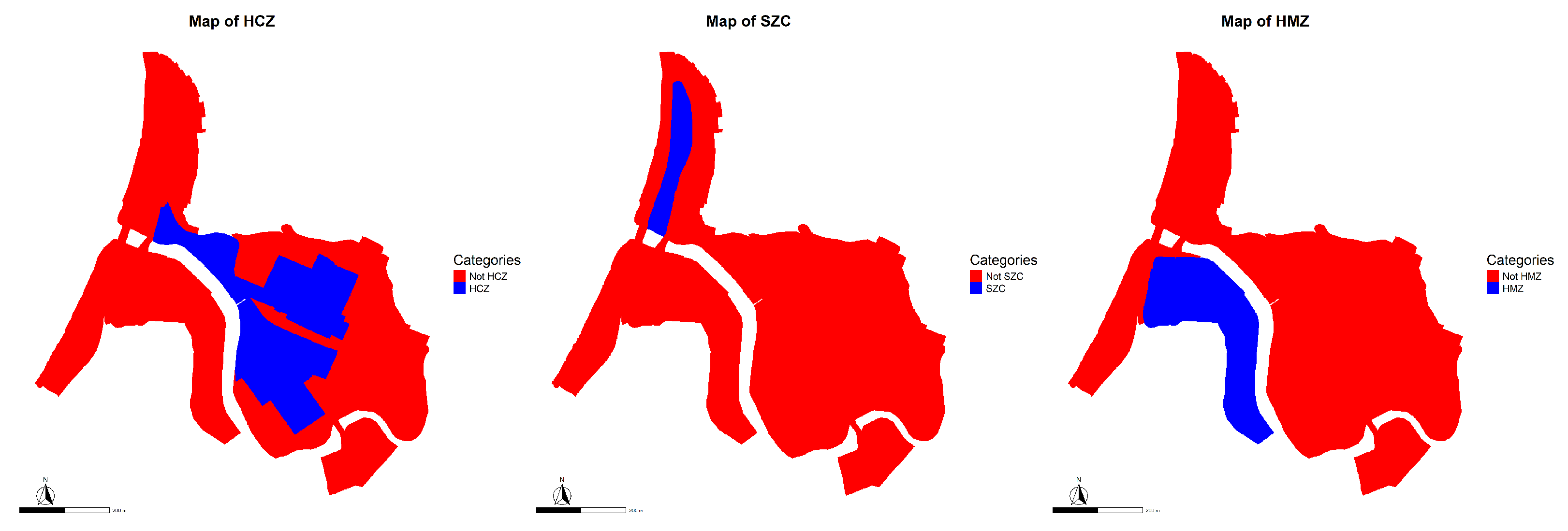
Categorical variables (Figure 11):
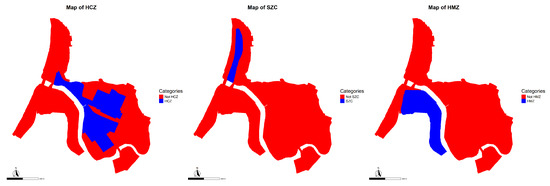
Figure 11.
HCZ (left), SZC (center) and HMZ (right).
- 3.
- Historical Conservation Zone (HCZ). Delimited by the Tomé Municipal Regulatory Plan in 2005, this zone aims to safeguard the morphological value of the founding industrial area. The units located within this polygon are subject to specific regulatory restrictions regarding land use and building typologies in order to preserve their heritage integrity.
- 4.
- Sectional Zone of the Coastal Border (SZC). Incorporated into the Sectional Plan of the Coastal Border in 2012, this normative figure regulates the development of the seafront, aiming to harmonize ecological, tourist, and urban interests within a particularly sensitive and contested area [54].
- 5.
- Historic Monument Zone (HMZ). This corresponds to the protected area designated under Exempt Decree No. 222 of the Ministry of Education, issued in 1999, which declares the Bellavista–Oveja Tomé complex a National Historic Monument. This designation imposes legal restrictions on permitted interventions, uses, and modifications to safeguard its historical, architectural, and cultural value [53].
4. Results
4.1. Predictive Accuracy of Models
The results of the cross-validation (see Table 2) revealed substantial differences between categories and models, both in performance metrics and in the values of Youden’s optimal threshold.

Table 2.
Cross-validation of training data.
In the “Historical” category, the model exhibited the best overall balance, achieving an average accuracy of , , and , surpassing and . The average optimal threshold of indicates adequate model calibration; therefore, it is suggested that this threshold be maintained as the final cutoff point in the classification stage.
In the “Historical Productive” category, the three algorithms obtained an average accuracy of and an F1 score close to , reflecting near-perfect performance but also suggesting possible structural overfitting. This situation does not stem from multicollinearity among the predictor variables but rather from strong collinearity between the dependent variable and the spatial predictors: areas without change are concentrated in heritage protection areas (HMZ), while changes are primarily located in secondary consolidation sectors (SZC).
This is compounded by a marked spatial imbalance between stable areas and polygons that actually changed, allowing the algorithms to reproduce dominant patterns with high accuracy without adequately capturing the variability of change. These factors explain the low thresholds (–) and the homogeneity of the metrics across models, indicating that, although the internal fit is outstanding, generalizability could be limited in contexts with greater territorial heterogeneity.
The “New” category showed greater predictive difficulty. Here, the RF model performed best (), outperforming RPART and . The average optimal threshold of indicates that the algorithm tends to underestimate the probability of new changes occurring, which requires a cutoff point below to maximize the detection of true positives. This adjustment increases sensitivity () without significantly reducing specificity (), so is recommended as the final operating threshold.
Finally, in the “Open Space Historical” category, the RPART model achieved the best performance (), achieving a remarkable balance between sensitivity () and specificity (). Its average threshold of 0.38 showed more stable calibration than that obtained with RF (), confirming that the decision tree more accurately captures the linear and categorical structures of this class. Consequently, the RPART model with a threshold of is defined as the final option for this category.
The final evaluation of the test set confirms the overall robustness of the models; however, it also reveals differences in their generalizability compared to the results obtained from cross-validation (see Table 3). In particular, the RF model maintained the best overall performance, achieving accuracy and F1 values above in the New and Historical Productive categories, demonstrating high predictive stability and an adequate transfer of learning to unobserved data. In contrast, Logistic Regression (LR) experienced a reduction in accuracy and F1 in the most unbalanced classes, reflecting its sensitivity to skewed distributions and the linearity of the predictors. The RPART model, for its part, showed intermediate performance, although it exhibited a slight decrease in sensitivity in categories with low spatial variability, possibly due to its tendency to overfit specific rules from the training set.

Table 3.
Model performance for test data.
