The Tolerance of Salinity in Rice Requires the Presence of a Functional Copy of FLN2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growing Conditions
2.2. Generation of KO Lines
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Assay
2.4. Analysis of Enzyme Activities and Sugar Content
2.5. Phloem Export of Sucrose
2.6. Characterization of Root System Architecture
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
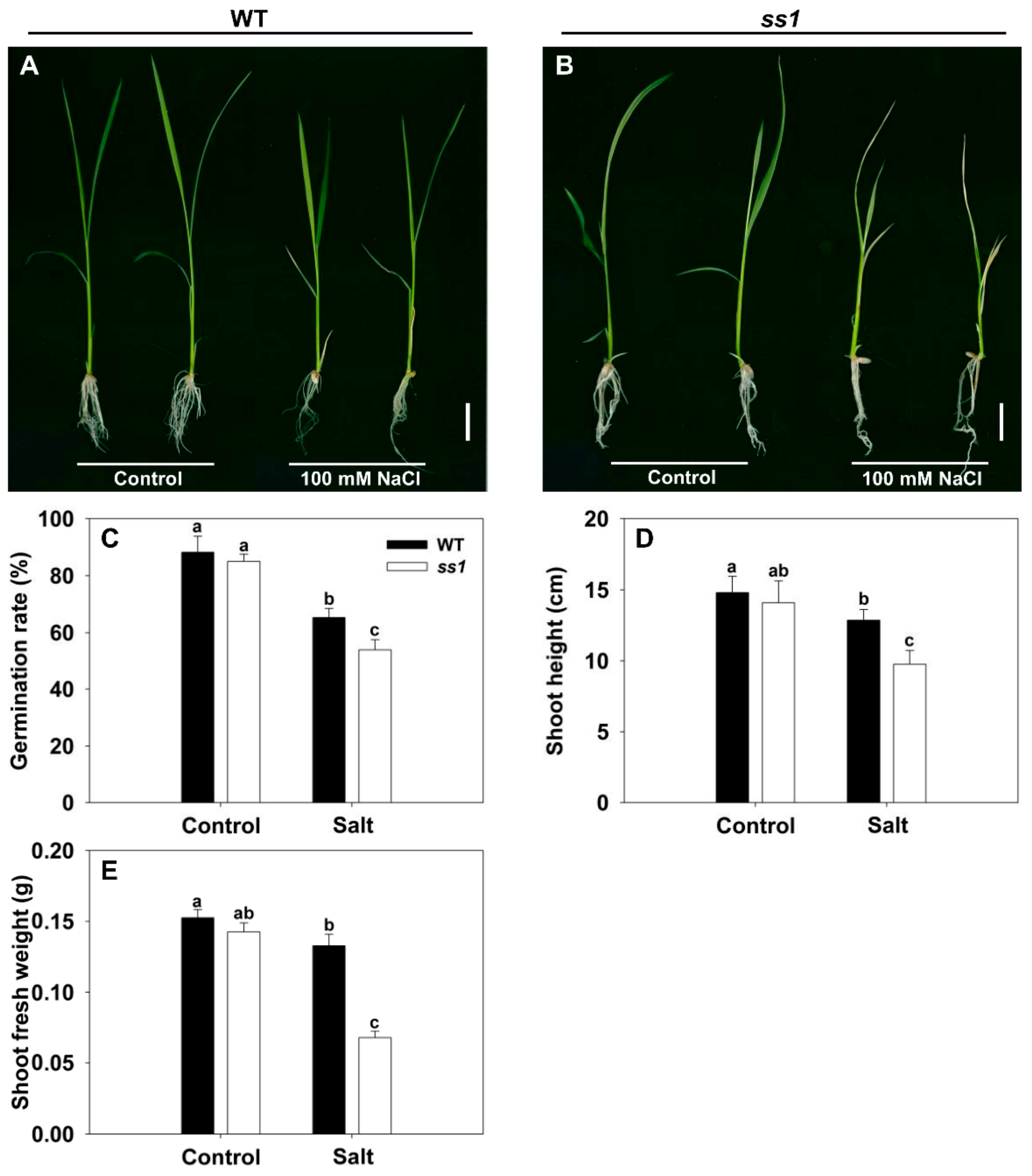
3.1. Selection of a Salinity-Hypersensitive Mutant
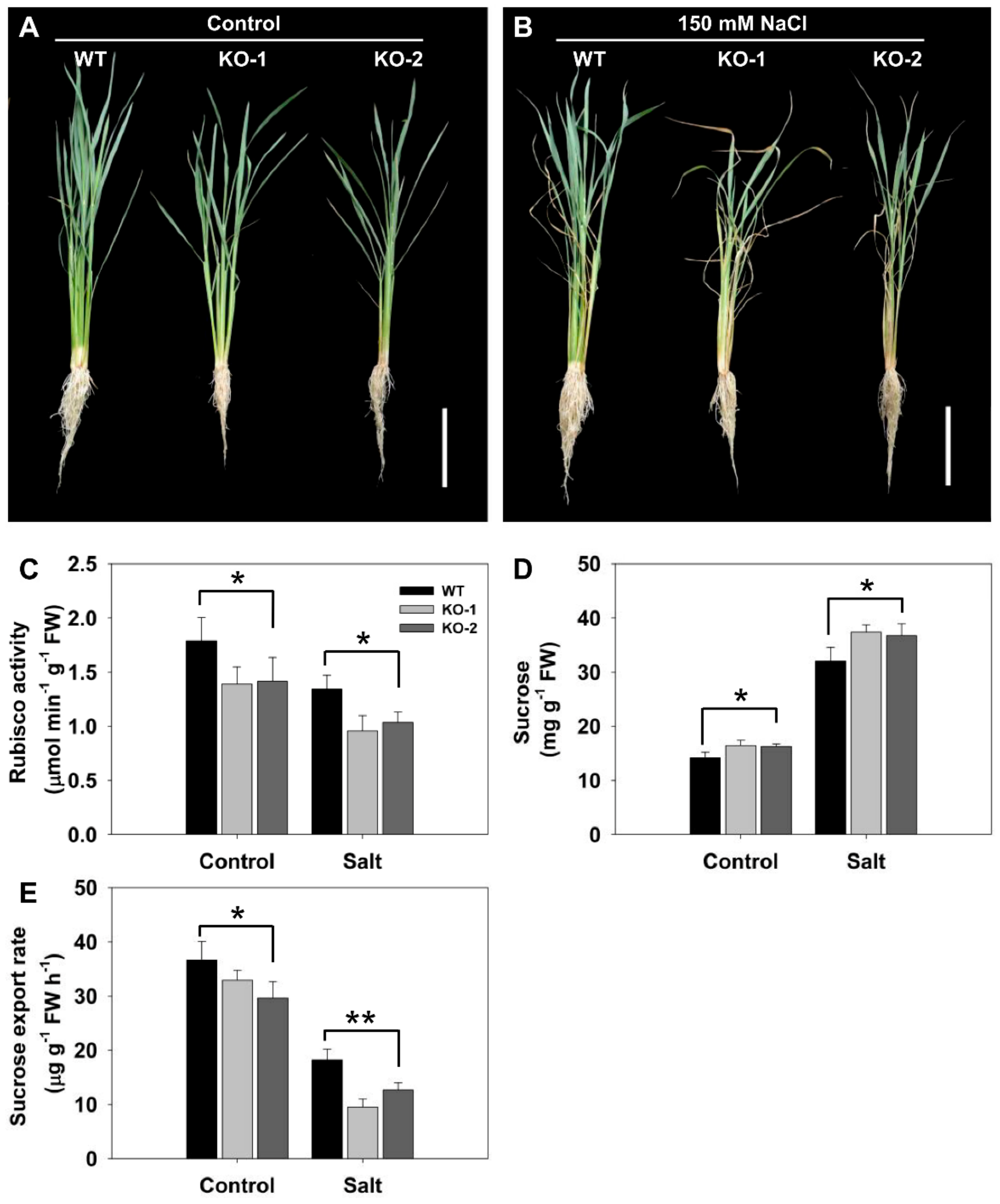
3.2. FLN2 Is Inducible by Salinity Stress and Its Absence Leads to a Loss in Tolerance
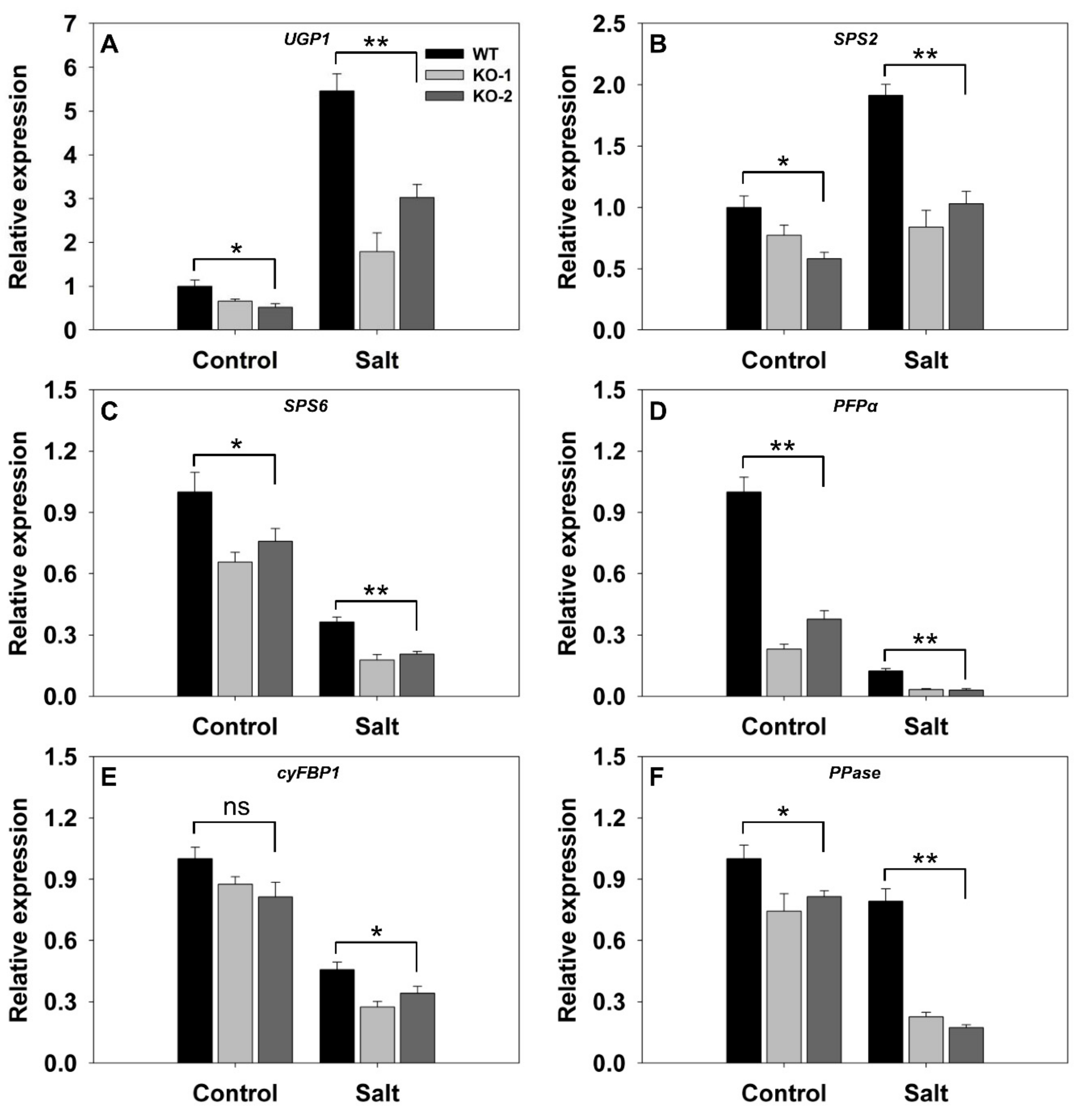
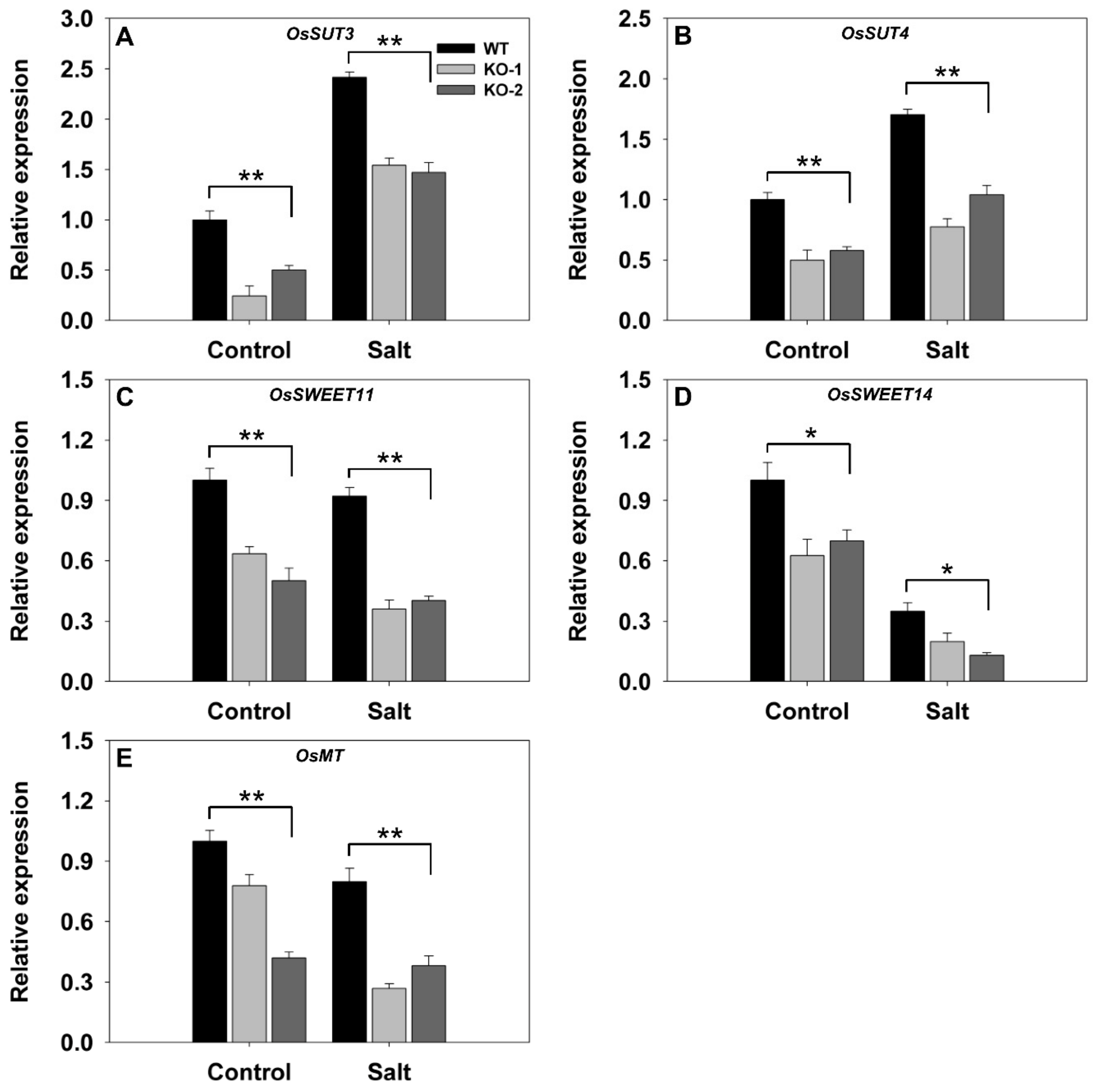
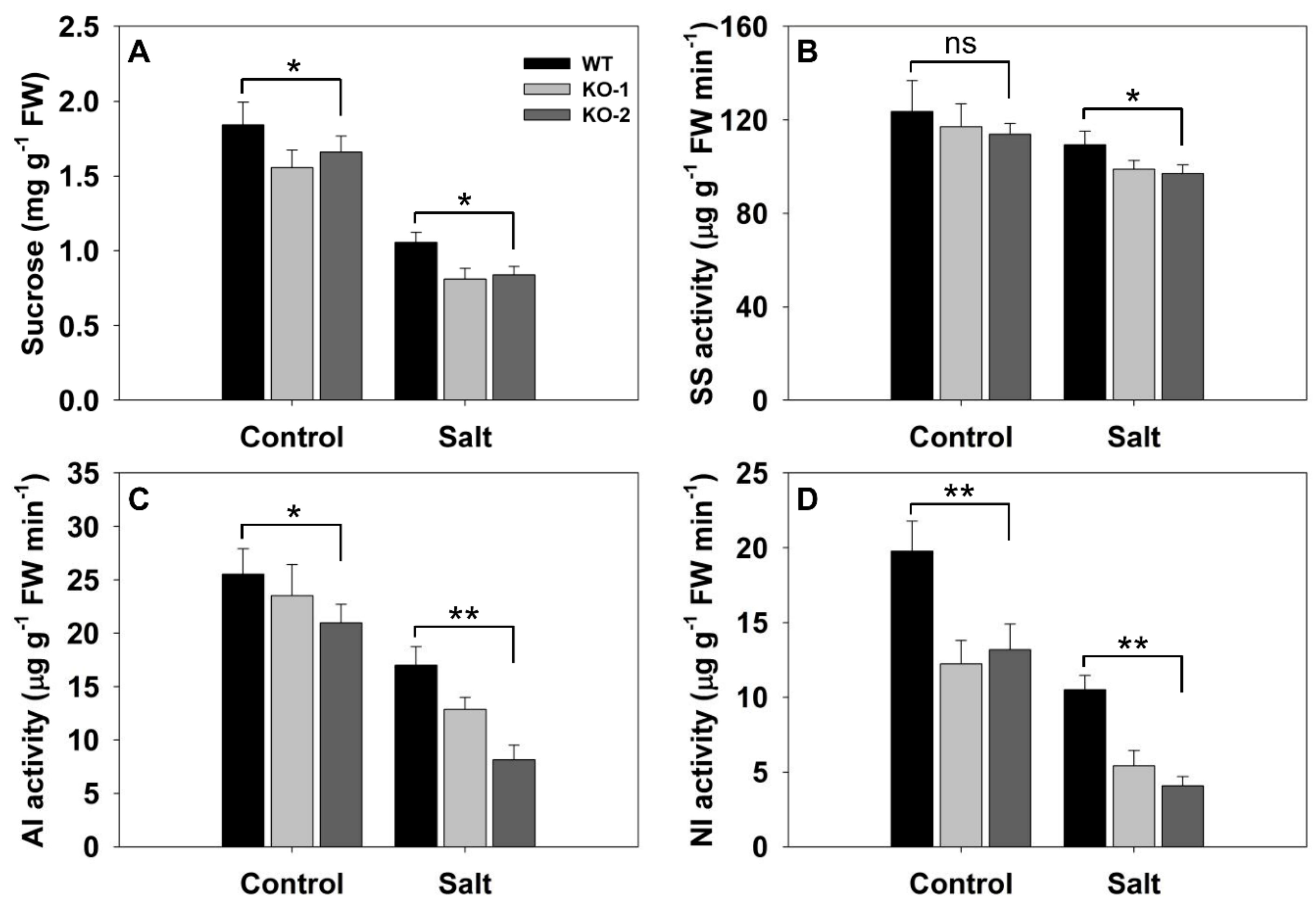
3.3. The Effect of Knocking Out FLN2 on Sucrose Metabolism and Partitioning
3.4. The Effect of Knocking Out FLN2 on the Biochemistry of the Root
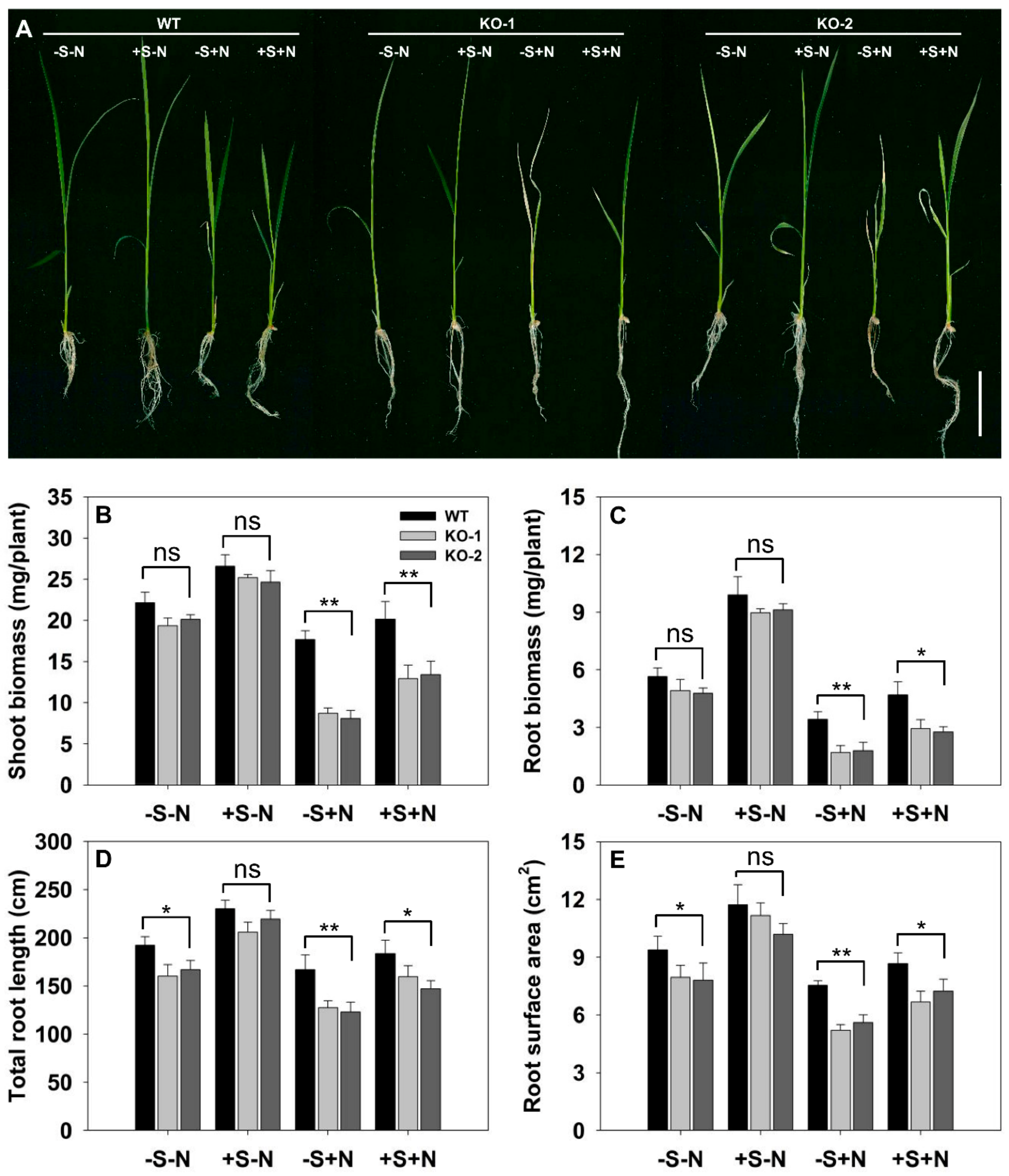
3.5. The Exogenous Supply of Sucrose Mitigates the Adverse Effects Induced by the Absence of FLN2
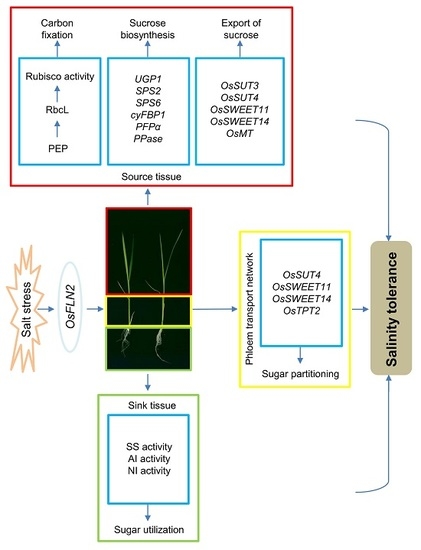
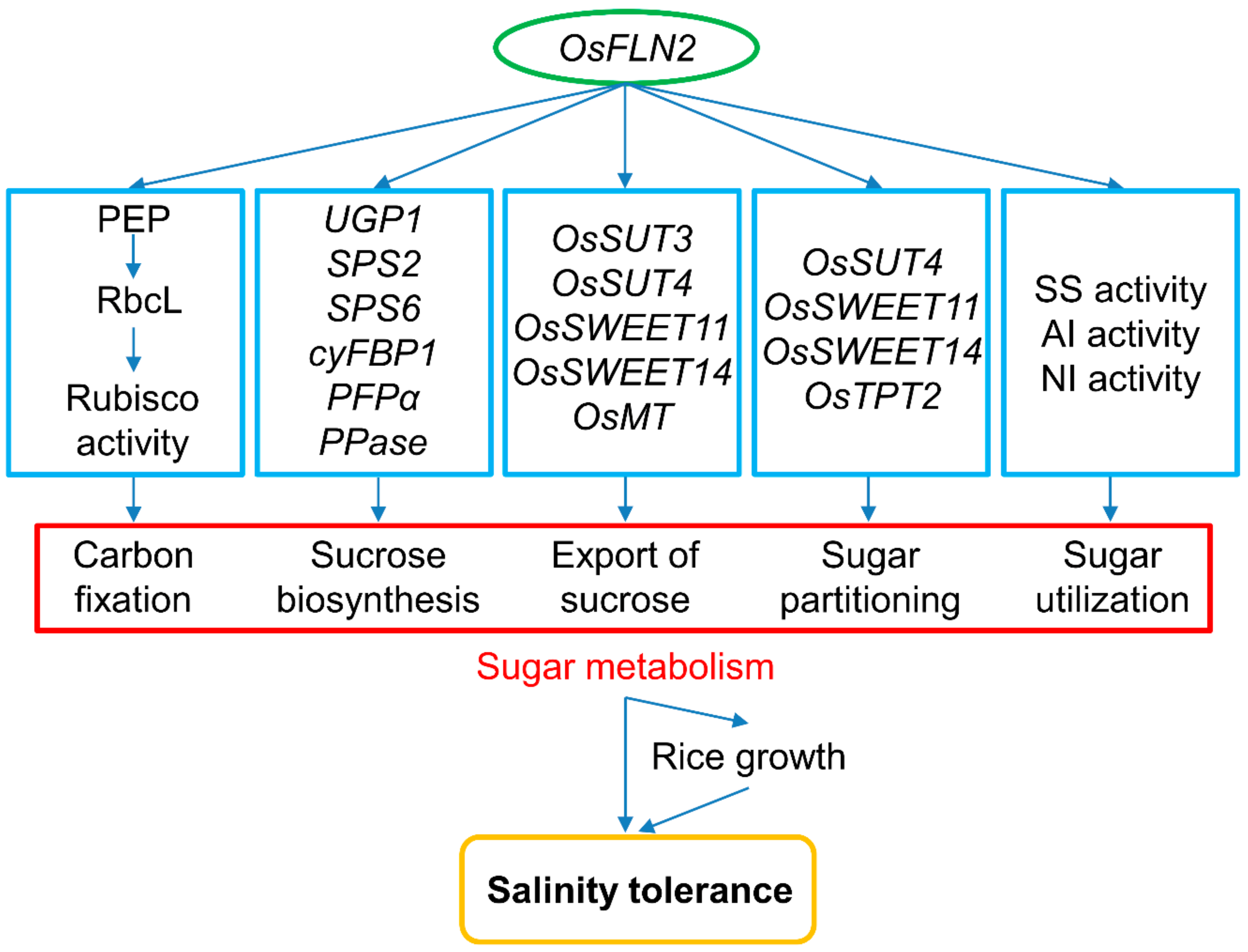
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Zhu, L.; Hu, J.; Ren, D.; Yu, L.; Xu, G.; et al. Variation in the abundance of OsHAK1 transcript underlies the differential salinity tolerance of an indica and a japonica rice cultivar. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 8, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, M.M.; Flexas, J.; Pinheiro, C. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: Regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; James, R.A.; Läuchli, A. Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 1025–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Sheen, J.; Jang, J.C. The role of hexokinase in plant sugar signal transduction and growth and development. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 44, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerepesi, I.; Galiba, G. Osmotic and salt stress-induced alteration in soluble carbohydrate content in wheat seedlings. Crop. Sci. 2000, 40, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Kojima, K.; Ide, Y.; Sasaki, S. Effects of saline and osmotic stress on proline and sugar accumulation in Populus euphratica in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2000, 63, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Tian, C.; Tang, C.; Rengel, Z. Improved tolerance of maize plants to salt stress by arbuscular mycorrhiza is related to higher accumulation of soluble sugars in roots. Mycorrhiza 2002, 12, 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- Reinders, A.; Sivitz, A.B.; His, A.; Grof, C.P.; Perroux, J.M.; Ward, J.M. Sugarcane ShSUT1: Analysis of sucrose transport activity and inhibition by sucralose. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, J.S.; Chen, L.Q.; Sosso, D.; Julius, B.T.; Lin, I.W.; Qu, X.Q.; Braun, D.M.; Frommer, W.B. SWEETs, transporters for intracellular and intercellular sugar translocation. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, C.; Grof, C.P. Sucrose transporters of higher plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slewinski, T.L.; Meeley, R.; Braun, D.M. Sucrose transporter1 functions in phloem loading in maize leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, W.; Weise, A.; Frommer, W.B.; Ward, J.M. Function