Abstract
Environmental education is an important tool for managing environmental problems, with a view to protecting the environment. Several significant factors, however, impede its implementation. Educators’ lack of knowledge and appropriate training on environmental topics results in difficulties in implementing environmental education programs. Nevertheless, environmental literacy is expected to lead to the manifestation of pro-environmental behavior. The aim of the present study was to examine the impacts of environmental training on pre-primary and primary school educators, and its influence on the formation of their environmental perceptions and attitudes. We investigated whether training triggers the implementation of environmental education programs, and its possible metacognitive effects on educators. Simple random sampling was used as a sampling method. A structured questionnaire was administered to 154 pre-primary and primary school teachers, and the data collection took place through the use of face-to-face interviews. The research findings indicated that educators were interested in environmental issues, and mainly used the media to obtain information about environmental issues. Gender and age were important characteristics influencing the performance and attitudes of environmental educators. It also became apparent that there are significant deficiencies in the capacity building of educators, and in the organization of environmental education in pre-primary and primary education, that negatively affect the implementation of environmental programs in schools.
1. Introduction
The international scientific community has advocated for the importance of environmental education for the management and mitigation of environmental and social issues [1]. Environmental education can be a useful tool for protecting the environment [2]. It is also a significant tool for educators’ and children’s information and awareness, as it provides knowledge on the environment and its problems, while emphasizing the causes that led to those problems and their consequences [3]. Environmental education is the vehicle for pro-environmental behaviors, which are the basis of environmental citizenship [4].
Through its principles and features, environmental education is able to equip students with the skills of investigation, analysis, critical thinking, empathy, participation, and cooperation, which are crucial for tackling pressing environmental and social issues. This is accomplished through its holistic and interdisciplinary character [5]. In order to achieve sustainability in future communities, it is vital to create environmental citizens; people with the knowledge and motivation to deal with the environmental challenges of our rapidly changing planet [6].
Even though environmental education has, to some degree, contributed to the awareness of the educational community, it has not yet led to a set of substantial changes [7]. These changes have been obstructed by various factors, including insufficient training for and limited knowledge on the principles and practices of environmental education among educators, as well as false perceptions of critical environmental issues [8]. Often, educators are concerned about the potential difficulty of implementing environmental education programs [9].
Previous research has pointed out that knowledge without framing other factors does not suffice to change attitudes, or lead people to adopt environmentally responsible behaviors [10,11]. Environmental awareness, profound knowledge, investing personally in environmental topics, and developing skills for strategic action are important variables which affect individuals’ environmental behaviors. A combination of these variables reinforces the citizen’s intention to become involved with environmental issues.
However, proper information, along with profound knowledge of environmental topics, is an indispensable precondition, because inadequate knowledge may shape false perceptions. Studies in Greece and abroad have shown that educators often misunderstand and have a limited or incorrect comprehension of environmental topics and phenomena, due to their inadequate knowledge [12,13].
Recognizing the importance of information and learning, Liarakou et al. [14] conducted a study and observed that educators’ inadequate scientific knowledge on specific environmental issues (such as renewable energy sources) resulted in them having unclear perceptions of relevant topics and being unable to describe them properly. Perceptions also involve scientific factors, as well as information acquired from the surrounding environment through the senses, which is organized and interpreted by mental processes in different ways depending on the individual’s personality and skills [15].
In Greece, a compulsory system of either public or private pre-primary and primary education is in place for children aged between 4 and 12 years old. Pre-primary education begins for children at the age of 4 years old and lasts for 2 years. Primary education starts at 6 years old and lasts for 6 years [16]. Pre-primary and primary school teachers are provided the opportunity to participate in environmental education training programs organized by the Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs. These programs run throughout the school year from October to June, and the participants receive an official certification of training.
As the COVID-19 pandemic has impacted educational services all over the world, it should be noted that in-service training programs in Greece now take place on e-learning platforms.
In-service training is a critical vehicle to transform teachers into modern professionals, by enhancing both their personal and professional development [17]. Surveys conducted in Turkey, Önalan, and Gürsoy [18] have recently found it has a positive effect on teachers’ practical skills, depending on the number and standards of the implemented in-service training programs. In another study in the Netherlands, conducted by Coenders and Terlouw [19], the researchers investigated the phenomenon of teachers’ professional knowledge growth in line with shifts in their attitudes. According to their findings, in-service training programs support teachers’ professional development, and facilitates their ability to adapt to potential changes in the school curricula by improving their skills in teaching within the frame of authentic learning. It should be stressed that continuing professional development is reasoned to bring benefits in the long-term, creating education systems characterized by educators with enthusiasm and commitment to their teaching audiences [20].
More specifically, Karamanou [21], in alignment with Bantounas [22], demonstrated that there is a positive correlation between pre-primary and primary environmental educators who received environmental training and the adoption of greener attitudes, environmental literacy, and the number of environmental education programs implemented at school by those educators. Zachariou et al. [23] proved that teachers characterized by environmental consciousness were more liable to engage with environmental education. In fact, their research revealed that educators’ adoption of environmentally friendly attitudes affected their decision about teaching environmental issues and implementing environmental programs in class. It should be noted that environmental education is not a compulsory subject at school for many European countries, including Greece.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the impacts of environmental training on pre-primary and primary educators, and its role on the formation of environmental perceptions and attitudes. We surveyed whether this training serves as a motivation for implementing environmental education programs in schools, and its metacognitive effects on trained educators.
