Genome-Wide In Silico Identification and Comparative Analysis of Dof Gene Family in Brassica napus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characterisation of BRASSICA Napus Dof Gene Family
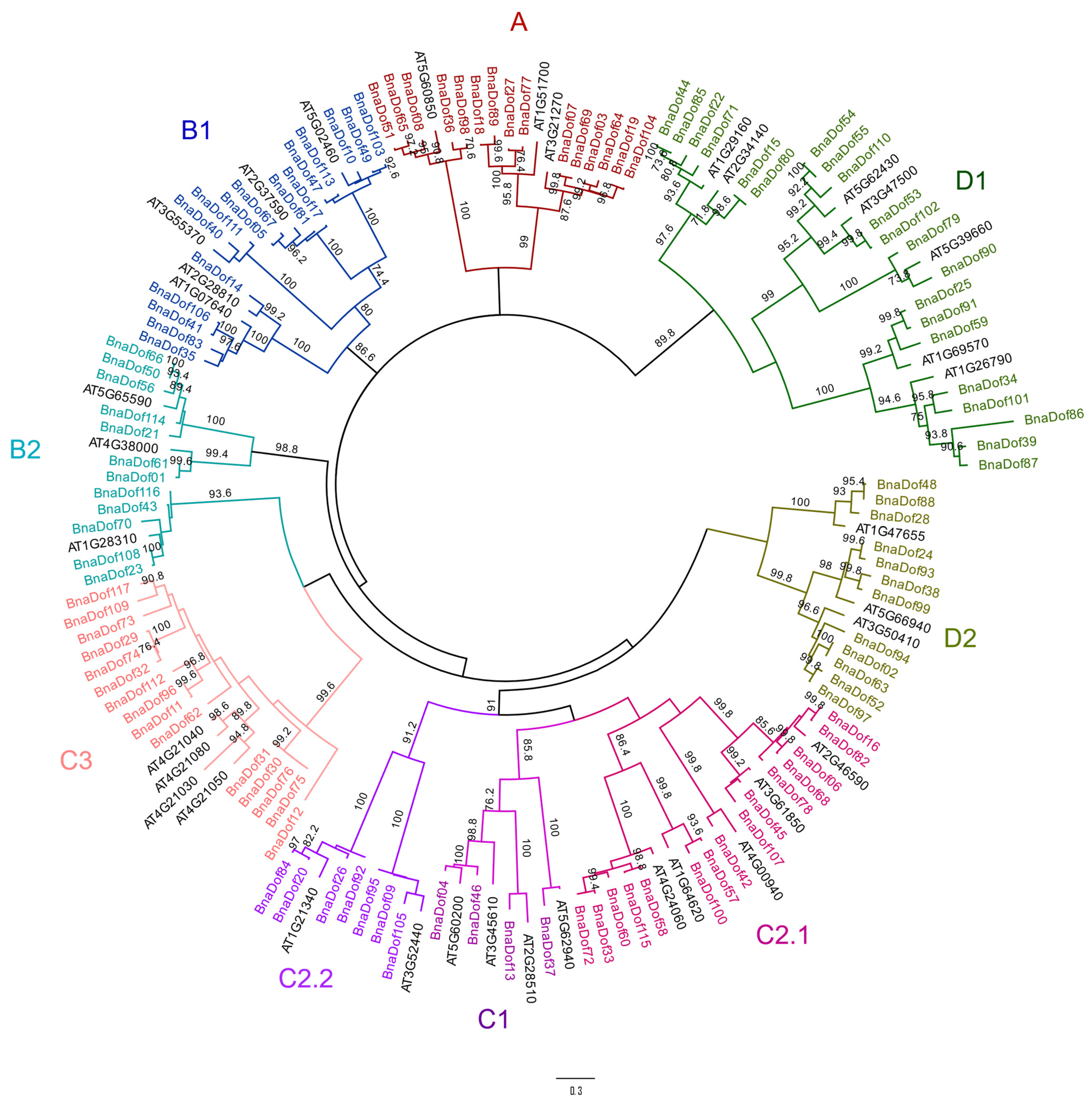
2.2. Phylogenetic Relationships of the Dof Gene Family in B. napus
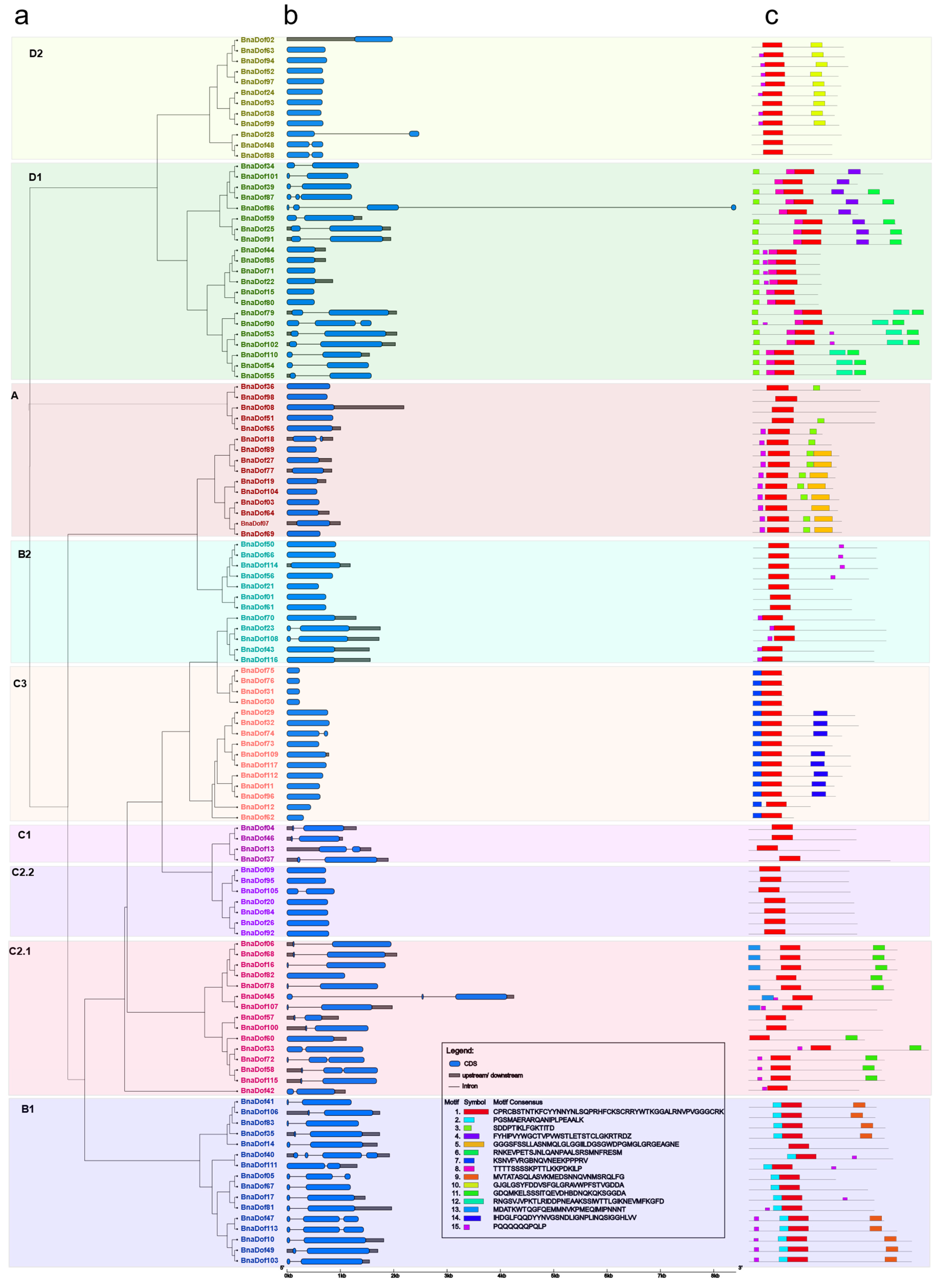
2.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motifs of BnaDofs
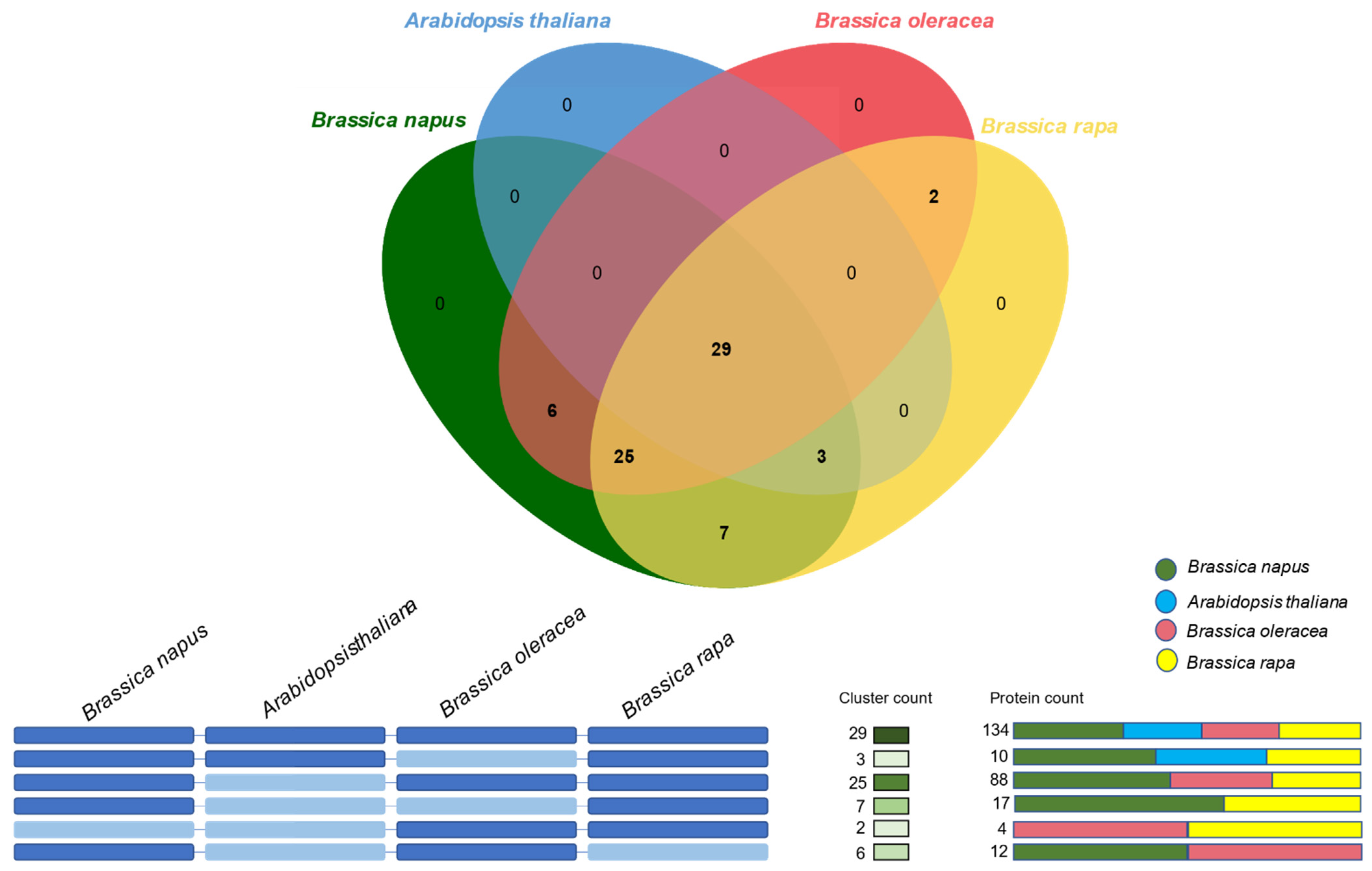
2.4. Orthologous Gene Clustering of Dof Gene Family in B. napus, B. oleracea, B. rapa, and Arabidopsis
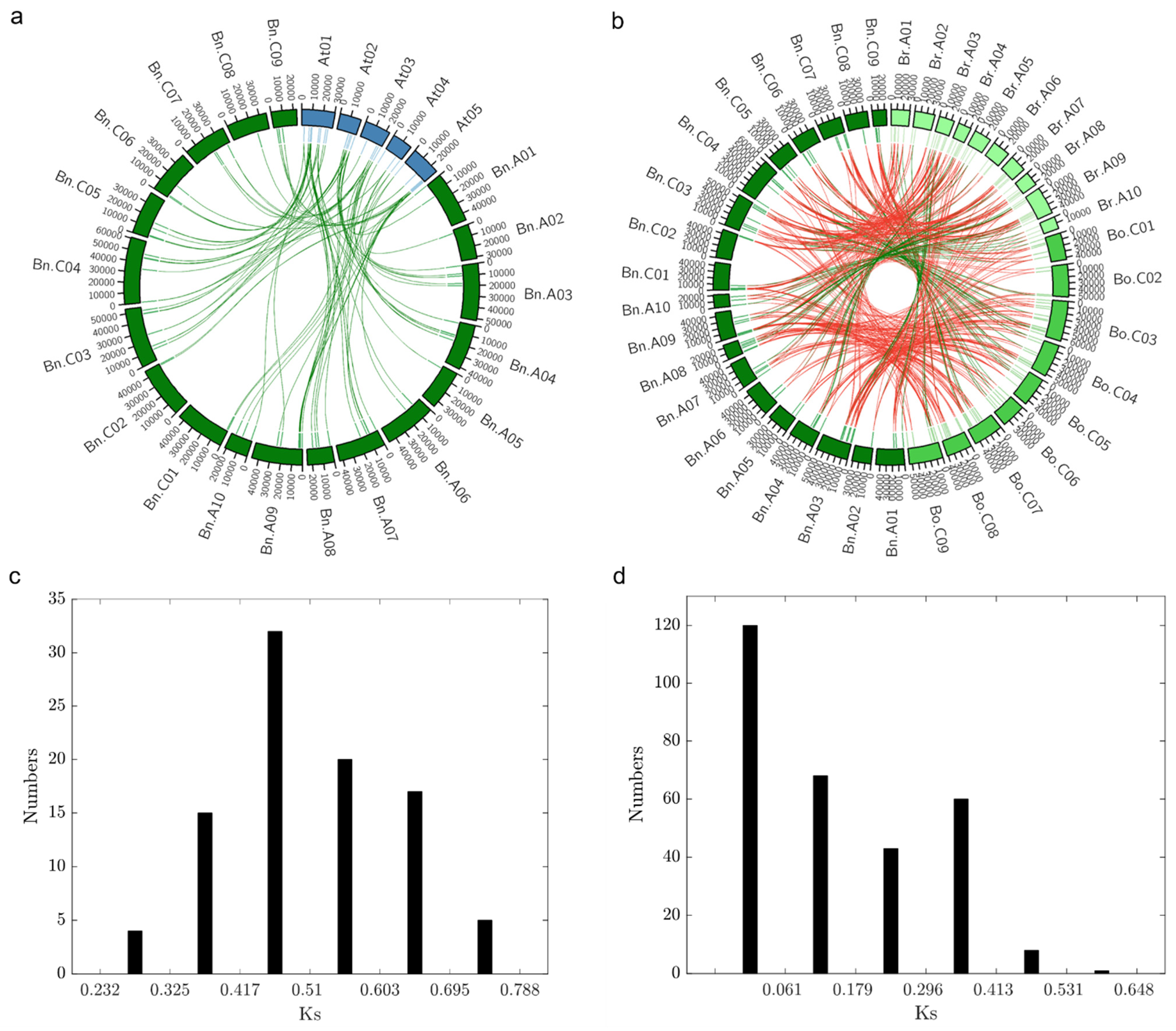
2.5. Evolution and Divergence of BnaDofs
2.6. Functional Annotation of BnaDofs and Promoter Analysis
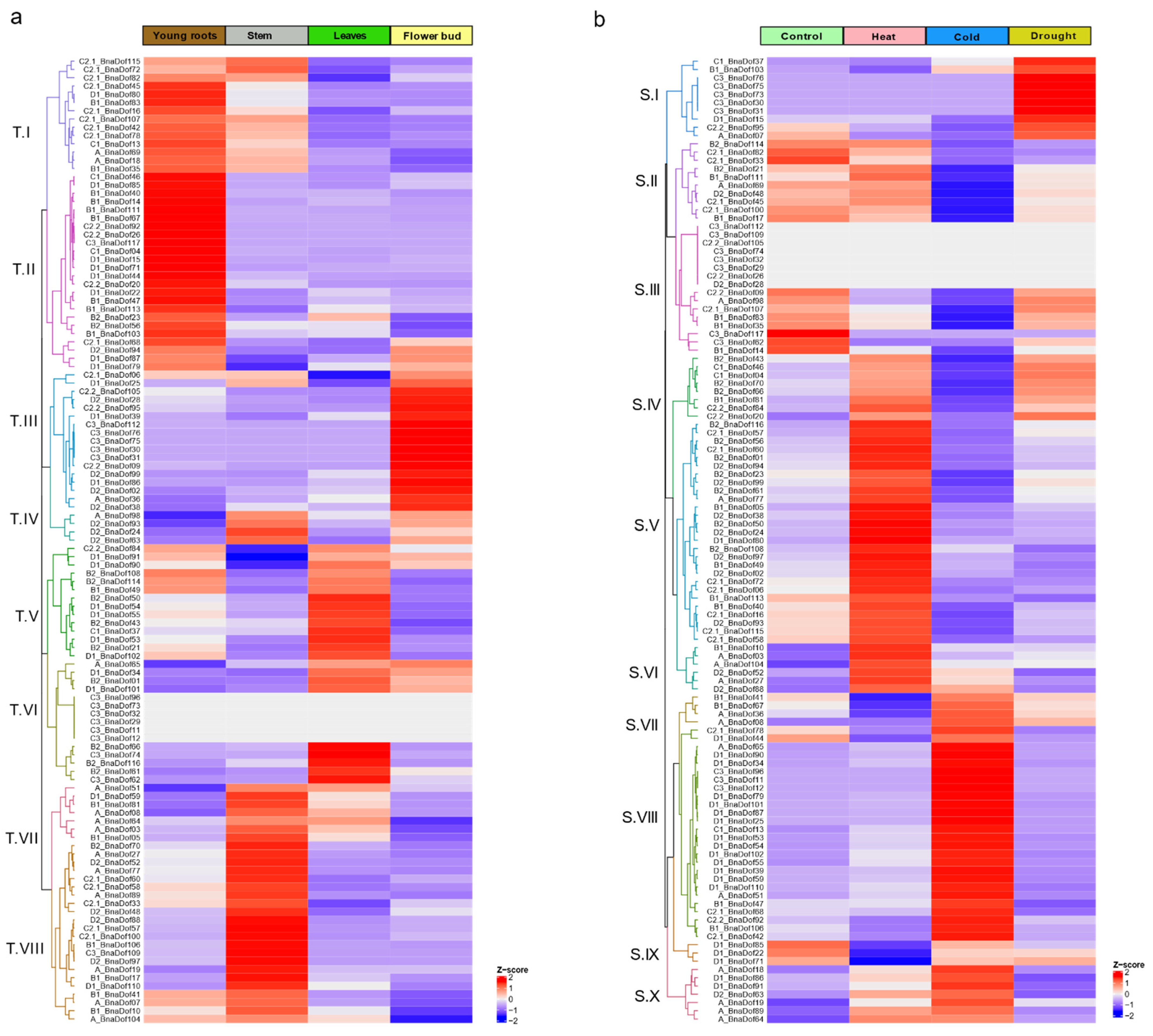
2.7. Tissue-Specific and Abiotic Stress-Responsive Expression Profiling of BnaDofs
3. Discussion
3.1. Systematic Analysis of BnaDofs
3.2. Expansion and Divergence of the Dof Gene Family in B. napus
3.3. Distinct Expression Patterns of BnaDofs during Development
