Abstract
In this review, we discuss the impact of s-process nucleosynthesis in asymptotic giant branch stars on the enrichment of heavy elements. We review the main steps made on this subject in the last 40 years and discuss the importance of modelling the evolution of the abundances of such elements in our Milky Way. From the comparison between model results and observations, we can impose strong constraints on stellar nucleosynthesis, as well as on the evolution of the Milky Way.
1. Introduction
Over 70% of the chemical species in nature are constituted by neutron capture processes, and more than 50% of the neutron capture elements that we find nowadays in the Sun were formed in the interior of asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars. It is not trivial to calculate precisely the production of such elements, and it is necessary to know the detailed nucleosynthesis in AGBs extended up to the heaviest stable nuclei. The majority of elements with are produced in massive stars and represent the “weak” s-process component, while for , the elements are formed in AGB stars and represent the “main” s-process component. Finally, very heavy elements, such as Pb, represent the “strong” s-process component, and they are formed in AGBs of low metallicity. The s-process elements are created by neutron capture on Fe seeds on timescales longer than the -decay in the nucleus, and the neutrons are released by two reactions, C(,n)O and Ne(,n)Mg. This is a sort of secondary process, because it depends upon the abundance of the seeds. However, it would be better to say that it is a complex process, since the neutron flux in turn depends on the stellar metallicity, and because of the presence of poisons (light elements that capture the neutrons, which then will not contribute to the s-process) such as N. For example, the formation of Pb is favoured by low stellar metallicity. In fact, when the abundance of Fe seeds is low, it is easier to form very heavy s-process elements, because the neutron capture is concentrated on a lower number of seeds. For the same reason, the light s-process elements (Sr, Y, Zr) are favoured by high metallicity. This kind of calculation was pioneered by Gallino et al. [1,2] and was also deeply studied by Busso et al. [3,4]. Although it is possible to foresee the behaviour of the abundances of chemical elements just by considerations based only on stellar nucleosynthesis, we need to adopt self-consistent chemical evolution models if we want to take into account the complexity of the processes and obtain detailed results to be compared to observations. In such models, we can also take into account the other production channels of neutron capture elements, such as production by the r-process and weak r-process (possibly in the future, the contribution of less studied rare processes such as i-process, p-process, or p-process), as well as iron abundance evolution, which is the tracer of metallicity in stars. Due to the complexity of the various sources and their strong metallicity dependency, the chemical evolution of neutron capture elements is more complex and demanding than that of elements and iron peak elements. On the other hand, thanks to the careful study of these elements, we can impose strong constraints on stellar nucleosynthesis and the formation and evolution of our Galaxy. In the present paper, we will present a selection of results obtained by adopting chemical evolution models, including detailed nucleosynthesis of s-process elements originating from AGB stars, during the last 40 years.
2. Galactic Chemical Evolution
Models of galactic chemical evolution are aimed at predicting how the abundances of chemical elements evolve in the gas in galaxies. The main ingredients necessary to build such models are the stellar birthrate function, in other words the star formation rate (SFR), which is normally assumed to be a continuous function in the Milky Way such as the Kennicutt (1998) law, and the initial mass function (IMF). Then, a fundamental ingredient is stellar nucleosynthesis, namely the amounts of chemical elements formed inside stars and restored into the interstellar medium (ISM) by means of stellar winds and supernova (SN) explosions. Supernovae can arise from massive stars () that explode by core-collapse, giving rise to Type II, Ib, and Ic supernovae, and have short lifetimes. These stars produce the bulk of -elements (e.g., C, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, Ca) and part of Fe. On the other hand, supernovae Type Ia arise from exploding white dwarfs in binary systems, which have longer lives and produce the bulk of Fe. However, low- and intermediate-mass stars () during the AGB phase can also be important element producers; in particular, they are responsible for N, C and for the bulk of the s-process component in neutron capture elements, as mentioned in the introduction. Concerning r-process elements, they should arise from massive stars (), either from core-collapse SNe or merging neutron stars. The roles of these sources are still under debate. We can divide galactic chemical evolution (GCE) models into two categories: analytical and numerical models, as we will describe in the following.
2.1. Analytical Chemical Models
The simplest and oldest analytical model is the Simple Model (Tinsley [5]), which assumes that the system is a closed box (no infall nor outflow), the IMF is constant in time, the initial gas has a primordial chemical composition, and there is instantaneous mixing of the stellar products with the ISM. In addition, there is the hypothesis of instantaneous recycling approximation (IRA), which states that all stars below 1 never die, while those above 1 die immediately. These assumptions lead to simple solutions for both primary (originating directly from H and He) and secondary (originating from metals) elements. The solution of the Simple Model for a primary element is:
where Z is the global metal content, is the so-called yield per stellar generation, and is the fractional mass of gas in the system. The solution for a secondary element, such as N and C, is:
where is the mass fraction and is the yield per stellar generation of a secondary element S, which originates from the primary element Z. Clearly, the adoption of IRA in the Simple Model is incorrect if one wants to model the evolution of elements mainly produced in long-living stars, such as s-process elements. In such cases, numerical models are necessary to take into account the stellar lifetimes, and the results they produce are quite different from those of the Simple Model, as we will see in the next sections.
2.2. Numerical Chemical Models
Numerical models take into account in detail stellar lifetimes, and therefore are particularly important to model elements produced by AGB stars and Type Ia supernovae. These models relax IRA, as well as the closed-box assumption, and allow for the infall or outflow of gas in the studied galaxy. The numerical models follow the evolution of single elements and take into account the nucleosynthesis products of stars of all masses in great detail. In the following, we will describe how the evolution of s-process elements has been interpreted and modelled by different authors, with particular attention to the contribution of AGB stars.
3. Early Results Based on Analytical Approach
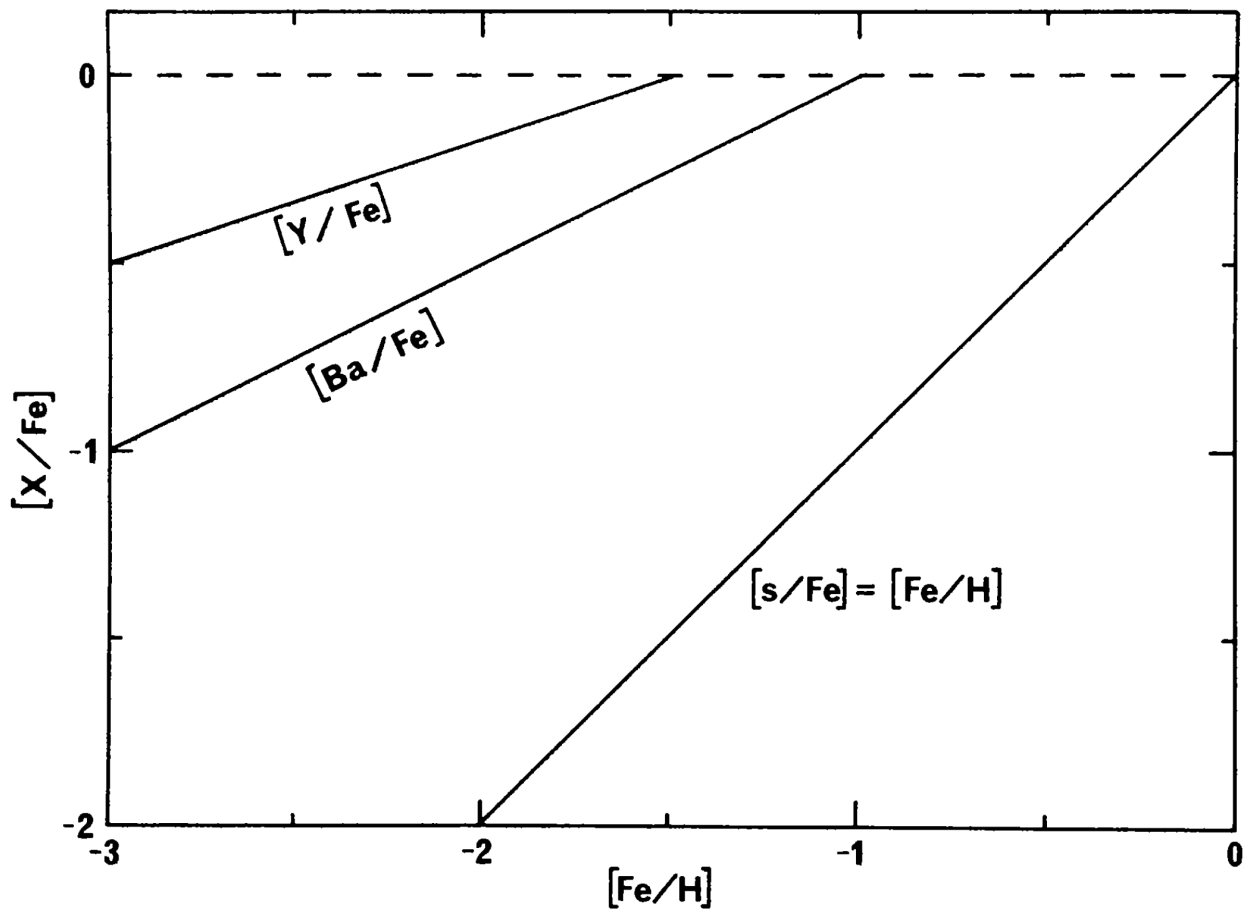
We start with the pioneering results shown by Truran [6]. Although he did not consider a real chemical evolution model, nor a detailed nucleosynthesis of the neutron capture elements, nevertheless, he used fundamental concepts of chemical evolution applied to the knowledge of s-process nucleosynthesis, in particular, the fact that s-process nucleosynthesis is expected to behave as a secondary process. Therefore, as described in the previous section, the secondary production dependent on the abundance of metal seeds (in particular iron) is expected to increase quadratically with iron abundance, and therefore the ratio of the secondary (i.e., s) element relative to the seed (i.e., Fe) should be linear, as shown in Figure 1 for the [s/Fe]1 line. However, it should be noted that such a behaviour for secondary elements is only valid in the framework of the Simple Model of chemical evolution, whose solution, both for primary and secondary elements, is obtained with IRA. Therefore, it is expected that in a realistic situation where the complexities of nucleosynthesis and stellar lifetimes are taken into account, elemental abundances do not follow the predictions of the Simple Model.
