Amyloid Fragmentation and Disaggregation in Yeast and Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Sup35 Protein and Its Prion Structures
2.1. Sup35 Protein Function and Architecture
2.2. [PSI+] Prion Variants
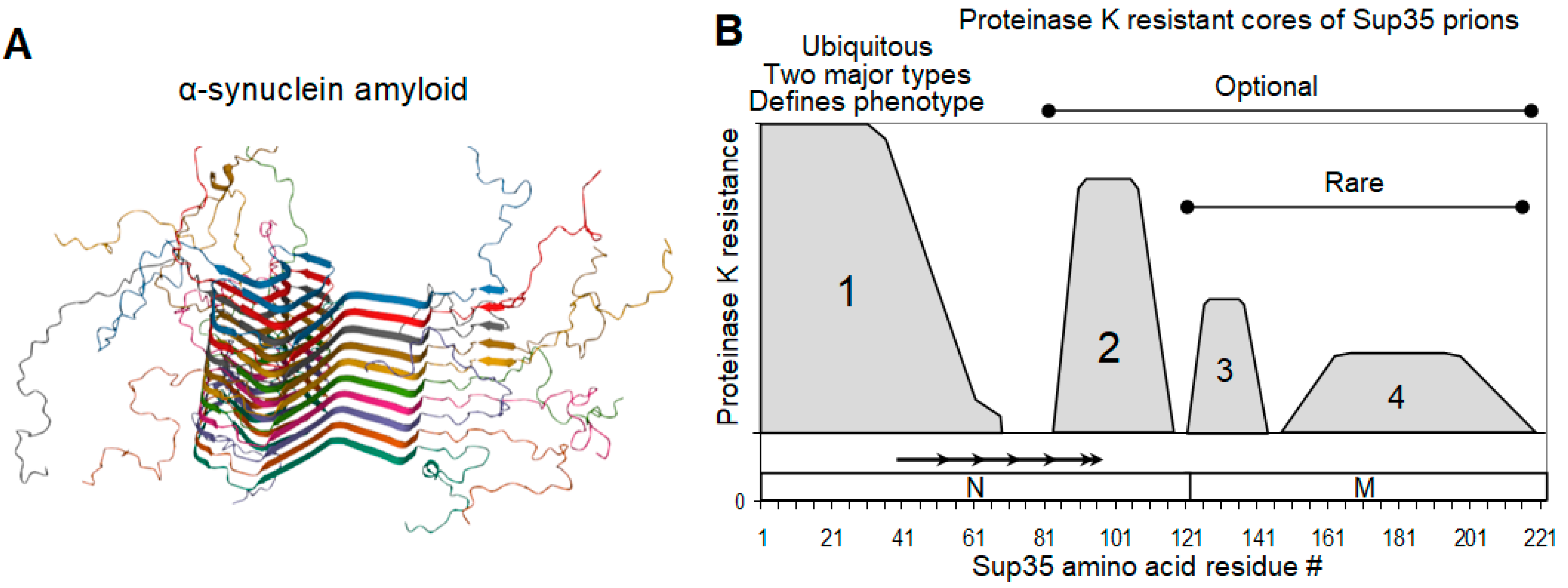
2.3. Sup35 Prion Structures
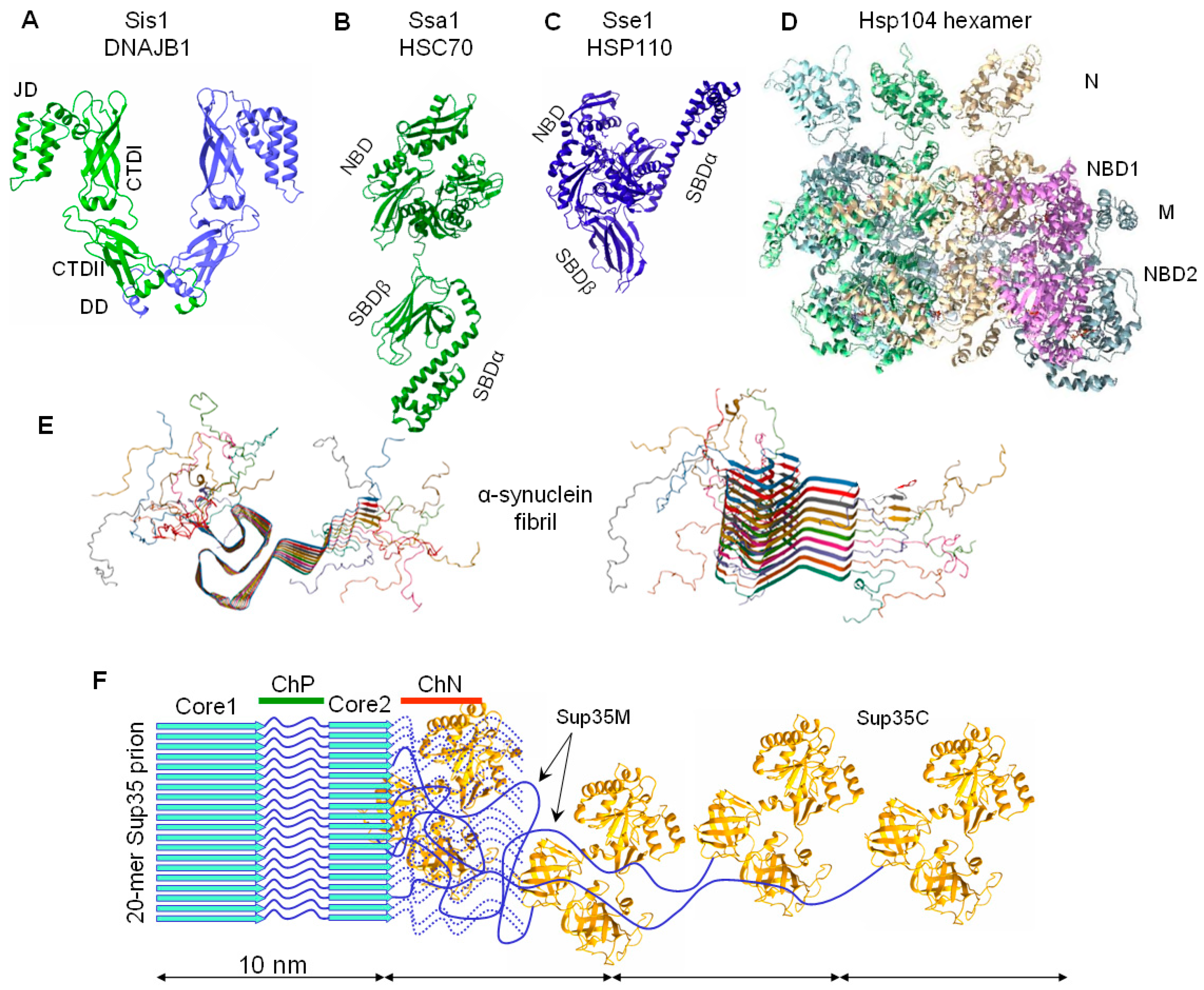
2.4. On the Equivalence of Sup35 In Vitro Fibrils and In Vivo Prions
3. Mechanisms for the Fragmentation and Disassembly of Amyloids in Yeast and Animals
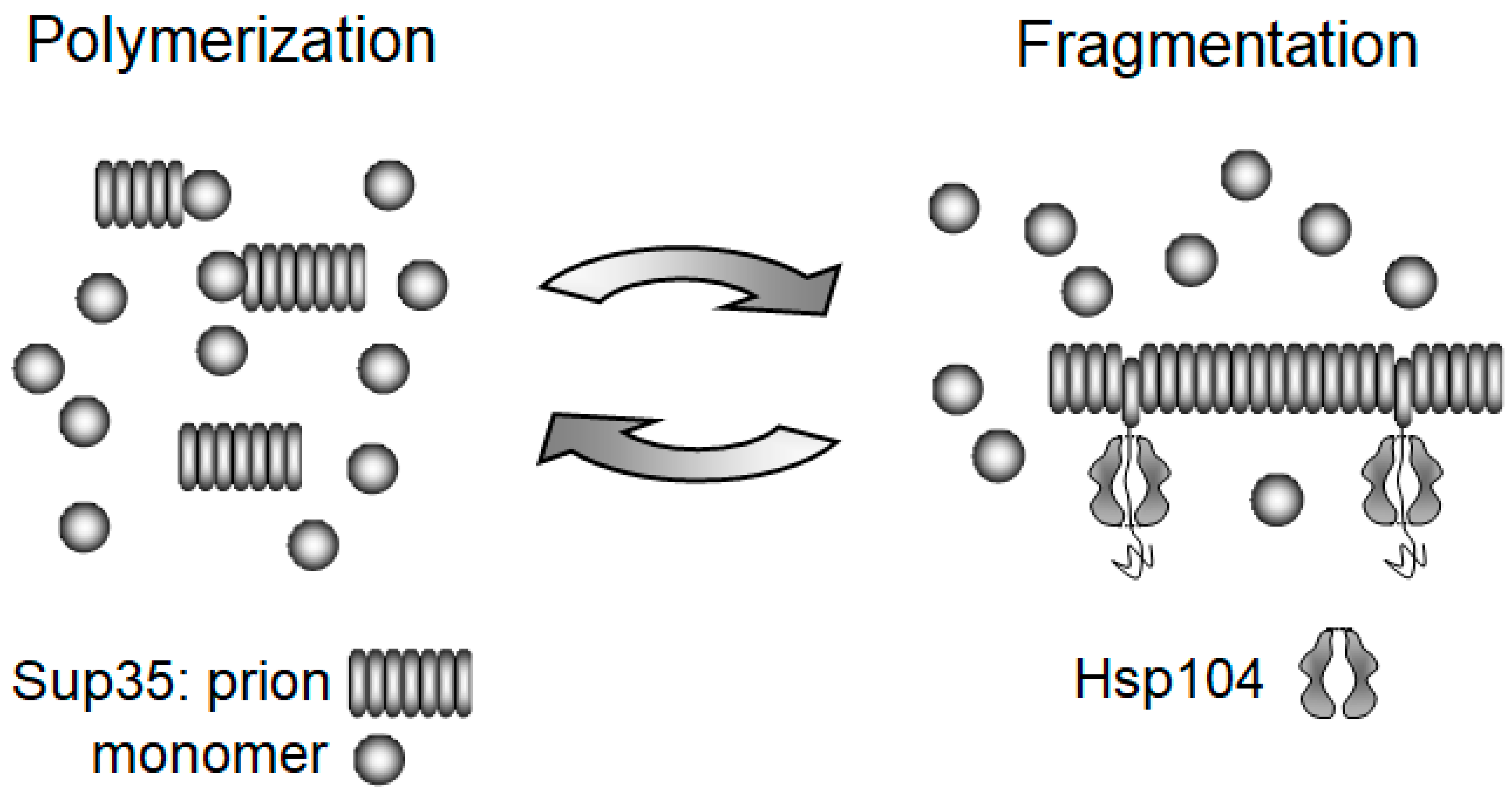
3.1. Replication of Yeast Prions
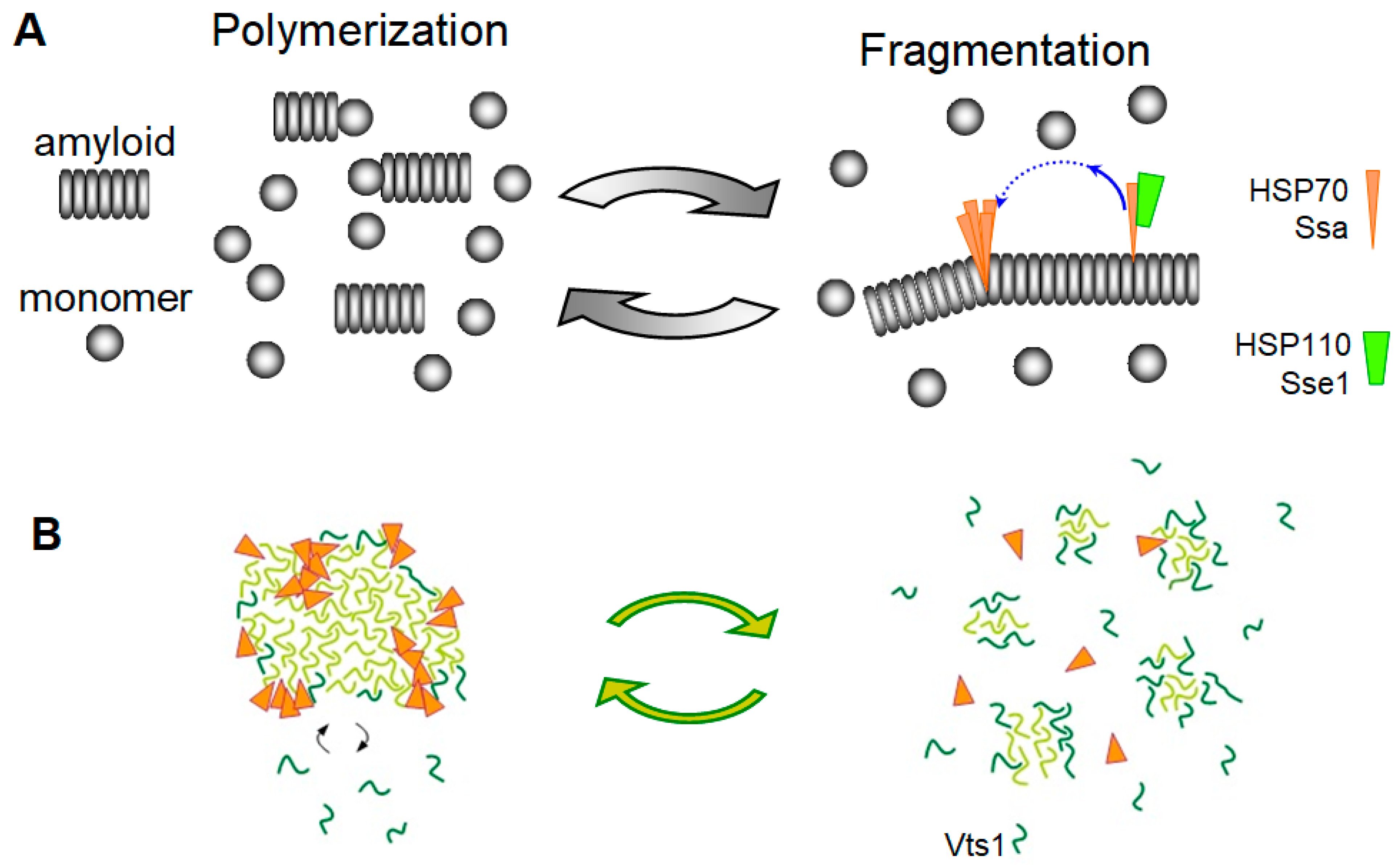
3.2. The Chaperone-Mediated Fragmentation of Yeast Prions
3.3. Amyloid Fragmentation in Animals
3.4. Yeast Prions Based on Putative “Soft” Amyloids or Non-Amyloid Structures
4. Elimination of Prions and Amyloids by Hsp104 and Related Chaperones
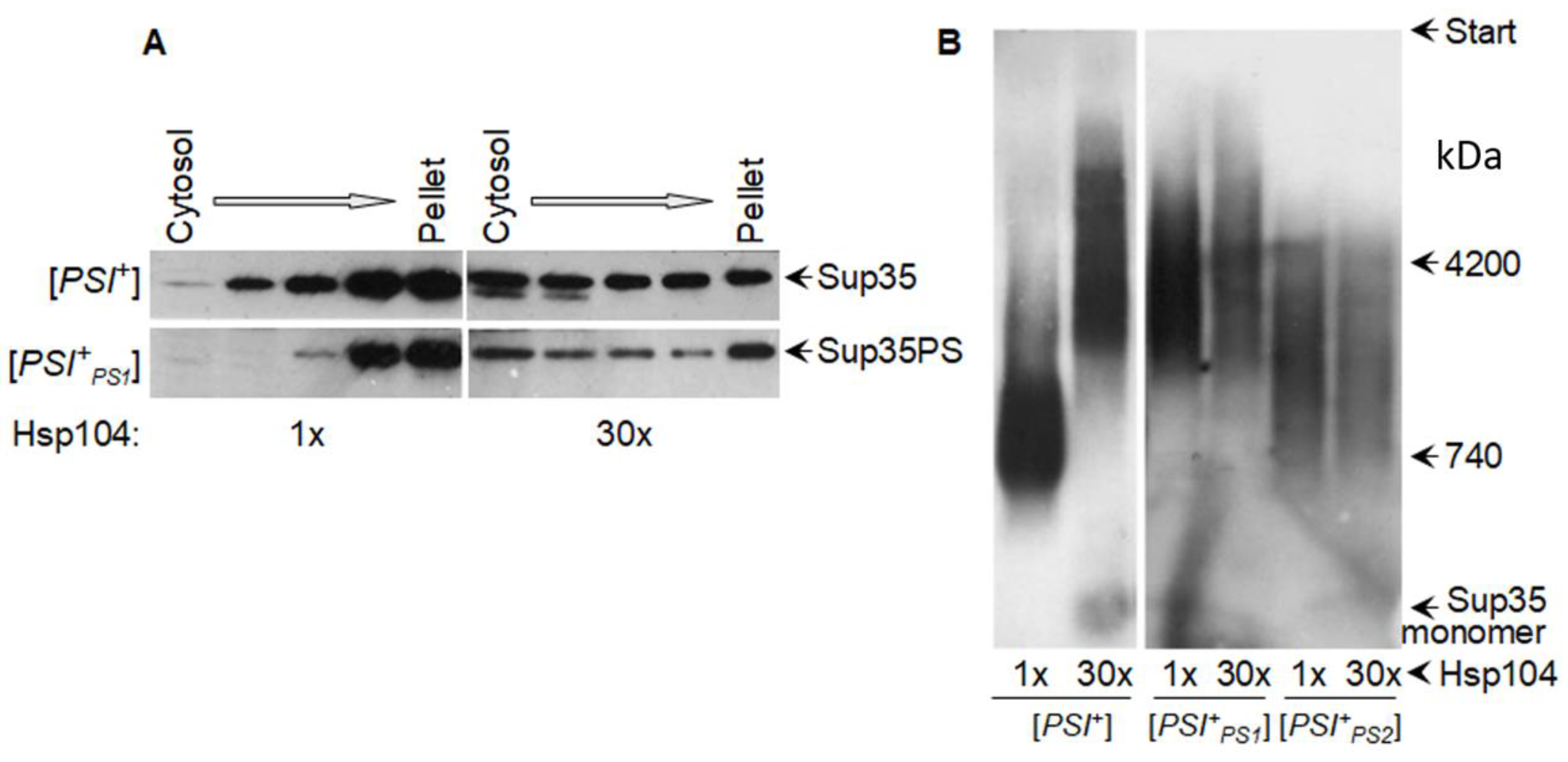
4.1. Overproduced Hsp104 Acts Differently at the Two Levels of Yeast Prion Structure
4.2. Elimination of Yeast Prions by Hsp104
4.3. The Therapeutic Potential of Protein Disaggregases
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiti, F.; Dobson, C.M. Protein Misfolding, Amyloid Formation, and Human Disease: A Summary of Progress over the Last Decade. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 27–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Biology and genetics of prions causing neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2013, 47, 601–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundin, P.; Melki, R.; Kopito, R. Prion-like transmission of protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedert, M.; Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Falcon, B. Like prions: The propagation of aggregated tau and α-synuclein in neurodegeneration. Brain 2017, 140, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Petit, F.; Hérard, A.-S.; Boluda, S.; Eddarkaoui, S.; Guillermier, M.; Letournel, F.; Martin-Négrier, M.-L.; Faisant, M.; Godfraind, C.; et al. Transmission of amyloid-beta and tau pathologies is associated with cognitive impairments in a primate. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleman, K.; Krüttner, S.; Alenius, M.; Dickson, B.J. Function of the Drosophila CPEB protein Orb2 in long-term courtship memory. Nat. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastushita-Sakai, T.; White-Grindley, E.; Samuelson, J.; Seidel, C.; Si, K. Drosophila Orb2 targets genes involved in neuronal growth, synapse formation, and protein turnover. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11987–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickner, R.B. Yeast and Fungal Prions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a023531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.S. Ψ, A cytoplasmic suppressor of super-suppressor in yeast. Heredity 1965, 20, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.; Tuite, M. The life of [PSI]. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroute, F. Non-Mendelian mutation allowing ureidosuccinic acid uptake in yeast. J. Bacteriol. 1971, 106, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickner, R.B. [URE3] as an altered URE2 protein: Evidence for a prion analog in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 1994, 264, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkatch, I.L.; Bradley, M.E.; Hong, J.Y.; Liebman, S.W. Prions affect the appearance of other prions: The story of [PIN+]. Cell 2001, 106, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Park, K.-W.; Yu, H.; Fan, Q.; Li, L. Newly identified prion linked to the chromatin-remodeling factor Swi1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.K.; Gavin-Smyth, J.; Liebman, S.W. The yeast global transcriptional co-repressor protein Cyc8 can propagate as a prion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, G.; Shimazu, N.; Tanaka, M. A yeast prion, Mod5, promotes acquired drug resistance and cell survival under environmental stress. Science 2012, 336, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, S.; Halfmann, R.; King, O.; Kapila, A.; Lindquist, S. A systematic survey identifies prions and illuminates sequence features of prionogenic proteins. Cell 2009, 137, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halfmann, R.; Wright, J.R.; Alberti, S.; Lindquist, S.; Rexach, M. Prion formation by a yeast GLFG nucleoporin. Prion 2012, 6, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernova, T.A.; Kiktev, D.A.; Romanyuk, A.V.; Shanks, J.R.; Laur, O.; Ali, M.; Ghosh, A.; Kim, D.; Yang, Z.; Mang, M.; et al. Yeast Short-Lived Actin-Associated Protein Forms a Metastable Prion in Response to Thermal Stress. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cereghetti, G.; Wilson-Zbinden, C.; Kissling, V.M.; Diether, M.; Arm, A.; Yoo, H.; Piazza, I.; Saad, S.; Picotti, P.; Drummond, D.A.; et al. Reversible amyloids of pyruvate kinase couple cell metabolism and stress granule disassembly. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 23, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, P.; Caudron, F. Mnemons and the memorization of past signaling events. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 69, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.C.S.; Lindquist, S. A heritable switch in carbon source utilization driven by an unusual yeast prion. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2320–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabortee, S.; Byers, J.S.; Jones, S.; Garcia, D.M.; Bhullar, B.; Chang, A.; She, R.; Lee, L.; Fremin, B.; Lindquist, S.; et al. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Drive Emergence and Inheritance of Biological Traits. Cell 2016, 167, 369–381.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- True, H.L.; Lindquist, S.L. A yeast prion provides a mechanism for genetic variation and phenotypic diversity. Nature 2000, 407, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namy, O.; Galopier, A.; Martini, C.; Matsufuji, S.; Fabret, C.; Rousset, J.-P. Epigenetic control of polyamines by the prion [PSI+]. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuite, M.F. Yeast models of neurodegenerative diseases. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2019, 168, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernoff, Y.O.; Grizel, A.V.; Rubel, A.A.; Zelinsky, A.A.; Chandramowlishwaran, P.; Chernova, T.A. Application of yeast to studying amyloid and prion diseases. Adv. Genet. 2020, 105, 293–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpionov, G.V.; Alexandrov, A.I.; Antonenko, Y.N.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. A protein polymerization cascade mediates toxicity of non-pathological human huntingtin in yeast. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnirov, V.V.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. Structure and replication of yeast prions. Cell 1998, 94, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfield, I.; Jones, K.M.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Dagkesamanskaya, A.R.; Poznyakovski, A.I.; Paushkin, S.V.; Nierras, C.R.; Cox, B.S.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Tuite, M.F. The products of the SUP45 (eRF1) and SUP35 genes interact to mediate translation termination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4365–4373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhouravleva, G.; Frolova, L.; Le Goff, X.; Le Guellec, R.; Inge-Vechtomov, S.; Kisselev, L.; Philippe, M. Termination of translation in eukaryotes is governed by two interacting polypeptide chain release factors, eRF1 and eRF3. EMBO J. 1995, 14, 4065–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Dagkesamanskaya, A.R.; Didichenko, S.A.; Chernoff, Y.O.; Inge-Vechtomov, S.G.; Smirnov, V.N. Deletion analysis of the SUP35 gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae reveals two non-overlapping functional regions in the encoded protein. Mol. Microbiol. 1993, 7, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsen, C.W.; Glover, J.R. Insight into molecular basis of curing of [PSI+] prion by overexpression of 104-kDa heat shock protein Hsp104. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzmann, T.M.; Jahnel, M.; Pozniakovsky, A.; Mahamid, J.; Holehouse, A.S.; Nüske, E.; Richter, D.; Baumeister, W.; Grill, S.W.; Pappu, R.V.; et al. Phase separation of a yeast prion protein promotes cellular fitness. Science 2018, 359, 6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehra, S.; Gadhe, L.; Bera, R.; Sawner, A.S.; Maji, S.K. Structural and Functional Insights into α-Synuclein Fibril Polymorphism. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, M.; Aguzzi, A. Molecular foundations of prion strain diversity. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2021, 72, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkatch, I.L.; Chernoff, Y.O.