Abstract
Recently, the increasing availability of digital cameras and the rapid advances in social media have led to the accumulation of a large number of geotagged photos, which may reflect people’s travel experiences in different cities and can be used to generate location recommendations for tourists. Research on this aspect mainly focused on providing personalized recommendations matching a tourist’s travel preferences, while ignoring the context of the visit (e.g., weather, season and time of the day) that potentially influences his/her travel behavior. This article explores context-aware methods to provide location recommendations matching a tourist’s travel preferences and visiting context. Specifically, we apply clustering methods to detect touristic locations and extract travel histories from geotagged photos on Flickr. We then propose a novel context similarity measure to quantify the similarity between any two contexts and develop three context-aware collaborative filtering methods, i.e., contextual pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling. With these methods, location recommendations like “in similar contexts, other tourists similar to you often visited …” can be provided to the current user. Results of the evaluation with a publicly-available Flickr photo collection show that these methods are able to provide a tourist with location recommendations matching his/her travel preferences and visiting context. More importantly, compared to other state-of-the-art methods, the proposed methods, which employ the introduced context similarity measure, can provide tourists with significantly better recommendations. While Flickr data have been used in this study, these context-aware collaborative filtering (CaCF) methods can also be extended for other kinds of travel histories, such as GPS trajectories and Foursquare check-ins, to provide context-aware recommendations.
1. Introduction
When visiting a new city, tourists often need help to effectively identify personally-interesting locations from a potentially overwhelming set of choices. Trip planning is a time-consuming task. This task is further complicated by the physical environment, as personally-interesting touristic locations may be scattered throughout a city. On the other hand, with the rapid advances in geotagged social media, recent years have witnessed many people publishing their travel information and experiences via social media, such as Foursquare check-ins and Flickr photos. Research has shown that experiences from past users in similar contexts can help the current users to solve their problems efficiently [1,2], e.g., choosing where to visit. Therefore, aggregating geotagged social media data has a high potential to help tourists identify locations of interest when visiting a new city.
Recently, analyzing geotagged social media data has gained significant attention. Research on this aspect focused, e.g., on landmark and hotspot discovery [3,4] place semantics extraction [5,6], behavior modeling [7,8] and community classification (e.g., [9]). There was also research using geotagged social media data for location and travel itinerary recommendation [10,11,12,13,14]. These studies recommended locations or itineraries matching tourists’ travel preferences and available time, while ignoring the context of the visit, such as weather and season. However, tourists’ preferences with regard to visiting a location are often influenced by the context in which they are [2]. For example, we may prefer to visit a park on a sunny day, while visiting a museum when it is rainy. Therefore, failing to consider these kinds of context information will lead to irrelevant and inappropriate recommendations.
This article aims to explore context-aware methods to provide location recommendations matching a tourist’s travel interests and visiting context (e.g., weather, season and time of the day) based on geotagged photos. More specifically, we extract each tourist’s travel history from Flickr photos, which reflects his/her travel preferences. We then propose a novel context similarity measure to quantify the similarity between any two contexts and develop three context-aware collaborative filtering (CaCF) methods to generate location recommendations, i.e., contextual pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling. By using a publicly-available Flickr dataset, the proposed methods are evaluated against other state-of-the-art methods to illustrate the benefits brought by considering context information in the recommendation process. These methods can provide tourists with personalized and context-aware location recommendations, such as “in similar contexts, other tourists similar to you often visited …”
2. Related Work
2.1. Recommendation Techniques and Context-Awareness
Recommendation systems provide a user with a personalized list of items (e.g., movies, songs and products) that meet his/her interests and needs. They are often classified into the following categories: collaborative filtering (recommending items other people with similar preferences liked in the past), content-based recommendation (providing a user with items similar to those he/she formerly preferred) and hybrid approaches. Among them, collaborative filtering (CF) is the most popular recommendation technique [15]. It makes recommendations based on users’ opinions (e.g., ratings) on different items. A rating is a tuple . Ratings can be expressed explicitly by users or inferred implicitly, e.g., from purchase history or travel trajectories. Due to its simplicity and intuitiveness, user-based CF (UCF) is often employed. Given an unknown rating (of an item by the current user) to be estimated, UCF firstly measures similarities between the current user and other users. The unknown rating is then predicted by aggregating the known ratings of the item by similar users.
Recently, researchers started to investigate how CF can be improved by considering context information, e.g., shopping purposes and seasons [16,17,18]. Adomavicius and Tuzhilin (2011) [19] proposed to classify context-aware CF (CaCF) approaches as follows: (1) contextual pre-filtering uses context information to filter out irrelevant ratings and then uses classic CF to generate recommendations; (2) contextual post-filtering uses classic CF to generate recommendations and then filters or re-ranks the results according to context information; (3) contextual modeling uses context information directly inside the CF process to generate recommendations.
Note that most of the above CF and CaCF methods were designed for movie, music and product domains and employed explicit ratings. There were also studies applying CF for restaurant recommendation [20], shop recommendation [21], event recommendation [22] exhibit recommendation in museums [23] and location recommendation using GPS trajectories [24]. However, many of them required users to explicitly state their interests or provide ratings, e.g., Horozov et al. (2006) [20] and Li et al. (2009) [22]. For others learning from users’ behavior, recommendations were often only adapted to users’ interests, while ignoring many contextual factors, such as weather and season, which might be also relevant for generating recommendations.
This article proposes three CaCF methods to derive personalized and context-aware location recommendations from the increasingly-available geotagged social media data, particularly Flickr photos. Our work differs from the techniques mentioned above on two aspects. Firstly, we derive location recommendations based on users’ implicit real-world travel histories, as inferred from Flickr photos. Secondly, we propose a similarity measure to quantify the similarity between any two contexts and develop three context-aware recommendation methods (i.e., pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling).
2.2. Analyzing Geotagged Social Media Data
Recently, the increasing availability of online social media (e.g., Foursquare and Flickr) has led to the accumulation of huge volumes of social media data. These data, especially those tagged with geographic location (e.g., latitude and longitude), contain much information about people’s travel, activities and behavior in various environments. In recent years, mining geotagged social media data has gained significant attention.