1.1. Environmental Literacy and Environmental Educators
Educators’ preparedness to teach environmental issues is dependent on them managing to build their own capacity for effectively teaching environmental education, through proper scientific knowledge and competencies in environmental issues.
Inadequate knowledge and perceptions regarding environmental education among educators can lead to unhelpful attitudes and behaviors, and even degrade students’ cognitive level in terms of their environmental education. Hence, a lack of knowledge and training among educators can result in hesitance to implement environmental education programs, or to an inability to support students to achieve the desired results [23].
Educator training is necessary because it can equip them with the appropriate knowledge, abilities, and skills, which can strengthen their environmental teaching. As Katsarou and Dedouli [24] pointed out, training has to take into account that educators have knowledge, educational experience, specific needs, and personal obligations and, at the same time that they wish to participate actively in all stages of training, from design to implementation. Moreover, most educators prefer experiential training, which mobilizes them and keeps their interest. Passive attendance often creates a sense of boredom.
According to Rokicka [25], pro-environmental behavior is not always compatible with a high interest in ecological issues, but is rather associated with cognitive, emotional, and behavioral components, which are affected by various factors. Kruglanski and Higgins [26] claim that awareness of environmental issues could lead people to adopt pro-environmental behaviors and increase the potential of their taking action for the environment. Therefore, raising awareness on environmental issues cultivates an interest in actively participating in environmental decision making [27].
According to Pe’er et al. [28], environmental knowledge and environmental attitudes are closely affiliated. This means that in-service training programs aiming to enhance teachers’ environmental literacy may serve as a means for the formation of the teacher’s own environmental attitudes. Environmental commitment and the influence of background factors are believed to be indicators of the existence of close relationship between the teachers’ background factors and environmental literacy issues [29].
Bantounas [22] examined the views and attitudes of primary school teachers in Rhodes Island, Greece, towards climate change and global warming. He observed a positive correlation between scientific knowledge and competency with: (a) teachers who had attended training programs; (b) teachers who had received environmental education; (c) teachers who had adopted environmentally friendly attitudes. Similar results were found by Karamanou [21], who focused on educators in the Prefecture of Ioannina, Greece. Therefore, it is evident that educators’ environmental awareness, perceptions, and attitudes play a critical role in their engagement with and teaching performance of environmental education.
1.2. Environmental Attitudes of Environmental Educators
According to Jung, attitudes are individuals’ psychological readiness to act or react in a specific way [30]. Attitudes are stored in memory and are shaped by knowledge and emotions that result from previous experiences with a certain issue. Attitudes can also predetermine the active or passive participation of an individual in any form of action. Changing attitudes and behaviors are governed by a multitude of other factors, such as the social and family environment, values which have been shaped through family, behavioral motives, and each individual’s personality [11].
Zachariou et al. [16] showed that educators’ environmental attitudes are linked to their decisions to engage in environmental education. Educators at all levels of education, and particularly in pre-school and primary education, can significantly affect students’ environmental attitudes and behaviors through environmental education programs and their personal environmental behavior. Students’ participation in these programs appears to have a positive effect on their knowledge and ideas concerning environmental topics, as suggested by Liarakou et al. [14]. If properly implemented, environmental education can have important benefits for the environment through its ability to shape environmentally responsible behaviors.
Teaching in primary education has evolved into a challenging issue, as educators have to prepare young learners to be future members of 21st century civil society [31]. Educators should be capable of creating a positive learning environment for their students, in order for them to become active in problem solving and equipped with skills relevant to addressing environmental issues and participating in environmental decision-making processes [32].
Pre-primary and primary educators have a major responsibility to educate their young students about a sustainable world [33]. Their attitudes serve as the ideal mentoring procedure for learners in environmental education. Through their own paradigms, environmental educators are able to create an interest in nature, which is critical in the learning process as it involves emotions as part of experiential learning. Educators’ behavior should inspire students to develop their personalities and act in sustainable ways, within the frame of environmental consciousness.
2. Materials and Methods
The flow chart in Figure 1 depicts the research methodology used in the survey. First, an elaborative literature review took place, followed by the design of a structured questionnaire, which was the tool for data collection. Personal interviews were then organized, addressing 154 teachers from the Directorate of Primary Education in Eastern Thessaloniki, Greece. The collected data were processed by the application of descriptive statistics. The results were discussed, and important conclusions were extracted. Any insightful proposals were highlighted and characterized by transferability and applicability for improving training and capacity building in environmental education, within pre-primary and primary school environments.
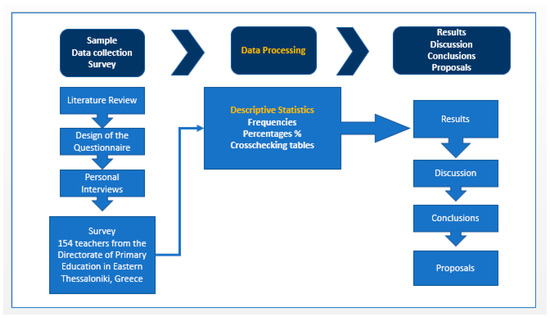
Figure 1.
Flow chart of the research methodology.