3.4. Potential Role of BnaDofs in Abiotic Stress Response
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of Dof Gene Family Members in B. napus
4.2. Evolutionary and Gene Duplication Analysis of BnaDofs
4.3. Gene Structure and Motif Analysis of BnaDofs
4.4. Functional Annotation and Promoter Analysis
4.5. Orthology and Collinearity Analysis of BnaDofs
4.6. Tissue-Specific Expression and Abiotic Stress Response Expression Profiling of BnaDofs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA, F.A.S. Oilseeds: World Markets and Trade; USDA Foreign Agricultural Service: Wasington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lohani, N.; Jain, D.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Engineering Multiple Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Canola, Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, S. A novel DNA-binding domain that may form a single zinc finger motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 3403–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, S.; Sheen, J. Involvement of maize Dof zinc finger proteins in tissue-specific and light-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, S. Dof1 and Dof2 transcription factors are associated with expression of multiple genes involved in carbon metabolism in maize. Plant J. 2000, 21, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagisawa, S. The Dof family of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijavetzky, D.; Carbonero, P.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J. Genome-wide comparative phylogenetic analysis of the rice and Arabidopsis Dof gene families. BMC Evol. Biol. 2003, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, N.; Deng, X.; Liu, D.; Li, M.; Cui, D.; Hu, Y.; Yan, Y. Genome-wide analysis of wheat DNA-binding with one finger (Dof) transcription factor genes: Evolutionary characteristics and diverse abiotic stress responses. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, H.; Iwabuchi, M.; Meshi, T. Arabidopsis GARP transcriptional activators interact with the Pro-rich activation domain shared by G-box-binding bZIP factors. Plant Cell Physiol. 