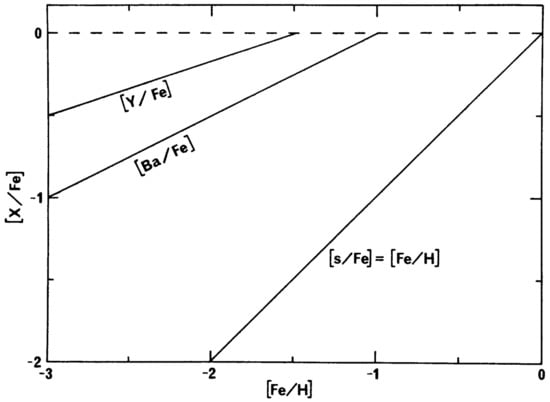
Figure 1.
Observed behaviour of the [Ba/Fe] ratio and [Y/Fe] ratio vs. [Fe/H], together with the expected trend for purely secondary elements ([s/Fe]) relative to Fe. Image reproduced with permission from Truran [6], copyright by the author.
Clearly, this simple assumption is not compatible with the behaviour suggested by the first observations of neutron capture elements in metal-poor stars, which showed a different behaviour of these elements relative to Fe, as shown also in Figure 1. Although Truran [6] made his considerations in the framework of the Simple Model, he envisaged the right solution to explain the early production of neutron capture elements, which should have originated from a different process: the r-process. This was indeed correct, and started a new line of thought. Clearly, the evolution of s-process elements relative to Fe as a function of Fe abundance along the entire Galactic lifetime cannot be explained by the Simple Model only, but needs the consideration of stellar lifetimes, as we will see in the next sections. In particular, stellar lifetimes are particularly important for s-process elements, which mainly originate from long-living low-mass stars (1–3). In any case, Truran’s interpretation suggested the scenario we follow now about the production of neutron capture elements in the early stages of evolution of our galaxy.
4. First Detailed Numerical Models
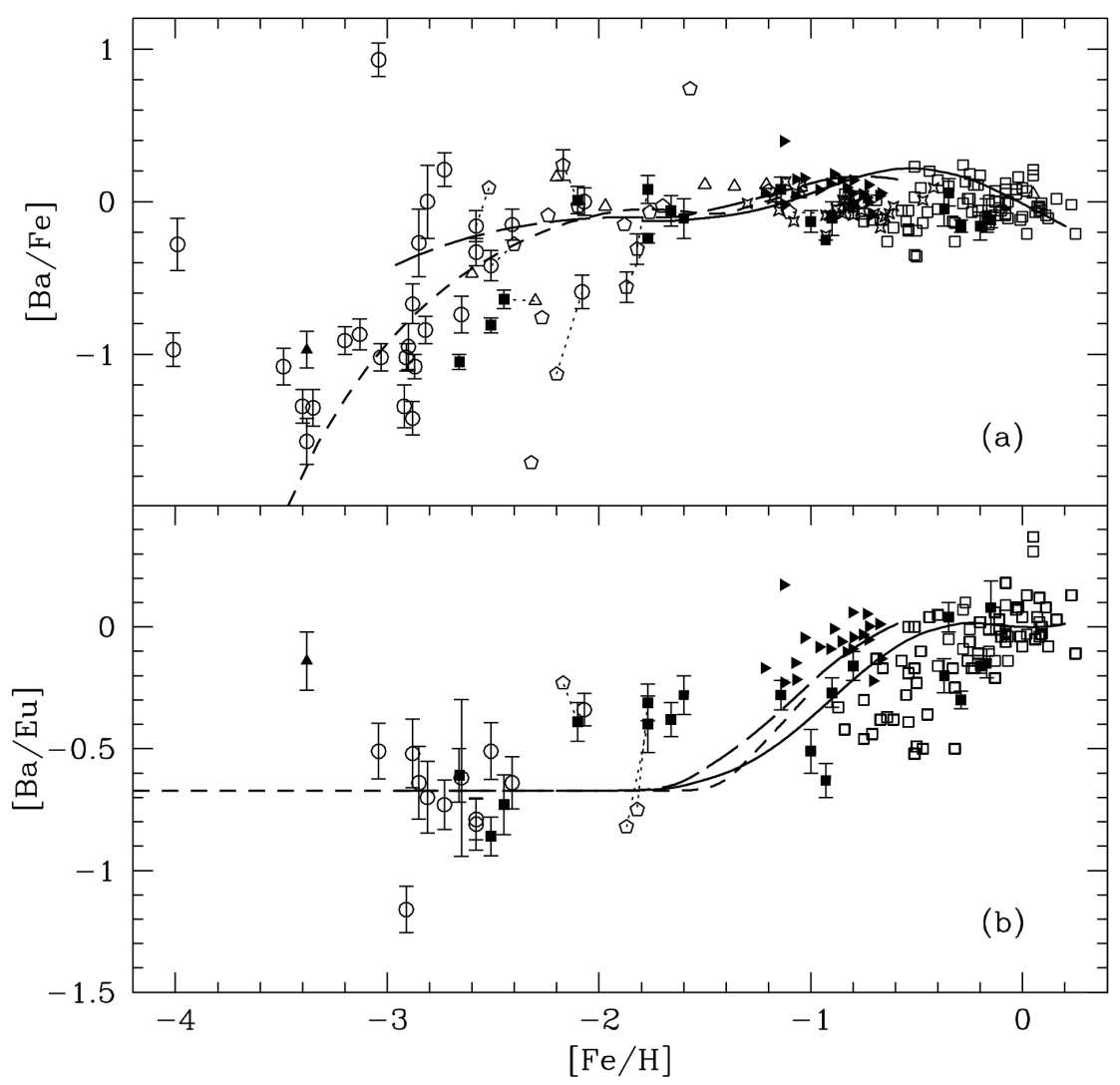
Travaglio et al. [7] studied for the first time the chemical evolution of the galaxy by tracing the elements Ba and Eu, using a detailed evolutionary numerical model that relaxes the IRA and is suitable for reproducing a large set of Galactic (local and non-local) and extragalactic constraints. Input stellar yields for neutron-rich nuclei were separated into their s-process and r-process components. In that work, a very detailed production of s-process elements in thermally pulsing AGB stars of low mass was considered; in particular, the combined action of two neutron sources was taken into account: the dominant reaction C(,n)O, which releases neutrons in radiative conditions during the interpulse phase, and the reaction Ne(,n)Mg, which is marginally activated during thermal instabilities [2]. It is worth noting the fundamental role played by the third dredge-up in the s-process nucleosynthesis, because it drives the formation of a pocket and is a primary process, since is created from the original H and He. The r-process yields adopted in this work are not a prediction of stellar nucleosynthesis models and were derived as the difference between the solar abundance and its s-process contribution, given by their GCE model at the time of formation of the solar system. This approach has become quite a standard procedure. However, it implies a single primary r-process component. It has been shown by comparison with metal-poor stars that this approach is valid only for elements heavier than A = 130 (e.g., Ba and beyond [8,9]); Travaglio et al. [10] invoked the need for a new process that, together with the s-process from AGB and a primary r-process, is able to provide an additional contribution to light neutron capture elements (Sr, Y, Zr). The astrophysical conditions that would create this additional contribution are still unknown, and both an s-process-like or an r-process-like mechanism was found to reproduce the abundance pattern between Sr and Ag observed in many of the most extreme metal-poor stars [11]. The s-process production in massive stars (weak s-process) was shown to be inefficient at low metallicity [12], so most authors have focused on the existence of a possible second r-process (also called the weak r-process; see [13]). However, the recent nucleosynthesis computations by Frischknecht et al. [14] and Limongi and Chieffi [15] showing that rotating massive stars can support the s-process have brought a new twist to the interpretation of the neutron capture element abundances of stars at very low metallicity (see also Section 6). Galactic evolution results, including both the s- and r-process contributions, were compared to the data in Figure 2. As one can see from that figure, the [Ba/Fe] ratio does not follow the behaviour predicted by the Simple Model; rather, after an initial linear increase, this ratio flattens at higher metallicities. This is the effect of taking into account in detail the stellar lifetimes of the stars producing both Ba and Fe. The Fe is produced mainly by Type Ia SNe, which originate from white dwarfs in binary systems, while Ba is formed mainly in low-mass stars. The ratio [Ba/Eu] has a different behaviour than [Ba/Fe], since, at variance with Fe, Eu is produced as an r-process element on very short timescales by massive stars. The initial flat behaviour is due to the r-process component of Ba, already suggested by Truran [6], which is produced on the same timescales as Eu; then, the increase of the ratio with increasing metallicity is due to the s-process component of Ba, which is the dominant component and is produced on long timescales by low-mass stars.
