Abstract
Ambient gas detection and measurement had become essential in diverse fields and applications, from preventing accidents, avoiding equipment malfunction, to air pollution warnings and granting the correct gas mixture to patients in hospitals. Gas leakage can reach large proportions, affecting entire neighborhoods or even cities, causing enormous environmental impacts. This paper elaborates on a deep review of the state of the art on gas-sensing technologies, analyzing the opportunities and main characteristics of the transducers, as well as towards their integration through the Internet of Things (IoT) paradigm. This should ease the information collecting and sharing processes, granting better experiences to users, and avoiding major losses and expenses. The most promising wireless-based solutions for ambient gas monitoring are analyzed and discussed, open research topics are identified, and lessons learned are shared to conclude the study.
1. Introduction
Sensors have been employed to collect signals from the environment, providing data to control systems for more than 2300 years, when the first noted system were developed by the Greeks to control the level of liquids using a floater, similar to those that are used today in water boxes to keep a water container at a constant level. With that it was possible to create a precise water clock, where time was measured by the constant dripping of water from the first container to another one, where the level changed proportionally to the water flow [1].
Control systems use sensors to collect data from the environment where they are installed, actuators to react to the environmental changes until the system achieves the expected state, and a controller responsible to process the data collected by sensors, to adjust the response of the actuators and to inform users regarding the system’s status; as simple examples, it is possible to highlight the temperature control system on air conditioners and showers. The loop between the controller and the plant can be performed through a dedicated network, or through the Internet, although the last option cannot provide the best quality of service (QoS) [1,2].
Wireless sensors networks (WSN) have been developed to enhance data collection from the environment and transferring process to databases, allowing remote monitoring of areas of interest and difficult access, for instance. Moreover, wireless actuators were also placed into networks known as Wireless Sensors and Actuators Networks (WSANs), working in a collaborative way to ensure automatic and intelligent decision making on certain events, reacting with environmental changes to provide the best user experience, without needing users’ interference [3,4,5,6,7].
Currently, control systems have reached complex levels where buildings are being automated to make the best decision for users, self-driving cars and autonomous planes are being experimented on, relying on autonomous decisions based on data provided by numerous sensors placed on vehicles. Hereafter, these data will be provided not only by the embedded sensors on devices being controlled, but also by data collected on other devices and even in other networks. These significant data will be shared among the devices in the same context by the Internet, through the Internet of Things (IoT) paradigm, allowing even more crucial precise decisions [8,9,10,11,12,13,14].
Mechanisms of sensing gases have been studied since the 19th century when the first method to notice the presence of unwanted gases at underground mines was performed by using canaries and observing their states. The presence of toxic gases is deadly for the birds and the workers would have enough time to leave the place without harm [15]. More recently, the detection of other gases has been studied with the purpose of avoiding incidents and accidents, as fires and explosions involving flammable gas leakages as well as providing better results from industrial processes involving chemical reactions [16,17,18,19].
Much research focuses on the sensing materials, always trying to improve gas measurements in terms of accuracy, precision, and response time. The sensors’ miniaturization is also a recurrent topic of research although these topics of study are mostly linked with the electrochemical transducers while techniques that make use of propagation characteristics have repeatability as a main theme of refinement [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28].
Several survey papers were published targeting particular characteristics of gas-sensing technologies. Chatterjee et al. [20], Mirzaei et al. [21], and Sun et al. [22] researched metal oxide nanostructures for sensing gases. Chatterjee et al. [20] studied hybrid gas transducers using graphene to sense toxic gases while Mirzaei et al. [21] approached these nanostructures focused on sensing volatile organic compounds (VOC), and Sun et al. [22] studied these nanostructures in general. In [23], the authors covered the detection of gases by carbon nanotubes (CNTs) transducers. Optical fiber transducers to detect oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are covered in [24]. E. Llobet [25] has studied nanomaterials as gas sensors. In [26] and [27] the authors have studied the use of polymers as gas transducers. The survey published Liu et al. [28] covered gas-sensing technologies in general, suggesting the use of wireless technologies to transfer information, although no wireless sensor has been reviewed.
The purpose of this survey is to provide a deep review and analyze the state-of-the-art of the available gas-measurement systems, performing a comparison of their used technologies, identifying and analyzing further opportunities related to the integration of embedded sensors with communication systems, using the IoT to enable devices and applications to be developed. Then, the main contributions of this survey are the following:
- An analysis of the gas-sensing technologies evolution;
- A deep literature review on the most promising technologies to sense environmental gases through wireless sensors;
- The analysis of the most promising wireless-based solutions for ambient gas monitoring;
- The identification of open research issues on gas-sensing technologies and wireless gas sensors;
- The lessons learned from this study on gas sensors are shared.
The rest of this document is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the most important gases, in terms of pollution monitoring, health issues, and accident prevention highlighting their main characteristics. Section 3 brings the opportunities in terms of IoT verticals and economic sectors offered by IoT-enabled multi-gas sensors. The evolution of gas-sensing technologies is addressed in Section 4. Technologies to sense gases and wireless communications support are elaborated in Section 5 and Section 6, respectively. The most promising solutions in terms of sensing methods and IoT-enabled solutions are discussed in Section 7 and open research topics are identified. Lessons learned are shared at Section 8 and, finally, Section 9 concludes the study.
2. Background on Environmental Gases
Some gases are the key to ensure the functionality of systems and entire industries, as well as the presence of other gases being a problem in other fields, causing the loss of entire production lines, as in the food industry, or even cause the loss of lives and explosions. In this section, the most important gases in terms of pollution monitoring and control, health issues, and accident prevention are listed with their main characteristics.
Oxygen (O2) is the most important gas for life, and is crucial in numerous fields. Patients under anesthesia, or recovering from surgery and from certain diseases need controlled O2 doses to keep them alive and fully recovered. The decrease of oxygen levels in enclosed spaces can be related with other gases leakage, which would lead people inside these spaces to asphyxiate, leading to an unconscious state, or even to death [29]. Numerous industrial processes rely on the correct concentration of this gas to achieve the best results, mainly chemical and combustion, which without the correct percentages will not grant the best performance of systems. Engine control systems depend on the correct mixture to achieve the expected performances, whether it is lower fuel consumption or power and speed [29,30,31,32].
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a colorless, odorless gas, generated by the oxidation and combustion of hydrocarbon, as well as by living beings in the respiration process. It is a key gas for the greenhouse effect, and the increase of its levels, in the presence of other gases, is related with atmospheric pollution. It is also the key gas on the oxygen production by the photosynthesis process. The accumulation of this gas in enclosed spaces can be responsible to suffocation; it can be deathly when the concentration of CO2 reaches levels above 3% [33,34,35].
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a result of the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbon fuels, due to the lack of oxygen or insufficient temperature. It is an odorless, colorless gas, mainly originating in enclosed or semi-enclosed spaces, such as closed parking garages, home heaters and fireplaces. It is well known that this gas has around 200 times more affinity to hemoglobin than oxygen, making the protein unable to carry the second gas to the body cells, leading to hypoxia, causing damage to body tissue. The poisoning symptoms are easily mistaken with fatigue. Depending on the exposition time and concentrations of this gas, it can be lethal or reduce lifetime, causing cardiovascular diseases and brain damage [19,20,35,36,37,38].
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are carbon-based organic compounds, in a vapor state at room temperature, generated by the combustion of fossil fuels, or natural emissions, where some compounds are toxic, affecting human health by causing irritation of the respiratory system and eyes, diseases as cardiovascular and respiratory malfunctions, or even cancer [39,40].
Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is a fossil fuel composed of a mixture of hydrocarbon gases, used in domestic situations and industry, to generate electricity, power heating systems, vehicular combustible and cooking. It is a highly flammable gas, capable of severe damage if a leakage is followed by an ignition; major explosions and fire incidents were reported in the literature, due to its gas leakage, in numerous countries, such as the 2011 Karakopru incident, where an entity plant was destroyed due to an explosion. The leakage of this gas can lead to great expense and the loss of many lives [17,18].
Ozone (O3) is present at the atmosphere, in high altitudes, where it is fundamental to maintaining life on Earth, acting as a natural filter to ultra violet (UV) light emitted by the Sun, avoiding skin cancer on humans and allowing the agriculture, by filtering the UVc light. The increase of this gas in lower atmospheric layers is an indicator of air pollution and bad air quality, being one of the causes of lung dysfunctions, worsen respiratory diseases [41,42,43,44].
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is an odorless, colorless, chemically stable, non-flammable gas used as electrical isolator in the electrical power industry, due to its capability of extinguishes electrical arcs in high tension. It is a non-toxic greenhouse gas, and it is not a risk if inhaled in proportions under 20%. The detection of this gas leakage is essential to prevent damage to high-power electrical equipment, and with that, avoiding failures on power distribution; the detection can be done by the SF6 itself or their sub-products, generated by electrical discharges [45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53].
Radon (Rn) is a colorless, odorless, radioactive gas that can be emitted from soil and rocks like granite and its long-term exposition is related to lung cancer. It can be generated from the decay of radium (Ra) and uranium (U), and it has a half-life from approximately 3.8 days. Radon can be transported through water, or carrier gases such as CO2, methane (CH4), Helium (He), and other gases. As this gas represent half of the radiation exposure to human beings, detection is crucial to avoid long term exposition, being a key factor in lung cancer prevention, mainly in underground miners, that suffer more contact with this radioactive gas [33,54,55,56,57,58,59].
Ammonia (NH3) is an irritant, corrosive, colorless gas, with a strong odor, employed in the production of fertilizers and explosives, as well as in the textile industry. It can be found as a refrigerant gas and in hygienic products. Its leakage can cause atmospheric, soil and water pollution, and severe damages to the eyes and respiratory system, causing even the death of people directly affected by the gas escape [20,60,61,62,63,64].
Nitric oxide (NO) is a colorless gas that can be lethal if its concentrations reach certain ambient levels. In the atmosphere, it is one of the compounds responsible to the smog pollution, causing irritation to exposed people. It is employed in the semiconductor industry, as well as on medicine, as muscular relaxant and in the treatment of hypertension, due to its vasodilation property. This gas can be one of the sub-products of fossil fuel combustion, and it is also produced naturally, by the human body, being an important signal of inflammation if its concentration in human breath reaches levels above 50 parts per billion (ppb); it is used to monitor the inflammation conditions of asthma patients’ lungs. The oxidation of NO results in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) [65,66].
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is a result of the combustion process of fossil fuels, as well as the oxidation of nitrogen. It is one of the pollutants responsible for the formation of acid rain, and it is toxic at low levels, 1 part per million (ppm) is the maximum recommended contact volume; its exposure is related with respiratory diseases, pulmonary malfunction and death. NO2 can be found in highway surroundings, as well as dense traffic areas; it can also be found indoors, as a result of the combustion of generators and heaters [39,67,68,69,70].
