Abstract
Orbit determination for non-cooperative targets represents a significant focus of research within the domain of space situational awareness. In contrast to cooperative targets, non-cooperative targets do not provide their orbital parameters, necessitating the use of observation data for accurate orbit determination. The increasing prevalence of low-cost, low-thrust spacecraft has heightened the demand for advancements in real-time orbit determination and parameter estimation for low-thrust maneuvers. This paper presents a novel dual-layer filter approach designed to facilitate real-time acceleration estimation for non-cooperative targets. Initially, the method employs a square-root cubature Kalman filter (SRCKF) to handle the nonlinearity of the system and a Jerk model to address the challenges in acceleration modeling, thereby yielding a preliminary estimation of the acceleration produced by the thruster of the non-cooperative target. Subsequently, a specialized filtering structure is established for the estimated acceleration, and two filtering frameworks are integrated into a dual-layer filter model via the cubature transform, significantly enhancing the estimation accuracy of acceleration parameters. Finally, to adapt to the potential on/off states of the thrusters, the Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) algorithm is employed to bolster the robustness of the proposed solution. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in achieving real-time orbit determination and acceleration estimation.
1. Introduction
Since the launch of the first artificial Earth satellite Sputnik 1, the number of space objects has escalated dramatically, leading to unprecedented challenges to space safety. In recent years, incidents such as collisions involving space debris and operational errors with satellites have become increasingly common, posing significant threats to the safety of on-orbit spacecraft and other space infrastructures. For example, in 2021, the Canadarm2 on the International Space Station detected holes resulting from impacts [1]; and in 2019, the European Aeolus satellite was compelled to execute an emergency avoidance maneuver to evade the Starlink 44 satellite [2]. These events, which garnered widespread global attention, highlight the critical need for robust space situational awareness. Consequently, to ensure space safety and maintain operational integrity, the development of space situational awareness technology has become imperative [3].
Space Situational Awareness (SSA) constitutes a significant research direction within the domain of space safety, aimed at acquiring a comprehensive understanding and monitoring of the status of all spacecraft within the space environment [4]. To address these challenges, advanced methods leveraging collaborative observations from both spaceborne and ground-based sensors have been developed for precise orbit determination and space situational awareness [5]. According to a survey conducted by Wang et al. [6], SSA technologies can be categorized into the following three primary branches: data acquisition, target identification, and target monitoring. Most of the target recognition and monitoring techniques are based on orbit determination technologies. Among these branches, orbit determination techniques for non-cooperative targets have emerged as a critical area of research [7]. As the prevalence of non-cooperative targets, including space debris and defunct satellites, continues to escalate, accurately and effectively determining their orbits is a substantial challenge within the field of SSA [8]. Furthermore, non-cooperative targets do not broadcast orbital information, necessitating reliance on observational equipment to obtain pertinent data. The presence of errors and uncertainties in observational data, combined with the unpredictability of the motion model associated with non-cooperative targets, significantly exacerbates the difficulties of orbit determination compared to cooperative targets [9]. While significant progress has been made in real-time state estimation, the challenge of perturbed initial orbit determination remains a critical area of research in astrodynamics [10]. Methods have been proposed for specific scenarios, such as LEO objects from radar observations [11], single-station radar measurements [12], and for cislunar orbits with short-arc optical data [13]. Nevertheless, this endeavor is essential for ensuring space safety, conducting orbital monitoring, and managing space traffic effectively. Accurate and robust on-board orbit determination is also essential for enabling autonomous spacecraft operations where ground control is limited or unavailable, and methods have been developed using error Kalman filtering [14]. The demand for precise orbit determination is particularly high in real-world space missions. For example, it is crucial for LEO satellites relying on GPS observations [15], and it extends to complex cislunar missions where orbits are affected by multi-body perturbations [13]. The requirement for high-accuracy orbit solutions is also exemplified by the Tianwen-1 orbiter’s needs during its mapping phase [16].
On the other hand, in recent years, the deployment of large satellite constellations such as Starlink and OneWeb, along with the increasing utilization of small satellites, has heightened the significance of low-thrust engines in satellite orbital maneuvers [17]. Although the acceleration provided by low-thrust engines is small in magnitude, its cumulative effect on the satellite’s velocity and position over time is significant, posing challenges for traditional orbit determination methods that rely on high-precision position and velocity data [18]. Furthermore, initial identification of thrust and orbit elements for continuous thrust spacecraft poses a unique challenge that has been addressed by recent research [19].
This paper chooses the continuous, tangential low-thrust maneuver as the primary test scenario due to its optimal efficiency and broad applicability in real-world missions. Tangential thrust is widely recognized as the most energy-efficient strategy for long-duration orbit raising transfers, as it maximizes orbital energy change by aligning the thrust vector with velocity [20]. This maneuver is critical for the long-arc orbit maneuver of all-electric satellites [21] and is essential for the maintenance of mega-constellations like Starlink [22]. By successfully estimating this challenging and representative low-thrust profile, our proposed filter demonstrates its robustness and general utility for various continuous low-thrust applications.
Several studies have focused on the challenges of orbit determination and low-thrust estimation for non-cooperative targets, exploring various approaches to address these issues. Due to the lack of acceleration information for these targets, accurately modeling their motion using traditional orbital dynamics equations presents significant difficulties. A promising approach is to model the acceleration as a stochastic process, as exemplified by some established models such as the Singer model [23], the Current Singer (CS) model [24], and the Jerk model [25]. The accuracy of the gravitational model is also crucial for precise state estimation. Various methods for gravitational field modeling have been proposed, including comparative assessments for complex scenarios such as binary asteroid landing [26]. Building upon the CS-Jerk model [27], Yin et al. [28] proposed a novel robust CS-Jerk filtering (RCSJF) algorithm that facilitates real-time estimation of non-cooperative target accelerations. Moreover, the orbital motion of the spacecraft is inherently nonlinear, which renders conventional linear filters inadequate for the orbit determination purpose. To address these nonlinear challenges, Huang et al. [29] employed the unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) [30] and subsequently introduced an Adaptive Weighted Strong Tracking Unscented Kalman Filter, thereby enhancing processing accuracy through the unscented transform. Other advanced filtering methods include an Analytical Second-Order Extended Kalman Filter for satellite relative orbit estimation [31], which can overcome the limitations of traditional linear filters. Additionally, to further improve the adaptability of orbit determination algorithms across diverse scenarios, the Interacting Multiple Model (IMM) [32] framework can be utilized to refine existing algorithms. Goff et al. [33] developed a novel combined algorithm based on the variable-state dimension algorithm and enhanced its adaptability by incorporating the IMM approach. Furthermore, Zhang et al. [34] proposed a dimensionality-variable interactive fusion strategy based on the IMM algorithm in their investigation of orbit determination and low-thrust estimation using solely angle measurements, thus increasing the robustness of the algorithm.
Nevertheless, despite the significant progress in these filtering techniques, research on robustly estimating the low-thrust acceleration of non-cooperative targets still faces several key limitations. Specifically, most existing methods either assume a simplified thrust model or primarily focus on improving a single-filter framework, which may not be robust enough to handle the complex and varying acceleration states of a real-world spacecraft. To address these limitations and enhance the accuracy and applicability of acceleration estimation, this paper presents a novel dual-layer filter specifically designed for the real-time acceleration estimation of low thrust in non-cooperative targets. The proposed method employs a dual-layer filter to independently model and estimate the low-thrust acceleration, subsequently utilizing the IMM approach for further improvements, thereby increasing the algorithm robustness to accommodate various acceleration states of the spacecraft.
The structure of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 outlines the methodology, starting with an introduction to the dynamics and observation model employed, followed by a detailed description of the dual-layer filter algorithm and the enhanced algorithm based on the IMM; Section 3 evaluates the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm through simulation experiments; Section 4 concludes by summarizing the main findings of the study.
2. Dual-Layer Filter for Acceleration Estimation
2.1. Dynamic and Measurement Model
2.1.1. Dynamic Model
In this study, we focus on the real-time orbit determination and acceleration estimation for a spacecraft with unknown thrust, specifically a low-thrust spacecraft. The spacecraft’s motion is modeled in a geocentric equatorial inertial frame, considering the primary gravitational force of the Earth, the dominant gravitational perturbation due to Earth’s oblateness ( effect), and the continuous thrust acceleration.
For targets undergoing unannounced low-thrust maneuvers, standard high-fidelity orbital propagators that typically model only conservative forces, such as gravity, and well-modeled non-conservative forces, such as atmospheric drag and solar radiation pressure, are insufficient for accurately characterizing the unknown and non-modeled thrust acceleration; thus, mathematical models for target tracking need to be employed. In 1997, Mehrotra et al. [25] introduced the Jerk model, which incorporates the rate of change of acceleration into the system model. This model assumes that the target’s rate of change of acceleration follows a zero-mean, stationary first-order time-correlated process and has demonstrated efficacy in tracking maneuvering targets. As an example, consider the structure in a given direction as follows:
where represents the rate of change of acceleration of the target at time t, is the Jerk maneuvering frequency of the target’s rate of change of acceleration, the value of is equal to the reciprocal of the time constant of the target’s Jerk maneuver, and is the white noise input.
Inspired by the aforementioned model, the state variable of the spacecraft is defined as follows:
where and represent the position and velocity vectors of the spacecraft in the J2000 Earth-centered inertial coordinate system, respectively, and and represent the acceleration and jerk vectors in the J2000 inertial coordinate system generated by the spacecraft thruster, respectively.
In order to estimate the unknown acceleration, let us substitute Equation (2) into the dynamics equation. Referring to the Jerk model, a new dynamics equation is then derived as follows:
where is Earth’s gravitational constant, is the process noise vector, and represents the acceleration due to the perturbation, which can be calculated by the following:
where is the second-degree zonal harmonic coefficient, and represents the Earth’s reference radius.
The dynamic equation serves as the foundation for the subsequent filtering process, which estimates the low-thrust acceleration of the spacecraft.
2.1.2. Measurement Model
In this study, the East-North-Up (ENU) coordinate frame is employed to characterize the relative motion between the observation station and the spacecraft. The origin of the ENU frame is situated at the center of the station, with the x-axis oriented towards the local east, the y-axis directed towards the north, and the z-axis conforming to the right-hand rule. Within the ENU frame, the range is defined as the magnitude of the target position vector, while the elevation angle E is specified as the angle between the target position vector and the x-y plane. Additionally, the azimuth angle A is defined as the angle between the projection of the target position vector onto the x-y plane and the x-axis, and the range rate is characterized as the rate of change of the range. Therefore, the observation equation can be expressed as follows:
where and represent the position and velocity vectors of the spacecraft in the local ENU coordinate system, which are obtained by converting the position and velocity vectors from the J2000 Earth-centered inertial frame, and the angle is computed using the four-quadrant arctangent function, atan2(x,y), to correctly determine the angle’s quadrant based on the signs of x and y.
The coordinate transformation is simplified by accounting only for Earth’s rotation, while complex effects like precession, nutation, and polar motion are neglected. The corresponding conversion formula is as follows:
where the transformation matrix maps vectors from the J2000 frame to the local ENU frame, with its components defined by the station’s instantaneous longitude and latitude as follows:
Additionally, and represent the station’s position and velocity due to Earth’s rotation, respectively. And is the Earth’s angular velocity vector. These vectors are expressed as follows:
where is the magnitude of the Earth’s angular velocity.
This series of transformation steps establishes a solid foundation for processing ground-based radar observation data, enabling its accurate use for subsequent orbit estimation.
2.2. Real-Time Estimation Filter
2.2.1. Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter
Due to the inherent nonlinearity of the orbital dynamic equation and the complex observation model, a conventional linear Kalman Filter introduces approximation errors in the propagation of the state and covariance, which are typically addressed by using higher-order nonlinear filtering techniques. A viable solution to this issue is the employment of the cubature Kalman Filter (CKF) [35]. This method, which is founded on the concept of the cubature transform, was introduced by Arasaratnam et al. [36] to mitigate the limitations of the UKF in high-dimensional state spaces, where the sigma-point distribution may lose representativeness and the covariance update process can become numerically ill-conditioned, thus increasing the risk of divergence. The fundamental principle of CKF is to address the integration of nonlinear functions and Gaussian distributions by transforming them into spherical radial forms.
Furthermore, during simulation computation, the accumulation of numerical errors may lead the covariance matrix P to lose its positive definiteness. To rectify this issue, we utilize the square root filter method for computation. This approach involves factoring the covariance matrix P into its square root matrix using Cholesky decomposition, followed by the direct update of S throughout the filtering process to maintain numerical stability.
