Abstract
Infection with Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) occurs in 50% of the world population, and is associated with the development of ulcer and gastric cancer. Serological diagnostic tests indicate an H. pylori infection by detecting antibodies directed against H. pylori proteins. In addition to line blots, multiplex assay platforms provide smart solutions for the simultaneous analysis of antibody responses towards several H. pylori proteins. We used seven H. pylori proteins (FliD, gGT, GroEL, HpaA, CagA, VacA, and HP0231) and an H. pylori lysate for the development of a multiplex serological assay on a novel microfluidic platform. The reaction limited binding regime in the microfluidic channels allows for a short incubation time of 35 min. The developed assay showed very high sensitivity (99%) and specificity (100%). Besides sensitivity and specificity, the technical validation (intra-assay CV = 3.7 ± 1.2% and inter-assay CV = 5.5 ± 1.2%) demonstrates that our assay is also a robust tool for the analysis of the H. pylori-specific antibody response. The integration of the virulence factors CagA and VacA allow for the assessment of the risk for gastric cancer development. The short assay time and the performance of the platform shows the potential for implementation of such assays in a clinical setting.
1. Introduction
Evalution™ (MyCartis, Zwijnaarde, Belgium) is a novel microfluidic assay platform, which allows the multiplexing of up to 150 individual particle populations, combined with advantageous conditions given by the microfluidic format and a short assay time [1]. Using different antigens immobilized on individual particle populations makes multiplex serology possible.
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori, HP) is a globally widespread Gram-negative bacterium with high prevalence (70–90%) in developing countries and lower prevalence (25–50%) in developed countries [2]. Infection of the human stomach with H. pylori leads initially to an asymptomatic chronic gastric inflammation, which can be followed by development of an atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer [2,3]. Therefore, H. pylori was declared as a type I carcinogen in 1994 [4]. Depending on the presence or absence of the virulence factor cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) and the vacuolating cytotoxin gene A (VacA) alleles determining cytotoxicity [5], H. pylori strains can be classified into type I or type II strains, whereof type I strains express the virulence factor CagA and produce the more cytotoxic variant of VacA, while type II strains do not [6]. Infection with type I strains increases the risk for development of gastric cancer [7]. The infection with H. pylori can be detected by invasive (via endoscopy and biopsy) and non-invasive (stool antigen test (SAT), urea breath test (UBT), and serology) methods. SAT and UBT have the advantage of indicating current, ongoing infection, but both tests are affected by several parameters, such as colonization density, nutrition, other bacteria present in the gastrointestinal tract, and co-medication, and thus, can produce false negative, as well as false positive results. Serology is mostly independent of these confounding factors, but can usually not differentiate past from present infection. However, due to the possibility of high throughput formats, serology can be used for population-based screening approaches. Moreover, certain antibody responses have been correlated with the presence of more severe gastric disease, and may thus have prognostic implications [8,9]. Thus, serologic assays which enable the analysis of multiple antibody responses in parallel from many patients may serve as a valuable tool for population-based screening and risk assessment.
Here we present the development and technical validation of a multiplex serological H. pylori assay using seven purified H. pylori proteins, a whole lysate of H. pylori, and three internal controls. In addition to the virulence factors CagA and VacA, the flagellar hook-associated protein 2 homologue (FliD) has been described as a sensitive marker for immunodetection of H. pylori [10]. The H. pylori gama-Glutamyltranspeptidase (gGT) is a virulence factor involved in immune evasion [11], the chaperonin GroEL was described as a biomarker for gastric cancer [12], H. pylori adhesin A (HpaA) is an adhesion protein involved in colonization [13], and the H. pylori oxidoreductase DsbK regulates several bacterial virulence factors [14]. Some of these proteins had previously been employed in serologic assays [9]. The assay was subsequently used to analyze serum samples of patients being negative, positive, or eradicated for H. pylori infection. In addition, analysis of the serological response of H. pylori positive patients to individual antigens was performed with regard to their disease state.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Technical Platform: Evalution™
All measurements were performed using the new microfluidic platform, Evalution™ (MyCartis, Zwijnaarde, Belgium) as described previously [1]. The central components are the disc-shaped, digitally encoded silicon microparticles, acting as a solid phase for immobilization of capture proteins e.g., antibodies or antigens, and the microfluidic cartridges. Sixteen microscale channels are presented on the cartridge to run up to 16 samples simultaneously or sequentially. Each channel can be loaded with an independent microparticle population or with a mix of several populations coated with different capture molecules. Both a real-time and end-point readout is feasible when imaging the particles in bright field and fluorescence. Each microparticle generates a highly contrasted pixel intensity; each pixel is a result, in total, there are approximately 1800 results per particle. For each population, the arithmetic mean fluorescence intensity of at least 20 particles per population is calculated and given as the population fluorescence (MFI).