2002, 43, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, S. Dof domain proteins: Plant-specific transcription factors associated with diverse phenomena unique to plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hir, R.; Bellini, C. The plant-specific dof transcription factors family: New players involved in vascular system development and functioning in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, Y.; Ishiduka, T.; Yamamoto, R.; Esaka, M. The Dof domain, a zinc finger DNA-binding domain conserved only in higher plants, truly functions as a Cys2/Cys2 Zn finger domain. Plant J. 2004, 37, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, J.; Mueller-Roeber, B.; Ruzicic, S. A novel bipartite nuclear localization signal with an atypically long linker in DOF transcription factors. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, B.; Denoeud, F.; Liu, S.; Parkin, I.A.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Chiquet, J.; Belcram, H.; Tong, C.; Samans, B. Early allopolyploid evolution in the post-Neolithic Brassica napus oilseed genome. Science 2014, 345, 950–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wu, J.; Cai, X.; Liang, J.; Freeling, M.; Wang, X. Gene retention, fractionation and subgenome differences in polyploid plants. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Tong, C.; Edwards, D.; Parkin, I.A.; Zhao, M.; Ma, J.; Yu, J.; Huang, S. The Brassica oleracea genome reveals the asymmetrical evolution of polyploid genomes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, S.; Bai, Y.; Mun, J.-H.; Bancroft, I.; Cheng, F. The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.-C.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, gkw982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korf, I.; Yandell, M.; Bedell, J. Blast; O’Reilly Media Inc., 2003. Available online: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/blast/0596002998/ (accessed on 7 April 2021).