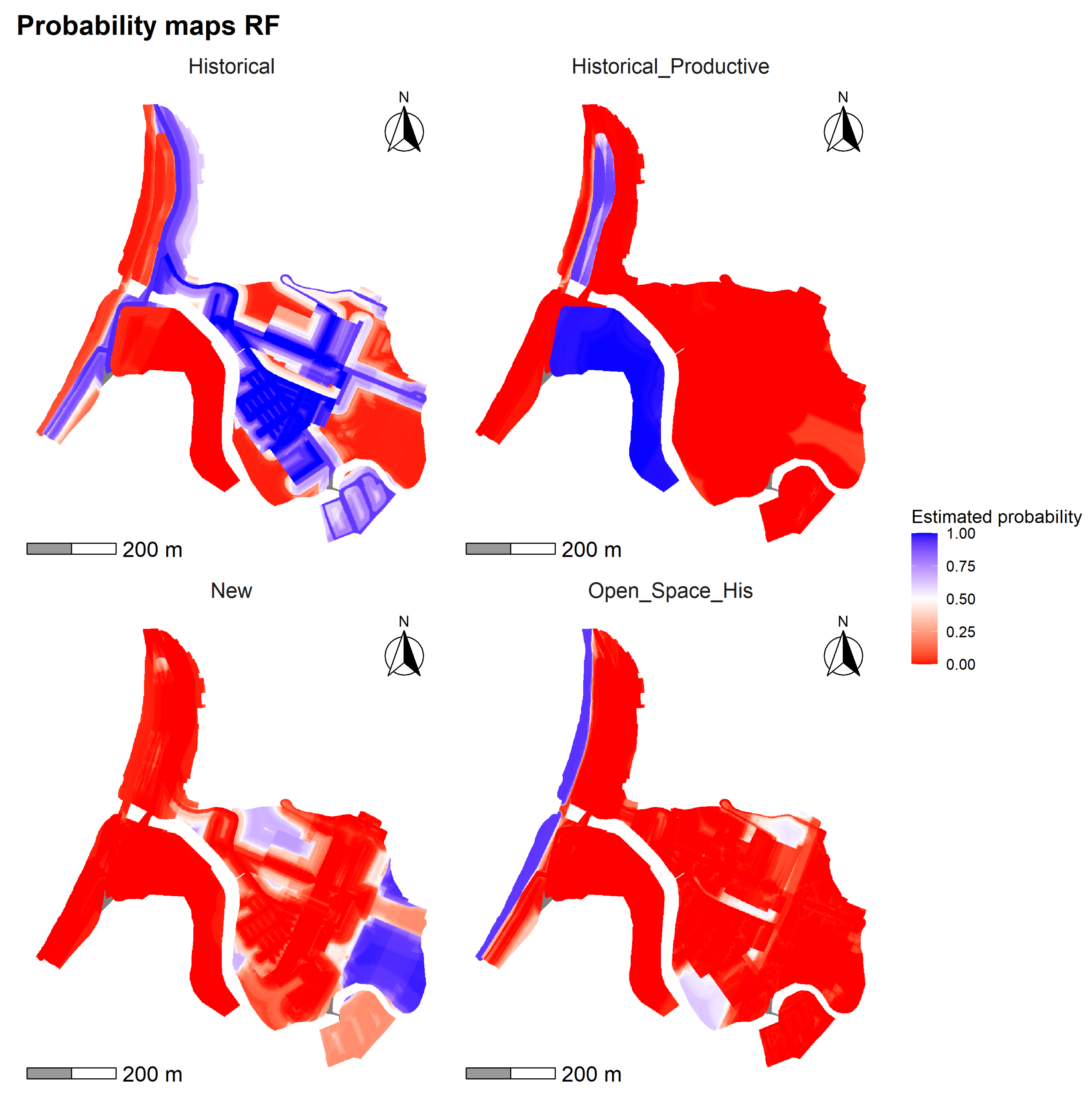
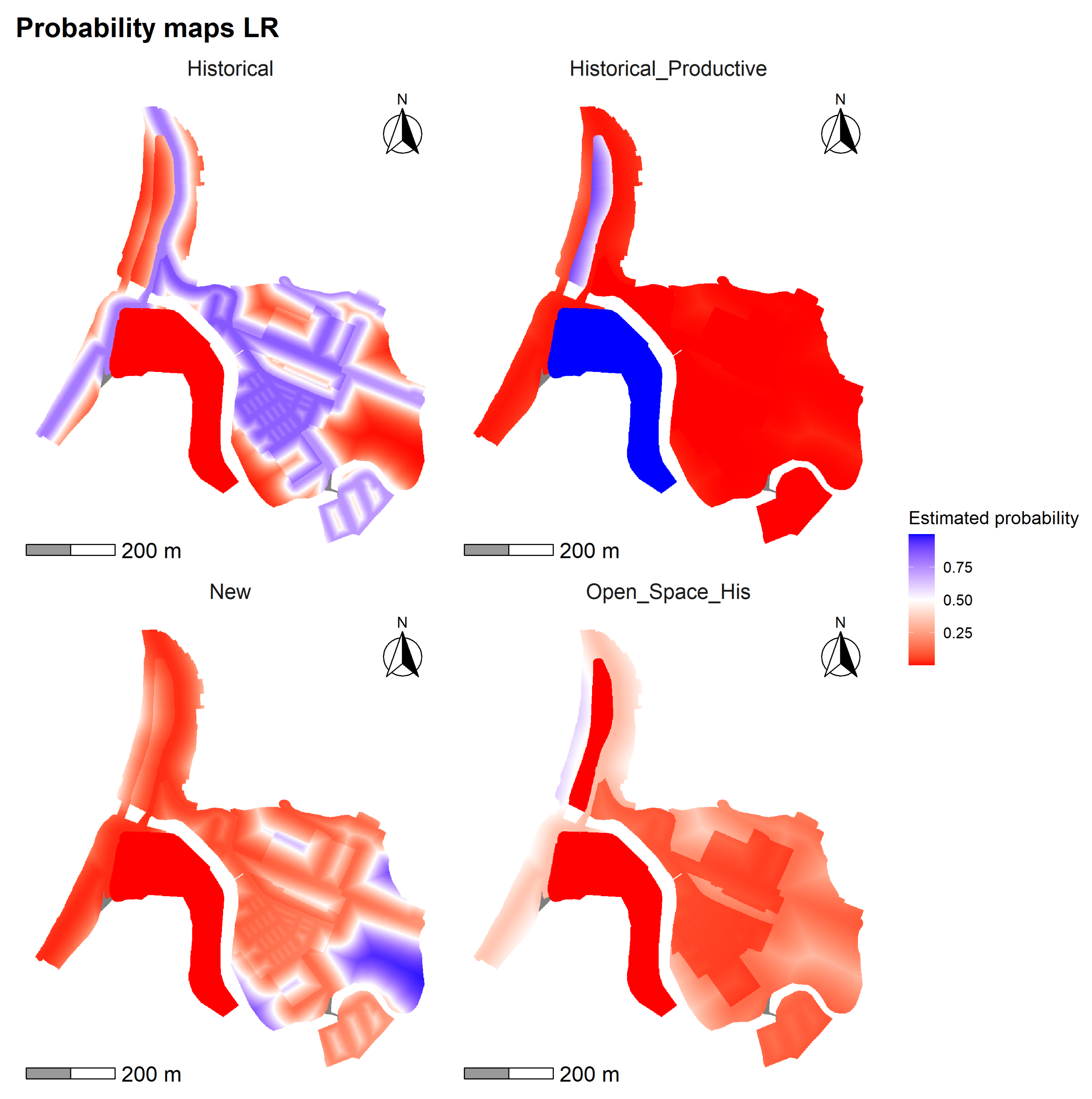
4.2. Transition Probability Maps
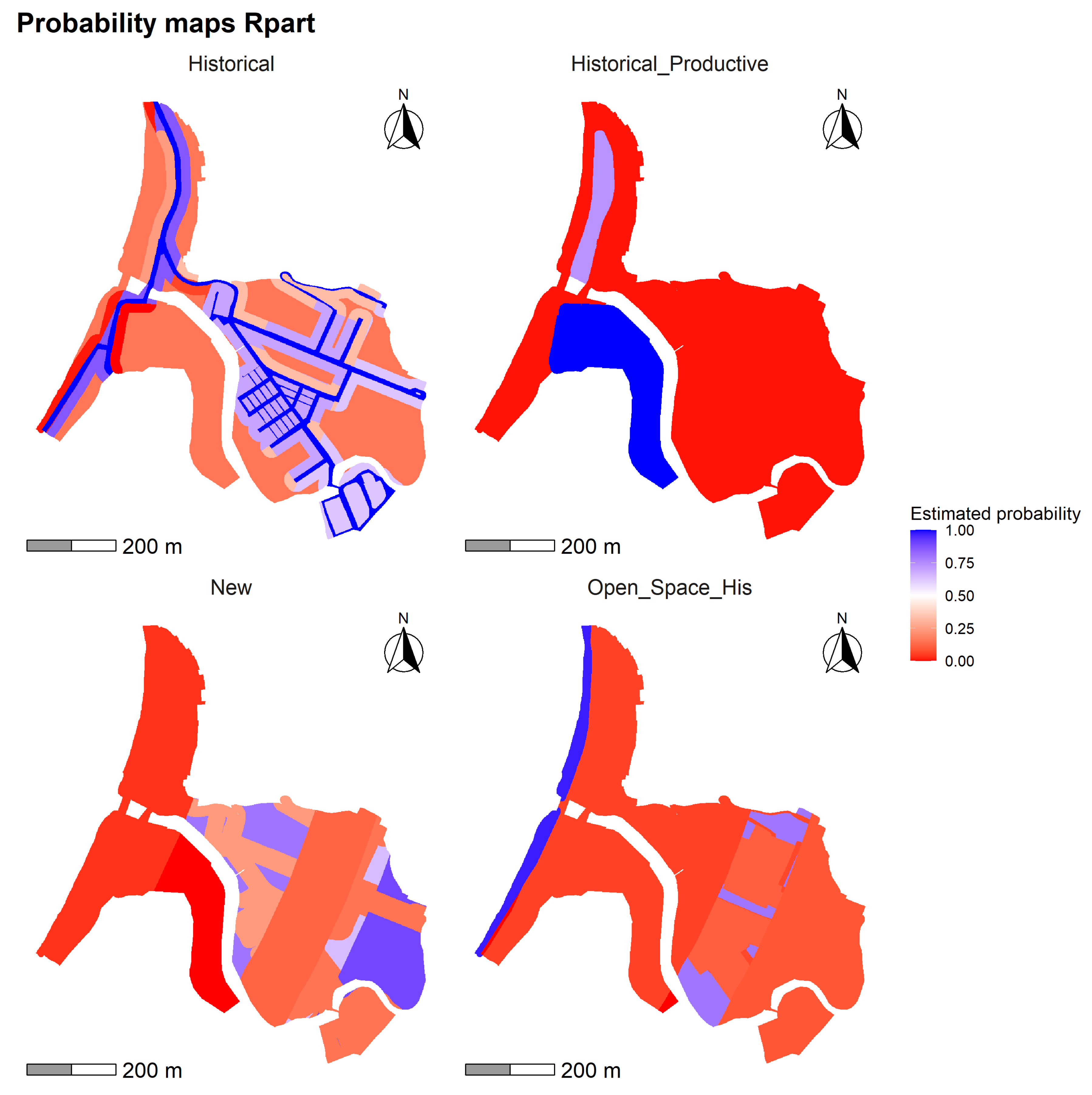
The Rpart model (Figure 12) exhibits a spatial distribution of change consistent with the historical and normative patterns of the study area. The “Historical” class shows high probabilities of persistence (), primarily concentrated in the eastern sector, where consolidated urban layouts are located and where there is greater proximity to the old road network. In the case of the “Historical Open Space” class, a more dispersed and low-probability distribution is observed, with specific concentrations in the far east, adjacent to areas protected by the HCZ. Meanwhile, the “Historic Productive” class reaches high values in the southwestern edge, within the perimeter of the Heritage Protection Zone (HMZ), reflecting the permanence of industrial functions close to the coastline. In contrast, the “New” class presents medium probabilities (–) in the center and south of the territory, coinciding with less regulated sectors and those further from historical urban infrastructure.

Figure 12.
Probability maps generated with the Rpart model for the land use classes: Historical Open Space, Historical, Historical Productive, and New.
The model (Figure 13) presents a more defined and contrasted spatial distribution of change than that observed in , allowing for a more precise representation of the historic urban structure. The “Historical” class exhibits high probabilities of persistence (mean = 0.452; max = 1), concentrated especially in the northeast sector, aligning with consolidated areas and proximity to the main traditional roads, as reflected by the low distance to the historic circulation network. In the case of “Historical Open Space”, the spatial pattern appears more dispersed and of lower intensity (mean = 0.092; SD = 0.236), suggesting a lower capacity of the model to predict this class, even in normatively protected sectors such as the . For its part, the “Historical Productive” class reaches high values in the southwest strip, within the HMZ polygon (max = 0.998; mean = 0.189), indicating the persistence of industrial uses linked to the coastal edge. Finally, the New class is concentrated in the south-central part of the study area, with relatively high probabilities (mean = 0.164; max = 0.974), aligned with areas of less regulation and greater distance from both the coast and the historic road layout.
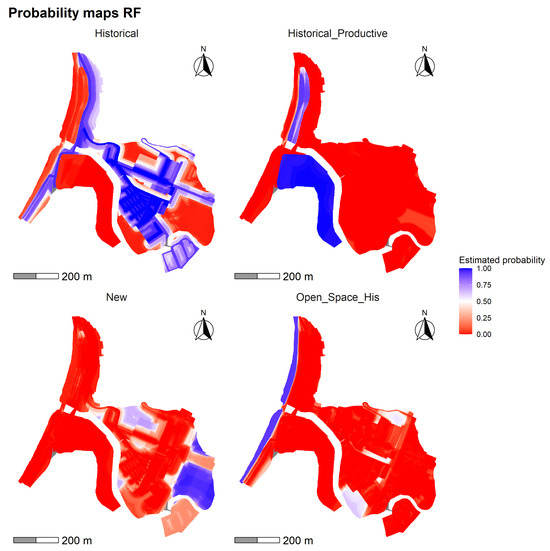
Figure 13.
Probability maps generated with the RF model for the land use classes: Historical Open Space, Historical, Historical Productive and New.
The model (Figure 14) presents a spatial distribution consistent with the general dynamics of the study area, albeit with less contrast than the decision tree-based models. The “Historical” class registers the highest probability of persistence (mean = 0.426; max. = 0.862), particularly prominent in the central-eastern sector, which corresponds to the consolidated urban layout and traditional infrastructure. The “Historical Productive” class achieves notably high values in the southwest corner (mean = 0.188; max. = 1), reinforcing its association with port and coastal areas, especially within the hmz polygon. In contrast, the New class exhibits a more dispersed distribution, with medium to low probabilities (mean = 0.220; max. = 0.986), covering peripheral sectors lacking specific regulatory frameworks. The “Historical Open Space” class, on the other hand, presents the lowest probabilities (mean = 0.167; max. = 0.605), with specific concentration areas located on the northeastern edge of the territory.
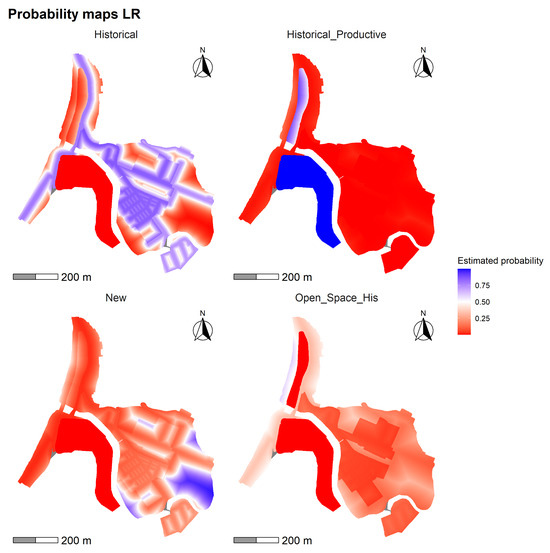
Figure 14.
