SceneDiffusion: Scene Generation Model Embedded with Spatial Constraints
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A grid-based spatial scene representation framework that integrates the characterization of objects with topological, directional, and distance-based relationships into a unified formalized description. This framework bridges qualitative and quantitative spatial representations, adapting to diverse application needs.
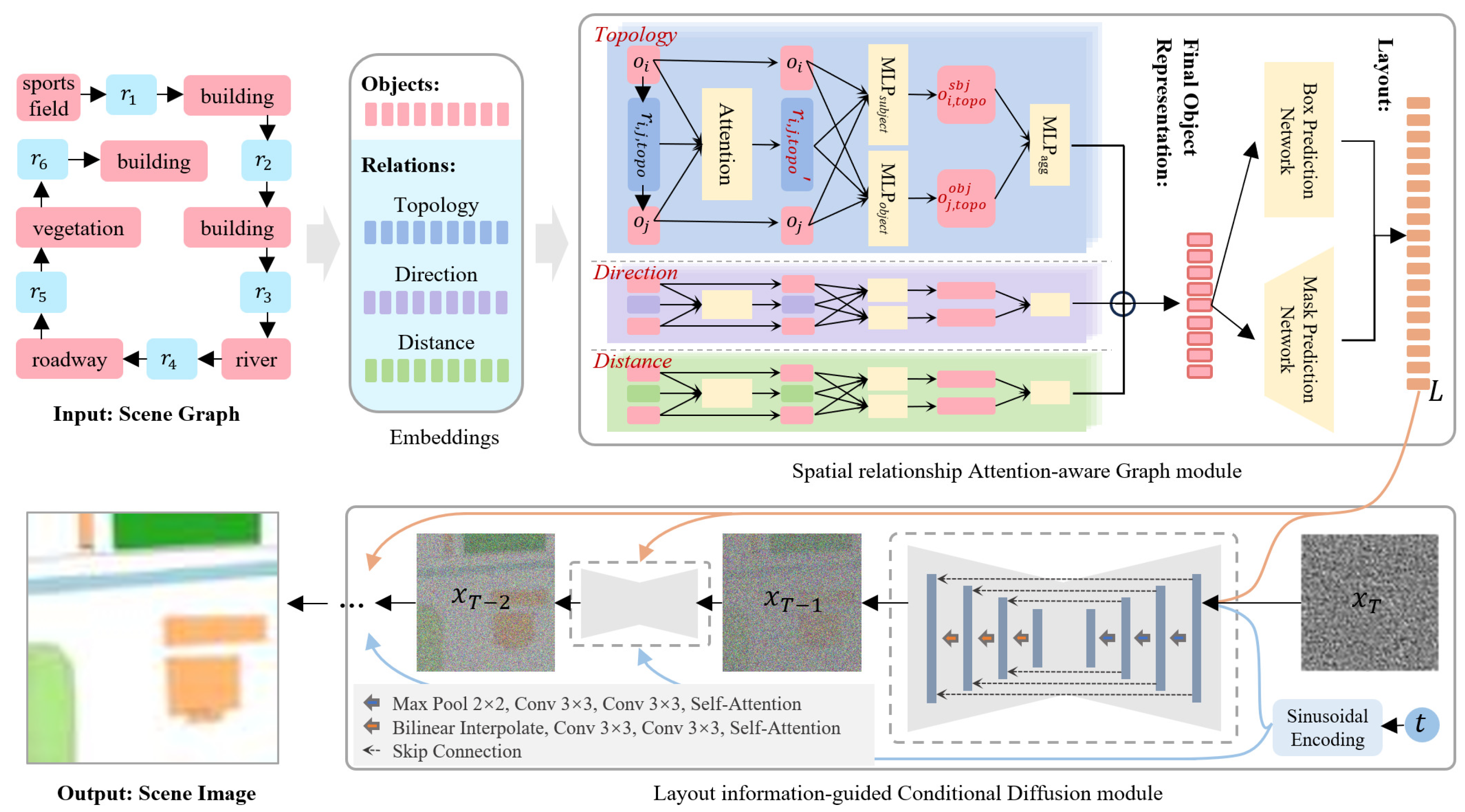
- A deep neural network embedded with spatial constraints for scene generation. By introducing a Spatial relationship Attention-aware Graph (SAG) module, the model adaptively learns spatial layouts under topological, directional, and distance constraints, enhancing its spatial comprehension. Further, a Layout information-guided Conditional Diffusion (LCD) module is incorporated to generate visually detailed and semantically consistent scene images.
