Developing and Validating an AI-TPACK Assessment Framework: Enhancing Teacher Educators’ Professional Practice Through Authentic Artifacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
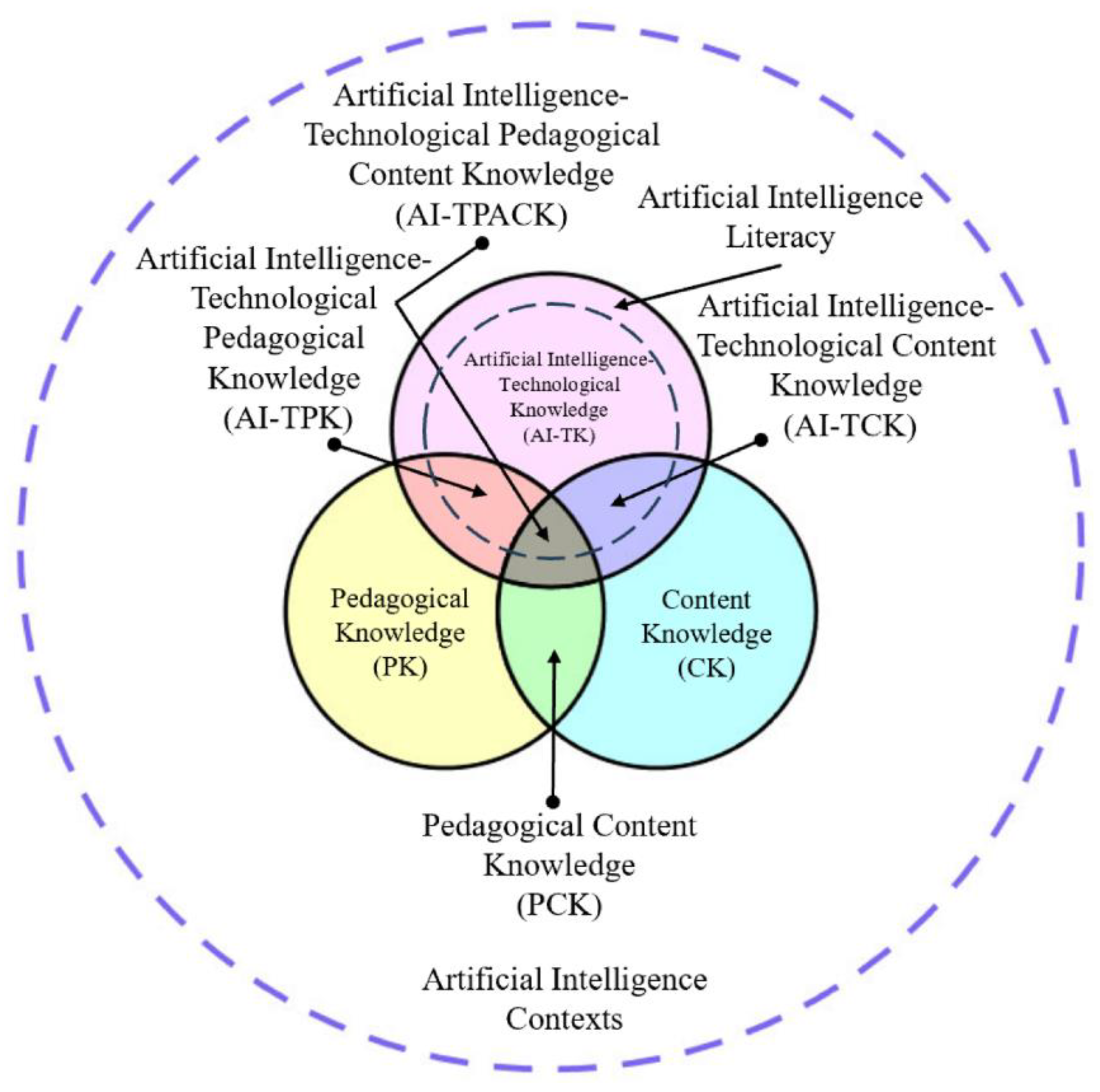
1.1. From TPACK to AI-TPACK
1.2. AI in Education: Current Trends
1.3. Teacher Education in the AI Age
1.4. Extending and Refining the TPACK Model
1.5. Early Conceptualizations and Empirical Advances
1.6. Assessing and Developing AI-TPACK
2. Research Aims and Questions
3. Methodology
3.1. Phase 1: Conceptual Grounding—Defining Purpose and Theoretical Foundation
3.2. Phase 2: Literature Integration—Building the Evidence Base
3.3. Phase 3: Instrument Development—Constructing the Assessment Tool
3.4. Phase 4: Implementation—Pilot Testing and Refinement
3.5. Phase 5: Evaluation—Validation and Finalization
4. Findings
4.1. Instrument Purpose and Theoretical Foundation
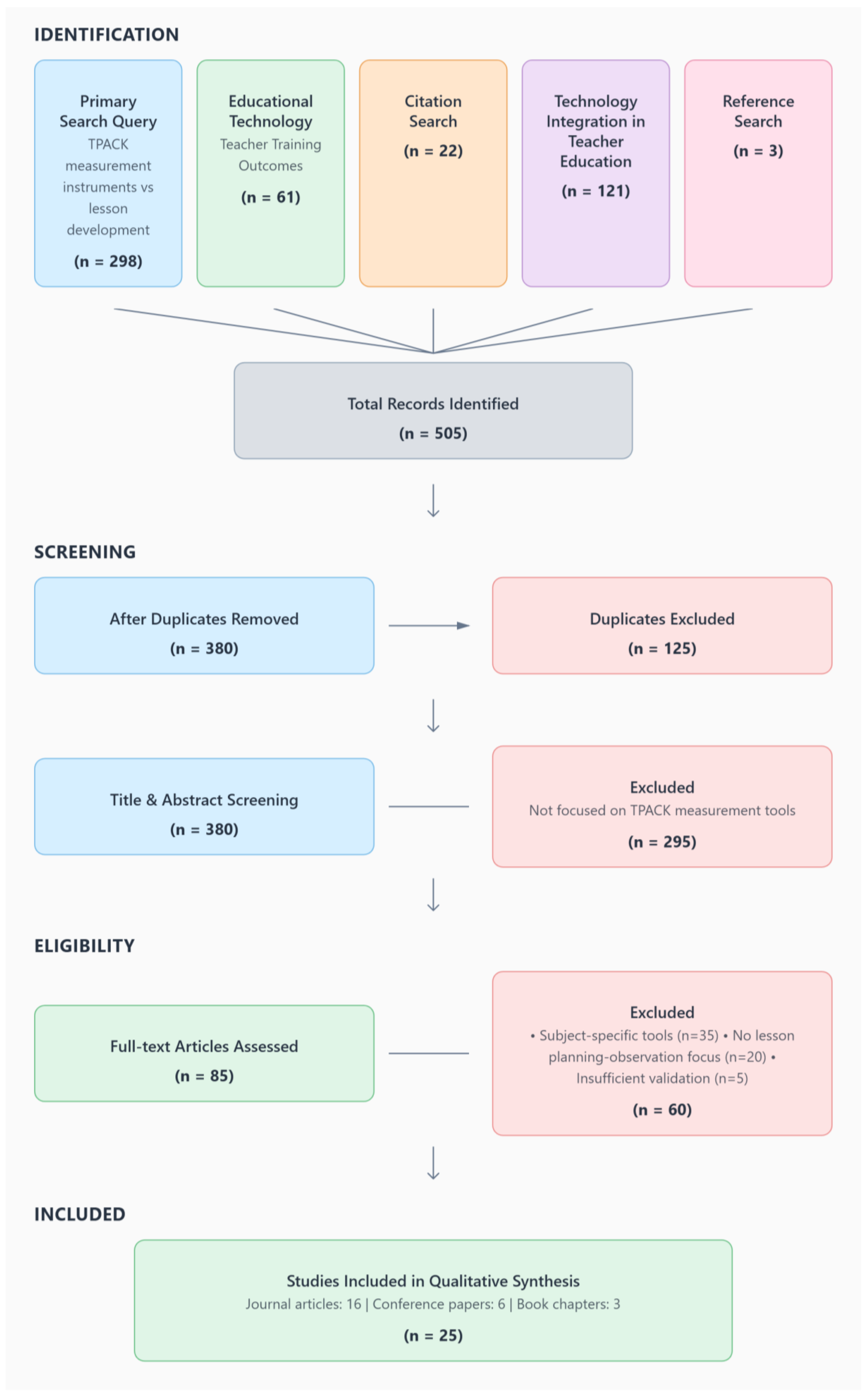
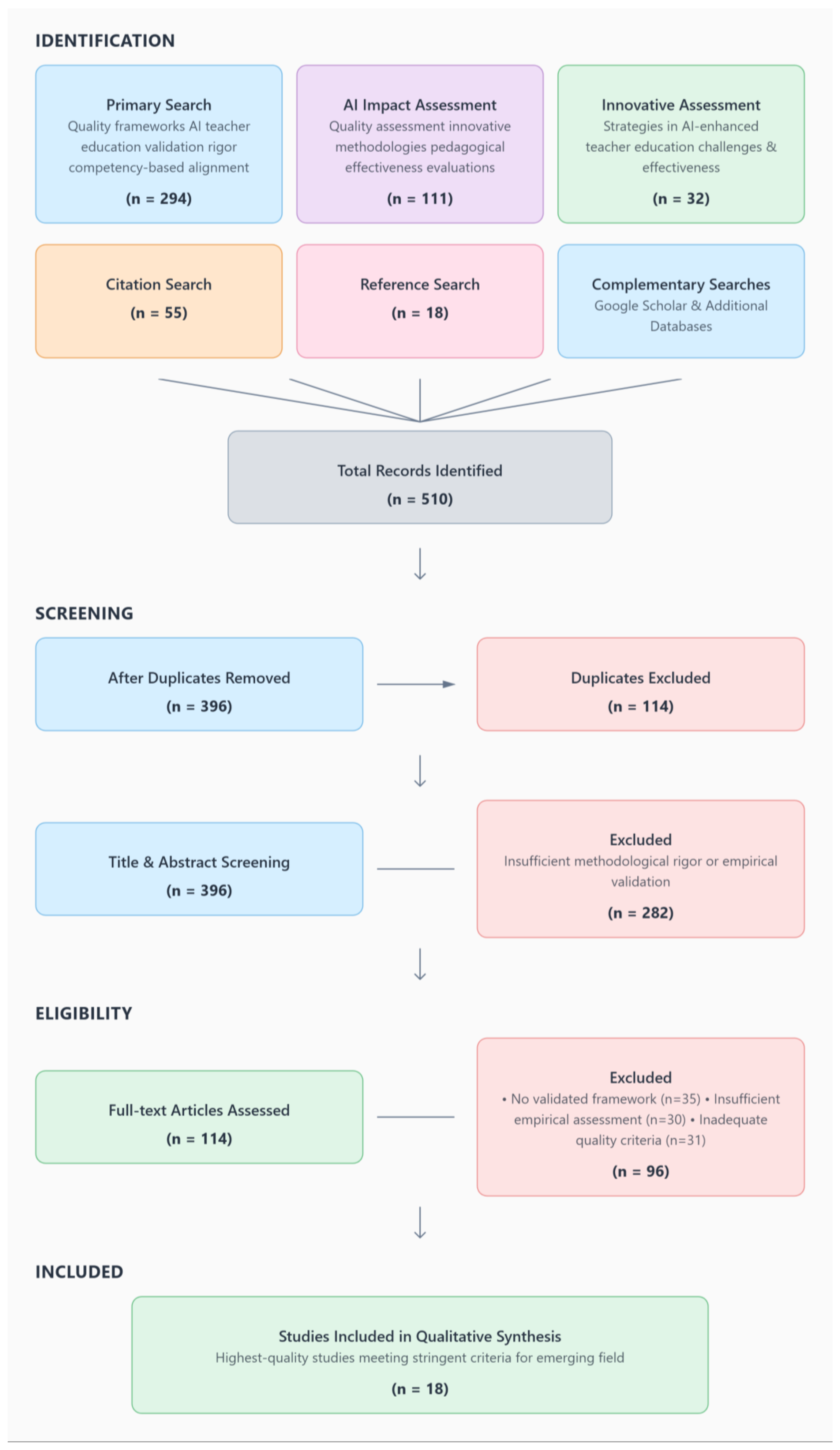
4.2. Systematic Literature Review
4.3. Initial Instrument Development and Content Validity Assessments
4.4. Field-Testing and Final Instrument Development
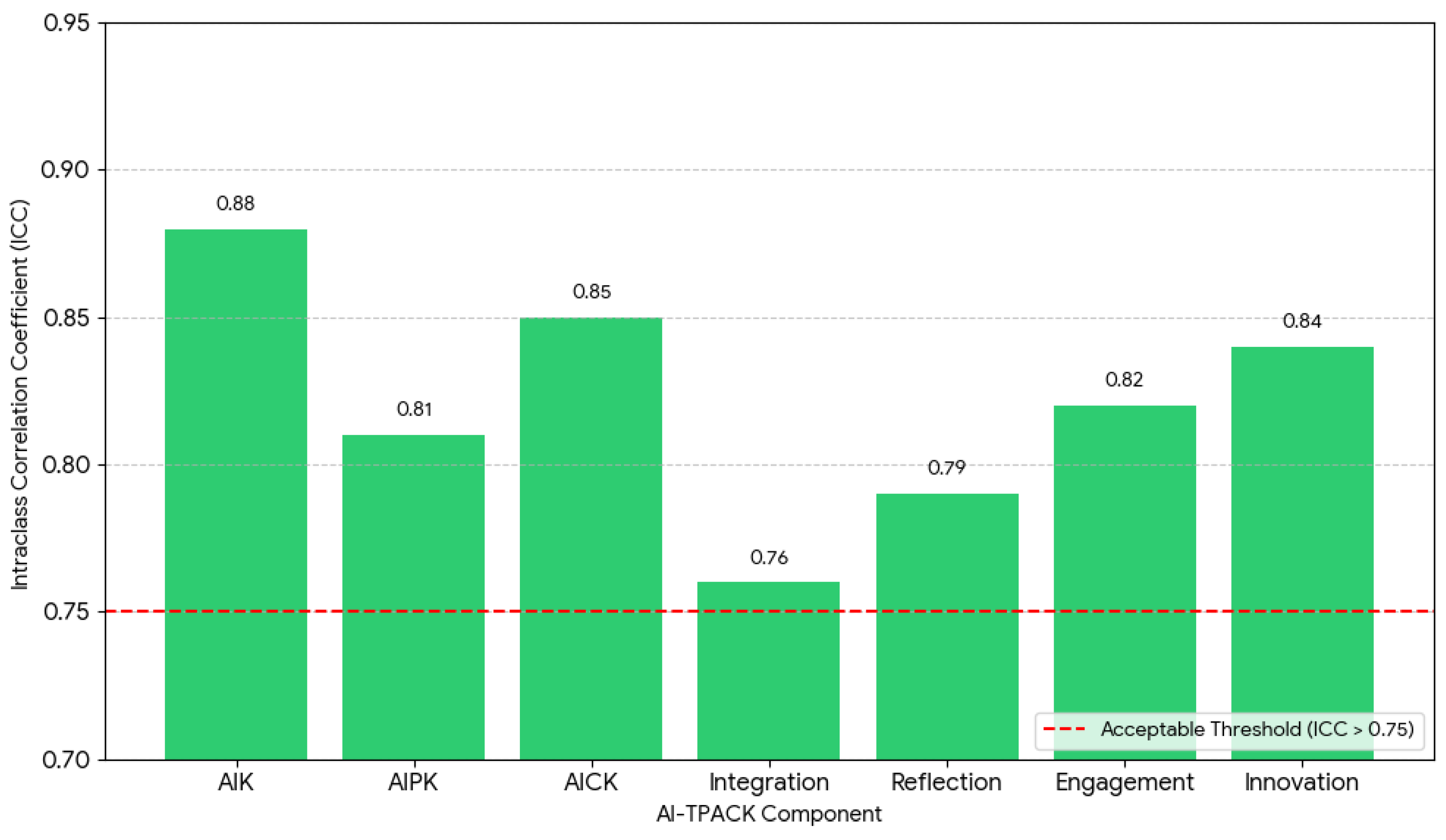
4.5. Inter-Rater Reliability
4.6. Statistical Findings and AI-TPACK Patterns
4.7. Identified Integration Patterns
5. Discussion
5.1. Practical Implications
5.2. Study Limitations and Future Research
6. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Category | Criterion ID | Assessment Indicator | Description | Measurement Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-1 | Understanding of AI Technologies | Comprehension of machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision | Foundational |
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-2 | Proficiency with Educational AI Tools | Ability to use AI tools specifically designed for education | Foundational |
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-3 | Technological Problem-Solving | Capability to troubleshoot technical issues related to AI tools | Foundational |
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-4 | Understanding of Technological Limitations | Recognition of AI tool constraints and challenges | Foundational |
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-5 | Ability to Evaluate New Tools | Critical assessment of emerging AI tools | Advanced |
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-6 | Understanding of Basic Algorithms | General comprehension of how AI systems operate | Advanced |
| AI-Technology Knowledge | ATK-7 | Technological Context Adaptation | Selection of appropriate tools for specific situations | Advanced |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-1 | Personalized Learning Implementation | Using AI to create individualized learning experiences | Teaching Strategies |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-2 | Automated and Immediate Feedback | Implementation of AI-based feedback systems | Teaching Strategies |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-3 | Differentiated Instruction | Using AI to support diverse learning needs | Teaching Strategies |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-4 | Advanced Classroom Management | Integrating AI into classroom organization and management | Teaching