In summary, the square-root cubature Kalman filter (SRCKF) is employed to recursively estimate the state variables. The specific recursive steps are as follows:
Prediction Step:
(1) Calculate the cubature points and perform nonlinear transformation
where and are the state and the square root matrices, respectively, of its corresponding covariance matrix after Cholesky decomposition. The caret symbol () over a variable denotes the reference value for the sigma points. The discrete time step is represented by k. The time index indicates an operation at the current time step, while indicates a prediction at time step k to obtain the state at time step . The nonlinear transformation in Equation (11) is equivalent to numerically integrating the dynamic Equation (3) forward one time step. The symbols and denote the i-th sigma point sampled from the posterior distribution at time step k and its corresponding propagated value at time step (indicated by the superscript ∗), respectively. Here, is the total number of sigma points, n is the dimension of the state vector , and represents the i-th column vector of the cubature point set, defined as , where is the identity matrix.
(2) Calculate the predicted state and the square-root matrices of covariance
where is the weighted center matrix, is the process noise matrix, Tria(·) represents the lower triangular matrix obtained after QR decomposition of the matrix, and Chol(·) represents the Cholesky decomposition of the matrix.
Observation Step:
(1) Calculate the sigma points and perform the nonlinear transformation
where the nonlinear transformation in Equation (15) is the observation equation corresponding to Equation (5) in this study.
(2) Calculate the state and covariance matrix of the predicted measurements
where is the weighted center matrix, and is the observation noise matrix, and the superscript “ZZ” denotes the variables associated with the measurement vectors and their auto-covariance.
(3) Calculate the cross-covariance matrix between the state and the observation
where is the weighted center matrix, and the superscript “XZ” denotes the cross-covariance between the state vector and the measurement vector.
(4) Calculate the Kalman filter gain
(5) Calculate the updated state and covariance matrix square root for the next time step
This method yields a preliminary acceleration estimation, which serves as a crucial initial value for the subsequent refinement, leading to a more accurate final estimation.
2.2.2. Dual-Layer Filter
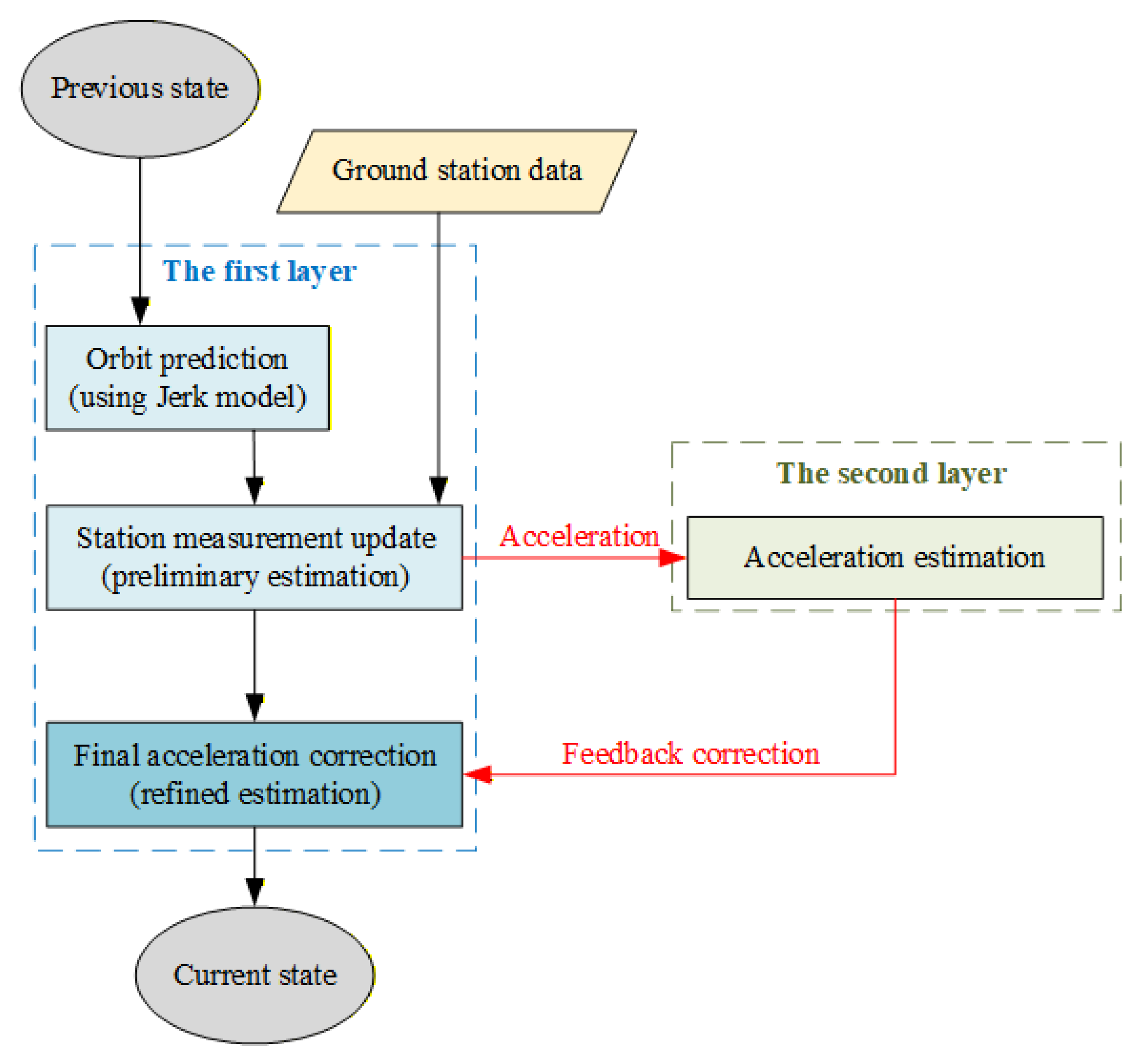
To enhance the accuracy of acceleration estimation, this paper presents a novel dual-layer filter structure, as illustrated in Figure 1. The fundamental concept involves transmitting the preliminary acceleration estimation results obtained from the first layer to the second layer for further refinement, followed by the feedback of the refined results to the first layer via the cubature transform.
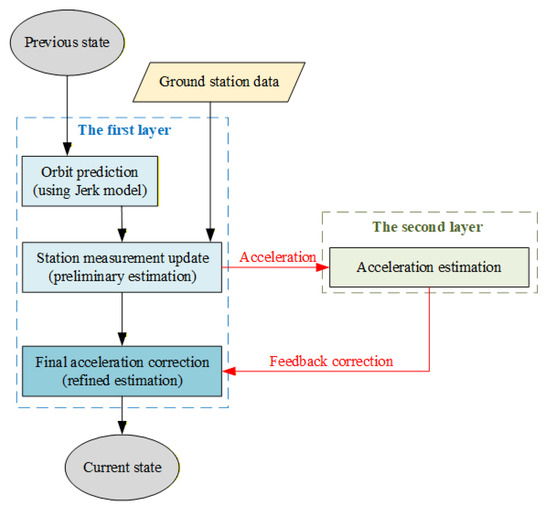
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the dual-layer filter structure.
The acceleration estimation initially derived from the first-layer filtering is employed as the observation value. Then a key component of this approach is the dynamic modeling of the low-thrust acceleration. In this paper, we assume the spacecraft is undergoing a low-thrust maneuver on a near-circular orbit. For such a scenario, the continuous thrust can be approximated as a time-varying acceleration whose components exhibit a quasi-periodic behavior. Specifically, we model the acceleration component as a sinusoidal function as follows:
where is the maximum thrust amplitude and is the phase angle. This model, while a simplified approximation, provides a robust basis for real-time estimation. The angular frequency corresponds to the spacecraft’s orbital angular frequency, which can be obtained dynamically from the position estimate r provided by the first-layer filter using the formula . This adaptive modeling approach enhances the filter’s ability to track continuous low-thrust maneuvers and improve the overall estimation accuracy.
It is essential to clarify that this method does not rely on the assumption of a precisely known frequency. Instead, the sinusoidal form is introduced because a constant tangential acceleration, when transformed into the inertial frame, analytically assumes a quasi-periodic nature, with its frequency inherently coupled to the spacecraft’s orbital mean motion (). The core benefit of this model is the introduction of this physical-based prior knowledge into the filtering process, which effectively constrains the acceleration state space. This structural constraint significantly enhances estimation accuracy compared to purely stochastic models and ensures the method’s robustness even when the actual orbital frequency deviates slightly from the calculated .
In light of the near-circular nature of the orbital motion, the state variable for the second-layer filter model is defined as follows:
The equation of prediction step assumes that the state variable remains constant.
Upon completion of the second-layer calculations, it is essential to feed back the results to the first layer in order to establish a closed loop. The implementation of this closed loop can be likened to the prediction and observation steps commonly found in conventional filter methods. In this context, we denote these as the transformation step and the correction step. The key distinction is that the prediction step in conventional filter entails recursively solving for state variables. Conversely, in our approach, we utilize the results from the second layer as observations to enhance the results of the first layer. The state variables in the second layer comprise the previously mentioned six quantities, thereby necessitating a transformation step. This step is also executed using cubature transform. The specific procedures are detailed in the following:
Transformation Step:
(1) Calculate the sigma points and perform nonlinear transformation
where (dimension ) and (dimension ) are the state defined in Equation (24) and the square root matrices, respectively, of its corresponding covariance matrix after Cholesky decomposition. The notation L2 represents the the posterior state estimation of the second filtering layer, and the notation proj represents the operation from the second filtering layer to the first one. Specifically, the symbol (dimension ) denotes the predicted vector obtained by mapping the state of the second layer back to the space of the first layer. The nonlinear transformation in Equation (26) maps the state variables of the second layer to the acceleration components of the first layer’s state vector, based on the model defined in Equation (23).
(2) Calculate the transformed state and the square-root matrices of covariance
where is the weighted center matrix (dimension ), and is the process noise covariance matrix of the second layer projected onto the acceleration space (dimension ).
Correction Step:
(1) Calculate the sigma points and perform transformation
where is the state vector of the first layer (dimension ), and is the square root covariance matrix of the first layer (dimension ). The transformation in Equation (30) extracts the acceleration component from the state variable of the first layer filter.
(2) Calculate the state and covariance matrix of the correction term
where is the weighted center matrix (dimension ), is the covariance matrix of the correction term (dimension ).
(3) Calculate the cross-covariance matrix between the state and the correction term
where is the cross-covariance matrix between the state and the correction term (dimension ), and is the weighted centered state matrix of the first layer (dimension ).
(4) Calculate the Kalman filter gain
where is the Kalman gain matrix (dimension ).
(5) Calculate the corrected state and the square root of covariance matrix
where is the updated state estimation of the first layer (dimension ), is the transformed state provided by the second layer (dimension ), and is the updated square-root covariance matrix of the first layer (dimension ).
This dual-layer structure, which we term the Dual-Layer Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter (DLSRCKF), provides a specialized framework for the low-thrust acceleration estimation, significantly enhancing the accuracy of the final estimation result.
2.2.3. IMM Algorithm
To accommodate diverse acceleration states of the spacecraft, we employ the IMM algorithm [37] to address the potential on–off behavior of the thruster. The detailed recursive steps from time step k to are outlined in the following:
(1) Input Mixing
where represents the credibility of each model calculated in the previous time step; is the given state transition matrix, indicating the possibility of switching between different states; and the superscript m denotes the fusion of results.
(2) Model Update
Each model is subsequently updated recursively. We consider the following two models: Model 1 represents the active state of the thruster, utilizing the dual-layer filter model previously described. Model 2 corresponds to the inactive state, with its state variables defined as follows:
The dynamic equation for the recursive step in Model 2 is as follows:
The observation equation for the update step in Model 2 is identical to that of Model 1 and also employs the SRCKF method for recursive updates. To facilitate the mixing and combination steps required by the standard IMM framework, we augment the state variables and covariance matrix of Model 2 to align with the dimensions of Model 1, thus creating a common state vector. The additional dimensions are initialized to zero.
(3) Credibility Update
where and represent the measurement errors and their covariance matrices, respectively, corresponding to each model.
(4) Output Mixing
This mixing process, achieved by introducing the IMM algorithm, enhances the robustness of the proposed method, enabling it to effectively accommodate varying thrust on–off conditions.