- A purpose-built spatial scene dataset containing relational descriptions and geographic semantics. The dataset includes both structured semantic representations (e.g., object attributes, relational predicates) and corresponding rasterized visual representations, enabling rigorous evaluation of the proposed method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Text-to-Image Generation
2.2. Diffusion Models
3. Method
3.1. Preliminaries
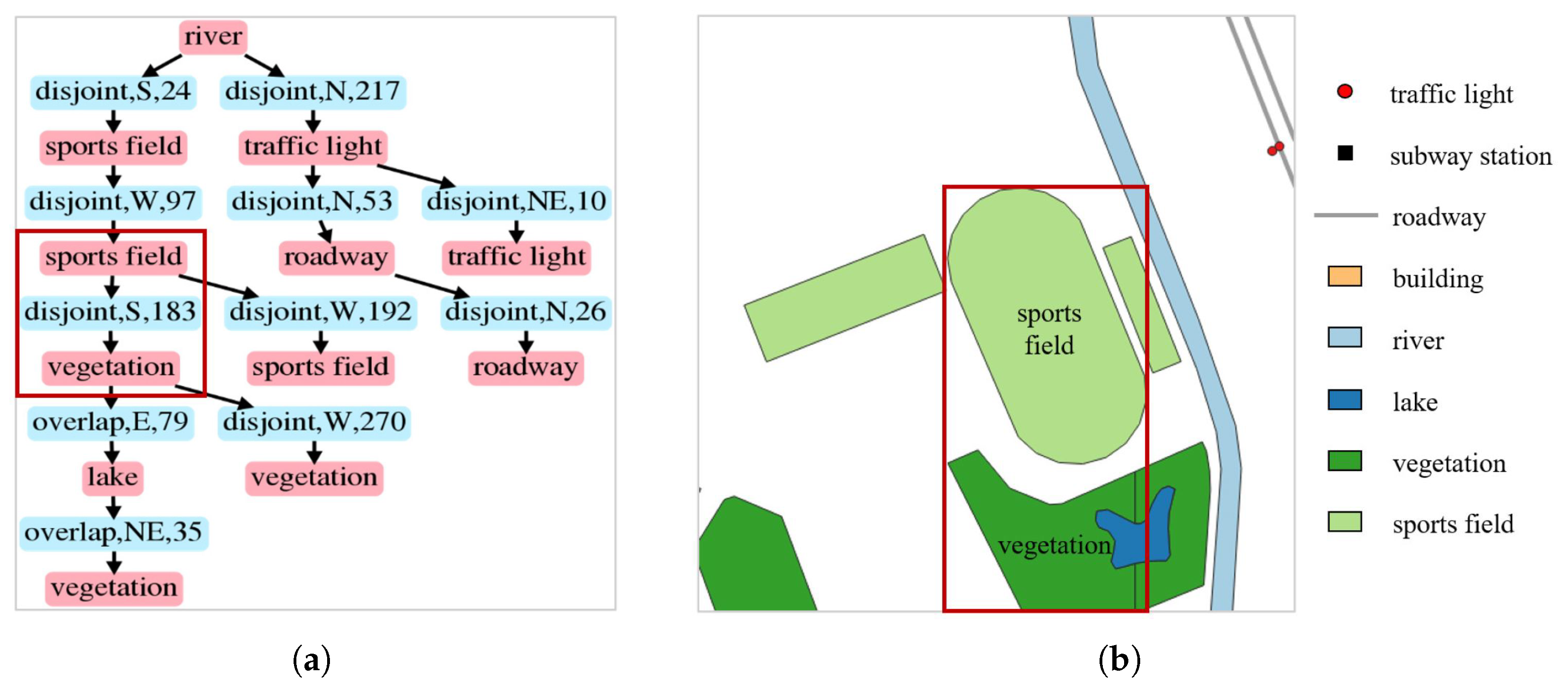
3.2. Spatial Scene Representation Framework
3.3. SceneDiffusion
3.3.1. Spatial Relationship Attention-Aware Graph Module
3.3.2. Layout Information-Guided Conditional Diffusion Module
4. Experiment
4.1. Geospatial Scene (GS) Dataset
4.2. Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Experimental Details
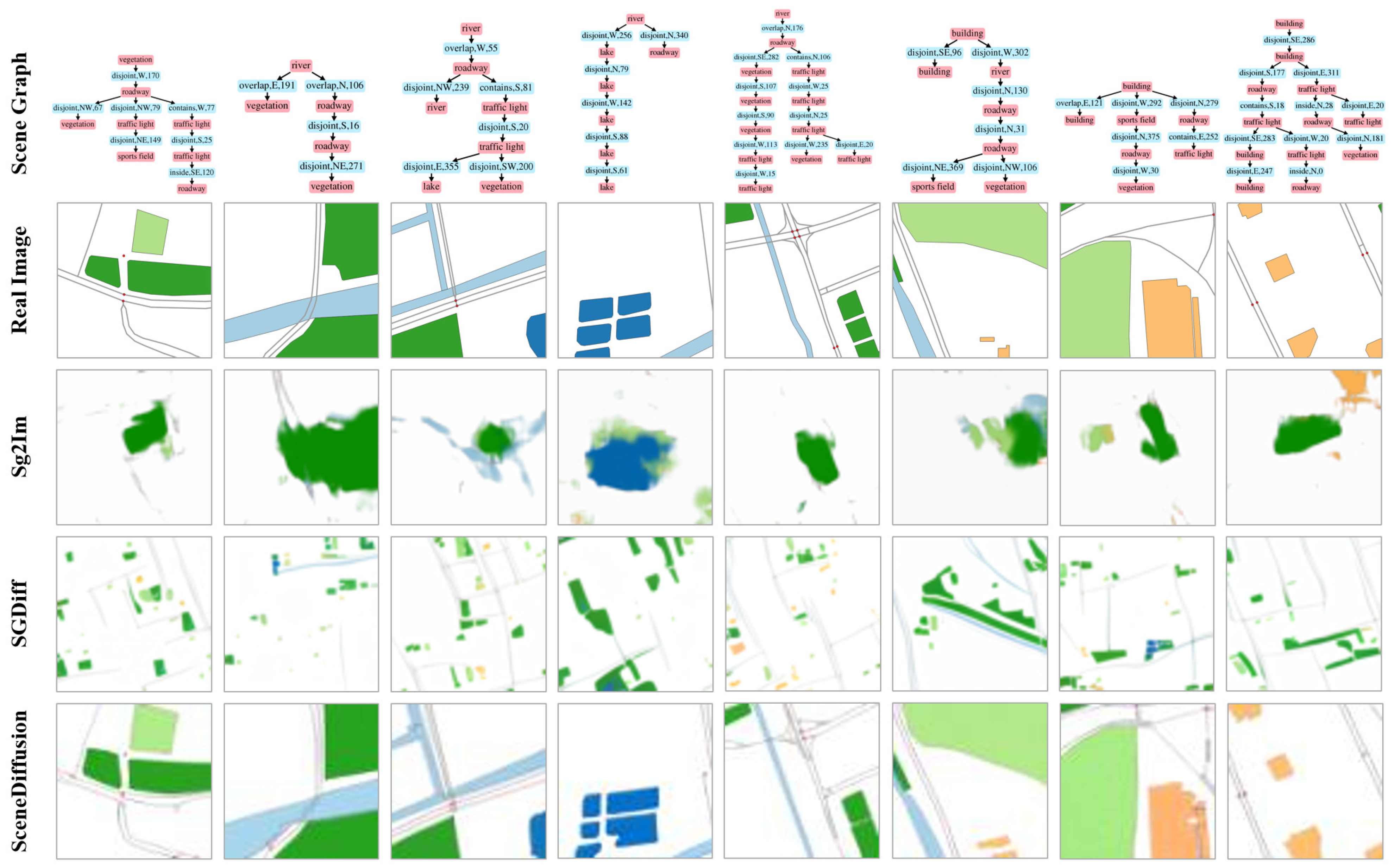
4.4. Qualitative and Quantitative Results
4.4.1. Qualitative Result Analysis
4.4.2. Quantitative Result Analysis
4.5. Ablation Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
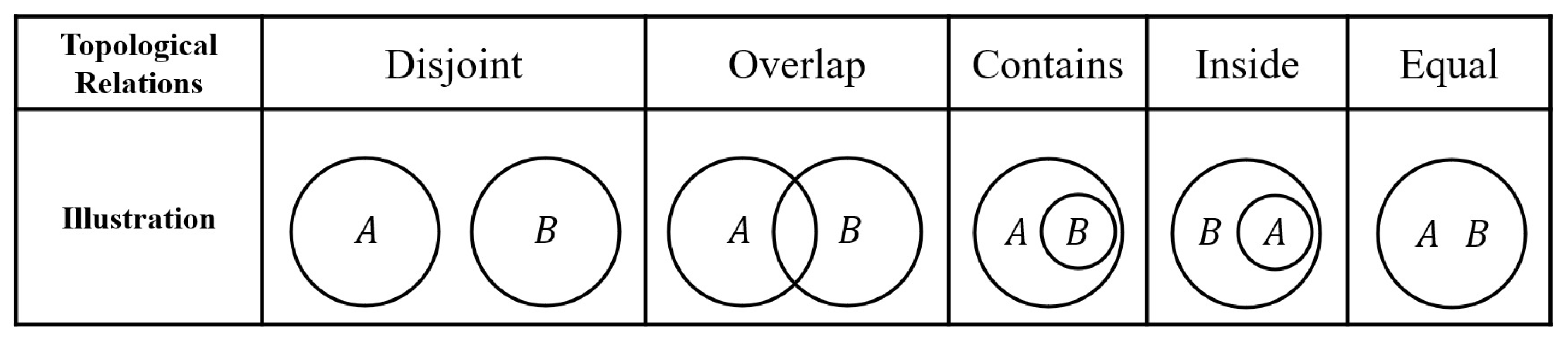
| Topological Relationships | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Disjoint | Object A and object B share no common grid cells, i.e., |
| Overlap | Objects A and object B share at least one common grid cell while neither completely contains the other, i.e., , and |
| Contains | All grid cells of object B form a proper subset of object A’s grid cells, i.e., |
| Inside | All grid cells of object A form a proper subset of object B’s grid cells, i.e., |
| Equal | Objects A and object B occupy exactly the same grid cells, i.e., |
Appendix A.2
| Coordinate Positional Relationship between and | Value Range of | Membership Degree Calculation Formula |
|---|---|---|
| does not exist | ||
| does not exist | ||
| does not exist |
References
- Gao, S. A review of recent researches and reflections on geospatial artificial intelligence. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2020, 45, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; He, Z.; Plaza, J.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Social media: New perspectives to improve remote sensing for emergency response. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1900–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, N.; Guo, D. A spatial scene reconstruction framework in emergency response scenario. J. Saf. Sci. Resil. 2024, 5, 400–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podell, D.; English, Z.; Lacey, K.; Blattmann, A.; Dockhorn, T.; Müller, J.; Penna, J.; Rombach, R. Sdxl: Improving latent diffusion models for high-resolution image synthesis. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.01952. [Google Scholar]