The study area was Eastern Thessaloniki, Greece, and included public school units supervised by the Directorate of Primary Education in Eastern Thessaloniki. This organization is supervised by the Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs, and is responsible for pre-primary and primary education issues. The target population under investigation consisted of primary school teachers and pre-school teachers employed by the Directorate of Primary Education in Eastern Thessaloniki.
Simple random sampling (SPS) was the sampling method used, as it is a simple and well-defined method [34] that secures an equal probability to select each case from the population included in the sample [35]. According to its formulas, the final sample was estimated at 154 teachers: (1 − α)100 = 95%, e = 0.05. A pre-sampling procedure included 20 teachers.
The data were collected by the use of a structured questionnaire and personal interviews with pre-school and primary school teachers, during 2019–2020. Interviewing is considered an effective method to collect statistical data; in sampling research it has been used on a large scale [36]. The average time for the interview used in this study was estimated at 25 min. The interviews were undertaken by an experienced interviewer. The interviews took place within the hours 9:00–13:00 on weekdays, when the school units were in operation, and from October to January. As the period of the interviews for data collection ended in January 2020, before the outbreak of COVID-19 in Greece, there was no direct impact from the pandemic on the analysis. The personnel division of the Directorate provided the necessary information about the population of pre-primary and primary teachers registered in the organization.
The design of the questionnaire was based on relevant studies which were conducted within an interdisciplinary and international framework, ensuring it was well designed and adjusted to the scope of investigation [37]. The content of the questionnaire was divided into three sections, aiming to investigate (1) the educator’s profile, (2) issues affecting their environmental consciousness, and (3) the impact of training in environmental education on their attitude (Appendix A).
In order to identify potential correlations between categorical variables, double-entry tables were generated and chi-square tests of independence were conducted [30,31]. In particular, the following relationships were examined:
- Gender and interest in environmental issues
- Age and sources used to acquire environmental information
- Training in environmental education and implementation of environmental education programs
- Training on environmental education issues and interest in environmental issues
- Training on environmental education issues and adoption of pro-environmental behaviors
Cramer’s V index was used to examine the intensity of the relationships between the tested parameters [38,39]. The data analyses were conducted with the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS ver. 20.0). In all statistical tests, the level of significance was defined as p ≤ 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Educator Profile
The educators’ profiles were first obtained, including their demographic and professional characteristics. Of the participants, 79.9% were women and 20.1% were men. The female respondents were mainly primary school teachers. The vast majority of male teachers were primary teachers (there was only one male pre-school teacher in the sample).
Most educators (62.3%) were experienced professionals with more than 20 years’ service as teachers. Moreover, over half of the professionals (55.2%) had received additional training and education after completing their basic university degree.
3.2. Environmental Consciousness Issues
The educators’ environmental consciousness was then examined, based on their interest, awareness, sources used to acquire environmental information, and the hierarchical importance they placed on challenging environmental issues.
Teacher interest in environmental issues is critical to efficiently serve the goals of environmental education. To this end, the results revealed that 50.65% of the educators had a high degree of interest in environmental issues, 41.56% deemed them average to important, and only a small percentage of educators (7.79%) had little interest. Moreover, the χ2 test of independence showed that there was a statistically significant relationship between gender and interest in environmental issues (χ2 = 7.317, d.f. = 2, p-value = 0.026 < 0.005). Cramer’s V index showed that the intensity of the relationship between these variables can be characterized as minor (Cramer’s V = 0.218, 0.10 < C.V < 0.30).
In an effort to further investigate the educators’ interest in environmental issues and the correlation with gender, a double-entry table and χ2 test were generated (Table 1). The analysis indicated that the percentage of female educators (52.8%) who were interested in environmental issues was higher compared to male educators (41.9%). As Kollmuss and Agyeman [11] have stated, although women often have less environmental knowledge, they are more concerned about the environment, and more willing to change their own behavior in order to contribute to its improvement.

Table 1.
Crosschecking results for the effect of gender on educators’ interest in environmental issues.
The way respondents obtain information on environmental issues was examined (Table 2). The analysis indicated that half of the respondents (50%) use television most frequently to inform themselves about environmental issues. In addition, a considerable share, 29.9%, used the internet, and 12.32% reported visiting the websites of specialized bodies in order to obtain information on environmental issues. However, fewer participants had other sources of information, such as family and friends (3.9%) or attendance of relevant seminars (3.2%).

Table 2.
Sources used by educators to acquire environmental information.
A double-entry table was used in order to examine whether age affects the information sources that respondents use in order to obtain information on environmental issues (Table 3). The results showed that television was the most frequently used information source for the majority of educators over the age of 35. However, educators younger than 35 years old preferred the internet. This could be explained by the fact that younger people are more familiar with the use of technology and smart devices, the use of which presupposes an internet connection for access to most of their functions.

Table 3.
Crosschecking results for the effect of educators’ ages on sources used to acquire environmental information.
Then, the respondents were asked to evaluate the importance of eight environmental problems using an eight-point scale, ranging from “very important” to “less important” (Table 4). Climate change was considered the most important environmental problem (with a prevailing rate of 1), followed by pollution (with a prevailing rate of 2), and water depletion (which was ranked third). Conversely, overpopulation was perceived as the least important problem by the respondents (with a prevailing rate of 8).

Table 4.
The educators’ views on the level of importance of challenging environmental issues.