Hydrogen sulphide (H2S) is a colorless, flammable, corrosive and toxic gas, which is poisonous even in low concentrations. Exposure to this gas can lead to damage to the human nervous system. Its generation can be either natural, from volcanic activities or from the decomposition of organic compounds, or due to the combustion of fossil fuels or from sewage. This gas can be found in coal mines, petroleum exploration and in diverse industrial processes [71,72,73].
Chlorine (Cl2) is broadly used in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries, water treatment and in domestic cleaning products. With a strong odor, in the gaseous state, it is extremely toxic; the exposure limit in workplaces are around 30 ppb. The inhalation of low concentration levels (50 ppm) of Cl2 can cause severe damage to the respiratory system and levels of 1000 ppm are enough to be fatal to humans. Numerous accidents involving transportation and industrial leakages have been reported over the years. Moreover, it has been used as chemical warfare agent from the First World War, to the Syrian Civil War in the present days [74,75,76,77].
Refrigerant gases: Temperature control is vital in certain areas, like the food industry, hospitals and data centers. Refrigerators and air conditioning systems rely on refrigerant gases to accelerate the thermal exchange and keep the ambient on the adequate temperature [78,79,80]. Not only can the malfunctioning of entire systems be caused by the leakage of refrigerant gases, but they can cause the increase of atmospheric pollution, the greenhouse effect and the destruction of the ozone layer. The first generation of refrigerant gases was composed of toxic and flammable gases, endangering workers that could be exposed to leakages. After that, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) and hydro-fluorocarbons (HFCs) were introduced; the last do not affect the ozone layer, by contrast with the first two [81,82].
Monitoring and controlling the level of these gases can grant better work conditions, reduce pollution levels, enhance life quality, decrease health disorders and death in the limit, and prevent equipment malfunction on industry. This section presented a background on the most relevant gases that are considered in the study.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Verticals Opportunities and Economic Impact
Environmental gas detection and measurement had become essential in diverse fields and applications, from preventing accidents (including life-saving), avoiding equipment malfunctions, warning about air pollution, and helping hospital patients [17,18,36,37,83]. Considering this scenario, the development of a sensor capable to attend these demands being able to collect information about numerous gases is crucial to avoid all the losses caused by unwanted gases.
The costs attributable to gas leakage are enormous: from the loss of production in the food industry, to reconstruction of buildings caused by flammable gas leakage followed by explosions, and the healthcare expenses to treat patients who suffered injuries by gas poisoning [17,18,36,37,83]. In the United States of America (USA) alone, the annual costs linked to carbon monoxide intoxication is over $1.3 billion, and the deaths as a consequence of this gas leakage are over 2000 per year [19,37].
Other gases represent an imminent risk to the population and to the environment, being linked to cancer, cardiovascular diseases, cognitive disabilities and respiratory failure [19,21,39,40,55,84,85,86,87,88]. Gas leakage can reach large proportions, affecting entire neighborhoods, or even cities. The magnitude of the environmental impact of such an incident can be catastrophic in terms of deaths and evaded area [17,18,39,83].
It was estimated by the International Labor Organization (ILO) that 4% of the Gross World Product (GWP) is expended on labor accidents and the percentage is higher when taking in account work-related health problems [16]. Another study has shown that, in a period of 40 years, accidents caused by gas leakage, fires, and explosions on oil sub-products storage tanks represented 90% of the accidents in this field, and human error were linked with 30% of all kind of incidents in the same industry. The same study showed that the average cost per casualty of the 10 most devastating incidents on this industry was around $114 million, reaching $330 million in the most expensive disaster up until publication [83].
Together with the development of a multi-gas sensor, the information collected by these devices should be easily available to the users and also to other devices that could use the provided data to contribute to the best experience to the users of this system as well as to decreasing avoidable costs, making possible investments on demanding areas [7,10,13,89].
The detection of gas leakage can be crucial to avoid all the health and environmental problems, not only by alerting people about incidents, giving them time to evade the area, but also by providing information to actuators that can act in order to stop the leakage and mitigate the consequences [17,18,19,20,21,36,39,83,84,85,86,90,91,92,93].
With the paradigm of the IoT, it is expected the number of connected devices will reach 50 billion by 2025 with an estimated increase of $1 to 2.5 trillion USD on the GWP by the same year [11,13,89]. The sectors (IoT verticals) where the impact of the new technologies will be introduced and the use of a multi-gas smart sensor can be seen on Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Illustration of Internet of Things (IoT) verticals and market opportunities for multi-gas smart sensors: smart homes, agriculture, smart cities, industry, healthcare, and smart grid.
A multi-gas sensor together with other devices integrated over IoT networks will have a positive impact on the sectors (IoT verticals) previously shown, allowing new investments by governments, companies, and people in sectors might demand more attention. The number of accidents related with the presence of determined substances should decrease, reducing the risks of specific activities, causing a positive effect on avoidable costs, and repairing the damage caused by such incidents [19,36,37,55].
4. Evolution of Gas-Sensing Technologies
The attempt of sensing gases had become necessary when several pitmen lost their lives during underground mine explorations due to the lack of O2 or to the leakage and accumulation of other colorless, odorless gases, mainly CO2, CO and CH4. During the 19th century explorations, miners used to have canaries with them while working in the mines to signalize the presence of unwanted gases: while the birds were in their pits, there was enough oxygen for them to breath; in contrast, if the canaries had succumbed or passed out, the quality of the air was not good enough for the people inside to breath, and they should leave the mine immediately [15,85,92].
Much has evolved in the last century, and gas sensing has become a key feature in numerous activities, such as medicine, sports, the industrial field, environmental monitoring and pollution control [28,31,32,34,35,93]. Oxygen sensors were the first to be developed: in 1956, Leland C. Clark developed the first electrochemical oxygen sensor, known as the Clark Cell [31,94,95]; in 1961, Peters and Mobius developed the Lambda probe to perform oxygen measurements in vehicle engines, helping with the admission control and fuel mixture to achieve the best performance, in terms of fuel consumption or in terms of power [31,96], and it has been produced by Bosch since 1976. Both developed sensors are consumable, reacting with oxygen, in order to provide an output value representing the gas concentration in the environment [97,98]. After the development of these expensive, and not so accurate sensors, the research for new technologies capable of granting more accurate measurements and more durable devices to this field have been taking advantage on many characteristics of the sensed gases; as an example, oxygen has magnetic characteristics, consequently, it can be measured by the attraction to a magnetic field. Other gases can be measured taking advantage on their ultrasonic properties or by optical spectrometry [28,31,96].
Gas sensors rely on a physical or chemical reaction with the gas that is trying to be sensed in order to generate a response proportional to the concentration of the gas, thus the speed of the reaction. Some of the sensors have a reversible reaction, while other have an irreversible one, the latter being expendable with 2 to 5 years of lifetime. The response generated by the presence of the target gas is either linear or non-linear, depending on the materials and target gases [28,97,98]. It is fundamental to grant the quality of the air patients are breathing at a hospital, as well as to provide the correct mixture to divers, in particular to deep diving, where the gas mixture the diver must breathe is different according to the time and depth of the activity. Not only to grant the quality of air, but also to avoid gas leakage and its consequences such as poisoning or explosions, sensing gases is of great importance at the industry [17,32,36,37].
Over time, other sensing methods were developed, exploring the propagation characteristics of the gases to perform measurements, and comparing with a reference to determine which gas is being sensed. The analyzed characteristics vary from signal attenuation, frequency shifting, propagation time, among others, and are performed by acoustic or optical sensors [28,31,94,97,98,99,100,101,102]. Moreover, the miniaturization of gas transducers has taken place in the research topics [20,21,22,25], as well as the development of wireless gas sensors, to monitor remote areas and easily collect and analyze data from the environment [34,35,95,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114].
With the IoT paradigm, gas sensors are becoming key devices to measure ambient gases, generate warnings related to the presence of unwanted gases and allow other systems, such as smart windows, smart curtains, automated exhaust systems, and automated heating ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, to automatically act in order to avoid damages from leakages [11,12].
5. Sensing Technologies
The methods to sense gases depend on the change of physical or chemical properties of a given material or property on the presence of the target gas, compared to an ideal environment. Some of the sensing methods use the reaction between the sensing element with the target gas to determine this gas concentration; other methods are based on the comparison of physical properties such as speed velocity and wave propagation between an ideal mean and the one with the gas being sensed.
In this section, the most promising available technologies and their sensing mechanisms, as well as their characteristics, are described in detail.
5.1. Electrochemical
Electrochemical gas sensors were the first gas sensors to be created, starting with the Clark Cell in 1956, to sense levels of oxygen. In 1976, the Lambda probe was developed to sense oxygen in combustion engines, constructed with a solid electrolyte Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia, requiring high temperatures to function properly; the working temperature is variable, and depends on the chosen electrolyte, which can be liquid or solid, the latter allowing the miniaturization of the sensors [113,114].
These sensors benefit from chemical reactions to sense a target gas where the product of the reaction and its speed is proportional to the gas target concentration. The materials used to compose these sensors have different target gases, depending on the temperature of the reaction. These sensors are basically composed of a membrane that separates the ambient gases from the electrolyte solution, the electrolyte, which is mainly composed by a liquid compound of acids or bases, and the electrodes that are consumed by the electrochemical reaction. The polarization of the electrodes and measurement of the variation of the output parameter is dependent on the sensing approaches, which could be potentiometric, voltametric, conductimetric, or amperometric. A filter, between the membrane and the environment gases, can be used to limit contact with unwanted gases, improving accuracy and sensitivity on these devices [31,90,92,115,116,117]. The representation of an amperometric electrochemical gas sensor is shown in Figure 2.
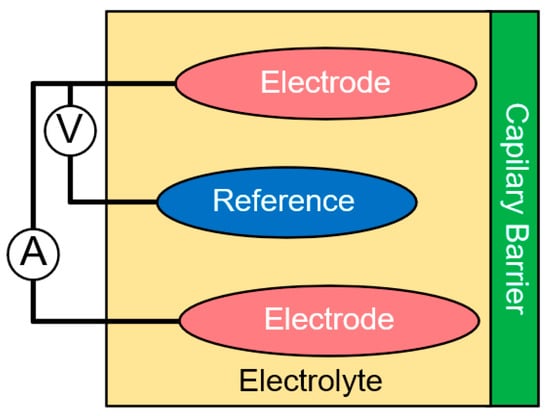
Figure 2.
Schematics of an amperometric electrochemical gas sensor, where the reduction of the cathode to hydroxyl ions generates a variation of the electrical current, proportional to the concentration of the target gas.
Electrochemical transducers are easily miniaturized, being able to reach the order of a few millimeters, which is beneficial to embed the sensors in printed circuit boards (PCBs). All sub types of electrochemical sensors rely on the reduction of the cathode to hydroxyl ions; when the anode material is completely oxidized, the sensor has reached the end of its lifetime and must be changed [31,32]. Electroanalytical measurements can be executed with four different sensing approaches, in where each sensing technique will better fit a different necessity of sensing gases: Potentiometric, Voltametric, Conductimetric and Amperometric [90,92,117].