Probability maps generated with the LR for the land use classes: Historical Open Space, Historical, Historical Productive, and New.
4.3. Analysis of the Explanatory
4.3.1. Rpart Analysis
Four decision trees generated using are analyzed to predict land-use classes with heritage value. The relative importance of the variables used in the classification and their implications for urban planning and heritage conservation are discussed below.
The tree corresponding to the “Historical” class (Figure 15) defines a characteristic profile of these lands: they are mostly located in central sectors near the coast, with good accessibility via local or secondary roads.

Figure 15.
Decision tree for the Historical class. VE1: Distance to the Historical Network (m); VE2: Distance to Beach (m).
However, the tree also reveals that certain properties outside these regulated areas can be classified as historical if they meet other relevant spatial criteria, such as a specific distance from roads, which indicates their belonging to a traditional urban fabric. These branches usually have an intermediate historical probability (approximately 60%), suggesting the presence of areas with heritage value not formally recognized by regulatory instruments. This situation poses a significant challenge for urban planning, as it highlights the existence of dispersed heritage outside official boundaries, which is potentially more vulnerable to urban renewal processes or real estate expansion [56].
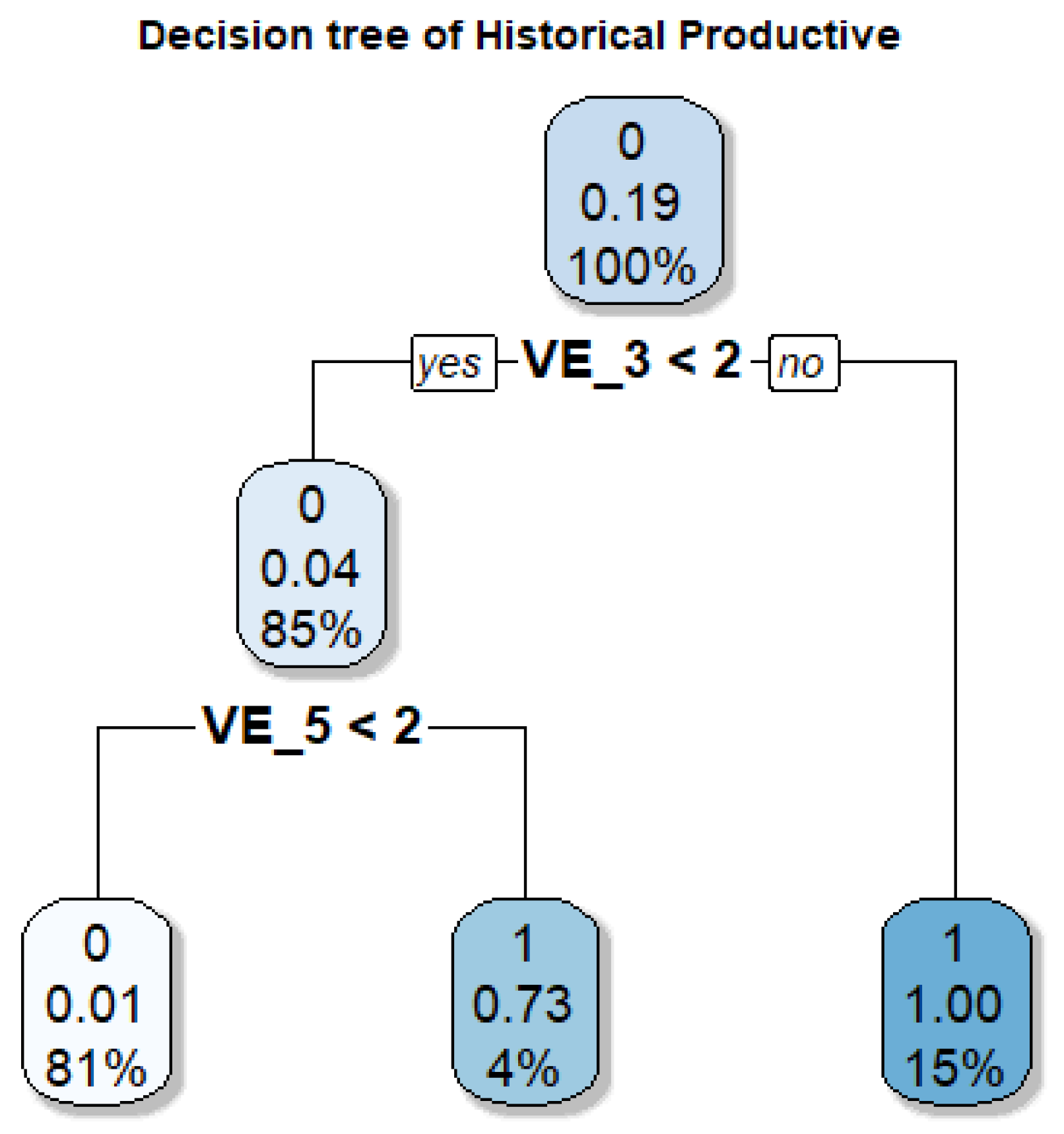
Figure 16 shows that historical productive uses are concentrated in specific industrial areas linked to foundational infrastructures rather than to a conventional center–periphery logic. This indicates that their conservation cannot rely on general spatial criteria but requires detailed identification and precise regulatory delimitation of these enclaves. The model underscores their localized and vulnerable character, highlighting the need for targeted protective measures.
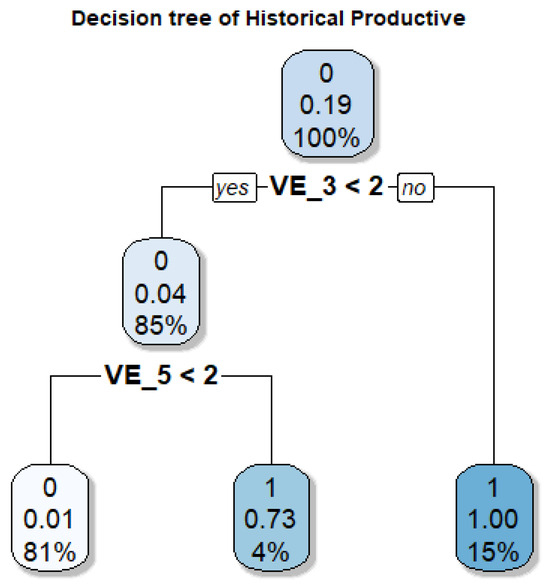
Figure 16.
Decision tree for the Historical Productive class. VE2: Distance to Beach (m).
