Abstract
Leaves are the most ubiquitous plant organs, whose macrostructures exhibit close correlations with environmental factors while simultaneously reflecting inherent genetic and evolutionary patterns. These characteristics render them highly significant for plant taxonomy, ecology, and related disciplines. Therefore, this study presents the first comprehensive evaluation of Malus leaf macrostructures for infraspecific classification. By establishing a trait-screening system, we conducted a numerical taxonomic analysis of leaf phenotypic variation across 73 Malus germplasm (34 species and 39 cultivars). Through ancestor-inclined distribution characteristic analysis, we investigated phylogenetic relationships at both the genus level and infraspecific ranks within Malus. A total of 21 leaf phenotypic traits were selected from 50 candidate traits based on the following criteria: high diversity, abundance, and evenness (D ≥ 0.50, H ≥ 0.80, and E ≥ 0.60); significant intraspecific uniformity and interspecific distinctness ( ≤ 10% and ≥ 15%). Notably, the selected traits with low intraspecific variability ( ≤ 10%) exhibit environmental robustness, likely reflecting low phenotypic plasticity of these specific traits under varying conditions. This stability enhances their taxonomic utility. It was found that the highest ancestor-inclined distribution probability reached 90% for 10 traceable cultivars, demonstrating reliable breeding lines. Based on morphological evidence, there was a highly significant correlation between the evolutionary orders of (Sect. Docyniopsis → Sect. Sorbomalus → Sect. Malus) and group/sub-groups (B1 → B2 → A). This study demonstrates that phenotypic variation in leaf macrostructures can effectively explore the affinities among Malus germplasm, exhibiting taxonomic significance at the infraspecific level, thereby providing references for variety selection. However, hybrid offspring may exhibit mixed parental characteristics, leading to blurred species boundaries. And convergent evolution may create false homologies, potentially misleading morphology-based taxonomic inferences. The inferred taxonomic relationships present certain limitations that warrant further investigation.
1. Introduction
Flowering crabapple (Malus spp.) refers to shrubs or small trees within the genus Malus of the Rosaceae family, characterized by fruit diameters of less than 5 cm [1]. China stands as the world’s largest gene center and genetic diversity hub for Malus species [2]. Globally, there are approximately 38 Malus species, with around 30 species found in China, 16 of which are endemic to the country [3]. According to statistics, there are approximately 200–700 cultivated crabapple varieties, encompassing both ornamental types and wild forms, which exhibit rich variations in tree architecture, flowers, leaves, and fruits [4]. Since the establishment of the genus Malus by Miller in 1754, the diversity and overlapping nature of morphological characteristics have led to severe issues of “synonymy” and “homonymy”, and the presence of numerous intermediate traits has made differentiation challenging, rendering Malus a notoriously “difficult genus” in plant taxonomy [5]. Regarding the taxonomy of the genus Malus, few researchers have explored the macrostructure of Malus leaves as a potential solution. Li et al. [6] revised the classification of wild Malus species based on herbarium specimens and numerical analysis. Liu et al. [7] supported the monophyly of Malus through nuclear phylogenetic analysis, while Forte et al. [8] inferred that section Sorbomalus comprises polyphyletic species using molecular DNA data. Previous studies have also employed molecular markers [9,10], isozymes [11], and palynology [12]. However, genetic distances estimated from different gene sequences often show inconsistencies [13]. And these investigations were limited by small sample sizes, focusing solely on species or varieties, and lacked the application of statistical methods to explore phylogenetic relationships. Ancestor-inclined distribution refers to the clustering of offspring and their parental lines through cluster analysis, thereby providing insights into their genetic relationships [14]. Building upon this methodological framework, Fan et al. [14] and Zhou et al. [15] conducted groundbreaking classification studies on Malus germplasm by analyzing floral organ and pollen phenotypic traits, respectively. However, no prior research has systematically applied this approach to the analysis of Malus leaf macrostructures.
Leaf macrostructures refer to the phenotypic characteristics of plant leaves that can be observed directly or under a dissecting microscope, such as leaf shape, size, pubescence, and venation patterns. These traits embody the plant’s genetic identity and phylogenetic evolutionary history, exhibiting distinct specificity at both genus and species levels [16]. Therefore, compared to molecular approaches, leaf macrostructures directly manifest outcomes of natural selection and ecological adaptation. Leaf venation is a regular network structure formed by interconnected vascular bundles and xylem components in plant leaves [17]. Research has shown that while leaf shape and size may vary among different individuals of the same species or across different parts of the same plant, the characteristics of higher-order venation patterns, vein branching forms, and areolation remain stable [18,19]. This stability suggests these traits are under strong genetic and phylogenetic constraints, making them valuable references for inferring evolutionary relationships and delineating both intergeneric and interspecific classifications. Currently, leaf macrostructures are widely utilized as significant taxonomic criteria in the classification studies of various plant groups, including the Sapindaceae [20], Prunus [21], Sorbus [22], Berberis [23], and Cymbidium [24]. However, current research on leaf macrostructures, particularly venation patterns, predominantly remains at the level of trait description [25]. Trait selection is primarily conducted through principal component analysis for dimensionality reduction, supplemented by correlation analysis and one-way ANOVA, lacking a scientific theoretical framework and systematic techniques for trait screening [26,27]. Furthermore, studies are often narrowly focused on the species or variety level, with classification results limited to germplasm identification and cluster group descriptions, failing to delve into the deeper phylogenetic and evolutionary relationships among germplasms [28].
This study investigates Malus germplasm through quantitative taxonomic and phylogenetic analyses of leaf macrostructures, aiming to (1) establish a theoretical and technical framework for screening phenotypic traits of Malus leaves; (2) evaluate the taxonomic significance of leaf macrostructure characteristics; (3) validate the grouping efficacy and infer evolutionary trends using the ancestor-inclined distribution analysis, thereby providing theoretical foundations for cultivar innovation and conservation of unique genotypes.