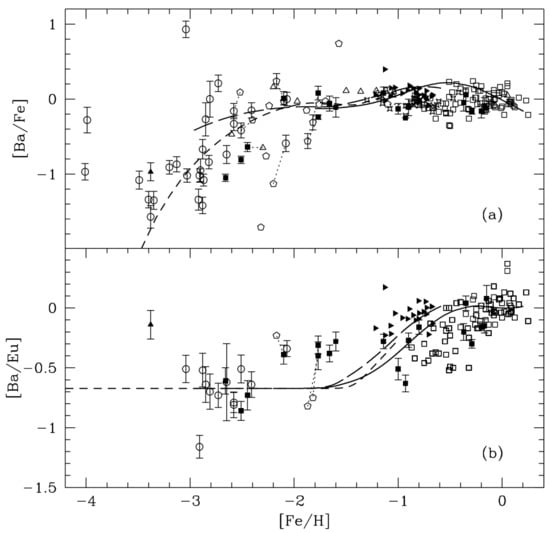
Figure 2.
[Ba/Fe] vs. [Fe/H] in panel (a) and [Ba/Eu] vs. [Fe/H] in panel (b). The short-dashed line describes the halo, the long-dashed line shows the thick disk, and the solid line is for the thin disk. Observational data are from Gratton and Sneden [16] (filled squares); Woolf et al. [17] (open squares); Francois [18] (pentagons); McWilliam et al. [19] and et al. [20] (circles); Norris et al. [21] (filled triangles); Jehin et al. [22] (filled tilted triangles); Mashonkina et al. [23] (open triangles). Thin dotted lines connect stars with different abundance determinations. Image reproduced with permission from Travaglio et al. [7]; copyright by the authors.
The resulting s-process distribution is also strongly dependent on stellar metallicity. For the standard model discussed in that paper, there is a sharp production of the Ba-peak elements around Z ∼ Z/4. Concerning the r-process yields, they made a simplified assumption in which the production of r-nuclei is a primary process that occurs in stars near the lowest mass limit for Type II supernova progenitors (>). With this model, it was possible to calculate the r-contribution for each nucleus at different evolutionary times, and in particular, at the formation of the solar system. Their results were also compared to spectroscopic abundances of elements from Ba to Eu at various metallicities (mainly from F and G stars), showing that the observed trends were explained with the assumption made regarding neutron capture nucleosynthesis (see Figure 2).
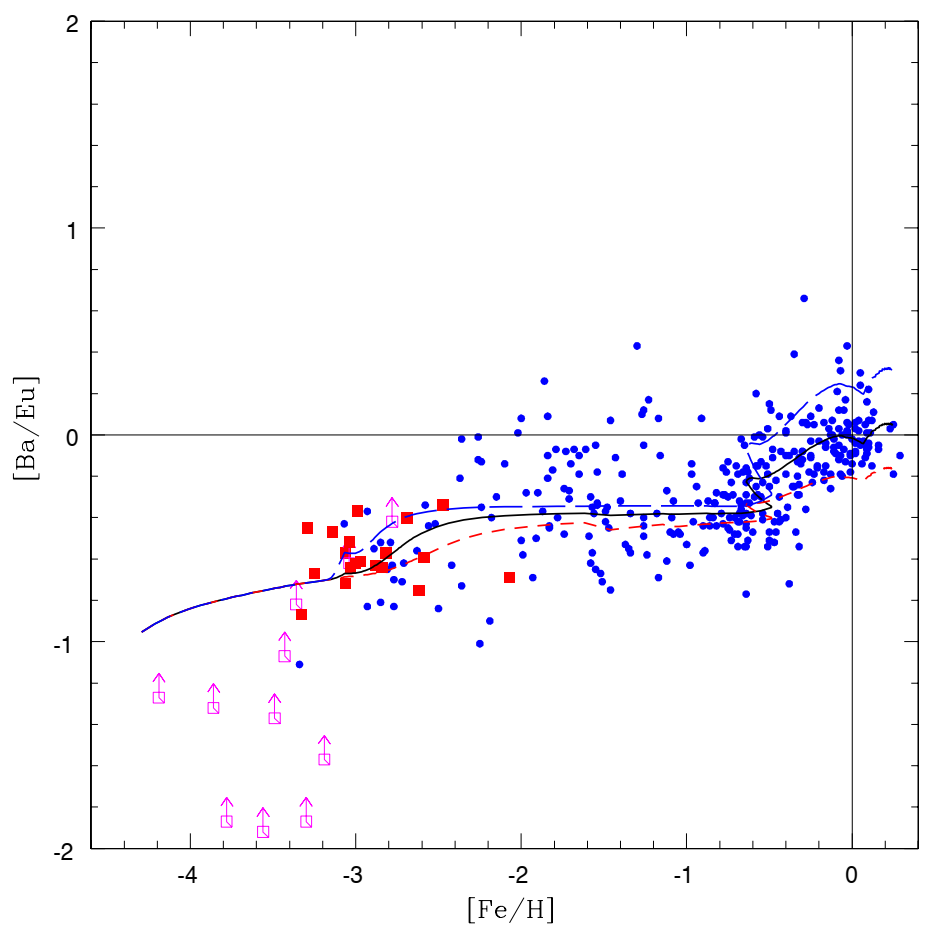
The main goal of the work of Cescutti et al. [24] was to follow the evolution of Ba and Eu abundances by means of a detailed chemical evolution model reproducing the abundance trends for other elements. The chemical evolution model is similar to the “two-infall” model of Chiappini et al. [25], where the halo and the thick disc form during a first fast gas infall episode, followed by a second longer infall event, which forms the thin disc. The main difference compared to the work of Travaglio et al. [7] is more detailed descriptions of the r-process production. It was concluded that for both Ba and Eu, it is necessary to assume an r-component originating in stars in the range 10–30 . This outcome was obtained thanks to the careful comparison of the GCE models to the results of the Large Programme led by R. Cayrel [26], and the high-quality abundances obtained for neutron capture elements by François et al. [27]; see Figure 3.
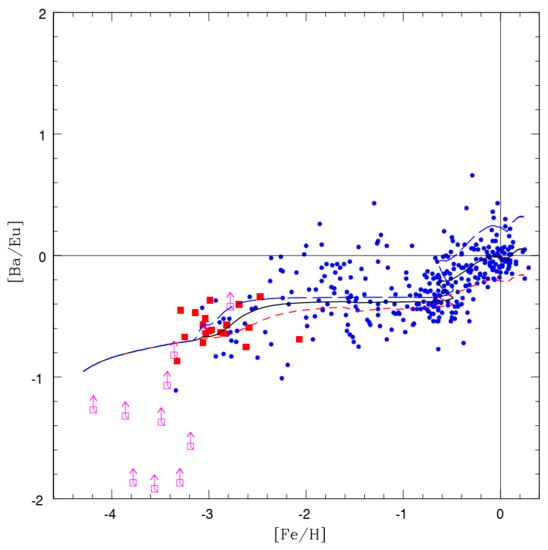
Figure 3.