Strategies |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-5 | Active Learning with AI | Encouraging student engagement through AI tools | Pedagogical Principles |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-6 | Collaborative Learning | Using AI to promote student cooperation | Pedagogical Principles |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-7 | Critical Thinking Development | Fostering critical thinking about AI | Pedagogical Principles |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge | APK-8 | Formative Assessment | Using AI for continuous assessment | Pedagogical Principles |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-1 | Subject-Specific AI Applications | Using AI tools relevant to specific academic subjects | Content Integration |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-2 | Concept Demonstration through AI | Explaining content concepts using AI tools | Content Integration |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-3 | Quality Content Creation | Developing learning materials using AI | Content Integration |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-4 | Information Search and Verification | Using AI for academic information retrieval and validation | Content Integration |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-5 | Appropriate Difficulty Levels | Adapting content difficulty for different students | Content Adaptation |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-6 | Content Relevance | Maintaining content relevance to learning objectives | Content Adaptation |
| AI-Content Knowledge | ACK-7 | Information Currency | Using AI to update current content | Content Adaptation |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-1 | Holistic Lesson Planning | Thoughtful integration of AI, pedagogy, and content | Integrated Planning |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-2 | Clear Learning Objectives | Defining clear goals for AI use | Integrated Planning |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-3 | Target Audience Adaptation | Adapting AI use to student needs | Integrated Planning |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-4 | Learning Sequence | Creating logical sequence of AI-based activities | Integrated Planning |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-5 | Effective Implementation | Smooth execution of AI activities in classroom | Implementation and Assessment |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-6 | Monitoring and Adaptation | Tracking progress and adjusting accordingly | Implementation and Assessment |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-7 | Reflection and Improvement | Self-evaluation and continuous improvement | Implementation and Assessment |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-8 | Learning Outcome Assessment | Measuring AI impact on student learning | Implementation and Assessment |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-1 | Privacy and Data Security | Protecting student privacy | Ethical Considerations |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-2 | Algorithmic Transparency | Explaining AI functionality to students | Ethical Considerations |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-3 | Bias Prevention | Identifying and preventing algorithmic bias | Ethical Considerations |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-4 | Responsible Use | Promoting thoughtful and responsible AI use | Ethical Considerations |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-5 | AI Literacy | Developing basic AI understanding among students | Literacy Development |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-6 | Critical Thinking about AI | Encouraging critical thinking about AI impacts | Literacy Development |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility | AER-7 | Digital Responsibility | Developing personal responsibility in technology use | Literacy Development |
| Main Category | Sub-Category | Criterion | Number of Indicators | Weight (%) | Corrected Weight (%) (Sum = 100%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIK | Basic AI Knowledge | 1. Identification of appropriate AI tools | 4 | 4.4 | 5.0 |
| Advanced AI Abilities | 2. Complex technical integration | 5 | 5.6 | 6.4 | |
| 3. Development of original solutions | 6 | 7.0 | 8.0 | ||
| AIPK | Pedagogical Approaches | 4. Alignment with learning objectives | 5 | 5.6 | 6.4 |
| Learning Design | 5. Interactive learning experiences | 6 | 7.0 | 8.0 | |
| 6. Transformation of pedagogical practices | 4 | 4.9 | 5.6 | ||
| AICK | Content Representation | 7. Adapting content presentation | 4 | 4.4 | 5.0 |
| Knowledge Processing | 8. Processing and organizing knowledge | 5 | 5.6 | 6.4 | |
| 9. Creation of new knowledge approaches | 5 | 5.5 | 6.3 | ||
| Integration | Foundational Integration | 10. Connection between components | 4 | 4.4 | 5.0 |
| Overall Integration | 11. Synergy between components | 6 | 7.0 | 8.0 | |
| Supporting Measures | Reflection | 12. Depth of reflection on AI use | 3 | 10.0 | 10.0 |
| Student Engagement | 13. Level of student engagement with AI | 4 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Innovation | 14. Level of innovation in AI use | 4 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| Total | 14 Criteria | 65 Indicators | 91.4% | 100% |
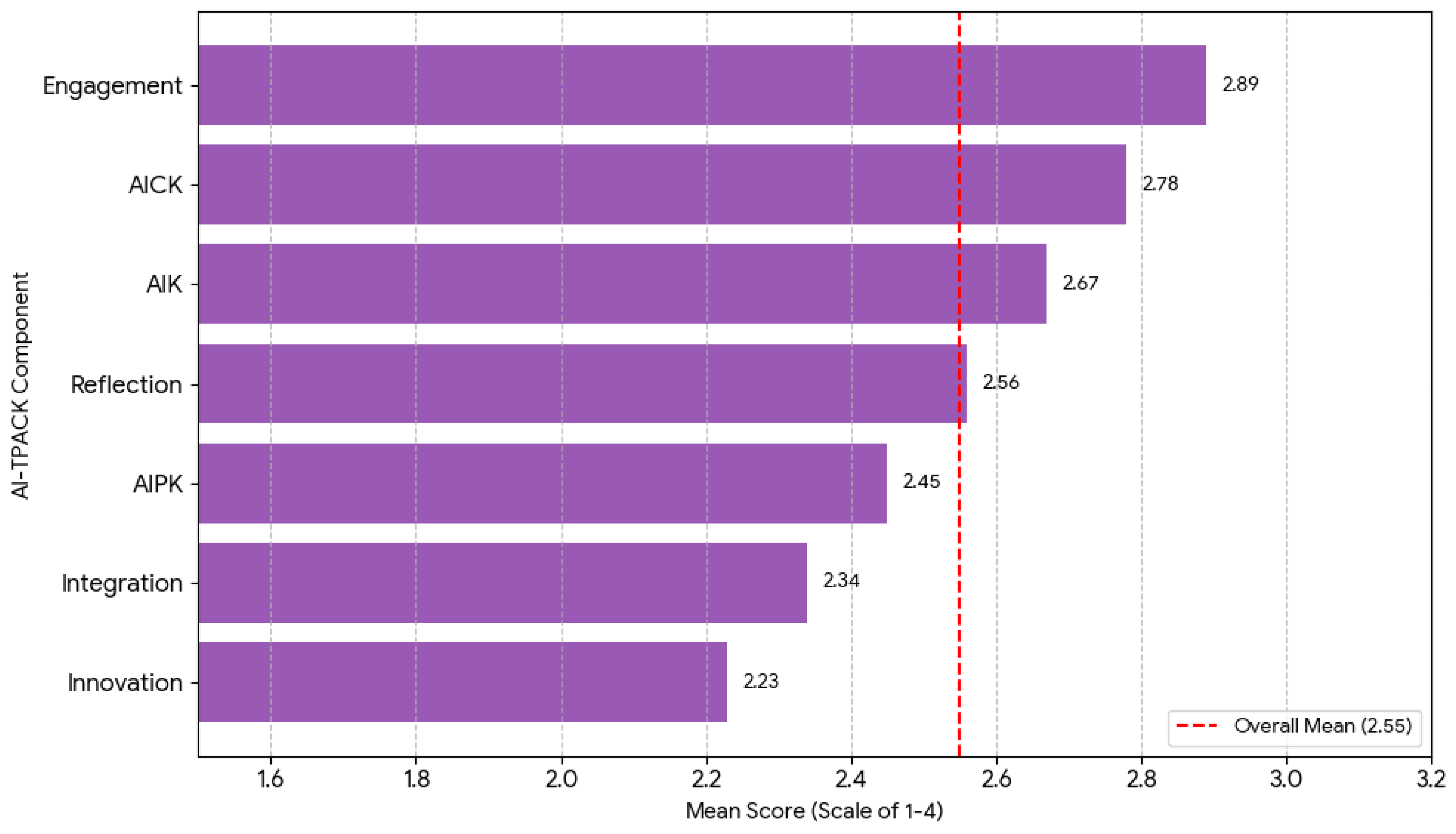
| Component | Mean | Standard Deviation | Minimum | Maximum | Median | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIK | 2.67 | 0.84 | 1.25 | 4.00 | 2.75 | 0.31 |
| AIPK | 2.45 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.50 | 0.37 |
| AICK | 2.78 | 0.76 | 1.50 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 0.27 |
| Integration | 2.34 | 0.88 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.25 | 0.38 |
| Reflection | 2.56 | 0.94 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.67 | 0.37 |
| Engagement | 2.89 | 0.71 | 1.75 | 4.00 | 3.00 | 0.25 |
| Innovation | 2.23 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 4.00 | 2.00 | 0.46 |
| Overall AI-TPACK | 2.55 | 0.73 | 1.20 | 3.85 | 2.60 | 0.29 |
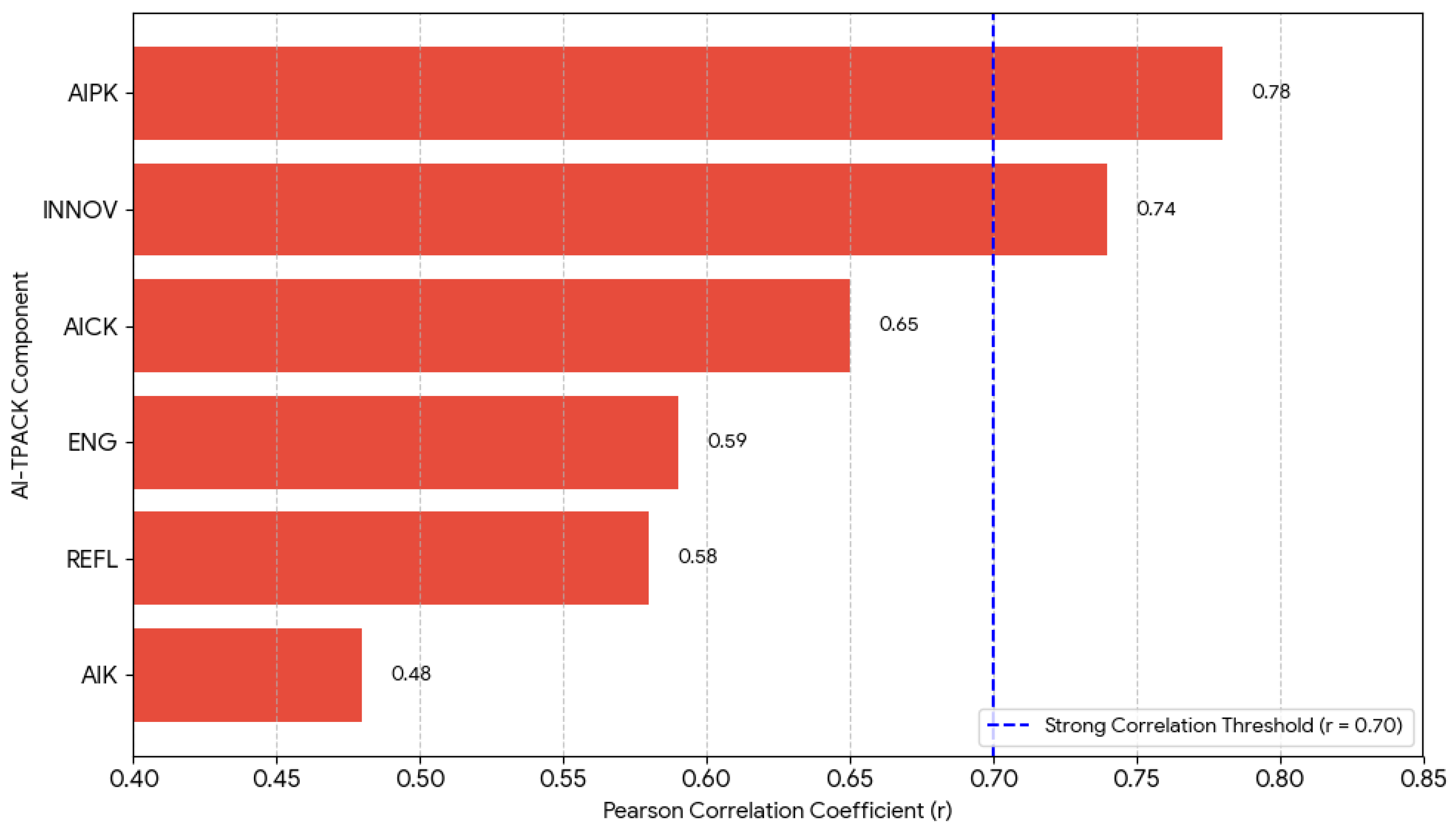
| AIK | AIPK | AICK | INT | REFL | ENG | INNOV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIK | 1.00 | ||||||
| AIPK | 0.67 ** | 1.00 | |||||
| AICK | 0.54 ** | 0.71 ** | 1.00 | ||||
| INT | 0.48 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.65 ** | 1.00 | |||
| REFL | 0.41 * | 0.56 ** | 0.62 ** | 0.58 ** | 1.00 | ||