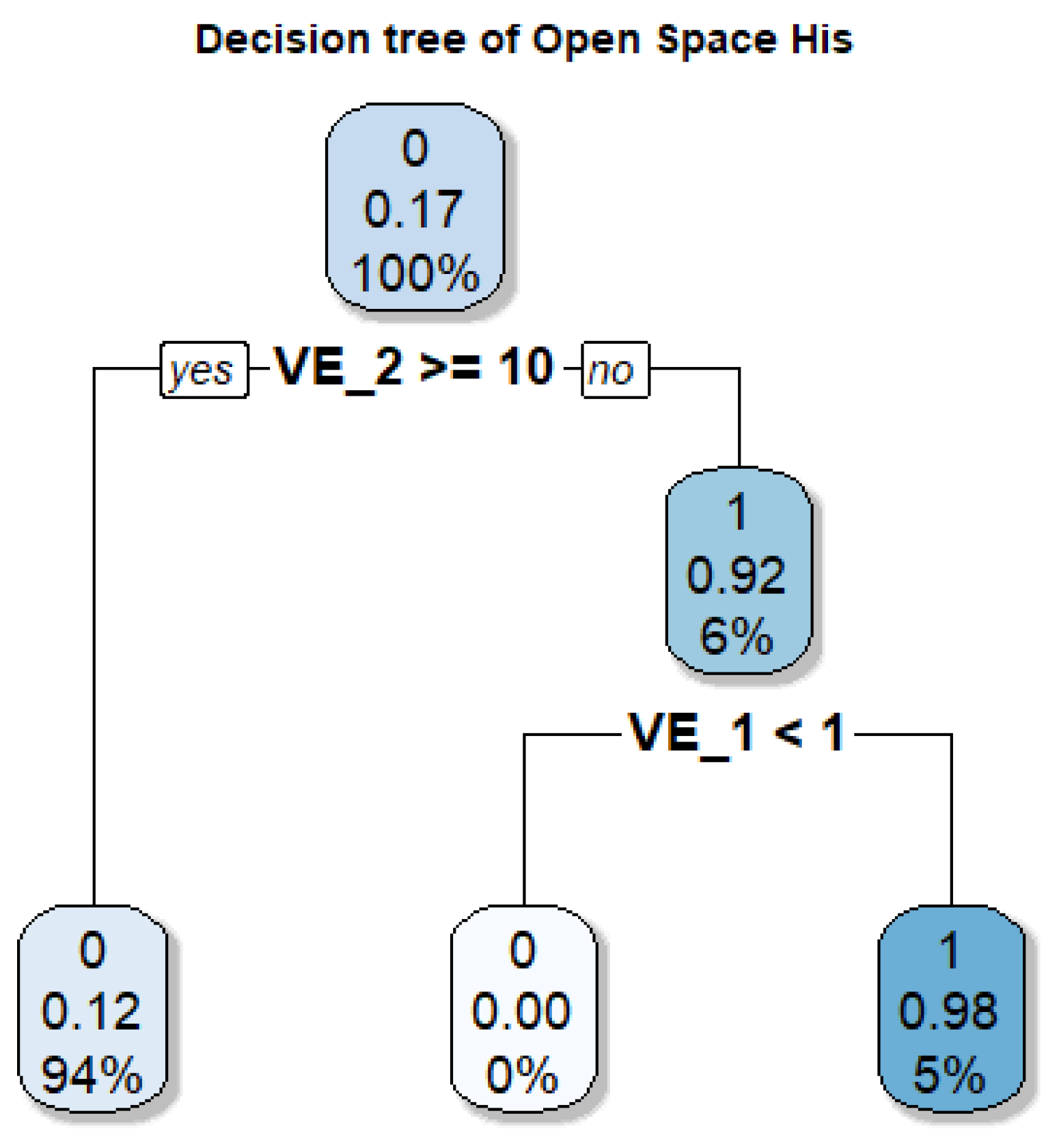
The decision tree for the “Historical Open Space” class (Figure 17) shows that distance to the coast () is the key variable. When m, the probability of belonging to this class reaches 92%, associated with founding plazas and coastal promenades in central or historical areas. A final branch isolates a subset with a 97% probability, defined by extreme proximity to the traditional road network ( m). Overall, the model highlights that preservation of these spaces depends on normative zoning and integration into the urban fabric, emphasizing the need for specific policies that recognize them as structural components of the urban landscape and as supports of collective memory [56].

Figure 17.
Decision tree for the Historical Open Space class. VE1: Distance to the Historical Network (m); VE2: Distance to Beach (m).
The decision tree for the “New” class (Figure 18) indicates that distance to the coast ( m) is the primary determinant, as properties located beyond this threshold show a high probability of being classified as “New” while those closer to the coastline rarely meet this condition, reflecting the peripheral pattern of urban growth on formerly rural or undeveloped land [57]. A secondary rule introduces the variable m, which reduces the likelihood of belonging to this class for properties adjacent to major roads, since these peri-urban strips are often designated for industrial or logistic uses rather than new residential developments. Overall, the model identifies new urbanization beyond 500–600 m from the coastline in unprotected areas, consistent with planning approaches aimed at defining clear limits for consolidated urban fabric and managing transitions to control uncontrolled growth and safeguard heritage around historical sites [56,57].
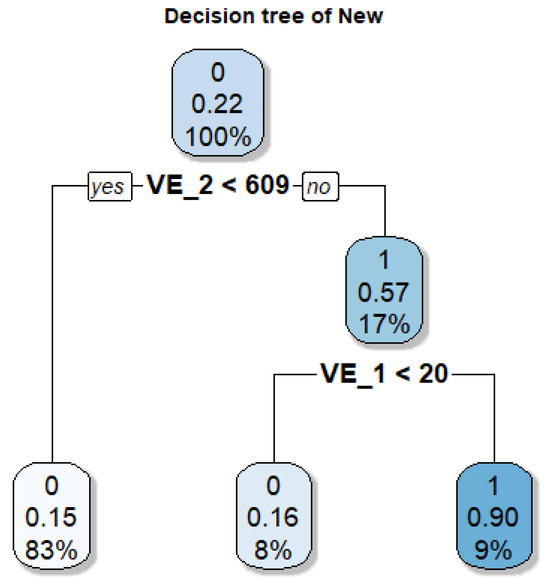
Figure 18.
Decision tree for the New class. VE1: Distance to the Historical Network (m); VE2: Distance to Beach (m).
Relative importance of driving variables
The results presented in Table 4 indicate that physical distances are the most influential variables in predicting land use. In particular, variables (distance to the historical road network) and (distance to the beach) account for between 45% and 67% of the explanatory importance in all the models evaluated. This preeminence suggests that the relative location concerning these structuring axes decisively influences the persistence of or change in land use, in line with the characteristic spatial patterns of radial and coastal development observed in heritage cities [58].

Table 4.
Relative importance of predictor variables (RPART model).
At a second level of relevance are the normative variables. Both (belonging to the HCZ) and (Heritage Protection Zone, HMZ) exhibit high importance in the models of the “Historical Productive” class and, to a lesser extent, in the “Historical” and “Historical Open Space” classes. This pattern highlights the role of these normative categories as territorial filters that restrict or favor certain land uses based on their recognized heritage value [58].
4.3.2. Random Forest Analysis
The variable importance analysis (Table 5) shows that, for the “Historical” class, distance to the “Historical Road Network” () accounts for 51% of explanatory power, confirming the structuring role of the foundational network [59]; for the “Historical Productive” class, the most influential variable is hmz (64.9%), highlighting the effectiveness of zoning regulations in preserving industrial heritage; for the “New” class, distance to the coast (58.5%) and distance to the “Historical Road Network” (30.3%) dominate, reflecting post-industrial urban expansion toward less regulated peripheral areas; finally, in the “Historical Open Spaces” class, distance to the coast () reaches 70.7%, emphasizing the historical coastal orientation of urbanization and the need to protect these areas for both their environmental and cultural value.

Table 5.
Relative importance of predictor variables in RF (%).
4.3.3. Logistic Regression Analysis
This section analyzes the results of the LR model applied to the four land-use classes. Table 6 summarizes the results obtained for this analysis.

Table 6.
Coefficients and odds ratios (ORs) of the LR model by land-use class. Coefficients marked with * are statistically significant ().