2. Results
2.1. Diversity and Variability of Leaf Phenotypic Traits in Malus Germplasm
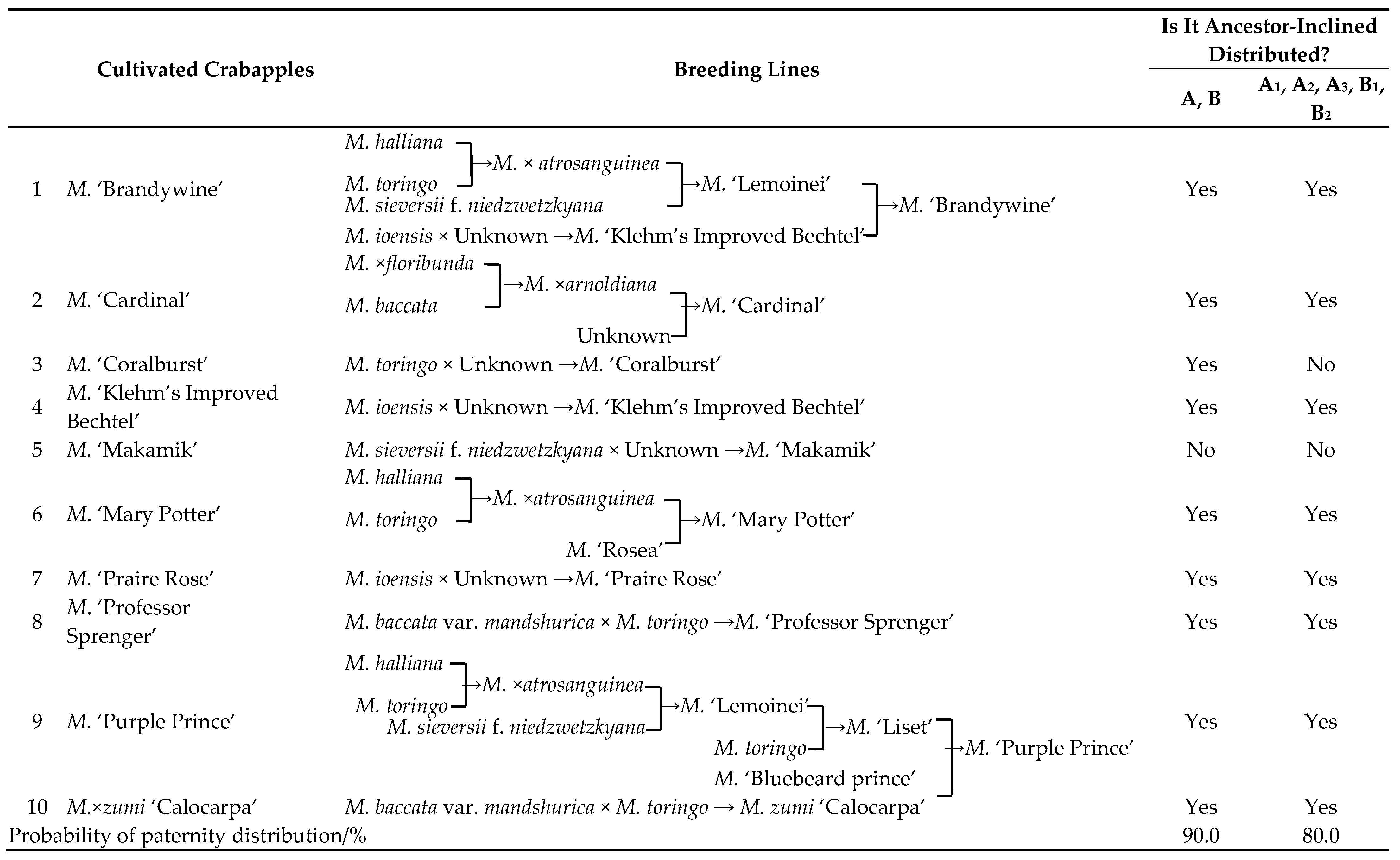
The Simpson’s Diversity Index (D), Shannon–Wiener Information Index (H), and Evenness Index (E) for the qualitative traits of Malus leaves ranged from 0.20 to 0.82, 0.35 to 1.76, and 0.41 to 1.00, respectively (Figure 1a), indicating variations in diversity, richness, and evenness across different traits. These variations hold significant taxonomic implications: Traits with high D, H, and E indices exhibit balanced polymorphism and are more likely to reflect genetic divergence, serving as reliable markers for delineating subpopulation classifications [29]. Conversely, low-diversity traits may represent evolutionarily conserved characteristics shared across Malus germplasm, suggesting environmental insensitivity. Evenness (approaching 1.00) serves as a key indicator of taxonomic utility, with higher values enhancing resolution in phylogenetic grouping analyses.
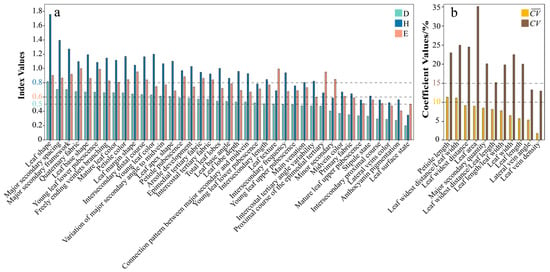
Figure 1.
Diversity and variability analysis of leaf phenotypic traits in Malus germplasm. (a): the bar plot of Simpson’s Diversity Index (D), the Shannon–Wiener Information Index (H), and the Evenness Index (E) for qualitative traits. If the values of D are ≥0.50, H are ≥0.80, and E are ≥0.60, the trait is considered to meet the required criteria; (b) the bar plot of the mean coefficient of variation () and the coefficient of variation () for quantitative traits. If is ≤10% and is ≥15%, the trait is considered to meet the required criteria.
For qualitative traits, 12 traits—leaf surface state, young leaf upper pubescence, mature leaf upper pubescence, anthocyanin pigmentation, stipule state, midvein color, main venation, lateral vein color, primary fabric, intersecondary proximal course, intercostal tertiary angle variability, and proximal course of the epimedial tertiary—exhibited D values below 0.50. Additionally, leaf texture and young leaf lower pubescence had H values below 0.8 (Figure 1a). Consequently, these low-diversity traits were excluded from the analysis. The remaining 24 qualitative traits demonstrated high diversity, rich variation information, and high evenness (D ≥ 0.50, H ≥ 0.80, and E ≥ 0.60) [30] and were retained. For quantitative traits, petiole length and leaf widest distance/leaf width showed mean coefficient of variation () values greater than 10%, while lateral vein angle and leaf vein density exhibited coefficient of variation () values exceeding 15% (Figure 1b). Therefore, these traits have been excluded from the analysis. The remaining seven quantitative traits displayed significant intraspecific uniformity and interspecific distinctness ( ≤ 10% and ≥ 15%) and were retained.
