Abstract
Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) plays an important role in various physiological functions and is abundant in the brain and skeletal muscle. Extracellular taurine is an endogenous agonist of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A and glycine receptors. Taurine actively accumulates in cells via the taurine transporter (TauT). Adult taurine-knockout (TauT−/−) mice exhibit lower body weights and exercise intolerance. To further examine the physiological role of taurine, we examined the effect of its depletion on mouse behavior, startle responses, muscular endurance, and body weight during development from postnatal day 0 (P0) until P60. In the elevated plus maze test, TauT−/− mice showed decreased anxiety-like behavior. In addition, TauT−/− mice did not show a startle response to startle stimuli, suggesting they have difficulty hearing. Wire-hang test revealed that muscular endurance was reduced in TauT−/− mice. Although a reduction of body weight was observed in TauT−/− mice during the developmental period, changes in body weight during 60% food restriction were similar to wild-type mice. Collectively, these results suggest that taurine has important roles in anxiety-like behavior, hearing, muscular endurance, and maintenance of body weight.
Keywords:
taurine; taurine transporter; knockout mice; brain; skeletal muscle; body weight; behavior 1. Introduction
Taurine (2-aminoethanesulfonic acid) is one of the most ubiquitous and abundant amino acids in mammalian tissues [1,2], whereby it plays important roles in various physiological functions [3] such as mitochondrial translation [4], Ca2+ homeostasis [5], cell volume regulation [6], stability of membranes [7], and antioxidant effects [8]. Although the capacity to synthesize taurine is limited in most tissues [9], high levels of intracellular taurine are maintained by the taurine transporter (TauT/SLC6a6) on the membrane [10]. TauT is a Na+-Cl− ion-dependent transporter expressed ubiquitously in mammalian tissues [10]. The development of TauT-knockout (TauT−/−) mice by two laboratories revealed the physiological functions of taurine [11,12]. TauT−/− mice exhibit shortened lifespan; cardiomyopathy; aging-dependent cardiac dysfunction; hepatitis; and renal, visual, auditory, and olfactory dysfunction [13,14,15]. Transcriptome microarray analysis of TauT−/− mice revealed that pro-fibrotic genes, such as S100 calcium-binding protein A4 (S100A4), actin alpha 2, smooth muscle (ACTA2), and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), were increased in TauT−/− mice hearts [16]. Based on the transcriptome-pathway analysis, the genes involved in the “organization of extracellular matrix,” such as galectin 3 (LGALS3), are enriched in old TauT−/− mice hearts, suggesting the contribution of these genes to fibrosis [16].
Taurine is present in high concentrations in the brain [17,18,19]. Moreover, taurine levels are high in the immature brain compared with the adult brain [18]. Taurine is required for the development of the central nervous system [20,21,22]. Our prior reports demonstrated that ambient taurine tonically activates gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptors and slows radial migration in the developing cerebral cortex [23]. In addition, taurine regulates the temporal specification of excitatory glutamatergic neuronal progenitors in the developing cortex [24]. In immature neurons, taurine inhibits the K+-Cl− cotransporter KCC2, which maintains low intracellular Cl− levels critical for mediating fast-hyperpolarizing synaptic inhibition by GABAA and glycine receptors via the with-no-lysine (WNK) protein kinase signaling pathway [25]. However, the effects of taurine depletion on adult mouse behaviors, such as locomotor activity, anxiety-like behavior, and startle response, have not yet been reported.