- Historical. The model for the Historical use category reveals that proximity to the foundational road network () is the most influential factor (, ): each additional meter of distance reduces the probability of belonging to this class by about 6%, confirming the concentration of heritage around the original roads and the role of accessibility in the permanence of land uses [45]. In contrast, distance to the beach () shows no relevant effect (coefficient close to zero, ). Among the zoning variables, the HCZ () has a significant positive effect (coefficient = , , ), whereas the Historic Heritage Zone (hmz, ) is not statistically significant. Conversely, SZC () presents a strong negative effect (coefficient = , , ), consistent with the predominance of contemporary activities along the coastline that displace traditional urban structures. Furthermore, the results confirm the need to direct urban growth away from heritage cores in order to prevent the erosion of the city’s historical identity [60].
- Historical Open Space. In the “Historical Open Space” class, distance to the old road network () shows a small but significant positive effect, reflecting the location of many founding squares on the edges of the historic core, while proximity to the coastline () is associated with a higher presence of such spaces, consistent with coastal promenades and parks. In contrast, belonging to a HCZ () significantly reduces the probability of this use (), due to regulatory criteria that prioritize architectural complexes over green areas, whereas neither hmz nor SZC present significant effects. These results reveal a regulatory gap, as the frequent exclusion of historic open spaces from formal protection schemes, such as HCZs, may lead to their abandonment, fragmentation, or change of use [61].
- Historical Productive. In the Historical Productive category, distance to the historic road network (, , ) slightly increases the probability of this use (4% higher odds per 100 m), while distance to the sea (, , ) shows that proximity to the coastline reinforces it, consistent with the port or riverside location of many founding industrial complexes. Regarding zoning, hmz () and HCZ (, ) are not significant, whereas the SZC displays a very large and highly significant coefficient (=5.11, , ), confirming that almost all historic productive uses are concentrated along the coastal border. This pattern aligns with international strategies for waterfront regeneration and industrial heritage recovery, which reconcile the conservation of the productive legacy with contemporary dynamics of urban transformation [62].
- New. The model for “New” land use shows a pattern largely opposite to that of historic uses: distance to the founding road network () moderately increases the probability of new developments (5% per 100 m), evidencing their location in peripheral areas structured by modern roads; meanwhile, distance to the coast () indicates that they tend to occur slightly further inland than historic uses. Among zoning variables, HCZ () shows that modern uses are also present within heritage-protected areas, while SZC () confirms its role as an active hub of recent urban expansion; in contrast, hmz () is not significant. These findings reinforce the need for a balanced planning approach: effectively protecting historic environments while guiding growth toward appropriate areas [60], recognizing that urban heritage can serve as a catalyst for sustainable revitalization if managed strategically and in an integrated manner [61].
To assess the presence of residual spatial dependence, Moran’s I was calculated for each class from the residuals of the final logistic regression models. The results (Table 7) show a strong and highly significant positive spatial autocorrelation in all categories: Historical (, p < 0.001), Historical Open Space (, ), Historical Productive (, ), and New (, ). These values confirm that the residual patterns are not randomly distributed in space, suggesting that spatial structures persist that were not fully captured by the model. This finding highlights the need to integrate explicit spatial approaches—such as autoregressive models or more complex spatial weights-based methods—to improve explanatory power and inferential validity in heritage urban contexts.

Table 7.
Moran’s I for residuals of the logistic regression models.
The results reveal that Logistic Regression models do not adequately capture the spatially structured components present in heritage dynamics. While the coefficients and likelihood ratios provide valuable information about the direction and magnitude of each variable’s effect, their interpretation must be approached with caution due to this inherent limitation. This does not invalidate the explanatory use of Logistic Regression—particularly useful for evaluating regulatory effectiveness and estimating marginal effects—but it illustrates that the transformation of urban heritage is guided by spatial patterns that extend beyond the scope of fully interpretable statistical models. Consequently, the need to complement these approaches with methods capable of explicitly representing spatial dependence is reinforced, aiming to improve accuracy and more comprehensively capture the underlying territorial structure.
5. Discussion
The results of this comparative study demonstrate that the analyzed methods , and offer complementary contributions to understanding land-use changes in heritage urban contexts, such as the Bellavista neighborhood of Tomé. While stood out for its high predictive accuracy, both and presented advantages in terms of interpretability, an essential quality for supporting urban planning decisions based on evidence that is understandable to multiple stakeholders [45,59].
5.1. Performance
In terms of predictive performance, the results indicate that the Random Forest model is the most robust and consistent for identifying transformation patterns in heritage urban contexts [63,64]. Its ability to capture non-linear interactions and complex spatial structures allowed it to maintain high performance both in cross-validation (average accuracy = 0.90; F1 = 0.82; = 0.75) and in the test set (Accuracy = 0.98; F1 = 0.96; = 0.95 in the New category), consolidating itself as the alternative with the greatest stability and generalisation to support urban planning processes in heritage contexts [18,21].
presented significant limitations in categories with imbalance or non-linear relationships, as evidenced in Open Space Historical, where it achieved a of only 0.26 and an F1 of 0.44 in cross-validation. The RPART model showed intermediate performance overall but stood out particularly in this category, achieving an accuracy of 0.92, a of 0.66, and an adequate balance between sensitivity (0.61) and specificity (0.98), suggesting that its hierarchical structure was particularly effective at capturing perimeter patterns in areas with well-defined edges. Likewise, the results revealed instances of structural overfitting, especially in the category, where high collinearity between the dependent variable and heritage regulations generated near-perfect metrics that do not necessarily translate into a high capacity for generalization. Finally, the incorporation of the Youden index (J) allowed for the definition of specific optimal thresholds for each category, avoiding the traditional cutoff point and improving the models’ discriminatory capacity. This refined adjustment strengthened classification coherence and provided a more transparent and defensible methodological criterion for its application in urban and heritage decision-making processes.
5.2. Interpretability
With regard to interpretability, notable differences arise among the approaches. , although less accurate in predictive terms, facilitates the estimation of the marginal effect of each variable using odds ratios, which are essential for quantifying the risks or benefits associated with zoning decisions [45]. This approach is especially useful in public policymaking scenarios, where regulations need to be supported by clear and replicable statistical evidence [57].
In the field of urban planning and heritage conservation, this model offers two key advantages. First, it provides quantitative evidence of the effectiveness of regulatory instruments, allowing for an assessment of whether protected areas actually reduce the risk of territorial transformation. Second, the use of standardized criteria, such as statistical significance and confidence intervals, facilitates communication of results to decision-makers, which is essential for justifying regulatory adjustments, prioritizing vulnerable areas, and supporting conservation interventions based on verifiable evidence. However, it should be noted that the model exhibits significant residual spatial autocorrelation, reflecting the presence of territorial patterns that are not fully captured and constituting an inherent limitation of explanatory models.
Rpart provides significant value for urban planning by translating complex relationships into explicit, hierarchical, and communicable rules [63,65]. Each partition of the tree is linked to a regulatory or morphological threshold, enabling the model’s results to be transparently associated with zoning criteria, land-use restrictions, and buffer zone delimitation. This capability to convert spatial patterns into operational statements (for example, “if the plot is not in a high-protection zone and the distance to the centerline exceeds X meters, then the risk of change increases”) facilitates its integration into territorial management instruments and enhances the traceability of decisions. Overall, Rpart enables the identification of heritage risk areas based on the interaction between regulatory and territorial factors, providing usable evidence to prioritize interventions and guide conservation policies in heritage urban contexts.