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Inge-Vechtomov, S.G.; Liebman, S.W. Genesis and variability of [PSI+] prion factors in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 1996, 144, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickner, R.B.; Son, M.; Edskes, H.K. Prion Variants of Yeast are Numerous, Mutable, and Segregate on Growth, Affecting Prion Pathogenesis, Transmission Barriers, and Sensitivity to Anti-Prion Systems. Viruses 2019, 11, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizhnikov, A.A.; Ryzhova, T.A.; Volkov, K.V.; Zadorsky, S.P.; Sopova, J.V.; Inge-Vechtomov, S.G.; Galkin, A.P. Interaction of Prions Causes Heritable Traits in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-C.; Wang, H.-L.; King, C.-Y. Strain-specific sequences required for yeast [PSI+] prion propagation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13345–13350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-W.; King, C.-Y. A complete catalog of wild-type Sup35 prion variants and their protein-only propagation. Curr. Genet. 2020, 66, 97–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-W.; Kushnirov, V.V.; King, C.-Y. Mutable yeast prion variants are stabilized by a defective Hsp104 chaperone. Mol. Microbiol. 2021, 115, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohhashi, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kurahashi, H.; Kamatari, Y.O.; Sugiyama, S.; Uluca, B.; Piechatzek, T.; Komi, Y.; Shida, T.; Müller, H.; et al. Molecular basis for diversification of yeast prion strain conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 2389–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryndushkin, D.S.; Alexandrov, I.M.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Kushnirov, V. V Yeast [PSI+] prion aggregates are formed by small Sup35 polymers fragmented by Hsp104. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 49636–49643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dergalev, A.; Alexandrov, A.; Ivannikov, R.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.; Kushnirov, V. Yeast Sup35 Prion Structure: Two Types, Four Parts, Many Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewmaker, F.; Wickner, R.B.; Tycko, R. Amyloid of the prion domain of Sup35p has an in-register parallel beta-sheet structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19754–19759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shewmaker, F.; Kryndushkin, D.; Chen, B.; Tycko, R.; Wickner, R.B. Two prion variants of Sup35p have in-register parallel β-sheet structures, independent of hydration. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 5074–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.D.; Comellas, G.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Covell, D.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Kloepper, K.D.; Courtney, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Barclay, A.M.; Kendall, A.; et al. Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human α-synuclein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, R.; Lindquist, S.L. Structural insights into a yeast prion illuminate nucleation and strain diversity. Nature 2005, 435, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyama, B.H.; Kelly, M.J.S.; Gross, J.D.; Weissman, J.S. The structural basis of yeast prion strain variants. Nature 2007, 449, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depace, A.H.; Santoso, A.; Hillner, P.; Weissman, J.S. A Critical Role for Amino-Terminal Glutamine/Asparagine Repeats in the Formation and Propagation of a Yeast Prion. Cell 1998, 93, 1241–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Diaz-Avalos, R.; King, C.Y. W8, a new Sup35 prion strain, transmits distinctive information with a conserved assembly scheme. Prion 2015, 9, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ghosh, R.; Dong, J.; Wall, J.; Frederick, K.K. Amyloid fibrils embodying distinctive yeast prion phenotypes exhibit diverse morphologies. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parham, S.N.; Resende, C.G.; Tuite, M.F. Oligopeptide repeats in the yeast protein Sup35p stabilize intermolecular prion interactions. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkundina, I.S.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Tuite, M.F.