2.2. Principal Component Analysis of Leaf Phenotypic Traits in Malus Germplasm
Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted on 31 selected leaf phenotypic traits to identify key classification characteristics through dimensionality reduction. Using an eigenvalue threshold of λ ≥ 0.90 [15], the first 12 principal components were extracted, accounting for 83.54% of the cumulative variance. Eigenvector absolute values > 0.60 were considered significant [6]. The eigenvector values of each trait in different principal components are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Characteristic value, contribution rate, and cumulative contribution rate of each principal component.
The first principal component (PC1) accounts for 15.53% of the total variance and primarily captures variation in leaf division and shape. PC2 explains 13.41% of the variance, predominantly reflecting leaf size, while PC3 (9.42%) primarily captures basal morphology. Collectively, the first three PCs demonstrate that leaf shape and size hold significant taxonomic value for Malus classification, encompassing substantial discriminatory information. In contrast, PCs 4–7 reveal a gradual shift in data structure from color and pubescence traits toward secondary and tertiary venation characteristics, indicating that vein architecture carries finer-scale taxonomic significance. PCs 8–10 characterize features of intersecondary veins, major secondary veins, and areolar morphology in Malus leaves, while PCs 11–12 primarily capture leaf apex and margin configurations. Consequently, low-contribution traits—including leaf length/leaf width, leaf shape, intersecondary length, intersecondary distal course, and major secondary framework—were excluded. The remaining 26 traits effectively capture the majority of information regarding the macroscopic structure of Malus leaves.
2.3. Pearson Correlation Analysis of Leaf Phenotypic Traits in Malus Germplasm
Following principal component analysis, 26 leaf phenotypic traits (21 qualitative and 5 quantitative) were selected for Pearson correlation analysis (Figure 2). Using a threshold of r > 0.80 [15], the results indicated that most leaf phenotypic traits were independent of each other, while a few exhibited highly significant (p < 0.01) correlations, such as leaf length and leaf widest distance (r = 0.81), leaf area and leaf length (r = 0.84), leaf width and leaf area (r = 0.83), leaf base angle and leaf base shape (r = 0.91), leaf lobe depth and total leaf lobes (r = 0.89), which reflect coordinated allometric growth during leaf development, as well as young leaf color and petiole color (r = 0.81), which may suggest shared biochemical pathways activated in young tissues (e.g., anthocyanin biosynthesis). Therefore, based on observational convenience, the traits of leaf widest distance, leaf area, leaf base shape, leaf lobe depth, and young leaf color were retained for quantitative classification.
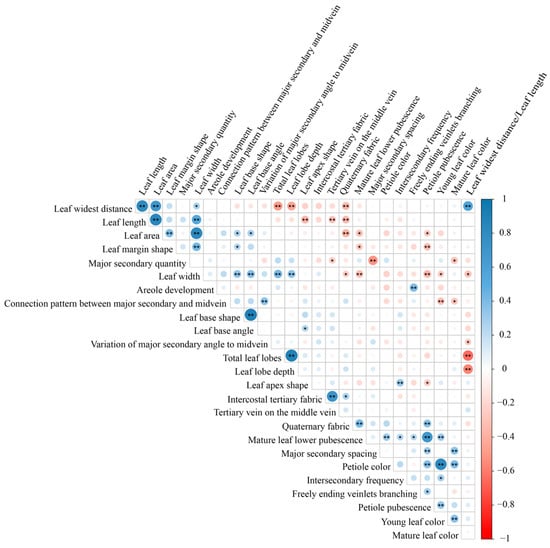
Figure 2.
Pearson correlation analysis of leaf phenotypic traits in Malus. Note: ** indicates significant correlation at the 0.01 level (two-sided), and * indicates significant correlation at the 0.05 level (two-sided). Blue dots indicate positive correlations, red dots indicate negative correlations, and the size of the dots represents the magnitude of the correlation coefficient.
2.4. Cluster Analysis of Leaf Phenotypic Traits in Malus Germplasm
Following Pearson correlation analysis, 21 leaf phenotypic traits (18 qualitative and 3 quantitative) were selected for subsequent analysis. Using Euclidean distance and Ward’s D2 linkage, hierarchical clustering was performed on 73 germplasm accessions (Figure 3). At a genetic distance of 16.41, the 73 Malus germplasms were divided into two major groups (A and B). Group A comprised 53 germplasms, characterized primarily by green young leaves and densely pubescent petioles; Group B consisted of 20 germplasms, distinguished mainly by brown-red to purple-red young leaves and sparsely pubescent or glabrous petioles. Further subdivision at a genetic distance of 12.02 resulted in five distinct subgroups (A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2). The leaf quantitative traits exhibit significant differentiation among these subgroups (Table 2).
Figure 3.
Clustering dendrogram of Malus germplasm. The scientific names of species are color-coded, with the same color indicating membership in the same group [5]. The color scheme is as follows: red font means species in Nothosect. Gymomalus; orange font means species in Sect. Chloromeles; yellow font means species in Sect. Docyniopsis; green font means species in Sect. Gymnomeles; cyan font means species in Sect. Malus; blue font means species in Sect. Sorbomalus; purple font means species in Sect. Yunnanensis; and black font means cultivars.

Table 2.
Leaf quantitative traits in Malus subgroups based on cluster analysis.
Subgroup A1: This cluster comprises 22 germplasm accessions (6 species and 16 cultivars). Key characteristics include major secondary spacing generally gradually or abruptly increasing proximally; intersecondary frequency typically being less than one per intercostal area; intercostal tertiary fabric being predominantly opposite percurrent; freely ending veinlets mostly having one branch or dendritic; a higher number of major secondary veins; a relatively short leaf widest distance; and the smallest leaf area.
Subgroup A2: This cluster consists of 10 germplasm accessions (2 species and 8 cultivars). Key characteristics include major secondary spacing generally gradually or abruptly increasing proximally; intersecondary frequency is typically one or more than one per intercostal area; intercostal tertiary fabric is opposite percurrent; freely ending veinlets are mostly with one branch; a higher number of major secondary veins; a longer leaf widest distance; and a relatively small leaf area.
Subgroup A3: This cluster comprises 21 germplasm accessions (11 species and 10 cultivars). Key characteristics include major secondary spacing that generally gradually increases proximally or is irregular; an intersecondary frequency that is typically less than one per intercostal area; an intercostal tertiary fabric that is predominantly mixed percurrent; freely ending veinlets that mostly have one branch or are unbranched; fewer major secondary veins; the shortest leaf widest distance; and a relatively large leaf area.