[Ba/Eu] vs. [Fe/H]. Data (filled squares) and lower limits (open square) by François et al. [27]; in blue observational data from Burris [28], Fulbright [29], Koch and Edvardsson [30], Honda et al. [31], Mashonkina and Gehren [32,33]. The solid line is the prediction of the best Model 1; the short-dashed line and the long-dashed line are the predictions of max and min models, which are able to include most the observational data for [Ba/Fe] vs. [Fe/H]. Image reproduced with permission from Cescutti et al. [24]; copyright by the authors.
In particular, the observed [Ba/Eu] ratio in metal poor stars at metallicities (epochs) when the enrichment by low-mass stars has not yet occurred appeared to be slightly enhanced compared to the ratio of the r-process for [Ba/Eu] ∼−0.7, observed in r-process rich stars [9]. In fact, stars in the range −2 < [Fe/H] <−1 have a mean [Ba/Eu] ∼ −0.4, as is also reproduced by the model of [24], assuming empirical yields, though it is not so well reproduced by the model of [7]. This implies the necessity of a production of Ba by massive stars (or a source with a comparable timescale) slightly higher than that expected for the pure r-process ratio. This source could be simply ascribed to a variation of the r-process for [Ba/Eu], but it can be also connected to the production of s-process Ba by low-metallicity rotating massive stars [14,15]. This extra production of barium on short timescales has also a (moderate) impact on the required fraction of s-process barium coming from AGB stars, which is therefore slightly lower, decreasing from 80% to 60%. Later on, Cescutti et al. [34] applied the same assumptions for Eu and Ba adopted in the solar vicinity to model the Galactic gradients. The results were in excellent agreement with the observational data, with a steep gradient for Eu and an almost flat gradient for Ba, due to delayed enrichment by AGB stars.
5. New s-Process Yields
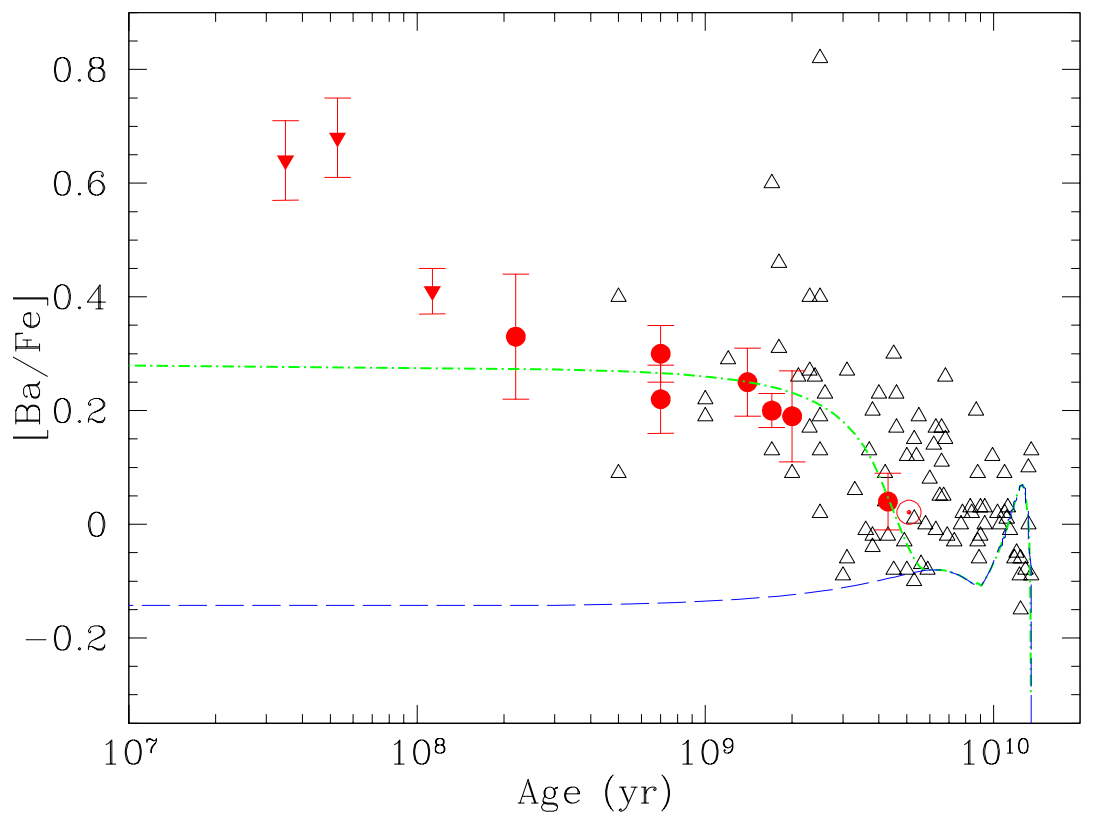
D’Orazi et al. [35] reported the discovery of a trend of increasing Ba abundance with decreasing age for a large sample of Galactic open clusters (OC). The observed pattern of [Ba/Fe] versus age could be reproduced with a GCE model, assuming a Ba yield from the s-process in low-mass stars higher than the typical one suggested by parameterized models of neutron-capture nucleosynthesis (see Figure 4). They therefore showed that this is possible in a scenario where the efficiency of the extra-mixing processes producing the neutron source C anti-correlate with the initial mass, with a larger efficiency for lower masses. This is similar to the known trend of extended mixing episodes acting in H-rich layers [36], and might suggest a common physical mechanism [37].
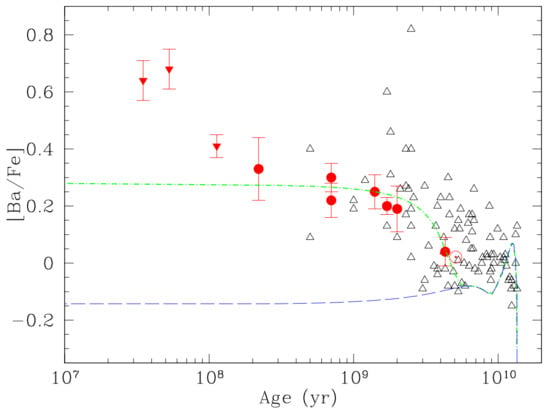
Figure 4.
Average [Ba/Fe] as a function of stellar age for the subsample of clusters whose analysis is based on dwarfs (filled circles and inverted triangles) compared with the abundance pattern of disk stars (open triangles) by Bensby et al. [38]. Filled triangles represent abundance measurements that probably need NLTE (non-local thermodynamic equilibrium) corrections (but see [39]). The model results are shown for two set of yields: the standard yields [4,7] with a long-dashed curve; the enhanced s-process yields with a dot-dashed curve. Both models show a peak at old ages due to the r-process from massive stars. Image reproduced with permission from D’Orazi et al. [35]; copyright by the authors.
Later, in Maiorca et al. [40], the analysis of OCs was extended to other elements besides Ba. This study derived abundances for four other elements with important s-process contributions, i.e., Y, Zr, La, and Ce. They used equivalent width measurements as well as the MOOG2 code [41], and their sample included 19 OCs of different ages, for which the spectra were obtained by the ESO Very Large Telescope using the UVES spectrometer. Thanks to these further abundance determinations, they confirmed for all the elements analysed in their study what was originally found only for barium. Their results require that very low-mass AGB stars (M ⪅ 1.5M) produce larger amounts of s-process elements (and hence activate the C-neutron source more efficiently) than previously expected. The role of these stars in producing neutron-rich elements in the Galactic disk has been so far underestimated, and their evolution and neutron-capture nucleosynthesis should now be reconsidered. The most recent observations have confirmed that the young clusters appear to be extremely enhanced in Ba, but the other s-process elements are not enhanced (see e.g., recent work by [39] and references therein). This cannot be explained in terms of s-process nucleosynthesis, and the current explanations for this Ba excess range from observational problems with Ba to the presence of a neutron capture process intermediate between s-process and r-process.
