Abstract
This study investigates the influence of banking service quality and customer trust on customer retention behavior, considering the mediating role of customer satisfaction and the moderating role of FinTech. In light of the growing digitalization in the banking sector, the study aims to understand how these constructs interact to drive long-term customer loyalty. A quantitative research approach was adopted using data collected through a structured questionnaire administered to banking customers. The relationships among variables were examined using Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), assessing both direct and indirect effects. The results show that banking service quality and customer trust significantly enhance customer satisfaction, which in turn positively influences customer retention behavior. Moreover, satisfaction was found to mediate the relationships between both service quality and trust with retention. FinTech demonstrated a strong direct effect on retention and also significantly moderated the satisfaction–retention link, amplifying its impact when FinTech services are effectively utilized. This study contributes to the relationship marketing literature by introducing FinTech as a novel moderating variable in the satisfaction–retention framework. It offers practical insights for banks aiming to enhance retention by improving service quality, fostering trust, and leveraging digital technologies to strengthen customer relationships.
1. Introduction
The rise of digital technologies has completely reshaped the way financial services operate. Banks are no longer just physical buildings—they have had to rethink how they engage with customers in an age where convenience and speed are expected (Tasca et al., 2016; Toader et al., 2018). This digital shift has opened the door for FinTech, which are often more flexible and tech-savvy, to step in with solutions that are faster, simpler, and designed with the user in mind. While the global discourse on FinTech continues to expand, most existing studies have concentrated on mature and highly competitive banking systems in developed economies, leaving emerging and constrained markets relatively underexplored. This imbalance limits our understanding of how FinTech transforms customer behavior in banking environments characterized by restricted market access and infrastructural limitations.
FinTech blends finance with innovation, offering services that go far beyond traditional banking—from mobile payments and Robo-advisors to instant digital loans. These tools have changed the game by making banking more personalized and accessible, especially in places where smartphones are widely used but access to traditional bank branches is limited (Al Nawayseh, 2020; Dahlberg et al., 2015; Gomber et al., 2017). As a result, FinTech is not just a trend—it is a major force in how customers now experience and expect financial services. However, the adoption and impact of FinTech remain context-specific. In developing or financially constrained markets such as Palestine, FinTech not only bridges the service-access gap but also represents a strategic lever for enhancing trust, satisfaction, and long-term customer retention in environments where traditional banking channels are limited.
In this context, the ability of banks to retain customers has become increasingly vital. Customer retention—defined as the continuation of a customer’s relationship with a firm (Keiningham et al., 2007)—is widely recognized as a strategic priority for service-oriented businesses (Coviello et al., 2001). In banking, where service differentiation is often limited, long-term retention directly contributes to profitability and competitive sustainability (Chinje, 2013). However, the factors that influence retention have evolved; while customer satisfaction remains a cornerstone, digital disruption has introduced new complexities. Satisfaction, commonly conceptualized as the fulfillment of customer expectations, has consistently shown a positive relationship with retention (E. W. Anderson & Sullivan, 1993; Gustafsson et al., 2005). Yet, satisfaction may no longer fully explain customer loyalty in the digital age, where services are increasingly commoditized, and alternatives are easily accessible. Accordingly, this study seeks to answer the following research question: To what extent does FinTech moderate the relationship between customer satisfaction and customer retention in the banking sector, particularly within the Palestinian context?
Customer retention behavior is influenced by various external and internal factors; this study specifically investigates the moderating effect of FinTech on the relationship between customer satisfaction and customer retention. Theoretically, this investigation draws upon three complementary frameworks: Expectancy-Disconfirmation Theory (EDT), Expectancy-Confirmation Theory (ECT), and Relationship Marketing Theory (RMT). According to EDT (Oliver, 1989), customer satisfaction results from the disconfirmation of expectations—when the actual performance of a service exceeds or falls short of initial expectations. This is particularly relevant in FinTech-driven digital banking, where enhanced speed, security, and convenience can lead to positive disconfirmation, reinforcing satisfaction and, consequently, retention. ECT (Oliver, 1980) supports this by explaining how satisfaction arises when perceived service performance aligns with expectations (Bhattacherjee, 2001). RMT adds a relational dimension, emphasizing trust and emotional bonds as critical to long-term customer relationships, especially in technology-mediated services. In short, this integrated theoretical approach highlights how FinTech can simultaneously shape customer expectations, fulfill or surpass them, and foster trust—altogether reinforcing retention.
In Palestine, where the banking sector operates under political and infrastructural constraints, physical access to financial services remains limited. Consequently, FinTech serves not merely as a technological enhancement but as a necessity that enables continuous financial inclusion and relationship maintenance. Customers increasingly rely on digital banking to overcome physical barriers, satisfy their need for convenience, and sustain their financial activities despite systemic challenges. Hence, examining FinTech’s moderating role in this context provides an opportunity to understand how technological adaptation can influence behavioral loyalty under conditions of constraint.
The adoption of this multi-theoretical framework in the Palestinian and other micro-markets could deal with significant issues presented by distinctive structural scenarios, such as a lack of competitive situation, limited access to the market, and increased consumer sensitivity toward service convenience and technology reliability (Magdy Rezk & Halim, 2022). In Palestine, there are actual constraints on the possibilities for physical access to banking services; thus, FinTech becomes not only a tool for service delivery but also a platform for expectation disconfirmation and relationship cultivation. Customers increasingly depend on it to accomplish their expectations of unhindered and simple banking services. FinTech adoption then influences customer satisfaction, needs fulfillment, and eventual retention. Thus, incorporating EDT, ECT, and RMT in this context emphasizes the role of technological advancement as both a cognitive and emotional driver of customer retention, especially within constrained and digitally evolving environments.
Prior studies have established the mediating role of satisfaction in the relationship between service quality, trust, and retention (Nazir et al., 2016; Ranaweera & Prabhu, 2003). Furthermore, it has been suggested that satisfaction alone does not always result in loyalty unless complemented by trust and perceived value (Madjid, 2013; Sheth & Sisodia, 1999). Nevertheless, a notable research gap persists: limited empirical evidence exists regarding how FinTech moderates the satisfaction–retention link, particularly in developing or semi-digitalized economies such as Palestine. Most existing models have not accounted for technological disruptors as strategic variables that interact with customer perceptions. This represents a significant oversight, particularly in regions where FinTech adoption is accelerating, and customer expectations are increasingly shaped by digital service standards. It also examines how banking service quality and customer trust influence satisfaction, with satisfaction posited as a mediator in their effect on retention.
The contribution of this study consists of two main contributions. Theoretically, it advances relationship marketing literature by incorporating FinTech as a dynamic contextual variable that can reshape traditional models of loyalty. Empirically, it provides fresh evidence from the Palestinian banking sector, where FinTech has become a strategic necessity rather than a convenience, demonstrating how digital innovation can sustain customer retention under conditions of market constraint. Practically, it offers actionable insights for banks aiming to leverage digital tools not only to improve operational efficiency but to foster deeper, more resilient customer relationships in a competitive, tech-driven environment.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews the relevant literature and develops the conceptual framework and hypotheses. Section 3 outlines the research methodology. Section 4 presents the results of the empirical analysis and discusses the findings and their implications. Finally, Section 5 concludes the study with limitations and directions for future research.
2. Theoretical Framework, Hypotheses Development and Conceptual Framework
2.1. Theoretical Framework
This study is primarily based on what (Oliver, 1989) thought in the EDT, which states that satisfaction to the customer is generated when the perceived performance of the service goes beyond (positive disconfirmation) or below (negative disconfirmation) pre-service expectations as characterized by the expectations set prior to service experience. In digital banking, FinTech-driven technologies have tremendously influenced such anticipated forms of consumer expectations. If digital service offerings go further by offering speed, security, and convenience than was expected, thereby creating positive disconfirmation, it enhances satisfaction. It increases the likelihood that competition will keep the customer.
Further, drawing from the ECT (Oliver, 1980) provides logic on which the framework is founded, suggesting that satisfaction occurs when expectations are confirmed. Where ECT concern ends with confirming a consumer’s expectations, EDT takes a step further by considering the psychological effects of the resultant misfit. Synthesizing this, EDT is currently the most appropriate description of consumer satisfaction in rapidly changing techno-geographic environments like digital banking.