Loading station, cartridges, different populations of microparticles, microparticle storage buffer (MCPS), and loading buffer were provided by MyCartis.
2.2. Antigens and Human Sera
Seven affinity-purified H. pylori proteins (FliD (HP_0752), gGT (HP_1118), GroEL (HP_0010), HpaA (HP_0797), CagA (HP_0547), VacA m1 (HP_0887), DsbK (HP_0231), were selected based on their functional importance as H. pylori virulence factors [6,7] or their previously determined functionality for serologic detection (unpublished data) of H. pylori infection. For CagA, the full-length sequence of H. pylori strain P12 was used. This strain was isolated from a duodenal ulcer patient, and contains both the VacA cytotoxin and a functional cag pathogenicity island (cagPAI) [15,16]. The antigens, a whole cell lysate of H. pylori strain 49,503 and three internal controls (human IgG as control for the detection system, goat-anti-human IgG as a control for addition of sample, and E. coli lysate as a control for unspecific binding) were immobilized as capture molecules to analyze the antibody response in 265 sera specimens. The Technical University of Munich (TUM) provided both recombinant antigens and sera. The study cohort is described elsewhere [17], and included random consecutive volunteers undergoing routine upper gastroscopy for gastrointestinal complaints between 2009 and 2012 in Bayreuth, Germany. The diagnosis as positive, negative, or eradicated for a H. pylori infection was determined by Warthin–Starry silver stain. An overview of the retrospective samples is given in Table 1, including information about gender and age of the study population. The study was approved by the ethics committee of the Technische Universität München (20 May 2009). Samples were only used if all necessary clinical information was available and clearly defined.

Table 1.
Overview of samples used in this study.
2.3. Antigen Immobilization
For the multiplex serological detection, a panel of eleven different microparticle populations were coupled with the protein of interest. The immobilization was performed using the MyCartis coupling protocol. Different coupling concentrations were tested and based on the height of the signal intensities and coefficients of variation (CVs) the best coupling concentration was determined. Each protein (120 μg) was coupled to a total number of 120,000 microparticles per population in a volume of 3.6 mL (except for CagA, 85 μg in 2.55 mL) using standard sulfo-NHS/EDC chemistry. Activation of the particles was performed for 1 h with 3.6 mL of activation mix containing 10 mg/mL sulfo-NHS and 50 mg/mL EDC in 100 mM MES + 0.25% (v/v) Tween 20 (pH 3.5). After activation, particles were washed three times with coupling buffer (100 mM MES + 0.25% (v/v) Tween 20; pH 4.9). Proteins were diluted in coupling buffer and incubated for 1 h with the activated particles. After immobilization, excessive protein was washed off with wash buffer (10 mM PBS + 0.25% (v/v) Tween 20). Microparticles were taken up in 3 mL storage buffer (MCPS, MyCartis), merged to a population mix, and aliquoted in an expedient size for longer storage at −20 °C.
2.4. Generation of Quality Control Samples
Different sera were pooled to obtain three different quality control samples (QC1, QC2, and QC3), which together cover low and medium/high ranges of reactivity for every antigen. For pool sample or single serum sample preparation, sera were selected based on their responses towards the chosen antigens using an in-house developed algorithm (based on [18]). The QC sample preparation was done by using positive samples with different antibody responses towards the selected antigens. For QC1 five and for QC2, four sera were pooled in different volume rations. For QC3, a single serum was used, which showed a suitable antibody response profile as a QC sample according to the used algorithm. The final dilution of the QC samples was 1:100 in sample buffer (BRE + 10% E. coli lysate (v/v) + 0.25% Tween 20 (v/v); BRE = Blocking Reagent for ELISA, Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). Ready-to-use QC samples were aliquoted and stored at −80 °C. The quality control samples were measured on each cartridge to ensure assay stability, both in screening and in validation.