There was research studying the identification of landmarks and touristic hotspots (e.g., highly-photographed places) from geotagged social media data [3,4,25,26]. Different clustering methods have been employed, such as K-means, mean shift clustering, density-based clustering (e.g., DBSCAN (density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise) and its variants) and spectral clustering. These studies were often extended to summarize geotagged photo collections and extract representative tags or photos and semantics for specific places [5,6,27].
In addition to landmark identification and place semantics extraction, there were also studies focusing on modeling people’s travel behavior by using geotagged social media data [7,8,28]. These approaches often built a database of travel trajectories and applied data mining techniques to identify locations of attraction and frequent travel sequences. While the above studies used geotagged photos, research attention has also been paid to other social media data (e.g., tweets) [29,30]. These approaches have been extended for other applications, such as determining land uses [31] and understanding city dynamics [30].
2.3. Location Recommendation Using Geotagged Social Media Data
In recent years, many methods have been proposed to derive location and trip recommendations based on social media data (e.g., Flickr photos and Foursquare check-ins) [32,33]. For example, De Choudhury et al. (2010) [34] extracted tourists’ Flickr photos, aggregated them into a location graph and constructed travel itineraries by considering users’ available time. Similarly, Sun et al. (2015) [14] built a recommendation system to provide users with the most popular landmarks, as well as the best route connecting them. These methods considered mainly location popularity and ignored a tourist’s travel preferences and, therefore, provided him/her with non-personalized recommendations.
There were many other studies focusing on personalized recommendations. For example, Cheng et al. (2011) [11] proposed a personalized travel recommendation algorithm by considering specific user profiles (e.g., gender, age), which were detected from Flickr photos. Based on CF, Clements et al. (2010) [10]predicted a user’s favorite locations using Flickr photos. They measured the similarity between the current user and other users by comparing their travel histories and used the similarity values to rank the locations. Similarly, Yin et al. (2014) [13] and Gao et al. (2015) [35] developed CF-based personalized recommendation methods and mainly addressed the cold-start problem (i.e., “new user” and “new item”). Shi et al. (2013) [12] proposed a personalized method to recommend nontrivial landmarks that are not typical locations and that are difficult to find in travel guides. Jiang et al. (2016) [36] developed a method to recommend personalized travel sequence (trip) based on multi-source big social media data. Zhang et al. (2016) [37] provided personalized trip recommendations considering POI availability, diversity and traveling time uncertainty. Note that the above methods focused on recommending locations or trips matching tourists’ interests and constraints, while ignoring the context of the visit, e.g., weather and season, which might be potentially relevant for generating recommendations.
Contrary to the above methods that provided non-context-aware recommendations, this article explores context-aware collaborative filtering methods to provide location recommendations matching a tourist’s travel interests, as well as his/her visiting context based on geotagged photos. We consider not only the popularity of locations and a tourist’s travel interests, as obtained from his/her travel history, but also the visiting context he/she is in (e.g., weather, season and time of the day). A similar research work was provided by Majid et al. (2013) [38], in which a contextual pre-filtering method was proposed. They first identified each location’s popular visiting context and filtered out locations whose popular context is different from the current context. An exact matching was employed: for example, if the current visiting context is “weekday-morning and warm-sunny”, only those locations having the popular context as “weekday-morning and warm-sunny” are kept. CF was then applied to rank the filtered set of locations and made context-aware location recommendations. In short, their method can be considered as a contextual pre-filtering CF method with “exact matching”. Our work differs from Majid et al. (2013) [38] on two aspects. Firstly, instead of using “exact matching”, we propose a similarity measure to quantify the similarity between any two contexts. Secondly, based on the similarity measure, we develop three CaCF methods (i.e., pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling). The evaluation results show that the proposed methods significantly outperform the state-of-the-art method. In other words, compared to “exact matching”, using the proposed context similarity measure significantly improves the recommendation performance.
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Definition and Methodology Overview
Definition 1
(geotagged photo). A geotagged photo is defined as a tuple , containing a photo ID , the contributing user ID , the photo’s taken location (represented as a latitude-longitude pair) and taken time .
We use to denote the collection of photos contributed by user , as the set of all users and as the collection of photos contributed by all users.
Definition 2
(touristic location). A touristic location is a geographic region within a city, such as a square, a park or a museum, that attracts many tourists to visit and take photos.
We use to denote the set of all locations and as the subset of locations visited by user .
Definition 3
(context model of visits). Context model of visits contains an ordered list of relevant context parameters (dimensions). Thus, , where is the number of relevant context parameters. Each parameter is a tuple , where is a unique label to denote the name of the parameter (e.g., “weather”) and is the set of valid values that can be assigned to it (e.g., all available weather conditions, “sunny” and “rainy”). denotes the space of the context model and is the set of all possible situations under which a visit can occur.
An example of is (“weather: sunny, rainy”, “season: spring, summer, fall, winter”), where “weather” and “season” are relevant context parameters. An exemplary element of can be (“sunny”, “fall”).
Definition 4
(context of visit). A context of visit is an instance of . , where . For example, (“sunny”, “spring”) is an exemplary context of a visit.
The recommendation task can be defined as: given a collection of geotagged photo , a particular user and his/her context of visit , find a set of locations that is most likely to visit.
We address the problem by aggregating the travel histories of other tourists (as extracted from geotagged photos) to provide the current user with location recommendations matching his/her travel preferences and visiting context. Particularly, CF, which recommends to a user the items that other users with similar preferences formerly used or visited, is employed.
Figure 1 gives an overview of the methodology. Based on the photo collection retrieved from Flickr, we first identify touristic locations using density-based clustering methods (Section 3.2). With the discovered locations, each tourist’s visited locations in each city are extracted and enriched with the context of the visit (Section 3.2). We analyze the “datetaken” information of photos to derive the temporal context (i.e., time of the day and season) and employ the Weather Underground API [39] to retrieve weather conditions. We use these travel histories to model tourists’ preferences. They are then used to estimate the similarities between tourists and the similarities between contexts (Section 3.3). For making location recommendations, we develop three context-aware methods, namely contextual pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling (Section 3.4). These methods differ in how and when context information is used.