In the context of cognitive perspectives, RMT (Möller & Halinen, 2000), adopts a practical and relational perspective based on trust and long-term customer value, which is essential in upholding customer relationships. Trust—especially in digital platforms—becomes crucial in reducing perceived risks and cultivating emotional connections, which elevate consumers’ satisfaction and loyalty behaviors. Consequently, by integrating EDT and RMT, this study could thoroughly and comprehensively explore all rational and emotional processes that provide and sustain customer loyalty in a digitally transforming banking environment.
2.2. Hypothesis Development
The evolution of RMT in service sectors, particularly in banking, emphasizes the importance of fostering long-term customer relationships through satisfaction, trust, and value creation. As banking services shift toward digital platforms, integrating traditional relationship constructs with emerging technological dimensions such as FinTech has become essential for sustaining loyalty and competitive advantage.
Drawing on EDT, ECT and RMT, this section links banking service quality, customer trust, satisfaction, and retention, while positioning FinTech as a moderating mechanism that shapes expectation formation, confirmation, and relationship strength. EDT explains satisfaction as the result of disconfirmed expectations, ECT focuses on how confirmed experiences reinforce satisfaction, and RMT highlights trust and commitment as relational outcomes. FinTech interacts with these processes by accelerating service delivery, confirming performance expectations, and reinforcing long-term relational bonds through convenience and transparency.
2.2.1. Banking Service Quality
In the banking sector, the concept of service quality carries exceptional importance given the intangible and trust-driven nature of financial services. Unlike products, banking services rely heavily on customer perceptions and interpersonal interactions. Service quality is often shaped by how customers compare their initial expectations with the actual service they experience (Parasuraman et al., 1988). This comparison forms what is known in the literature as the “expectation-performance gap,” which is central to the SERVQUAL model—a widely used but not universally accepted tool for evaluating service quality.
Yet, not all customers evaluate services the same way. Recent research emphasizes that cultural and regional differences play a critical role in how service quality is perceived and assessed (Teeroovengadum, 2022). In banking, where transactions are sensitive and highly personalized, these cultural influences can be even more pronounced. For instance, what is seen as efficient service in one context might feel impersonal or rushed in another. Dimensions like transaction speed, clerk proficiency, service reliability, confidentiality, and responsiveness were empirically related to customer satisfaction (Amin & Isa, 2008; Pakurár et al., 2019; Tamaruddin et al., 2020). Further, the most visible service attributes, such as well-arranged cash tellers, long service hours, and the realizable operation of digital platforms, dramatically affect the customer’s perception and satisfaction (Raza et al., 2020). In addition, face-to-face exchanges and company-employee interactions play two vital roles in reinforcing the perception of service quality and building long-term customer relationships (Iyer et al., 2018).
In theory, the link between service quality and customer satisfaction is forcefully underpinned by EDT (Oliver, 1989). When service performance is conceived to exceed our expectations, satisfaction arises through positive disconfirmation. In the context of FinTech, this theoretical link EDT becomes even stronger because customers’ expectations of digital banking services—such as transaction speed, usability, and reliability—are constantly compared to their perceived performance. When FinTech innovations deliver beyond expected convenience and security, they generate positive disconfirmation, thereby enhancing satisfaction and reinforcing technology-driven trust. Over and above this, the appraisal-emotion-coping framework (Bagozzi, 1992) posits that satisfaction comes with the emotional response resulting from the cognitive evaluation of service quality. In this view, satisfaction is not only transactional but also affective in nature (Rust & Oliver, 1994), further reinforcing its dependence on perceived service excellence.
Multiple empirical studies affirm that the link between service quality and satisfaction is robust across service domains, including telecommunications, hospitality, healthcare, and especially retail banking (Bitner et al., 2010; Islam et al., 2020; Levesque & McDougall, 1996). In digital and automated banking contexts, attributes such as system usability, reliability, and responsiveness continue to be primary drivers of customer satisfaction (Ahmad et al., 2010; Carlson & O’Cass, 2011). Thus, through the lens of EDT, FinTech service quality is not merely technical but psychological—anchored in expectation and its confirmation or disconfirmation. Accordingly, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H1:
There is a significant positive relationship between Banking Service Quality and Customer Satisfaction.
2.2.2. Banking Customer Trust
Trust is a foundational pillar in building and sustaining long-term customer relationships, especially in the banking sector, where services involve high levels of perceived risk, uncertainty, and information asymmetry. A broad sense of trust means an extension contingent upon positive expectations engaging fairness, reliability, and integrity in personal relationships (Rousseau et al., 1998; Zhang et al., 2018). Trust within the banking sector speaks specifically of a customer’s conviction in the institution’s competence, propriety, as well as goodwill (Alalwan et al., 2017), especially in the implementation of sensitive transactions, protection of personal financial information (Fungáčová et al., 2019; Yuen et al., 2018).
It has long been the case that in a technologically mediated interaction, the personal touch is unavoidable. In the new context opened up by blockchain and internet applications, the question of digital trust has become increasingly complicated, forcing it to involve aspects like security, ease of navigation, interface usability, and system reliability (Herington & Weaven, 2009). In an online banking environment, friendliness, clarity, and immediacy contribute to trustworthiness (Zhou et al., 2021). This takes trust to another level entirely: trust in a bank’s mobile application relates to the app’s functionality, but it is also heavily interwoven with the perceived moral standards and transparency of the parent institution (Cheung & Lee, 2001).
Although trust and satisfaction are conceptually distinct, they are closely intertwined. A longstanding debate in the literature concerns the direction of causality between the two constructs. Some scholars argue that satisfaction leads to trust—when customers are consistently satisfied, their confidence in the provider grows (Al-Ansi & Han, 2019; Kingshott et al., 2018). Others suggest that trust precedes satisfaction, especially in contexts where perceived risk is high and affective comfort plays a central role in shaping the overall evaluation (Pavlou & Fygenson, 2006; Ribbink et al., 2004). Both perspectives are theoretically sound, but in financial services, the dominant view is that trust operates as a key antecedent of satisfaction (Sirdeshmukh et al., 2002).
Ultimately, customer trust contributes significantly to satisfaction by providing psychological assurance, fostering perceived fairness, and enhancing emotional attachment to the institution. From the perspective of RMT, trust functions as the cornerstone of long-term relationships between banks and customers. In FinTech-driven banking, RMT suggests that maintaining relational bonds through digital channels—via transparency, personalized service, and consistent digital reliability—can strengthen trust and emotional engagement, leading to higher satisfaction. This role becomes even more critical in digital and automated banking settings, where customer evaluations rely heavily on perceived credibility and system dependability rather than interpersonal relationships (R. E. Anderson & Swaminathan, 2011; Luarn & Lin, 2003). Hence, RMT extends beyond traditional human interaction to include technological touchpoints that serve as substitutes for relational quality in digital banking ecosystems. Based on the theoretical foundations and empirical evidence, this study posits the following hypothesis:
H2:
There is a significant positive relationship between Banking Customer Trust and Customer Satisfaction.
2.2.3. Mediating Role of Customer Satisfaction
Customer satisfaction plays a crucial role in shaping how individuals respond to services over time, particularly in the banking industry. It goes beyond a simple reaction—it represents a mental and emotional assessment of the overall service experience. When customers feel that their expectations have been met or even surpassed, they are more likely to feel fulfilled and valued (Cronin et al., 2000; Hellier et al., 2003).
In banking, this satisfaction stems from both rational judgments about the quality and efficiency of services, and emotional reactions during their interactions with staff or digital platforms. Together, these elements influence key behaviors like customer loyalty and the likelihood of maintaining a long-term relationship with the bank (E. W. Anderson & Sullivan, 1993; Gustafsson et al., 2005).
A vast body of empirical research supports the direct link between customer satisfaction and customer retention. Satisfied customers are more likely to continue their relationship with a service provider, engage in repeat purchases, and exhibit favorable behavioral intentions such as positive word of mouth and reduced switching behavior (Jones et al., 2000; Petruzzellis et al., 2006; Reichheld & Sasser, 1990). In fact, retention has been shown to be one of the most profitable outcomes of satisfaction, as even a marginal increase in retention can significantly enhance a firm’s financial performance (Reichheld et al., 2000). This connection is so critical that national-level customer satisfaction indices are often used to forecast industry-wide retention trends and profitability.
However, satisfaction is not simply a direct antecedent of retention; it also acts as a mediator that channels the effects of other relationship-building constructs such as service quality and trust. Numerous studies have indicated that the positive influence of service quality on customer retention is largely transmitted through satisfaction (Cronin et al., 2000; Tsoukatos & Rand, 2006). That is, when customers perceive a high level of service performance—reliable, responsive, and consistent—it enhances their satisfaction, which in turn increases the likelihood of maintaining the relationship with the provider (Rahman, 2013).