| ENG | 0.52 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.69 ** | 0.59 ** | 0.71 ** | 1.00 | |
| INNOV | 0.59 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.58 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.68 ** | 0.63 ** | 1.00 |
Appendix B. Full AI-TPACK Artifact Assessment Tool
Introduction to the Tool
- Part A: Basic Unit Information
- Identification Details:
- Instructor Name: _______________
- Content Area: _______________
- Course Type: (Lecture/Seminar/Lab/Other) _______________
- Academic Hours: _______________
- Number of Activities in the Unit: _______________
- Part B: AI-TPACK Analysis by Components
- 1. AIK—Artificial Intelligence Knowledge
| Level | Description | Examples | Score |
| Basic | Single AI tool, simple use | Using ChatGPT for information retrieval | 1 |
| Intermediate | Multiple AI tools or advanced single tool | Leonardo AI + ChatGPT + Canva | 2 |
| Advanced | Creating applications/bots, complex integration | Base44, NotebookLM, bot development | 3 |
| Innovative | Original AI solutions, unique applications | Custom applications, innovative integrations | 4 |
- Detailed Criteria:
- Criterion 1: Identification and Selection of AI Tools (4 indicators)
- 1.1 Identifies AI tools suitable for the content area
- 1.2 Selects tools based on clear pedagogical objectives
- 1.3 Adapts tool selection to students’ proficiency levels
- 1.4 Considers technical limitations and accessibility
- Criterion 2: Technical Application of AI (5 indicators)
- 2.1 Integrates multiple AI tools effectively
- 2.2 Customizes AI tool settings for specific contexts
- 2.3 Addresses technical issues in AI implementation
- 2.4 Optimizes AI tool performance for educational use
- 2.5 Demonstrates understanding of AI capabilities and limitations
- Criterion 3: Innovation and AI Development (5 indicators)
- 3.1 Develops original AI-based solutions
- 3.2 Creates innovative applications using AI platforms
- 3.3 Adapts existing AI tools for novel educational purposes
- 3.4 Experiments with advanced AI technologies
- 3.5 Shares and documents AI innovations for others
- Unit Score: ___/4
- 2. AIPK—AI-Pedagogical Knowledge
| Level | Description | Examples | Score |
| Substitution | AI replaces existing tools | AI instead of a dictionary or Google search | 1 |
| Augmentation | AI enhances existing activities | Creating diverse exercises, personalized feedback | 2 |
| Modification | AI enables significant redesign | Interactive learning, simulations | 3 |
| Transformation | AI creates entirely new possibilities | Human-AI collaboration, innovative learning experiences | 4 |
- Detailed Criteria:
- Criterion 4: Basic Pedagogical Integration (4 indicators)
- 4.1 Uses AI to appropriately replace traditional teaching tools
- 4.2 Enhances existing activities through AI augmentation
- 4.3 Aligns AI use with specific learning objectives
- 4.4 Maintains pedagogical focus during AI integration
- Criterion 5: Designing Learning Experiences (5 indicators)
- 5.1 Redesigns learning experiences using AI capabilities
- 5.2 Creates interactive learning environments with AI
- 5.3 Promotes student autonomy through AI-supported learning
- 5.4 Encourages collaborative learning enriched by AI
- 5.5 Adapts teaching methods to leverage AI advantages