3. Simulation and Results
3.1. Simulation Setups
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm, we applied it to estimate the low-thrust acceleration of a spacecraft moving on a circular orbit at an altitude of 1000 km. The initial orbital elements are presented in Table 1. With reference to the existing literature [33] on orbit determination, fifteen ground-based radars are uniformly distributed at 0° latitude to ensure comprehensive coverage of the spacecraft trajectory, with an observation frequency of 1 Hz. To simulate realistic scenarios, Gaussian noise was added to the observation data based on the specified observation errors. The observation errors were configured as follows: range error of 1 m, angular error of 0.01 deg, and velocity error of 50 mm/s. Notably, a higher observation frequency and reduced observation errors contribute to increased accuracy in the results; however, these factors are ultimately constrained by the intrinsic precision of the sensors. Considering practical sensor accuracy, we adjusted the parameters accordingly.

Table 1.
Initial orbital elements of the maneuvering target.
In this numerical experimental verification, the spacecraft is modeled as a point mass. Its true trajectory is generated by numerically integrating the high-fidelity dynamics equations, which account for the Earth’s central gravity, the perturbation, and the commanded low-thrust acceleration. This setup serves as a standard baseline for evaluating the orbit determination performance.
The low-thrust acceleration is applied along the tangential direction of the spacecraft’s orbit to maximize the change in orbital energy. Therefore, the specific expression of the thrust acceleration vector in the inertial frame is defined as , where a is the magnitude of the low-thrust acceleration, and is the instantaneous velocity vector of the spacecraft in the inertial frame.
3.2. Validation of the Dual-Layer Filter
To evaluate the accuracy of the dual-layer filtering algorithm in estimating the low-thrust acceleration, a tangential acceleration is applied to the spacecraft, with its specific magnitude shown in Table 2. The algorithm parameters are initialized as follows:

Table 2.
Thrust acceleration in the velocity vector direction for simulated cases.
The initial state variable for the first-layer filtering algorithm is
where denotes the spacecraft position vector derived from the observation equation at the first and second observation point.
And the initial covariance matrix is as follows:
For the first layer, as indicated in the formula, the initial state vector is initialized using the measurements from the first two time steps, which is a common heuristic approach for track initialization. The position components are directly obtained from the first observation, while the velocity components are approximated by the finite difference between the positions at the first and second time steps. Correspondingly, the initial error covariance matrix is set with relatively large variances. This setting accounts for the measurement noise present in the observation data and the approximation error inherent in the difference method, ensuring that the true state lies within the filter’s initial uncertainty ellipsoid.