Taurine also occurs in particularly high concentrations in skeletal muscle [11]. TauT−/− mice show a more than 98% reduction in muscle taurine content [12,26]. In addition, TauT−/− mice exhibit exercise intolerance in both treadmills and forced swimming tests [26,27], as well as muscular structural defects, such as myofibril derangement and the appearance of autophagic bodies [12,14]. TauT−/− mice exhibit accelerated skeletal muscle aging and growth, and differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), which is a member of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily, was elevated during aging in TauT−/− mice [28]. A previous report found that adult TauT−/− mice fed a normal diet had lower body weights and visceral fat, although the body weights of TauT−/− mice fed a diet containing 60% fat increased to a level comparable to that of wild-type (WT) mice [29]. TauT−/− mice showed lower fasting blood glucose and were more tolerant against glucose injection [29]. Metabolism of fatty acids was suppressed by the downregulation of genes and enzymes involved in fatty acids β-oxidation [27]. Taurine reduced obesity in WT mice fed a high-fat diet, suppressed increases in adipocyte size, body fat, and body weight [30] and improved insulin sensitivity, and increased energy expenditure and adaptive thermogenesis by elevating the browning of white adipose tissue [31]. Body weight and height of infants at birth were significantly higher in the high taurine intake pregnant women compared to infants in low taurine intake pregnant women [32]. However, changes in body weight of TauT−/− mice during development remain unclear.
In this study, to further examine the physiological role of taurine, we used TauT−/− mice to investigate the effects of taurine deficiency on body weight changes during development and in adult mice during food restriction. In addition, we measured muscular endurance. Furthermore, to examine the effects of taurine deficiency on behavior, we performed several behavioral analyses.
2. Results
2.1. TauT−/− Mice Showed Decreased Anxiety-Like Behavior
We performed a behavioral analysis of TauT−/− mice. To assay general locomotor activity levels and anxiety, we performed an open field test. Percentages of time spent in the center (WT, 9.3 ± 3.1%, n = 12; TauT+/−, 7.4 ± 2.0%, n = 12; TauT−/−, 4.7 ± 1.4%, n = 8) and time spent in the corner (WT, 59.2 ± 5.7%; TauT+/−, 61.9 ± 3.7%; TauT−/−, 60.4 ± 4.7%) were similar between genotypes (Figure 1A,B). Moreover, no significant difference in the total distance moved was found between genotypes (WT, 3354.1 ± 234.1 cm; TauT+/−, 3690.5 ± 214.9 cm; TauT−/− mice, 3891.4 ± 582.9 cm; Figure 1C). From these results, TauT+/− and TauT−/− mice both showed normal locomotor activity. To examine anxiety-like behavior, we performed an elevated plus maze test. The percentage of time spent in the open arm was increased in TauT−/− mice compared with WT and TauT+/− mice, although there were no significant differences between groups (WT, 13.5 ± 2.3%, n = 13; TauT+/−, 14.7 ± 4.4%, n = 11; TauT−/−, 28.6 ± 10.5%, n = 11; Figure 1D). The percentage of time spent in the closed arm was significantly decreased in TauT−/− mice compared with WT and TauT+/− mice (WT, 78.4 ± 3.3%; TauT+/−, 77.8 ± 5.8%; TauT−/−, 52.8 ± 9.0%). In addition, the percentage of time spent in the center was significantly increased in TauT−/− mice compared with WT mice and showed an increased trend compared with WT mice (p = 0.06; WT, 8.1 ± 1.4%; TauT+/−, 7.4 ± 1.6%; TauT−/−, 18.6 ± 3.1%). No significant difference in total distance moved was observed between genotypes (WT, 1329.7 ± 58.2 cm; TauT+/−, 1274.9 ± 61.1 cm; TauT−/−, 1117.1 ± 67.0 cm; Figure 1E). These results suggest that TauT−/− mice showed decreased anxiety-like behavior and had difficulty making decisions underlying approach/avoidance conflict and risk assessment.
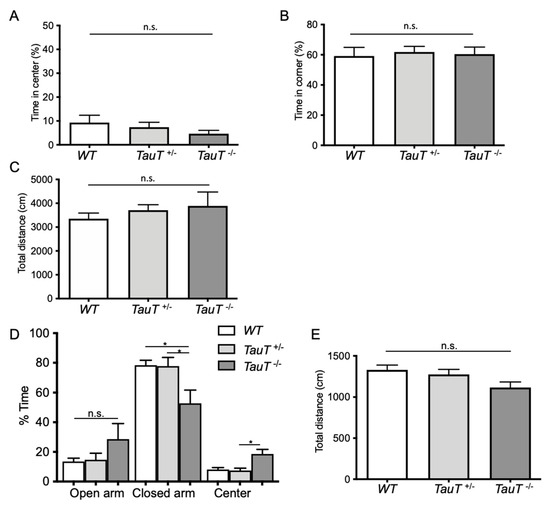
Figure 1.