of the cytosolic N-terminus of sucrose transporter AtSUT2 in substrate affinity. FEBS Lett. 2000, 485, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endler, A.; Meyer, S.; Schelbert, S.; Schneider, T.; Weschke, W.; Peters, S.W.; Schmidt, U.G. Identification of a vacuolar sucrose transporter in barley and Arabidopsis mesophyll cells by a tonoplast proteomic approach. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, C.J.; Nyamdari, B.; Tsai, C.J.; Harding, S.A. The tonoplastlocalized sucrose transporter in Populus (PtaSUT4) regulates whole-plant water relations, responses to water stress, and photosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.J.; Sun, M.H.; Lu, J.; Kang, H.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. An apple sucrose transporter MdSUT2.2 is a phosphorylation target for protein kinase MdCIPK22 in response to drought. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 625–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, N.; Hirose, T.; Scofield, G.N.; Whitfeld, P.R.; Furbank, R.T. The sucrose transporter gene family in rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 2003, 44, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, C.; Hajirezaei, M.R.; Fernie, A.R.; Roessner-Tunali, U.; Czechowski, T.; Hirner, B.; Frommer, W.B. The sucrose transporter StSUT1 localizes to sieve elements in potato tuber phloem and influences tuber physiology and development. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.J.; Sun, M.H.; Kang, H.; Lu, J.