3.3. The Role of Training in Environmental Education Issues on the Educators’ Attitudes
The educators’ environmental literacy and preparedness to teach environmental subjects were then investigated. We examined whether training in environmental topics affects the decision to take on environmental education programs.
As presented in Table 5, there was a significant correlation between teachers’ environmental training and the performance of environmental education programs. In particular, 88% of respondents who claimed to have received special training had implemented environmental education programs. On the other hand, it should not be disregarded that 46.3% teachers who had implemented environmental education programs had not received any special training on environmental science.

Table 5.
Crosschecking results for the correlation between the educators’ training in environmental education and implementation of environmental education programs.
Moreover, the χ2 independence test indicated that there was a statistically significant relationship between training in environmental education and implementing environmental education programs (χ2 = 31.218, d.f. = 1, p-value = 0.000 < 0.005). The intensity of this relationship was satisfactory (Cramer’s V = 0.450 and 0.30 < C.V < 0.50). It was thus indicated that educators’ decision to implement environmental education programs is positively affected by relevant training.
The relevance of teachers’ training on environmental education issues to their interest in environmental issues was surveyed. Table 6 reveals that most of the educators (60%) who were trained in environmental education expressed a strong interest in environmental issues. Specifically, 38% considered environmental issues average to important, while only 2% reported a minor degree of interest. Among teachers who had never received training in environmental education issues, almost half (46.3%) claimed to have an average to high degree of interest in environmental issues, while 16.7% were less interested.

Table 6.
Crosschecking results for the correlation between educators’ training on environmental education issues and their interest in environmental issues.
In addition, the χ2 test of independence showed that there was a statistically significant relationship between training on environmental education issues and interest in environmental issues (χ2 = 15.638, d.f. = 2, p-value = 0.000 < 0.005). Cramer’s V index indicated that the intensity of the relationship between these variables was satisfactory (Cramer’s V = 0.343 and 0.30 < C.V < 0.50), while the relevance was of less importance.
The teachers’ environmentally friendly attitudes were also investigated in relation to the training they had received on environmental education issues. The findings reflected the important correlation of these variables, as a statistically important relationship between training in environmental education issues and the teachers’ environmentally friendly attitudes was found. In fact, it became particularly apparent for two variables; namely “recycling” and “use of alternative means of transport”. Almost all (99%) of the teachers who had attended environmental education programs stated that they recycle their waste (Table 7).

Table 7.
Results of the Pearson chi-square tests regarding the relationship between the educators’ training on environmental education issues and adoption of pro-environmental behaviors.
The χ2 test of independence showed that training on environmental education issues had positively affected the teachers in adopting pro-environmental behaviors such as recycling in their private life (χ2 = 24.781 d.f. = 1, p-value = 0.000 < 0.005). The intensity of the relationship between the two parameters was strong (Cramer’s V = 0.401 and 0.30 < C.V < 0.50).
4. Discussion
Important findings emerged from the case study and it is essential to further analyze them. The educators’ interest in environmental issues was examined first in this study. A majority of the educators claimed to have a high to average degree of interest in environmental issues. There was a remarkable distinction by gender; women reported being more interested in this subject. On the one hand, there is a gender imbalance in this area in many countries, represented by a shortage of male teachers in pre-primary and primary education [40,41,42], which at the same time explains their low inclusion in this sampling procedure. On the other hand, female educators tend to show a greater devotion to and a more stratified interest in environmental issues compared to their male colleagues [11,43].
With regards to awareness of environmental issues, the media was the educators’ main source of information, with similar results found by Skanavis et al. [44], also in Greece, proving that there has not been a shift over the last twenty years. Television was preferred by older educators, and the internet by younger educators. According to Wilkins et al. [45], traditional means such as television and radio are more familiar to older people for obtaining information about environmental issues rather than the internet, which is preferred by younger people.
It should be noted that the Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs does not list environmental education as a compulsory subject in school. Stanišić and Maksić [46] note the same is true for many European countries. This means that there is no syllabus and consequently there is a lack of institutional in-house data addressing environmental issues available for teachers. Therefore, as the validity of information could not be officially controlled and the respondents were still reliant on the media, this is a serious indication of a policy the gap in environmental education. The contribution of the media to strengthening interest in the environment should not be undervalued, as the high level of publicity and the easy access which characterize the media have contributed to the development and dissemination of environmental movements, and to the quest for a global solution to environmental protection [47].
The data analysis revealed the effect of training in environmental education issues on the educators’ decision to take on environmental education programs. More specifically, almost nine in ten of the trained educators had implemented environmental education programs. Additionally, approximately half of the respondents had implemented environmental education programs without receiving any training to effectively perform their role as environmental educators. The question arising from this is whether these educators were well prepared, mainly in terms of scientific knowledge and the cognitive field, to efficiently teach environmental themes. Environmental issues are characterized by high complexity, which suggests a special scientific background may be needed in order to comprehend some environmental parameters in sufficient depth [46,48].
Furthermore, the majority of educators who had been trained in environmental education expressed a notable interest in environmental issues. Specifically, approximately nine out of ten of the respondents showed an average to high interest in environmental issues. At the same time, the respective proportion of teachers who had never received any training was almost five in ten. These results indicate that the educators’ participation in environmental training plays a major role developing personal concerns about the preservation of the natural environment. Furthermore, it became apparent that there was latent environmental concern even in non-trained educators. This may have been driven by their environmental perceptions, demographic characteristics such as gender [49], or by certain experiences. Recent studies have indicated that devastated or undisturbed natural environments are closely affiliated with what people perceive as “quality of life” [50,51,52]. These kinds of perceptions, in turn, affected the educators’ views on environmental issues [53].