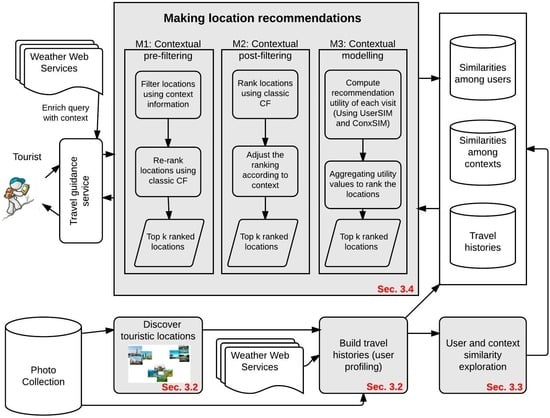
Figure 1.
Overview of the methodology. CF, collaborative filtering; Sec., section.
3.2. Touristic Location Detection and Travel History Extraction
3.2.1. Touristic Location Detection
Before identifying touristic locations from the geotagged photo collection, we need to filter out photos contributed by local residents. Due to the lack of home information in many Flickr users’ profiles, several heuristic algorithms have been proposed to differentiate between local residents and tourists [14,34,40]. Because of its simplicity and intuitiveness, the heuristic rule employed in De Choudhury et al. (2010) [34]and Kadar and Gede (2013) [40] is used. It assumes that while most tourists concentrate their visits within a short time period of several days, local residents of a city tend to take pictures of the city over a much longer period of time. Thus, tourists and local residents can be differentiated by checking the span of the taken time between their first and last photos. Following Kadar and Gede (2013) [40], we set the time span threshold as 5 days.
After filtering out photos contributed by local residents, we can then detect touristic locations from the remaining photos. Finding touristic locations from a collection of geotagged photos can be considered as a clustering problem of identifying highly photographed locations. As mentioned before, different clustering algorithms have been proposed, such as K-means, spectral clustering and density-based clustering (e.g., DBSCAN). Due to its ability to discover clusters with arbitrary shapes and insensitiveness to noise, DBSCAN is employed to identify highly photographed locations (i.e., touristic locations) for each city. It requires two parameters: the radius (Eps) and the minimum number of points within a cluster (MinPts). The output of DBSCAN is a set of photo clusters (locations) for each city. Each element is a touristic location, where is the group of photos within the cluster. can be used to compute the geographic boundary of the cluster (touristic location), as well as to identify the semantics (e.g., categories) or name of this touristic location, both of which are beyond the scope of this paper. In this paper, we simply represent each touristic location as a unique label (e.g., location A).
3.2.2. Travel History Extraction
Once the touristic locations are detected for each city, we can then extract the locations visited by each tourist.
Definition 5
(visit). A visit is defined as a tuple , where is the user who made visit to location at time and in the context of .
To extract each tourist’s visits, we firstly sort his/her photos according to the taken time. If a photo is contained in a particular photo cluster (i.e., touristic location), a visit made by to location at time is detected. Note that a tourist might take more than one photo in a visit to a location. Therefore, if a set of consecutive photos taken by the same user is contained in the same photo cluster and the time difference between the first and last photos within the set is smaller than a duration threshold , we consider this set of photos to belong to the same visit and use the median taken time of these photos as the visit time .
To identify the context of visit for each detected visit , we mainly use location and time . In this article, due to their availability, we focus on the following dimensions (parameters): “season”, “time of the day” and “weather”. We use to derive the first two dimensions. Similar to Lee et al. (2010) [41], abstraction of the raw time-stamp is applied: (1) “season”: spring (March–May), summer (June to August), fall (September–November) and winter (December–February); (2) “time of the day”: morning (6:00–12:00), afternoon (12:00–18:00), night (18:00–6:00). To derive the weather condition, we retrieve weather information for location at time using the Weather Underground API and classify the raw weather information into the following three conditions: “rainy_or_snowy”, “clear” (e.g., sunny) and “cloudy”. In other words, = (“season: spring, summer, fall, winter”, “time of the day: morning, afternoon, night”, “weather: rainy_or_snowy, clear, cloudy”).
With these, the locations visited by each tourist together with the contexts of the visit can be identified from the photo collection. This set of visits can be considered as the tourist’s profile and reflects his/her travel preferences and interests.
3.3. User Similarity and Context Similarity Exploration
3.3.1. User Similarity
To identify other tourists whose “travel experiences” can be used for generating recommendations for the current user (tourist), a user similarity measure (based on the Sørensen–Dice coefficient) is developed by comparing the locations visited by tourists.
and are the number of locations visited by tourists and , and is the number of locations commonly visited by them.
Obviously, two tourists sharing a set of locations visited by a few people might be more correlated than others who shared a set of locations visited by many people [24]. For instance, many people have visited Big Ben and Tower Bridge, two well-known landmarks in London. It might not be the case that all of these people are similar to each other. However, if two users visited a location that is not very popular, they might indeed share some similar travel preferences. Therefore, location popularity is considered when measuring user similarity. Due to its simplicity, inverse document frequency (IDF), which is often used in information retrieval to measure whether a term (e.g., word) is common or rare across all documents [42], is employed to measure the popularity of a location .
is the number of all tourists, and is the number of tourists who visited . The values of range from 0–1. The larger , the less popular a location is. Therefore, Equation (1) is extended as:
Similarity values range from 0–1. Zero means that both tourists did not share any common location histories, and 1 means that they visited the same set of locations. By applying the measure, we can build a user similarity matrix USim_MUU. Each element in it represents the similarity between two users.
3.3.2. Context Similarity
In general, “experiences” (i.e., visits in this article) happening in contexts similar to the current one are more useful for making location recommendations than those happening in dissimilar contexts. Therefore, we propose a heuristic-based approach for measuring similarity between any two contexts.
We assume that if visits happening in a context (situation) are similar to visits happening in another context, these two contexts (situations) can be considered as similar. Note that for “visits”, we do not mean each individual visit, but rather an aggregation of all of the visits happening in the context. Based on this assumption, we measure the similarity between any two contexts with the following two steps:
- The profile of each context (situation) is represented as a vector , where denotes the context, and (see Definitions 3 and 4). Each member of the vector corresponds to the usage of a location in this situation , and therefore, is equal to the number of locations in the application scenario (e.g., in a given city). We use the term frequency-inverse document frequency (TF-IDF) measure to compute the value of each . TF-IDF is used in the field of information retrieval to measure how important a word is to a document in a collection or corpus. It increases proportionally with the number of times a word appears in the document, but is offset by the frequency of the word in the corpus [42]. The latter part controls for the fact that some words are generally more common than others. Therefore, is computed as:is the number of visits in context that visited location ; represents the number of visits in ; denotes the number of visits in all contexts that visited ; and is the total number of visits in all contexts. The first part of Equation (4) denotes how often was visited in , while the second part measures whether was commonly or rarely visited across all contexts.The profile of a context can be considered as an aggregated view of the usage of different locations in this context (situation), which can be used to characterize the context.