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. A CIPK protein kinase targets sucrose transporter MdSUT2.2 at Ser254 for phosphorylation to enhance salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormit, A.; Trentmann, O.; Feifer, I.; Lohr, C.; Tjaden, J.; Meyer, S.; Schmidt, U.; Martinoia, E.; Neuhaus, H.E. Molecular identification and physiological characterization of a novel monosaccharide transporter from Arabidopsis involved in vacuolar sugar transport. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3476–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Kanai, M.; Osakabe, Y.; Ohiraki, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi -Shinozaki, K. Monosaccharide absorption activity of Arabidopsis roots depends on expression profiles of transporter genes under high salinity conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43577–43586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, K.; Jones, A.M.; Chong, K. Reduced expression of a gene encoding a Golgi localized monosaccharide transporter (OsGMST1) confers hypersensitivity to salt in rice (Oryza sativa). J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4595–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Kang, S.; He, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, J.; Zeng, D.; Zhang, G.; Dong, G.; Gao, Z.; et al. The newly identified heat-stress sensitive albino 1 gene affects chloroplast development in rice. Plant Sci. 2018, 267, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Feng, H.; Hu, Q.; Qu, H.; Chen, A.; Yu, L.; Xu, G. Improving rice tolerance to potassium deficiency by enhancing OsHAK16p:WOX11-controlled root development. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hu, J.; Ren, D.; Xu, G.; Qian, Q. Driving the expression of RAA1 with a drought-responsive promoter enhances root growth in rice, its accumulation of potassium and its tolerance to moisture stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 147, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hu, Q.; Luo, L.; Yang, T.