Potentiometric Sensors: they have as an output the electrical tension proportional to the equilibrium potential of an indicator electrode, where the absence of the target gas results on the output of 0 Volts (V). This measurement method results in high selective transducers, which are able to measure only low concentrations of the target gases [90,92,117].
Voltametric Sensors: they have output current as a function of the concentration of the target gas and the applied potential, generating measurements of low gas concentration; this allows the measurement of more than one gas, with the variation of the input electrical potential. The applied potential, as well as the choice of the electrodes, can result in a highly selective transducer [90,92,117].
Conductimetric Sensors: they are mostly used by detecting the presence of the target gas after a determined threshold; this relies on the measurement of the resistance of the solution, which means that these sensors are not selective and more than one gas can change its resistance [90,92,117].
Amperometric Sensors: these have the variation of the electrical current as a sensing parameter, where the reduction of the cathode to hydroxyl ions generate a current, proportional to the concentration of the target gas. The cathode and anode must be linked with a resistor, in where the variation of the current on the load resistor can be measured as a tension value [32,93,118,119].
5.2. Metal Oxide Semiconductors
Metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) gas sensors are broadly used in hospitals to grant the correct mixture of O2 and nitrogen (N2) to patients as well as at the industry to avoid toxic gas leakages. These sensors are simple to fabricate, easy to reproduce, and are of low cost, compared to other technologies. The sensors can be fabricated using commercial complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) processes, which means the easy fabrication of numerous components, with low cost, and identical characteristics [120].
These sensors operate at high temperatures, the reaction with the target gas generates a variation on its internal resistance and the sensor responds with a proportional output tension, according to the concentration of the gas it is sensing; the sensors are normally designed within a heater. The transducers are sensitive to more than one gas and the temperature of operation is a key to determine the gas that will be sensed [28,29,38,120,121].
MOS sensors are usually constructed with a ceramic tube where the heater is placed in contact with the electrode; the sensing layer is made with the metal oxide semiconductor, placed in between the electrode and a heater; the sensor could also be printed in a ceramic wafer [22,30,118]. Figure 3 shows both MOS sensors, where (a) represents the tubular gas sensor and (b) the wafer gas sensor.
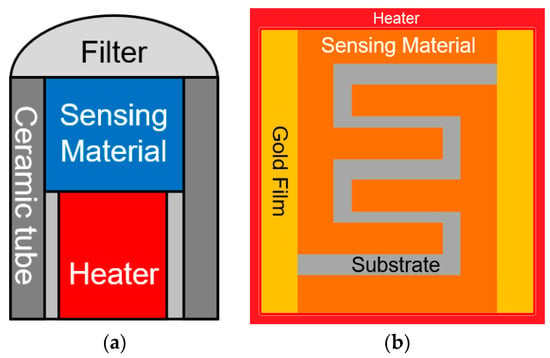
Figure 3.
Illustration of metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors, where: (a) is a tubular metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) sensor, and (b) is a wafer MOS sensor.
These sensors can be easily miniaturized, including the use of nanomaterials to develop the sensing elements, which have demonstrated an increased performance on these transducers; the use of an external stimulus, as ultraviolet (UV) light, have shown better efficiency on measurements at room temperature [118,119]. The most common materials used on these transducers are tin oxide (SnO2), zinc oxide (ZnO), tungsten trioxide (WO3) and titanium dioxide (TiO2). The transducers need to be heated to achieve the sensing point, and are consumed with the reaction with the gas it is sensing, making necessary a periodic calibration and limiting the lifetime of these devices. The heating process must be adequate to the target gas, as the sensor will respond to different gases if the temperature is not suitable for the gas of interest. A physical gas filter, to eliminate interference from other gases, can be added to the sensing element, upgrading the performance of the measurements [28,38,119,120].
These sensors, in contact with the target gas and elevated temperature, have their internal resistance altered, which also vary the output voltage; the variation of the internal resistance is determined by the concentration of the target gas and the semiconductor that composes the transducer. The concentration of the target gas (R) is calculated as a relation between the internal resistance on the presence of the target gas (Rs) and the output resistance at the presence of a reference gas (Ro), as shown in Equation (1) [70].
R = Rs/Ro,
There are two types of MOS sensors, the n-type, where there are more electrons than protons, and the p-type, where the number of electrons is inferior, and the electricity flows through the positive holes. The n-type sensor have the internal resistance decreased by reducing gases, and increased by the oxidizing gases, whereas the p-type presents the opposite effect [28,122,123]. The use of UV light within the sensing element allows a lower sensing temperature, produces lower internal resistance, as electrons are inducted to pair, and the resistance of the sensing material will increase, proportionally to the increase of the target gas [29].
Over the past 10 years, the use of nanostructures as metal oxide semiconductors to sense gases has become a topic of interest of some research groups, with reports of ameliorated sensing characteristics [22,65,66,118,119]. Response time and energy consumption are also topics of research, where the most part of commercial solutions have response times of seconds, sometimes reaching a few minutes; the energy consumption of these devices can reach the order of 500 milliwatts (mW) or even higher, due to the necessity of the heater. As the miniaturization of the devices has shown better response times, of the order of seconds to milliseconds, and power consumption of 80 mW, as reported by the Stratulat et al. [124], it has a good potential to be used integrated in an IoT solution. Although no commercial solutions were found employing nanomaterials or microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), this has shown to be a promising technology to future products, allowing the development of embedded systems to measure gas concentrations in diverse scenarios, with lower power consumption than the traditional MOS transducers [125].
5.3. Catalytic
Catalytic gas sensors are used to detect combustible gases in environments with concentrations of at least 15% of O2. These sensors perform the detection by measuring the variation on the internal resistance, which occurs when combustible gases are present in the ambient atmosphere. The process of detecting gas on this type of sensor consists on the chemical reaction between the catalytic element and the combustible gases on the environment, generating an elevation on the temperature on the sensor, which causes the variation on its resistance [126,127,128].
These sensors have been reported to display fast response times, although they are not accurate in determining the concentration of the gas; it only detects combustible gases and respond with the change on its resistance [126,127,128]. These sensors can be deployed on environments with humidity and temperature variations, without losing its capacity of detecting the target gases.
The lifetime of these sensors will depend on the concentration of the target gas in the environment in which it has been deployed, being operative for 10 years in normal conditions; the presence of corrosive gases and exposure of the sensor to the target gases in concentration levels above the recommended can limit the lifetime to months of operation [126,127,128].
Catalytic gas sensors are composed of two semiconductor elements: a passive element, used as reference, and one active element that reacts with the target gas, generating an elevation in the temperature and, thus, generating a variation in the internal resistance. The reaction between the target gas and the catalytic element is responsible for the consumption of these kind of gas sensor, and the exposure of catalytic gas sensors to concentrations above the upper flammable limit will deteriorate the catalytic element, therefore, the sensor will lose its capacity to detect the target gas, providing invalid results [126,127,128]. Figure 4 shows the concept of the catalytic gas sensors. The target gas burns the detector material, elevating the temperature, and thus, the internal resistance, allowing measuring the target gas’ concentration.
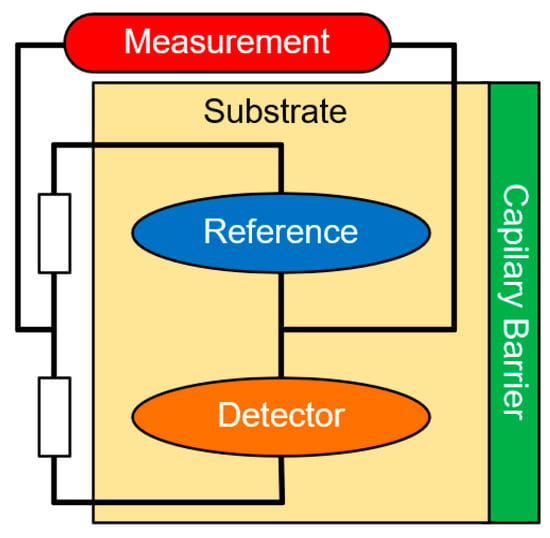
Figure 4.
Representation of catalytic gas sensor. The target gas burns the detector material, raising the temperature and its internal resistance, allowing the measurement of the concentration.
5.4. Polymers
Volatile organic compounds can be toxic above certain concentrations, causing harmful health effects, such as cancer, and are difficult to detect with electrochemical transducers. The polymer transducers used to detect gas are useful to sense these common organic compounds, present at the industry and household, in everyday use products [21,39,40,64].
Doping polymers by redox reactions, which is a reversible process, generates conductors or semiconductors which can be used to sense gases by the variation of these materials’ conductivity. The doping level can be changed by the reaction between the polymer and the sensed gas, making the sensing process effective. The conductivity variation is affected by the exposition of these compounds to certain gases, proportionally to the target gases concentration on the ambient. Thus with this variation, it is possible to calculate the concentration of the gases, with a short response time and, depending on the sensing material and target gas, high accuracy. These materials can also sense inorganic gases, however the sensitivity and accuracy can be compromised, as the main target gases to these compounds are the VOCs [26,28,129,130].
The electrical conductivity of polymers alone is extremely low, making the use of these compounds alone unpractical for sensing gases; the conductive polymers were reported to be used in biosensors, generating electric signals from biological data. Non-conducting polymers can be used with other sensing techniques to improve sensibility, accuracy and response time. Research has demonstrated the use of these compounds with capacitive, mass sensitive, calorimetric and wave-dependent sensors [28,130,131].
Gas sensors based on polymers have been used for over 35 years, with good accuracy and response time dependent on the chosen materials, reaching 11 min and recovery time of a few minutes; these sensors also present low stability, in some cases after one month of operation [126]. They run at room temperature, with low energy demand, while they can be easily affected by environmental changes, present inadequate selectivity, and are consumable, with a lifetime of approximately 6 months. The sensors can be easily reproduced in large scale, into portable devices, with low fabrication costs, although more researches on these compounds should be conducted to achieve better reliability levels. These transducers can be used with other sensing techniques, to achieve greater sensing properties [26,28,126,129].
5.5. Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) were first observed in 1991, have been investigated for over 20 years as gas sensors, and became the assured materials in terms of sensing characteristics to low gas concentrations at room temperature, lower response times and good corrosion resistance. These transducers can respond physically or chemically to different gases; to O2 and CO2 the response is reversible and linear, whereas to other gases, irreversible chemical reactions may happen. It also has higher costs due to the difficulty in fabrication and reproduction. The use of CNTs to sense gases can be set as individual CNTs, or arrays, where multiple units of these transducers make the measurements [28,132].