Similarly, trust has been shown to influence retention both directly and indirectly through satisfaction. Trust reduces perceived uncertainty and strengthens emotional engagement, leading to higher satisfaction levels, which then reinforce customer loyalty (Garbarino & Johnson, 1999; Hart & Johnson, 1999). In instances where customers experience service recovery or unexpected performance, satisfaction may diminish unless trust is present to buffer the negative effects. Hence, satisfaction acts as a crucial link that converts relational constructs into sustained behavioral outcomes.
Viewed through the lens of both ECT and RMT, customer satisfaction serves as a cognitive and relational bridge between expectation fulfillment and long-term commitment. ECT explains that satisfaction emerges when customers’ expectations of financial technology or service delivery are confirmed, while RMT complements this by asserting that satisfaction strengthens relational bonds over time. Therefore, satisfaction operates as a key mediating mechanism linking perceived digital service quality and trust with customer retention, particularly within FinTech-enabled banking.
This mediating role is particularly important in the banking sector, where differentiation is limited, and customers often evaluate service providers based on their cumulative experience rather than isolated transactions. As the sector becomes increasingly digitalized, banks face greater challenges in fostering customer loyalty; satisfaction, therefore, emerges as a strategic lever to bridge quality and trust with behavioral outcomes like retention (Cambra-Fierro et al., 2021; Nazir et al., 2016). Based on this theoretical foundation and empirical evidence, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H3:
There is a significant positive relationship between Customer Satisfaction and Customer Retention Behavior.
H4:
Customer Satisfaction mediates the relationship between Banking Service Quality and Customer Retention Behavior.
H5:
Customer Satisfaction mediates the relationship between Banking Customer Trust and Customer Retention Behavior.
2.2.4. Moderating Role of FinTech
The rapid advancement of digital technologies has redefined the delivery and perception of financial services, giving rise to FinTech as a disruptive force across the global banking sector. FinTech, broadly defined as the integration of financial services with digital technologies, enhances service accessibility, efficiency, and customization (Mainardes & Freitas, 2023; Murinde et al., 2022). From mobile banking and digital wallets to Robo-advisory platforms, FinTech innovations have transformed how customers interact with financial institutions, reshaping their expectations and experiences.
In traditional service models, customer satisfaction has been regarded as a primary driver of retention. However, as digital transformation accelerates, the dynamics of satisfaction and loyalty may no longer function in isolation from technological factors. The increasing use of FinTech solutions introduces a new contextual layer that potentially strengthens the satisfaction–retention relationship. When customers engage with a bank’s FinTech services—such as mobile apps, digital customer service, or AI-driven tools—they may perceive greater value, convenience, and responsiveness, which enhances their satisfaction and deepens their commitment to the institution (Raza et al., 2020).
Recent research has shown that trust in digital technology is a key factor influencing how people adopt and continue using FinTech services (Liébana-Cabanillas et al., 2018; Xie et al., 2021). Whether or not a customer sticks with a financial app often depends on how secure, private, and easy to use the platform feels—and whether they find it genuinely useful (Cao et al., 2018). These elements do not just shape usage habits; they can also strengthen the link between a positive experience and long-term loyalty.
As financial markets become increasingly digital and competitive, the role of FinTech in shaping customer relationships is becoming even more important. In fact, satisfied customers who view their bank’s digital tools as trustworthy and easy to navigate are often more loyal than customers with similar satisfaction levels but lower trust in technology. In this way, FinTech is no longer just a delivery tool—it is a strategic element that can significantly boost the effects of satisfaction on customer retention (Al-Ghraibah, 2020; Kalinić et al., 2020).
From a theoretical standpoint, the ECT (Oliver, 1980) helps explain how FinTech works as a moderator. According to this theory, when customers’ expectations of a service are confirmed—or even exceeded—their satisfaction grows, making them more likely to stay loyal. In a digital context, effective FinTech platforms help meet these rising expectations and, in turn, strengthen the satisfaction–retention relationship. ECT posits that customer retention is primarily determined by the degree to which service experiences confirm initial expectations. As customers increasingly rely on FinTech platforms, their initial expectations of digital banking solutions rise, particularly in markets with limited physical banking infrastructure, such as Palestine. If these heightened expectations are confirmed through positive digital service interactions, customers’ satisfaction intensifies, subsequently strengthening their likelihood of retention. Thus, ECT reinforces the idea that FinTech innovations, by confirming or exceeding customer expectations, can substantially moderate and enhance the traditional satisfaction-retention relationship, especially in digitally constrained or smaller market contexts.
Thus, the moderating role of FinTech can also be connected with Relationship Marketing Theory, where digital interaction channels serve as new relational touchpoints enhancing engagement, and with Expectancy-Disconfirmation Theory, as FinTech-driven experiences continually shape, disconfirm, and reset customer expectations. Together, these theories offer a holistic framework linking FinTech innovation with satisfaction and retention in digital banking.
Despite growing recognition of FinTech’s role in customer experience, limited empirical research has explored its interaction effects with established constructs like satisfaction and trust. This study addresses this gap by examining whether FinTech moderates the relationship between customer satisfaction and retention and whether it exerts a direct influence on retention behavior.
Based on this rationale, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H6:
There is a significant positive relationship between FinTech and Customer Retention Behavior.
H7:
FinTech moderates the relationship between Customer Satisfaction and Customer Retention Behavior.
3. Methodology
3.1. Population, Sample, and Procedure
This study’s target population comprised banking product customers from Palestinian banks who were testing the developed model. Palestinian financial institutions were chosen because they operate in a particular market with specific characteristics, such as limited physical access to banking opportunities because of geopolitical restrictions and digital transformation development, including an expanding mobile penetration base and technology adoption. Additional reasons to focus on Palestinian banking customers are that the specific constraints of this market enhance consumers’ dependence on FinTech solutions as principal contributors to contentment and retention. Therefore, studying experiences, adoption, and assessment of FinTech innovations among Palestinian banking customers is crucial in unlocking the digital transformation potential and retaining consumer loyalty within the region.
For this study, exploring the moderating influence of FinTech on the link between customer satisfaction and customer retention behavior, it is envisaged that there may be a case for a quantitative research design. Therefore, the convenience sampling method was selected due to practical constraints and the many people under consideration (Bougie & Sekaran, 2019). After carefully confirming the appropriateness and quality of the questionnaire, it was distributed manually, following the G*Power guidelines provided by (Hair et al., 2016). Because of the limited sample size for the measurement and structural models of five variables, the least number of cases due to the minimum sample size needed to have 80% power with R2 of at least 0.25 is only 70 observations. This study managed to catch 292 valid questionnaires. The data was collected over the period from 14 September 2024 to 9 December 2025.
3.2. Measures of Study and Data Analysis
A structured survey consisting of 21 items was used to collect data from the study participants (see Appendix A). All items were assessed using a five-point Likert scale, with response options ranging from 1 = ‘Never’ to 5 = ‘Always,’ including 2 = ‘Rarely,’ 3 = ‘Sometimes,’ and 4 = ‘Often.’ It was positioned as such that it allowed for the subtle nuances of participant responses, opening the channels of frequency of behaviors and practices in regard to the perceived constructs. A scale of five items grounded in the established literature was attained for FinTech in view of established literature (Zhengmeng et al., 2024).
A four-item scale grounded in established literature was used to measure customer satisfaction, drawing upon validated scales by Boonlertvanich (2019) and Kant and Jaiswal (2017). To evaluate customer retention behavior, a four-item scale adopted from previous research validated by Hawkins and Hoon (2019) was employed.
Banking customer trust was measured using a four-item scale based on established measures validated by Ennew and Binks (1996). Lastly, banking service quality was assessed via a four-item scale adopted from Boonlertvanich (2019), reflecting dimensions such as responsiveness, assurance, tangibility, empathy, and reliability.
3.3. Psychometric Validation and Data Analysis
To make sense of the data, the study relied on structural equation modeling, specifically through the PLS method, using Smart-PLS 4 software. The PLS-SEM method was employed for data analysis, following best practices for variance-based structural equation modeling as outlined by (Ringle et al., 2022). Therefore, internal consistency reliability and convergent and discriminant validity were initially evaluated for the measurement model. The path modeling approach of PLS was employed to test the research hypotheses using multiple regression analysis. A bootstrapping procedure with 10,000 samples was conducted. In this study, due to the need to analyze complex models, PLS-SEM was particularly chosen, which allows for an easy comparison using descriptive analysis.