Subgroup B1: This cluster includes 7 germplasm accessions (3 species and 4 cultivars). Key characteristics include major secondary spacing that is entirely regular; an intersecondary frequency that is typically less than one per intercostal area; an intercostal tertiary fabric that is predominantly opposite percurrent; freely ending veinlets that mostly have one branch or are unbranched; the highest number of major secondary veins; a longer leaf widest distance; and a relatively large leaf area.
Subgroup B2: This cluster consists of 13 germplasm accessions (12 species and 1 cultivar). Key characteristics include major secondary spacing that generally gradually increases proximally; an intersecondary frequency that is typically less than one per intercostal area; an intercostal tertiary fabric that is predominantly opposite or alternate percurrent; freely ending veinlets that mostly have one branch; the fewest major secondary veins; the longest leaf widest distance; and the largest leaf area.
2.5. Analysis of Ancestor-Inclined Distribution Characteristic in Malus Germplasm
The classification system of the genus Malus primarily falls into two categories: one, represented by Koehne [31], groups species based on the persistence of fruit calyx; the other, more influential system, proposed by Rehder [32], classifies species according to leaf lobing. This system has been further refined by Chinese scholars such as Yu Dejun [33], Li Yunong [34], and Qian Guanze [5]. Based on Qian Guanze’s [5] revised system, the 34 Malus species in this study belong to seven sections (Figure 3): Sect. Docyniopsis (2 species), Sect. Yunnanensis (2 species), Sect. Sorbomalus (4 species), Sect. Chloromeles (4 species), Sect. Malus (10 species), Sect. Gymnomeles (8 species), and Nothosect. Gymomalus (4 species).
The distribution of these seven sections across the two major clusters (A and B) was relatively balanced, accounting for 55.9% and 44.1%, respectively. Within the five subgroups, the species were predominantly distributed in A3 (32.4%) and B2 (35.3%). Specifically, Sect. Docyniopsis was found exclusively in subgroup B1, while Sect. Yunnanensis was evenly distributed between A3 (50%) and B2 (50%). Sect. Sorbomalus showed an uneven distribution, with 25% in A1 and 75% in B2. Sect. Chloromeles was evenly distributed across four subgroups (A1, A3, B1, and B2, each 25%). Sect. Malus exhibited an uneven distribution, with 10% in A1, 10% in A3, 40% in B1, and 40% in B2. Sect. Gymnomeles was unevenly distributed across A1 (37.5%), A2 (12.5%), A3 (37.5%), and B2 (12.5%). Finally, Nothosect. Gymomalus was evenly distributed between A3 (50%) and B2 (50%).
The distribution proportions of the aforementioned Malus species across the five subgroups are ranked as follows: B2 (92.3%) > A3 (52.4%) > B1 (42.9%) > A1 (27.3%) > A2 (20.0%). Given the relatively low proportions of Malus species in subgroups A1 and A2, these were merged with A3 to form a consolidated group A. We hypothesize that the evolutionary sequence of the three Malus germplasm groups (A, B1, B2) may be B1 → B2 → A. Aligning this with the evolutionary sequence of the three sections in the classical classification system (Sect. Docyniopsis → Sect. Sorbomalus → Sect. Malus) [35], we assigned values to these groups: B1 (1) → B2 (2) → A (3); Sect. Docyniopsis (1) → Sect. Sorbomalus (2) → Sect. Malus (3). The results revealed a highly significant correlation between these two sets of evolutionary data (R2 = 0.713, p < 0.01).
According to the literature [36,37,38], among the 39 tested Malus cultivars, 10 could be traced back to their full or partial parental origins, involving 7 parental species (Malus. baccata, M. baccata var. mandshurica, M. ×floribunda, M. halliana, M. ioensis, M. sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana, and M. toringo). These 10 cultivars exhibited distinct ancestor-inclined distribution characteristics across the two major groups (A, B) and the five subgroups (A1, A2, A3, B1, and B2), with ancestor-inclined distribution probabilities reaching 90.0% and 80.0%, respectively (Table 3). The breeding frequency of the seven parental species, ranked from highest to lowest, was as follows: M. toringo (35.0%) > M. halliana, M. ioensis, M. sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana (15.0%) > M. baccata var. mandshurica (10.0%) > M. baccata, M. × floribunda (5.0%).

Table 3.
Parent traceability and identification of ancestor-inclined distribution characteristics of Malus cultivars.
3. Discussion
3.1. Screening System for Macrostructural Classification Traits of Malus Leaves
Among plant organs, leaves exhibit the greatest number of traits [39]. During plant evolution, leaves display considerable plasticity and are highly susceptible to environmental factors such as light, temperature, and moisture [40]. Variations in leaf shape, epidermal characteristics, and anatomical structures can occur not only between species but also within species [41], highlighting the diversity and multidimensional nature of leaf macrostructures. However, an excessive number of variable dimensions can obscure the specificity of different subjects. Therefore, selecting representative traits is a critical aspect of numerical classification [42].
The study established a theoretical and technical framework for screening taxonomic leaf traits of Malus leaves: traits with low diversity and evenness were first eliminated through diversity and variability analysis → low-contribution traits were then removed via principal component analysis → strongly correlated traits were further excluded through correlation analysis. This process effectively identified 21 key leaf phenotypic traits. These traits collectively reflect the color, pubescence, shape, and size of Malus leaves, as well as the shape, number, structure, and development of leaf veins.
Consistent with this study, Chu et al. [43] conducted numerical classification on 28 M. halliana cultivars in Henan Province, finding that traits such as young leaf color and pubescence at flowering could serve as criteria for cultivar classification within the M. halliana group. Similarly, Feng et al. [28] compared the morphological characteristics of 25 Osmanthus fragrans cultivars (clones), identifying mature leaf color, leaf cross-section, and leaf width as primary classification criteria. This study further demonstrates that venation-related traits remain applicable for classification at the infraspecific level. This study provides supplementary morphological evidence for traditional taxonomy, advances quantitative systematics through leaf trait quantification, and establishes a theoretical and technical framework for screening phenotypic classification traits of Malus leaves. The developed system offers significant guidance for extracting macrostructural features of plant leaves.