- The similarity between two contexts is then computed by using the cosine similarity measure. This is mainly because cosine similarity is often used for measuring the similarity between objects that are represented as vectors, and it measures the cosine of the angle between these two vectors [43]. Therefore, the similarity between two contexts (denoted as A and B) can be measured as the cosine similarity between their corresponding profile vectors.Similarity values range from 0–1. Please note that the measure is computed based on tourists’ visiting behavior, which is suitable for the task of location recommendation. It might not be directly used in other application scenarios. However, we argue that the key ideas behind it are still applicable.In the evaluation (Section 4), due to the diverse characteristics of different cities (which potentially influence tourists’ visiting behavior in different contexts), we assume that context similarity is city-dependent. Therefore, we build a context similarity matrix CSim_MCC for each city. Each element in CSim_MCC represents the similarity between two contexts in the city.
3.4. Context-Aware Location Recommendation
As mentioned before, Adomavicius and Tuzhilin (2011) [19] proposed that context information can be included into CF by contextual pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling. However, this classification has not been applied to location recommendations in the tourism domain. In this section, we apply this classification and develop three methods to derive personalized and context-aware location recommendations.
3.4.1. Contextual Pre-Filtering
The basic idea of contextual pre-filtering is to filter out irrelevant locations before using classic CF (i.e., non-contextual CF). Therefore, we develop the following contextual pre-filtering approach (CaCF_Pre):
- Filter out locations whose contextual profile is not similar to the current context. We also filter out locations that have been visited by the current user who asks for recommendation. We represent the contextual profile of a location as a vector . is the number of all possible contexts (situations) in which visits can happen. Each member of the vector corresponds to the percentage of visits in context (situation) and is computed as:is the number of visits in context that visited location , and denotes the number of visits in all contexts that visited . The contextual profile of a location can be considered as an aggregated view of the visit distributions across all contexts (situations). We then use the following measure to quantify the appropriateness of visiting location in context :Note that is the set of all possible contexts. If does not exceed a threshold , we consider that is not suitable to be recommended for the current context and, thus, filter it out. The results of this step are a set of candidate locations that are suitable to visit in the current context.
- Apply classic CF to rank the candidate locations obtained from Step 1. Recall that CF recommends to a user items that other people with similar preferences “liked” in the past. Therefore, we aggregate the locations visited by all of the other tourists (weighted by their similarity values with the current user u, which can be obtained from USim_MUU) to order the candidate locations. Specifically, the predicted preference of the current user to a candidate location is computed as:where if user visited location . Otherwise, . is the set of all other users (excluding the current user ).Based on Equation (8), the candidate locations can be re-ranked, and the top k number of these locations can be returned to the current user as the recommendation results.
3.4.2. Contextual Post-Filtering
Different from contextual pre-filtering, contextual post-filtering (CaCF_Post) firstly uses classic CF and then adjusts the results according to context information.
- Apply classic CF to rank all of the locations. Specifically, aggregate the locations visited by all other tourists (weighted by their similarity values with the current user u, which can be obtained from USim_MUU; see Equation (8)). The results of this step are a set of candidate locations and their corresponding predicted values.
- For each candidate location, compute its visit probability in the current context . The visit probability of a location is calculated as the fraction of the neighbors (i.e., all of the other tourists) who visited in similar contexts, i.e., contexts whose similarity value with is larger than a threshold .The denominator denotes the number of neighbors, and the numerator represents the number of neighbors who visited location in similar contexts.
- The final predicted value for each candidate location is computed as:where is the predicted value computed from Step 1.
With these, we can re-rank the candidate locations and return the top k number of locations to the current user as the recommendation results.
3.4.3. Contextual Modeling
Compared to the above approaches, contextual modeling uses context information directly inside the CF process. Note that the CF process can be considered as “useful opinion identification” and “opinion aggregation”. Therefore, we design the following contextual modeling approach (CaCF_Mdl).
- For each of the other tourists’ visit , compute its recommendation utility to the current user in the current context .The recommendation utility of a visit can be considered as “how useful we can use the visit to generate recommendations for the current user in the current context ”.
- For each location that has not been visited by , predict ’s preference rating for , which is computed by considering the recommendation utility of each existing visit to the location . Therefore, the predicted preference of the current user for a location can be calculated as:denotes the set of all visits, and is the set of visits to location .
- Rank the locations according to the predicted values and return the top k number of locations to the current user as the recommendation results.
4. Evaluation and Discussion
This section evaluates the proposed CaCF methods against some benchmarking methods. The evaluation was implemented using Python and PostgreSQL. Section 4.1 describes the dataset. Section 4.2 presents how we processed the dataset to detect touristic locations and extracted each tourist’s travel history. We describe the experimental setting in Section 4.3. The results are presented and discussed in Section 4.4.
4.1. Dataset
We used the public API of Flickr (particularly flickr.photos.search) to retrieve geotagged photos for six cities in Europe between 1 January 2008 and 31 December 2013. Only metadata of each photo were kept, which contained “photoid”, “owner”, “title”, “dateupload”, “datetaken”, “tags”, “lat”, “lon”, and so on. In total, we collected 2,627,139 geotagged photos from 79,951 users (Table 1).

Table 1.
Details of the dataset.
We firstly removed the metadata of photos whose upload time (“dateupload”) is identical to its taken time (“datetaken”). To further clean the dataset, we separated the photos according to the cities where they were taken. For each city’s photos, we filtered out photos contributed by local residents of that city, using the heuristic rule introduced in Section 3.2.1. Figure 2 shows the spatial distribution of the remaining photos in different cities.