In addition, training the educators in environmental education revealed that these respondents were keener to adopt “greener attitudes” towards waste management and transportation, which are two major environmental problems in urban environments such as Thessaloniki. This is possibly an indication of how environmental education affects educators’ views about the environment in which they work and live. Their experiences could be considered as showing greater sensitivity, and recognizing environmental problems as something that directly affects their quality of life.
5. Conclusions
This case study aimed to examine the impact of environmental training on pre-primary and primary educators. The findings provided critical insights into in-service training in environmental education, and its influence on teachers’ perceptions and the adoption of greener attitudes. In particular, it became apparent that in-service training which focuses on improving the teachers’ environmental literacy has two beneficial effects. The first is that serves as motivation for implementing environmental education programs in schools, and the second involves the meta-cognitive skills of the trained educators that lead to environmentally friendly attitudes. The research limitations and practical implications of this case study include the evaluation of the provided in-service training programs on environmental education for pre-primary and primary teachers.
In light of the findings related to the educators’ profiles, especially gender, it is clear different dynamics occur in the formation of environmental interest. Women tend to be more interested in environmental schemes than men, who are the minority among pre-primary and primary educators.
The educators’ dependence on the media to access environmental information highlights serious deficiencies in the organization and performance of the school curriculum, and the devaluation of the state for preparing future active citizens who are able to participate in environmental decision making. Unless environmental education is provided as a compulsory subject at school, citizens will not be able to efficiently develop participatory skills and become actively involved in environmental issues.
With regards the educators’ preferences around seeking environmental information via the television or the internet, these methods mean they need to spend a lot of time not only collecting the relevant information, but also examining the source reliability. Since the information they obtain does not come directly from scientific sources or competent environmental and educational bodies, they must filter and crosscheck the validity of this information very carefully.
Training in environmental education issues has played a positive role in changing educators’ attitudes. This was expressed by their nature-based interests, and their creativity in teaching environmental themes and implementing environmental programs. One of the critical impacts of their participation in training programs was the meta-cognitive skills they developed, including changing their attitudes to more environmentally friendly ones.
In addition, taking part in recycling and using alternative means of transport were the top of the teachers’ “green agendas” for improving their wellbeing, as they were mainly urban dwellers. Moreover, these green attitudes may be related to the educators’ experiential learning. Therefore, new opportunities for educators in environmental training are necessary in order to achieve behavior change. The cognitive frame of educators should be enhanced and further improved to serve as motivation for taking over environmental programs, while it should be taken into consideration that environmental stimuli play an important role in educators’ attitudes.
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the alarming threat to human health, both now and in the future, of imbalances of ecosystems. This imbalance derives from pressures on land use and land use change, environmental degradation, climate change, and overpopulation, all of which are worsening already existing environmental problems. This represents key evidence that educational curricula need to integrate environmental education to empower people towards the preservation of the natural environment and promote their development within the framework of sustainable development, in order to build societal resilience. Thus, environmental education should be at the top of the agenda in the development of new school curricula—as possible scenarios after COVID-19 demonstrate that human societies will suffer new pandemics in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P.; methodology, software, validation, V.A.; investigation, K.A.; writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, D.P., V.A. and K.A.; supervision, D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
The appendix is the questionnaire used to collect the research data.

Alexandria University of Sindos
Department of Agriculture, School of Geotechnical Sciences
Professor Stamatis Angelopoulos
Tel.: 2310013104 & 6978333882
E-mail: stamagg40@gmail.com
QUESTIONNAIRE
Dear colleague
This questionnaire is a key research tool that will be utilized for the preparation of my master’s thesis. It aims to investigate your views on environmental issues and the implementation of environmental programs. The information you provide is strictly confidential and will only be used for research purposes. Please answer the following questions carefully and honestly. This work is part of the obligations of Postgraduate students arising from the Postgraduate Program “Environmental Management and Environmental Education”, while it has been approved by the Coordinating Committee and the Assembly of the Department. Thank you for your time to complete it.
Yours sincerely
Katerina Anthrakopoulou—Pre-primary school teacher
A. ATTITUDES TOWARDS ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES-ENVIRONMENTAL BEHAVIORS
- How concerned do you feel about environmental issues?
- □
- Extremely
- □
- Moderately
- □
- Somewhat
- □
- Slightly
- □
- Not at all
- What sources of information do you use to obtain information on environmental issues (please choose only one answer)
- □
- Television/newspapers/magazines
- □
- Internet browsing
- □
- Searching the websites of specialized bodies
- □
- Books
- □
- Training programs/seminars
- □
- Conversations with friends/family
- □
- Other (please specify)............................................................................................................
- Please prioritize the following environmental issues in terms of their importance, where 1 = the most important and 8 = the least important
RANKING 1 Air/soil/water pollution 2 Water depletion 3 Depletion of non-renewable sources 4 Overpopulation 5 Climate change 6 Biodiversity loss (fauna and flora) 7 Waste/toxic waste management 8 Health problems due to environmental degradation 9 Other (please specify) - Have you adopted any special consumer’s purchase behavior, due to interest in the environment?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- Which of the following do you apply in your personal life?