- Criterion 6: Transformative Pedagogical Practice (5 indicators)
- 6.1 Creates new pedagogical approaches enabled by AI
- 6.2 Promotes human-AI collaboration in learning
- 6.3 Transforms traditional classroom dynamics with AI
- 6.4 Enables personalized learning pathways through AI
- 6.5 Develops AI-enriched assessment strategies
- Unit Score: ___/4
- 3. AICK—AI-Content Knowledge
| Level | Description | Examples | Score |
| Presentation | AI presents existing content | Displaying eye diseases using AI | 1 |
| Processing | AI assists in organizing and adapting content | Mind maps, personalized summaries | 2 |
| Creation | AI participates in creating new content | Accompanying images, new outputs | 3 |
| Innovation | AI enables new content approaches | Digital VTS, virtual experiences | 4 |
- Detailed Criteria:
- Criterion 7: Content Presentation and Adaptation (4 indicators)
- 7.1 Uses AI to present existing content in accessible formats
- 7.2 Adjusts content complexity with AI assistance
- 7.3 Creates visual representations of abstract concepts
- 7.4 Organizes and structures content using AI tools
- Criterion 8: Content Enrichment and Processing (5 indicators)
- 8.1 Enriches content with AI-generated examples and illustrations
- 8.2 Creates multimedia content using AI tools
- 8.3 Develops interactive content experiences with AI
- 8.4 Curates and summarizes content from multiple AI sources
- 8.5 Personalizes content delivery based on student needs
- Criterion 9: Knowledge Creation and Innovation (5 indicators)
- 9.1 Generates new content in collaboration with AI
- 9.2 Develops original case studies and scenarios with AI
- 9.3 Creates domain-specific applications using AI
- 9.4 Explores new approaches to content delivery with AI
- 9.5 Synthesizes knowledge from multiple AI sources
- Unit Score: ___/4
- Part C: Integration Analysis
- 4. Level of AI Integration in Pedagogical Design
| Level | Description | Indicators | Score |
| Separate | AI as an additional, disconnected activity | AI appears only in a specific part | 1 |
| Partially Integrated | AI linked to learning objectives | AI supports some objectives | 2 |
| Fully Integrated | AI integrated across all unit stages | AI in planning, implementation, reflection | 3 |
| Integrative | AI as an inseparable part of pedagogy | Unit cannot function without AI | 4 |
- Detailed Criteria:
- Criterion 10: Basic Integration Methods (4 indicators)
- 10.1 Connects AI use to learning objectives
- 10.2 Aligns AI tools with pedagogical strategies
- 10.3 Balances AI and non-AI learning activities
- 10.4 Maintains consistency across learning stages
- Criterion 11: Strategic Integration Planning (5 indicators)
- 11.1 Plans systematic AI integration throughout the curriculum
- 11.2 Sequences AI activities optimally for learning progression
- 11.3 Aligns AI use with assessment strategies
- 11.4 Considers long-term impacts of AI integration
- 11.5 Adjusts integration based on feedback and student outputs
- Criterion 12: Advanced Synergistic Integration (5 indicators)
- 12.1 Creates seamless integration across all TPACK components
- 12.2 Develops synergies between AI, pedagogy, and content
- 12.3 Embeds AI as an essential component, not an add-on
- 12.4 Achieves integration in all stages of planning, implementation, and reflection