3.2. Taxonomic Significance of Malus Leaf Macrostructures
Leaf venation, a two-dimensional branching network in plant leaves [44], plays a critical role in water transport efficiency, gas exchange rates, and overall plant performance [45]. Its structural organization reflects significant environmental adaptation strategies [46]. Strong constraints on environmental resources arise from selective pressures on leaf shape and function [17]. Studying the variation in leaf macrostructures can reveal interactions between genetics and the environment, reflecting the genetic patterns and extent of variation within populations.
In this study, cluster analysis based on the macrostructures of leaves from 73 Malus germplasms revealed that species within the same section were relatively concentrated in their distribution. The hypothesized evolutionary sequence of the three Malus germplasm groups (B1 → B2 → A) showed a highly significant correlation (R2 = 0.713, p < 0.01) with the evolutionary data of the three sections (Sect. Docyniopsis → Sect. Sorbomalus → Sect. Malus) in the classical classification system. Thus, the classification results of this study align well with the classical system represented by Rehder, providing insights into the evolutionary relationships among some sections. The study reveals that apparent inconsistencies between morphological and genetic data have emerged in recent taxonomic research [6]. At the species level, the clustering results demonstrate strong concordance with molecular phylogenetic studies:
Sect. Gymnomeles: M. hupehensis and M. domestica var. binzi cluster in A2, matching Zhou et al.’s [15] floral trait analyses. M. baccata and M. toringo form A1, corroborating Cho et al.’s [47] plastome characterization and comparative analyses evidence.
Sect. Malus: M. orientalis, M. domestica, and M. sylvestris group in A3, consistent with Liu et al. [7] and Höfer et al. [27]’s nuclear phylogenies.
Sect. Docyniopsis: M. tschonoskii and M. doumeri (primitive members) cluster in B1, aligning with Li et al.’s [6] and Forte et al.’s [8] molecular data.
Sect. Sorbomalus: M. fusca, M. daochengensis, and M. parttii form B2, supporting Forte et al.’s [8] hypothesis of their close affinity to Sorbomalus. Furthermore, only M. transitoria clustered within group A1, suggesting that the Sect. Sorbomalus likely comprises polyphyletic species. These validate that leaf macrostructures can be a reliable proxy for species delimitation in Malus, particularly when integrated with molecular data. However, certain discrepancies with molecular data persist—notably, the unexpectedly distant relationship between M. sieversii f. niedzwetzkyana and M. domestica—which warrant further investigation through multi-omics approaches.
At the cultivar level, among the 10 cultivars with fully or partially traceable parental origins, a clear ancestor-inclined distribution pattern was observed across the two major groups (A, B) and the five subgroups (A1, A2, A3, B1, B2), with ancestor-inclined distribution probabilities reaching 90.0% and 80.0%, respectively. This indicates that leaf macrostructures can be effectively applied to analyze genetic relationships among Malus germplasms. These findings align with the results of this study, suggesting that leaf macrostructures can serve as a reliable method for identification within genera or among species.
3.3. Evolutionary Trends in Malus Leaf Macrostructure and Breeding Implications
Phenotypic data analysis revealed that the most primitive group, B1, exhibited densely pubescent lower leaf surfaces, regular spacing of major secondary veins, and a high number of major secondary veins, with highly significant differences (p < 0.01) compared to the other four groups. Wang et al. [48] observed a trend from simple to complex in the surface ornamentation of pollen exine of Subgen. Yulania. Zhou et al. [49] discovered that crabapple floral organs exhibit a progressive decline in structural regularity from the species level to the cultivar level. Based on this, we hypothesize that the evolutionary trend of Malus leaf macrostructures is as follows: dense → sparse lower pubescence, high → low number of major secondary veins, and regular → irregular spacing of major secondary veins. Patterns of trait variation across resource and environmental gradients (light, water, nutrients, and temperature) probably reflect adaptation [50]. From an ecological functional perspective, the inferred evolutionary trend may reflect Malus taxa’s gradual adaptation to more stable, humid, and temperate environments, reducing selective pressures for defense and tolerance against extreme physical conditions (drought, intense light, high temperatures, strong winds). This adaptation manifests morphologically as decreased resource allocation to physical defense structures (pubescence) and costly hydraulic/support systems (number of major secondary veins). Notably, the selected traits exhibiting low intraspecific variability ( ≤ 10%) demonstrate environmental insensitivity, likely reflecting limited phenotypic plasticity of these specific traits across varying conditions. However, this study has certain limitations: leaf macrostructure may vary with age or growth conditions, the lack of molecular validation, potential blending of parental traits in hybrid offspring obscuring species boundaries, and convergent evolution potentially creating false homologies that may mislead morphology-based taxonomy. Consequently, the inferred taxonomic relationships should be interpreted with caution.
For a long time, ornamental crabapples have been important woody flowering plants in landscape design. Research on crabapple flower color [51], flowering period [4], and floral fragrance [52] has been relatively well established. With the continuous advancement of breeding efforts, variegated foliage varieties of ornamental crabapples, such as ‘Duojiao’ [53] and ‘Datang Tingliang’ [54], have emerged in recent years, providing additional dimensions for exploring ornamental traits in crabapples. This study found that cultivars with young leaves ranging from brown-red to purple-red, strong anthocyanin pigmentation, and red to purple petioles, including M. ‘Centurion’, M. ‘May’s Delight‘, and M. ‘Pink Prince’, clustered into a distinct group (A2). Building upon previous studies of ancestor-inclined distribution in floral organs [15] and pollen [14], we hypothesize that certain macrostructural leaf traits in Malus may be heritable across generations, with offspring exhibiting significant ancestor-inclined distribution patterns in cluster analyses. Breeding Implications: Selecting cultivars with vibrant leaf coloration from cluster A2 as parental lines for hybridization could facilitate the development of new ornamental-leaf cultivars. This strategy provides a targeted breeding framework, leveraging heritable leaf traits to achieve desired aesthetic characteristics. In breeding practices, it is essential to account for dominant/recessive inheritance patterns, polygenic control mechanisms, and the selection of parental lines based on pigment metabolic pathways. The study reveals that chlorophyll determines the fundamental coloration of Malus leaves [55]. During leaf development, chlorophyll and carotenoid content progressively increase while anthocyanin levels decrease, with chlorophyll concentrations consistently surpassing other pigments [56]. This dynamic results in the gradual greening of mature leaves and produces unstable color transition phases. Therefore, future research should integrate classification traits with ornamental traits, such as the duration and extent of color transition, to provide a more robust theoretical foundation for the breeding of foliage-focused crabapple varieties.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Site and Materials
A total of 73 Malus germplasms (34 species and 39 varieties) (Table 4) were used in this study, all sourced from the national repository of Malus germplasm in Yangzhou (Jiangdu District, Yangzhou City, Jiangsu Province, China, 119°55′ E, 32°42′ N). The trees, aged between 7 and 10 years, had reached the flowering and maturity stage.