2.5. Multiplex Assay Procedure
Serum samples and quality control samples were stored frozen in aliquots at −80 °C. Thawed on ice, samples were vortexed and centrifuged at 4 °C and 3220g for 10 min. Subsequently, samples were diluted 1:100 in sample buffer. For blocking unspecific bindings, a 20 min incubation at room temperature was performed. Meanwhile, a cartridge was filled with the multiplexed population mix using the loading station. A minimum of 20 microparticles per population was used for each measurement. To avoid aggregation or lipid accumulation in channels, samples were filtered by centrifugation for 3 min with 2500g at 4 °C in a filter plate (Pall GmbH, Dreieich, Germany, AcroPrep 96 0.2 μm, PN5042). After removing liquid from the inlet wells of the cartridge, a minimum of 80 μL filtrated sample was transferred to the wells, and microparticles were incubated for 30 min with the sample under a constant flow by applying a differential pressure of 300 mbar between inlet and outlet well. The inlet wells were emptied after incubation time, and filled with 100 μL wash buffer and washed with constant flow for 1 min/300 mbar. Wells were emptied again and filled with 50 μL of the detection antibody (goat-anti-human IgG (Fc) PE, Cat # 109 116 09, Jackson Dianova, Hamburg, Germany) in a final concentration of 5 μg/mL diluted in BRE + 0.25% Tween 20. After incubation of the detection antibody under constant flow for 5 min/300 mbar, again, a wash step was performed. For the final imaging, the last liquid was removed, and the inlet wells were filled with wash buffer. For the readout, each channel was scanned, and the particles were imaged from the bottom of the cartridge in a bright field and fluorescence imaging mode. An evaluated protocol of instrumental settings was used for all measurements: laser power 10 mW, temperature 25 °C/37 °C/37 °C (inlet wells/transit zone/detection zone), exposure time 100 ms, channel flush pressure for reading was 50 mbar. Generated MFI values were exported as an excel file by the Evalution™ Explore software (Version 1.6.6, MyCartis, Zwijnaarde, Belgium, 2015). Every sample had its own sample specific background. MFI values of the antigen carrying microparticles of a sample were corrected by subtracting the MFI value of the E. coli microparticle of the corresponding sample.
2.6. Intra- and Inter-Assay Precision
For the intra-assay precision, two positive and one negative sample were measured in 13 replicates within one run, each sample on one cartridge. For the inter-assay precision, four cartridges with six negative and six positive serum samples were measured on four different days by one operator. Additionally, three quality control samples were measured on each validation cartridge. All results were expressed as mean, standard deviation (SD), and as percentage coefficient of variation (% CV).
2.7. Cutoff Definition and Statistical Analysis
For the statistical analysis, an antigen-specific cutoff was calculated for each antigen. This included the identification of outliers by using the interquartile range (IQR). Values were treated as outliers if values were not between Q1 − 1.5 × IQR and Q3 + 1.5 × IQR. Outliers were excluded from the cutoff calculations. For the calculations, data of 63 H. pylori negative sera were used. Except for FliD, a cutoff for each antigen was defined as the mean MFI of negative sera + X × SD. The individual X for an antigen was determined by best results for sensitivity and specificity at the lowest possible value for X. The best result for the antigens gGT, GroEL, HpaA, CagA, and the H. pylori lysate, was defined by the highest possible value of the sum of sensitivity and specificity. The best result for the antigens VacA and HP0231 was defined by the highest possible specificity. Due to the problem that mean and SD of FliD were zero, an arbitrary cutoff was chosen for FliD. Dividing the antigen-specific MFI value of the samples by the antigen-specific cutoff yielded the signal-to-cutoff (S/CO) ratios. Antigens with a S/CO ratio > 1 were considered to be reactive (positive).
To perform statistical analysis, MFI or S/CO values were used in the software RStudio (Version 3.2.16, RStudio Inc., Boston, MA, USA, 2015) and WEKA (Version 3.8.0, The University of Waikato, Hamilton, New Zealand, 2016). Significant differences between two distributions were shown using the Mann–Whitney U test. Odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were determined, to quantify the association between two properties.