- 12.5 Creates holistic learning ecosystems integrating AI
- Unit Score: ___/4
- Part D: Additional Qualitative Metrics
- 5. Depth of Reflection on AI
- 0 points: No reflection on AI use
- 1 point: Technical reflection only (worked/did not work)
- 2 points: Pedagogical reflection (impact on learning)
- 3 points: Critical reflection (advantages and disadvantages)
- Criterion 13: Depth of Reflection on AI Use (3 indicators)
- 13.1 Reflects on technical aspects of AI implementation
- 13.2 Analyzes the pedagogical impact of AI integration
- 13.3 Critically evaluates ethical and societal implications of AI use
- 6. Student Engagement with AI
- Passive observation (1 point)
- Guided use (2 points)
- Active creation (3 points)
- Critical thinking about AI (4 points)
- 7. Innovation in AI Use
- Routine use (1 point)
- Creative application (2 points)
- Innovative problem-solving (3 points)
- Innovative methodological development (4 points)
- Criterion 14: Student Engagement and Innovation (4 indicators)
- 14.1 Promotes student engagement with AI tools at appropriate levels
- 14.2 Encourages student creativity through collaboration with AI
- 14.3 Promotes critical thinking about AI’s role and limitations
- 14.4 Develops innovative approaches to AI-enhanced learning
- Unit Score: ___/4
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- Part E: Overall AI-TPACK Score Calculation
- Calculation Formula:
- AI-TPACK Score = [(AIK + AIPK + AICK + Integration) × 0.7] + [(Reflection + Student Engagement + Innovation) × 0.3]
- AI-TPACK Score Calculation Guidelines
- Calculate the Core Group (70% of the total score): Sum the scores of the AIK, AIPK, AICK, and Integration components. Multiply this sum by 0.7.
- Calculate the Extended Group (30% of the total score): Sum the scores of the Reflection, Student Engagement, and Innovation components. Multiply this sum by 0.3.
- Final Score (Raw): Add the results from steps 1 and 2 to obtain the raw final AI-TPACK score.
- The weights (70% and 30%) indicate the relative importance of each component group in the final score.
- Raw to Normalized Score Conversion Table
| Final Score (Raw) | Normalized Final Score | Proficiency Level |
| 3.7–5.8 | 1.0–1.4 | Basic Level (Beginner) |
| 5.9–9.1 | 1.5–2.4 | Intermediate Level (Developing) |
| 9.2–12.4 | 2.5–3.4 | Intermediate-High Level (Proficient) |
| 12.5–14.8 | 3.5–4.0 | Advanced Level (Expert Proficiency) |
- Final Score: ___/4.0
- Part F: Qualitative Comments
- Strengths in AI Integration:
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- Areas for Improvement:
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- Unique Patterns Identified in AI Use:
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- Recommendations for Further Development:
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- ___________________________________________________________________________
- Instructions for Use:
- Evaluate each instructional unit separately.
- Rate each component based on evidence from the document.
- Calculate the overall score.
- Document qualitative insights.
- Compare patterns across different units.
- To facilitate the assessment process, we have developed a dedicated application which simplifies data entry and automatically calculates the final scores.