Table 4.
The list of Malus germplasm.
4.2. Trait Measurement, Description, and Encoding
The selection of leaf macrostructure traits was conducted with reference to the Manual of Leaf Architecture [57]. Additionally, traits were further selected and supplemented based on their distinctiveness and recognizability. A total of 50 phenotypic traits of Malus leaves were selected, including 39 qualitative traits and 11 quantitative traits. From 2021 to 2024 (May to July), these traits were observed and recorded repeatedly over four consecutive years for validation and correction. Standard specimens (healthy trees with uniform growth vigor) were selected following the principles of typicality, standardization, and consistency. For each germplasm, a minimum of five randomly selected trees were sampled. From the sun-exposed, current-year shoots of each tree, mature leaves were collected from the mid-canopy region and pooled to form a composite sample of 30 leaves representing that germplasm. The leaf venation specimens of Malus were prepared using the clearing method [16]. After preparation, three complete leaf venation specimens from each germplasm were selected for observation and recording of traits using a stereomicroscope (Leica DM 5000 B, Germany), followed by scanning and photography. Quantitative traits of the leaves were measured using ImageJ software (version 1.53). Qualitative traits were encoded using ordinal numerical coding, employing a consecutive series of non-negative integers (0, 1, 2, 3, …). Binary traits were typically assigned 0 for “no” and 1 for “yes” [28]. Quantitative traits were directly used in numerical form for subsequent analysis (Table 5).

Table 5.
Description and encoding of phenotypic traits in Malus leaves.
4.3. Selection of Categorical Traits
(1) Qualitative Traits: The diversity, richness, and evenness of qualitative traits were assessed using Simpson’s Diversity Index (D), the Shannon–Wiener Information Index (H), and the Evenness Index (E). Traits were considered to meet the criteria of diversity, richness, and evenness if D ≥ 0.50, H ≥ 0.80, and E ≥ 0.60 [30].
where represents the total number of germplasms, denotes the number of germplasms classified into the -th level of each trait, and indicates the total number of levels for each trait.
(2) Quantitative Traits: The intraspecific uniformity and interspecific distinctness of quantitative traits were assessed using the mean coefficient of variation () and coefficient of variation () as described by Zhou et al. [15]. Traits were considered to meet the criteria of significant intraspecific uniformity and interspecific distinctness if ≤ 10% and ≥ 15% [15].
where is the number of germplasms, and represent the standard deviation and mean of observed values for each trait within a germplasm, while and denote the standard deviation and mean of trait values across all germplasms.
(3) Principal Component and Correlation Analysis: The original data were standardized to eliminate dimensional differences. Principal component analysis and correlation analysis were then conducted on the selected traits to further reduce dimensionality.
4.4. Cluster Analysis and Ancestor-Inclined Distribution Characteristic
The Euclidean distances of the screened leaf traits were calculated, followed by hierarchical clustering of Malus germplasms using the Ward.D2 linkage. The outline of the study procedure is shown in Figure 4. As shown in Figure 4, following the breeding pedigrees, when an offspring cultivar clusters within the same group/subgroup as one of its parental species, this indicates ancestor-inclined distribution. The ancestor-inclined distribution probability is calculated as the proportion of all pedigreed cultivars exhibiting this pattern.
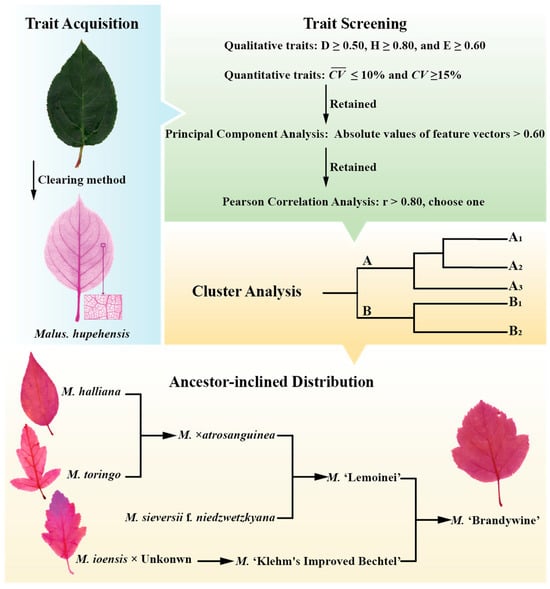
Figure 4.
Outline of the study procedure.
4.5. Data Processing
Principal component analysis and correlation analysis were performed using SPSS Statistics 26 [58]. Data visualization was conducted using the R 4.3.1 program [59]. The bar charts were plotted using the “ggplot2” package [60], the correlation heatmap was generated with the “corrplot” package [61], and the cluster analysis plot was created using the “ggsci” package [62].
5. Conclusions
This study presents the first comprehensive evaluation of Malus leaf macrostructures for infraspecific classification. Many scholars have investigated the origins and phylogenetic relationships of Malus species using herbarium specimens, numerical analyses, nuclear phylogenetics, and DNA sequencing—yet largely overlooked the critical taxonomic value of leaf macrostructure. This study established a theoretical and technical system for screening leaf phenotypic classification traits in Malus, which can effectively reduce the dimensionality of numerous leaf phenotypic traits and identify traits that are high diversity, abundance, and evenness, as well as significant intraspecific uniformity and interspecific distinctness. These traits can serve as a reliable basis for the classification of Malus germplasm. In the cluster analysis, species within the same group exhibited relatively concentrated distributions, and traceable cultivars showed clear ancestor-inclined distribution characteristics. The hypothesized evolutionary sequence of the three groups (B1 → B2 → A) showed a highly significant correlation with the evolutionary data of the three sections (Sect. Docyniopsis → Sect. Sorbomalus → Sect. Malus) in the classical classification system. Therefore, the phenotypic variation in Malus leaf macrostructures can effectively elucidate phylogenetic relationships within the genus Malus, providing novel perspectives for infraspecific taxonomic studies. The diversity of young leaf colors offers valuable references for ornamental leaf-type cultivar selection. However, this study has certain limitations: the lack of molecular validation, potential blending of parental traits in hybrid offspring obscuring species boundaries, and convergent evolution potentially creating false homologies that may mislead morphology-based taxonomy. Consequently, the inferred taxonomic relationships should be interpreted with caution. Future studies should integrate molecular phylogenetics and controlled horticultural experiments to evaluate phenotypic plasticity and decipher complex hybridization histories.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.F. and W.Z.; methodology, Y.F. and T.Z.; software, H.L.; validation, H.L. and J.M.; formal analysis, Y.F. and H.L.; investigation, H.L. and J.M.; resources, W.Z.; data curation, Y.F. and H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.F.; writing—review and editing, J.F. and T.Z.; supervision, W.Z.; funding acquisition, W.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Jiangsu Forestry Science and Technology Innovation and Promotion Project, Jiangsu Provincial Forestry Bureau, China (No. LYKJ [2024] 03).