In the Random Forest model, the hierarchy of variables is derived from identifying which predictors most effectively separate cases of change from those of no change—that is, renewal processes versus conservation processes. In practical terms, the importance assigned by the Random Forest (RF) indicates which territorial factors have the greatest discriminatory capacity to differentiate areas where the territory tends to remain stable from those where consistent patterns of urban transformation emerge. This prioritization constitutes a strategic input for planning, as it allows for focusing interventions on areas with greater heritage vulnerability and adjusting urban regulations based on quantitative and reproducible evidence. Thus, the model not only improves the understanding of the drivers of change but also strengthens the transparency of the decision-making process by offering objective criteria to guide conservation and land management policies.
5.3. Performance vs. Interpretability
Overall, as summarized in the Table 8, the results indicate that there is no universally optimal model; rather, the selection depends directly on the analytical objective and the type of evidence required by the planning processes. If the central purpose is to maximize predictive robustness and capture complex territorial patterns, the Random Forest model emerges as the most consistent alternative. When the focus is on quantifying marginal effects and rigorously evaluating the effectiveness of regulatory instruments, Logistic Regression offers irreplaceable advantages due to the clarity and traceability of its coefficients and odds ratios. Finally, if the goal is to communicate understandable and directly applicable decision rules in planning instruments—especially in contexts with perimeter structures or defined regulatory boundaries—Rpart is the most suitable tool because of its ability to translate complex relationships into explicit thresholds. Consequently, the methodological choice must align with specific management needs: prediction, explanation, or regulatory communication, understood as complementary dimensions that, together, strengthen evidence-based urban planning and heritage conservation.

Table 8.
Comparison of the , , and methods, highlighting their advantages, limitations, and usefulness for modeling land-use change in heritage urban contexts.
From an urban planning perspective, these findings suggest that modeling land-use change in heritage areas should combine approaches by integrating the predictive capacity of advanced algorithms with the readability of simpler models. This combination favors more effective urban heritage management by coordinating technical knowledge with regulatory frameworks and social participation [7,53,55,61].
6. Conclusions and Future Works
In this work, we demonstrate the importance of comparatively evaluating different models to address specific issues in heritage planning and conservation. The study focuses on the Bellavista neighborhood of Tomé, a historic district where this type of analysis had not been previously applied. We analyze three main models (Random Forest, Logistic Regression, and RPART) and compare them not only in terms of predictive capacity but also regarding how each translates territorial factors into useful information for urban managers and conservationists. This dual approach, both predictive and interpretive, allows for a deeper understanding of the dynamics of urban transformation and their relationship to the area’s heritage vulnerability.
The aim was to determine how the different explanatory frameworks offered by these models can support the identification of heritage risks, the evaluation of regulatory effectiveness, and the prioritization of interventions in historic urban environments. The main findings regarding the performance and interpretability of the models are as follows: first, the Random Forest model can serve as an early warning system to identify critical areas of urban transformation, establishing a solid foundation for guiding territorial monitoring and prioritizing preventive interventions; second, Logistic Regression is a particularly valuable tool for evaluating the effectiveness of heritage protection zones, as its coefficients and likelihood ratios allow for rigorous quantification of the influence of each regulatory and morphological factor on changes; third, the RPART model stands out for its ability to translate spatial patterns into explicit regulatory rules, facilitating their direct incorporation into urban planning instruments such as regulatory plans, buffer zones, and differentiated densification criteria. Together, these approaches constitute a complementary and replicable methodological framework that enhances evidence-based urban decision-making and heritage management.
Future research should delve deeper into the multiscale validation of models through their comparative application in different cities. This would allow for the evaluation of their performance under varying regulatory, morphological, and territorial dynamics. It is also pertinent to integrate information sources from participatory processes (such as citizens’ perceptions of heritage value, everyday practices, and informal land use) in order to capture social dimensions that traditional spatial models do not typically represent. It is also relevant to incorporate post hoc analyses, such as SHAP values, which allow the contribution of each variable to the model’s result to be broken down. Incorporating these inputs would enhance the robustness and territorial sensitivity of the proposed approaches, strengthening their capacity to adapt to changing urban contexts and contributing to more comprehensive, inclusive, and evidence-based heritage planning.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.G.-A.; methodology, P.G.-A.; software, P.G.-A.; validation, P.G.-A., M.I.L. and C.R.-M.; formal analysis, P.G.-A., M.I.L. and C.R.-M.; investigation, P.G.-A., M.I.L. and C.R.-M.; resources, P.G.-A., M.I.L. and C.R.-M.; data curation, P.G.-A.; writing—original draft preparation, P.G.-A.; writing—review and editing, C.R.-M.; visualization, P.G.-A. and C.R.-M.; supervision, M.I.L. and C.R.-M.; project administration, P.G.-A. and C.R.-M.; funding acquisition, P.G.-A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the PhD Program of Economics and Information Management (Faculty of Business Science—University of Bío-Bío), Nucleus Millennium Project NupatS NCS2024_014 and Fondecyt Regular 1190992.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Pseudocode Scheme of the Spatial Land-Use Change Modelling
| Algorithm A1: Pseudocode Scheme: Spatial Land-Use Change Modelling: Steps 1 and 2 |
 |
| Algorithm A2: Pseudocode Scheme of the Spatial Land-Use Change Modelling: Steps 3, 4, 5 and 6. |
 |
References
- Wolfram, M.; Borgström, S.; Farrelly, M. Urban transformative capacity: From concept to practice. Ambio 2019, 48, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, H.; Singh, M.K.; Gupta, M.P.; Madaan, J. Moving towards smart cities: Solutions that lead to the Smart City Transformation Framework. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2020, 153, 119281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, M.; Lloyd, S.; Haines, A.; Ding, D.; Hutchinson, E.; Belesova, K.; Davies, M.; Osrin, D.; Zimmermann, N.; Capon, A.; et al. Transforming cities for sustainability: A health perspective. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardopoulos, I. Industrial building adaptive reuse for museum. Factors affecting visitors’ perceptions of the sustainable urban development potential. Build. Environ. 2022, 222, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bastawissi, I.Y.; Raslan, R.; Mohsen, H.; Zeayter, H. Conservation of Beirut’s urban heritage values through the historic urban landscape approach. Urban Plan. 2022, 7, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnsour, J.; Arabeyyat, A.; Hyasat, A.; Al-Habees, M.; Aldweik, R. The Impact of Urbanization on Cultural Heritage Buildings in Jordan: As-Salt as a Case Study. Future Cities Environ. 2023, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, B.; Kloos, M.; Reicher, C. Heritage Impact Assessment Index Within Urban Development Context: The Case of Masjed-e Jame of Isfahan in Iran. Heritage 2024, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H. Impact of Urbanization on Cultural Heritage: A Quantitative Analysis. Adv. Educ. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Res. 2024, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cheng, R.; Dan, Y.; Wang, L. Cultural Heritages Lead to Less Dense and Greener Cities—Evidence from 371 Chinese Cities. Land 2025, 14, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nations, U. Transforming Our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. 2015. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/2030agenda (accessed on 5 June 2025).