The fabrication process of these devices generate impurities that are inserted into the nanotubes, and must be cleaned, in order to generate precise measurements; the cleaning process is of key importance in making CNTs work properly, what impacts negatively on producing these transducers in large scale [133]. CNTs are constructed from graphene sheets, which are rolled, in order to produce these transducers. The angle and the radius in which the sheets are rolled determine whether the carbon nanotube will be metallic or semiconductor. The rolling process also determine if the CNT will be single-walled or multi-walled [25,28,134,135].
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) are constructed from a single graphene sheet. The use of a single SWCNT presents worse sensing characteristics than using a single multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT); although the use of a network of SWCNTs have been reported by Wang et al. [23] to present better sensing characteristics and mechanical resistance, as well as faster response and recovery times [20,23,25,69,132,133,134,135].
MWCNTs are composed of two or more graphene sheets, displayed concentrically, and supported by Van der Waals forces. The chemical bonds, similar to the ones found on graphite, provide unique mechanical characteristics to the MWCNTs. The use of more than one graphene sheet provides better sensing characteristics to these transducers [20,25].
The sensing mechanisms of CNTs are described as the variation of conductivity or electrical resistance due to direct contact with the target gas; the variations of the electrical characteristics are proportional to the concentration of the gas [134]. As no commercial solutions were found, the developed sensors should be analyzed with known concentrations of the target gas to ensure the correct calibration and analysis of the gases. No reports on the linearity of these transducers were found.
One of the drawbacks of using CNTs is the recovery time; when the target gas is in contact with the transducer, the gas penetrates the nanotubes, as the material absorbs the gas, the time that is necessary for the CNT recover from this contact is higher than other sensors, which can lead to inaccurate readings, causing malfunction of the systems dependent on the measurements [132]. The combination of CNTs with other sensing techniques have been reported to reduce the recovery time, as well as improve sensing and mechanical characteristics, as in the combination of CNTs and polymers to sense environmental gases [20,131].
5.6. Acoustic
Sound propagates differently depending on the propagation medium: in gases, the ultrasonic speed is a function of the temperature, pressure, humidity and the gas mixture properties. Taking advantage of these characteristics, acoustic waves can be used to determine whether a gas is present in the ambient or not. The analysis of the gases can be performed by the speed of the sound, by the attenuation of the signal, the acoustic impedance, or the combination these characteristics [28,31,99,135]. Figure 5 shows the schematic used in the acoustic gas-sensing approaches.
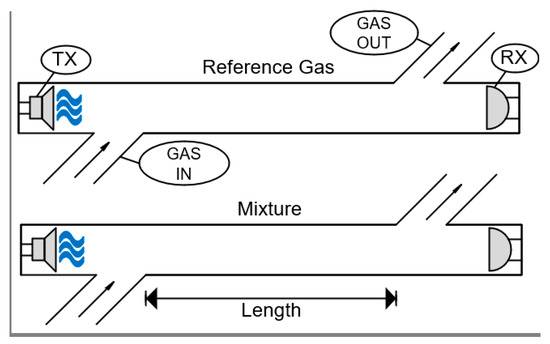
Figure 5.
Ultrasonic speed-based gas sensor, which measures the target gas by a comparison of the sonic speed in the air and the sonic speed in the presence of the target gas.
The most used and studied technique is based on the difference of sonic speed in different propagation medium, using the propagation time in a fixed distance to determine the composition of a given gas mixture. Equation (2) shows the dependency of the sound speed in relation to the gaseous propagation medium [100].
where c is the speed of the sound, in meters per second; k is the average specific heat ratio; R is the gas constant; T is the temperature, in kelvin; and M is the average molecular weight [100]. The approach is efficient by measuring concentrations in binary gases, in other words, it is useful to measure gas concentrations in systems where there is only the possibility of having two types of gases. When more gases are added to the system, the detection can present a false positive to a given gas, due to the presence of another gas in the proportions that would generate the same sound speed in the propagation medium [101]. Moreover, the temperature variations can influence the sensing process; the calibration must take in consideration the working temperature of the system where the sensor will function, and analyze the possible moisture in these temperatures. A sensor using this technology combined with another sensing technique can refine the sensing accuracy, as well as the selectivity. Prototypes using this technology have been proposed by Minglei et al. [101], and Sonoyama et al. [100].
c = √(kRT/M),
The attenuation of the acoustic signal is a reference to the scattered energy in a defined propagation distance. When a signal propagates through a gaseous medium, the equilibrium of the gases is broken and the molecules exchange energy through collisions, generating thermal energy. The energy generated is proportional to the energy consumed by the gaseous molecules creating the movement that leads to the collisions. It is said that the acoustic energy is absorbed by the system, and the level of absorption is proportional to the concentration of the gases that compose the propagation medium [28,99,102]. Prototypes of acoustic attenuation gas sensing were developed by Perculescu et al., to sense CH4, CO2, N2, ethylene (C2H4) and air [102]; and by Shengying and Minglei to sense SF6 [99]. The attenuation of the signal is calculated using Equation (3), where Po and P are the acoustic pressure in two different points, α is the attenuation coefficient and X is the distance from Po to P [99].
P = Po e(−αX),
Acoustic impedance analysis is a less studied technique to sense gases, and no commercial uses of this technique have been identified. The gas is sensed through its density using Equation (4), where Z is the acoustic impedance, ρ is the gas density, and c is the sonic speed. This technique can generate detection errors, as a given gas mixture can be mistaken to another, as they can present the same density. It also could be used within another detection technique [133].
Z = ρc,
The use of only one duct, considering the theoretical measurements of the ultrasonic speed, acoustic impedance and attenuation in air or other gases could decrease the energy consumption of the sensors based on this technique, as well as be more precise, considering the fact that the reference chamber could suffer variations, by contrast with the environmental changes in the ambient where the system is installed. The gas that should be detected can penetrate the reference tube, or temperature changes could easily be different from the ones on the second tube.
5.7. Optic
It is well known that specific gases absorb different wavelengths, and every gas has its peculiar absorption property to different wavelengths; the wavelengths and the target gases are listed in the High-Resolution Transmission Molecular Absorption Database (HITRAN) [136]. Many techniques explore these optical characteristics to measure gas concentrations in the environment, and other rely on adding materials that react with gases in the presence of light, reflecting, absorbing or shifting wavelength from the emitted beam to fiber optics, in other words, these materials react with the target gas in the presence of determined wavelengths, emitting a different wavelength, absorbing or reflecting the emitted light. The materials used to produce these effects are normally nanomaterials, employing polymers or metals [28,97].
The fluorescence-quenching sensors are normally composed by a matrix of nanomaterials, permissible and sensitive to the target gas, mainly composed of polymers and in some cases metals, attached to the tip of a fiber optic, with a 50:50 Y-type optical coupler. On the one tip of the coupler, a light source is attached, and an optical spectrometer is installed on the other. The polymer matrix, with the target gas and adequate wavelength and energy, will react and emit a different wavelength, where the intensity of the light is proportional to the gas concentration. The response time is variable, being approximately a few seconds, depending on the chosen materials, intensity of the light source and target gas concentrations [28,94,97,115]. Figure 6 illustrates this technique of sensing gases.
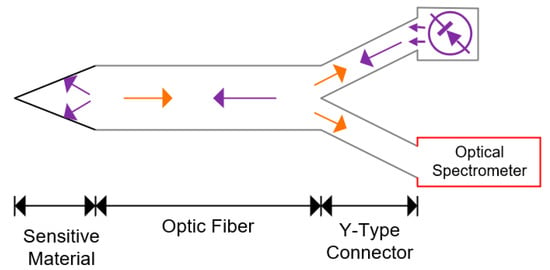
Figure 6.
The fluorescent-quenching effect gas detector—this measures the target gas by evaluating the reflected wavelength from the sensing material on the presence of the gases.
Absorption spectroscopy techniques, such as tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) consists in the emission of a modulated wavelength at a determined frequency and amplitude trough a fixed length with the presence of the gas; part of the light is absorbed, and then the light beam is detected by a photo-diode; on the TDLAS technique, the gas is sensed by the analysis of the harmonics of the signal, making use of the Beer–Lambert law [28,31,98]. Shao et al. [137] discussed integration between the optical spectrometry and electrochemistry to sense NH3, without any calibration. Iwata et al. [138] presented another sensor, using ultraviolet (UV) absorption spectroscopy with a calcium fluorite (CaF2) window to analyze breath moisture in parts per billion levels.
Optical time domain reflectometry (OTDR) is a common technique used in optical networks, and had been studied to sense chemicals, using the reflected light signal as a measurement parameter. The signal is attenuated and scattered by the optical fiber, depending on the length and specifications of the fiber; part of the scattered signal returns to the source, being able to measure the level of the signal and compare with the expected returning signal in normal operational conditions, with the absence of the target gas [116].
Infrared (IR)-based gas sensors use the target gas absorption of IR light to determine which gas is present on the environment, and it is possible to determine its concentration by the level of attenuation on the signal. The light beam is emitted by a diode and received by a photo-detector, analyzed by a micro-controller unit (MCU) and displayed on a screen or shared with other devices [28]. CO2 sensors based on IR light have been developed over the past 4 years, researchers focused on meliorate characteristics of these sensors, whether it was the response time, sensitivity, accuracy and selectivity of the devices [2,78,139,140,141]. Figure 7 shows a representation of an optical gas sensor, coupled with a duct.
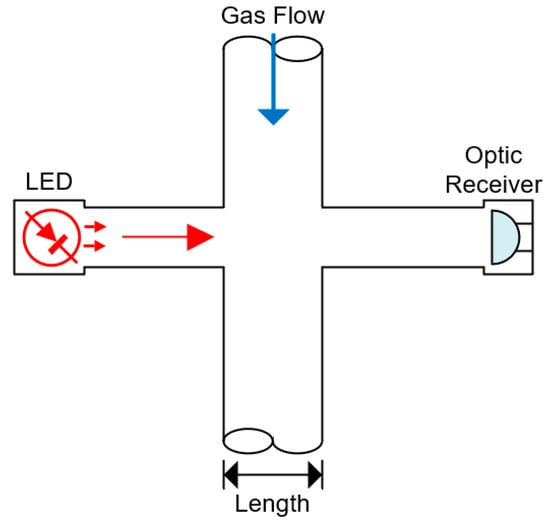
Figure 7.
Optical gas sensor coupled with a duct with gas flow. The measurement of the target gas occurs by evaluating the differences of the generated wavelength and the received one, after passing through the gas on a pipeline.
6. IoT-Based Wireless Gas Sensors
Over the last 20 years, the research and development of smart sensors for different purposes have become essential in many areas, such as environmental monitoring and pollution control, residential and industrial automation, protective equipment and assisted living devices [3,6,7,142]. The necessity of remote monitoring of numerous parameters has led to the development of wireless sensors in numerous fields. Moreover, wireless sensors and the construction of WSANs facilitated the automation process, data collection, transfer, processing, and storage. More recently, these smart sensors have acquired the capacity of performing machine-to-machine (M2M) communications, simplifying the communication and interoperation between devices, granting numerous possibilities in control systems and automation [11,12].