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. The role of the N-terminal oligopeptide repeats of the yeast Sup35 prion protein in propagation and transmission of prion variants. Genetics 2006, 172, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Collins, S.R.; Toyama, B.H.; Weissman, J.S. The physical basis of how prion conformations determine strain phenotypes. Nature 2006, 442, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, A.I.; Polyanskaya, A.B.; Serpionov, G.V.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Kushnirov, V.V. The Effects of Amino Acid Composition of Glutamine-Rich Domains on Amyloid Formation and Fragmentation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernoff, Y.O.; Lindquist, S.L.; Ono, B.; Inge-Vechtomov, S.G.; Liebman, S.W. Role of the chaperone protein Hsp104 in propagation of the yeast prion-like factor [PSI+]. Science 1995, 268, 880–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paushkin, S.V.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Smirnov, V.N.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. Propagation of the yeast prion-like [PSI+] determinant is mediated by oligomerization of the SUP35-encoded polypeptide chain release factor. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsell, D.A.; Kowal, A.S.; Singer, M.A.; Lindquist, S. Protein disaggregation mediated by heat-shock protein Hsp104. Nature 1994, 372, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, C.-Y.; Tittmann, P.; Gross, H.; Gebert, R.; Aebi, M.; Wuthrich, K. Prion-inducing domain 2-114 of yeast Sup35 protein transforms in vitro into amyloid-like filaments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, J.R.; Kowal, A.S.; Schirmer, E.C.; Patino, M.M.; Liu, J.J.; Lindquist, S. Self-seeded fibers formed by Sup35, the protein determinant of [PSI+], a heritable prion-like factor of S. cerevisiae. Cell 1997, 89, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patino, M.M.; Liu, J.J.; Glover, J.R.; Lindquist, S. Support for the prion hypothesis for inheritance of a phenotypic trait in yeast. Science 1996, 273, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paushkin, S.V.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Smirnov, V.N.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. In vitro propagation of the prion-like state of yeast Sup35 protein. Science 1997, 277, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, L.J.; Cole, D.J.; Cox, B.S.; Ridout, M.S.; Morgan, B.J.T.; Tuite, M.F. The number and transmission of [PSI+] prion seeds (Propagons) in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Tyedmers, J.; Bukau, B.; Mogk, A. Hsp70 targets Hsp100 chaperones to substrates for protein disaggregation and prion fragmentation. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuite, M.F.; Mundy, C.R.; Cox, B.S. Agents that cause a high frequency of genetic change from [PSI+] to [psi-] in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 1981, 98, 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxa, U.; Keller, P.W.; Cheng, N.; Wall, J.S.; Steven, A.C. In Sup35p filaments (the [PSI+] prion), the globular C-terminal domains are widely offset from the amyloid fibril backbone. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, F.E.; Pan, K.M.; Huang, Z.; Baldwin, M.; Fletterick, R.J.; Prusiner, S.B. Structural clues to prion replication. Science 1994, 264, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, L.C. Proteopathic Strains and the Heterogeneity of Neurodegenerative Diseases. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2016, 50, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, J.R.; Lindquist, S. Hsp104, Hsp70, and Hsp40: A novel chaperone system that rescues previously aggregated proteins. Cell 1998, 94, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagriantsev, S.N.; Gracheva, E.O.; Richmond, J.E.; Liebman, S.W. Variant-specific [PSI+] infection is transmitted by Sup35 polymers within [PSI+] aggregates with heterogeneous protein composition. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 2433–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Wang, X.; Xi, W.; Richardson, R.; Laue, T.M.; Denis, C.L. The non-prion SUP35 preexists in large chaperone-containing molecular complexes. Proteins 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondheimer, N.; Lopez, N.; Craig, E.A.; Lindquist, S. The role of Sis1 in the maintenance of the [RNQ+] prion. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higurashi, T.; Hines, J.K.; Sahi, C.; Aron, R.; Craig, E.A. Specificity of the J-protein Sis1 in the propagation of 3 yeast prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16596–16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipton, K.A.; Verges, K.J.; Weissman, J.S. In vivo monitoring of the prion replication cycle reveals a critical role for Sis1 in delivering substrates to Hsp104. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.K.; Li, X.; Du, Z.; Higurashi, T.; Li, L.; Craig, E.A. [SWI], the prion formed by the chromatin remodeling factor Swi1, is highly sensitive to alterations in Hsp70 chaperone system activity. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilke, B.A.; Ciesielski, S.J.; Ziegelhoffer, T.; Kamiya, E.; Tonelli, M.; Lee, W.; Cornilescu, G.; Hines, J.K.; Markley, J.L.; Craig, E.A. Broadening the functionality of a J-protein/Hsp70 molecular chaperone system. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1007084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, M.E.; Edskes, H.K.; Hong, J.Y.; Wickner, R.B.; Liebman, S.W. Interactions among prions and prion “strains” in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99 (Suppl. 4), 16392–16399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryndushkin, D.S.; Smirnov, V.N.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Kushnirov, V.V. Increased expression of Hsp40 chaperones, transcriptional factors, and ribosomal protein Rpp0 can cure yeast prions. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 23702–23708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troisi, E.M.; Rockman, M.E.; Nguyen, P.P.; Oliver, E.E.; Hines, J.K. Swa2, the yeast homolog of mammalian auxilin, is specifically required for the propagation of the prion variant [URE3-1]. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 97, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsell, D.A.; Kowal, A.S.; Lindquist, S. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hsp104 protein. Purification and characterization of ATP-induced structural changes. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 4480–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorter, J.; Southworth, D.R. Spiraling in Control: Structures and Mechanisms of the Hsp104 Disaggregase. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a034033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, S.N.; Yokom, A.L.; Lin, J.; Jackrel, M.E.; Rizo, A.N.; Kendsersky, N.M.; Buell, C.E.; Sweeny, E.A.; Mack, K.L.; Chuang, E.; et al. Ratchet-like polypeptide translocation mechanism of the AAA+ disaggregase Hsp104. Science 2017, 357, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellaneda, M.J.; Franke, K.B.; Sunderlikova, V.; Bukau, B.; Mogk, A.; Tans, S.J. Processive extrusion of polypeptide loops by a Hsp100 disaggregase. Nature 2020, 578, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeymer, C.; Werbeck, N.D.; Schlichting, I.; Reinstein, J. The molecular mechanism of Hsp100 chaperone inhibition by the prion curing agent guanidinium chloride. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7065–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummer, E.; Oguchi, Y.; Seyffer, F.; Bukau, B.; Mogk, A. Mechanism of Hsp104/ClpB inhibition by prion curing Guanidinium hydrochloride. FEBS Lett. 2013, 587, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escusa-Toret, S.; Vonk, W.I.M.; Frydman, J. Spatial sequestration of misfolded proteins by a dynamic chaperone pathway enhances cellular fitness during stress. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desantis, M.E.; Leung, E.H.; Sweeny, E.A.; Jackrel, M.E.; Cushman-Nick, M.; Neuhaus-Follini, A.; Vashist, S.; Sochor, M.A.; Knight, M.N.; Shorter, J. Operational plasticity enables Hsp104 to disaggregate diverse amyloid and nonamyloid clients. Cell 2012, 151, 778–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erives, A.J.; Fassler, J.S. Metabolic and chaperone gene loss marks the origin of animals: Evidence for Hsp104 and Hsp78 chaperones sharing mitochondrial enzymes as clients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelt, H.; Kirstein-Miles, J.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Chi, K.; Scholz, S.R.; Morimoto, R.I.; Bukau, B. Metazoan Hsp70 machines use Hsp110 to power protein disaggregation. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4221–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Carroni, M.; Nussbaum-Krammer, C.; Mogk, A.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Szlachcic, A.; Guilbride, D.L.; Saibil, H.R.; Mayer, M.P.; Bukau, B. Human Hsp70 Disaggregase Reverses Parkinson’s-Linked α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 781–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorter, J. The mammalian disaggregase machinery: Hsp110 synergizes with Hsp70 and Hsp40 to catalyze protein disaggregation and reactivation in a cell-free system. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentink, A.S.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Feufel, J.; Ubartaitė, G.; Schneider, C.P.; de los Rios, P.; Hennig, J.; Barducci, A.; Bukau, B. Molecular dissection of amyloid disaggregation by human HSP70. Nature 2020, 587, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, B.T.; Wickner, R.B. Heritable activity: A prion that propagates by covalent autoactivation. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2083–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, I.A.; Yarovoy, B.P. Cytoduction as a new tool in studying the cytoplasmic heredity in yeast. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1977, 14, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urakov, V.N.; Vishnevskaya, A.B.; Alexandrov, I.M.; Kushnirov, V.V.; Smirnov, V.N.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. Interdependence of amyloid formation in yeast: Implications for polyglutamine disorders and biological functions. Prion 2010, 4, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Han, T.W.; Xie, S.; Shi, K.; Du, X.; Wu, L.C.; Mirzaei, H.; Goldsmith, E.J.; Longgood, J.; Pei, J.; et al. Cell-free Formation of RNA Granules: Low Complexity Sequence Domains Form Dynamic Fibers within Hydrogels. Cell 2012, 149, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Qamar, S.; Lin, J.Q.; Schierle, G.S.K.; Rees, E.; Miyashita, A.; Costa, A.R.; Dodd, R.B.; Chan, F.T.S.; Michel, C.H.; et al. ALS/FTD Mutation-Induced Phase Transition of FUS Liquid Droplets and Reversible Hydrogels into Irreversible Hydrogels Impairs RNP Granule Function. Neuron 2015, 88, 678–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-S.; Kato, M.; Wu, X.; Litsios, A.; Sutter, B.M.; Wang, Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Wood, N.E.; Lemoff, A.; Mirzaei, H.; et al. Yeast Ataxin-2 Forms an Intracellular Condensate Required for the Inhibition of TORC1 Signaling during Respiratory Growth. Cell 2019, 177, 697–710.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagaudrière-Gesbert, C.; Newmyer, S.L.; Gregers, T.F.; Bakke, O.; Ploegh, H.L. Uncoating ATPase Hsc70 is recruited by invariant chain and controls the size of endocytic compartments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, A.K.; Smejkal, T.; Itakura, A.K.; Garcia, D.M.; Jarosz, D.F. A Non-amyloid Prion Particle that Activates a Heritable Gene Expression Program. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 251–265.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, B.; Ness, F.; Tuite, M. Analysis of the generation and segregation of propagons: Entities that propagate the [PSI+] prion in yeast. Genetics 2003, 165, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemmaghami, S.; Huh, W.-K.; Bower, K.; Howson, R.W.; Belle, A.; Dephoure, N.; O’Shea, E.K.; Weissman, J.S. Global analysis of protein expression in yeast. Nature 2003, 425, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, F.; Cox, B.S.; Wongwigkarn, J.; Naeimi, W.R.; Tuite, M.F. Over-expression of the molecular chaperone Hsp104 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae results in the malpartition of [PSI+] propagons. Mol. Microbiol. 2017, 104, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnirov, V.V.; Kochneva-Pervukhova, N.V.; Chechenova, M.B.; Frolova, N.S.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. Prion properties of the Sup35 protein of yeast Pichia methanolica. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorkovskiy, A.; Reidy, M.; Masison, D.C.; Wickner, R.B. Hsp104 disaggregase at normal levels cures many [PSI +] prion variants in a process promoted by Sti1p, Hsp90, and Sis1p. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4193–E4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, H.; Edskes, H.K.; Wickner, R.B. [URE3] prion propagation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Requirement for chaperone Hsp104 and curing by overexpressed chaperone Ydj1p. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 8916–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkatch, I.L.; Bradley, M.E.; Masse, S.V.; Zadorsky, S.P.; Polozkov, G.V.; Inge-Vechtomov, S.G.; Liebman, S.W. Dependence and independence of [PSI+] and [PIN+]: A two-prion system in yeast? EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveenko, A.G.; Barbitoff, Y.A.; Jay-Garcia, L.M.; Chernoff, Y.O.; Zhouravleva, G.A. Differential effects of chaperones on yeast prions: CURrent view. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnirov, V.V.; Kryndushkin, D.S.; Boguta, M.; Smirnov, V.N.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D. Chaperones that cure yeast artificial [PSI+] and their prion-specific effects. Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, 1443–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.E.; Saba, F.; Silberman, R.E.; Zhao, X. Mechanisms for curing yeast prions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villali, J.; Dark, J.; Brechtel, T.M.; Pei, F.; Sindi, S.S.; Serio, T.R. Nucleation seed size determines amyloid clearance and establishes a barrier to prion appearance in yeast. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, K.K.; Debelouchina, G.T.; Kayatekin, C.; Dorminy, T.; Jacavone, A.C.; Griffin, R.G.; Lindquist, S. Distinct prion strains are defined by amyloid core structure and chaperone binding site dynamics. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnam, G.P.; Birchmore, J.L.; Chernoff, Y.O. Destabilization and recovery of a yeast prion after mild heat shock. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 432–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howie, R.L.; Jay-Garcia, L.M.; Kiktev, D.A.; Faber, Q.L.; Murphy, M.; Rees, K.A.; Sachwani, N.; Chernoff, Y.O. Role of the Cell Asymmetry Apparatus and Ribosome-Associated Chaperones in the Destabilization of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae Prion by Heat Shock. Genetics 2019, 212, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, I.M.; Vishnevskaya, A.B.; Ter-Avanesyan, M.D.; Kushnirov, V.V. Appearance and propagation of polyglutamine-based amyloids in yeast: Tyrosine residues enable polymer fragmentation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15185–15192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Gracia, P.; Colom, A.; Camino, J.D.; Fernández-Higuero, J.Á.; Orozco, N.; Dulebo, A.; Saiz, L.; Cremades, N.; Vilar, J.M.G.; et al. All-or-none amyloid disassembly via chaperone-triggered fibril unzipping favors clearance of α-synuclein toxic species. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105548118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorter, J. Hsp104: A weapon to combat diverse neurodegenerative disorders. NeuroSignals 2007, 16, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosser, D.D.; Ho, S.; Glover, J.R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Hsp104 enhances the chaperone capacity of human cells and inhibits heat stress-induced proapoptotic signaling. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 8107–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Bianco, C.; Shorter, J.; Régulier, E.; Lashuel, H.; Iwatsubo, T.; Lindquist, S.; Aebischer, P. Hsp104 antagonizes alpha-synuclein aggregation and reduces dopaminergic degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2008, 118, 3087–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Han, Y.-L.; Song, J.; Wang, Y.; Jing, Y.-Y.; Shi, Q.; Tian, C.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Li, C.-P.; Han, J.; et al. Heat shock protein 104 inhibited the fibrillization of prion peptide 106-126 and disassembled prion peptide 106-126 fibrils in vitro. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman-Nick, M.; Bonini, N.M.; Shorter, J. Hsp104 suppresses polyglutamine-induced degeneration post onset in a drosophila MJD/SCA3 model. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacher, C.; Garcia-Oroz, L.; Rubinsztein, D.C. Overexpression of yeast hsp104 reduces polyglutamine aggregation and prolongs survival of a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 3425–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyal, S.H.; Schmidt, E.; Kitagawa, K.; Sondheimer, N.; Lindquist, S.; Kramer, J.M.; Morimoto, R.I. Polyglutamine aggregates alter protein folding homeostasis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 5750–5755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, V.; Régulier, E.; Abbas-Terki, T.; Hassig, R.; Brouillet, E.; Aebischer, P.; Luthi-Carter, R.; Déglon, N. Neuroprotection by Hsp104 and Hsp27 in lentiviral-based rat models of Huntington’s disease. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, K.L.; Shorter, J. Engineering and Evolution of Molecular Chaperones and Protein Disaggregases with Enhanced Activity. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackrel, M.E.; Yee, K.; Tariq, A.; Chen, A.I.; Shorter, J. Disparate Mutations Confer Therapeutic Gain of Hsp104 Function. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 2672–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackrel, M.E.; Desantis, M.E.; Martinez, B.A.; Castellano, L.M.; Stewart, R.M.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Shorter, J. Potentiated Hsp104 variants antagonize diverse proteotoxic misfolding events. Cell 2014, 156, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeny, E.A.; Jackrel, M.E.; Go, M.S.; Sochor, M.A.; Razzo, B.M.; DeSantis, M.E.; Gupta, K.; Shorter, J. The Hsp104 N-terminal domain enables disaggregase plasticity and potentiation. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Lin, J.; Noll, M.M.; Torrente, M.P.; Mack, K.L.; Murillo, O.H.; Jackrel, M.E.; Shorter, J. Potentiating Hsp104 activity via phosphomimetic mutations in the middle domain. FEMS Yeast Res. 2018, 18, foy042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, A.; Lin, J.; Jackrel, M.E.; Hesketh, C.D.; Carman, P.J.; Mack, K.L.; Weitzman, R.; Gambogi, C.; Hernandez Murillo, O.A.; Sweeny, E.A.; et al. Mining Disaggregase Sequence Space to Safely Counter TDP-43, FUS, and α-Synuclein Proteotoxicity. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 2080–2095.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.J.; Bao, A.; Bell, B.; Ling, C.; Jackrel, M.E. Drivers of Hsp104 potentiation revealed by scanning mutagenesis of the middle domain. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, M.; Miot, M.; Masison, D.C. Prokaryotic Chaperones Support Yeast Prions and Thermoto lerance and Define Disaggregation Machinery Interactions. Genetics 2012, 192, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, Z.M.; Sweeney, K.; Kim, H.; Yan, X.; Castellano, L.M.; Jackrel, M.E.; Lin, J.; Chuang, E.; Gomes, E.; Willicott, C.W.; et al. Therapeutic genetic variation revealed in diverse Hsp104 homologs. Elife 2020, 9, e57457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalska, K.; Zhang, K.; March, Z.M.; Hatzos-Skintges, C.; Pintilie, G.; Bigelow, L.; Castellano, L.M.; Miles, L.J.; Jackrel, M.E.; Chuang, E.; et al. Structure of Calcarisporiella thermophila Hsp104 Disaggregase that Antagonizes Diverse Proteotoxic Misfolding Events. Structure 2019, 27, 449–463.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupo, R.R.; Shorter, J. Skd3 (human ClpB) is a potent mitochondrial protein disaggregase that is inactivated by 3-methylglutaconic aciduria-linked mutations. Elife 2020, 9, e55279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.M.; Benaroudj, N.; Goldberg, A. Proteasomes and their associated ATPases: A destructive combination. J. Struct. Biol. 2006, 156, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, C.; Snoberger, A.; Belcastro, M.; Murphy, J.; Kisselev, O.G.; Smith, D.M.; Sokolov, M. Archaeal Unfoldase Counteracts Protein Misfolding Retinopathy in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 7248–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittelmeier, J.; Sandhof, C.A.; Ries, H.M.; Druffel-Augustin, S.; Mogk, A.; Bukau, B.; Nussbaum-Krammer, C. The HSP110/HSP70 disaggregation system generates spreading-competent toxic α-synuclein species. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaegd, K.; Schymkowitz, J.; Rousseau, F. Transcellular Spreading of Tau in Tauopathies. Chembiochem 2018, 19, 2424–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kushnirov, V.V.; Dergalev, A.A.; Alexandrov, A.I. Amyloid Fragmentation and Disaggregation in Yeast and Animals. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121884
Kushnirov VV, Dergalev AA, Alexandrov AI. Amyloid Fragmentation and Disaggregation in Yeast and Animals. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(12):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121884
Chicago/Turabian StyleKushnirov, Vitaly V., Alexander A. Dergalev, and Alexander I. Alexandrov. 2021. "Amyloid Fragmentation and Disaggregation in Yeast and Animals" Biomolecules 11, no. 12: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121884
APA StyleKushnirov, V. V., Dergalev, A. A., & Alexandrov, A. I. (2021). Amyloid Fragmentation and Disaggregation in Yeast and Animals. Biomolecules, 11(12), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121884