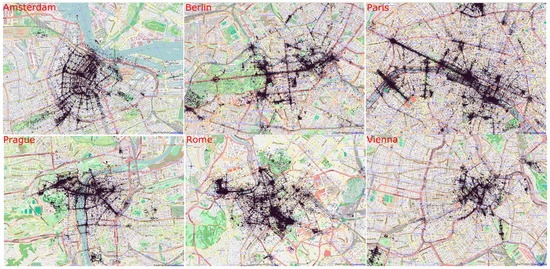
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of photos in different cities (map data © OpenStreetMap contributors, CC-BY-SA).
4.2. Touristic Location Detection and Travel History Extraction
As introduced in Section 3.2, we applied DBSCAN to cluster photos and detect touristic locations. DBSCAN has two parameters, MinPts and Eps. We did a sensitivity analysis of these two parameters. Figure 3 demonstrates how the numbers of detected clusters change over different MinPts and Eps. Apart from the curve for MinPts = 60, the other curves are changing similarly. When the value of Eps is around 30 meters, the cluster counts reach a maximum value. The number of detected clusters is always decreasing with the increase of MinPt, and the decreasing becomes slow when MinPts is more than 100. Here, we set MinPts = 100 and Eps = 30 m and consequently found 120 clusters (touristic locations). Figure 4 shows the detected touristic locations in different cities.
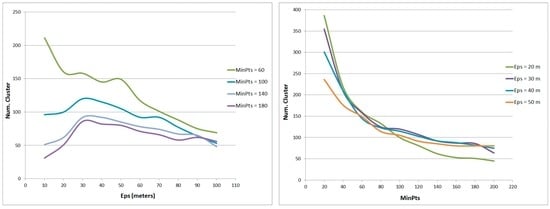
Figure 3.
The number of clusters (touristic locations) detected with different values of parameters. MinPts, minimum of points; Eps, the radius.
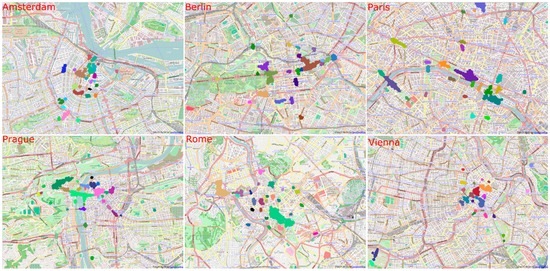
Figure 4.
The detected touristic locations in different cities (map data © OpenStreetMap contributors, CC-BY-SA).
Based on the list of touristic locations, we then extracted each tourist’s travel history. To detect visits from photos, we set the visit duration threshold as eight hours, which is comparable to the opening duration of many sightseeing sites in Europe. For each visit, we used its timestamp to derive “season” and “time of the day” and used the Weather Underground API to retrieve “weather”. In total, we extracted 21,541 visits from 1257 tourists. Table 2 summarizes the number of tourists and its distribution across the number of locations visited in each city.

Table 2.
Summary of tourists and their distribution in different cities. Num.loc denotes the number of locations
4.3. Experimental Setup
Objectives: For the experimental evaluation, we were mainly interested in comparing the proposed CaCF methods with the classic CF method (i.e., non-contextual CF) and other state-of-the-art context-aware methods. We would like to answer the following questions: (1) Does considering context information in CF improve recommendation performance? (2) Do the proposed context-aware methods outperform state-of-the-art methods? Does employing the proposed context similarity measure improve the recommendation performance?
Benchmarking methods: In order to address the above objectives, we implemented the following benchmarking methods:
- Classic CF (“nonCaCF”): This is a non-contextual CF, which recommends to a user the locations that other users with similar preferences visited in the past. It can be implemented by using only the second step of CaCF_Pre (see Section 3.4.1).
- Contextual pre-filtering with “exact matching” (“CaCF_Pre_EM”): This is a state-of-the-art method proposed in Majid et al. (2013) [38]. To implement it, we identified each location ’s popular visiting context (i.e., the context in which most visits to happened) and then filtered out locations whose popular visiting context is different from the current context using an exact matching (see Section 2.3 for more details). Classic CF was then developed to re-rank the filtered set of locations.
Evaluation Framework: For the evaluation, only tourists who visited at least two cities were selected. For each tourist , we used one of his/her visited cities as the test city and all other cities as training cities . In other words, we predicted the locations actually visited by in city , based on his/her travel history in . Visits made by in city were used to obtain: the number (denoted as k) of locations actually visited by and the set of contexts associated with visits to these locations. This set of contexts was used as the inputs for the context-aware recommendation (CaCF) algorithms. For each algorithm, we recommended k locations for the test user to visit in city .
To measure the performance of the proposed methods and benchmarking methods, we compared the recommendation list with the actual list of locations visited by in city . Precision and recall are the most popular metrics for evaluating information retrieval systems [44]. Herlocker et al. (2004) [45] argued that recall is impractical for evaluating the recommendation quality. Therefore, precision was used in this study to evaluate the recommendation quality, and it was defined as the fraction of recommended locations that were actually visited by . Additionally, we also employed mean average precision (MAP), which has been shown to have especially good discrimination and stability for measuring ranking effectiveness [44]. It was computed as the mean of the average precision (AP) values of all of the queries, and the AP of each query is calculated as the average of the precision values at each correct recommendation (i.e., the recommended location was actually visited by the test user ).
4.4. Evaluation Results and Discussion
4.4.1. Sensitivity Analysis
Before comparing the methods, we implemented a sensitivity analysis to study the effect of the context similarity threshold on CaCF_Pre and CaCF_Post. We performed some experiments by varying the threshold values. The results are shown in Figure 5.
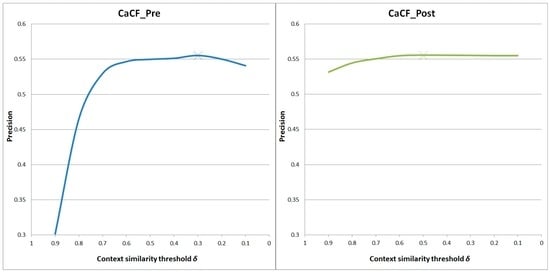
Figure 5.
Impact of context similarity threshold on recommendation quality.