The initial state variable for the second-layer filtering algorithm is
And the initial covariance matrix is
For the second layer, the state vector is initialized to zero due to the unknown maneuver status. However, the initial covariance is set to a relatively large value compared to typical low-thrust magnitudes. This large uncertainty serves as a weak prior, ensuring the filter remains sensitive to rapidly capture the true acceleration once the maneuver begins.
The process noise covariance matrices and are computed using the general formula , where is the continuous-time noise intensity and is the input noise vector for the time step .
For the first-layer: The continuous-time intensity is , and the input vector is as follows:
For the second-layer: The continuous-time intensity is , and the input vector is as follows:
The difference in the magnitude of and represents the core of the tuning strategy, explicitly designed to decouple the two estimation layers, as follows: the extremely small ensures the first layer maintains orbit consistency and acts primarily as a smoother, while the larger grants the second-layer the necessary responsiveness to quickly and accurately track the high-frequency maneuver.
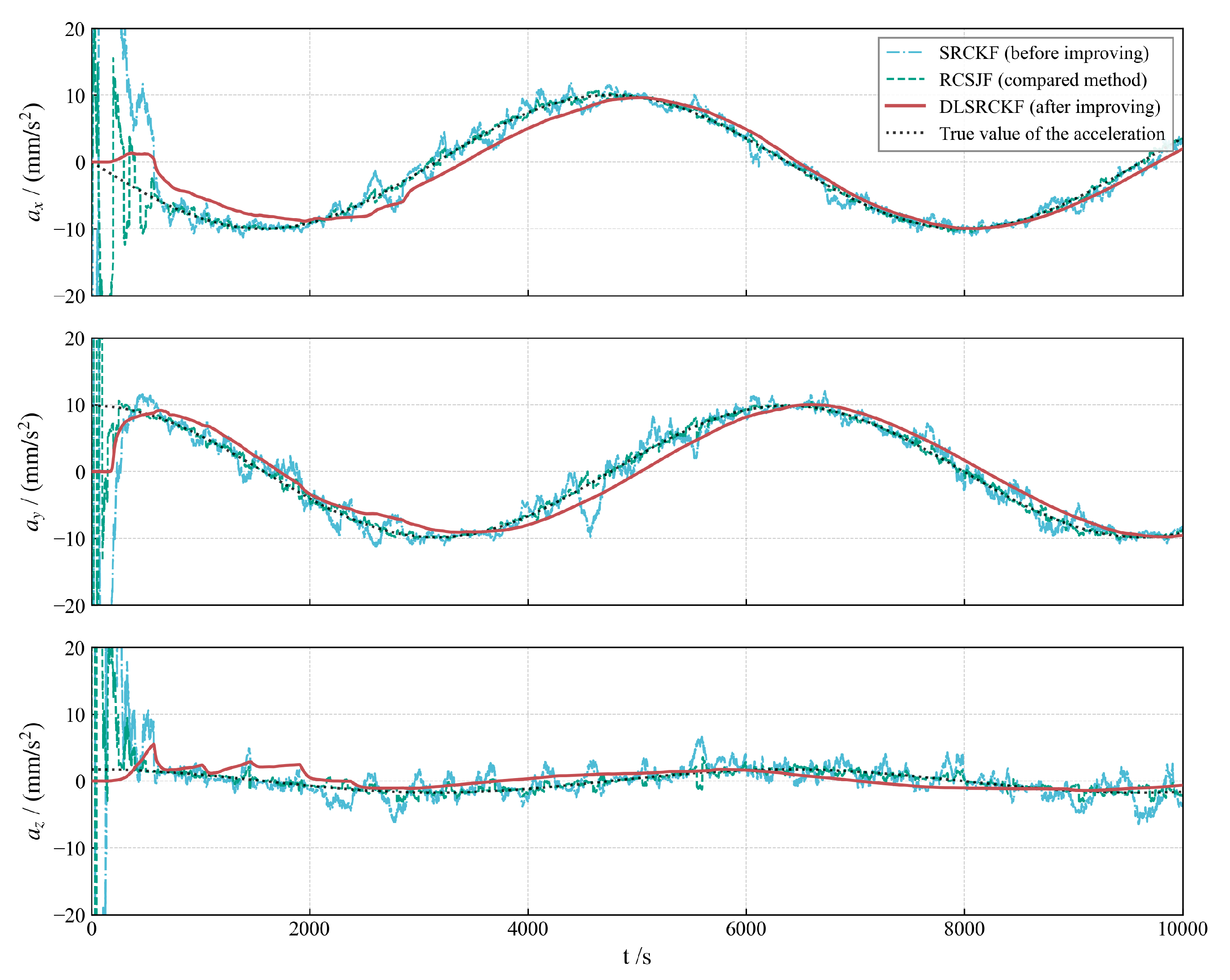
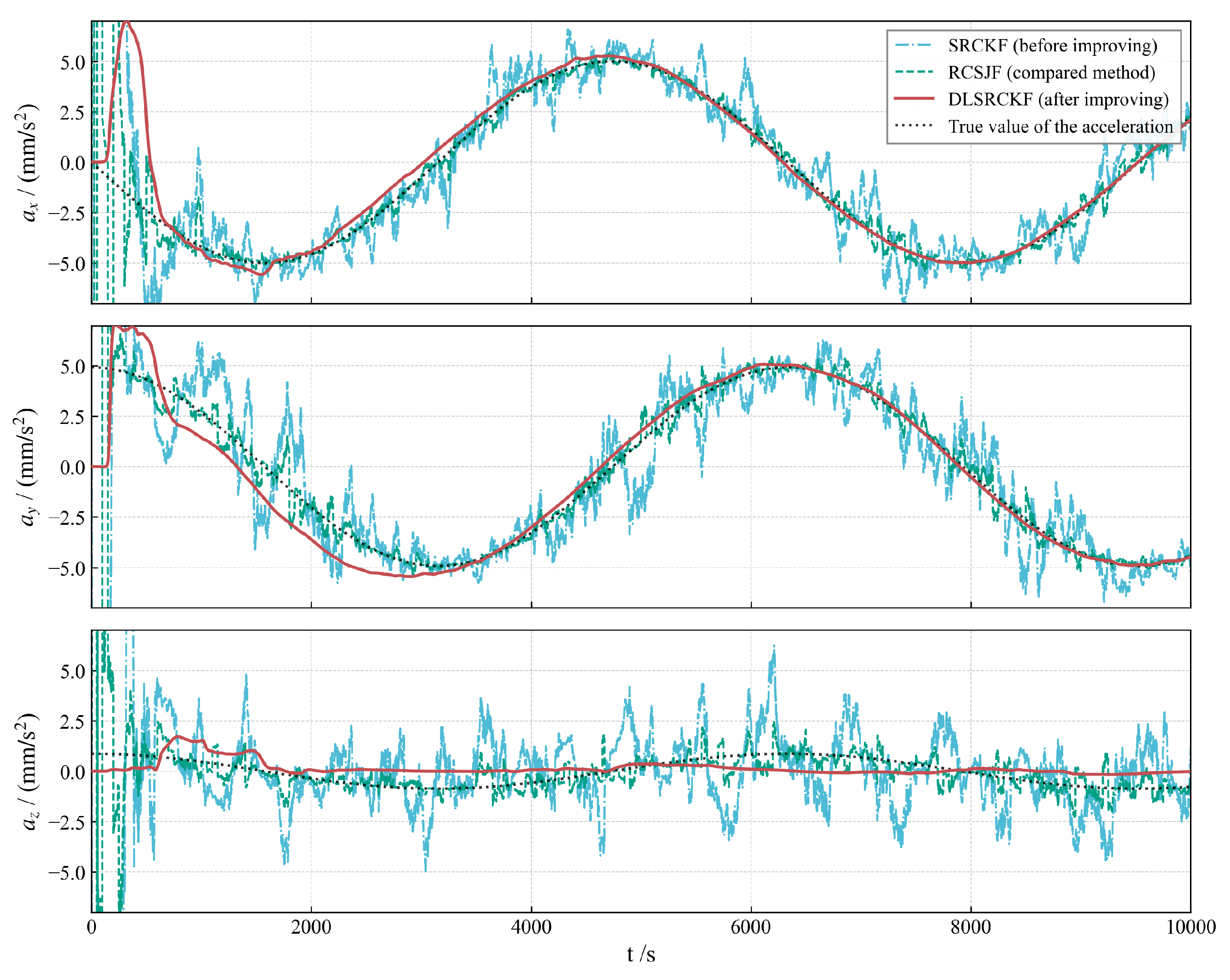
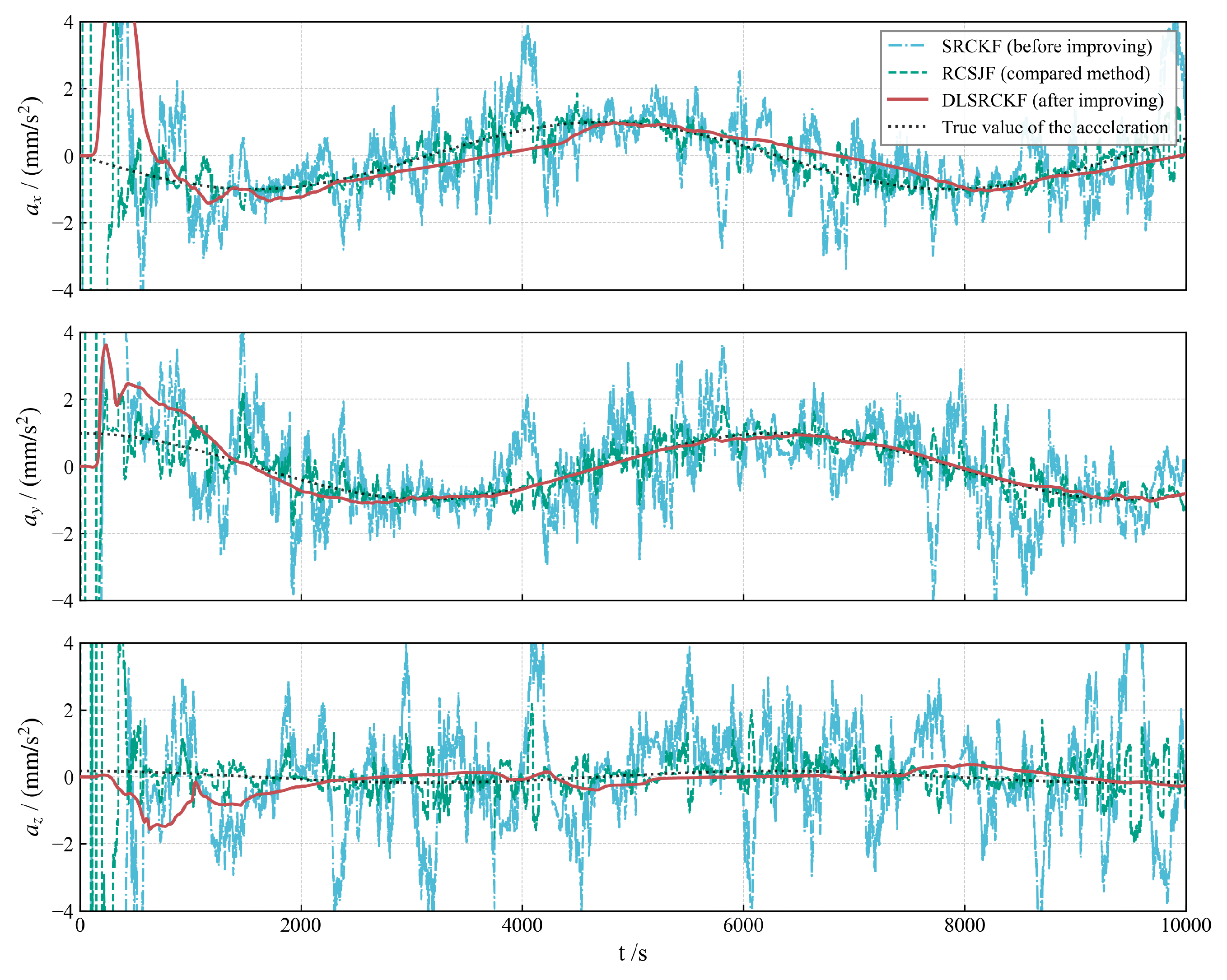
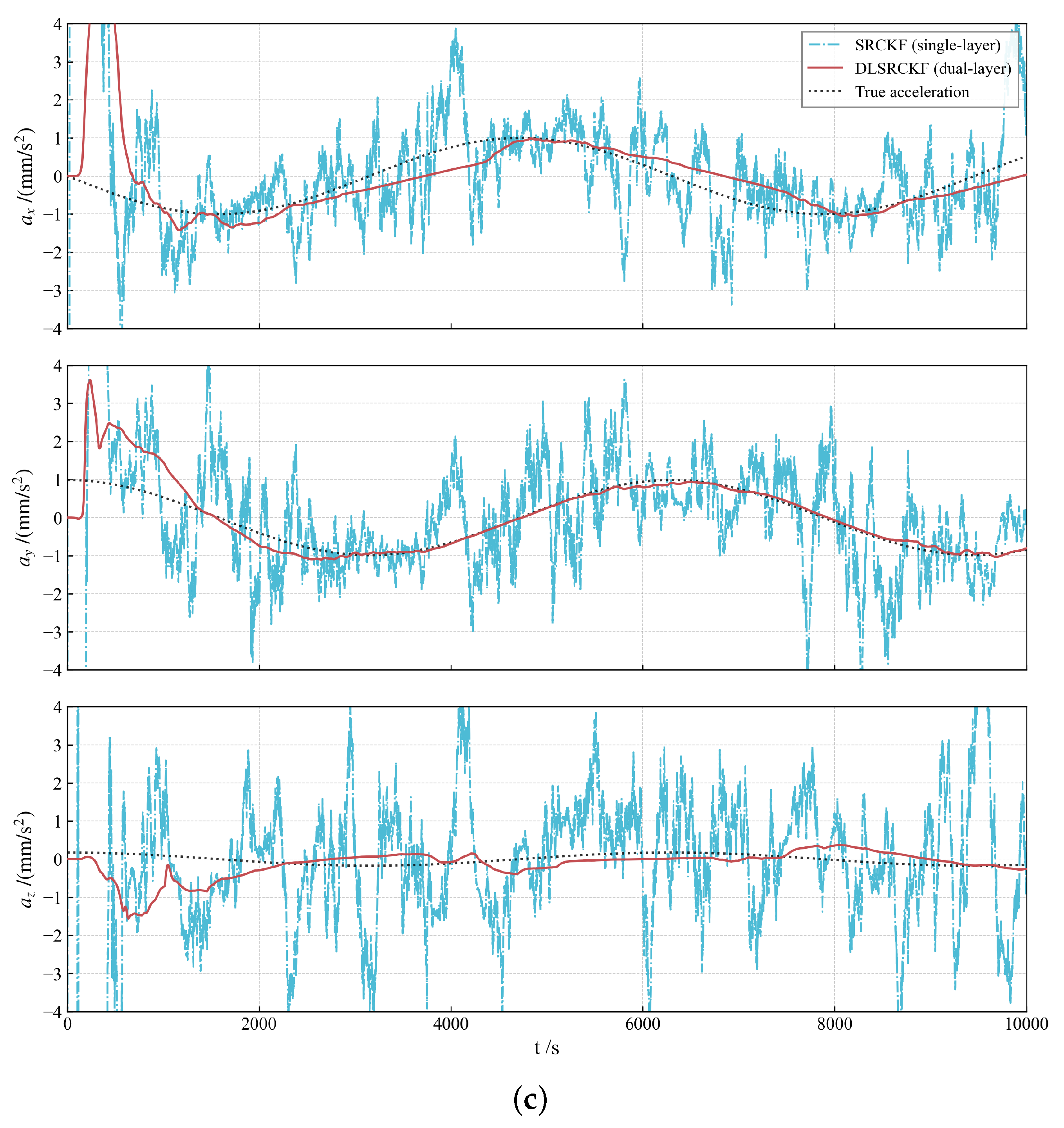
Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4 illustrate the acceleration estimation performance across different scenarios. The results indicate that the incorporation of a specific acceleration filter structure into the basic SRCKF algorithm effectively mitigates noise and enhances estimation accuracy. As the magnitude of the actual applied acceleration diminishes, the original filter algorithm SRCKF encounters difficulties in achieving accurate acceleration estimation due to noise interference. In contrast, the new algorithm DLSRCKF maintains its capacity to estimate the acceleration with high accuracy. A comparison with the existing method RCSJF [28] in the literature further demonstrates that the core advantage of our proposed dual-layer filter lies in its ability to provide more accurate acceleration estimations, particularly for the challenging task of estimating low thrusts. The key parameters for the RCSJF filter were adopted directly from the relevant settings in the work by Yin et al.
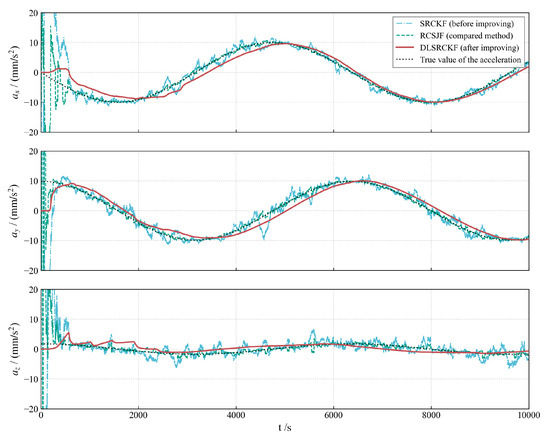
Figure 2.
Low-thrust acceleration estimation for case 1 with 10 .
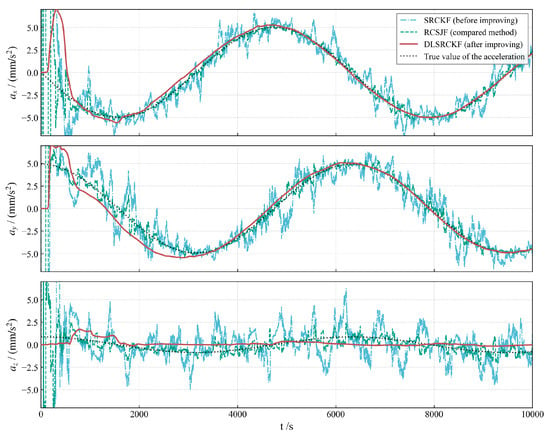
Figure 3.
Low-thrust acceleration estimation for case 2 with 5 .
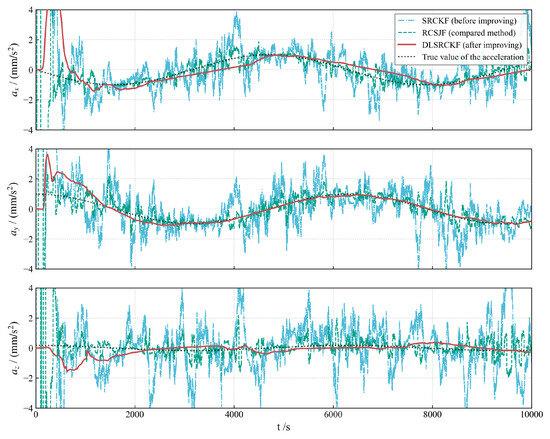
Figure 4.
Low-thrust acceleration estimation for case 3 with 1 .