- Jokilehto, J. A History of Architectural Conservation; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Lin, F.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Spatial Planning Strategies for Urban Ecology and Heritage Conservation in Macau: An Investigation of Ultra-High-Density Cities. Information 2024, 15, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, C.; Green, G.M.; Grove, J.M.; Evans, T.P.; Schweik, C.M. A Review and Assessment of Land-Use Change Models: Dynamics of Space, Time and Human Choice; CIPEC Collaborative Report Series 1; Indiana University and USDA Forest Service: South Burlington, VT, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, F.; Guo, F.; Cai, J.; Dong, J. Urban built heritage protection and realistic dilemmas: The development process, protection system, and critical thinking of historic districts in Dalian. Built Herit. 2023, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandarin, F.; Van Oers, R. The Historic Urban Landscape: Managing Heritage in an Urban Century; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, Q. Assessment of urbanization impact on cultural heritage based on a risk-based cumulative impact assessment method. Herit. Sci. 2023, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J.F.; Paegelow, M.; Camacho-Olmedo, M.T.; Houet, T. Modelling land use/cover changes: A comparison of conceptual approaches and software. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 51, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Z. Integrating multi-source urban data with interpretable machine learning for uncovering the multidimensional drivers of urban vitality. Land 2024, 13, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, W.; Meng, Z.; Liu, X. Review of land use change detection—A method combining machine learning and bibliometric analysis. Land 2023, 12, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Reenberg, A. Rethinking Global Land Use in an Urban Era; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, B.; Liu, J.; Shen, Y. Land-Use Evolution and Driving Forces in Urban Fringe Archaeological Sites: A Case Study of the Western Han Imperial Mausoleums. Land 2025, 14, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, A.; Soltani, A.; Abdi, M.H.; Zarei, M. Driving forces behind land use and land cover change: A systematic and bibliometric review. Land 2022, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tong, X. Using exploratory regression to identify optimal driving factors for cellular automaton modeling of land use change. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Chen, Z.; Huang, J. Predicting urban expansion to assess the change of landscape character types and its driving factors in the mountain city. Land 2023, 12, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L. Land Use Change in the Russian Far East and Its Driving Factors. Land 2025, 14, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, J.; Djordjević, S.; Chen, A.S. Using public participation within land use change scenarios for analysing environmental and socioeconomic drivers. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sikder, S.; Omrani, H.; Teller, J. Cellular automata in modeling and predicting urban densification: Revisiting the literature since 1971. Land 2022, 11, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z. Effects of land-use change on carbon emission and its driving factors in Shaanxi Province from 2000 to 2020. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 68313–68326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, C. Interpretable Machine Learning: A Guide for Making Black Box Models Explainable. 2022. Available online: https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/ (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Doshi-Velez, F.; Kim, B. Towards a rigorous science of interpretable machine learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1702.08608v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, W.J.; Singh, C.; Kumbier, K.; Abbasi-Asl, R.; Yu, B. Interpretable machine learning: Definitions, methods, and applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22071–22080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C. Stop explaining black box machine learning models for high stakes decisions and use interpretable models instead. Nat. Mach. Intell. 2019, 1, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, A.; Lambin, E.F. Predicting land-use change. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 85, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, G.R.; Malanson, J. Comparison of the structure and accuracy of two land change models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2005, 19, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sánchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Atkinson, B.; Ripley, B. rpart: Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees. R Package Version 4.1.23. 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rpart (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Ribeiro, M.T.; Singh, S.; Guestrin, C. “Why Should I Trust You?”: Explaining the Predictions of Any Classifier. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 1135–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.A.; Stone, C.J. Classification and Regression Trees; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Quantifying the spatio-temporal process of township urbanization: A large-scale data-driven approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Arroyo, M.; Gómez-Martínez, M.A.; Back, M.; Setälä, H.; MacGregor-Fors, I. Urban gradient resolution matters! Avian diversity patterns in a boreal green city. Urban Ecosyst. 2025, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, D.R.; Edwards, T.C., Jr.; Beard, K.H.; Cutler, A.; Hess, K.T.; Gibson, J.; Lawler, J.J. Random forests for classification in ecology. Ecology 2007, 88, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dehghani, A.; Soltani, A.; Nateghi, K. Balancing Urban Growth and Environmental Change: Land Use Patterns in Tehran and Sydney. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2025, 26, 100691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getu, K.; Bhat, H.G. Application of geospatial techniques and binary logistic regression model for analyzing driving factors of urban growth in Bahir Dar city, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, S. Applied Logistic Regression Analysis; SAGE Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fluss, R.; Faraggi, D.; Reiser, B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Johnson, K. Applied Predictive Modeling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. randomForest: Breiman and Cutler’s Random Forests for Classification and Regression. R Package Version 4.7-1.1. 2002. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=randomForest (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Murray-Rust, N.J.; Rounsevell, M.D.A. lulcc: Land Use Change Modelling in R. R Package Version 1.1-8. 2014. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=lulcc (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- Robin, X.; Turck, N.; Hainard, A.; Tiberti, N.; Lisacek, F.; Sanchez, J.-C.; Müller, M. pROC: Display and Analyze ROC Curves. R Package Version 1.18.5. 2011. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=pROC (accessed on 3 March 2024).
- González-Albornoz, P.; López, M.I.; Carmona, P.; Rubio-Manzano, C. Digitalization and Spatial Simulation in Urban Management: Land-Use Change Model for Industrial Heritage Conservation. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera Ojeda, R.; López Meza, M.I.; Morales Ortiz, M.F. Procesos Contemporáneos de Activación Patrimonial: Tensiones, Disputas y Consensos Entre Las Comunidades. El Caso de Bellavista en Tomé, Chile; SciELO Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2021; pp. 195–217. [Google Scholar]
- López Meza, M.I.; Carrasco, J.A.; Herrera, R.; Morales, M.F.; Medel, M. Mapa de Actores Sociales y Espacios Patrimoniales en Conflicto. El Caso de Los Barrios Post-Industriales de Tomé, Chile; SciELO Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2023; pp. 123–144. [Google Scholar]
- López Meza, M.I.; Carrasco, J.A.; Herrera Ojeda, R.; Allende, P. Red de Actores y Patrimonialización de Barrios Post-Industriales: Bellavista Tomé en Chile, 2008–2017; SciELO Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2023; pp. 18–40. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Zhou, T.; Han, Y.; Ikebe, K. Urban heritage conservation and modern urban development from the perspective of the historic urban landscape approach: A case study of Suzhou. Land 2022, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al shawabkeh, R.; AlHaddad, M.; al_fugara, A.; Arar, M.; Alhammad, R.; alshraah, M.; alhamouri, M. Toward sustainable urban growth: Spatial modeling for the impact of cultural and natural heritage on city growth and their role in developing sustainable tourism. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 69, 639–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttormsen, T.S.; Skrede, J.; Guzman, P.; Fouseki, K.; Bonacchi, C.; Pastor Pérez, A. Assemblage urbanism: The role of heritage in urban placemaking. J. Cult. Herit. Manag. Sustain. Dev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Dang, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, S. Multi-scenario simulation of urban land change in Shanghai by random forest and CA-Markov model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 55, 102045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martell, C.A.R.; Chujandama, M.P.C.; Lazo, K.M.A. Uso de Suelo Urbano y la Conservación del Inmueble en el Barrio San Pedro En Chazuta. Cienc. Lat. Rev. Científica Multidiscip. 2024, 8, 3421–3436. [Google Scholar]
- Ripp, M.; Clifford, J. Heritage-Based Urban Development. Encyclopedia 2025, 5, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Wang, S.; Cheng, A. Industrial heritage and urban renewal: A quantitative study and optimization strategies for Chengdu East Suburb Memory. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1537211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yadari, M.; Jawab, F.; Moufad, I.; Arif, J. Logistics Sprawl and Urban Congestion Dynamics Toward Sustainability: A Logistic Regression and Random-Forest-Based Model. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Z. Evaluating the change and trend of construction land in Changsha City based GeoSOS-FLUS model and machine learning methods. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Shaokang, L. Explainable Artificial Intelligence for Urban Planning: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Trends from a New Perspective. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).