YES NO 1 Recycling 2 Turning off lights 3 Use of energy-efficient light bulbs 4 Reducing water use 5 Use of alternative means of transport 6 Avoiding single-use plastics 7 Reduction of plastic carrier bags via the use of reusable shopping bags 8 Reduction of meat consumption 9 Thermostat setting for lower energy consumption 10 Regular maintenance of energy-efficient appliances 11 Household adoption of energy-efficient appliances 12 Participation in environmental actions
B. KNOWLEDGE-PERCEPTIONS ON CLIMATE CHANGE
- 6.
- In recent years, the term climate change has been widely acknowledged. Why do you think this has happened?
AGREE DISAGREE 1 Because it is a very important issue that concerns everyone 2 Because the effects are apparent 3 Because scientists and environmentalists are pushing to deal with it 4 Because governments have realized the importance of climate change for humanity and our planet 5 The media promotes climate change issues because they attract the public interest 6 Behind the publicity for climate change are hidden economic, business, or political interests 7 Other (please specify): Which of the above reasons do you think is the most important? (Write only the number) …………………… - 7.
- According to your views climate change … (please choose only one answer)
- □
- ... is a very serious issue that needs to be faced immediately.
- □
- … is a very important issue that mainly the next generations will have to deal with.
- □
- … is important, but there are more serious environmental and social issues to deal with.
- □
- … has as gained more attention than needed. It is neither that important nor unprecedented. There have been cold and hot climates also in the past (e.g., glacier season).
- 8.
- Climate change is mainly due to … (please choose only one answer)
- □
- Natural processes (e.g., volcanic eruptions)
- □
- Anthropogenic activities
- □
- I don’t know
- 9.
- Climate change is responsible for … (please choose only one answer)
- □
- the ozone hole
- □
- the greenhouse effect
- 10.
- Global warming is due to … (please choose only one answer)
- □
- increased emissions solar radiation
- □
- increased emissions from coal combustion
- 11.
- What is your view on the greenhouse effect? (please choose only one answer)
- □
- Greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon
- □
- Greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon that was intensified by anthropogenic activities
- □
- Greenhouse effect has been caused by human activities
- □
- I don’t know
- 12.
- Below are some activities that contribute to climate change. Which, in your opinion, are the ones that have the largest share of responsibility?
GREAT
RESPONSIBILITYLESS
RESPONSIBILITY1 Deforestation 2 Asphalt paving and extensive construction 3 Production of electricity from coal 4 Fuels from industries/transportation/heating 5 Chemical processes in industry 6 Livestock/agriculture 7 Waste 8 Combustion of natural gas 9 The forest fires 10 Volcanic eruptions - 13.
- There are some effects of climate change below. Which do you consider as more important and which as less important?
VERY
IMPORTANTLESS
IMPORTANT1 Extreme weather effects 2 Glaciers and sea ice melting/sea level rise 3 Rise in temperature 4 Desertification and water scarcity 5 Forced migration of populations due to reduction of arable soil, food, and water 6 Significant problem of poverty/malnutrition/hunger 7 Economic costs for countries affected by extreme weather effects 8 Increases in forest fire risk 9 Increases in diseases and epidemics 10 Other (please specify) - 14.
- Do you think that climate change can be reversed if appropriate measures are taken?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- □
- I don’t know
C. TRAINING-ENVIRONMENTAL EDUCATION PROGRAMS
- 15.
- Have you been trained in Environmental Education?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- 16.
- If yes, please specify in which way?
- □
- A course in university
- □
- Postgraduate studies (e.g., master)
- □
- Seminars/conferences
- 17.
- Have you received any training on climate change?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- 18.
- Have you implemented any environmental education programs, during school activities?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- 19.
- If Yes, why did you get involved with an environmental education program? (please choose only one answer, the most important for you)
- □
- I regard environmental education as important
- □
- To mobilize students on environmental issues
- □
- It emerged due to the children’s interest
- □
- It emerged after my colleagues’/manager’s motivation
- □
- It was a random choice
- □
- Other ………………………………….(please specify)
- 20.
- If you have implemented an environmental education program, choose the subject(s) you focused on:
- □
- Weather/climate/climate change
- □
- Forest
- □
- Water
- □
- Waste/recycling
- □
- Pollution
- □
- Energy
- □
- Fauna/endangered species/stray animals
- □
- School garden
- □
- Urban environment/neighborhood
- □
- Soil/agriculture/nutrition
- □
- Other:………………………………………………………… (please specify)
- 21.
- If you haven’t implemented any environmental education programs, which were the main reasons? (Put 1 for the most important reason, 2 for the second …… 5 for the least important)
RANKING 1 Lack of personal time 2 Lack of teaching time 3 Insufficient knowledge 4 Bureaucratic procedures 5 It is out of my interests 6 Other ……………………………………(please specify) - 22.
- Are you interested in implementing any environmental education programs?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- 23.
- Are you interested in implementing any environmental education programs related to climate change?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
- 24.
- Which of the following factors do you consider as the most important one for the implementation of environmental education programs? (please choose only one answer)
- □
- Teachers’ environmental consciousness
- □
- Appropriate training
- □
- Rich educational material
- □
- Infrastructuresand technical equipment (e.g., computers in the classroom, experiments)
- □
- Support from the official staff of the Directorate of Primary Education on environmental education issues
- □
- Support from the manager of the school unit
- □
- Collaboration with colleagues
- □
- Children’s interest
- □
- Other …………………………………… (please specify)
D. DEMOGRAPHIC CHARACTERISTICS—STUDIES
- 25.