- Baraheem, S.S.; Nguyen, T.V. Sketch-to-image synthesis via semantic masks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 29047–29066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, P.; Chaudhry, R.; Vinay, V. Scene graph embeddings using relative similarity supervision. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 2328–2336. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Gupta, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Image generation from scene graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1219–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Ashual, O.; Wolf, L. Specifying object attributes and relations in interactive scene generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4561–4569. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, D.M.; Sugimoto, A. Visual-relation conscious image generation from structured-text. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 290–306. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Huang, Z.; Song, Y.; Hong, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Cui, B.; Ghanem, B.; Yang, M.H. Diffusion-based scene graph to image generation with masked contrastive pre-training. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.11138. [Google Scholar]
- Rombach, R.; Blattmann, A.; Lorenz, D.; Esser, P.; Ommer, B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 10684–10695. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, L.; Li, B.; Yala, A.; Darrell, T. Llm-grounded diffusion: Enhancing prompt understanding of text-to-image diffusion models with large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.13655. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Chen, C.; Ma, J.; Lu, H.; Lin, X. Compositional text-to-image synthesis with attention map control of diffusion models. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–27 February 2024; Volume 38, pp. 5544–5552. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PmLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; He, X.; Fu, T.J.; Jampani, V.; Akula, A.; Narayana, P.; Basu, S.; Wang, X.E.; Wang, W.Y. Training-free structured diffusion guidance for compositional text-to-image synthesis. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.05032. [Google Scholar]