Figure 5 shows that the threshold does affect the recommendation quality of CaCF_Pre and CaCF_Post. Compared to CaCF_Post, the threshold has a higher impact on the recommendation results of CaCF_Pre. This might be explained by the ways they incorporate context information: CaCF_Pre filters out locations that are not suitable to visit in the current context; CaCF_Post generates a set of candidate locations using the non-contextual CF, and adjusts the results according to context information.
The recommendation performance of both methods increases when decreasing the threshold. However, the quality becomes worse after a certain point, i.e., = 0.3 for CaCF_Pre and = 0.5 for CaCF_Post. For the following experiments, we set = 0.3 for CaCF_Pre and = 0.5 for CaCF_Post.
4.4.2. Algorithm Comparisons
In the following, we compare the recommendation performance of the proposed CaCF methods and the benchmarking methods. Figure 6 shows the results.
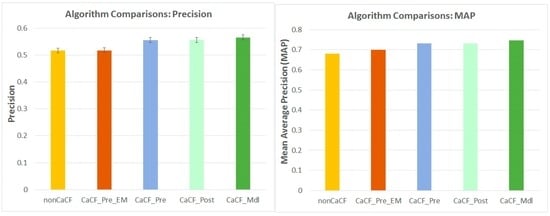
Figure 6.
Comparisons of the proposed CaCF methods with the benchmarking methods (Vertical error bars in the left graph denote 95% confidence intervals). MAP, mean average precision; EM, exact matching; Mdl, modeling.
Non-contextual CF (nonCaCF) versus context-aware CF (CaCF): In terms of recommendation performance, all of the proposed CaCF methods (i.e., CaCF_Pre, CaCF_Post, CaCF_Mdl) achieve significantly better results than nonCaCF (with all p < 0.001), with improvements of 7.65%, 7.72% and 9.47% respectively for precision and with improvements of 7.58%, 7.75% and 9.81% respectively for MAP. This is consistent with what we expected: as the proposed CaCF methods are aware of the context the user is in, they might generate recommendations that are more suitable to visit.
CaCF_Pre_EM versus context-aware CF (CaCF_Pre, CaCF_Post, CaCF_Mdl): In terms of recommendation performance, all of the proposed CaCF methods achieve significantly better results than CaCF_Pre_EM (i.e., contextual pre-filtering with exact matching) (with all p < 0.001), with improvements of 7.45%, 7.53% and 9.27% respectively for precision and with improvements of 4.48%, 4.64% and 6.64% respectively for MAP. CaCF_Pre_EM even performs just slightly better than nonCaCF. The reason for its poor performance is that it uses exact matching to filter out locations whose popular visiting context is not the same as the current context, which really filters out many relevant locations.
CaCF_Pre versus CaCF_Post versus CaCF_Mdl: Among all of the methods, CaCF_Mdl performs the best, followed by CaCF_Post and, finally, CaCF_Pre. The differences between CaCF_Mdl and the other two are significant (with all p < 0.001). CaCF_Pre and CaCF_Post perform similarly, and no significant difference is obtained from the comparisons (precision: p = 0.76; MAP: p = 0.39). The diverse performance of these methods might be explained by the ways they incorporate context information: CaCF_Pre filters out locations that are not suitable to visit in the current context; CaCF_Post generates a set of candidate locations using the non-contextual CF and adjusts the results according to context information; CaCF_Mdl uses context similarity and user similarity to measure the recommendation utility of each visit to the current user and then aggregates all of the visits by considering their utility values for making location recommendations.
4.4.3. Recommendations with Different Numbers of Training Locations
The number of training locations (i.e., locations a tourist has visited before asking for recommendations) reflects the amount of information (i.e., travel history) available about a tourist. In the following, we investigate how the performance changes when generating recommendations for tourists with different numbers of training locations (Figure 7).
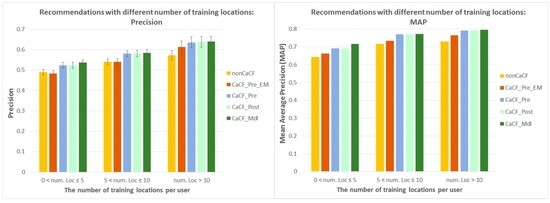
Figure 7.
Performance comparisons of the recommendation methods with different numbers of training locations (vertical error bars in the left graph denote 95% confidence intervals).
Figure 7 shows an upwards trend for the recommendation performance of all of the recommendation methods when the number of training locations increases. This is consistent with our expectation: with the increase of the number of training locations, more information about a tourist is available for the recommendation methods, and therefore, the recommendation performance is improved.
4.4.4. Summary of the Results and Discussions
In summary, the main findings of the experiments are as follows:
- All of the proposed CaCF methods significantly outperform classic CF (i.e., non-contextual CF, nonCaCF).
- The proposed methods (i.e., CaCF_Pre, CaCF_Post and CaCF_Mdl) perform significantly better than the state-of-the-art context-aware location recommendation method (i.e., CaCF_Pre_EM).
- Among all of the proposed context-aware location recommendation methods, CaCF_Mdl performs the best, followed by CaCF_Post and, finally, CaCF_Pre.
- With the increase of the number of training locations, the recommendation performance of all of the proposed methods is improved.
In general, these findings are consistent with what we expected.
- The experiment results show that by aggregating other tourists’ travel histories (i.e., as derived from geotagged photos), we can provide the current user with location recommendations matching his/her travel preferences and context of the visit. The results confirm the findings of Wexelblat (1999) [1] and Zheng et al. (2011) [24] and suggest that experiences from past users (especially those users similar to the current user) can help the current user to solve his/her own problems efficiently, e.g., choosing where to visit next.
- We expect that as the proposed methods (i.e., CaCF_Pre, CaCF_Post and CaCF_Mdl) are aware of the context the user is in, they might generate location recommendations that are more suitable to visit. These experiments confirm this expectation and show that including context information in the recommendation process can help to improve the recommendation quality.
- As can be seen from Figure 6 and Figure 7, the proposed methods significantly outperform the state-of-the-art context-aware method. This suggests that the way that context information is integrated into CF greatly affects the recommendation performance. Specifically, the experiments show that compared to “exact matching”, using the proposed context similarity measure significantly improves the recommendation performance.