Many authors have focused on the proposal and creation of gas sensors to attend to specific target gases in particular conditions [32,34,103,108,110]. As examples, Sieber et al. [32] proposed an oxygen gas sensor for personal protective equipment without wireless transmissions; in [34] the authors have developed a CO2 gas sensor for remotely monitoring the levels of this gas, transferring the data through the General Packet Radio System (GPRS).
Recently, systems for indoor air quality monitoring and even to control gas leakages based on the data collected by smart sensors have been proposed [93,103,104,108]. They present different characteristics whether they are to do with the sensing mechanism or the implemented communication protocols. Many contributions towards wireless gas sensors and IoT-enabled gas sensors are only published on proceedings, and to the best of authors knowledge, almost no commercial solution is available on the market. In this section, the main characteristics and requirements of IoT-enabled gas sensors and the most relevant smart gas sensors proposed in the literature will be reviewed, emphasizing the main characteristics of the proposals.
6.1. Sensing Requirements for IoT-Based Gas Sensors
The demand on IoT environments might change in compliance with the applications and their specifications. In general, IoT networks are known for their low energy consumption, low power transmissions, and reduced number of data transfer through the network. Besides, it is essential that the devices on the network can operate for long periods, generate precise data and communicate with other devices on the network. Other applications may demand real-time data acquisition, exhibition of the collected information to users, long-range communications, and battery-based devices [11,12].
To attend to these characteristics, it is essential to choose correctly the sensing technology for these applications, as well as the network characteristics, in order to avoid energy loss with poorly selected protocols on the communication stack, starting with the Layer 2 protocols, attending to the communication requirements in terms of mobility, security, area of coverage, and energy consumption.
For long-range communication, protocols such as Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN), SigFox, Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT), GPRS, and Long-Term Evolution for Machines (LTE-M) have been proposed in scenarios with low power consumption, some of those for low data transfer and other attending more frequent transmissions in short periods. These protocols are compatible with Internet Protocol (IP) networks, which allow M2M communications through high-layer protocols.
For short-range communications, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi and ZigBee are the most common technologies proposed for sensors; energy consumption may limit the usage of some of these protocols in terms of IoT-enabled devices, as some devices should be able to operate on batteries for several years. Following the TCP/IP stack, the network layer protocol is dependent on the layer 2 protocol; in some cases, as the IEEE 802.15.4, it is necessary an adaptation protocol in between the layers 2 and 3, the IPv6 over Low Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (6LowPAN) that ensures the IPv6 addressing on low power networks using the IEEE 802.15.4 as a medium access protocol [11,13,14].
The communication between devices with different layer medium access protocols must happen on WSN and IoT environments. It can easily be performed through the application layer protocol. The hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) and the hypertext transfer protocol secure (HTTPS) can be modified to perform this bridge between lower protocols, although they were not developed to perform this kind of functionalities. Other protocols such as the constrained application protocol (CoAP) and message queuing telemetry transport (MQTT) were designed to allow M2M in different scenarios, as the first implements a request/respond scenario and the last attends a publish/subscribe scenario. Transport layer protocols are dependent on the application protocols [13].
Traditionally, in WSANs all the devices communicate through the same protocols. For example, if a temperature sensor operates by Wi-Fi and HTTP, it only communicates with other devices operating with these protocols. Moreover, in these networks, the collected data are not always available for users through the Internet. The integration and communication among devices with different protocols should be supported in IoT-based smart environments. For instance, a gas sensor supporting IEEE 802.15.4 and MQTT should be able to communicate with a smart window with a GPRS module and operate with CoAP. This integration is possible through mediator software, called middleware, where data gathered by sensors are transferred and stored on this software, and it makes the necessary adaptations for these data being suitable for other devices under different communication protocols [13,89].
In terms of energy consumption, IoT-ready sensors based on batteries should be able to operate for long periods, reaching the mark of years, mainly in outdoor environments. For gas sensors, it would be desirable to maintain the operation until the transducer lifetime expires. It would be possible to combine energy sources, including solar panels to recharge the batteries. Some gas sensing technologies consume less energy, as the transducers do not need a temperature compensation and can be turned off during the measurement intervals, as the acoustic and optic methods for detecting gases. Other technologies, such as electrochemical, MOS, and catalytics require a pre-heating time, and thus, turning off these transducers would influence negatively on the performance and capacity of delivering correct measurement values. For indoor environments, the proposed sensors could rely on the power grid energy, mitigating the necessity of batteries.
The stability of the transducers must be sufficient to provide accurate measurements, which in some technologies, such as MOS, electrochemical, and catalytic can be reached through periodic calibration. These calibrations must be performed according to the characteristics of the transducers; smart sensors can also analyze collected data to predict the necessity of calibration, as two discrepant measurements occur in sequence, the calibration must be performed, granting better accuracy to the measurements.
6.2. Gas-Sensing Solutions for IoT and Wireless Sensors and Actuators Networks (WSANs)
During the past two decades, authors have focused on proposing and developing wireless gas sensors for diverse applications. The primary approaches on wireless gas sensors were made for monitoring large areas with no specific wireless protocol implemented. Sensors were able to transmit the sensed information through satellite networks or the Industrial, Scientific and Medical (ISM) bands through simple modulation techniques [2,143,144]. Later, systems to transfer sensed data through other technologies were proposed, using cellular networks for long range [34,105,109,110]. Bluetooth, ZigBee and Wi-Fi have been used to short range communications [104,107,108].
Recently, other systems have been proposed to attend the demand of remotely sensing gases in different ambiences, such as industrial, domestic or even outdoor remote areas [34,105,109,110,111]. As new communication protocols are emerging, they are being used to cover wireless sensors networks, when the characteristics of these networks correspond to those of these protocols. Some authors have proposed sensors with more than one wireless protocol [104,110], and different cellular networks have been used to perform the transmission, from the GPRS to the LTE [34,105,109,110].
To attend to the demand for gas sensing on smart cities and remote area monitoring, sensors with different characteristics of the sensing elements, data transfer and energy consumption have been proposed, as in these scenarios, energy supply from power lines may not be available and batteries will not keep sensors functioning for long periods. A CO sensor using electrochemical transducers, employing techniques to reduce energy consumption or to grant the necessary power supply by alternative means, as solar panels and aeolic generators, was proposed by Baranov et al. [104] to monitor urban areas with ZigBee, although no middleware integration nor online website was reported to provide data exhibition to the users.
Based on the second generation of mobile communications, different researchers have proposed gas sensors to attend the remote area-monitoring perspective. GPRS technology was used in [34] and [112]. The first presented a CO2 sensor for monitoring this gas concentration in remote areas with an optical sensing element and a Global Positioning System (GPS) module; the collected data is stored on a database, as well as on a SD-card and exhibit on a web page. In the second, authors have proposed a VOC, NO2 and O3 sensor with MOS transducers to collect information on urban air pollution, where data is stored on an online database. Based on the Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM), Sun et al. [108] proposed and developed a CO and NO2 sensor with electrochemical elements to monitor air quality on urban areas, collecting data mainly during the 2015 Hong Kong marathon. Dong et al. [103] proposed a natural gas wireless sensor with a MOS transducer, with deployments in different networks, allowing easy adaptation to divergent scenarios, through the GPRS, 3G, 4G, LoRaWAN and Bluetooth networks; although this work was focused on environmental monitoring and automation, the sensor was not integrated on a middleware with a dashboard, to facilitate the visualization of the collected data.
Research focused on gas sensors for indoor monitoring has started with the development of new devices with the capacity of sensing at least one target gas with good precision and alert the users by enabling an alarm, which become a commercial product, installed in many houses, apartments and offices.
Wireless gas sensors focused on indoor monitoring were proposed in the literature by some authors, with different characteristics. Peng et al. [145] presented a ZigBee-based optical gas sensor to monitor VOCs in enclosed environments, displaying the collected information in real-time in an online dashboard. A system to detect and withhold CH4 leakages in industrial environments was proposed by Somov et al. [111], based on catalytic gas sensors and with the ZigBee stack to perform the system’s communication.
Focusing on indoor environmental quality control, a photoacoustic-based CO2 sensor was proposed by [106], employing a Z-Wave transceiver to make the communication with a gateway, responsible to transfer data to an online dashboard with periodic data collection and transmission. Suh et al. [107] presented a portable dual gas detector for H2S and CO based on Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, operating with MOS transducers and communicating with smartphones; the sensed data being transferred to an online spreadsheet. To avoid accidents related to gas leakages, a CO and LPG gas sensor was proposed based on the MOS technology connected through the 6LoWPAN over the IEEE 802.15.4 [146]. Sensed data is transferred to a local MQTT broker and stored on a local database to validate the proposed wireless communication.
To improve the life quality of incontinence patients, Perez et al. [147] proposed a MOS sensor to detect NH3, methylmercaptan (C3SH), and dimetylsulfide ((CH3)2S). These gases are present in urine and feces, which allows caretakers to be aware of these patients need through smartphone alerts. The proposed system is connected to a smartphone through BLE, allowing alerts on these devices. It is also small and hence able to be used by these patients as a gadget.
Jelicic et al. [93], Kumar et al. [110] and Choi et al. [105] have proposed multi-gas wireless sensors based on ZigBee. The first proposed a sensor to detect and VOC with MOS transducers deploying a solution that is capable for detecting people on the environment to perform the gas sensing, which helps to decrease energy consumption. The second presented a SO2, NO2, CO, CO2, and O2 sensor with electrochemical transducers with periodic calibration, to monitor greenhouse gases. The last developed a CO, CO2, NO2, and CH4 sensor operating with MOS, electrochemical and optical transducers, to monitor air pollution in diverse environments.
7. Discussion and Open Issues
In the previous two sections, the authors presented the most important sensing technologies for ambient gas detection and the most promising IoT-enabled sensing solutions. This section brings the discussion towards the best solutions for sensing gases and the most promising wireless communication solutions in the related literature, as well as the suggestion of open research topics.
7.1. Sensing Technologies
Table 1 shows the main characteristics of the sensing technologies reviewed in this survey paper. To the best of the authors’ knowledge, until the date of this publication, no authors have reported the approximately lifetime of carbon nanotubes transducers for sensing gases.

Table 1.
Main gas sensing technologies available for Internet of Things (IoT)-enabled gas sensors.
The studied solutions for gas monitoring in connected environments mostly apply the most antique technologies to sense gases, as the electrochemical, MOS and catalytic, as these technologies are the most available on the market. These technologies also consume less energy than acoustic and optical gas sensors, which is not the best option for battery-based sensors. Polymers have a short lifetime and carbon nanotubes were not found in commercial solutions, being unviable for IoT-based solutions.
Despite the possibility of interference from other gases and environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, sensors based on chemical reactions can have their precision and accuracy increased with the employment of recalibration processes along with filters for other gases.