References
- Admiraal, W., van Vugt, F., Kranenburg, F., Koster, B., Smit, B., Weijers, S., & Lockhorst, D. (2017). Preparing pre-service teachers to integrate technology into K–12 instruction: Evaluation of a technology-infused approach. Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 26(1), 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdullatif, A. M. (2024). Modeling teachers’ acceptance of generative artificial intelligence use in higher education: The role of AI literacy, intelligent TPACK, and perceived trust. Education Sciences, 14(11), 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, B. T., Pileggi, S. F., & Karimi, F. (2024). A social perspective on AI in the higher education system: A semisystematic literature review. Electronics, 13(8), 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archambault, L., & Crippen, K. (2009). Examining TPACK among K-12 online distance educators in the United States. Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education, 9(1), 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Avalos, B. (2011). Teacher professional development in teaching and teacher education over ten years. Teaching and Teacher Education, 27(1), 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayre, C., & Scally, A. J. (2014). Critical values for Lawshe’s content validity ratio: Revisiting the original methods of calculation. Measurement and Evaluation in Counseling and Development, 47(1), 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobula, M. (2024). Generative artificial intelligence (AI) in higher education: A comprehensive review of challenges, opportunities, and implications. Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education, (30). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, M., Torrington, J., Lai, J. W. M., Petocz, P., & Alfano, M. (2024). How should we change teaching and assessment in response to increasingly powerful generative Artificial Intelligence? Outcomes of the ChatGPT teacher survey. Education and Information Technologies, 29, 15403–15439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I. (2023). Towards Intelligent-TPACK: An empirical study on teachers’ professional knowledge to ethically integrate artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools into education. Computers in Human Behavior, 138, 107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I., Gedrimiene, E., Siklander, S., & Muukkonen, H. (2024). The affordances of artificial intelligence-based tools for supporting 21st-century skills: A systematic review of empirical research in higher education. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 40(3), 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C. S., Koh, J. H. L., & Tsai, C.-C. (2013). A review of technological pedagogical content knowledge. Educational Technology & Society, 16(2), 31–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, S., & Bhattacharjee, K. K. (2020). Adoption of artificial intelligence in higher education: A quantitative analysis using structural equation modelling. Education and Information Technologies, 25(5), 3443–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. K. F. (2023a). Future research recommendations for transforming higher education with generative AI. Computers and AI in Education, 6, 100197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. K. F. (2023b). The impact of Generative AI (GenAI) on practices, policies and research direction in education: A case of ChatGPT and Midjourney. Interactive Learning Environments, 32, 6187–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. K. F., & Chai, C. S. (2020). Sustainable curriculum planning for artificial intelligence education: A self-determination theory perspective. Sustainability, 12(14), 5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T. K. F., Xia, Q., Zhou, X., Chai, C. S., & Cheng, M. (2023). Systematic literature review on opportunities, challenges, and future research recommendations of artificial intelligence in education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 4, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S., Deb, J. P., Pradhan, P., & Mishra, A. (2024). Validation of the teachers AI-TPACK scale for the Indian educational setting. International Journal of Experimental Research and Review, 43, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A., & Sweeney, T. (2017). Can an objective measure of technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK) supplement existing TPACK measures? British Journal of Educational Technology, 48(4), 928–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebner, M., Lienhardt, C., Rohs, M., & Meyer, I. (2010). Microblogs in higher education—A chance to facilitate informal and process-oriented learning? Computers & Education, 55(1), 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garet, M. S., Porter, A. C., Desimone, L., Birman, B. F., & Yoon, K. S. (2001). What makes professional development effective? Results from a national sample of teachers. American Educational Research Journal, 38(4), 915–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, C. R. (2011). Theoretical considerations for understanding technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK). Computers & Education, 57(3), 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guskey, T. R. (2002). Professional development and teacher change. Teachers and Teaching, 8(3), 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J. B., Hofer, M. J., Blanchard, M. R., Grandgenett, N. F., Schmidt, D. A., van Olphen, M., & Young, C. A. (2010). Testing a TPACK-based technology integration observation instrument. In D. Gibson, & B. Dodge (Eds.), Proceedings of SITE 2010—Society for information technology & teacher education international conference (pp. 4352–4359). Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE). [Google Scholar]
- Hofer, M., Grandgenett, N., Harris, J., & Swan, K. (2011). Testing a TPACK-based technology integration observation instrument. In M. Koehler, & P. Mishra (Eds.), Proceedings of SITE 2011—Society for information technology & teacher education international conference (pp. 4352–4359). Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education (AACE). [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, W., Bialik, M., & Fadel, C. (2019). Artificial intelligence in education: Promises and implications for teaching and learning. Center for Curriculum Redesign. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, J. (2005). The role of teacher knowledge and learning experiences in forming technology-integrated pedagogy. Journal of Technology and Teacher Education, 13(2), 277–302. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-W. (2024). Development of a TPACK educational program to enhance pre-service teachers’ teaching expertise in artificial intelligence convergence education. International Journal of Advanced Science, Engineering and Information Technology, 14(1), 19552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmons, R., Graham, C. R., & West, R. E. (2020). The PICRAT model for technology integration in teacher preparation. Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education, 20(1), 176–198. [Google Scholar]
- Koehler, M. J., Mishra, P., & Cain, W. (2013). What is technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK)? Journal of Education, 193(3), 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T. K., & Li, M. Y. (2016). A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine, 15(2), 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, J., Bremerich-Vos, A., Buchholtz, C., Fladung, I., & Glutsch, N. (2020). General pedagogical knowledge, pedagogical adaptivity in written lesson plans, and instructional practice among preservice teachers. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 52(5), 616–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küchemann, S., Avila, K., Dinc, Y., Boolzen, C., Revenga Lozano, N., Ruf, V., Stausberg, N., Steinert, S., Fischer, F., Fischer, M., Kasneci, E., Kasneci, G., Kuhr, T., Kutyniok, G., Malone, S., Sailer, M., Schmidt, A., Stadler, M., Weller, J., & Kuhn, J. (2024). Are large multimodal foundation models all we need? On opportunities and challenges of these models in education [Preprint]. EdArXiv. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J. R., & Koch, G. G. (1977). An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics, 33(2), 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawshe, C. H. (1975). A quantitative approach to content validity. Personnel Psychology, 28(4), 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Zhang, Y., & Wang, H. (2025). A case study of teachers’ generative artificial intelligence integration processes and factors influencing them. Teaching and Teacher Education, 153, 105157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Regalado, O., Núñez-Rojas, N., López-Gil, O. R., Lloclla-Gonzáles, H., & Sánchez Rodríguez, J. (2024). Artificial intelligence in university education: Systematic review. Research Square. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, S., & Reeves, T. C. (2018). Conducting educational design research. Routledge. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P., & Koehler, M. J. (2006). Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A framework for teacher knowledge. Teachers College Record, 108(6), 1017–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P., Warr, M., & Islam, R. (2023). TPACK in the age of ChatGPT and Generative AI. Journal of Digital Learning in Teacher Education, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenda, M. (2015). In search of the elusive ADDIE model. Performance Improvement, 54(2), 40–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourlam, D., Chesnut, S., & Bleecker, H. (2021). Exploring preservice teacher self-reported and enacted TPACK after participating in a learning activity types short course. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 37(3), 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D. T. K., Lee, M., Tan, R. J. Y., Hu, X., Downie, J. S., & Chu, S. K. W. (2023). A review of AI teaching and learning from 2000 to 2020. Education and Information Technologies, 28(7), 8445–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D. T. K., Leung, J. K. L., Chu, S. K. W., & Qiao, M. S. (2021). Conceptualizing AI literacy: An exploratory review. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 2, 100041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, D. T. K., Leung, J. K. M., & Chu, S. K. W. (2025). Investigating the mediating role of TPACK on teachers’ AI competency and their teaching performance in higher education. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 6, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y., Zhang, C., Xu, B., Zhou, Y., & Wijaya, T. T. (2024). Teachers’ AI-TPACK: Exploring the relationship between knowledge elements. Sustainability, 16(3), 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). (2023). OECD digital education outlook 2023: Towards an effective digital education ecosystem. OECD Publishing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paivio, A. (1991). Dual coding theory: Retrospect and current status. Canadian Journal of Psychology/Revue canadienne de psychologie, 45(3), 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesovski, I., Santos, R., Henriques, R. A. P., & Trajkovik, V. (2024). Generative AI for customizable learning experiences. Sustainability, 16(7), 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puentedura, R. R. (2006, August). Transformation, technology, and education. Hippasus. [Google Scholar]
- Puentedura, R. R. (2013). SAMR and TPCK: An introduction. Hippasus. [Google Scholar]
- Radianti, J., Majchrzak, T. A., Fromm, J., & Wohlgenannt, I. (2020). A systematic review of immersive virtual reality applications for higher education: Design elements, lessons learned, and research agenda. Computers & Education, 147, 103778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J. M., & Koehler, M. J. (2015). Context and technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK): A systematic review. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 47(3), 186–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S., & Norvig, P. (2020). Artificial intelligence: A modern approach (4th ed.). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, D. A., Baran, E., Thompson, A. D., Mishra, P., Koehler, M. J., & Shin, T. S. (2009). Technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK): The development and validation of an assessment instrument for preservice teachers. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 42(2), 123–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifert, H., & Lindmeier, A. (2024). Developing a performance-based assessment to measure pre-service secondary teachers’ digital competence to use digital mathematics tools. Journal für Mathematik-Didaktik, 45(2), 317–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, N. (2019). Should robots replace teachers? AI and the future of education. John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.-L. (2024). Application of large language models in the field of education. Theoretical and Natural Science, 34(1), 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B. L., Dahal, N., Hasan, M. K., Paudel, S., & Kapar, H. (2025). Generative AI on professional development: A narrative inquiry using TPACK framework. Frontiers in Education, 10, 1550773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulman, L. S. (1986). Those who understand: Knowledge growth in teaching. Educational Researcher, 15(2), 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stender, A., Brückmann, M., & Neumann, K. (2017). Transformation of topic-specific professional knowledge into personal pedagogical content knowledge through lesson planning. International Journal of Science Education, 39(12), 1690–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J., Ma, H., Zeng, Y., Han, D., & Jin, Y. (2023). Promoting the AI teaching competency of K-12 computer science teachers: A TPACK-based professional development approach. Education and Information Technologies, 28, 1509–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X., Cheng, G., & Ling, M. H. (2025). Artificial intelligence in teaching and teacher professional development: A systematic review. Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence, 8, 100355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyssen, C., Huwer, J., Irion, T., & Schaal, S. (2023). From TPACK to DPACK: The “digitality-related pedagogical and content knowledge”-model in STEM-education. Education Sciences, 13(8), 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondeur, J., Scherer, R., Siddiq, F., & Baran, E. (2018). Enhancing pre-service teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK): A mixed-method study. Educational Technology Research and Development, 68, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tondeur, J., van Braak, J., Ertmer, P. A., & Ottenbreit-Leftwich, A. (2017). Understanding the relationship between teachers’ pedagogical beliefs and technology use in education: A systematic review of qualitative evidence. Educational Technology Research and Development, 65(3), 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). (2023). Guidance for generative AI in education and research. UNESCO. [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen, T., Sointu, E. T., Mäkitalo-Siegl, K., & Kukkonen, J. (2015). Developing a TPACK measurement instrument for 21st century pre-service teachers. Seminar.net—International Journal of Media, Technology and Lifelong Learning, 11(2), 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J., Fisser, P., Pareja Roblin, N., Tondeur, J., & van Braak, J. (2013). Technological pedagogical content knowledge—A review of the literature. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, 29(2), 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voogt, J., Westbroek, H., Handelzalts, A., Walraven, A., McKenney, S., Pieters, J., & De Vries, B. (2011). Teacher learning in collaborative curriculum design. Teaching and Teacher Education, 27(8), 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, Y. (2024). Embracing the future of Artificial Intelligence in the classroom: The relevance of AI literacy, prompt engineering, and critical thinking in modern education. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, E., McDermott, R., & Snyder, W. M. (2002). Cultivating communities of practice: A guide to managing knowledge. Harvard Business Press. [Google Scholar]
- Willermark, S. (2018). Technological pedagogical and content knowledge: A review of empirical studies published from 2011 to 2016. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 56(3), 315–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M., & Luo, L. (2025). The status quo and future of AI-TPACK for mathematics teacher education students: A case study in Chinese universities [Preprint]. arXiv, arXiv:2503.13533. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.-F., Tseng, C. C., & Lai, S.-C. (2024). Enhancing teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs in AI-based technology integration into English speaking teaching through a professional development program. Teaching and Teacher Education, 144, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J. R. (2016). Cultural implications in educational technology: A survey. In Handbook of research on educational communications and technology (pp. 1–10). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Zawacki-Richter, O., Marín, V. I., Bond, M., & Gouverneur, F. (2019). Systematic review of research on artificial intelligence applications in higher education—Where are the educators? International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 16(1), 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Expert | Degree/Field | Current Role | Years of Experience (Tech Integration/AI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | Ph.D./Learning Tech | Head of Digital Innovation Unit | 12 |
| E2 | Ed.D./Curriculum Design | Lecturer, Teacher Ed. | 8 |
| E3 | Ph.D./Cognitive Science | AI in Education Consultant | 10 |
| E4 | M.A./Special Education | Consultant of Educational Technology | 5 |
| E5 | M.A./STEM Education | Instructional Designer, AI/Ed Tech | 9 |
| Category | Criterion ID Range | Core Assessment Indicator Examples |
|---|---|---|
| AI-Technology Knowledge (AIK) | ATK-1 to ATK-7 | Understanding AI Technologies, Proficiency with Educational AI Tools, Technological Problem-Solving |
| AI-Pedagogical Knowledge (AIPK) | APK-1 to APK-8 | Personalized Learning Implementation, Automated and Immediate Feedback, Differentiated Instruction |
| AI-Content Knowledge (AICK) | ACK-1 to ACK-7 | Subject-Specific AI Applications, Concept Demonstration through AI, Quality Content Creation |
| AI-TPACK Integration | AIT-1 to AIT-8 | Holistic Lesson Planning, Clear Learning Objectives, Effective Implementation, Reflection and Improvement |
| AI Ethics and Responsibility (AER) | AER-1 to AER-7 | Privacy and Data Security, Algorithmic Transparency, Bias Prevention, Responsible Use, AI Literacy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eyal, L. Developing and Validating an AI-TPACK Assessment Framework: Enhancing Teacher Educators’ Professional Practice Through Authentic Artifacts. Educ. Sci. 2025, 15, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111452
Eyal L. Developing and Validating an AI-TPACK Assessment Framework: Enhancing Teacher Educators’ Professional Practice Through Authentic Artifacts. Education Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111452
Chicago/Turabian StyleEyal, Liat. 2025. "Developing and Validating an AI-TPACK Assessment Framework: Enhancing Teacher Educators’ Professional Practice Through Authentic Artifacts" Education Sciences 15, no. 11: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111452
APA StyleEyal, L. (2025). Developing and Validating an AI-TPACK Assessment Framework: Enhancing Teacher Educators’ Professional Practice Through Authentic Artifacts. Education Sciences, 15(11), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci15111452






