The Dynamic Changes in the Main Substances in Codonopsis pilosula Root Provide Insights into the Carbon Flux between Primary and Secondary Metabolism during Different Growth Stages
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Materials
2.3. Determination of Crude Polysaccharide Content and Monosaccharide Composition Assay
2.4. Soluble Protein Analysis
2.5. Total Phenolics, Total Flavonoids, and Anthocyanins Assay
2.6. Determination of Lobetyolin and Atractylenolide III
2.7. Determination of Vitamins and β-Carotene
2.8. Antioxidant Capacity Assay
2.9. Expression Pattern of Genes Involved in Primary and Secondary Metabolism (Carbohydrate and Terpenoid Biosynthesis Pathways)
2.10. Statistical Analysis of the Data
3. Results
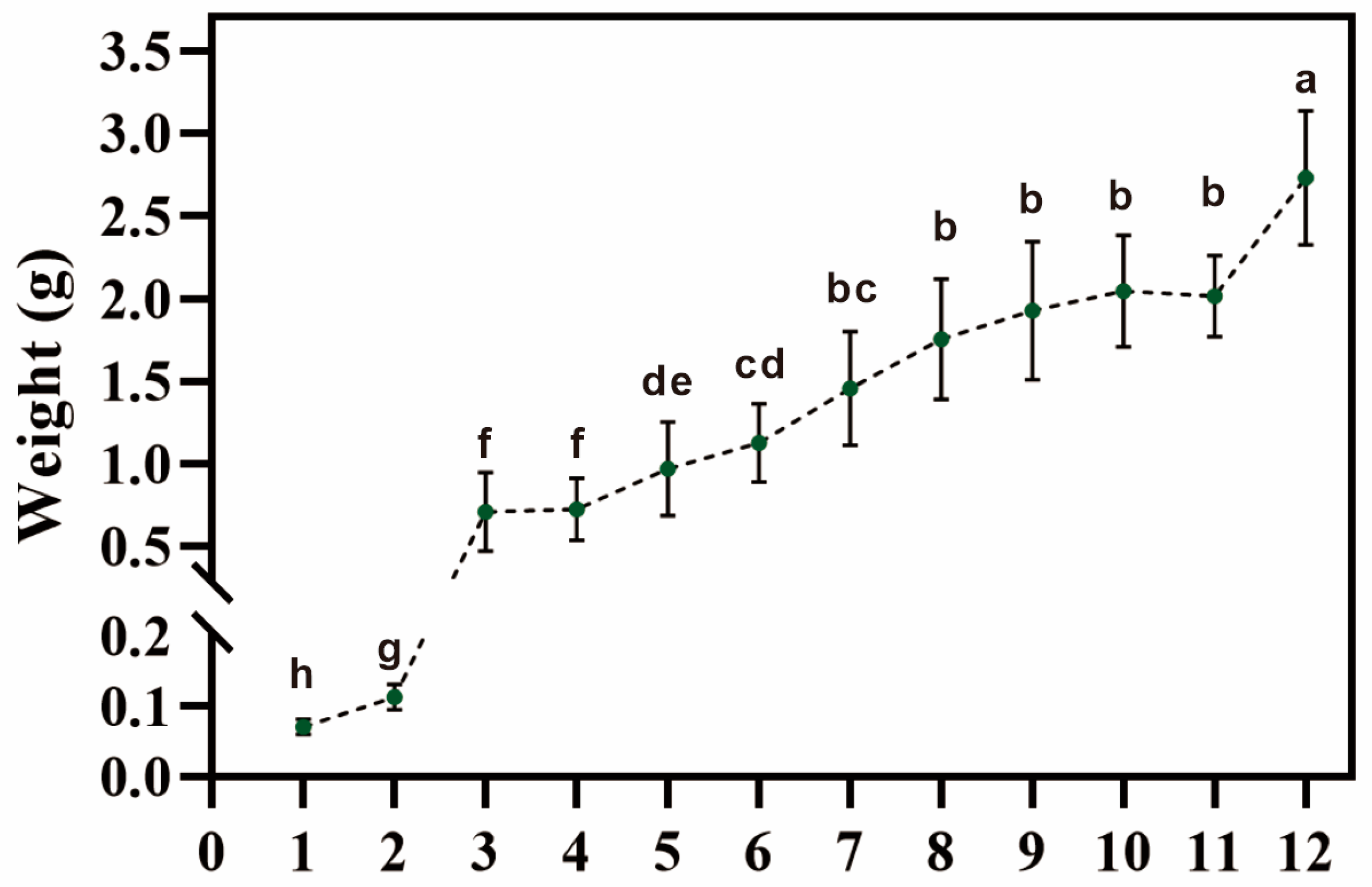
3.1. Root Biomass at Different Development Stages Showed a Continuous Increase
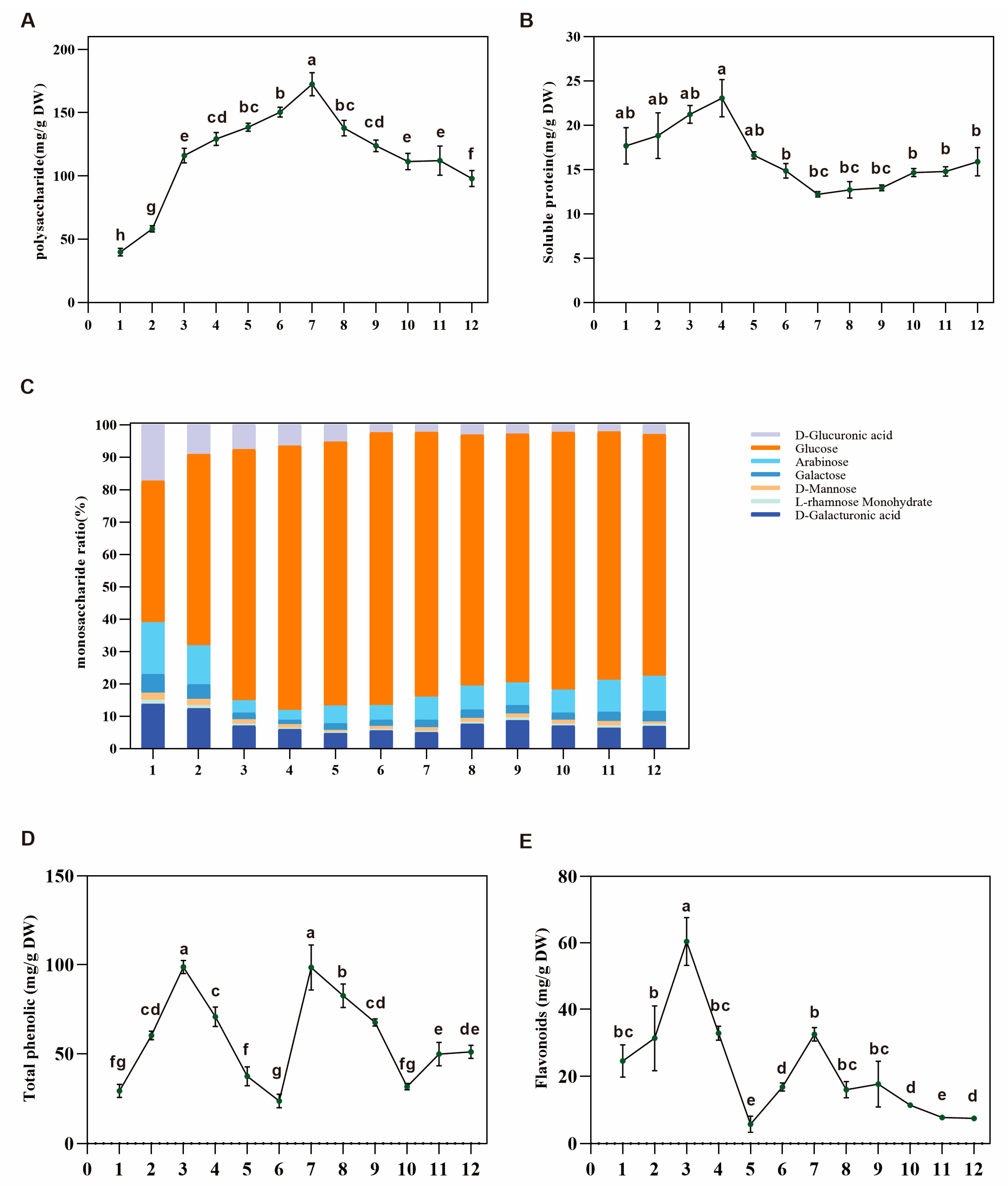
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Polysaccharides, Soluble Protein, and Total Phenolics and Flavonoids Indicated the Carbon Flux between Primary and Secondary Metabolism in Dangshen