- Gender
- □
- Man
- □
- Woman
- 26.
- Age
- □
- Up to 35
- □
- 35–50
- □
- Over 50
- 27.
- Type of employment
- □
- Permanent staff
- □
- Non-Permanent staff
- 28.
- Years of employment
- □
- 1–10
- □
- 11–20
- □
- Over 20
- 29.
- Employment as
- □
- Primary school teacher
- □
- Pre-primary school teacher
- 30.
- Studies (you can choose more than one answer)
- □
- Bachelor
- □
- Marasleio Teaching School
- □
- Master
- □
- Ph. D
- 31.
- Is your Master or Ph. D related to environmental studies?
- □
- Yes
- □
- No
Thank you for your time and cooperation!
References
- Flogaiti, Ε. Education for the Environment and Sustainability, 2nd ed.; Pedio: Athens, Greece, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Eneji, C.; Akpo, D.; Edung, E. Historical Groundwork of Environmental Education (Fundamentals and Foundation of Environmental Education). Int. J. Contin. Educ. Dev. Stud. 2017, 3, 110–123. [Google Scholar]
- Karageorgakis, S. Environment. Philosophy and Environmental Education; Eftopia Publications: Athens, Greece, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gunningham, N.; Kagan, R.A.; Thornton, D. Social license and environmental protection: Why businesses go beyond compliance. Corp. Environ. Responsib. 2017, 29, 485–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, P.; Lazaropoulos, S.; Mastoras, Μ.; Theodosiadou, P. Educational approaches and methods in Environmental Education. In Proceedings of the 5th Pan-Hellenic Conference of the Hellenic Institute of Applied Pedagogy and Education on “I learn how to learn”, Athens, Greece, 7–9 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, Y.; Hadjichambis, A.C.; Hadjichambi, D. Teachers’ Perceptions on Environmental Citizenship: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flogaiti, Ε. Education for the Environment and Sustainability; Ellinika Grammata: Athens, Greece, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Frantz, C.M.; Mayer, F.S. The importance of connection to nature in assessing environmental education programs. Stud. Educ. Eval. 2014, 41, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskolia, Μ. Theory and Practice in Environmental Education: The Personal Theories of Educators; Metaixmio: Athens, Greece, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hungerford, H.R.; Volk, T.L. Changing Learner Behavior through Environmental Education. J. Environ. Educ. 1990, 21, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollmuss, A.; Agyeman, J. Mind the gap: Why do people act environmentally and what are the barriers to pro-environmental behavior? Environ. Educ. Res. 2002, 8, 239–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daskolia, M.; Flogaitis, E.; Papageorgiou, E. Kindergarten Teachers’ Conceptual Framework on the Ozone Layer Depletion. Exploring the Associative Meanings of a Global Environmental Issue. J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2006, 15, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Roehrig, G.H.; Bhattacharya, D.; Varma, K. In-Service teachers’ attitudes, knowledge and classroom teaching of Global Climate Change. Sci. Educ. 2015, 24, 12–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liarakou, G.; Athanasiadis, I.; Gavrilakis, C. What Greek Secondary School Students Believe about Climate Change? Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2011, 6, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Georgas, D. Social Psychology; Ellinika Grammata: Athens, Greece, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- EURYDICE. Available online: https://eacea.ec.europa.eu/national-policies/eurydice/content/early-childhood-education-and-care-33_en (accessed on 15 May 2021).
- Sakkoulis, D.P.; Asimaki, A.; Vergidis, D.K. In-service Training as a Factor in the Formation of the Teacher’s Individual Theory of Education. Int. Educ. Stud. 2018, 11, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Önalan, O.; Gürsoy, E. EFL Teachers’ views and needs on in-service training as a part of professional development: A case study in Turkish context. Bartin Univ. J. Fac. Educ. 2020, 9, 373–387. [Google Scholar]
- Coenders, F.; Terlouw, C. A Model for In-service Teacher Learning in the Context of an Innovation. J. Sci. Teach. Educ. 2015, 26, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlberg, M.; Bezzina, C. The professional development needs of beginning and experienced teachers in four municipalities in Sweden. Prof. Dev. Educ. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanou, C. Environmental Education for Sustainability in the Modern School: Teachers’ Perceptions and Practices. The Case of Primary Education Teachers in the Prefecture of Ioannina. Bachelor’s Thesis, School of Human Studies, Hellenic Open University, Patras, Greece, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Badounas, A. Teachers’ Views, Attitudes and Perceptions regarding Climate Change and Global Overheat. Case Study: Teachers of Discipline PE70 (Primary Teachers) of Primary Education in the Prefecture of Dodecanese. Master’s Thesis, Department of Preschool Education and Educational Planning, University of the Aegean, Rhodes, Greece, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariou, F.; Tsami, E.; Chalkias, C.; Bersimis, S. Teachers’ attitudes towards the environment and environmental education: An empirical study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Educ. 2017, 12, 1567–1593. [Google Scholar]