6. More Recent Numerical Models
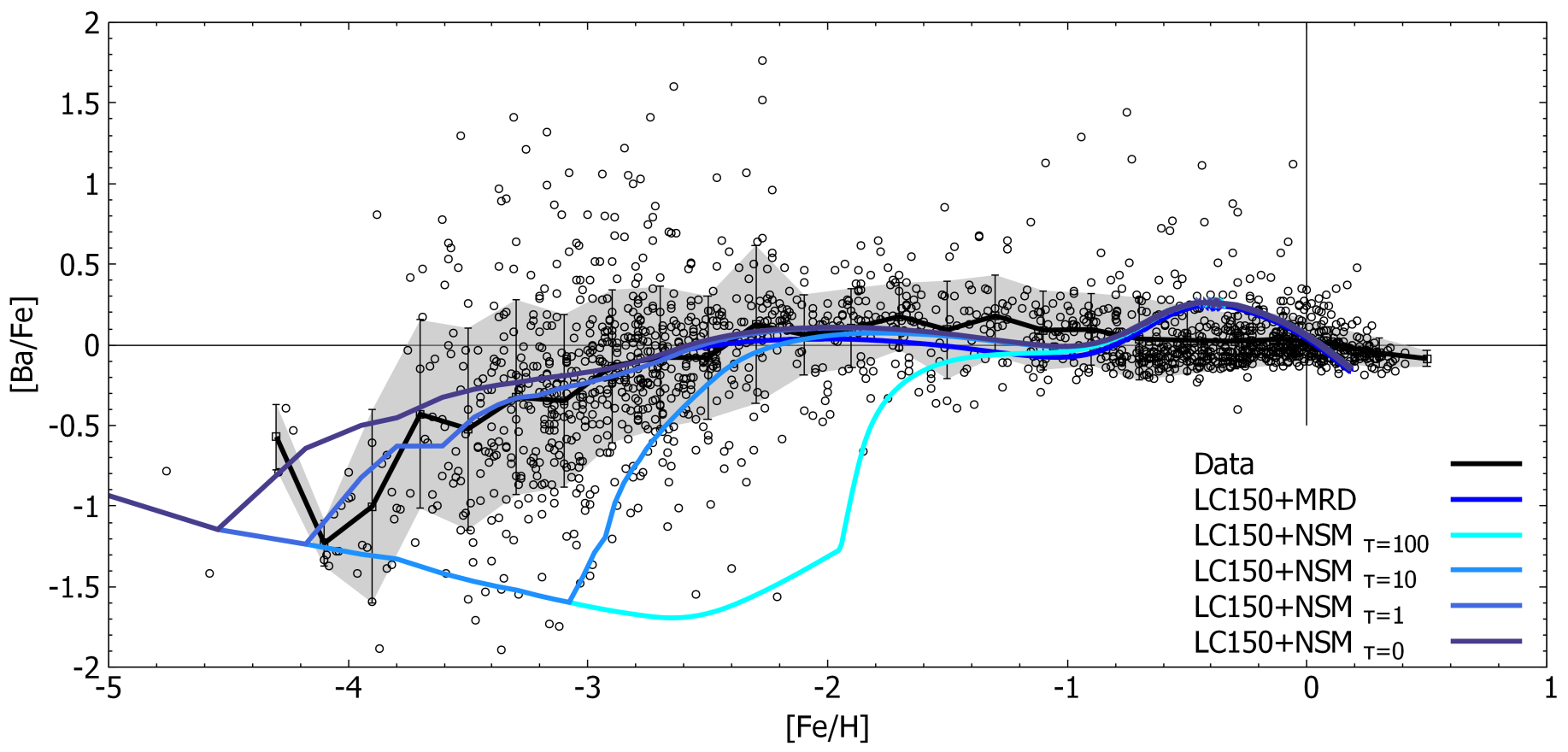
Rizzuti et al. [42] presented a detailed study on the evolution of Sr and Ba in the Milky Way. These two elements have a predominant s-process origin, and Rizzuti et al. adopted the yields from AGB stars in the range 1.5–3.0 from Cristallo et al. [43,44]. However, there is also a minor s-process contribution from massive stars, and yields of Limongi and Chieffi [15] and Frischknecht [14] were tested. A small r-process component in the production of Sr and Ba was also taken into account by considering either SNe or merging neutron stars. As one can see from Figure 5, the best model assumes the AGB yields from Cristallo et al. [43,44], the massive rotating star yields from Limongi and Chieffi [15] with rotational speed of 150 Km/s, and the r-component of Ba from magneto-rotationally driven SNe (see [45]).
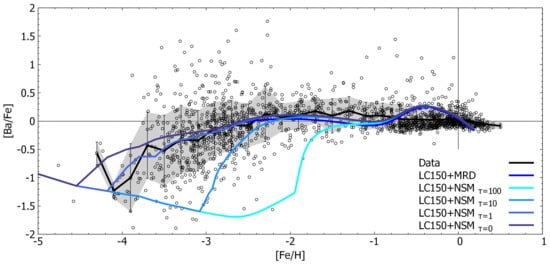
Figure 5.
Comparison between observed and predicted [Ba/Fe] ratios vs. [Fe/H]. The black dots, track, and shadowed area are the observations (sources listed in Table 1 of [42]); the dark blue line is the model with magneto-rotationally driven SNe (see [45]) as r-process sources; the lighter blue line is the model with neutron star mergers as r-process sources with variations in the time delay (from darker to lighter), with = 0, 1, 10, and 100 Myr. Image reproduced with permission from Rizzuti et al. [42]; copyright by the authors.
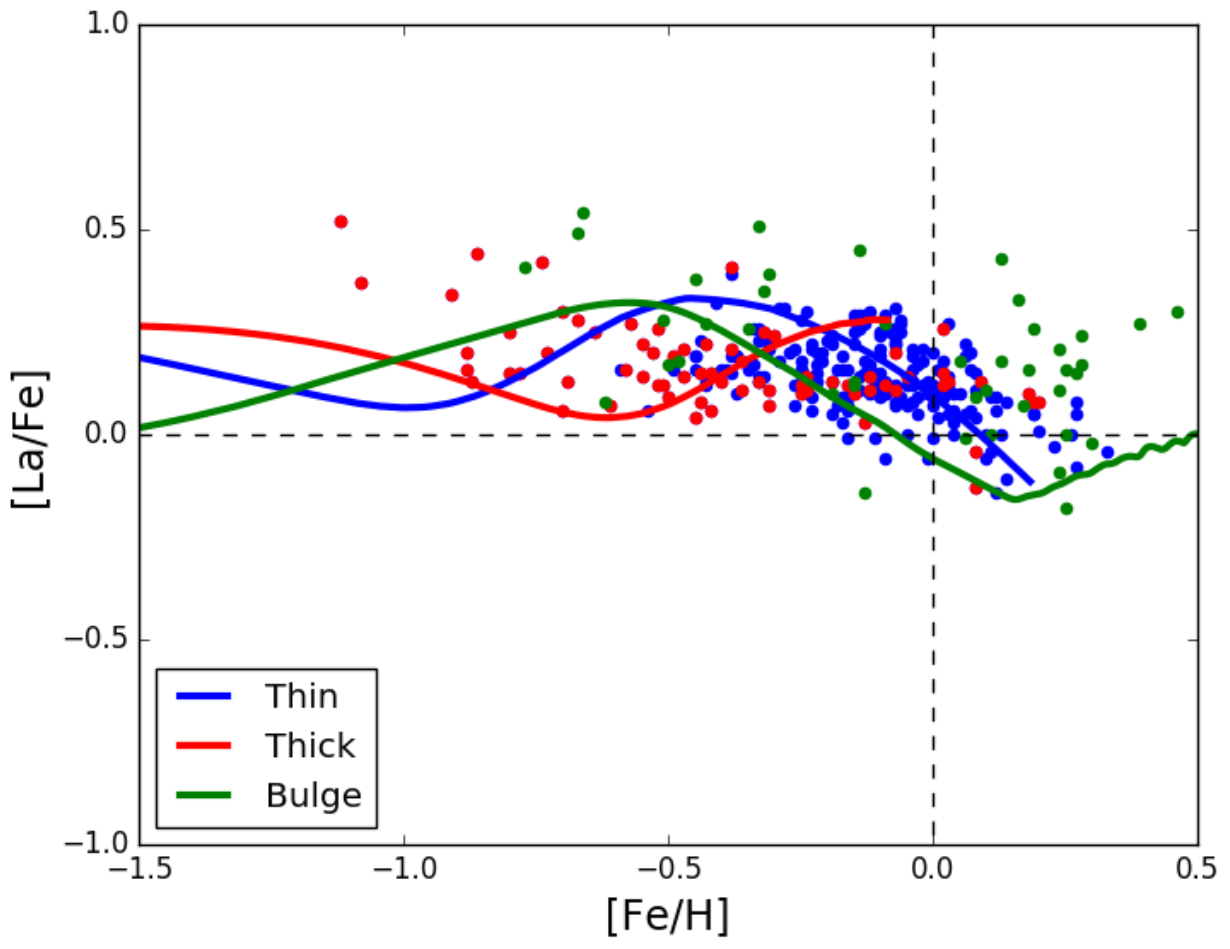
In Grisoni et al. [46], the evolutions of Zr, La, Ce, and Eu in the different components (thick, thin-disk, and bulge) of the Milky Way were followed. The models for the thick and thin disks were from Grisoni et al. [47] and the model for the bulge was from Matteucci et al. [48]. Again, the yields adopted in Grisoni et al. [46] from the s-process in AGB stars (1.3–3.0M) are from Cristallo et al. [43,44], together with the s-process contribution by massive rotating stars from Frischknecht et al. [14]. As an example, we show in Figure 6 the predicted and observed abundances, relative to Fe, of La, which is predominantly produced by the s-process, as opposed to Eu, which is a pure r-process element. As one can see, the agreement between theory and observations is good. This means that the stellar yields, which are the most important parameters in GCE models, are the appropriate ones. Moreover, the agreement ensures that also the assumed histories of star formation in the different Galactic components (thick, thin-disk, and bulge) are correct.