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Y.; Yu, L.; Xu, G. Rice potassium transporter OsHAK1 is essential for maintaining potassium-mediated growth and functions in salt tolerance over low and high potassium concentration ranges. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 2747–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, C.; He, L.; Qiu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Zeng, D.; Hu, J.; Ren, D.; et al. Knocking out the gene RLS1 induces hypersensitivity to oxidative stress and premature leaf senescence in rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, B.; Guo, L.; Zeng, D.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, L.; Hu, J.; Ren, D.; Yu, L.; et al. OsHAK1 controls the vegetative growth and panicle fertility of rice by its effect on potassium-mediated sugar metabolism. Plant Sci. 2018, 274, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhu, L.; Ren, D.; Yu, L.; Xu, G.; Qian, Q. OsHAK1, a high-affinity potassium transporter, positively regulates responses to drought stress in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.J.; Wi, S.J.; Choi, Y.J.; An, G.; Park, K.Y. Increased polyamine biosynthesis enhances stress tolerance by preventing the accumulation of reactive oxygen species: T-DNA mutational analysis of Oryza sativa lysine decarboxylase-like protein 1. Mol. Cells 2012, 34, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Loka, D.A.; Fitzsimons, T.R.; Zhou, Z.; Oosterhuis, D.M. Potassium deficiency limits