3. Results
3.1. Assay Development and Technical Assay Validation
The incubation times for the samples and the detection antibody were investigated during assay development. Four different incubation times (10/20/30/40 min) were tested for four samples. In Figure 1a,b the results for all H. pylori antigens of two exemplary samples are depicted. Saturation of the signal was not reached for every antigen at the same time point. However, after 30 min of sample incubation, a plateau was achieved for most antigens. To keep the assay as short as possible without loss of sensitivity, 30 min was set as the final incubation time for samples. For examination of the incubation time of the detection antibody, a kinetic for 11 min was performed with measurements at every 30 s (see Figure 1c). Even if not all antigens showed the same MFI value, after 5 min of incubation with the detection antibody, saturation was achieved for all antigens. Therefore, 5 min was set as the final incubation time for the detection antibody.
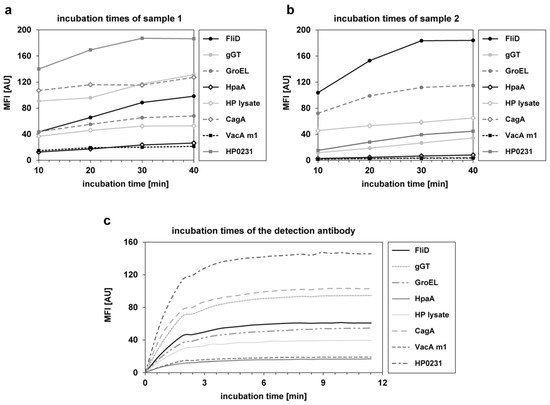
Figure 1.
Investigation of the incubation times for the samples and the phycoerythrin labeled anti-human IgG detection antibody. (a,b) Four different incubation times (10 min, 20 min, 30 min, and 40 min) were tested in four samples. Depicted are the MFI values of all used H. pylori antigens of two samples. (c) Kinetic of incubation with the detection antibody for 11 min. A measurement was performed approximately every 30 s.
After assay development, a technical validation was performed to demonstrate the precision of the assay. Intra- and inter-assay precision of the multiplex serological H. pylori was assigned to a mean intra-assay precision of 3.7 ± 1.2% CV and a mean inter-assay precision of 5.5 ± 3.0% CV across all eight antigens and all samples, thus indicating a stable test system.
3.2. Analysis of Clinical Samples
A total number of 265 serum samples from patients with defined clinical H. pylori status (see Table 1) have been studied with the developed multiplex serological H. pylori assay. Patients had either a negative, positive, or eradicated status for H. pylori infection. The antigens FliD, gGT, GroEL, HpaA, and the H. pylori lysate were chosen for the classification of the H. pylori infection status. CagA and VacA are of high diagnostic significance, as they have been shown to markedly increase the risk for premalignant changes, gastric carcinoma, MALT lymphoma, and ulcers [19,20]. Antigens of these two most important virulence factors were included, as well as the oxidoreductase HP0231. The distribution of antibody reactivity towards the seven H. pylori antigens and one H. pylori whole cell lysate is shown as boxplots in Figure 2. The reactivity of H. pylori negative and H. pylori positive samples were significantly different for all antigens (see p values in Table 2). Also, the comparison of H. pylori positive and H. pylori eradicated samples yielded only p values below the Bonferroni corrected significance level (α′ = 1.25 × 10−3). When H. pylori negative and H. pylori eradicated samples were compared, only VacA m1 and HP0231 provided p values above the significance level. By generation of S/CO ratios, the specificity and sensitivity of every single antigen was calculated. All five antigens for classification into HP negative or positive yielded a specificity >95%, and a sensitivity >82% (see Table 2). The three antigens for patient stratification showed high specificity, but CagA and VacA m1 had a lower sensitivity for the assessment of the infection status compared to the five other antigens. However, sensitivity of HP0231 was relatively high at 84.2%. Besides the H. pylori lysate with the best overall performance in this study, FliD showed the best sensitivity (95.7%) as a single antigen. Using a combined statistical analysis of the S/CO ratios of the four single antigens FliD, gGT, GroEL, and HpaA, a sensitivity of 99.3% could be achieved. Figure 2 indicates that the serological response to the selected antigens, especially FliD, HpaA, and H. pylori lysate, allow a relatively distinct separation of the H. pylori eradicated samples from the H. pylori negative and H. pylori positive samples. Using the five antigens for the classification of the infection status (FliD, gGT, GroEL, HpaA, and the H. pylori whole lysate) in a random forest algorithm together with the H. pylori positive samples, 73% of the H. pylori eradicated samples could be assigned correctly. However, when H. pylori negative, H. pylori positive, and H. pylori eradicated samples were used in a random forest algorithm, only 57% of the H. pylori eradicated samples could be classified correctly.