Some authors have employed the combination of two sensing technologies like acoustic and optic methods, resulting in a better detection capacity without environmental interference and with no need for periodic calibration, reducing the complexity of the proposed solutions [148,149]. Moreover, these technologies do not need a temperature compensation and do not require the employment of heaters and a pre-heating time, which also reduce the energy consumption of these solutions.
7.2. Wireless Gas Sensors
Table 2 summarizes the main aspects of the most promising systems, in terms of sensing technologies, wireless protocols, and their focus. It includes a brief description of each proposal highlighting their strengths and weakness.

Table 2.
Comparison among the studied approaches for remotely sensing gases.
In terms of wireless transmission protocols, in short-range communication the ZigBee protocol is the most applied to the studied proposals. This protocol uses the IEEE 802.15.4 physical and MAC layers, although it does not allow the use of IPv6 on the final devices, as the pure IEEE 802.15.4 deployed with the 6LoWPAN adaptation layer. As this protocol can be used in mesh networks, the energy consumption and communication range on the network can be greater than Wi-Fi applications with one single access point, which is more suitable for IoT applications.
Regarding long-range communications, cellular technologies were more explored in wireless gas sensors. The second generation of mobile communications was applied in four solutions, as these networks are still operating and the cost to use these networks is small, compared to the costs of deploying a new network to operate wireless devices, as the LoRaWAN. The monitoring process of remote areas, such as big farms, where the coverage of legacy mobile networks is poor, protocols as LoRaWAN may be more suitable for these scenarios.
Most of the studied solutions do not support M2M communications and were not integrated though an IoT platform or middleware solution, which are important features on smart environments and IoT-ready solutions. These aspects allow devices to act in favor of users in determined situations, such as stopping gas leakages, opening windows to help with the ventilation, or even warning users with alarms. The M2M communication feature can be achieved through IoT platforms that store and forward data to other devices with the same context of the sensors. Moreover, these platforms can also exhibit the collected information for the final users.
7.3. Open Issues
In the sequence of the presented discussion, the following open issues are identified and proposed for further research studies:
- Gas sensing could provide valuable data to diverse applications, using the IoT paradigm, offering important data for decisions taken by smart devices. They can provide better experiences to users.
- The improvement of sensing characteristics, miniaturization of transducers and combination of sensing technologies are topics with great potential for research.
- Creation of customized multi-gas smart sensors since, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, there are no these kind of solutions in the literature.
- Proposals following a plug-and-play approach based on IoT focusing on the end-user empowerment to properly configure these devices according to their needs.
- Performance evaluation, demonstration, and validation of available gas transducer proposals in real environments since they only were studied through theoretical and laboratory prototype approaches.
8. Lessons Learned
The review of the state of the art of gas-sensing technologies has demonstrated the need for more research into ameliorating the sensing characteristics of the transducers to achieve better levels of reliability. The use of these devices can grant better results in numerous fields, as well as grant security to people.
Many researchers mistake metal oxide semiconductors for electrochemical and catalytic sensors; the principle of operation and their sensing characteristics are similar, although the fabrication techniques, sensing methods, as well as the types of materials to construct the transducers differ in quite a few aspects.
As presented above, ZigBee is chosen by many authors due to its easy deployment characteristics and lower power consumption, compared to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. Nevertheless, the standard IEEE 802.15.4 with the 6LoWPAN should be considered as a relevant alternative in future solutions given its promising characteristics.
Despite the potential of some sensing techniques, no further investigations on these topics were found. Commercial solutions are more focused on using the most researched and antique technologies such as the metal oxide semiconductors and electrochemical transducers, even knowing that these sensors can lead to mistakes due to interference from other gases. Decreasing the final prices of these transducers could help to make gas sensors ubiquitous systems.
9. Conclusions
The opportune scenario of the IoT will lead to the development of smart sensors to attend different contexts, as household users, industries, environmental monitoring, as well as remote electrical distribution stations; the data collected by these sensors will be publicly available through the Internet. This system could be linked to public and health authorities in order to develop public policies according to the risks of each region, decreasing the costs of public health and improving the quality of life. Other smart devices may receive the sensed data to make the best decisions in a smart environment to protect and provide the best experience to the users.
A wide smart network can provide important data, as well as actions through these data, to reduce costs in numerous governmental and private sectors, allowing investment in other areas of necessity. In addition, the development of one unique device, capable of collecting data from numerous gases of interest, with the capacity to be a modular device, allowing users to use only the transducers that correspond to the target gases of a given application, is crucial to make gas-sensing technology more affordable. One important characteristic of the device is the fact that a user without technical knowledge should be able to install the chosen transducers as well as deploy the sensor in the network used to transfer the data.
More research should be conducted in order to improve transducer’s sensitivity, accuracy and selectivity, together with the miniaturization of these devices, which would make easier the deployment and mobility of such devices, along with the use of them in personal protective equipment. Moreover, the combination of more than one technology to sense gases could result in better sensing characteristics, mitigating drawbacks from the isolated sensing techniques. Furthermore, it is necessary to make these technologies more affordable; reducing the costs of production of these devices is fundamental to make the benefits of these sensors ubiquitous.
Author Contributions
J.B.A.G. collected and performed a deep analysis and reviewed the related literature on the topic, wrote the first draft of the document, performed the comparison study and identified some open research issues. J.J.P.C.R. supervised the study, consolidated the comparison analysis and open issues, reviewed the structure and the first draft. R.A.L.R., N.K., and S.K. reviewed the text carefully, verified the comparison study, and reviewed the issues identified. All the authors contributed equally to the scope definition, motivation, and focus of the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by National Funding from the FCT—Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia through the UID/EEA/0008/2019 Project; by the Government of the Russian Federation, Grant 08-08; by RNP, with resources from MCTIC, Grant No. 01250.075413/2018-04, under the Centro de Referência em Radiocomunicações—CRR project of the Instituto Nacional de Telecomunicações (Inatel), Brazil; and by Brazilian National Council for Research and Development (CNPq) via Grants No. 431726/2018-3 and 309335/2017-5.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gopal, M.; Singh, V. Control Systems Engineering; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume SMC-6, No. 9. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Cacho, M.; Delgado, E.; Prieto, J.A.G.; López, J. Network adaptive deadband: NCS data flow control for shared networks. Sensors 2012, 12, 16591–16613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lin, H.J. Design and Implementation of Smart Home Control Systems Based on Wireless Sensor Networks and Power Line Communications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 4430–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.L.; Pirmez, L.; Carmo, L.R.; Pires, P.F.; Delicato, F.C.; Khan, S.U.; Zomaya, A.Y. A Decentralized Damage Detection System for Wireless Sensor and Actuator Networks. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2016, 65, 1363–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Singh, K.D.; Chaouchi, H.; Bonnin, J.M. Wireless sensor networks: A survey on recent developments and potential synergies. J. Supercomput. 2014, 68, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, L.M.; Velez, F.J.; Lebres, A.S. Survey on the characterization and classification of wireless sensor network applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1860–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.M.L.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Elias, A.G.F.; Zarpelão, B.B. Ubiquitous monitoring solution for Wireless Sensor Networks with push notifications and end-to-end connectivity. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2014, 10, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, B.; Vamvoudakis, K.G.; Modares, H.; Lewis, F.L. Optimal and Autonomous Control Using Reinforcement Learning: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 2042–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Dakheel, J.; Tabet Aoul, K. Building Applications, Opportunities and Challenges of Active Shading Systems: A State-of-the-Art Review. Energies 2017, 10, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, C.; Chong, E.; Maciejewski, A. Multiple-Scenario Unmanned Aerial System Control: A Systems Engineering Approach and Review of Existing Control Methods. Aerospace 2016, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fuqaha, A.; Guizani, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Aledhari, M.; Ayyash, M. Internet of Things: A Survey on Enabling Technologies, Protocols, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 2347–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, J.; Chatzimisios, V.; Vazquez-Gallego, P.; Alonso-Zarate, F. A Survey on Application Layer Protocols for Internet of Things. Trans. IoT Cloud Comput. 2015, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Da Cruz, M.A.A.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Korotaev, V. Performance evaluation of IoT middleware. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 109, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Kozlov, S.A.; Rabêlo, R.A.L.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. MAC layer protocols for internet of things: A survey. Future Internet 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, M. Canaries in the coal mine. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1469–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, M.; Frey, M.; Passetti, E. Accidents at Work and Costs Analysis: A Field Study in a Large Italian Company. Ind. Health 2014, 52, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Turgut, P.; Arif Gurel, M.; Kadir Pekgokgoz, R. LPG explosion damage of a reinforced concrete building: A case study in Sanliurfa, Turkey. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2013, 32, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Sam Mannan, M.; Do Jo, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Keren, N.; Wang, Y. Incident analysis of Bucheon LPG filling station pool fire and BLEVE. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galada, H.C.; Gurian, P.L.; Corella-Barud, V.; Pérez, F.G.; Velázquez-Angulo, G.; Flores, S.; Montoya, T. Applying the mental models framework to carbon monoxide risk in northern Mexico. Rev. Panam. Salud Pública 2009, 25, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, S.; Ray, A.K.; Chakraborty, A.K. Graphene-metal oxide nanohybrids for toxic gas sensor: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Detection of hazardous volatile organic compounds (VOCs) by metal oxide nanostructures-based gas sensors: A review. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 15119–15141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.F.; Liu, S.B.; Meng, F.L.; Liu, J.Y.; Jin, Z.; Kong, L.T.; Liu, J.H. Metal oxide nanostructures and their gas sensing properties: A review. Sensors 2012, 12, 2610–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, D.; Zhang, Y. Gas sensors based on deposited single-walled carbon nanotube networks for DMMP detection. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 345502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, C.S.; Lo, Y.L.; Sung, T.W. Review on recent developments of fluorescent oxygen and carbon dioxide optical fiber sensors. Photonic Sens. 2011, 1, 234–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llobet, E. Gas sensors using carbon nanomaterials: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 179, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakard, B.; Carquigny, S.; Segut, O.; Patois, T.; Lakard, S. Gas Sensors Based on Electrodeposited Polymers. Metals 2015, 5, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratoddi, I.; Venditti, I.; Cametti, C.; Russo, M.V. Chemiresistive polyaniline-based gas sensors: A mini review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 220, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, S.; Liu, H.; Hu, S.; Zhang, D.; Ning, H. A survey on gas sensing technology. Sensors 2012, 12, 9635–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Wu, Y.; Lin, C. High performance oxygen sensor utilizing ultraviolet irradiation assisted ZnO nanorods under low operation temperature. In Proceedings of the the 8th Annual IEEE International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, Suzhou, China, 7–10 April 2013; pp. 