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
Thank you for the test materials provided by the National Crabapple Germplasm Center of Yangzhou, China.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhou, T.; Shen, X.C.; Zhou, D.J.; Fan, J.J.; Zhao, M.M.; Zhang, W.X.; Cao, F.L. Advances in the Classification of Crabapple Cultivars. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2018, 45, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.R.; Zhang, W.X.; Di, C.Y.; Lu, X.J. Leaf Color and Pigments of 48 Ornamental Crabapple Germplasms Leaves. Fujian J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 37, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.Z.; Tang, G.G. A Review on the Plant Taxonomic Study on the Genus Malus Miller. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.). 2005, 29, 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, W.Y.; Fan, J.J.; Zhang, W.X. Phenological stability of ornamental crabapple and its response to temperature change. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2020, 44, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.Z. Research on the Taxonomy of the Genus Malus Mill. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.C.; Liu, J.Q.; Gao, X.F. A Revision of the Genus Malus Mill. (Rosaceae). Eur. J. Taxon. 2022, 853, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.B.; Ren, C.; Kwak, M.; Hodel, R.G.J.; Xu, C.; He, J.; Zhou, W.B.; Huang, C.H.; Ma, H.; Qian, G.Z.; et al. Phylogenomic Conflict Analyses in the Apple Genus Malus s.l. Reveal Widespread Hybridization and Allopolyploidy Driving Diversification, with Insights into the Complex Biogeographic History in the Northern Hemisphere. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 1020–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, A.V.; Ignatov, A.N.; Ponomarenko, V.V.; Dorokhov, D.B.; Savelyev, N.I. Phylogeny of the Malus (Apple Tree) Species, Inferred from the Morphological Traits and Molecular DNA Analysis. Russ. J. Genet. 2002, 38, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzak, J.; Paprštein, F.; Henychová, A.; Sedlák, J. Comparison of Genetic Diversity Structure Analyses of SSR Molecular Marker Data within Apple (Malus × Domestica) Genetic Resources. Genome 2012, 55, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kišek, M.; Jarni, K.; Brus, R. Hybridisation of Malus Sylvestris (L.) Mill. with Malus × Domestica Borkh. and Implications for the Production of Forest Reproductive Material. Forests 2021, 12, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo Santalla, P.; Chu, N.T.; Georges, D. Characterisation of crabapple Clones by Isozyme Electrophoresis. Acta Hortic. 2000, 508, 301–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Zhao, M.M.; Fan, J.J.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Y.X.; Cao, F.L. Study on Relationship between Pollen Exine Ornamentation Pattern and Germplasm Evolution in Flowering Crabapple. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltis, E.D.; Soltis, P.S. Contributions of Plant Molecular Systematics to Studies of Molecular Evolution. In Plant Molecular Evolution; Doyle, J.J., Gaut, B.S., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 45–75. ISBN 978-94-010-5833-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.P.; Peng, Y.; Ma, J.Z.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhao, M.M.; Zai, X.M. Characteristics of Phenotypic Variation of Malus Pollen at Infrageneric Scale. Plants 2024, 13, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Ning, K.; Zhang, W.X.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.Q.; Zhang, D.L.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Bian, J. Phenotypic Variation of Floral Organs in Flowering Crabapples and Its Taxonomic Significance. Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Shen, K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.Q. Study on Venation Characteristics of 25 Sorbus Species. Wild Plant Resour. 2022, 41, 8–14+24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonder, B.; Violle, C.; Bentley, L.P.; Enquist, B.J. Venation Networks and the Origin of the Leaf Economics Spectrum. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Yu, X.L.; Li, J.X. Characteristcs of the leave venation for species of styrax from Hunan and their significances on plant classification. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2010, 30, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.G.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, C.R.; Song, X.H.; Ye, C. Leaf Architecture of Eurya and its Taxonomic Significance. Bull. Bot. Res. 2009, 29, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.M.; Wang, Z.X.; Cao, M.; Liu, J.H.; Lin, Q.; Xia, N.H. Leaf Venation and Its Systematic Significance in Sapindaceae of China. Plant Divers. Resour. 2014, 36, 419–432. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=GkDm8A2i92Ua6vqCVyzpyk10ne67G_oolEuBGUmG_hABK5RdP0wIQc-vzstNhxOoN3NTPITXkwal7GFQ-z66BEWzJjq282qNAzm77GPr7D-_-31ZdMAXAFweKGjE0KK9cXx0CDt-ecMPKBbbShYRTbQkbJ-9APA_y1vkbDxCJdneLGZcmpPc9w==&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Huang, W.X. Leaf Architecture of Genus Prunus L. sensulato (s. l.) and Its Taxonomic Significance. Master’s Thesis, South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.F.; Li, M.; Huang, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.R. Leaf venation characteristics of simple-leavedtaxa of Sorbus in China. Guihaia 2022, 42, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Q.; Liu, P.L.; Shen, K.; Wang, Y.K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.Q. Leaf Venation Patterns of Fourteen Species of Berberis in Shaanxi Province. Shaanxi For. Sci. Technol. 2021, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.Y.; Luo, T.; Zhang, N. Leaf Structure Characteristics of Five Species of Cymbidium. Plant Sci. J. 2019, 37, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.N. The Taxonomic Significance of Embryo Sac Development, Leaf Vein Type and Carpel Number to Malus hupehensis and Its Related Species. Master’s Thesis, Liaocheng University, Liaocheng, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, C.; Singh, S.K.; Pramanick, K.K.; Verma, M.K.; Srivastav, M.; Singh, R.; Bharadwaj, C.; Naga, K.C. Morphological and Biochemical Diversity among the Malus Species Including Indigenous Himalayan Wild Apples. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 233, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfer, M.; Eldin Ali, M.A.M.S.; Sellmann, J.; Peil, A. Phenotypic Evaluation and Characterization of a Collection of Malus Species. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2014, 61, 943–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Huang, J.H.; Hu, S.Q. Numerical classification of 25 color-leafed Osmanthus fragrans clones (cultivars). J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 45, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.N.; Feng, T.J.; Sun, L.; Liu, X.R.; Liu, Y.B.; Wang, P. Differences and influencing factors of understory vegetation species diversity between typical plantations and natural forests in the loess area of western Shanxi Province, northern China. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2025, 47, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.F.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhu, L.L.; Jiang, H.; Sun, T.T.; Yu, W.W. Phenotypic diversity analysis of fruit traits of 78 North American crabapple cultivars. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 1–12. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/32.1161.S.20240428.0943.002 (accessed on 28 April 2024).