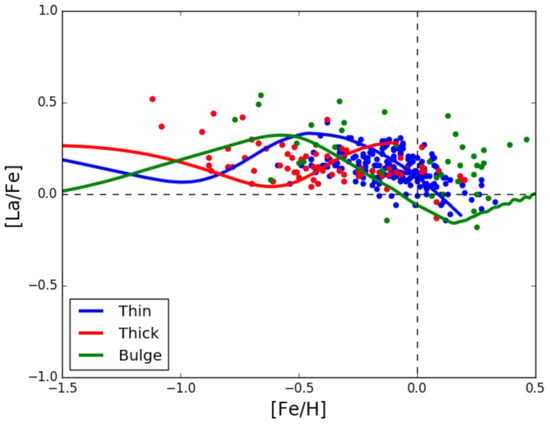
Figure 6.
Comparison between observed and predicted [La/Fe] ratios vs. [Fe/H]. The theoretical thick disk is shown by the red curve, the thin disk by the blue one, and the bulge by the green one. The data points for the three components are indicated by the same colours as the theoretical curves. Image reproduced with permission from Grisoni et al. [46]; copyright by the authors.
In particular, the SFR in the Galactic bulge must have been very intense and have quickly consumed the gas, followed by the milder SFR in the thick disk, and even milder SFR in the thin disk. These assumptions on the SFR in the three Galactic components ensure good agreement for other chemical elements as well, such as -elements [47,48].
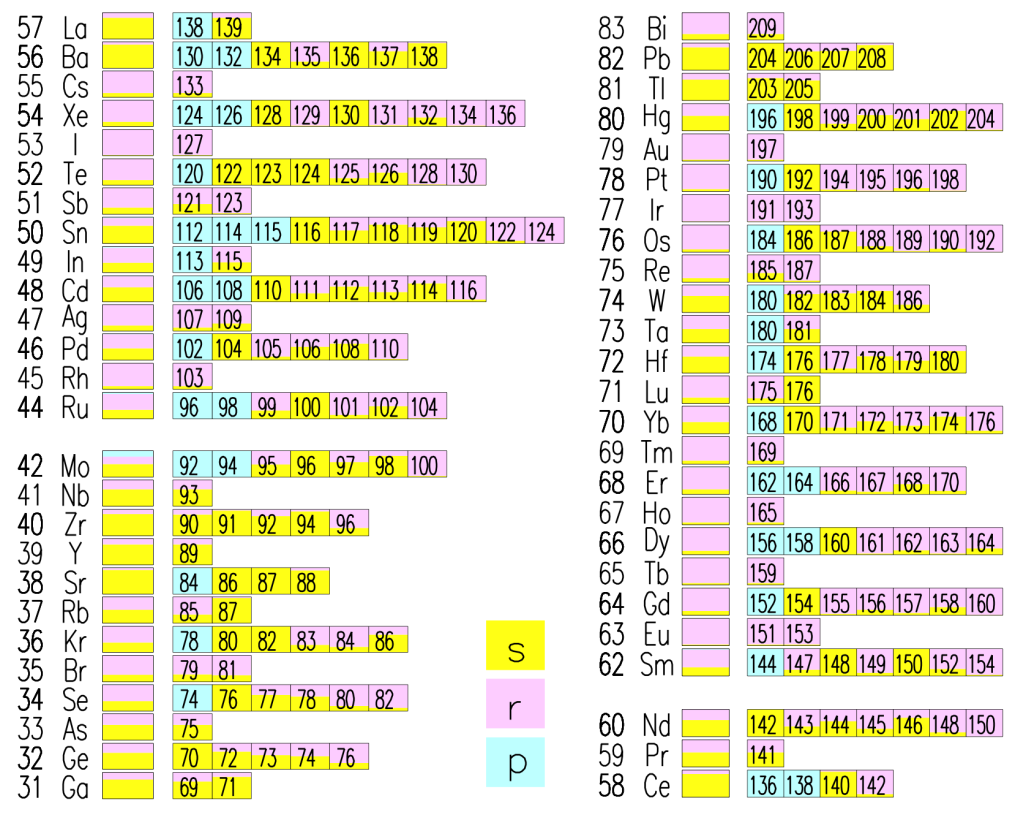
Prantzos et al. [49] presented an interesting method based on GCE models for assessing the s- and r- fractions of the solar system abundances. They used accurate yields from low- and intermediate-mass stars, as well as from rotating massive stars. The method consists of running models with only one component (s- and r-) at the time. In Figure 7, we report the table with the contributions from s-, r-, and p-process to the heavy elements by [49].
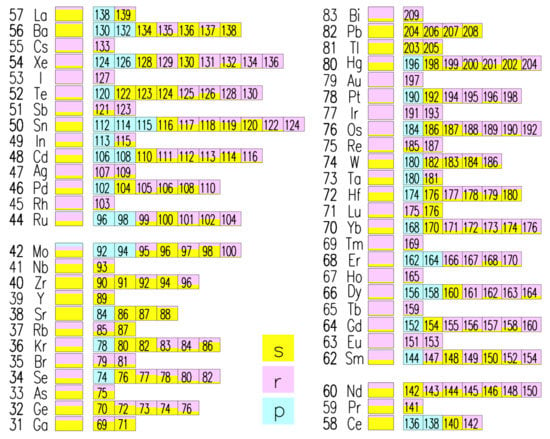
Figure 7.
Contributions of the s-, r-, and p- processes to the solar chemical composition. The contribution of each process is proportional to the coloured area of the corresponding box. Image reproduced with permission from Prantzos et al. [49]; copyright by the authors.