- Ma, J.; Li, M.-Y.; Wang, F.; Tang, J.; Xiong, A.-S. Genome-wide analysis of Dof family transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipka, V.; Kwon, C.; Panstruga, R. SNARE-ware: The role of SNARE-domain proteins in plant biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 23, 147–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nei, M.; Dudley, J.; Tamura, K. MEGA: A biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief. Bioinform. 2008, 9, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Dong, Z.; Fang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Y.Q.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Xia, Q. OrthoVenn2: A web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W52–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-h.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bielawski, J.P. Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2000, 15, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Vang, S.; Yu, J.; Wong, G.K.-S.; Wang, J. Correlation between Ka/Ks and Ks is related to substitution model and evolutionary lineage. J. Mol. Evol. 2009, 68, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Haubold, B.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Molecular systematics of the Brassicaceae: Evidence from coding plastidic matK and nuclear Chs sequences. Am. J. Bot. 2001, 88, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Bishop, J.; Mitchell-Olds, T.; Koch, M. Molecular systematics and evolution of Arabidopsis and Arabis. Plant Biol. 1999, 1, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, F.; Trick, M.; Drou, N.; Lim, Y.P.; Park, J.-Y.; Kwon, S.-J.; Kim, J.-A.; Scott, R.; Pires, J.C.; Paterson, A.H. Comparative analysis between homoeologous genome segments of Brassica napus and its progenitor species reveals extensive sequence-level divergence. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1912–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.A.; Haubold, B.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Comparative evolutionary analysis of chalcone synthase and alcohol dehydrogenase loci in Arabidopsis, Arabis, and related genera (Brassicaceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2000, 17, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Genome triplication drove the diversification of Brassica plants. Hortic. Res. 2014, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Adams, K.L. Global insights into duplicated gene expression and alternative splicing in polyploid Brassica napus under heat, cold, and drought stress. Plant Genome 2020, 13, e20057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Hu, T.; Ye, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Li, H.; Ye, Z. Genome—Wide analysis of plant—Specific Dof transcription factor family in tomato. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2013, 55, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, J.; Cui, J.; Xu, X.; Liang, G.; Luo, X.; Chen, X.; Tang, X.; Hu, K.; Qin, C. Genome-wide identification and expression profile of Dof transcription factor gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.-l.; Cheng, Q.; Zhao, L.; Mao, A.; Yang, J.; Yu, S.; Weng, Y.; Xu, Y. Identification and characterisation of Dof transcription factors in the cucumber genome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriele, S.; Rizza, A.; Martone, J.; Circelli, P.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. The Dof protein DAG1 mediates PIL5 activity on seed germination by negatively regulating GA biosynthetic gene AtGA3ox1. Plant J. 2010, 61, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santopolo, S.; Boccaccini, A.; Lorrai, R.; Ruta, V.; Capauto, D.; Minutello, E.; Serino, G.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. DOF AFFECTING GERMINATION 2 is a positive regulator of light-mediated seed germination and is repressed by DOF AFFECTING GERMINATION 1. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, G.; Veciana, N.; Boix, M.; Rovira, A.; Henriques, R.; Monte, E. The photoperiodic response of hypocotyl elongation involves regulation of CDF1 and CDF5 activity. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 169, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, L.M.; McIntyre, C.L.; Gresshoff, P.M.; Xue, G.-P. Members of the Dof transcription factor family in Triticum aestivum are associated with light-mediated gene regulation. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2009, 9, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornara, F.; Panigrahi, K.C.; Gissot, L.; Sauerbrunn, N.; Rühl, M.; Jarillo, J.A.; Coupland, G. Arabidopsis DOF transcription factors act redundantly to reduce CONSTANS expression and are essential for a photoperiodic flowering response. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, A.-R.; Nebauer, S.G.; Carrillo, L.; Fernández-Nohales, P.; Marqués, J.; Renau-Morata, B.; Granell, A.; Pollmann, S.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Molina, R.-V. Characterization of tomato Cycling Dof Factors reveals conserved and new functions in the control of flowering time and abiotic stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, A.R.; Carrillo, L.; Lasierra, P.; Nebauer, S.G.; Dominguez-Figueroa, J.; Renau-Morata, B.; Pollmann, S.; Granell, A.; Molina, R.V.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J. Multifaceted role of cycling DOF factor 3 (CDF3) in the regulation of flowering time and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis. PlantCell Environ. 