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, W.; Smith, P.; Leigh, S.; Covington, J. Oxygen Sensors Based on Screen Printed Platinum and Palladium Doped Indium Oxides. Proc. Eurosens. 2017, 1, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuk, P.; Jantz, R. Oxygen gas sensing technologies: A comprehensive review. In Proceedings of the 2015 9th International Conference on Sensing Technology, ICST, Auckland, New Zealand, 8–10 December2015; pp. 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sieber, A.; Enoksson, P.; Krozer, A. Smart electrochemical oxygen sensor for personal protective equipment. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaubien, S.E.; Ciotoli, G.; Lombardi, S. Carbon dioxide and radon gas hazard in the Alban Hills area (central Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2003, 123, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakkannan, N.; Nagaraj, B. Online monitoring of geological methane storage and leakage based on wireless sensor networks. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, S23–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rasyid, M.U.H.; Nadhori, I.U.; Alnovinda, Y.T. CO and CO2 pollution monitoring based on wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Aerospace Electronics and Remote Sensing (IEEE ICARES 2015), Bali, Indonesia, 3–5 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hampson, N.B. Cost of accidental carbon monoxide poisoning: A preventable expense. Prev. Med. Rep. 2016, 3, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampson, N.B.; Dunn, S.L. Carbon monoxide poisoning from portable electrical generators. J. Emerg. Med. 2015, 49, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y. Insight into the mechanism of CO oxidation on WO3(001) surfaces for gas sensing: A DFT study. Sensors 2017, 17, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzón, J.P.; Huertas, J.I.; Magaña, M.; Huertas, M.E.; Cárdenas, B.; Watanabe, T.; Maeda, T.; Wakamatsu, S.; Blanco, S. Volatile organic compounds in the atmosphere of Mexico City. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.S.; Razzak, S.A.; Hossain, M.M. Catalytic oxidation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs)—A review. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 140, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colindres, S.C.; Aguir, K.; Sodi, F.C.; Vargas, L.V.; Salazar, J.M.; Febles, V.G. Ozone sensing based on palladium decorated carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 6806–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvall, R.M.; Long, R.W.; Beaver, M.R.; Kronmiller, K.G.; Wheeler, M.L.; Szykman, J.J. Performance evaluation and community application of low-cost sensors for ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Sensors 2016, 16, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tsow, F.; Zhang, X.; Peng, J.H.; Forzani, E.S.; Chen, Y.; Crittenden, J.C.; Destaillats, H.; Tao, N. Real-time ozone detection based on a microfabricated quartz crystal tuning fork sensor. Sensors 2009, 9, 5655–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagura, T.; Makita, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Menck, C.F.M.; Schuch, A.P. Biological sensors for solar ultraviolet radiation. Sensors 2011, 11, 4277–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.; Sthel, M.; Lima, G.; da Silva, M.; Schramm, D.; Miklós, A.; Vargas, H. A sulfur hexafluoride sensor using quantum cascade and CO2 laser-based photoacoustic spectroscopy. Sensors 2010, 10, 9359–9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Dong, Z. Thermodynamic modeling and analysis of an optical electric-field sensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 7125–7135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zhang, C.; Ren, M.; Albarracín, R.; Ye, R. Electrochemical and infrared absorption spectroscopy detection of SF6 decomposition products. Sensors 2017, 17, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, R.; Gui, Y.; Zeng, H. Gas sensing analysis of ag-decorated graphene for sulfur hexafluoride decomposition products based on the density functional theory. Sensors 2016, 16, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, L.; Tie, J.; Dong, X. Gas sensitivity and sensing mechanism studies on Au-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays for detecting SF6 decomposed components. Sensors 2014, 14, 19517–19532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, H.; Gui, Y. Synthesis of graphene-based sensors and application on detecting SF6 decomposing products: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luo, C.; Tang, J. Sensitivity characteristic analysis of adsorbent-mixed carbon nanotube sensors for the detection of SF6 decomposition products under PD conditions. Sensors 2013, 13, 15209–15220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Luo, C.; Dong, X.; Zhou, L. Analysis of the sensitivity of K-type molecular sieve-deposited MWNTs for the detection of SF6 decomposition gases under partial discharge. Sensors 2015, 15, 28367–28384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnacho, F.; Khamlichi, A.; Rovira, J. The design and characterization of a prototype wideband voltage sensor based on a resistive divider. Sensors 2017, 17, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Rodríguez, P.; Fernández-Serantes, L.A.; Otero-Pazos, A.; Calvo-Rolle, J.L.; de Cos Juez, F.J. Radon Mitigation Approach in a Laboratory Measurement Room. Sensors 2017, 17, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.S. Who Handbook on Indoor Radon: A Public Health Perspective; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Volume 67. [Google Scholar]
- Nikezic, D.; Yu, K.N. Are radon gas measurements adequate for epidemiological studies and case control studies of radon-induced lung cancer? Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2005, 113, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, R.W.; Steck, D.J.; Smith, B.J.; Brus, C.P.; Fisher, E.F.; Neuberger, J.S.; Lynch, C.F. The Iowa radon lung cancer study-phase I: Residential radon gas exposure and lung cancer. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 272, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, S.; Hill, D.; Auvinen, A.; Barros-Dios, J.M.; Baysson, H.; Bochicchio, F.; Deo, H.; Falk, R.; Forastiere, F.; Hakama, M.; et al. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: Collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. Br. Med. J. 2005, 330, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannides, K.; Papachristodoulou, C.; Stamoulis, K.; Karamanis, D.; Pavlides, S.; Chatzipetros, A.; Karakala, E. Soil gas radon: A tool for exploring active fault zones. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2003, 59, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xiong, M.; Yang, T.; Zakharova, G.S. Highly sensitive and selective ammonia gas sensors based on PbS quantum dots/TiO2 nanotube arrays at room temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 236, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Do, J.S.; Li, J. Highly sensitive room temperature ammonia gas sensor based on Ir-doped Pt porous ceramic electrodes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renganathan, B.; Sastikumar, D.; Gobi, G.; X Rajeswari Yogamalar, N.; Chandra Bose, A. Nanocrystalline ZnO coated fiber optic sensor for ammonia gas detection. Opt. Laser Technol. 2011, 43, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, M.; Jayatissa, A.H. Ammonia gas sensing behavior of graphene surface decorated with gold nanoparticles. Solid-State Electron. 2012, 78, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, M.; Salehi, A.; Boroumand, F.A.; Mosleh, N. Fabrication of a Room Temperature Ammonia Gas Sensor Based on Polyaniline with N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatty, H.K.; Leijonmarck, S.; Antelius, M.; Stemme, G.; Roxhed, N. An amperometric nitric oxide sensor with fast response and ppb-level concentration detection relevant to asthma monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatty, H.K.; Stemme, G.; Roxhed, N. A wafer-level liquid cavity integrated amperometric gas sensor with ppb-level nitric oxide gas sensitivity. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluis, W.W.; Allaart, M.A.F.; Piters, A.J.M.; Gast, L.F.L. The development of a nitrogen dioxide sonde. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, J.H.; Wikle, H.C.; Chin, B.A. Passive chemiresistor sensor based on iron (II) phthalocyanine thin films for monitoring of nitrogen dioxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 148, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabassum, R.; Pavelyev, V.S.; Moskalenko, A.S.; Tukmakov, K.N.; Islam, S.S.; Mishra, P. A Highly Sensitive Nitrogen Dioxide Gas Sensor Using Horizontally Aligned SWCNTs Employing MEMS and Dielectrophoresis Methods. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2017, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, P.J.D.; Aujla, A.; Grant, K.H.; Brundle, A.G.; Thompson, M.R.; Vande Hey, J.; Leigh, R.J. Practical use of metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors for measuring nitrogen dioxide and ozone in urban environments. Sensors 2017, 17, 1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, C.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Y. Highly sensitive and selective H2S sensor based on porous ZnFe2O4 nanosheets. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 246, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samanta, S.; Singh, A.; Roy, M.; Singh, S.; Basu, S.; Chehimi, M.M.; Roy, K.; Ramgir, N.; Navaneethan, M.; et al. Fast Response and High Sensitivity of ZnO Nanowires—Cobalt Phthalocyanine Heterojunction Based H2S Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17713–17724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek Alaie, M.; Jahangiri, M.; Rashidi, A.M.; Haghighi Asl, A.; Izadi, N. A novel selective H2S sensor using dodecylamine and ethylenediamine functionalized graphene oxide. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dang, T.; Duc Hoa, N.; Van Duy, N.; Van Hieu, N. Chlorine Gas Sensing Performance of On-Chip Grown ZnO, WO3, and SnO2 Nanowire Sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 4828–4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, C.B.; Scott, P.; Abramova, E.; Gardner, C.; Laskin, D.L.; Gow, A.J. Acute chlorine gas exposure produces transient inflammation and a progressive alteration in surfactant composition with accompanying mechanical dysfunction. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 278, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govier, P.; Coulson, J.M. Civilian exposure to chlorine gas: A systematic review. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 293, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCoste, J.B.; Browe, M.A.; Wagner, G.W.; Rossin, J.A.; Peterson, G.W. Removal of chlorine gas by an amine functionalized metal–organic framework via electrophilic aromatic substitution. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12474–12477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.W.; Chiang, C.C. Sandwiched long-period fiber grating fabricated by MEMS process for CO2 gas detection. Micromachines 2016, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çengel, Y.A.; Boles, M.A. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach with Student Resources DVD; McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cengel, Y.A. Heat Transfer: A Practical Approach; McGraw-Hill Science/Engineering/Math: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Genta, C.; Marotta, C.; Migliardini, F. Study and Development of a Complete System for Recovery, Recycle, and Disposal of Refrigerant Gas from Existent Plants. J. Eng. (USA) 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandehari, M.; Aghamohamadnia, M.; Dobler, G.; Karpf, A.; Buckland, K.; Qian, J.; Koonin, S. Mapping Refrigerant Gases in the New York City Skyline. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.I.; Lin, C.C. A study of storage tank accidents. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2006, 19, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.; Brooks, H.; Boitano, S.; Barman, S. Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 23rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, J.W.; Guha, P.K.; Udrea, F.; Covington, J.A. CMOS interfacing for integrated gas sensors: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1833–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sam Boling, C.; Mason, A.J. CMOS Amperometric ADC with High Sensitivity, Dynamic Range and Power Efficiency for Air Quality Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adgate, J.L.; Goldstein, B.D.; McKenzie, L.M. Potential public health hazards, exposures and health effects from unconventional natural gas development. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8307–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fthenakis, V.M. Overview of potential hazards. In McEvoy’s Handbook of Photovoltaics: Fundamentals and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1195–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Da Cruz, M.A.A.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Korotaev, V.V.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. A Reference Model for Internet of Things Middleware. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mu, X.; Yang, Y.; Mason, A.J. Low power multimode electrochemical gas sensor array system for wearable health and safety monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 3391–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; Yin, P.; Cheng, P.; Liu, Y.; Schwebel, D.C.; Qi, J.; Ning, P.; Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; et al. Poisoning deaths in China, 2006–2016. Bull. World Health Organ. 2018, 96, 314–326A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalk, R. The miners’ canary. Bull. Atomic Sci. 1982, 38, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelicic, V.; Magno, M.; Brunelli, D.; Paci, G.; Benini, L. Context-adaptive multimodal wireless sensor network for energy-efficient gas monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharudin, S.; Isha, K.M.; Mahmud, Z.; Herman, S.H.; Noor, U.M. Performance evaluation of optical fiber sensor using different oxygen sensitive nano-materials. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Photonics (ICP 2013), Melaka, Malaysia, 28–30 October 2013; pp. 309–312. [Google Scholar]