7. The s-Processing in AGB Stars Revisited Adopting Magneto Hydrodynamics Mixing
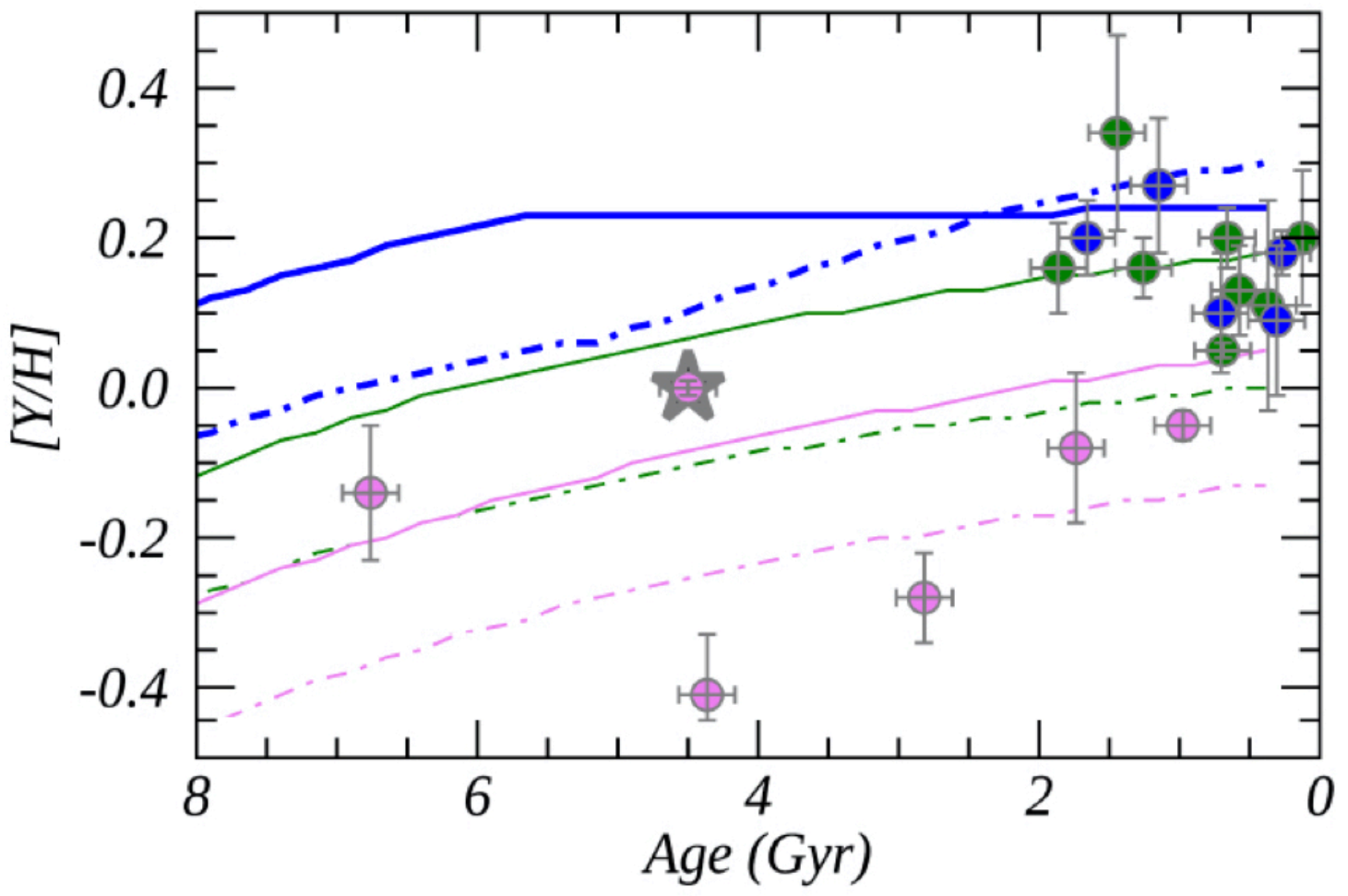
In Busso et al. [50], they assumed that magneto hydrodynamics (MHD) processes induce the penetration of protons below the convective boundary, when the third dredge-up occurs. There, the n-source can subsequently operate, merging its effects with those of the Ne(,n)Ne reaction, which is activated at the temperature peaks characterizing AGB stages. Busso et al. also provided a grid of abundance yields, as produced through their MHD mixing scheme, uniformly sampled in mass and metallicity. In that paper, they showed that MHD-induced mixing is adequate to drive slow n-capture phenomena, accounting for observations of evolved stars and isotopic ratios in presolar SiC grains, as in Liu et al. [51]. Moreover, in Magrini et al. [52], these new yields were included in a GCE model and the results were compared with a sample of abundances and ages of OCs located at different Galactocentric distances. It was shown that the magnetic mixing causes a less efficient production of Y at high metallicity. Since a non-negligible fraction of stars with supersolar metallicity are produced in the inner disk, their Y abundances are affected by the reduced yields. Thanks to the results of the new AGB yields based on MHD mixing, the GCE model of [52] was able to reproduce the observed trends for [Y/H] versus age at different Galactocentric distances, improving the outcome of previous AGB yields (see Figure 8).
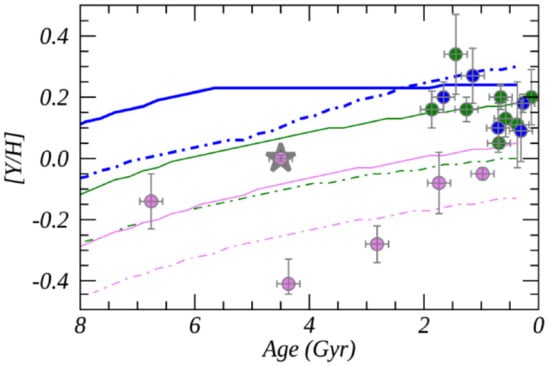
Figure 8.
[Y/H] vs. age; sample of Gaia-ESO idr5 clusters in three radial bins (Galactocentric radius (RGC) < 6.5 kpc in blue, 6.5 kpc < RGC < 9 kpc in green, and RGC > 9 kpc in pink), compared with results of the GCE model for the thin disk at three RGC = 6, 8, and 10 kpc, with the yields computed with AGB models adopting mixing triggered by magnetic fields (continuous curves) and those with the FRUITY yields (dot-dashed lines). The star marks the abundance ratio at the solar age and the Galactocentric distance. Image reproduced with permission from Magrini et al. [52]; copyright by the authors.
8. Conclusions
In this paper, we have summarized the main results obtained in the last 40 years relating to the importance of s-process production by AGB stars on the enrichment of heavy elements in our Milky Way. To achieve these results, one needs to adopt a detailed GCE model taking into account chemical yields from stars and stellar lifetimes. By comparing model results and data on s-process elements measured in Galactic stars, it is concluded that s-process elements such as Ba have a main s-process component produced in low-mass stars and appearing on long timescales, together with a faster component that has a r-process origin [24]. Very likely, this component originates on short time scales from massive stars or neutron star–neutron star mergers [45,53]. New detailed yields from AGB stars taking into account MHD processes have also allowed the reproduction of recent data of Y observed in open cluster stars.
In conclusion, by means of Galactic archaeology, together with more and more precise chemical yields (i.e., [3,4,50]), we are able to impose constraints on the origin of chemical elements, as well as on the history of star formation in galaxies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, writing—original draft preparation, G.C.; writing—review and editing, F.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by the European Union (ChETEC-INFRA, project no. 101008324).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notes
| 1 | It is adopted the notation [A/B]≡ log(N/N) − log(N/N)), for elements A and B. |
| 2 | http://www.as.utexas.edu/~chris/moog.html, accessed on 10 February 2022. |
References
- Gallino, R.; Busso, M.; Picchio, G.; Raiteri, C.M.; Renzini, A. On the Role of Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars in Producing a Solar System Distribution of s-Process Isotopes. Astrophys. J. 1988, 334, L45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallino, R.; Arlandini, C.; Busso, M.; Lugaro, M.; Travaglio, C.; Straniero, O.; Chieffi, A.; Limongi, M. Evolution and Nucleosynthesis in Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars. II. Neutron Capture and the S-Process. Astrophys. J. 1998, 497, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Lambert, D.L.; Beglio, L.; Gallino, R.; Raiteri, C.M.; Smith, V.V. Nucleosynthesis and Mixing on the Asymptotic Giant Branch. II. Carbon and Barium Stars in the Galactic Disk. Astrophys. J. 1995, 446, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Gallino, R.; Lambert, D.L.; Travaglio, C.; Smith, V.V. Nucleosynthesis and Mixing on the Asymptotic Giant Branch. III. Predicted and Observed s-Process Abundances. Astrophys. J. 2001, 557, 802–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, B.M. Evolution of the Stars and Gas in Galaxies. Fund. Cosmic Phys. 1980, 5, 287–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truran, J.W. A new interpretation of the heavy element abundances in metal-deficient stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1981, 97, 391–393. [Google Scholar]
- Travaglio, C.; Galli, D.; Gallino, R.; Busso, M.; Ferrini, F.; Straniero, O. Galactic Chemical Evolution of Heavy Elements: From Barium to Europium. Astrophys. J. 1999, 521, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Lawler, J.E.; Ivans, I.I.; Burles, S.; Beers, T.C.; Primas, F.; Hill, V.; Truran, J.W.; Fuller, G.M.; et al. The Extremely Metal-poor, Neutron Capture-rich Star CS 22892-052: A Comprehensive Abundance Analysis. Astrophys. J. 2003, 591, 936–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Gallino, R. Neutron-capture elements in the early galaxy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 46, 241–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travaglio, C.; Gallino, R.; Arnone, E.; Cowan, J.; Jordan, F.; Sneden, C. Galactic Evolution of Sr, Y, And Zr: A Multiplicity of Nucleosynthetic Processes. Astrophys. J. 2004, 601, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, F.; Beers, T.C.; Cowan, J.; Elliot, T.; Farouqi, K.; Gallino, R.; Heil, M.; Kratz, K.L.; Pfeiffer, B.; Pignatari, M. Nucleosynthesis in the Early Galaxy. Astrophys. J. 2007, 671, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiteri, C.M.; Gallino, R.; Busso, M. S-Processing in Massive Stars as a Function of Metallicity and Interpretation of Observational Trends. Astrophys. J. 1992, 387, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcones, A.; Montes, F. Production of Light-element Primary Process Nuclei in Neutrino-driven Winds. Astrophys. J. 2011, 731, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischknecht, U.; Hirschi, R.; Pignatari, M.; Maeder, A.; Meynet, G.; Chiappini, C.; Thielemann, F.K.; Rauscher, T.; Georgy, C.; Ekström, S. s-process production in rotating massive stars at solar and low metallicities. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 456, 1803–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongi, M.; Chieffi, A. Presupernova Evolution and Explosive Nucleosynthesis of Rotating Massive Stars in the Metallicity Range −3 ≤ [Fe/H] ≤ 0. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 237, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, R.G.; Sneden, C. Abundances of neutron-capture elements in metal-poor stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 287, 927–946. [Google Scholar]
- Woolf, V.M.; Tomkin, J.; Lambert, D.L. The r-Process Element Europium in Galactic Disk F and G Dwarf Stars. Astrophys. J. 1995, 453, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, P. Abundance of barium in metal poor stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1996, 313, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- McWilliam, A.; Preston, G.W.; Sneden, C.; Searle, L. Spectroscopic Analysis of 33 of the Most Metal Poor Stars. II. Astron. J. 1995, 109, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliam, A. Barium Abundances in Extremely Metal-poor Stars. Astron. J. 1998, 115, 1640–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.E.; Ryan, S.G.; Beers, T.C. Extremely Metal-poor Stars. The Carbon-rich, Neutron Capture Element–poor Object CS 22957-027. Astrophys. J. 1997, 489, L169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehin, E.; Magain, P.; Neuforge, C.; Noels, A.; Parmentier, G.; Thoul, A.A. Abundance correlations in mildly metal-poor stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 341, 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Mashonkina, L.; Gehren, T.; Bikmaev, I. Barium abundances in cool dwarf stars as a constraint to s- and r-process nucleosynthesis. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 343, 519–530. [Google Scholar]