reproductive success by altering carbohydrate and protein balances in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2018, 145, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Yi, X.; Huang, Q.; Peng, M.; Guo, A. Comparative proteomics of Thellungiella halophila leaves from plants subjected to salinity reveals the importance of chloroplastic starch and soluble sugars in halophyte salt tolerance. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 2174–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrandino, A.; Lovisolo, C. Abiotic stress effects on grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.): Focus on abscisic acid-mediated consequences on secondary metabolism and berry quality. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 103, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundmark, M.; Cavaco, A.M.; Trevanion, S.; Hurry, V. Carbon partitioning and export in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana with altered capacity for sucrose synthesis grown at low temperature: A role for metabolite transporters. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, Y.; Ding, R.; Ji, Y.; Wang, C. Arabidopsis AtSUC2 and AtSUC4, encoding sucrose transporters, are required for abiotic stress tolerance in an ABA-dependent pathway. Physiol. Plant 2015, 153, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, D.; Liu, S.; Gong, X.; Cui, Z.; Cui, N.; Cao, H.; Rao, L.; Wang, C. Sucrose transporter AtSUC9 mediated by a low sucrose level is involved in Arabidopsis abiotic stress resistance by regulating sucrose distribution and ABA accumulation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1574–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibraheem, O.; Dealtry, G.; Roux, S.; Bradley, G. The