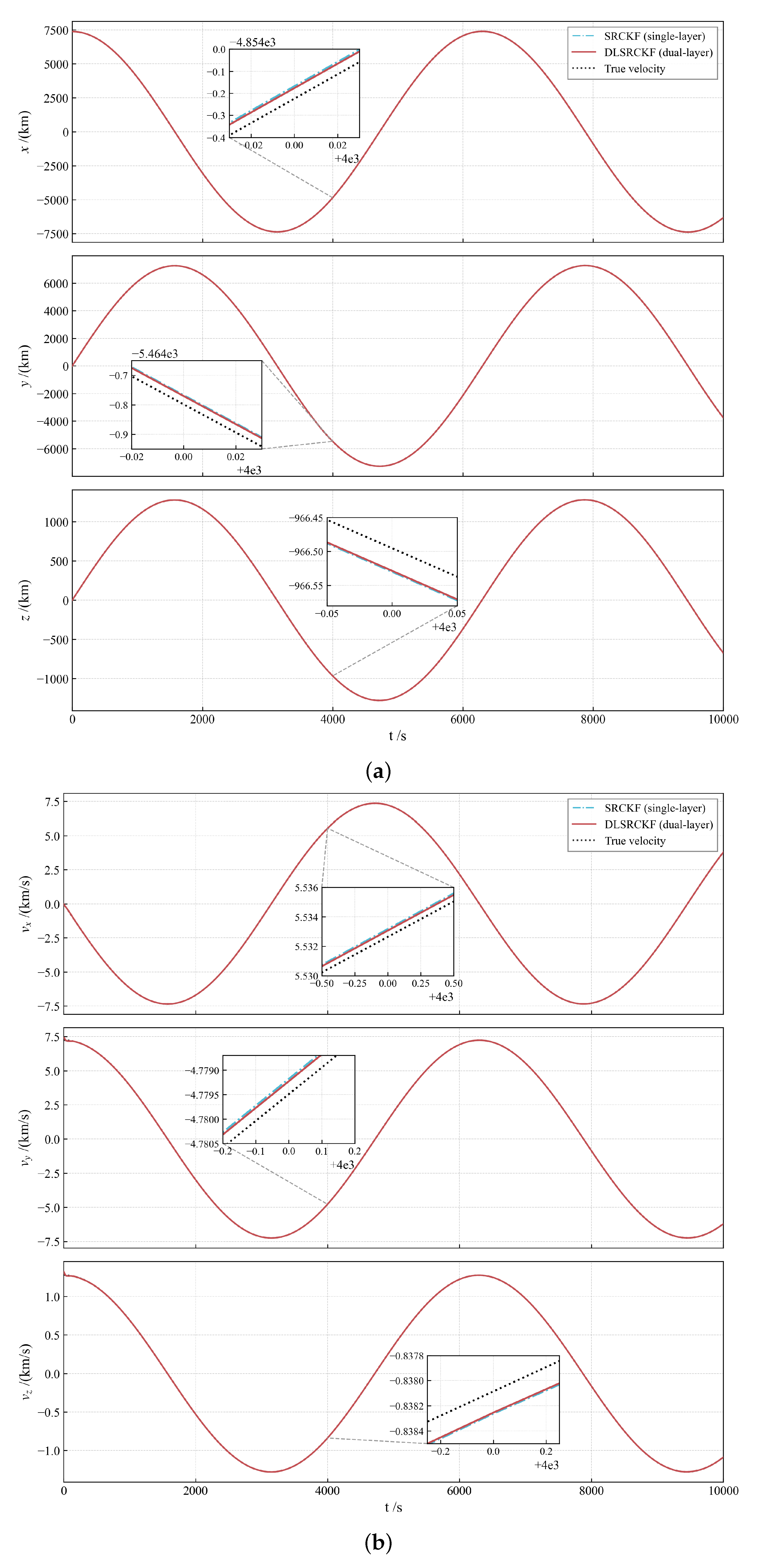
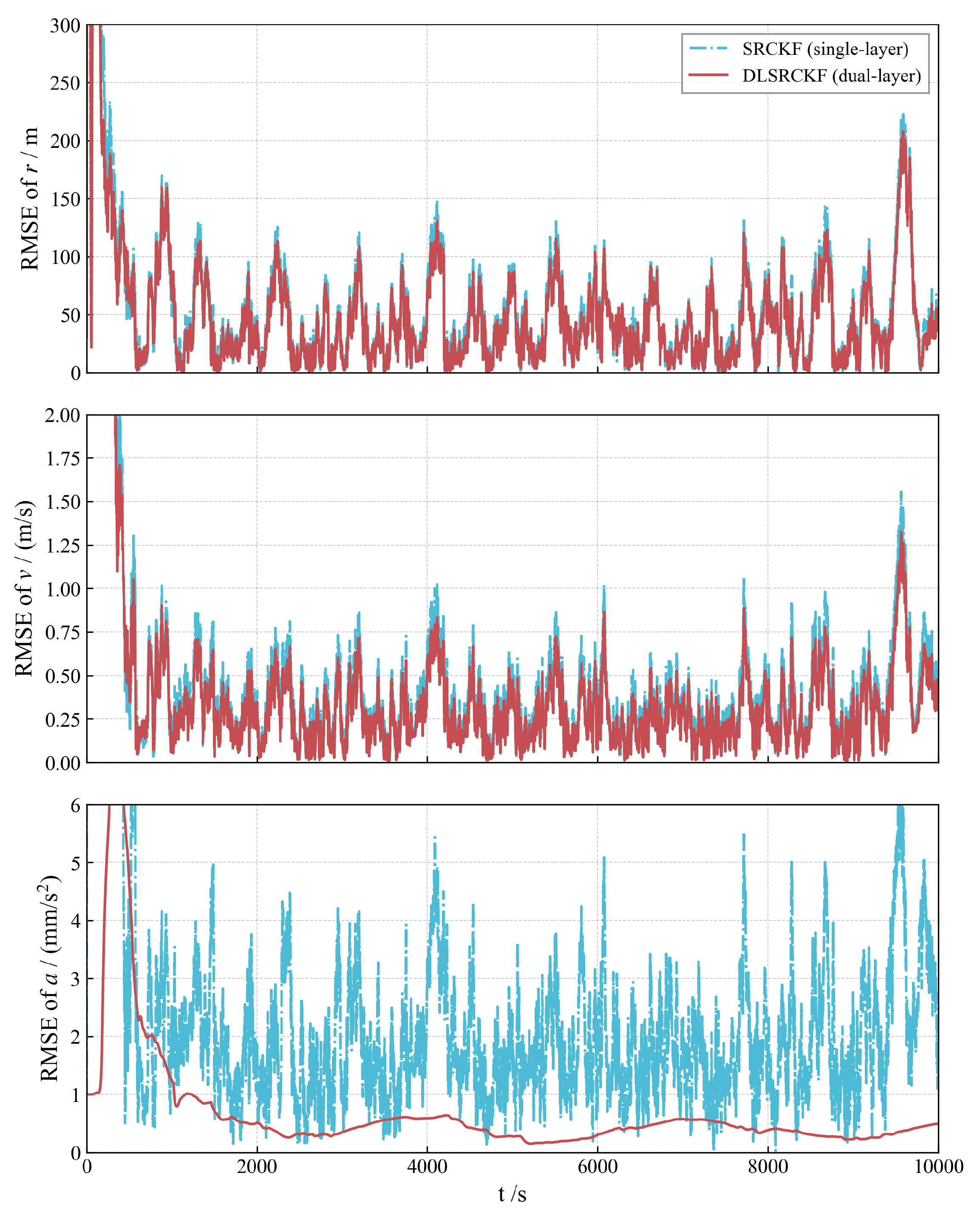
The complete state estimation results, including the time history of position, velocity, and acceleration (Figure 5a–c) and their corresponding RMSE (Figure 6), provide a quantitative comparison between the dual-layer filter and the single-layer filter. Figure 5a–c shows that the DLSRCKF provides a much smoother trajectory estimate than the noisier SRCKF, particularly in the acceleration plots. Crucially, the RMSE comparison in Figure 6 confirms that, while position and velocity RMSEs are comparable, the DLSRCKF achieves a significantly lower and more consistent acceleration RMSE, demonstrating that the dual-layer decoupling strategy effectively isolates the maneuver estimation task and yields superior accuracy for the unknown low thrust [36].
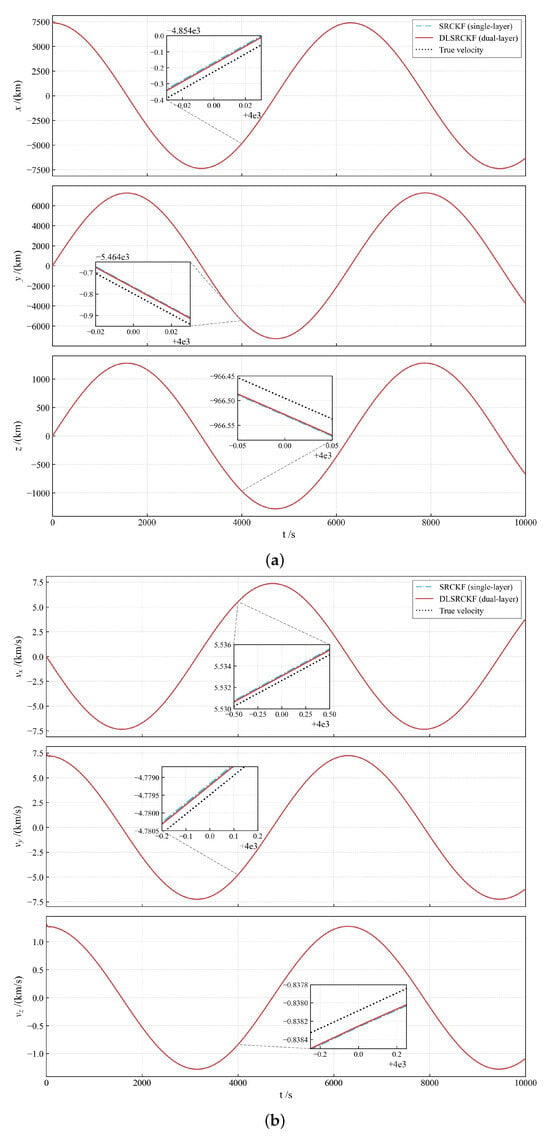
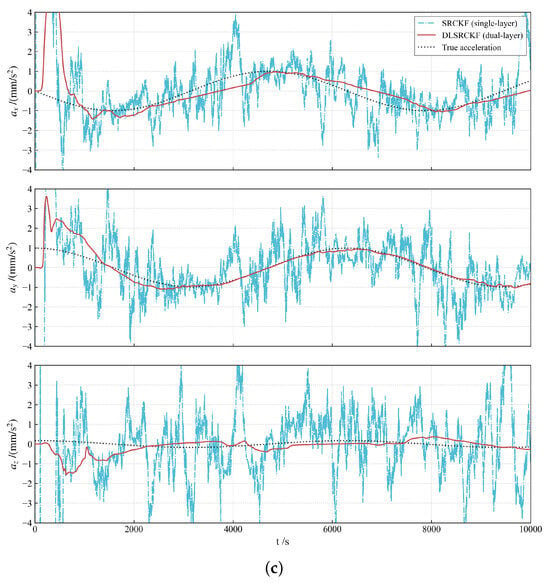
Figure 5.
(a) The comparison of full state (position, velocity, and low-thrust acceleration): Performance of the dual-layer filter versus the single-layer filter (part 1: position). (b) The comparison of full state (position, velocity, and low-thrust acceleration): Performance of the dual-layer filter versus the single-layer filter (part 2: velocity). (c) The comparison of full state (position, velocity, and low-thrust acceleration): Performance of the dual-layer filter versus the single-layer filter (part 3: acceleration).
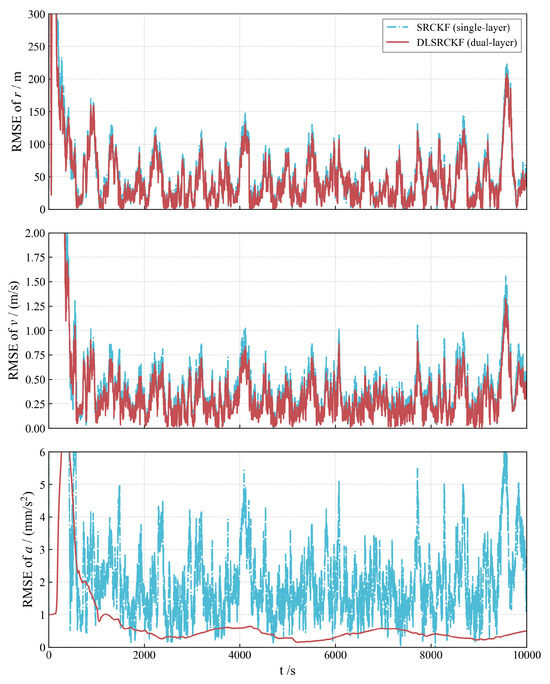
Figure 6.
Root mean square error (RMSE) comparison for position, velocity, and low-thrust acceleration.
Table 3 presents the RMSE of acceleration estimation for both the single-layer and dual-layer methods calculated during the stable tracking phase (specifically for s). The results indicate that the proposed DLSRCKF method consistently outperforms the SRCKF across all test cases. Notably, in the low-thrust scenario (), the DLSRCKF achieves a significantly lower RMSE of , demonstrating the superior accuracy and robustness of the dual-layer architecture.

Table 3.
Acceleration estimation RMSE comparison between SRCKF and DLSRCKF ( s).