In addition to the direct effects under examination, the study also included mediation and moderation analysis. For mediation analysis, it allowed for a closer look at whether the influence of banking service quality and banking customer trust on customer retention behavior worked through other factors, particularly customer satisfaction. Additionally, moderation analysis was used to explore whether FinTech strengthens the relationship between customer satisfaction and customer retention behavior.
3.4. PLS-SEM Model Specification
To ensure transparency, reproducibility, and methodological rigor, the partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) procedure is formally specified below, encompassing both the measurement and structural components.
Measurement Model: Each latent construct in this study was operationalized as reflective, represented by a set of observed indicators. The reflective measurement model is expressed as:
where denotes the observed indicator of construct ; represents the standardized outer loading; is the latent construct; and indicates the measurement error term.
The reflective constructs and their respective measurement items were defined as follows:
- Banking Service Quality (QBS): QBS1–QBS4;
- Banking Customer Trust (CT): CT1–CT4;
- Customer Satisfaction (CS): CS1–CS4;
- Customer Retention Behavior (CRB): CRB1–CRB4;
- FinTech (FT): FT1–FT5.
Structural Model: The inner (structural) model delineates the hypothesized relationships among latent constructs and is expressed as follows:
where – are standardized path coefficients, and and represent the residual terms.
Indirect (mediated) effects were evaluated via the following paths:
The moderating role of FinTech was assessed through the interaction term .
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Measurement Model
The measurement model was assessed in terms of indicator reliability, internal consistency, and both convergent and discriminant validity (Ajouz et al., 2020). In accordance with the guidelines proposed by (Hair et al., 2016), items with factor loadings below 0.4 were removed which are (CS4 and QBS4). The retained items demonstrated outer loadings ranging from 0.701 to 0.842, all of which were statistically significant at the 0.05 level, thereby confirming acceptable indicator reliability.
To evaluate the reliability of the constructs, both Cronbach’s alpha and composite reliability (CR) were examined. All Cronbach’s alpha values surpassed the recommended minimum threshold of 0.70, indicating satisfactory internal consistency, indicating internal consistency. Similarly, CR values were also above the advised minimum of 0.70. As shown in Table 1, Cronbach’s alpha ranged from 0.708 to 0.846, composite reliability (Rho_a) varied between 0.722 and 0.854, and composite reliability (Rho_c) ranged from 0.828 to 0.891. These results confirm the reliability of the model (Hair et al., 2019).
All items were standardized, and reliability and validity were verified through Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability (CR), and average variance extracted (AVE), as presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Assessment of the Measurement Model.
Table 1.
Assessment of the Measurement Model.
| Constructs | Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability | AVE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rho_a | Rho_a | ||||
| CRB | Customer Retention Behavior | 0.735 | 0.739 | 0.834 | 0.558 |
| CS | Customer Satisfaction | 0.720 | 0.723 | 0.843 | 0.642 |
| FT | FinTech | 0.846 | 0.854 | 0.891 | 0.620 |
| QBS | Banking Service Quality | 0.708 | 0.722 | 0.836 | 0.631 |
| CT | Banking Customer Trust | 0.722 | 0.724 | 0.828 | 0.546 |
The subsequent step involved assessing convergent validity, which was confirmed by Average Variance Extracted (AVE) values meeting or exceeding the threshold of 0.50. As presented in Table 1, AVE values ranged from 0.546 to 0.642, thereby surpassing the recommended minimum and affirming the establishment of convergent validity (Hair et al., 2019).
Discriminant validity was further assessed using multiple approaches. According to the Fornell-Larcker criterion, discriminant validity was established as the square roots of the AVE values for each construct were greater than the corresponding inter-construct correlations, indicating adequate discriminant validity as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Discriminant Validity Based on Fornell-Larcker criterion.
Additionally, the heterotrait-monotrait (HTMT) ratio of correlation was examined (Henseler et al., 2015), with all resulting values falling below the recommended threshold of 0.85, as shown in Table 3. These results confirm that discriminant validity was successfully established (Al Zeer et al., 2023).

Table 3.
Discriminant Validity Based on HTMT criterion.
4.2. Structural Model
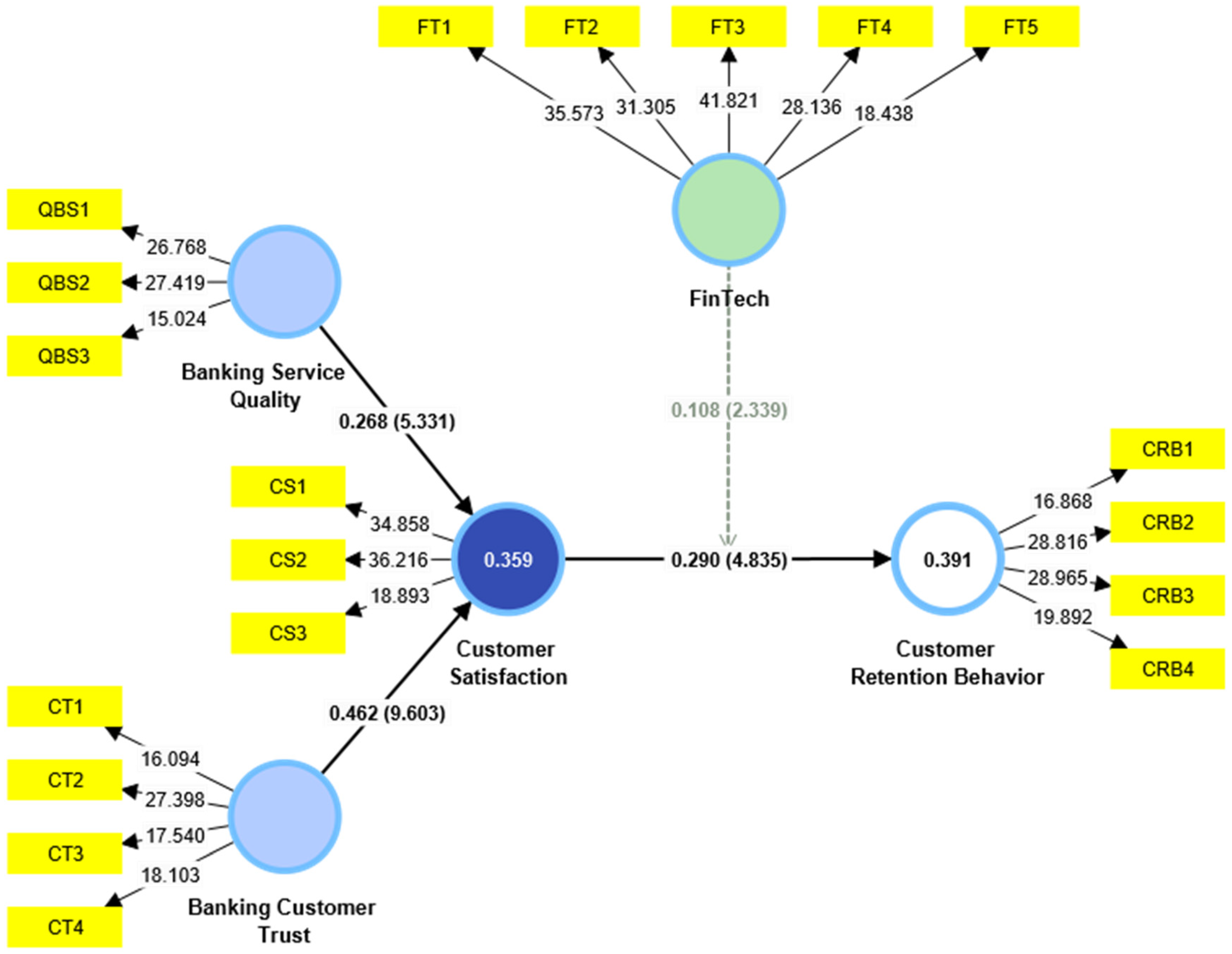
Figure 1’s PLS bootstrapping results show that the proposed model explains 39.1% of the variance in customer retention behavior, underscoring the model’s robustness in capturing how customer satisfaction shape customer loyalty. Each latent construct (e.g., QBS, CS, CT, FT) is measured by strongly loaded indicators that meet recommended thresholds, affirming reliability and convergent validity. The statistically significant path coefficients further confirm meaningful relationships among the constructs, revealing how service quality, trust, and related factors collectively drive customer retention behavior. In sum, by demonstrating a relatively high explanatory power, the model highlights the importance of these determinants in enhancing customer satisfaction effectiveness and sustaining customer retention in complex banking environments.