- Koehne, B.A.E. Deutsche Dendrologie; Verlag von Ferdinand Enke: Stuttgart, Germany, 1893. [Google Scholar]
- Rehder. Manual of Cultivated Trees and Shrubs in North America; Macmillan Company: New York, NY, USA, 1940. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.J. Taxonomy of Deciduous Fruit Trees; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N. Research of Germplasm Resources of Malus Mill; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2001; ISBN 7-109-06805-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.N. Progress in Research on the Origin and Evolution of Genus Malus in the World. J. Fruit Sci. 1999, 16, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiala, J.L.; Daniels, G.S. Flowering Crabapples: The Genus Malus; Timber Press: Portland, OR, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Qu, X.L.; Guo, L.; Sun, F.Y.; Mao, Z.Q.; Shen, X. Advances on Ornamental Crabapple Resources. J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2008, 39, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Zhou, S.L.; Zhang, Z.S.; Shen, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, D.L.; Shu, H.R. Relationships of Species, Hybrid Species and Cultivars in Genus Malus Revealed by AFLP Markers. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2009, 45, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bodor-Pesti, P.; Taranyi, D.; Deák, T.; Nyitrainé Sárdy, D.Á.; Varga, Z. A Review of Ampelometry: Morphometric Characterization of the Grape (Vitis Spp.) Leaf. Plants 2023, 12, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Shi, Z.M.; Feng, Q.H.; Liu, F. Response of leaf morphometric traits of Quercus species to climate in the temperate zone of the North-South Transect of Eastern China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, L.; Ni, X.L.; Li, J. Study on the Developmental Anatomy of Structures and AerenchymaFormation in Potamogeton perfoliatus Stems and Leaves. Acta Bot. Boreal.-Occident. Sin. 2018, 38, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.; Hu, Z.M. Mathematic Classification of 46 Species in Rhododendron with the Morphologic Characters. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2009, 45, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, A.X.; Yang, Y.J.; Tang, G.G.; Tong, L.L. Studies on Numerical Taxonomy of the Malus halliana Koehne Cultivars in Henan. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2009, 36, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth Nebelsick, A.; Uhl, D.; Mosbrugger, V.; Kerp, H. Evolution and Function of Leaf Venation Architecture: A Review. Ann. Bot. 2001, 87, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.Q.; Xiong, Y.J.; Yin, M.Q.; Wang, X.L.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, Z.F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Yang, D.M. Leaf Venation Architecture in Relation to Leaf Size Across Leaf Habits and Vein Types in Subtropical Woody Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 873036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollman, R.; Çiftçi, A.; Kaleli, B.S.; Erol, O. Teasing out Elevational Trends in Infraspecific Prunus Taxa: A Vein Analysis Approach. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2023, 86, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Yamada, T.; Maki, M.; Kim, S.-C. Plastome Characterization and Comparative Analyses of Wild Crabapples (Malus Baccata and M. Toringo): Insights into Infraspecific Plastome Variation and Phylogenetic Relationships. Tree Genet. Genomes 2021, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Cao, Y.; Guo, W.; Ma, L.; Liu, X.L. Morphological Characteristics of Pollen from 44 Species of Subgen. Yulania. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2023, 50, 2417–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhang, D.L.; El-Kassaby, Y.A.; Fan, J.J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, G.B.; Cao, F.L. A Binary-Based Matrix Model for Malus Corolla Symmetry and Its Variational Significance. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Wright, I.J.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Craine, J.M.; Oleksyn, J.; Westoby, M.; Walters, M.B. The Evolution of Plant Functional Variation: Traits, Spectra, and Strategies. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2003, 164, S143–S164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Fan, J.J.; Jiang, W.L.; Zhang, W.X.; Wang, G.P. Analysis and evaluation on flower color characteristics of the Malus ‘Purple Prince’ half- sib progenies. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 43, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.J.; Zhang, W.X.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, D.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.B.; Cao, F.L. Discrimination of Malus Taxa with Different Scent Intensities Using Electronic Nose and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Sensors 2018, 18, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Mao, Y.F.; Zhang, C.H.; Zhang, D.J.; Shen, X. A New Ornamental Crabapple Cultivar ‘Duojiao’. Acta Hortic. 2019, 46, 2908–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.J.; Huang, Y.; Wan, S.W.; Zhang, R.F.; Ma, R.Q.; Sun, J.L.; Sha, G.L. Malus ‘Datang Tingliang’: A new ornamental crabapple cultivar. J. Nanjing For. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 46, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, W.X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Zhao, P.P. Changes of Leaf Color and Dynamics of Pigment Componentsin Ornamental Crabapple. North. Hortic. 2021, 4, 57–63. Available online: http://bfyy.paperonce.org/oa/DArticle.aspx?type=view&id=20201172 (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Han, W.X.; Jiang, H.; Bian, J.; Yun, J.H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Peng, Y. Leaf color change and its correlation with pigment content in 10 ornamental crabapple varieties in spring. J. Zhejiang Univ. Agric. Life Sci. 2020, 46, 562–570. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, B.; Daly, D.; Hickey, L.; Johnson, K.; Mitchell, J.; Wilf, P.; Wing, S. Manual of Leaf Architecture; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-84593-584-9. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics forWindows; Armonk: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot (accessed on 19 June 2025).
- Xiao, N. Ggsci: Scientific Journal and Sci-Fi Themed Color Palettes for “Ggplot2”. 2024. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggsci (accessed on 19 June 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).