3.3. The Contents of Lobetyolin and Atractylenolide III Might Provide Information for the Harvest Time of Dangshen
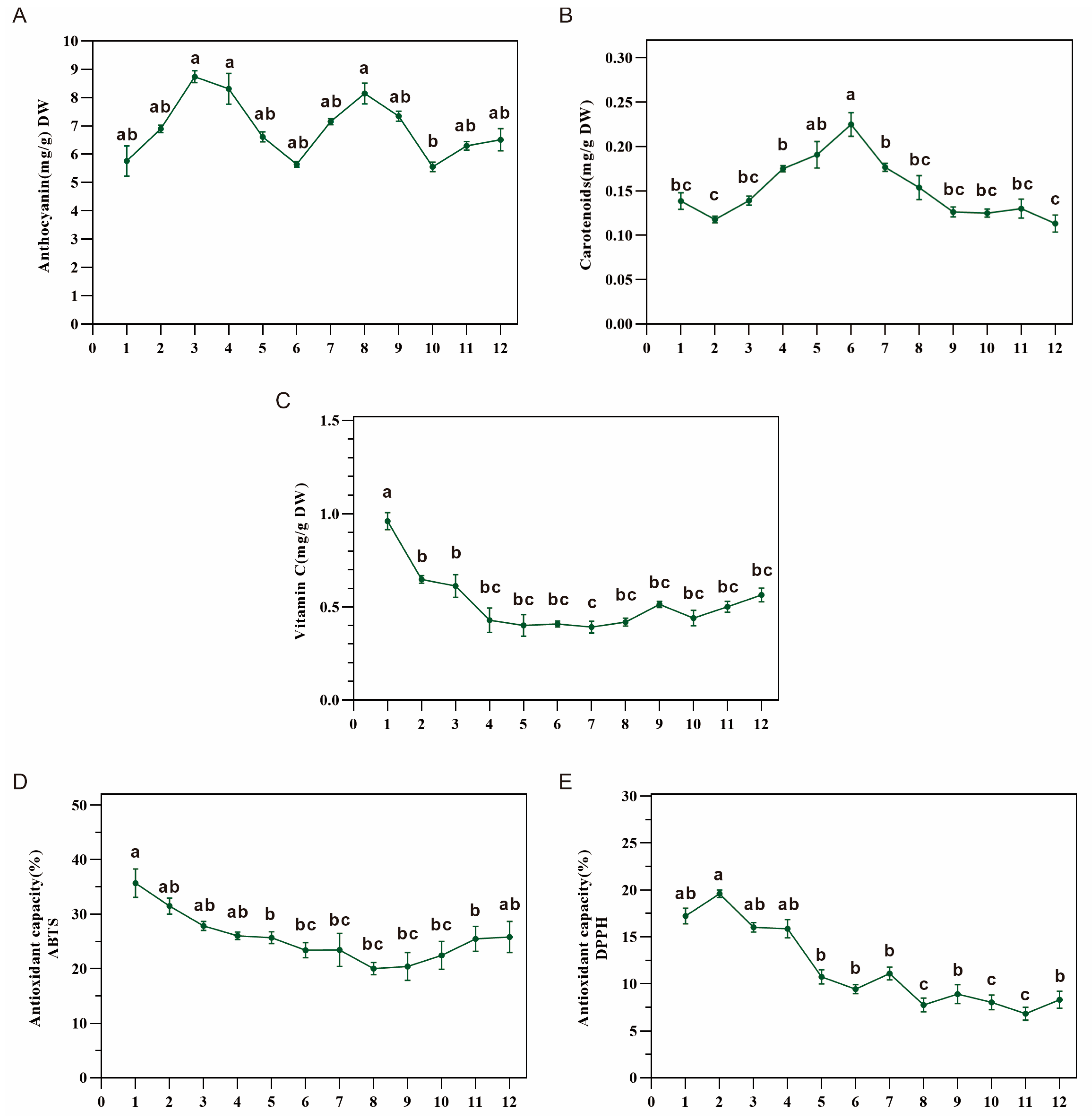
3.4. Antioxidant Capacity in Dangshen Was Correlated with Vitamin C Content
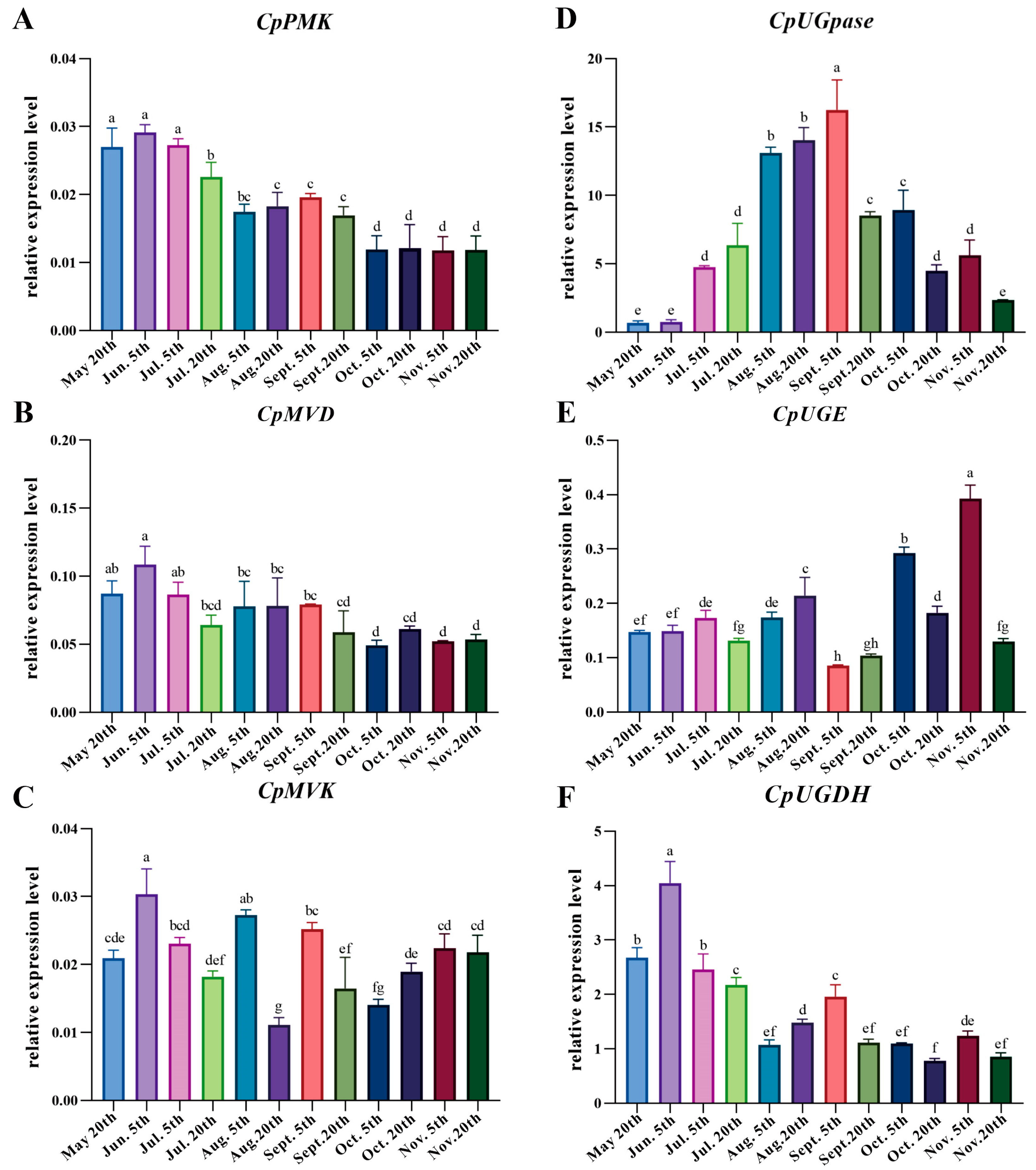
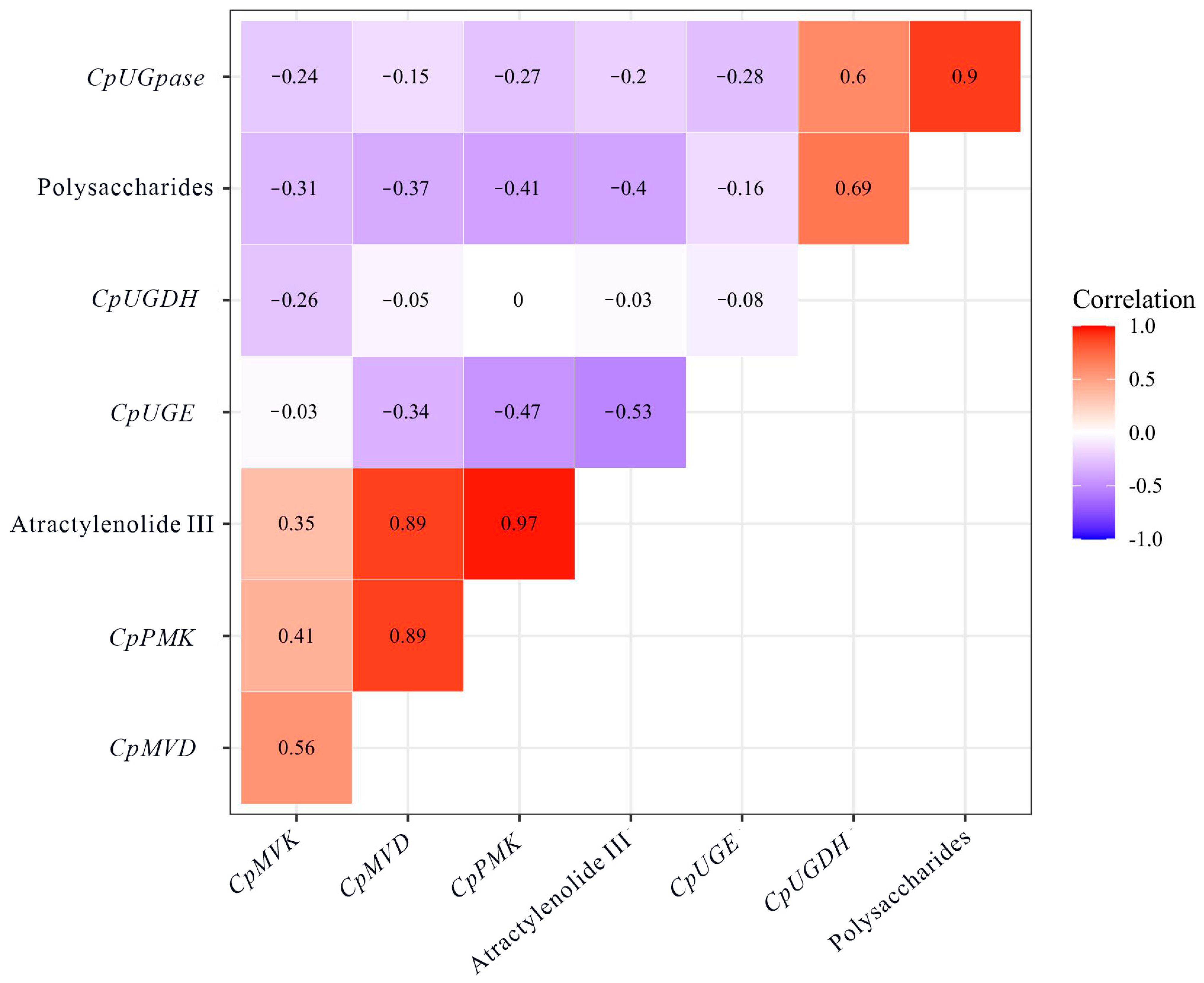
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Carbohydrate, Atractylenolide III, and Expression of Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Xie, C.; Liu, X. Prediction for the potential distribution area of Codonopsis pilosula at global scale based on Maxent model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2017, 28, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume I, pp. 293–294.