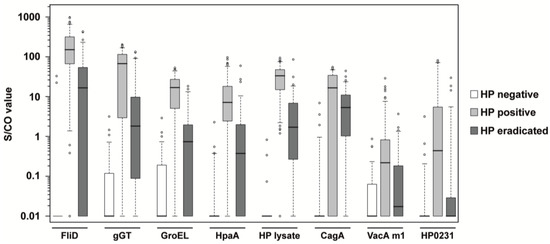
Figure 2.
Boxplots of S/CO values in HP negative, HP positive and HP eradicated samples. Every box represents the interquartile range and the horizontal line inside the box is the median. Whiskers show the 5th and the 95th percentiles. Outliers are plotted as circles. For every antigen, the S/CO values of H. pylori negative samples (n = 63) are shown in white boxes, H. pylori positive samples (n = 139) are shown in light gray boxes, and samples of patients being eradicated for H. pylori (n = 63) are shown in dark gray boxes.

Table 2.
Cutoff values, p values, specificity and sensitivity of every antigen in the multiplex H. pylori assay.
The group of H. pylori positive samples contained subcategories of different disease state: asymptomatic, atrophy (chronic atrophic gastritis), intestinal metaplasia, and ulcer. Atrophy or intestinal metaplasia status is considered to be a premalignant condition, bearing an increased risk for gastric cancer development [21]. Antibody response to CagA, VacA m1, and HP0231 of the H. pylori positive samples were examined in more detail. The S/CO distribution differs for the subgroups (Figure 3); most of the groups showed very heterogeneous S/CO values, but the variance for CagA in the intestinal metaplasia group was more distinct. ORs, as well as 95% Cis, were calculated for the comparison of the different H. pylori positive subgroups (Table 3). The ORs of CagA (5.3) and VacA m1 (6.7) were significant in the comparison of the asymptomatic group with the atrophic group. In the comparison of the asymptomatic group with the intestinal metaplasia group, an even higher OR of CagA (6.0) was observed. In contrast, the OR of VacA m1 (1.7) decreased, and was not significant anymore. By taking the atrophic group and the intestinal metaplasia group together to a group called premalignant changes, CagA was still significant with an OR of 5.9 and a 95% CI of 2.2–15.4, but VacA m1 was not significant. HP0231 showed sometimes ORs > 1, but they were not significant. ORs in the comparison of the asymptomatic with the ulcer group were for CagA and VacA m1 greater than 1, but also not significant.
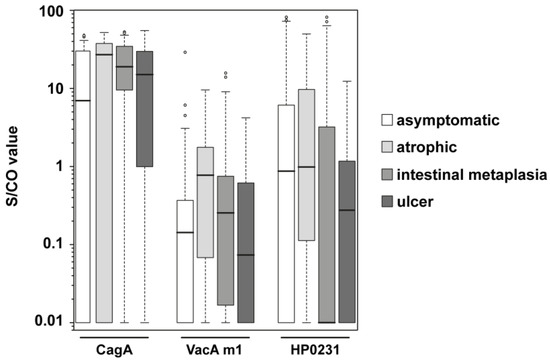
Figure 3.
Boxplots of S/CO values of CagA, VacA m1 and HP0231 in different subgroups of HP positive samples. Every box represents the interquartile range and the horizontal line inside the box is the median. Whiskers show the 5th and the 95th percentiles. Outliers are plotted as circles. S/CO values of IgG responses towards CagA, VacA m1, and HP0231 are shown for H. pylori positive asymptomatic samples (n = 66; white boxes), H. pylori positive atrophic samples (n = 18; light gray boxes), H. pylori positive intestinal metaplasia samples (n = 41; gray boxes) and H. pylori positive ulcer samples (n = 14; dark gray boxes).

Table 3.
Odds ratios and confidence intervals of different patient groups.