effect of drought and salinity on the expressional levels of sucrose transporters in rice (Oryza sativa Nipponbare) cultivar plants. Plant Omics 2011, 4, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Siahpoosh, M.R.; Sanchez, D.H.; Schlereth, A.; Scofield, G.N.; Furbank, R.T.; Van Dongen, J.T.; Kopka, J. Modification of OsSUT1 gene expression modulates the salt response of rice Oryza sativa cv. Taipei 309. Plant Sci. 2012, 182, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemens, P.A.; Patzke, K.; Deitmer, J.; Spinner, L.; Le Hir, R. Overexpression of the vacuolar sugar carrier AtSWEET16 modifies germination, growth, and stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Ma, H.; Feng, S.; Gong, S.; Wang, J. A novel sugar transporter from Dianthus spiculifolius, DsSWEET12, affects sugar metabolism and confers osmotic and oxidative stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Ma, H.; Feng, S.; Gong, S.; Wang, J. DsSWEET17, a tonoplast-localized sugar transporter from Dianthus spiculifolius, affects sugar metabolism and confers multiple stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, J.B. Sugar as a key component of the shoot branching regulation network. Plant Cell Environ. 2015, 38, 1455–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platten, J.D.; Egdane, J.A.; Ismail, A.M. Salinity tolerance, Na+ exclusion and allele mining of HKT1;5 in Oryza sativa and O. glaberrima: Many sources, many genes, one mechanism? BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, A.R.; Flowers, T.J. Salinity resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) and a pyramiding