- Chefer, H.; Alaluf, Y.; Vinker, Y.; Wolf, L.; Cohen-Or, D. Attend-and-excite: Attention-based semantic guidance for text-to-image diffusion models. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2023, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Gan, Z.; Li, L.; Lin, K.; Wu, C.; Duan, N.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zeng, M.; et al. Reco: Region-controlled text-to-image generation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 14246–14255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Rao, A.; Agrawala, M. Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 3836–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, Q.; Hu, J.; Chemerys, P.; Fu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tulyakov, S.; Ren, J. Snapfusion: Text-to-image diffusion model on mobile devices within two seconds. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, K.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H. Forget-me-not: Learning to forget in text-to-image diffusion models. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 1755–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Li, J.; Hoi, S. Blip-diffusion: Pre-trained subject representation for controllable text-to-image generation and editing. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Park, D.H.; Azadi, S.; Zhang, G.; Chopikyan, A.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H.; Rohrbach, A.; Darrell, T. More control for free! image synthesis with semantic diffusion guidance. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2–7 January 2023; pp. 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kawar, B.; Ganz, R.; Elad, M. Enhancing diffusion-based image synthesis with robust classifier guidance. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.08664. [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy, R.; Pan, Z.; Balakrishnan, K.; Cheng, Q.; Jeon, Y.; Yang, H.; Kim, J. Gradient-Free Classifier Guidance for Diffusion Model Sampling. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.15393. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Salimans, T. Classifier-free diffusion guidance. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.12598. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G.; Liang, X.; Lin, L. Law-diffusion: Complex scene generation by diffusion with layouts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 22669–22679. [Google Scholar]