- Cescutti, G.; François, P.; Matteucci, F.; Cayrel, R.; Spite, M. The chemical evolution of barium and europium in the Milky Way. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 448, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, C.; Matteucci, F.; Gratton, R. The Chemical Evolution of the Galaxy: The Two-Infall Model. Astrophys. J. 1997, 477, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayrel, R.; Depagne, E.; Spite, M.; Hill, V.; Spite, F.; François, P.; Plez, B.; Beers, T.; Primas, F.; Andersen, J.; et al. First stars V-Abundance patterns from C to Zn and supernova yields in the early Galaxy. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 416, 1117–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, P.; Depagne, E.; Hill, V.; Spite, M.; Spite, F.; Plez, B.; Beers, T.C.; Andersen, J.; James, G.; Barbuy, B.; et al. First stars. VIII. Enrichment of the neutron-capture elements in the early Galaxy. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 476, 935–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, D.L.; Pilachowski, C.A.; Armandroff, T.E.; Sneden, C.; Cowan, J.J.; Roe, H. Neutron-Capture Elements in the Early Galaxy: Insights from a Large Sample of Metal-poor Giants. Astrophys. J. 2000, 544, 302–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulbright, J.P. Abundances and Kinematics of Field Halo and Disk Stars. I. Observational Data and Abundance Analysis. Astron. J. 2000, 120, 1841–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, A.; Edvardsson, B. Europium abundances in F and G disk dwarfs. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 381, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Honda, S.; Aoki, W.; Kajino, T.; Ando, H.; Beers, T.C.; Izumiura, H.; Sadakane, K.; Takada-Hidai, M. Spectroscopic Studies of Extremely Metal-Poor Stars with the Subaru High Dispersion Spectrograph. II. The r-Process Elements, Including Thorium. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 474–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashonkina, L.; Gehren, T. Barium and europium abundances in cool dwarf stars and nucleosynthesis of heavy elements. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 364, 249–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mashonkina, L.; Gehren, T. Heavy element abundances in cool dwarf stars: An implication for the evolution of the Galaxy. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 376, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescutti, G.; Matteucci, F.; François, P.; Chiappini, C. Abundance gradients in the Milky Way for α elements, iron peak elements, barium, lanthanum, and europium. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 462, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazi, V.; Magrini, L.; Randich, S.; Galli, D.; Busso, M.; Sestito, P. Enhanced Production of Barium in Low-Mass Stars: Evidence from Open Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2009, 693, L31–L34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonnel, C. Clues for non-standard mixing on the red giant branch from 12C/13C and 12C/14N ratios in evolved stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1994, 282, 811–820. [Google Scholar]
- Busso, M.; Wasserburg, G.J.; Nollett, K.M.; Calandra, A. Can Extra Mixing in RGB and AGB Stars Be Attributed to Magnetic Mechanisms? Astrophys. J. 2007, 671, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensby, T.; Feltzing, S.; Lundström, I.; Ilyin, I. α-, r-, and s-process element trends in the Galactic thin and thick disks. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 433, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratella, M.; D’Orazi, V.; Sheminova, V.; Spina, L.; Carraro, G.; Gratton, R.; Magrini, L.; Randich, S.; Lugaro, M.; Pignatari, M.; et al. The Gaia-ESO Survey: A new approach to chemically characterising young open clusters. II. Abundances of the neutron-capture elements Cu, Sr, Y, Zr, Ba, La, and Ce. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 653, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiorca, E.; Randich, S.; Busso, M.; Magrini, L.; Palmerini, S. s-processing in the Galactic Disk. I. Super-solar Abundances of Y, Zr, La, and Ce in Young Open Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2011, 736, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sneden, C. The nitrogen abundance of the very metal-poor star HD 122563. Astrophys. J. 1973, 184, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuti, F.; Cescutti, G.; Matteucci, F.; Chieffi, A.; Hirschi, R.; Limongi, M. The contribution from rotating massive stars to the enrichment in Sr and Ba of the Milky Way. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 5244–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Straniero, O.; Gallino, R.; Piersanti, L.; Domínguez, I.; Lederer, M.T. Evolution, Nucleosynthesis, and Yields of Low-Mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars at Different Metallicities. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 797–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristallo, S.; Piersanti, L.; Straniero, O.; Gallino, R.; Domínguez, I.; Abia, C.; Di Rico, G.; Quintini, M.; Bisterzo, S. Evolution, Nucleosynthesis, and Yields of Low-mass Asymptotic Giant Branch Stars at Different Metallicities. II. The FRUITY Database. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 197, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielemann, F.K.; Arcones, A.; Käppeli, R.; Liebendörfer, M.; Rauscher, T.; Winteler, C.; Fröhlich, C.; Dillmann, I.; Fischer, T.; Martinez-Pinedo, G.; et al. What are the astrophysical sites for the r-process and the production of heavy elements? Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 2011, 66, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisoni, V.; Cescutti, G.; Matteucci, F.; Forsberg, R.; Jönsson, H.; Ryde, N. Modelling the chemical evolution of Zr, La, Ce, and Eu in the Galactic discs and bulge. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 2828–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisoni, V.; Spitoni, E.; Matteucci, F.; Recio-Blanco, A.; de Laverny, P.; Hayden, M.; Mikolaitis, Ŝ.; Worley, C.C. The AMBRE project: Chemical evolution models for the Milky Way thick and thin discs. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 3637–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, F.; Grisoni, V.; Spitoni, E.; Zulianello, A.; Rojas-Arriagada, A.; Schultheis, M.; Ryde, N. The origin of stellar populations in the Galactic bulge from chemical abundances. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 5363–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prantzos, N.; Abia, C.; Cristallo, S.; Limongi, M.; Chieffi, A. Chemical evolution with rotating massive star yields II. A new assessment of the solar s- and r-process components. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 491, 1832–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, M.; Vescovi, D.; Palmerini, S.; Cristallo, S.; Antonuccio-Delogu, V. s-processing in AGB Stars Revisited. III. Neutron Captures from MHD Mixing at Different Metallicities and Observational Constraints. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Gallino, R.; Cristallo, S.; Bisterzo, S.; Davis, A.M.; Trappitsch, R.; Nittler, L.R. New Constraints on the Major Neutron Source in Low-mass AGB Stars. Astrophys. J. 2018, 865, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrini, L.; Vescovi, D.; Casali, G.; Cristallo, S.; Viscasillas Vázquez, C.; Cescutti, G.; Spina, L.; Van Der Swaelmen, M.; Randich, S. Magnetic-buoyancy-induced mixing in AGB stars: A theoretical explanation of the non-universal relation of [Y/Mg] to age. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 646, L2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perego, A.; Thielemann, F.K.; Cescutti, G. r-Process Nucleosynthesis from Compact Binary Mergers. In Handbook of Gravitational Wave Astronomy; Bambi, C., Katsanevas, S., Kokkotas, K.D., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 1–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).