approach to breeding varieties for saline soils. Funct. Plant Biol. 1986, 13, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A.R.; Yeo, M.E.; Flowers, S.A.; Flowers, T.J. Screening of rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes for physiological characters contributing to salinity resistance, and their relationship to overall performance. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1990, 79, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Thomson, M.J.; Shah-E-Alam, M.; de Ocampo, M.; Egdane, J.; Ismail, A.M. Exploring novel genetic sources of salinity tolerance in rice through molecular and physiological characterization. Ann. Bot. 2016, 117, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Hu, J.; Dong, L.; Zeng, D.; Guo, L.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, L.; Qian, Q. The Tolerance of Salinity in Rice Requires the Presence of a Functional Copy of FLN2. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010017
Chen G, Hu J, Dong L, Zeng D, Guo L, Zhang G, Zhu L, Qian Q. The Tolerance of Salinity in Rice Requires the Presence of a Functional Copy of FLN2. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guang, Jiang Hu, Liuliu Dong, Dali Zeng, Longbiao Guo, Guangheng Zhang, Li Zhu, and Qian Qian. 2020. "The Tolerance of Salinity in Rice Requires the Presence of a Functional Copy of FLN2" Biomolecules 10, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010017
APA StyleChen, G., Hu, J., Dong, L., Zeng, D., Guo, L., Zhang, G., Zhu, L., & Qian, Q. (2020). The Tolerance of Salinity in Rice Requires the Presence of a Functional Copy of FLN2. Biomolecules, 10(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010017