- He, J.Y.; Ma, N.; Zhu, S.; Komatsu, K.; Li, Z.Y.; Fu, W.M. The genus Codonopsis (Campanulaceae): A review of phytochemistry, bioactivity and quality control. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, P.; Deng, Y.; Jin, Q.; Shi, Q.; et al. Evaluation of antidiabetic potential of selected traditional Chinese medicines in STZ-induced diabetic mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.X. Immunological adjuvant effect of a water-soluble polysaccharide, CPP, from the roots of Codonopsis pilosula on the immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Guan, M. The contribution of side chains to antitumor activity of a polysaccharide from Codonopsis pilosula. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu., H.; Sun, X.; et al. Exploring on the bioactive markers of Codonopsis Radix by correlation analysis between chemical constituents and pharmacological effects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 236, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C. Anticancer Properties of Lobetyolin, an Essential Component of Radix Codonopsis (Dangshen). Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2021, 11, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoou, M.S.; Nam, S.Y.; Jin, M.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Roh, S.S.; Choi, I.H.; Woo, N.; Lim, S.; Kim, D.H.; et al. Ameliorative effect of atractylenolide III in the mast cell proliferation induced by TSLP. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, L. Atractylenolide III reduces NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Th1/Th2 imbalances in both in vitro and in vivo models of asthma. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 1360–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsędek, A. Natural antioxidants and antioxidant capacity of Brassica vegetables: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, Z.L. The research status of that Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide is as an immune adjuvant. Guide China Med. 2013, 11, 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Larbat, R.; Robin, C.; Lillo, C.; Drengstig, T.; Ruoff, P. Modeling the diversion of primary carbon flux into secondary metabolism under variable nitrate and light/dark conditions. J. Theor. Biol. 2016, 402, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Cao, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Xiao, P. Quantitative and HPLC fingerprint analysis combined with chemometrics for quality evaluation of Codonopsis Radix processed with different methods. Chin. Herb. Med. 2019, 11, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.J.; Feng, Q.; Sun, H.F.; Zhang, X.J.; Li, X.X.; Li, J.K.; Gao, J.P. Response of Bioactive Metabolite and Biosynthesis Related Genes to Methyl Jasmonate Elicitation in Codonopsis pilosula. Molecules 2019, 24, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isah, T. Stress and defense responses in plant secondary metabolites production. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chen, C.; Sun, P.; Liu, S.; Wei, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, F. Comparative Study on Contents of 5 Active Ingredients in Different Varieties and Harvesting Periods of Codonopsis Radix. China Pharm. 2020, 31, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reno, C.; Marchuk, L.; Sciore, P.; Frank, C.B.; Hart, D.A. Rapid isolation of total RNA from small samples of hypocellular, dense connective tissues. Biotechniques 1997, 22, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Niu, J.; Li, B.; Huang, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Hu, S.; Li, L.; Wang, D.; et al. Molecular characterization and overexpression of smjmt increases the production of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. Separation and quantification of component monosaccharides of the tea polysaccharides from Gynostemma Pentaphyllum by HPLC with indirect UV detection. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevag, M.G.; Lackman, D.B.; Smolens, J. The isolation of the components of Streptococcal nucleoproteins in serologically active form. J. Biol. Chem. 1938, 124, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, T. Refinement of the coomassie blue method of protein quantitation. a simple and linear spectrophotometric assay for less than or equal to 0.5 to 50 microgram of protein. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 86, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, Y.P.; Wang, Z.Z. The Arabidopsis PAP1 transcription factor plays an important role in the enrichment of phenolic acids in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12168–12175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, Y.L.; Goh, J.K.; Lim, Y.Y. Assessment of in vitro antioxidant capacity and polyphenolic composition of selected medicinal herbs from Leguminosae family in Peninsular Malaysia. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 50, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, H.; Ogasawara, F.; Sato, K.; Higo, H.; Minobe, Y. Isolation of a Regulatory Gene of Anthocyanin Biosynthesis in Tuberous Roots of Purple-Fleshed Sweet Potato. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 1252–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.E.; Zhang, X.T.; Zhang, R.M.; Hou, J.; Gao, J.P. Simultaneous determination of lobetyolin and atractylenolide iii in Codonopsis radix by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimczak, I.; Gliszczyńska-Świgło, A. Comparison of UPLC and HPLC methods for determination of vitamin C. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yue, Z.; Zhong, X.; Lei, J.; Tao, P.; Li, B. Distribution of primary and secondary metabolites among the leaf layers of headed cabbage (Brassica oleracea var. capitata). Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, J.; Li, E.; Fan, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Qiu, S.; Gao, Z.; et al. The comparison of antioxidative and hepatoprotective activities of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide (CP) and sulfated CP. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 24, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Kuang, Z.; Li, B.; Lu, X.; Cao, X.; Kang, J. Selection of suitable reference genes for qRT-PCR expression analysis of Codonopsis pilosula under different experimental conditions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4169–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, L.; Bai, R.; Zheng, X.; Ma, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, B.; Hu, F. Structural characterization of a pectic polysaccharide from Codonopsis pilosula and its immunomodulatory activities in vivo and in vitro. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ha, S.; Liu, Y. Comparison of polysaccharide content and antioxidant activity of Codonopsis pilosula in different producing areas. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2019, 47, 184–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Liang, Z.Y.; Zhang, L.X. Study on composition and immunological activities of crude polysaccharide isolated from the Codonopsis pilosula. J. Northwest A&F Univ. 2012, 40, 199–202. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, I.S.; Cho, S.S. Effects of lobetyolin on xanthine oxidase activity in vitro and in vivo: Weak and mixed inhibition. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 1667–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; An, P.; Wang, Y. Dynamic changes of the contents of lobetyolin contained in DangShen at different sampling periods. West. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2014, 27, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Spoelstra-de, M.A.; Elbers, P.; Oudemans-Van, S.H.M. Vitamin C: Should we supplement? Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2018, 24, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.P.; Wang, D.; Cao, L.Y.; Sun, H.F. Transcriptome sequencing of Codonopsis pilosula and identification of candidate genes involved in polysaccharide biosynthesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.-S.; Zhang, T.; Wang, L.; Dong, S.; Wang, D.-H.; Li, B.; Cao, X.-Y. The Dynamic Changes in the Main Substances in Codonopsis pilosula Root Provide Insights into the Carbon Flux between Primary and Secondary Metabolism during Different Growth Stages. Metabolites 2023, 13, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030456
Wang S-S, Zhang T, Wang L, Dong S, Wang D-H, Li B, Cao X-Y. The Dynamic Changes in the Main Substances in Codonopsis pilosula Root Provide Insights into the Carbon Flux between Primary and Secondary Metabolism during Different Growth Stages. Metabolites. 2023; 13(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Sheng-Song, Tong Zhang, Long Wang, Shuai Dong, Dong-Hao Wang, Bin Li, and Xiao-Yan Cao. 2023. "The Dynamic Changes in the Main Substances in Codonopsis pilosula Root Provide Insights into the Carbon Flux between Primary and Secondary Metabolism during Different Growth Stages" Metabolites 13, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030456
APA StyleWang, S.-S., Zhang, T., Wang, L., Dong, S., Wang, D.-H., Li, B., & Cao, X.-Y. (2023). The Dynamic Changes in the Main Substances in Codonopsis pilosula Root Provide Insights into the Carbon Flux between Primary and Secondary Metabolism during Different Growth Stages. Metabolites, 13(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030456