4. Discussion
During assay development, the incubation times for the samples and the detection antibody were optimized in order to keep them as short as possible, without a loss of sensitivity. The microfluidic system allows a short assay protocol, with a 35 min assay incubation time in total. This is less than one third of the assay time needed in other commercially available immunoblot systems. Besides a high technical assay precision, very good results were achieved for specificity and sensitivity of the selected antigens. The H. pylori lysate showed the best sensitivity (99.3%) and specificity (100%) in this study, and the overall performance was better compared to other commercial tests (claimed in the test manual), which also use a H. pylori lysate, e.g., anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG (Orgentec Diagnostika GmbH, Main, Germany) or Helico Blot 2.1 (MP Biomedicals Asia Pacific Pte Ltd., the Cavendish Singapore Science Park, Singapore). In comparison to another multiplex serological assay by Michel et al. [22], which showed 89% sensitivity and 82% specificity, we received higher sensitivity and specificity for FliD and the H. pylori lysate. The other antigens for sample classification used in our assay yielded lower sensitivity (82.0–87.1%) than Michel et al. [22], but higher specificity (95.2–97.4%). The clinical classification as positive or negative for an H. pylori infection of these samples was determined by Warthin–Starry silver stain, after taking a biopsy, and not by serology. Therefore, a comparison of sensitivity and specificity of our assay with a non-invasive clinical classification method (e.g., ELISA) was not possible. However, sensitivity and specificity of the different H. pylori antigens and the lysate in our assay should be confirmed with another set of samples positive and negative for H. pylori.
FliD showed the best sensitivity (95.7%) as a single antigen, but also, 2 of 63 H. pylori negative samples were reactive to FliD, giving the specificity of 96.8%. Exactly these two samples showed also reactivity towards one other H. pylori antigen. Therefore, we suspect that these two H. pylori negative patients had a former H. pylori infection, which was eradicated or lost a long time ago. The H. pylori lysate is probably not sensitive enough to detect this low reactivity. However, a reduced sensitivity for CagA and VacA m1 was expected due to the fact that these antigens are virulence factors, and not expressed by each H. pylori strain [23].
Although the seroresponses to FliD, HpaA, and H. pylori lysate allowed a relative distinct separation of the H. pylori eradicated samples, classification using a random forest algorithm achieved only 57% correctly classified H. pylori eradicated samples. The reasons, therefore, could be on the one hand, the very diverse time points of H. pylori eradication (i.e., samples were taken between 1 and 17 years after eradication), and on the other hand, the individual decline of antibody titers in the different patients, which is dependent on the antibody baseline before eradication [24,25]. The described study was not a prospective trial planned to analyze serum samples at a fixed time point after eradication, but to analyze patient serum samples retrospectively from a cohort of patients undergoing gastroscopy. As patient enrolment and sample acquisition is difficult, due to limited patient numbers, exclusion of serum samples outside of a pre-selected time window after eradication would have substantially diminished the number of analyzed samples below a critical threshold. Using samples obtained before and after eradication of the same patient might allow for definition of a decline rate, e.g., 25% [25], as an indicator of a successful eradication. However, antibodies directed against CagA can be detected also for a very long time after H. pylori eradication [26,27], which we confirmed in our findings: CagA seropositivity was the most frequently reactive (76.2%) in the samples from eradicated individuals.
Our study on the subgroups of the H. pylori positive samples showed a strong correlation of gastric pathologies (atrophy or intestinal metaplasia) with the seropositivity for CagA. VacA m1 seropositivity was, in our study, more predictive for atrophic than for intestinal metaplasia samples, which was also observed by Pan et al. [28]. Gwack et al. [29] analyzed H. pylori positive patients with or without gastric cancer, and could observe, only for CagA, and not for VacA, a significant OR. We assume that even if VacA seems to have a correlation with chronic atrophic gastritis, as seen in our study and by Pan et al. [28] as well as by Gao et al. [30], there is no direct relation to gastric cancer [29], and only CagA has relevance in estimations of the risk for developing gastric cancer. However, the received ORs for CagA and VacA m1 in the atrophic group were in the same range as reported by Gao et al. [30], but in contrast to Gao et al. [30], we could not observe significant ORs for the seroresponse to antigen HP0231. Furthermore, CagA seropositivity could also be associated with ulcer (OR = 2.5) as observed in our study, which is in accordance with previous studies [31,32], but the 95% CI did not show a significance. However, it has to be mentioned that high variability of the S/CO values in the different groups was observed, and due to small sample sets, 95% CIs were very broad.