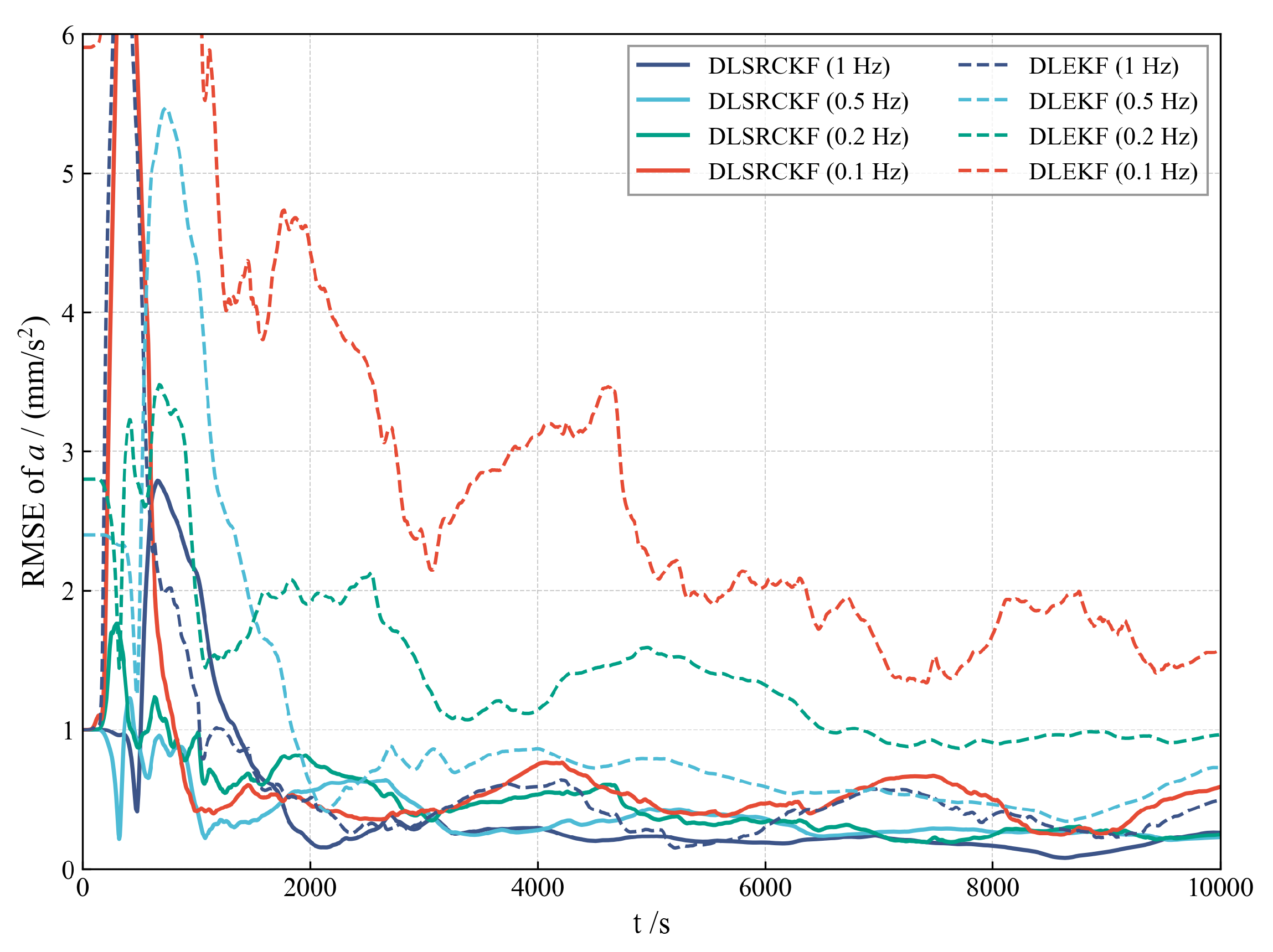
To justify the selection of the nonlinear SRCKF over simpler alternatives, we conducted a direct comparison of its performance against EKF. As illustrated in Figure 7, the estimation accuracy of the EKF significantly degrades as the observation frequency is reduced. For instance, when the data rate drops from 1 Hz to 0.1 Hz, the EKF’s reliance on first-order linearization struggles to accurately propagate the state and covariance, leading to a substantial increase in estimation error. Conversely, the SRCKF, by utilizing the spherical-radial cubature rule to better capture the nonlinear dynamics, maintains superior accuracy and robustness across the lower observation rates. This empirical evidence validates the necessity of employing a high-fidelity nonlinear filter like the SRCKF for this challenging continuous low-thrust orbit determination problem.
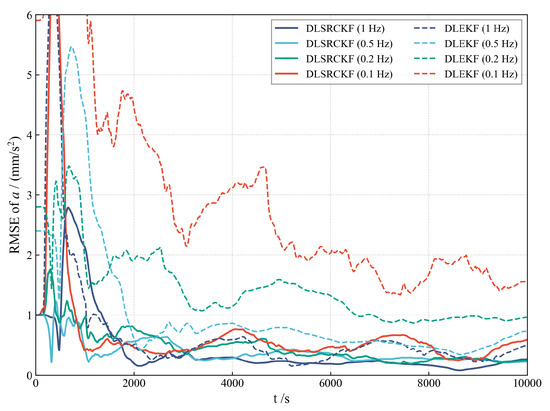
Figure 7.
Comparative RMSE of SRCKF vs. EKF under varying observation rates.
3.3. Robustness Analysis and Covariance Consistency Check
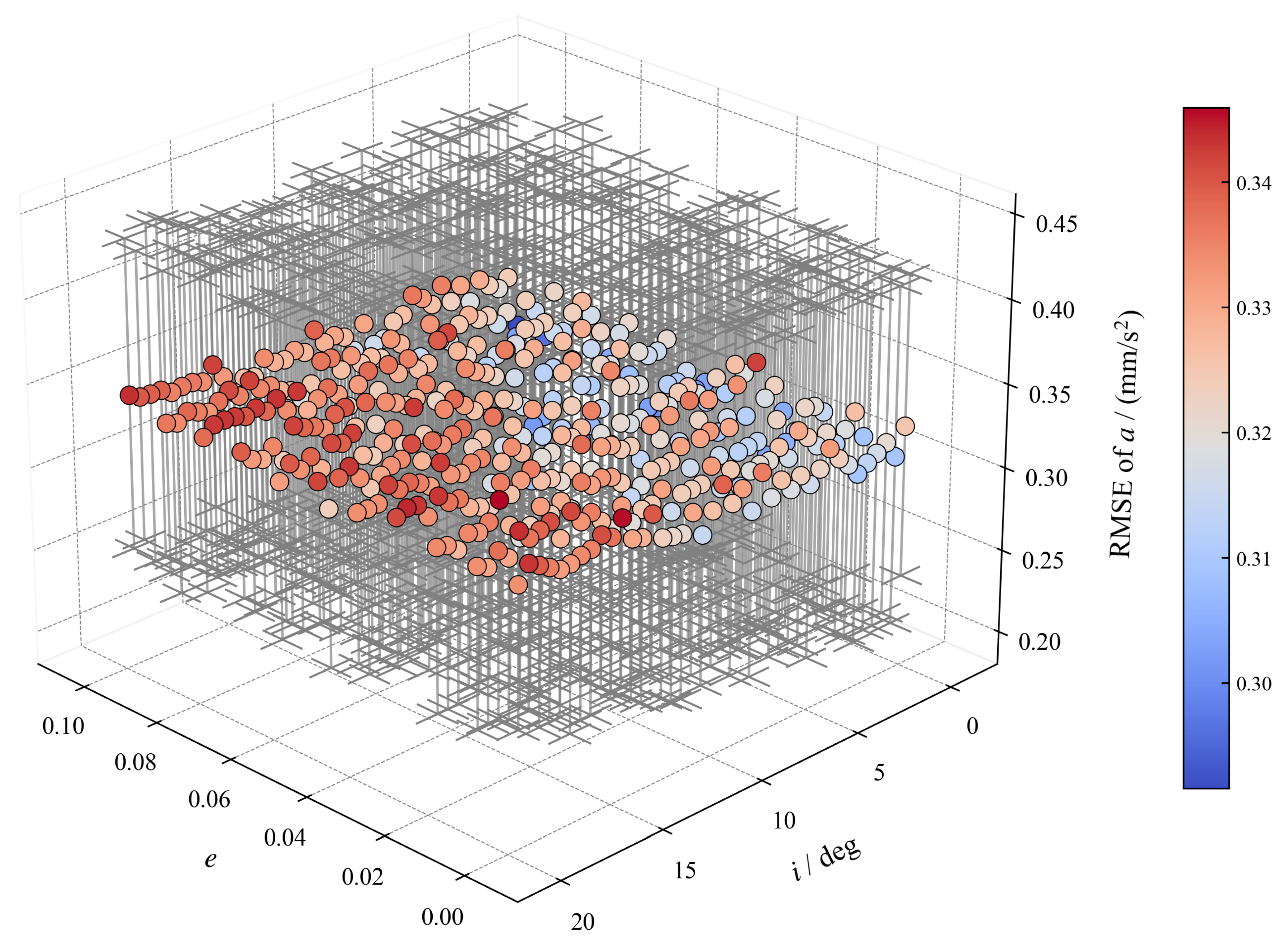
To validate the filter’s robustness and applicability domain across the LEO environment, a comprehensive analysis was conducted by varying the following two key orbital parameters: eccentricity (e) and inclination (i). The simulation grid covered e from 0 to 0.1 and i from to , representing a significant portion of the LEO parameter space.
The resulting final low-thrust acceleration estimation RMSE (based on 100 Monte Carlo runs) for each parameter combination is mapped in Figure 8. Figure 8 plots the average RMSE, with the error bars representing one standard deviation () across the 100 runs. The figure demonstrates that the DLSRCKF maintains a highly consistent and stable performance across the tested orbital parameter grid, with the overall average acceleration bias calculated at a low . This low and stable bias confirms that the dual-layer strategy is robust against changes in orbital geometry and exhibits systematic performance, effectively addressing non-circular orbits.
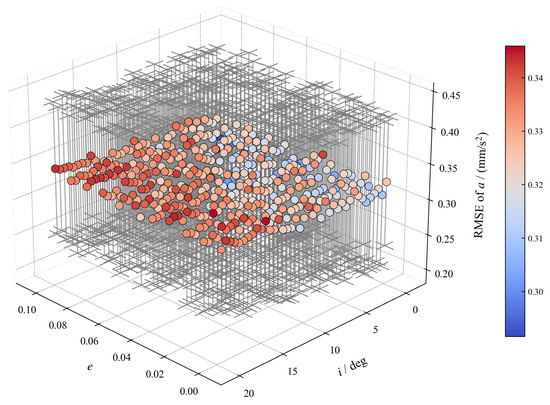
Figure 8.
Low-thrust acceleration estimation RMSE across different i and e (N=100).
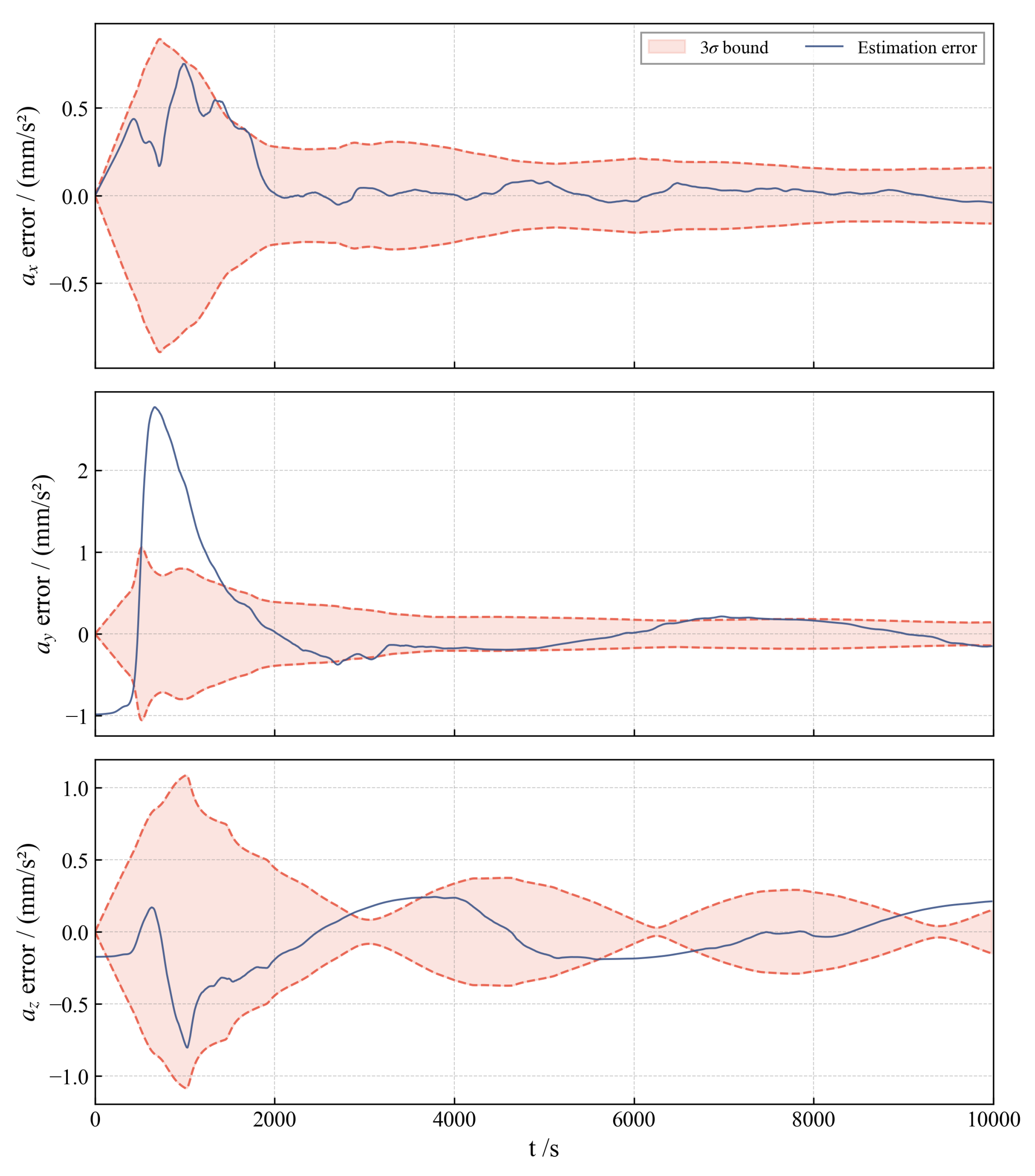
Figure 9 illustrates the filter’s statistical integrity by plotting the RMSE against the filter covariance envelope for a representative scenario (). The RMSE curves for the x and y components track and remain contained within the bounds, confirming statistical consistency. The z-axis error is observed to be relatively larger; this is expected because the true acceleration in the normal direction approaches zero, which intrinsically makes acceleration estimation in this direction more challenging. Overall, the consistent containment of the RMSE curves within the bounds validates the filter’s statistical consistency and reliability.