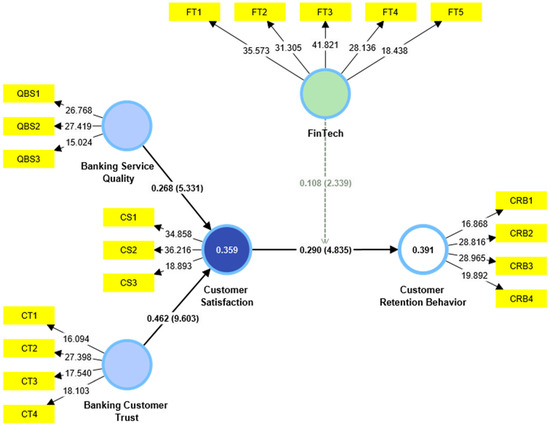
Figure 1.
Structural Model Results.
All hypotheses were supported at the 0.05 level of significance, as illustrated in Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6, underscoring the strong interrelationships among the investigated constructs. Notably, the confirmed moderating role of FinTech provides deeper insight into how enhancements in FinTech solutions can shape and strengthen customer retention behavior.

Table 4.
PLS-SEM Results: Path Coefficients of the Adjusted Model.

Table 5.
PLS-SEM of Mediation Results.

Table 6.
PLS-SEM of Moderation Results.
When examining the individual hypotheses, Hypothesis 1 (H1) evaluated the effect of banking service quality on customer satisfaction, with the PLS results indicating a significant relationship (β = 0.268, t = 5.331, p < 0.05). Although this path coefficient is moderate, it underscores the pivotal role of consistently high-quality services in shaping customers’ overall satisfaction. In a competitive banking environment—where product offerings can be similar—maintaining strong service quality can provide a distinctive edge, particularly under crisis conditions when customer expectations for reliable and responsive support are heightened.
Hypothesis 2 (H2) explored the impact of banking customer trust on customer satisfaction, yielding a stronger effect than service quality (β = 0.462, t = 9.603, p < 0.05). This finding highlight trust as a crucial element in the development and maintenance of favorable customer perceptions. Trust becomes especially salient in crises, where financial uncertainty may erode customer confidence. Accordingly, banks that prioritize transparency and demonstrate consistent reliability are more likely to foster robust satisfaction levels among their clientele.
Moving forward, Hypothesis 3 (H3) examined the linkage between customer satisfaction and customer retention behavior, revealing a positive and statistically significant relationship (β = 0.290, t = 4.835, p < 0.05). This result confirms that satisfied customers are more inclined to stay with their current financial service provider. Moreover, it reinforces the notion that satisfaction is an essential driver of loyalty, contributing to long-term customer engagement—an outcome particularly beneficial in periods marked by market turbulence or organizational restructuring.
4.2.1. Mediation Analysis
Mediation analysis was conducted to investigate the extent to which customer satisfaction acts as a pathway linking both banking service quality and banking customer trust to customer retention behavior. The results demonstrate statistically significant indirect effects in both cases. Specifically, the effect of banking service quality on retention through customer satisfaction yielded an indirect coefficient of 0.078 (H4: t = 3.573, p < 0.05), while the effect of banking customer trust on retention through satisfaction was 0.134 (H5: t = 4.010, p < 0.05).
These findings indicate that higher service quality and stronger trust do not, by themselves, guarantee customer loyalty; rather, they operate through enhanced customer satisfaction to influence retention. In practical terms, banks must recognize that simply providing superior services or cultivating trust is insufficient unless these efforts also heighten overall satisfaction. By focusing on customer satisfaction as a critical mediator, financial institutions can more effectively translate improvements in service quality and trust into long-term retention, which is particularly vital in crisis situations where customer confidence can be easily undermined.
4.2.2. Moderation Analysis
A moderation analysis was conducted to examine the extent to which FinTech strengthens the effect of Customer Satisfaction on Customer Retention Behavior. First, the model was assessed without the interaction term (FinTech × Customer Satisfaction), revealing that customer satisfaction accounted for 23.4% of the variance in customer retention behavior. However, once the interaction was included, the R2 value rose to 39.1%, indicating a notable increase of 15.8% in explained variance. In addition, the results demonstrated a strong main effect of FinTech on retention (H6: β = 0.416, t = 7.263, p < 0.05), suggesting that higher FinTech adoption independently enhances loyalty outcomes.
More importantly, the interaction between FinTech and customer satisfaction was significant (H7: β = 0.108, t = 2.339, p = 0.019), confirming that FinTech further amplifies the positive influence of satisfaction on retention. From a practical standpoint, these findings imply that banks seeking to reinforce customer loyalty should not only focus on raising satisfaction levels but also invest in advanced, user-friendly FinTech platforms. When these two factors—high satisfaction and robust FinTech—are combined, customers exhibit substantially higher retention levels, particularly in volatile market or crisis contexts.
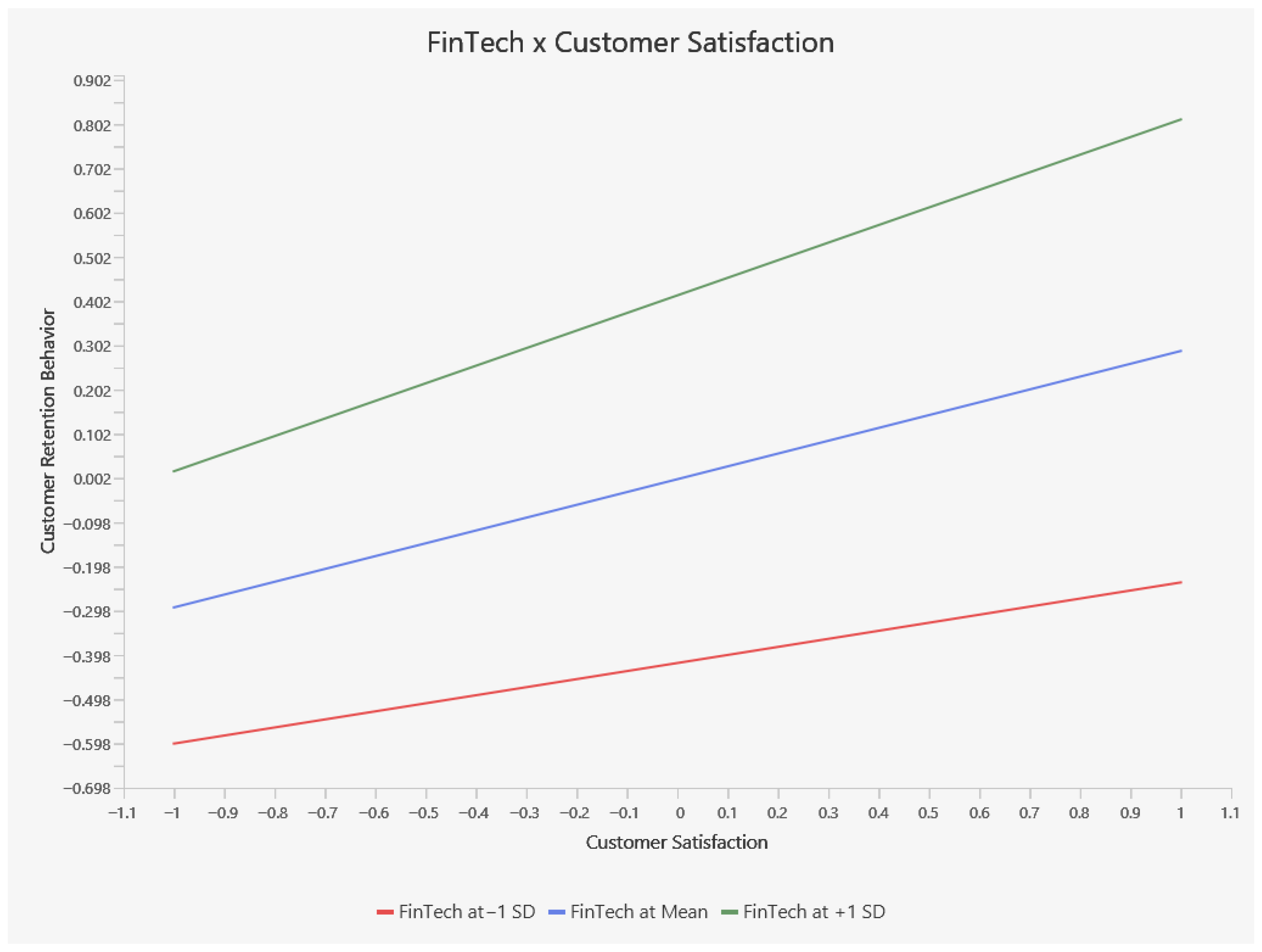
Additionally, the slope analysis is presented to better understand the nature of moderation effects. In Figure 2, the slope analysis clarifies how FinTech moderates the relationship between customer satisfaction (horizontal axis) and customer retention behavior (vertical axis) by illustrating different FinTech levels (e.g., red = −1 SD, blue = mean, green = +1 SD). One observation suggests that when FinTech usage is low, the slope is especially steep, meaning even modest increases in Satisfaction can result in comparatively larger gains in Retention. However, another perspective notes that at high FinTech (green line), retention may rise more sharply as satisfaction improves, underscoring FinTech’s power to intensify this relationship. These seemingly contrasting views can be reconciled by recognizing that high FinTech often elevates the overall baseline of retention (i.e., customers start off more loyal), whereas low FinTech can make incremental boosts in satisfaction more impactful. Thus, FinTech serves as a key moderator: it can both raise the baseline level of retention for high-adoption customers and amplify or alter how strongly satisfaction translates into retention across varying levels of FinTech engagement.