In summary, we developed a multiplex serological H. pylori assay, which is a robust, specific, and sensitive approach for the analysis of the H. pylori-specific antibody response. Through the integration of the virulence factors CagA and VacA m1, it was possible to study the correlation with development of gastric cancer. Seropositivity of CagA was associated with an approximately six times higher risk for premalignant changes in comparison to H. pylori positive patients, without expression of the virulence factor CagA (CagA seronegative patients). Therefore, it is possible to make estimations about the risk for gastric cancer based on the CagA antibody reactivity of serum samples without the need of a biopsy and long-lasting culturing of bacteria. Altogether, the Evalution™ platform is an excellent technology for multiplex serological assay development, especially to keep incubation times as short as possible, which we demonstrated with our developed multiplex H. pylori assay. The very short assay time and the relatively small instrument would allow the implementation of the assay as a point of care testing, and at the same time, allows the analysis of multiple samples in parallel.
Acknowledgments
We thank Thomas Koelblen for technical assistance with protein purification. L.T. is supported by ANR sintesys, fondation ARC and Fondation pour la recherche médicale.
Author Contributions
A.F., A.G., T.O.J. and N.S.M. conceived and designed the experiments. A.G., T.O.J. and N.S.M. supported A.F. in writing the manuscript; A.G. performed the experiments; A.F. analyzed the data; H.P. supported all data analysis of the multiplex serological assay; F.T., J.S., L.F., L.T., M.G. and H.M. contributed reagents, samples and materials and supported A.F. in writing the manuscript; A.F. was the lead in writing the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The Natural and Medical Sciences Institute at the University of Tuebingen (NMI) received partial funding for this study. A.F., A.G., H.P., T.O.J. and N.S.M. are/were employees of the NMI. F.T. was and J.S. is an employee of MyCartis (Zwijnaarde, Belgium). F.T. and J.S. (MyCartis) had no influence on the experimental processing and data evaluation. MyCartis provided the instrument, cartridges and microparticles. L.F, L.T., G.M. and H.M. have no conflict of interest.
References
- Falconnet, D.; She, J.; Tornay, R.; Leimgruber, E.; Bernasconi, D.; Lagopoulos, L.; Renaud, P.; Demierre, N.; van den Bogaard, P. Rapid, sensitive and real-time multiplexing platform for the analysis of protein and nucleic-acid biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, B.E.; Cohen, H.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1997, 10, 720–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iarc Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Schistosomes, Liver Flukes and Helicobacter Pylori. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1994; Volume 61, pp. 1–241. [Google Scholar]
- Atherton, J.C.; Cao, P.; Peek, R.M., Jr.; Tummuru, M.K.; Blaser, M.J.; Cover, T.L. Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of helicobacter pylori. Association of specific vaca types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17771–17777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Z.; Censini, S.; Bayeli, P.F.; Telford, J.L.; Figura, N.; Rappuoli, R.; Covacci, A. Analysis of expression of caga and vaca virulence factors in 43 strains of helicobacter pylori reveals that clinical isolates can be divided into two major types and that caga is not necessary for expression of the vacuolating cytotoxin. Infect. Immun. 1995, 63, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaser, M.J.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Kleanthous, H.; Cover, T.L.; Peek, R.M.; Chyou, P.H.; Stemmermann, G.N.; Nomura, A. Infection with helicobacter pylori strains possessing caga is associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma of the stomach. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 2111–2115. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, R.; Malekzadeh, R.; Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Pawlita, M.; Murphy, G.; Islami, F.; Sotoudeh, M.; Michel, A.; Etemadi, A.; Waterboer, T.; et al. Multiplex H. pylori serology and risk of gastric cardia and noncardia adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4876–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Michel, A.; Weck, M.N.; Arndt, V.; Pawlita, M.; Brenner, H. Helicobacter pylori infection and gastric cancer risk: Evaluation of 15 H. pylori proteins determined by novel multiplex serology. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6164–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifeh Gholi, M.; Kalali, B.; Formichella, L.; Gottner, G.; Shamsipour, F.; Zarnani, A.H.; Hosseini, M.; Busch, D.H.; Shirazi, M.H.; Gerhard, M. Helicobacter pylori flid protein is a highly sensitive and specific marker for serologic diagnosis of H. pylori infection. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmees, C.; Prinz, C.; Treptau, T.; Rad, R.; Hengst, L.; Voland, P.; Bauer, S.; Brenner, L.; Schmid, R.M.; Gerhard, M. Inhibition of t-cell proliferation by H. pylori gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1820–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Ye, F.; Michel, A.; Murphy, G.; Sasazuki, S.; Taylor, P.R.; Qiao, Y.L.; Park, S.K.; Yoo, K.Y.; Jee, S.H.; et al. H. pylori blood biomarker for gastric cancer risk in east asia. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsohn, E.; Nystrom, J.; Bolin, I.; Nilsson, C.L.; Svennerholm, A.M. Hpaa is essential for helicobacter pylori colonization in mice. Infect. Immun. 2006, 74, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Anderl, F.; Kruse, T.; Schindele, F.; Jagusztyn-Krynicka, E.K.; Fischer, W.; Gerhard, M.; Mejias-Luque, R. Helicobacter pylori hp0231 influences bacterial virulence and is essential for gastric colonization. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, W.; Winhager, L.; Rohrer, S.; Zeiller, M.; Karnholz, A.; Hoffmann, R.; Zimmer, R.; Haas, R. Strain-specific genes of Helicobacter pylori: Genome evolution driven by a novel type IV secretion system and genomic island transfer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 6089–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, R.; Meyer, T.F.; van Putten, J.P.M. Aflagellated mutants of Helicobacter pylori generated by genetic transformation of naturally competent strains using transposon shuttle mutagenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 8, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formichella, L.; Romberg, L.; Bolz, C.; Vieth, M.; Geppert, M.; Gottner, G.; Nolting, C.; Walter, D.; Schepp, W.; Schneider, A.; et al. A novel line immunoassay based on recombinant virulence factors enables highly specific and sensitive serologic diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planatscher, H.; Rimmele, S.; Michel, G.; Potz, O.; Joos, T.; Schneiderhan-Marra, N. Systematic reference sample generation for multiplexed serological assays. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudi, J.; Kolb, C.; Maiwald, M.; Zuna, I.; von Herbay, A.; Galle, P.R.; Stremmel, W. Serum antibodies against helicobacter pylori proteins vaca and caga are associated with increased risk for gastric adenocarcinoma. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y.; Kodama, T.; Kashima, K.; Graham, D.Y. Antibody against helicobacter pylori caga and vaca and the risk for gastric cancer. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 52, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugano, K. Premalignant conditions of gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 906–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, A.; Waterboer, T.; Kist, M.; Pawlita, M. Helicobacter pylori multiplex serology. Helicobacter 2009, 14, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, J.C. H. pylori virulence factors. Br. Med. Bull. 1998, 54, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Furuyama, N.; Ozawa, K.; Ohnuma, K.; Iinuma, K. Long-term follow-up study of serum immunoglobulin g and immunoglobulin a antibodies after helicobacter pylori eradication. Pediatrics 1999, 104, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchildon, P.; Balaban, D.H.; Sue, M.; Charles, C.; Doobay, R.; Passaretti, N.; Peacock, J.; Marshall, B.J.; Peura, D.A. Usefulness of serological igg antibody determinations for confirming eradication of helicobacter pylori infection. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2105–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorberg, M.; Engstrand, L.; Strom, M.; Jonsson, K.A.; Jorbeck, H.; Granstrom, M. The diagnostic value of enzyme immunoassay and immunoblot in monitoring eradication of helicobacter pylori. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1997, 29, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veijola, L.; Oksanen, A.; Sipponen, P.; Rautelin, H. Evaluation of a commercial immunoblot, helicoblot 2.1, for diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1705–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.F.; Formichella, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.L.; Li, Z.X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.M.; Goettner, G.; Ulm, K.; et al. Helicobacter pylori antibody responses and evolution of precancerous gastric lesions in a chinese population. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwack, J.; Shin, A.; Kim, C.S.; Ko, K.P.; Kim, Y.; Jun, J.K.; Bae, J.; Park, S.K.; Hong, Y.C.; Kang, D.; et al. Caga-producing helicobacter pylori and increased risk of gastric cancer: A nested case-control study in korea. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Weck, M.N.; Michel, A.; Pawlita, M.; Brenner, H. Association between chronic atrophic gastritis and serum antibodies to 15 helicobacter pylori proteins measured by multiplex serology. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2973–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, A.M.; Perez-Perez, G.I.; Lee, J.; Stemmermann, G.; Blaser, M.J. Relation between helicobacter pylori caga status and risk of peptic ulcer disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, T.; Ghonaim, M.M.; Yousef, A.R.; Khalifa, A.; Al Qurashi, H.; Shaqhan, M.; Samaha, M. Association of helicobacter pylori caga gene with gastric cancer and peptic ulcer in saudi patients. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).