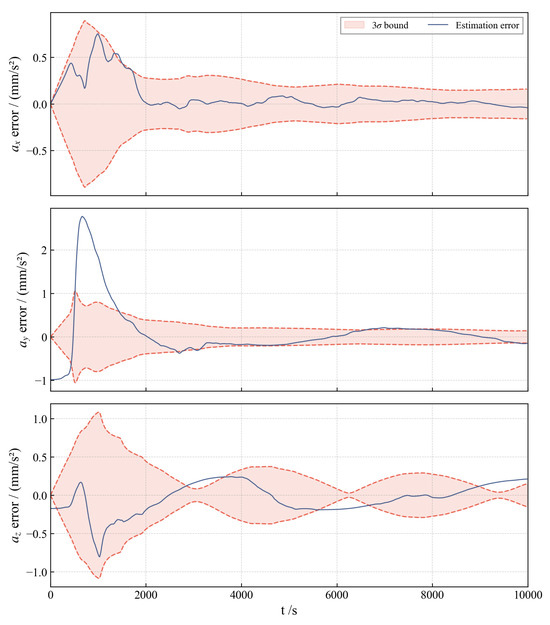
Figure 9.
Low-thrust acceleration RMSE in covariance envelope (). The red dashed lines represent the error bounds.
3.4. Validation of the IMM Algorithm Based on DLSRCKF
Recognizing that spacecraft thrusters do not operate solely in an `on’ or `off’ state but rather transition between these two modes, a novel IMM algorithm has been developed based on the dual-layer filtering technique discussed previously. The simulation results presented below will substantiate the effectiveness of this new algorithm.
The spacecraft is initially in an off state, and then turns on at 3000 s, applying a tangential acceleration of 1 mm/s2. The initial state variable of the off model, as described in Section 2.2.3, is , the initial covariance matrix is , and the initial model confidence is . The state transition matrix between the on and off states is set as follows:
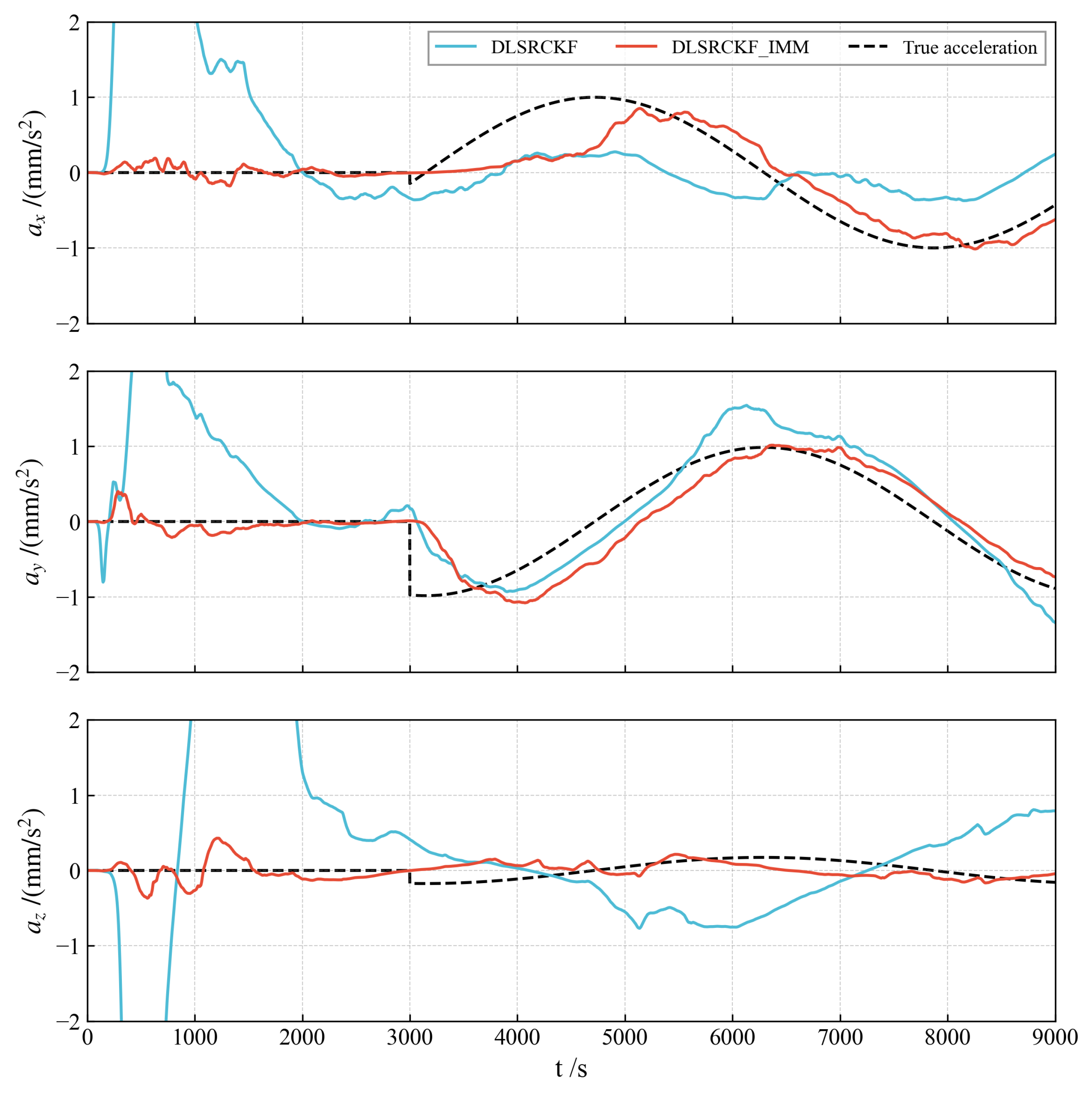
As illustrated in Figure 10, the accuracy of the single dual-layer filter algorithm significantly deteriorates when the spacecraft does not operate exclusively in a specific on–off state. The newly developed IMM algorithm, built upon this foundation, markedly enhances the estimation accuracy of acceleration, particularly during the off state. Moreover, it effectively captures acceleration changes during the on state.
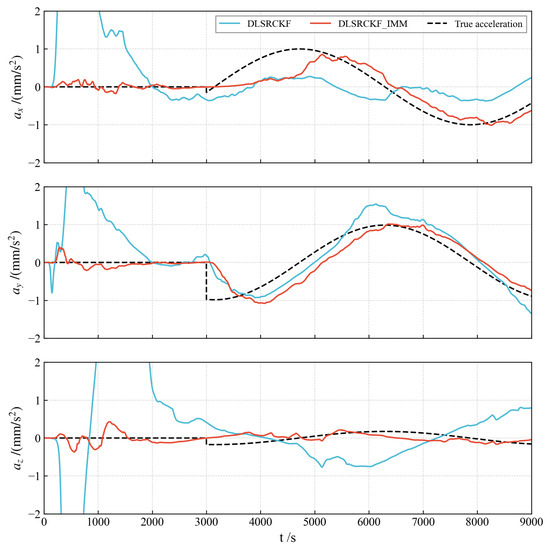
Figure 10.
Estimation for time-varying acceleration.
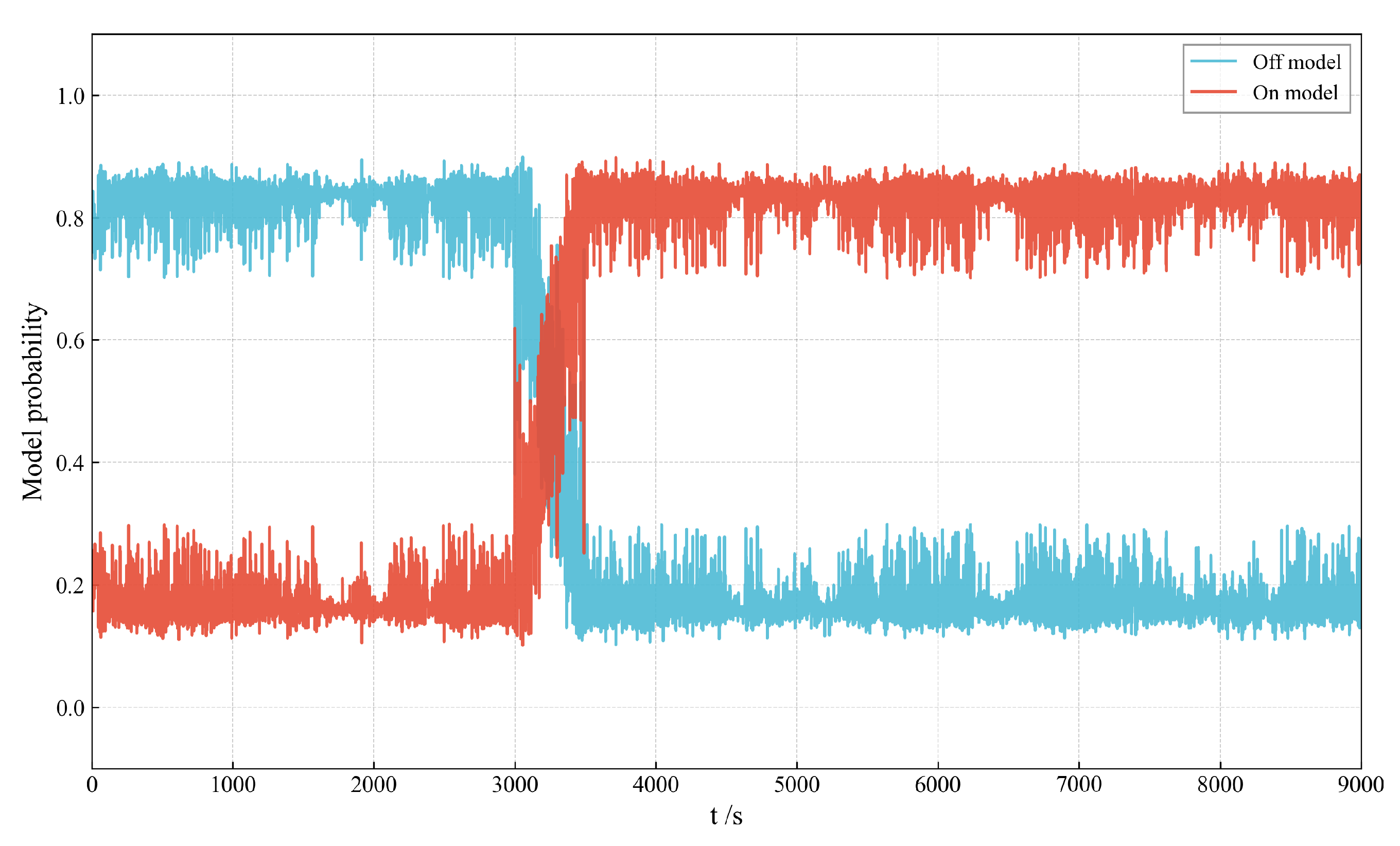
The robust performance enhancement provided by IMM is substantiated by the mode probability analysis, as shown in Figure 11. The figure illustrates the temporal evolution of the model probability. The results show that, during the initial phase and stable off-periods of the simulation, the filter correctly assigns a probability close to one to the off model. Crucially, as the active maneuver initiates, the probability for the on model rapidly increases and dominates the total probability, allowing the filter to switch to the appropriate dynamic model for tracking the low-thrust acceleration.