- The above results show that among all of the proposed CaCF methods, the contextual modelling method (CaCF_Mdl) might be more suitable for generating location recommendations matching a user’s travel preferences and the context of the visit. As both the contextual pre-filtering (CaCF_Pre) and contextual post-filtering (CaCF_Post) methods have one parameter to calibrate (i.e., context similarity threshold ), it is therefore recommended to use CaCF_Mdl for context-aware location recommendations.
Several main limitations of this work should be also pointed out. Firstly, this research uses DBSCAN to detect touristic locations and employs CF for making recommendations. For the evaluation, we use datasets of several big cities in Europe, each of which contains many geotagged photos from various users. As both DBSCAN and CF work well with big datasets (like the datasets used in this paper), the proposed methods might not perform well when using small datasets with a low number of users, e.g., geotagged photo datasets from small cities and rural regions. To provide recommendations based on these small datasets, the proposed CaCF methods can be combined with content-based or knowledge-based approaches. Secondly, this work represents the values of each context parameter as a set of categories (e.g., context parameter “time of the day” has values like “morning”, “afternoon” and “night”). While categorized values might simplify the model complexity, sometimes, it might not be easy to transfer the raw context data into corresponding categories. Fuzzy logic or gradual scales (e.g., [46]) might be employed to address this issue. Thirdly, this paper shows that considering context information (i.e., the set of “season”, “time of the day” and “weather” in this paper) can significantly improve recommendation performance. This research can be enhanced by investigating how each single context parameter contributes to the performance improvement. We regard this as a future work and would like to further expand it to develop a computational method to identify relevant context parameters even before applying the proposed context-aware recommendation methods. Finally, in the current research, we divide the datasets into training and test data to evaluate the proposed methods. While this evaluation approach helps to compare the recommendation performance, it can be improved by using experiments with human participants (e.g., tourists). For example, we can ask each participant to comment on the recommendation results generated by the proposed methods. These kinds of human experiments will also help to further investigate whether the significant performance improvement when considering context information (as shown in this paper) really brings much better recommendation results to tourists. We expect that similar evaluation results can be obtained in these experiments.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
This article investigated how geotagged photos on social media can be aggregated to derive location recommendations matching a tourist’s travel preferences and the context of the visit (e.g., weather, season and time of the day). Specifically, we applied clustering methods to detect touristic locations and extracted travel histories from geotagged Flickr photos. We then proposed a novel similarity measure to quantify the similarity between any two contexts and developed three context-aware collaborative filtering (CaCF) methods, i.e., contextual pre-filtering, post-filtering and modeling. These methods can provide tourists with “social advice” for choosing where to visit, i.e., location recommendations like “in similar contexts, other tourists similar to you often visited …”
We evaluated the proposed methods against other state-of-the-art location recommendation methods by using a publicly-available Flickr photo collection, which contained geotagged photos in six European cities. The results of the evaluation show that: (1) the proposed methods are able to provide a tourist with location recommendations matching his/her preferences and current visiting context; (2) more importantly, compared to other state-of-the-art methods, the proposed methods, which employ the context similarity measure, can provide tourists with significantly better location recommendations. In other words, compared to exact matching, using the proposed context similarity measure significantly improves the recommendation performance.
In conclusion, by aggregating other tourists’ travel histories (e.g., as extracted from geotagged photos), personalized and context-aware location recommendations can be provided for the current user. While Flickr data have been used in this study, the proposed CaCF methods can be also extended for other kinds of location histories, such as GPS trajectories and Foursquare check-ins, to provide context-aware recommendations. These methods can be also applied to consider more context information, such as visiting purposes and companion (with whom).
As a next step, we will further address the quality issues (e.g., representativeness, incompleteness, tagging errors and bias) of social media data and develop methods to clean them. In the meantime, we would like to extend the proposed algorithms from location recommendation to sequence and itinerary recommendation (e.g., recommending a sequence of locations to visit). Sequence recommendation needs to consider not only travel distance, but also item diversity, the co-occurrence interaction effects of items and other constraints. We are also interested in developing more comprehensive CaCF methods, by using fuzzy definitions and gradual scales in the context model. Furthermore, the current research employed CF for deriving location recommendations from geotagged photos. While CF is an effective recommendation technique requiring little domain knowledge, it suffers from the “cold-start” problem (“new user” and “new item”). We will address these issues by integrating other recommendation techniques, e.g., content-based or knowledge-based recommendations. We expect that hybrid techniques will further improve the recommendation performance. We also would like to design a human experiment to further investigate the benefits of considering context information in location recommendation for tourists. Moreover, we are also interested in extending our methods to generate not only location recommendations, but also explanations for why these locations are recommended.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Wexelblat, A.D. Footprints: Interaction History for Digital Objects. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H. Learning from Location Histories for Location Recommendations in LBS. Ph.D. Thesis, Vienna University of Technology, Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kisilevich, S.; Mansmann, F.; Keim, D. P-DBSCAN: A density based clustering algorithm for exploration and analysis of attractive areas using collections of geo-tagged photos. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference and Exhibition on Computing for Geospatial Research & Application, New York, NY, USA, 21–23 June 2010.
- Yang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Hou, L. Identifying points of interest by self-tuning clustering. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGIR 2011, Beijing, China, 17–20 April 2011.
- Jaffe, A.; Naaman, M.; Tassa, T.; Davis, M. Generating summaries and visualization for large collections of geo-referenced photographs. In Proceedings of the MIR’06, New York, NY, USA, 26–27 October 2006.
- Rattenbury, T.; Naaman, M. Methods for extracting place semantics from flickr tags. ACM Trans. Web 2009, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, P.; Andrienko, N.; Andrienko, G.; Kisilevich, S. Discovering landmark preferences and movement patterns from photo postings. Trans. GIS 2010, 14, 833–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.T.; Zha, Z.J.; Chua, T.S. Mining travel patterns from geotagged photos. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2012, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wen, Y.; Chua, T.; Huang, J.; Zhu, W.; Li, X. Joint content replication and request routing for social video distribution over cloud CDN: A community clustering method. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2016, 26, 1320–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clements, M.; Serdyukov, P.; De Vries, A.P.; Reinders, M.J.T. Using flickr geotags to predict user travel behaviour. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGIR 2010, Geneva, Switzerland, 19–23 July 2010.