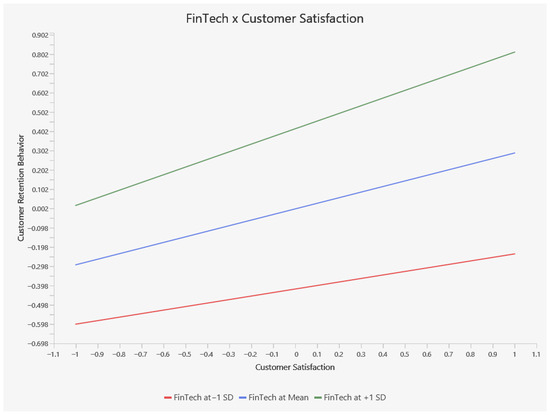
Figure 2.
Simple Slope Analysis.
4.3. Discussion
The results of this study strongly align with existing research on RMT, EDT and ECT, particularly emphasizing the roles of service quality, trust, and customer satisfaction in driving retention behaviors in banking environments. As indicated by the structural model results, the model explains 39.1% of the variance in customer retention behavior, which reinforces previous findings about the significance of customer satisfaction and related constructs in determining customer loyalty. This supports the integrated view that both cognitive evaluations and affective trust-based relationships are vital to understanding retention.
Consistent with the EDT (Oliver, 1989), the significant positive relationship identified between banking service quality and customer satisfaction supports prior studies (Amin & Isa, 2008; Pakurár et al., 2019; Parasuraman et al., 1988), indicating that customers’ perceptions of service excellence profoundly impact their satisfaction levels. Although the effect size here is moderate, it aligns with research highlighting service quality as a foundational element that directly influences customer evaluations and satisfaction, especially crucial in competitive and crisis contexts (Teeroovengadum, 2022). This also complements ECT by showing that when expected service quality is met or exceeded, confirmation occurs, reinforcing satisfaction.
This finding agrees with prior empirical evidence suggesting that customer satisfaction results from the cognitive comparison process inherent in both EDT and ECT frameworks—where expectation-performance alignment determines post-service satisfaction (Oliver, 1980; Bhattacherjee, 2001). The confirmation of this relationship suggests that in digital or FinTech-enabled banking, customers’ expectations of reliability, speed, and transparency are central determinants of satisfaction formation. Hence, the results reaffirm that the mechanisms described in EDT and ECT continue to hold true in the evolving context of technology-mediated financial services.
The strong relationship between customer trust and satisfaction affirms previous studies emphasizing the critical role of trust in financial services (Alalwan et al., 2017; Fungáčová et al., 2019). Trust, particularly salient under conditions of uncertainty and financial instability, was demonstrated as a more potent antecedent of satisfaction compared to service quality. This finding substantiates the literature suggesting that trust provides psychological assurance and enhances satisfaction, thereby becoming a cornerstone in fostering robust, long-term relationships (Kingshott et al., 2018; Sirdeshmukh et al., 2002). RMT is especially relevant here, as it highlights trust and emotional connection as essential to building enduring customer relationships, beyond transactional satisfaction.
The alignment with RMT confirms that customer relationships in FinTech environments are not solely built on functionality but also on relational equity and emotional bonding. This study’s results thus agree with Morgan and Hunt’s (1994) commitment-trust theory, which posits trust as the central mechanism sustaining long-term relationships. In cases where previous studies reported weaker associations between trust and satisfaction, those contexts often involved low-risk or non-financial settings; in contrast, the high-stakes nature of banking amplifies trust’s influence. Hence, the present findings extend RMT’s validity to digital financial ecosystems, where technological credibility substitutes for human assurance.
Further, the confirmed mediating role of customer satisfaction between service quality, trust, and retention behavior validates previous theoretical and empirical propositions (Cronin et al., 2000; Tsoukatos & Rand, 2006). The mediation analysis clarifies that superior service quality and trust alone are insufficient for ensuring retention; they must effectively translate into customer satisfaction, a crucial psychological and affective intermediary. This finding aligns with assertions from (Garbarino & Johnson, 1999) about satisfaction’s strategic mediating role, particularly in sectors characterized by minimal differentiation and significant relational dependence, such as banking. This mediating effect is theoretically congruent with both ECT and RMT. Therefore, the mediation results validate that satisfaction operates as a bridge converting transactional perceptions (from service quality and trust) into enduring behavioral outcomes (retention). Moreover, this mediating role reinforces that emotional and cognitive satisfaction act in tandem, particularly within FinTech-mediated services where experience continuity replaces physical interactions.
Notably, this study also expands on existing knowledge by confirming the moderating role of FinTech in the satisfaction-retention link, aligning with the ECT (Oliver, 1980) and further informed by EDT (Oliver, 1989). The considerable increase in explained variance (23.4% to 39.1%) upon adding FinTech interaction suggests that FinTech is considered in a key enabling role that goes beyond mere customer satisfaction into customer loyalty (Mainardes & Freitas, 2023; Raza et al., 2020). This moderate effect reflects both positive disconfirmation (from EDT) and expectation confirmation (from ECT), as FinTech helps to exceed or meet evolving customer expectations. Furthermore, FinTech plays a dual role in lifting the retention baseline while intensifying the link between satisfaction and retention. This finding is consistent with prior works focusing on the particular effects of digital transformation on customer expectations and resultant retention, most markedly in constrained markets like Palestine (Al-Ghraibah, 2020; Magdy Rezk & Halim, 2022).
These results suggest that FinTech functions not merely as a technological tool but as a relational and cognitive enhancer, bridging EDT’s “disconfirmation” process and RMT’s relationship reinforcement mechanism. The agreement with previous studies lies in the observation that FinTech-induced satisfaction emerges when technology confirms or exceeds expectations of efficiency, reliability, and transparency—consistent with ECT predictions. Where some earlier research suggested that digitalization may erode relational closeness, this study contradicts that view by demonstrating that FinTech can, in fact, strengthen relational bonds by enabling consistent expectation confirmation and continuous engagement.
Overall, the integration of EDT, ECT, and RMT provides a holistic understanding of how digital service quality, trust, and expectation dynamics collectively drive retention behavior in modern banking. The findings both support and extend prior theoretical work by illustrating how technological trust and digital satisfaction mechanisms operate jointly to enhance retention in FinTech ecosystems. This theoretical integration implies that in technology-mediated banking, customer satisfaction is not a static construct but an evolving outcome of expectation management (ECT/EDT) and relational bonding (RMT), offering new insights into sustaining customer loyalty amid digital transformation.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the influence of banking service quality and customer trust on customer retention behavior, with customer satisfaction as a mediating variable and FinTech as a moderator. The findings confirm that both banking service quality (β = 0.268, t = 5.331) and customer trust (β = 0.462, t = 9.603) significantly and positively influence customer satisfaction. In turn, customer satisfaction positively affects customer retention behavior (β = 0.290, t = 4.835). Moreover, satisfaction was found to mediate the effects of service quality (β = 0.078, t = 3.573) and trust (β = 0.134, t = 4.010) on retention. Importantly, FinTech had a direct positive effect on customer retention (β = 0.416, t = 7.263) and moderated the satisfaction–retention relationship (β = 0.108, t = 2.339), strengthening the link when digital financial services were effectively utilized. These findings emphasize the multi-dimensional nature of customer loyalty in digital banking environments, where traditional service factors and technological innovation jointly influence long-term relationship outcomes.