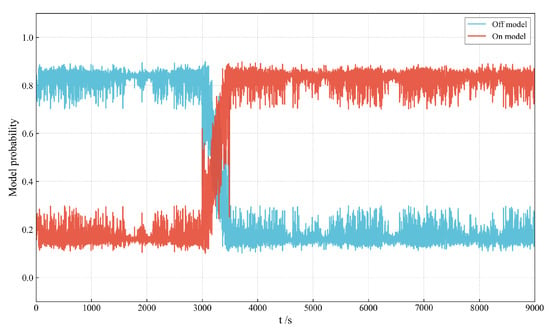
Figure 11.
Temporal evolution of mode probabilities: Off model vs. on model.
4. Conclusions
This paper addresses the challenge of low-thrust acceleration estimation for non-cooperative targets and proposes a dual-layer filter framework based on the SRCKF algorithm. The algorithm initially employs a dual-layer filtering structure to obtain a preliminary estimation of the low-thrust acceleration, effectively mitigating the influence of noise in the estimation process and enhancing overall accuracy. Building on this foundation, an IMM approach is integrated to further tackle the challenges posed by the on/off switching of spacecraft thrusters, thereby enabling precise identification of acceleration changes. Simulation results validate the algorithm’s capability to accurately track spacecraft trajectories and estimate maneuver acceleration. Notably, even in the presence of small accelerations and thruster on/off transitions, the algorithm maintains a high degree of estimation accuracy.
Furthermore, the flexibility of the proposed dual-layer architecture allows for seamless integration with higher-fidelity orbital dynamics models. Incorporating well-modeled environmental forces, such as solar radiation pressure or atmospheric drag, primarily serves as an extension to the dynamics of the first-layer filter. By accounting for these known forces, the first layer’s model error is reduced, which in turn allows for a smaller process noise covariance (). This refinement does not fundamentally alter the role of the second-layer, which can then focus its estimation effort more purely and accurately on the unknown, active maneuver acceleration, enhancing the overall consistency and precision of the filter in real-world scenarios.
The robust performance of DLSRCKF against model mismatch is intrinsically linked to the carefully tuned decoupling of its two layers. Unmodeled disturbances from environmental forces are managed by the first layer. The highly constrained process noise of the first layer is set to ensure strong orbit consistency; this value forces the filter to treat unmodeled environmental residuals as minor, bounded perturbations, effectively preventing them from propagating into and corrupting the primary orbit states. When the assumed acceleration model does not perfectly match reality, the robustness stems from the second layer’s adaptability. The relatively process noise in the second layer is intentionally chosen to provide the filter with high dynamic responsiveness. This flexibility allows the second layer to rapidly adjust its state estimation, treating the small deviations from the modeled maneuver profile as part of the process noise to maintain accurate actual maneuver estimation and prevent filter divergence.
Despite its advantages, the algorithm’s performance could be further improved. A current challenge is the inherent delay in capturing abrupt acceleration changes immediately after thruster activation; furthermore, the integration of multiple models may result in performance under specific conditions that is inferior to that of a single model. Future research may focus on several enhancements as follows: exploring more efficient filter algorithms, such as those that incorporate neural networks, to improve the algorithm’s responsiveness to acceleration changes; and introducing additional state models into the IMM framework to increase adaptability to various acceleration change scenarios.
In conclusion, the algorithm proposed in this paper provides an effective solution to the issue of low-thrust acceleration estimation for non-cooperative targets and possesses significant theoretical and practical value. With further research, it is anticipated that the algorithm will find broader applications.
Author Contributions
Z.W. completed preliminary research and provided the numerical part; Z.W., P.Z. and F.J. conceived and wrote the paper; and F.J. supervised the overall work and reviewed the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12532018).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Peng Zhang was employed by the company State Grid Electric Power Engineering Research Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| CKF | Cubature Kalman Filter |
| CS | Current Singer (Model) |
| DLSRCKF | Dual-Layer Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter |
| ENU | East-North-Up (Coordinate System) |
| IMM | Interacting Multiple Model |
| LEO | Low Earth Orbit |
| RCSJF | Robust CS-Jerk Filtering |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SRCKF | Square-Root Cubature Kalman Filter |
| SSA | Space Situational Awareness |
| UKF | Unscented Kalman Filter |
| Latin Symbols | |
| a | Magnitude of low-thrust acceleration |
| Acceleration vector | |
| Maximum amplitude of thrust acceleration | |
| Perturbation acceleration vector due to Earth’s term | |
| A | Azimuth angle |
| e | Orbital eccentricity |
| E | Elevation angle |
| Nonlinear state transition function | |
| Process noise input matrix | |
| Nonlinear measurement function | |
| i | Orbital inclination |
| Identity matrix of dimension | |
| Jerk vector (rate of change of acceleration) | |
| Second-degree zonal harmonic coefficient of the Earth | |
| Kalman gain matrix | |
| k | Discrete time step index |
| Likelihood function | |
| M | Mean anomaly |
| Markov chain transition probability matrix | |
| m | Total number of cubature sigma points () |
| n | Dimension of the state vector |
| State error covariance matrix | |
| Process noise covariance matrix | |
| Continuous-time process noise intensity | |
| Position vector | |
| Semi-major axis | |
| Measurement noise covariance matrix | |
| Earth’s reference radius | |
| Coordinate transformation matrix from J2000 to ENU frame | |
| Square-root factor of the covariance matrix | |
| t | Time variable |
| Time step interval | |
| Velocity vector | |
| Process noise vector | |
| State vector | |
| Measurement residual vector | |
| Measurement vector | |
| Greek Symbols | |
| Maneuvering frequency of the Jerk model | |
| Model probability in IMM | |
| Mixing probability weight in IMM | |
| Longitude of the observation station | |
| Earth’s gravitational constant | |
| Cubature point vector | |
| Range | |
| Range rate | |
| Latitude of the observation station | |
| Phase angle of the periodic acceleration | |
| Right ascension of the ascending node (RAAN) | |
| Spacecraft orbital angular frequency | |
| Earth’s angular velocity vector | |
| Subscripts | |
| Indices identifying the first layer and second layer filters | |
| k | Discrete time step index |
| Posterior state estimation at time step k conditioned on measurement history up to time step k | |
| Prior state prediction at time step propagated by the dynamic model, conditioned on measurement history up to time step k | |
| L2 | Denoting the posterior state estimation of the second layer filter |
| off | Denoting the thrust-off mode |
| on | Denoting the thrust-on mode |
| proj | Denoting variables projected from the second layer back to the first layer’s space |
| Components along the axes in the reference frame | |
| Superscripts | |
| ∗ | Propagated cubature point vector after nonlinear transformation |
| XZ | Cross-covariance between the state vector and the measurement vector |
| ZZ | Innovation covariance of the measurement vector |
References
- Howell, E. Space Station Robotic Arm Hit by Orbital Debris in ‘Lucky Strike’. Space.com. 2021. Available online: https://www.space.com/space-station-robot-arm-orbital-debris-strike (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- ESA. ESA Spacecraft Dodges Large Constellation. European Space Agency. 2019. Available online: https://www.esa.int/Space_Safety/ESA_spacecraft_dodges_large_constellation (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Kennewell, J.A.; Vo, B.-N. An overview of space situational awareness. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, Istanbul, Turkey, 9–12 July 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, M.; Scheeres, D. Applied Reachability for Space Situational Awareness and Safety in Spacecraft Proximity Operations. In AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Reston, VA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sajjad, N.; Mirshams, M.; Hein, A.M. Spaceborne and ground-based sensor collaboration: Advancing resident space objects’ orbit determination for space sustainability. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, S.; Mu, J.; Hao, X.; Zhu, W.; Hu, J. Research Advancements in Key Technologies for Space-Based Situational Awareness. Space Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 9802793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, G.; Bi, X.; Zhao, H.; Liang, B. Non-cooperative maneuvering spacecraft tracking via a variable structure estimator. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verspieren, Q. The United States Department of Defense space situational awareness sharing program: Origins, development and drive towards transparency. J. Space Saf. Eng. 2021, 8, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, D.; Baoyin, H. Real-time hybrid method for maneuver detection and estimation of non-cooperative space targets. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossà, A.; Losacco, M.; Armellin, R. Perturbed initial orbit determination. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 401–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez, C.; Mercier, F.; Dolado, J.-C. A novel initial orbit determination algorithm from Doppler and angular observations. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Space Debris, Darmstadt, Germany, 18–21 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez, R.G.; Navarro, E.S.; Píriz, J.A.R. Single track orbit determination analysis for low Earth orbit with approximated J2 dynamics. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.00317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, B.; Liu, X.; Cheng, H.; Shen, M.; Wang, P.; Xin, X. Initial orbit determination of some cislunar orbits based on short-arc optical observations. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceresoli, M.; Colagrossi, A.; Silvestrini, S.; Lavagna, M. Robust Onboard Orbit Determination Through Error Kalman Filtering. Aerospace 2025, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hackel, S.; Jäggi, A. Precise orbit determination of the Sentinel-3A altimetry satellite using ambiguity-fixed GPS carrier phase observations. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Kong, J.; Cao, J.; Huang, H.; Man, H.; Yan, J.; Li, X. Precise orbit determination for Tianwen-1 during mapping phase. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Ren, D.; Wu, D.; Jiang, F. DNN estimation of low-thrust transfer time: Focusing on fast transfers in multi-asteroid rendezvous missions. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 204, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Sun, C.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; Fang, Q. Space Noncooperative Target Trajectory Tracking Based on Maneuvering Parameter Estimation. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Tao, X.; Li, Z. Initial Identification of Thrust and Orbit Elements for Continuous Thrust Spacecraft in Circular Orbit. Aerospace 2023, 10, 1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechichian, J.A.; Bernard, E.; Cherian, C. Orbit Raising with Low-Thrust Tangential Acceleration in Presence of Earth Shadow. J. Spacecr. Rockets 1998, 35, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadalavada, P.; Farabi, T.; Dutta, A. Sequential Low-Thrust Orbit-Raising of All-Electric Satellites. Aerospace 2020, 7, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Luo, Y.; Hu, W. Orbit Determination for Continuously Maneuvering Starlink Satellites Based on an Unscented Batch Filtering Method. Sensors 2025, 25, 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, R.A. Estimating Optimal Tracking Filter Performance for Manned Maneuvering Targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1970, AES-6, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Kumar, K.S.P. A ‘current’ statistical model and adaptive algorithm for estimating maneuvering targets. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 1984, 7, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, K.; Mahapatra, P.R. A jerk model for tracking highly maneuvering targets. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1997, 33, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zeng, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y. A comparative assessment of gravitational field modeling methods for binary asteroid landing. Astrodynamics 2024, 8, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Wang, B. A motion model for tracking highly maneuvering targets. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Radar Conference, Long Beach, CA, USA, 25 April 2002; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.; Yang, Z.; Luo, Y. Adaptive Tracking Method for Non-Cooperative Continuously Thrusting Spacecraft. Aerospace 2021, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Li, H.; Wen, G.; Wang, Z. Application of Adaptive Weighted Strong Tracking Unscented Kalman Filter in Non-Cooperative Maneuvering Target Tracking. Aerospace 2022, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julier, S.J.; Uhlmann, J.K. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 401–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shang, M.; Yin, J. Analytical Second-Order Extended Kalman Filter for Satellite Relative Orbit Estimation. Aerospace 2024, 11, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairallah, N.; Kassas, Z.M. An Interacting Multiple Model Estimator of LEO Satellite Clocks for Improved Positioning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 95th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2022-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 19–22 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Goff, G.M.; Black, J.T.; Beck, J.A. Orbit Estimation of a Continuously Thrusting Spacecraft Using Variable Dimension Filters. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2015, 38, 2407–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shu, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Yin, W. Orbit Determination and Thrust Estimation for Noncooperative Target Using Angle-Only Measurement. Space Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 0073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Ding, D. Strong tracking cubature Kalman filter for real-time orbit determination for impulse maneuver satellite. In Proceedings of the 2017 36th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Dalian, China, 26–28 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Arasaratnam, I.; Haykin, S. Cubature Kalman Filters. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, H.A.P.; Bar-Shalom, Y. The interacting multiple model algorithm for systems with Markovian switching coefficients. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1988, 33, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.