- Niazi, A.; Anthony, C.J. Development of Oxygen Sensor by Integrating the Low Cost Printed Circuit Board Technology and Solid Electrolyte Membrane. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Systems (ICBES 2014), Prague, Czech Republic, 14–15 August 2014; Volume 137, pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Shuk, P.; Jantz, R.; Guth, H.U. Oxygen sensor with advanced oxide electrode materials. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2012, 5, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Formenti, F.; McPeak, H.; Obeid, A.N.; Hahn, C.E.W.; Farmery, A.D. Optimizing design for polymer fiber optic oxygen sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 3358–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Kamble, S.S.; Radhakrishnan, J.K. Tunable Diode Laser Absorption Spectroscopy based Oxygen Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2012 Sixth International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Kolkata, India, 18–21 December 2012; Volume 4, pp. 130–135. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, S.; Shan, M. An acoustic method on sulfur hexafluoride concentration detection. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Workshop on Electronics, Computer and Applications, IWECA 2014, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8–9 May 2014; pp. 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Sonoyama, M.; Kato, Y.; Fujita, H. Application of ultrasonic to a hydrogen sensor. In Proceedings of the IEEE Sensors, Kona, HI, USA, 1–4 November 2010; pp. 2141–2144. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, M.; Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, J. Gas concentration detection using ultrasonic based on wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Engineering (ICISE 2010), Hangzhou, China, 3–5 December 2010; pp. 2101–2106. [Google Scholar]
- Petculescu, A.; Hall, B.; Fraenzle, R.; Phillips, S.; Lueptow, R.M. A prototype acoustic gas sensor based on attenuation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 1779–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz Perez, A.; Bierer, B.; Scholz, L.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. A Wireless Gas Sensor Network to Monitor Indoor Environmental Quality in Schools. Sensors 2018, 18, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, J.H.; Cho, I.; Kang, K.; Kweon, S.-J.; Lee, M.; Yoo, H.-J.; Park, I. Fully integrated and portable semiconductor-type multi-gas sensing module for IoT applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; JOE Wong, K.C.; Wei, P.; Ye, S.; Huang, H.; Yang, F.; Westerdahl, D.; Louie, P.K.K.; Luk, C.W.Y.; Ning, Z. Development and application of a next generation air sensor network for the Hong Kong marathon 2015 air quality monitoring. Sensors 2016, 16, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rasyid, Y.T. M Udin Harun and Nadhori, Isbat Uzzin and Sudarsono, Amang and Alnovinda, Pollution monitoring system using gas sensor based on wireless sensor network. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Innov. 2016, 6, 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Hancke, G.P. Energy efficient environment monitoring system based on the IEEE 802.15.4 standard for low cost requirements. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 2557–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somov, A.; Baranov, A.; Spirjakin, D. A wireless sensor-actuator system for hazardous gases detection and control. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 210, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltchanov, S.; Levy, I.; Etzion, Y.; Lerner, U.; Broday, D.M.; Fishbain, B. On the feasibility of measuring urban air pollution by wireless distributed sensor networks. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Duan, S.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, G.; Tao, R. MEMS-Based Smart Gas Metering for Internet of Things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranov, A.; Spirjakin, D.; Akbari, S.; Somov, A.; Passerone, R. POCO: ‘Perpetual’ operation of CO wireless sensor node with hybrid power supply. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 238, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, N.; Cha, H.; Ha, R. Micro sensor node for air pollutant monitoring: Hardware and software issues. Sensors 2009, 9, 7970–7987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Yin, H.; Mason, A.J. Rapid measurement of room temperature ionic liquid electrochemical gas sensor using transient double potential amperometry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 242, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, N.; Sato, T.; Anggraini, S.A.; Ikeda, H.; Zhuiykov, S. A review of mixed-potential type zirconia-based gas sensors. Ionics 2014, 20, 901–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-S.; Syu, J.-J. The Development of a Highly Sensitive Fiber-Optic Oxygen Sensor. Inventions 2016, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eich, S.; Schmälzlin, E.; Löhmannsröben, H.G. Distributed fiber optical sensing of oxygen with optical time domain reflectometry. Sensors 2013, 13, 7170–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, F.R.; Xavier, M.G. Electrochemical Sensors. Nanosci. Appl. 2017, 74, 155–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, Y. A micro oxygen sensor based on a nano sol-gel TiO2 thin film. Sensors 2014, 14, 16423–16433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertuna, A.; Faglia, G.; Ferroni, M.; Kaur, N.; Munasinghe Arachchige, H.M.M.; Sberveglieri, G.; Comini, E. Metal oxide nanowire preparation and their integration into chemical sensing devices at the sensor lab in Brescia. Sensors 2017, 17, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P.K.; Benedict, S.S.; Kallat, S.; Bhat, N. A Suspended Low Power Gas Sensor with In-Plane Heater. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2017, 26, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, L.K.; Luo, J.C.; Chen, M.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, J.Z.; Chen, I.C.; Hsu, C.C.; Tian, W.C. A photoactivated gas detector for toluene sensing at room temperature based on new coral-like ZnO nanostructure arrays. Sensors 2016, 16, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binions, R.; Naik, A.J.T. Metal oxide semiconductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Semicond. Gas Sens. 2013, 10, 433–466. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, B. Fabrication of p-Type ZnO: N films by oxidizing Zn3N2 films in oxygen plasma at low temperature. Materials 2017, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratulat, A.; Serban, B.-C.; de Luca, A.; Avramescu, V.; Cobianu, C.; Brezeanu, M.; Buiu, O.; Diamandescu, L.; Feder, M.; Ali, S.Z.; et al. Low power resistive oxygen sensor based on sonochemical SrTi-0.6-Fe-0.4-O-2.8 (STFO40). Sensors 2015, 15, 17495–17506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlalia, A.; Filipovic, L.; Selberherr, S. Modeling and Simulation of Novel Semiconducting Metal Oxide Gas Sensors for Wearable Devices. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 1960–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotcenkov, G. Handbook of Gas Sensor Materials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Grossel, S.S. Hazardous gas monitoring: A guide for semiconductor and other hazardous occupancies (2000). J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2002, 15, 249–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutic, D.; Sanati, M.; Spetz, A.L. Gas Sensors. In Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Oxide Nanomaterials; Sberveglieri, G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 411–450. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byshkin, M.S.; Buonocore, F.; Di Matteo, A.; Milano, G. A unified bottom up multiscale strategy to model gas sensors based on conductive polymers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 211, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liang, W.; Mai, J.D.; Liu, L.; Bin Lee, G.; Li, W.J. Rapid fabrication of nanomaterial electrodes using digitally controlled electrokinetics. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2014, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Kim, K.B.; Jin, J.H.; Min, N.K. Evaluation of surface cleaning procedures in terms of gas sensing properties of spray-deposited CNT film: Thermal- and O2 plasma treatments. Sensors 2017, 17, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S. New developments in ultrasonic gas analysis and flowmetering. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Beijing, China, 2–5 November 2008; pp. 508–516. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, Y.T.; Ahmad, A.L.; Zein, S.H.S.; Tan, S.H. A review on carbon nanotubes in an environmental protection and green engineering perspective. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2010, 27, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Volder, M.F.L.; Tawfick, S.H.; Baughman, R.H.; Hart, A.J. Carbon nanotubes: Present and future commercial applications. Science 2013, 339, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, I.E.; Rothman, L.S.; Hill, C.; Kochanov, R.V.; Tan, Y.; Bernath, P.F.; Birk, M.; Boudon, V.; Campargue, A.; Chance, K.V.; et al. The HITRAN2016 molecular spectroscopic database. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiative Transf. 2017, 203, 3–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Huang, Y.; Tao, S. Simultaneous monitoring of ammonia and moisture using a single fiber optoelectrode as a transducer. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, T.; Katagiri, T.; Matsuura, Y. Real-time analysis of isoprene in breath by using ultraviolet-absorption spectroscopy with a hollow optical fiber gas cell. Sensors 2016, 16, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, L.; Burton, G.; Davies, B.; Risk, D.; Wild, P. Highly sensitive coated long period grating sensor for CO2 detection at atmospheric pressure. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysokiński, K.; Napierała, M.; Stańczyk, T.; Lipiński, S.; Nasiłowski, T. Study on the sensing coating of the optical fibre CO2 sensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 31888–31903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, G.; Horvath, C.; Aktary, M.; Van, V. Silicon microring refractometric sensor for atmospheric CO2 gas monitoring. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansen, W.; De Wachter, D.; Callewaert, L.; Lambrechts, M.; Claes, A. A smart sensor for the voltammetric measurement of oxygen or glucose concentrations. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1990, 1, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, K.G.; Zeng, K.; Grimes, C.A. A wireless, passive carbon nanotube-based gas sensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2002, 2, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, D.D.; McGill, R.A.; Chung, R.; Nguyen, V. Performance of an embedded SAW sensor for filter bed monitor and the development of a wireless monitoring prototype system. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium (IEEE IFCS 1998), Pasadena, CA, USA, 29 May 1998; pp. 602–607. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, C.; Qian, K.; Wang, C. Design and Application of a VOC-Monitoring System Based on a ZigBee Wireless Sensor Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 2255–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.B.A.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Al-Muhtadi, J.; Arunkumar, N.; Rabelo, R.A.L.; Furtado, V. An IoT-Based Smart Solution for Preventing Domestic CO and LPG Gas Accidents. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 10th Latin-American Conference on Communications (IEEE LATINCOM 2018), Guadalajara, Mexico, 14–16 November 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz Pérez, A.; Kallfaß-de Frenes, V.; Filbert, A.; Kneer, J.; Bierer, B.; Held, P.; Klein, P.; Wöllenstein, J.; Benyoucef, D.; Kallfaß, S.; et al. Odor-Sensing System to Support Social Participation of People Suffering from Incontinence. Sensors 2016, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, L.; Ortiz Perez, A.; Bierer, B.; Eaksen, P.; Wollenstein, J.; Palzer, S. Miniature Low-Cost Carbon Dioxide Sensor for Mobile Devices. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 2889–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittstock, V.; Scholz, L.; Bierer, B.; Perez, A.O.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S. Design of a LED-based sensor for monitoring the lower explosion limit of methane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 247, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).