5.1. Theoretical Implications
This research contributes to relationship marketing and digital banking literature by validating an integrated model that combines service quality, trust, satisfaction, and retention with FinTech as a moderating factor. Unlike previous studies that treated these variables in isolation, this study illustrates how digital transformation interacts with relational constructs to shape customer behavior. It also enriches the theoretical understanding of satisfaction as both a mediator and a central mechanism in enhancing loyalty, particularly in technology-driven service contexts.
5.2. Practical Implications
For practitioners, the findings underscore the importance of delivering high-quality, trustworthy banking services to foster customer satisfaction. However, this is not sufficient in itself; satisfaction must be supported by effective FinTech platforms to convert into actual retention. Banks should invest in digital innovations that are secure, user-friendly, and aligned with customer needs, as these technologies not only enhance direct loyalty outcomes but also amplify the effects of satisfaction. This is particularly relevant in competitive environments where customer expectations are shaped by their broader digital experiences.
5.3. Limitations and Future Research Directions
This study is subject to several limitations. Firstly, it was conducted within a specific geographical and banking context, which may restrict the extent to which the findings can be generalized to other regions or financial settings. Future studies could replicate the model in other regions or sectors to examine contextual variations. Second, the FinTech variable was treated as a single construct; future research could explore different types of FinTech services and their distinct effects. Additionally, longitudinal studies could provide deeper insights into how satisfaction and retention evolve over time. Including variables such as digital trust, user experience, or risk perception could also add depth to the model.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A., S.I. and H.N.; methodology, M.A.; data collection, S.I. and H.N.; formal analysis, M.A.; writing—original draft preparation (introduction, methodology, analysis, and discussion), M.A.; writing—literature review and final manuscript editing, M.S.; supervision, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Palestine Ahliya University and Al-Ahliyya Amman University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Palestine Ahliya University (Project identification code: 10/R.C/PAU/2024) on 10 September 2024.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
During the preparation of this manuscript, the authors used Chat GPT 5.0 for the interpreting the graphical analysis of the moderating role of FinTech. The authors have reviewed and edited the output and take full responsibility for the content of this publication.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
| Constructs and Related Measurement Items | |
| Customer Retention Behavior | |
| CRB1 | The bank maintains regular communication to strengthen its relationship with customers. |
| CRB2 | The bank is committed to sustaining its long-term relationship with me as a customer. |
| CRB3 | Bank employees make efforts to ensure that I continue my relationship with the bank. |
| CRB4 | Bank employees continuously improve their performance to meet my expectations and maintain my loyalty to the bank. |
| Customer Satisfaction | |
| CS1 | Overall, I am fully satisfied with the level of services I have received from the bank. |
| CS2 | The variety of services and products offered by the bank adequately meets all my needs. |
| CS3 | Achieving customer satisfaction is a top priority for the bank. |
| CS4 | I find the bank’s services to be the most satisfying compared to other banks. |
| FinTech | |
| FT1 | The bank effectively utilizes technology to enhance its financial services. |
| FT2 | The bank employs financial technology to improve the quality of services provided. |
| FT3 | The bank delivers electronic banking services efficiently. |
| FT4 | I can easily access my bank account and services online. |
| FT5 | The bank’s mobile application facilitates convenient management of my banking account. |
| Banking Service Quality | |
| QBS1 | The bank offers a diverse range of banking services. |
| QBS2 | The bank provides its services promptly and efficiently. |
| QBS3 | The fees charged for banking services are reasonable. |
| QBS4 | The bank meets its customers’ needs with a high level of service quality. |
| Banking Customer Trust | |
| CT1 | I am confident in the bank’s ability to safeguard my funds. |
| CT2 | I believe the bank can be trusted to conduct financial transactions securely. |
| CT3 | I believe that the bank’s management acts in the best interest of its customers. |
| CT4 | I feel a sense of confidence and assurance when dealing with the bank. |
References
- Ahmad, A., Saif, I., & Safwan, N. (2010). An empirical investigation of Islamic banking in Pakistan based on perception of service quality. African Journal of Business Management, 4(6), 1185. [Google Scholar]
- Ajouz, M., Abdullah, A., & Kassim, S. (2020). Acceptance of Sharīʿah—Compliant precious metal-backed cryptocurrency as an alternative currency: An empirical validation of adoption of innovation theory. Thunderbird International Business Review, 62(2), 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalwan, A. A., Dwivedi, Y. K., & Rana, N. P. (2017). Factors influencing adoption of mobile banking by Jordanian bank customers: Extending UTAUT2 with trust. International Journal of Information Management, 37(3), 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ansi, A., & Han, H. (2019). Role of halal-friendly destination performances, value, satisfaction, and trust in generating destination image and loyalty. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 13, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghraibah, O. B. (2020). Online consumer retention in Saudi Arabia during COVID 19: The moderating role of online trust. Journal of Critical Reviews, 7(9), 2464–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Al Nawayseh, M. K. (2020). Fintech in COVID-19 and beyond: What factors are affecting customers’ choice of fintech applications? Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(4), 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zeer, I., Ajouz, M., & Salahat, M. (2023). Conceptual model of predicting employee performance through the mediating role of employee engagement and empowerment. International Journal of Educational Management, 37(5), 986–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M., & Isa, Z. (2008). An examination of the relationship between service quality perception and customer satisfaction: A SEM approach towards Malaysian Islamic banking. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management, 1(3), 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E. W., & Sullivan, M. W. (1993). The antecedents and consequences of customer satisfaction for firms. Marketing Science, 12(2), 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R. E., & Swaminathan, S. (2011). Customer satisfaction and loyalty in e-markets: A PLS path modeling approach. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 19(2), 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagozzi, R. P. (1992). The self-regulation of attitudes, intentions, and behavior. Social Psychology Quarterly, 55, 178–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacherjee, A. (2001). Understanding information systems continuance: An expectation-confirmation model. MIS Quarterly, 25, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitner, M. J., Zeithaml, V. A., & Gremler, D. D. (2010). Technology’s impact on the gaps model of service quality. In Handbook of service science (pp. 197–218). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Boonlertvanich, K. (2019). Service quality, satisfaction, trust, and loyalty: The moderating role of main-bank and wealth status. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 37(1), 278–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougie, R., & Sekaran, U. (2019). Research methods for business: A skill building approach. John Wiley & Sons. [Google Scholar]
- Cambra-Fierro, J. J., Fuentes-Blasco, M., Huerta-Álvarez, R., & Olavarría, A. (2021). Customer-based brand equity and customer engagement in experiential services: Insights from an emerging economy. Service Business, 15, 467–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X., Yu, L., Liu, Z., Gong, M., & Adeel, L. (2018). Understanding mobile payment users’ continuance intention: A trust transfer perspective. Internet Research, 28(2), 456–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J., & O’Cass, A. (2011). Developing a framework for understanding e-service quality, its antecedents, consequences, and mediators. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 21(3), 264–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, C. M., & Lee, M. K. (2001). Trust in internet shopping: Instrument development and validation through classical and modern approaches. Journal of Global Information Management (JGIM), 9(3), 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinje, N. B. (2013). Customer Relationship Management (CRM) implementation within the banking and mobile telephony sectors of Nigeria and South Africa. University of the Witwatersrand. [Google Scholar]
- Coviello, N., Milley, R., & Marcolin, B. (2001). Understanding IT-enabled interactivity in contemporary marketing. Journal of Interactive Marketing, 15(4), 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J. J., Jr., Brady, M. K., & Hult, G. T. M. (2000). Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments. Journal of Retailing, 76(2), 193–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlberg, T., Guo, J., & Ondrus, J. (2015). A critical review of mobile payment research. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 14(5), 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennew, C. T., & Binks, M. R. (1996). The impact of service quality and service characteristics on customer retention: Small businesses and their banks in the UK. British Journal of Management, 7(3), 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fungáčová, Z., Hasan, I., & Weill, L. (2019). Trust in banks. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 157, 452–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbarino, E., & Johnson, M. S. (1999). The different roles of satisfaction, trust, and commitment in customer relationships. Journal of Marketing, 63(2), 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomber, P., Koch, J.-A., & Siering, M. (2017). Digital Finance and FinTech: Current research and future research directions. Journal of Business Economics, 87, 537–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafsson, A., Johnson, M. D., & Roos, I. (2005). The effects of customer satisfaction, relationship commitment dimensions, and triggers on customer retention. Journal of Marketing, 69(4), 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2019). Rethinking some of the rethinking of partial least squares. European Journal of Marketing, 53(4), 566–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, C. W., & Johnson, M. D. (1999). Growing the trust relationship. Marketing Management, 8(1), 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins, D. L., & Hoon, S. (2019). The impact of customer retention strategies and the survival of small service-based businesses. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3445173 (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Hellier, P. K., Geursen, G. M., Carr, R. A., & Rickard, J. A. (2003). Customer repurchase intention: A general structural equation model. European Journal of Marketing, 37(11/12), 1762–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herington, C., & Weaven, S. (2009). E-retailing by banks: E-service quality and its importance to customer satisfaction. European Journal of Marketing, 43(9–10), 1220–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J. U., Shahid, S., Rasool, A., Rahman, Z., Khan, I., & Rather, R. A. (2020). Impact of website attributes on customer engagement in banking: A solicitation of stimulus-organism-response theory. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 38(6), 1279–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P., Davari, A., & Paswan, A. (2018). Determinants of brand performance: The role of internal branding. Journal of Brand Management, 25, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M. A., Mothersbaugh, D. L., & Beatty, S. E. (2000). Switching barriers and repurchase intentions in services. Journal of Retailing, 76(2), 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinić, Z., Liébana-Cabanillas, F. J., Muñoz-Leiva, F., & Marinković, V. (2020). The moderating impact of gender on the acceptance of peer-to-peer mobile payment systems. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 38(1), 138–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, R., & Jaiswal, D. (2017). The impact of perceived service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction: An empirical study on public sector banks in India. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 35(3), 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiningham, T. L., Cooil, B., Aksoy, L., Andreassen, T. W., & Weiner, J. (2007). The value of different customer satisfaction and loyalty metrics in predicting customer retention, recommendation, and share-of-wallet. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 17(4), 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingshott, R. P., Sharma, P., & Chung, H. F. (2018). The impact of relational versus technological resources on e-loyalty: A comparative study between local, national and foreign branded banks. Industrial Marketing Management, 72, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levesque, T., & McDougall, G. H. (1996). Determinants of customer satisfaction in retail banking. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 14(7), 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liébana-Cabanillas, F., Marinkovic, V., De Luna, I. R., & Kalinic, Z. (2018). Predicting the determinants of mobile pay-ment acceptance: A hybrid SEM-neural network approach. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 129, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luarn, P., & Lin, H.-H. (2003). A customer loyalty model for e-service context. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 4(4), 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Madjid, R. (2013). Customer trust as relationship mediation between customer satisfaction and loyalty at Bank Rakyat Indonesia (BRI) Southeast Sulawesi. The International Journal of Engineering and Science, 2(5), 48–60. Available online: https://www.theijes.com/papers/v2-i5/Part.1/F0251048060.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2025).
- Magdy Rezk, W., & Halim, M. A. A. (2022). Financial technology (Fintech) in the Arab countries challenges and opportunities. L’Egypte Contemporaine, 113(547), 33–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardes, E. W., & Freitas, N. P. d. (2023). The effects of perceived value dimensions on customer satisfaction and loyalty: A comparison between traditional banks and fintechs. International Journal of Bank Marketing, 41(3), 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R. M., & Hunt, S. D. (1994). The commitment-trust theory of relationship marketing. Journal of Marketing, 58(3), 20–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K., & Halinen, A. (2000). Relationship marketing theory: Its roots and direction. Journal of Marketing Management, 16(1–3), 29–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murinde, V., Rizopoulos, E., & Zachariadis, M. (2022). The impact of the FinTech revolution on the future of banking: Opportunities and risks. International Review of Financial Analysis, 81, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, B., Ali, M., & Jamil, M. (2016). The impact of brand image on the customer retention: A mediating role of customer satisfaction in Pakistan. International Journal of Business and Management Invention, 5(3), 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, R. L. (1980). A cognitive model of the antecedents and consequences of satisfaction decisions. Journal of Marketing Research, 17(4), 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, R. L. (1989). Processing of the satisfaction response in consumption: A suggested framework and research propositions. Journal of Consumer Satisfaction, Dissatisfaction and Complaining Behavior, 2, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pakurár, M., Haddad, H., Nagy, J., Popp, J., & Oláh, J. (2019). The service quality dimensions that affect customer satisfaction in the Jordanian banking sector. Sustainability, 11(4), 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1988). Servqual: A multiple-item scale for measuring consumer perc. Journal of Retailing, 64(1), 12–37. [Google Scholar]
- Pavlou, P. A., & Fygenson, M. (2006). Understanding and predicting electronic commerce adoption: An extension of the theory of planned behavior. MIS Quarterly, 30, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzellis, L., d’Uggento, A. M., & Romanazzi, S. (2006). Student satisfaction and quality of service in Italian universities. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 16(4), 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H. (2013). Customer satisfaction and loyalty: A case study from the banking sector. Central European Business Review, 2(4), 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaweera, C., & Prabhu, J. (2003). The influence of satisfaction, trust and switching barriers on customer retention in a continuous purchasing setting. International Journal of Service Industry Management, 14(4), 374–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S. A., Umer, A., Qureshi, M. A., & Dahri, A. S. (2020). Internet banking service quality, e-customer satisfaction and loyalty: The modified e-SERVQUAL model. The TQM Journal, 32(6), 1443–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichheld, F. F., Markey, R. G., Jr., & Hopton, C. (2000). The loyalty effect-the relationship between loyalty and profits. European Business Journal, 12(3), 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Reichheld, F. F., & Sasser, W. E. (1990). Zero defeofions: Quoliiy comes to services. Harvard Business Review, 68(5), 105–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ribbink, D., Van Riel, A. C., Liljander, V., & Streukens, S. (2004). Comfort your online customer: Quality, trust and loyalty on the internet. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 14(6), 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringle, C. M., Wende, S., & Becker, J.-M. (2022). SmartPLS 4. SmartPLS GmbH. Available online: http://www.smartpls.com (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Rousseau, D. M., Sitkin, S. B., Burt, R. S., & Camerer, C. (1998). Not so different after all: A cross-discipline view of trust. Academy of Management Review, 23(3), 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, R. T., & Oliver, R. L. (1994). Service quality: Insights and managerial implications from the frontier. In Service quality: New directions in theory and practice (pp. 1–20). SAGE Publications, Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Sheth, J. N., & Sisodia, R. S. (1999). Revisiting marketing’s lawlike generalizations. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 27(1), 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirdeshmukh, D., Singh, J., & Sabol, B. (2002). Consumer trust, value, and loyalty in relational exchanges. Journal of Marketing, 66(1), 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaruddin, T., Firdaus, A., & Endri, E. (2020). Customer satisfaction mediates the effect of self service technology on customer loyalty in of islamic bank E-banking services in Indonesia. ILTIZAM Journal of Shariah Economics Research, 4(2), 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Tasca, P., Aste, T., Pelizzon, L., & Perony, N. (2016). Banking beyond banks and money. Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Teeroovengadum, V. (2022). Service quality dimensions as predictors of customer satisfaction and loyalty in the banking industry: Moderating effects of gender. European Business Review, 34(1), 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toader, E., Firtescu, B. N., Roman, A., & Anton, S. G. (2018). Impact of information and communication technology infrastructure on economic growth: An empirical assessment for the EU countries. Sustainability, 10(10), 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukatos, E., & Rand, G. K. (2006). Path analysis of perceived service quality, satisfaction and loyalty in Greek insurance. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 16(5), 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J., Ye, L., Huang, W., & Ye, M. (2021). Understanding FinTech platform adoption: Impacts of perceived value and perceived risk. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, 16(5), 1893–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, K. F., Wang, X., Wong, Y. D., & Zhou, Q. (2018). The effect of sustainable shipping practices on shippers’ loyalty: The mediating role of perceived value, trust and transaction cost. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 116, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L., Yan, Q., & Zhang, L. (2018). A computational framework for understanding antecedents of guests’ perceived trust towards hosts on Airbnb. Decision Support Systems, 115, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhengmeng, C., Malik, M., Hussain, M., & Hussain, S. (2024). Exploring customer retention dynamics: A comparative investigation of factors affecting customer retention in the banking sector using mediation-moderation approach. Heliyon, 10(19), e36919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q., Lim, F. J., Yu, H., Xu, G., Ren, X., Liu, D., Wang, X., Mai, X., & Xu, H. (2021). A study on factors affecting service quality and loyalty intention in mobile banking. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 60, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).