- Cheng, A.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.T.; Hsu, W.H.; Liao, H.Y.M. Personalized travel recommendation by mining people attributes from community-contributed photos. In Proceedings of the ACM Multimedia 2011, Firenze, Italy, 28 November–1 December 2011.
- Shi, Y.; Serdyukov, P.; Hanjalic, A.; Larson, M. Nontrivial landmark recommendation using geotagged photos. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2013, 4, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Cui, B.; Sun, Y.; Hu, Z.; Chen, L. LCARS: A spatial item recommender system. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2014, 32, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fan, H.; Bakillah, M.; Zipf, A. Road-based travel recommendation using geo-tagged images. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 53, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, F.; Rokach, L.; Shapira, B. Introduction to recommender systems handbook. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Ricci, F., Rokach, L., Shapira, B., Kantor, P.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Adomavicius, G.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Sen, S.; Tuzhilin, A. Incorporating contextual information in recommender systems using a multidimensional approach. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2005, 23, 103–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatzoglou, A.; Amatriain, X.; Baltrunas, L.; Oliver, N. Multiverse recommendation: N-dimensional tensor factorization for context-aware collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the ACM RecSys 2010, Barcelona, Spain, 26–30 September 2010.
- Panniello, U.; Gorgoglione, M. Incorporating context into recommender systems: An empirical comparison of context-based approaches. Electron. Commer. Res. 2012, 12, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomavicius, G.; Tuzhilin, A. Context-aware recommender systems. In Recommender Systems Handbook; Ricci, F., Rokach, L., Shapira, B., Kantor, P.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 217–253. [Google Scholar]
- Horozov, T.; Narasimhan, N.; Vasudevan, V. Using location for personalized POI recommendations in mobile environments. In Proceedings of the SAINT ’06, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 23–27 January 2006.
- Takeuchi, Y.; Sugimoto, M. CityVoyager: An outdoor recommendation system based on user location history. In Ubiquitous Intelligence and Computing; Ma, J., Jin, H., Yang, L.T., Tsai, J.J.P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 625–636. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.H.; Lee, F.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, C.Y. A multi-stage collaborative filtering approach for mobile recommendation. In Proceedings of the ICUIMC ’09, Suwon, South Korea, 15–16 January 2009.
- Bohnert, F. Non-Intrusive User Modelling and Behaviour Prediction in Museums. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, Melbourne, Austrilia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Z.; Xie, X.; Ma, W.Y. Recommending friends and locations based on individual location history. ACM Trans. Web 2011, 5, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, L.S.; Naaman, M. Generating diverse and representative image search results for landmarks. In Proceedings of the WWW ’08, Beijing, China, 21–25 April 2008.
- Crandall, D.J.; Backstrom, L.; Huttenlocher, D.; Kleinberg, J. Mapping the world’s photos. In Proceedings of the WWW ’09, Madrid, Spain, 20–24 April 2009.
- Chen, W.C.; Battestini, A.; Gelfand, N.; Setlur, V. Visual summaries of popular landmarks from community photo collections. In Proceedings of the ACM Multimedia 2009, Beijing, China, 19–23 October 2009.
- Arase, Y.; Xie, X.; Hara, T.; Nishio, S. Mining people’s trips from large scale geo-tagged photos. In Proceedings of the ACM Multimedia 2010, Firenze, Italy, 25–29 October 2010.
- Cheng, Z.; Caverlee, J.; Lee, K.; Sui, D.Z. Exploring millions of footprints in location sharing services. In Proceedings of the ICWSM 2011, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011.
- Noulas, A.; Scellato, S.; Mascolo, C.; Pontil, M. Exploiting semantic annotations for clustering geographic areas and users in location-based social networks. In Proceedings of the ICWSM 2011, Barcelona, Spain, 17–21 July 2011.
- Frias-Martinez, V.; Soto, V.; Hohwald, H.; Frias-Martinez, E. Characterizing urban landscapes using geolocated tweets. In Proceedings of the SocialCom/PASSAT ’12, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 3–5 September 2012.
- Bao, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wilkie, D.; Mokbel, M.F. A Survey on recommendations in location-based social networks. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2015, 19, 525–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefalas, P.; Symeonidis, P.; Manolopoulos, Y. A graph-based taxonomy of recommendation algorithms and systems in LBSNs. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2016, 28, 604–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Choudhury, M.; Feldman, M.; Amer-Yahia, S.; Golbandi, N.; Lempel, R.; Yu, C. Automatic construction of travel itineraries using social breadcrumbs. In Proceedings of the HT2010, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 6–9 June 2010.
- Gao, H.; Tang, J.; Liu, H. Addressing the cold-start problem in location recommendation using geo-social correlations. Data Min. Knowl. Dis. 2015, 29, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Qian, X.; Mei, T.; Fu, Y. Personalized travel sequence recommendation on multi-source big social media. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2016, 2, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liang, H.; Wang, K. Trip recommendation meets real-world constraints: POI availability, diversity, and traveling time uncertainty. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, A.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Mirza, H.T.; Hussain, I.; Woodward, J. A context-aware personalized travel recommendation system based on geotagged social media data mining. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 662–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API | Weather Underground. Available online: http://www.wunderground.com/weather/api/ (accessed on 25 October 2016).
- Kádár, B.; Gede, M. Where do tourists go: Visualizing and analysing the spatial distribution of geotagged photography. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovis. 2013, 48, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Park, S.E.; Kahng, M.; Lee, S.; Lee, S. Exploiting contextual information from event logs for personalized recommendation. In Computer and Information Science 2010; Lee, R., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 121–139. [Google Scholar]
- Salton, G.; McGill, M.J. Introduction to Modern Information Retrieval; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, A. Modern information retrieval: A brief overview. Bull. IEEE Comput. Soc. Tech. Commit. Data Eng. 2001, 24, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, C.; Raghavan, P.; Schütze, H. Introduction to Information Retrieval; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Herlocker, J.L.; Konstan, J.A.; Terveen, L.G.; Riedl, J.T. Evaluating collaborative filtering recommender systems. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2004, 22, 5–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Sagl, G.; Mburu, L.; Fan, H. A contextualized and personalized model to predict user interest using location-based social networks. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 58, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).