2017, 40, 748–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.W.; Zhang, B.; Hao, Y.J.; Huang, J.; Tian, A.G.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. The soybean Dof-type transcription factor genes, GmDof4 and GmDof11, enhance lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant J. 2007, 52, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Liang, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ijaz, B.; Hua, J. Overexpression of GhDof1 improved salt and cold tolerance and seed oil content in Gossypium hirsutum. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 218, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, J. Maize transcription factor Zmdof1 involves in the regulation of Zm401 gene. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 66, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, L.; Lei, W.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Gao, J.; Cheng, J.; Sun, Y.; Fan, Z.; Yu, D. Genome-wide identification of cold responsive transcription factors in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renau-Morata, B.; Carrillo, L.; Dominguez-Figueroa, J.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Molina, R.V.; Nebauer, S.G.; Medina, J. CDF transcription factors: Plant regulators to deal with extreme environmental conditions. J. Exp. Bot. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, R.; Liang, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, J. Genome-wide identification and analysis of the EIN3/EIL gene family in allotetraploid Brassica napus reveal its potential advantages during polyploidization. Bmc Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, B.-S.; Choi, S.S. Introns: The functional benefits of introns in genomes. Genom. Inform. 2015, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohani, N.; Golicz, A.A.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Genome-wide analysis of the Hsf gene family in Brassica oleracea and a comparative analysis of the Hsf gene family in B. oleracea, B. rapa and B. napus. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 515–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, M.; Xu, W.; Lin, A.; Lu, K.; Li, J. Genome wide identification and comparative analysis of glutathione transferases (GST) family genes in Brassica napus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Shi, L.; Xu, F.; Ding, G. Genome-Wide Dissection of the CRF Gene Family in Brassica napus Indicates that BnaCRF8s Specifically Regulate Root Architecture and Phosphate Homeostasis against Phosphate Fluctuation in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Hu, J.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Feng, S.; Li, M.; Li, N.; Song, X. Identification, evolution and expression analyses of whole genome-wide TLP gene family in Brassica napus. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, K.; Kong, L.; Yu, S.; Li, R.; Liu, K.; Yu, X. Comparative analysis of basic helix–loop–helix gene family among Brassica oleracea, Brassica rapa, and Brassica napus. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguero, M.; Atif, R.M.; Ochatt, S.; Thompson, R.D. The role of the DNA-binding One Zinc Finger (DOF) transcription factor family in plants. Plant Sci. 2013, 209, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruta, V.; Longo, C.; Lepri, A.; De Angelis, V.; Occhigrossi, S.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. The DOF Transcription Factors in Seed and Seedling Development. Plants 2020, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Risueno, M.Á.; Díaz, I.; Carrillo, L.; Fuentes, R.; Carbonero, P. The HvDOF19 transcription factor mediates the abscisic acid-dependent repression of hydrolase genes in germinating barley aleurone. Plant J. 2007, 51, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legris, M.; Nieto, C.; Sellaro, R.; Prat, S.; Casal, J.J. Perception and signalling of light and temperature cues in plants. Plant J. 2017, 90, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinomura, T.; Nagatani, A.; Chory, J.; Furuya, M. The induction of seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana is regulated principally by phytochrome B and secondarily by phytochrome A. Plant Physiol. 1994, 104, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualberti, G.; Papi, M.; Bellucci, L.; Ricci, I.; Bouchez, D.; Camilleri, C.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. Mutations in the Dof zinc finger genes DAG2 and DAG1 influence with opposite effects the germination of Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1253–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.H.; Lim, P.O.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, D.S.; Hong, S.H.; Nam, H.G. The Arabidopsis COG1 gene encodes a Dof domain transcription factor and negatively regulates phytochrome signaling. Plant J. 2003, 34, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papi, M.; Sabatini, S.; Bouchez, D.; Camilleri, C.; Costantino, P.; Vittorioso, P. Identification and disruption of an Arabidopsis zinc finger gene controlling seed germination. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.M.; Cufr, C.A.; Denzel, M.A.; Neff, M.M. The Dof transcription factor OBP3 modulates phytochrome and cryptochrome signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yuan, T.; Tarkowská, D.; Kim, J.; Nam, H.G.; Novák, O.; He, K.; Gou, X.; Li, J. Brassinosteroid biosynthesis is modulated via a transcription factor cascade of COG1, PIF4, and PIF5. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, J.; Martínez-Almonacid, I.; Sonntag, A.; Molina, I.; Moya-Cuevas, J.; Bissoli, G.; Muñoz-Bertomeu, J.; Faus, I.; Niñoles, R.; Shigeto, J. PRX2 and PRX25, peroxidases regulated by COG1, are involved in seed longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Araki, T.; Endo, M. Circadian clock during plant development. J. Plant Res. 2018, 131, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.H.; Ito, S.; Imaizumi, T. Flowering time regulation: Photoperiod-and temperature-sensing in leaves. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, T.; Schultz, T.F.; Harmon, F.G.; Ho, L.A.; Kay, S.A. FKF1 F-box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science 2005, 309, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.S.; Kubota, A.; Imaizumi, T. Circadian clock and photoperiodic flowering in Arabidopsis: CONSTANS is a hub for signal integration. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dai, H. Brassica napus Cycling Dof Factor1 (BnCDF1) is involved in flowering time and freezing tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 80, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rueda-Romero, P.; Barrero-Sicilia, C.; Gómez-Cadenas, A.; Carbonero, P.; Oñate-Sánchez, L. Arabidopsis thaliana DOF6 negatively affects germination in non-after-ripened seeds and interacts with TCP14. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, A.; Mejia-Guerra, M.K.; Kurz, K.; Liang, X.; Welch, L.; Grotewold, E. AGRIS: The Arabidopsis gene regulatory information server, an update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 39 (Suppl. 1), D1118–D1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.P.; Onodera, Y.; Touno, S.M.; Takaiwa, F. Synergism between RPBF Dof and RISBZ1 bZIP activators in the regulation of rice seed expression genes. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, M.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J.; Schmidt, R.J.; Carbonero, P. An endosperm-specific DOF protein from barley, highly conserved in wheat, binds to and activates transcription from the prolamin-box of a native B-hordein promoter in barley endosperm. Plant J. 1998, 16, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Zhou, W.; Dong, Q.; Jiang, H.; Cheng, B. The DOF-domain transcription factor ZmDOF36 positively regulates starch synthesis in transgenic maize. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, S.; Matsunaga, S.; Yonemura, M.; Uchiyama, S.; Azuma, T.; Fukui, K. Identification of a novel plant MAR DNA binding protein localized on chromosomal surfaces. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, H.; Ludlow, R.A.; Lu, M.; An, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of Dof Genes and Their Response to Abiotic Stress in Rose (Rosa chinensis). Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Gao, X.; Ma, K.; Li, D.; Jia, C.; Zhai, M.; Xu, Z. The walnut transcription factor JrGRAS2 contributes to high temperature stress tolerance involving in Dof transcriptional regulation and HSP protein expression. Bmc Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renau-Morata, B.; Molina, R.V.; Carrillo, L.; Cebolla-Cornejo, J.; Sánchez-Perales, M.; Pollmann, S.; Domínguez-Figueroa, J.; Corrales, A.R.; Flexas, J.; Vicente-Carbajosa, J. Ectopic expression of CDF3 genes in tomato enhances biomass production and yield under salinity stress conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, O.S.; Deng, X.W. Plant hormone signaling lightens up: Integrators of light and hormones. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Jha, B. Transcription factors in plants and ABA dependent and independent abiotic stress signalling. Biol. Plant. 2010, 54, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, N.A.; Amin, I.; Wani, W.; Wani, S.A.; Shikari, A.B.; Wani, S.H.; Masoodi, K.Z. Abscisic acid: A key regulator of abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Gene 2017, 11, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Gojobori, T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1986, 3, 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Törönen, P.; Medlar, A.; Holm, L. PANNZER2: A rapid functional annotation web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W84–W88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolser, D.; Staines, D.M.; Pritchard, E.; Kersey, P. Ensembl plants: Integrating tools for visualizing, mining, and analyzing plant genomics data. In Plant Bioinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 115–140. [Google Scholar]
- Krzywinski, M.; Schein, J.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lohani, N.; Babaei, S.; Singh, M.B.; Bhalla, P.L. Genome-Wide In Silico Identification and Comparative Analysis of Dof Gene Family in Brassica napus. Plants 2021, 10, 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040709
Lohani N, Babaei S, Singh MB, Bhalla PL. Genome-Wide In Silico Identification and Comparative Analysis of Dof Gene Family in Brassica napus. Plants. 2021; 10(4):709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040709
Chicago/Turabian StyleLohani, Neeta, Saeid Babaei, Mohan B. Singh, and Prem L. Bhalla. 2021. "Genome-Wide In Silico Identification and Comparative Analysis of Dof Gene Family in Brassica napus" Plants 10, no. 4: 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040709
APA StyleLohani, N., Babaei, S., Singh, M. B., & Bhalla, P. L. (2021). Genome-Wide In Silico Identification and Comparative Analysis of Dof Gene Family in Brassica napus. Plants, 10(4), 709. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040709