- Baykal, G.; Karagoz, H.F.; Binhuraib, T.; Unal, G. ProtoDiffusion: Classifier-free diffusion guidance with prototype learning. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Hanoi, Vietnam, 5–7 December 2024; pp. 106–120. [Google Scholar]
- Randell, D.A.; Cui, Z.; Cohn, A.G. A spatial logic based on regions and connection. KR 1992, 92, 165–176. [Google Scholar]
- Prim, R.C. Shortest connection networks and some generalizations. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1957, 36, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sara, U.; Akter, M.; Uddin, M.S. Image quality assessment through FSIM, SSIM, MSE and PSNR—A comparative study. J. Comput. Commun. 2019, 7, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Models | FID | SSIM | PSNR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sg2Im | 154.59 | 0.51 | 11.12 dB |
| SGDiff | 189.47 | 0.43 | 11.95 dB |
| SceneDiffusion | 67.15 | 0.69 | 17.80 dB |
| Variants | FID | SSIM | PSNR |
|---|---|---|---|
| only Topo | 114.53 | 0.60 | 14.44 dB |
| only Dir | 124.55 | 0.61 | 15.13 dB |
| only Dist | 126.72 | 0.53 | 10.40 dB |
| w/o Attn | 103.37 | 0.64 | 15.58 dB |
| SceneDiffusion | 67.15 | 0.69 | 17.80 dB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Tu, J.; Guo, D. SceneDiffusion: Scene Generation Model Embedded with Spatial Constraints. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070250
Yu S, Zhu J, Li J, Li X, Wang K, Tu J, Guo D. SceneDiffusion: Scene Generation Model Embedded with Spatial Constraints. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2025; 14(7):250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070250
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shanshan, Jiaxin Zhu, Jiaqi Li, Xunchun Li, Kai Wang, Jian Tu, and Danhuai Guo. 2025. "SceneDiffusion: Scene Generation Model Embedded with Spatial Constraints" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 14, no. 7: 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070250
APA StyleYu, S., Zhu, J., Li, J., Li, X., Wang, K., Tu, J., & Guo, D. (2025). SceneDiffusion: Scene Generation Model Embedded with Spatial Constraints. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 14(7), 250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi14070250