- Katsarou, E.; Dedouli, M. Training and Evaluation in the Space of Education; Pedagogical Institute, Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs: Athens, Greece, 2008; pp. 38–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rokicka, E. Attitudes toward Natural Environment. Int. J. Sociol. 2002, 32, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglanski, A.W.; Higgins, E.T. Social Psychology: Handbook of Basic Principles, 2nd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Petkou, D. Effects of Mass Media on the Attitudes and Behaviors of Primary Education Teachers on Environmental Matters. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Forestry and Management of the Environment and Natural Resources, Democritus University of Thrace, Orestiada, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pe’er, S.; Goldman, D.; Yavetz, B. Environmental Literacy in Teacher Training: Attitudes, Knowledge, and Environmental Behavior of Beginning Students. J. Environ. Educ. 2007, 39, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, D.; Yavetz, B.; Pe’er, S. Environmental Literacy in Teacher Training in Israel: Environmental Behavior of New Students. J. Environ. Educ. 2006, 38, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.; Bohner, G.; Wanke, M. Attitudes and Attitude Change; Psychology Press: East Sussex, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Van Werven, I.M.; Coelen, R.J.; Jansen, E.P.W.A.; Hofman, W.H.A. Global teaching competencies in primary education. Comp. J. Comp. Int. Educ. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Panula, E.; Jeronen, E.; Lemmetty, P. Teaching and Learning Methods in Geography Promoting Sustainability. Educ. Sci. 2020, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beery, T.; Magntorn, O. Pre-Service Early Childhood Educator Experience in a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siardos, G.K. Multivariate Statistical Analysis Methods. Part I: Exploring the Relations between Variables; Zitis Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Taherdoost, H. Sampling Methods in Research Methodology; How to Choose a Sampling Technique for search. Int. J. Acad. Res. Manag. 2016, 5, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kiochos, P.A. Statistics; Interbooks Publishing: Athens, Greece, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Heinrichs, A.J.; Kiernan, N. Initial results of a statewide extension program in calf and heifer management in Pennsylvania. J. Dairy Sci. 1994, 77, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresti, A. Categorical Data Analysis; John Willey & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dafermos, V. Social Statistics with SPSS; Ziti Publications: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, K.F.; Moosa, S.; Van Bergen, P.; Bhana, D. The Plight of the Male Teacher: An Interdisciplinary and Multileveled Theoretical Framework for Researching a Shortage of Male Teachers. J. Men’s Stud. 2020, 28, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, K.; Sullivan, V.; Jansen, E.; McDonald, P.; Sumsion, J.; Irvine, S. A man in the centre: Inclusion and contribution of male educators in early childhood education and care teaching teams. Early Child Dev. Care 2018, 190, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Waniganayake, M. An exploratory study of gender and male teachers in early childhood education and care centres in China. Comp. J. Comp. Int. Educ. 2017, 48, 518–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antrakopoulou, K.; Petkou, D.; Andrea, V. The Knowledge and Attitudes of Primary School Teachers towards Environmental Issues and their Effect on the Implementation of Environmental Education Programs. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual EUROMED Academy of Business (ΕΜAΒ) Conference Business Theory and Practice Across Industries and Markets Virtual Conference, 9–10 September 2020; EuroMed Press: Sicily, Italy, 2020; pp. 1263–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Skanavis, Κ.; Petreniti, Β.; Giannopoulou, Κ. The dedication of educators to Environmental Education. In Proceedings of the International Exhibition and Conference for Environmental Technology HELECO ’05, Athens, Greece, 3–6 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkings, E.J.; Wilkins, E.J.; Miller, H.M.; Tilak, E.; Schuster, R.M. Communicating information on nature-related topics: Preferred information channels and trust in sources. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanišić, J.; Maksić, S. Environmental Education in Serbian Primary Schools: Challenges and Changes in Curriculum, Pedagogy, and Teacher Training. J. Environ. Educ. 2014, 45, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostarella, I.; Theodosiadou, S.; Tsantopoulos, G. The coverage of environmental issues by the Greek media from the editors’ perspective. In Proceedings of the Global Virtual Conference, 8–12 April 2013; EDIS: Zilina, Slovak Republic, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarenko, A.V.; Kolesnik, A.I. Raising Environmental Awareness of Future Teachers. Int. J. Instr. 2018, 11, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkou, D. Τhe contribution of mass media to the environmental awareness of Primary Education Teachers: Exploring the Impact of Gender. In Proceedings of the 11th Conference of the EuroMed Academy of Business, Valletta, Malta, 12–14 September 2018; pp. 1653–1655. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, S.; Nieuwenhuizen, W.; Farjon, J.; van Hinsberg, A.; Dirkx, J. In which natural environments are people happiest? Large-scale experience sampling in the Netherlands. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 205, 103972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.; Kim, S.; Buckman, S. Multiple Perspectives on the Meaning and Effects of Resiliency. In Handbook of Quality of Life and Sustainability; Martinez, J., Mikkelsen, C.A., Phillips, R., Eds.; International Handbooks of Quality-of-Life; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Chen, B.; Kwan, M.P. How does urban expansion impact people’s exposure to green environments? A comparative study of 290 Chinese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, V.; Petkou, D.; Bilbilis, M. Environmental programs’ evaluation: A teacher-based study in the urban city of Thessaloniki. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual EUROMED Academy of Business (ΕΜAΒ) Conference Business Theory and Practice Across Industries and Markets Virtual Conference, 9–10 September 2020; EuroMed Press: Sicily, Italy, 2020; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).