(A–C) In the open field test, mice were placed in the center of the open field apparatus and their movement was tracked for 10 min. The percentage of time spent in the center (A), percentage of time spent in the corner (B), and total distance moved in an open field (C) were measured for WT, TauT+/−, and TauT−/− mice. (D,E) In the elevated plus maze test, mice were placed in the center of the elevated plus maze and allowed to explore for 5 min. The percentage of time spent in the open arms, closed arms, and center (* p < 0.05, n.s. = not significant by Kruskal–Wallis test) (D) and total distance moved (E) in the elevated plus maze were measured. Error bars represent S.E.M.
2.2. TauT−/− Mice Showed Difficulty Hearing
Next, we performed the startle response test and checked the dependence of startle responses on startle stimulus intensity (60 to 120-dB pulse, WT n = 6, TauT−/− n = 6). WT mice showed a startle response to startle pulses between 90 and 120 dB (Table 1). In total, 50% of WT mice showed a startle response to a startle pulse of 90 dB. All WT mice showed startle responses to startle pulses between 100 and 120 dB. However, no TauT−/− mice exhibited a startle response to any startle pulse. From these results, TauT−/− mice likely have difficulty hearing.

Table 1.
Startle response test. Numbers of mice showing a startle response to the startle pulse.
2.3. Muscular Endurance Was Reduced in TauT−/− Mice
A previous report suggested that exercise capacity (as determined by a treadmill test) was reduced in TauT−/− mice [27]. Therefore, to measure muscular endurance, a wire-hang test was performed. Each mouse was placed on a wire mesh and then turned upside down. The latency to fall was measured. Latency to fall was reduced in TauT−/− mice compared with WT mice (WT, 552.6 ± 32.4 s, n = 7; TauT−/−, 462.6 ± 32.6 s, n = 6; Figure 2). These results suggest that muscular endurance was reduced in TauT−/− mice.
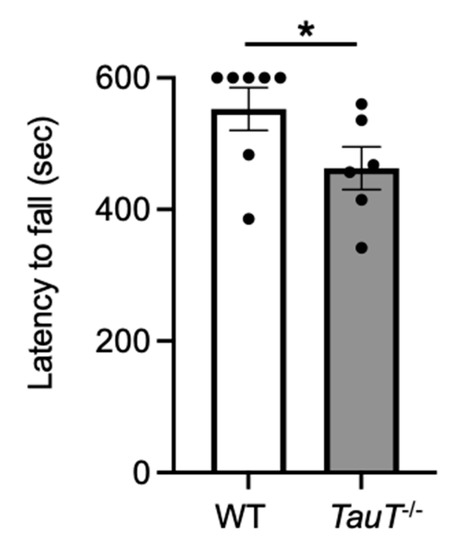
Figure 2.
Muscular endurance was reduced in TauT−/− mice. Wire-hang test was performed. Average latency to fall from the wire mesh of two trials in WT and TauT−/− mice. * p < 0.05 by Mann-Whitney test. Error bars represent S.E.M. Closed circles represent animals.
2.4. Body Weight Gain Was Reduced in TauT−/− Mice during Development
Adult TauT−/− mice showed reduced body weights [29], so we examined changes in body weight during development from postnatal day 0 (P0) until P60. The body weight of each mouse was measured every 2 days. At birth, there were no differences in body weights between genotypes for either male (WT, 1.39 ± 0.05 g, n = 15; TauT+/−, 1.41 ± 0.03 g, n = 39; TauT−/−, 1.35 ± 0.02 g, n = 13) or female (WT, 1.37 ± 0.03 g, n = 23; TauT+/−, 1.38 ± 0.02 g, n = 39; TauT−/−, 1.38 ± 0.03 g, n = 16) mice (Figure 3A,B). However, body weights of male TauT−/− mice were significantly lower compared with male WT and TauT+/− mice between P4 onward (WT, n = 12; TauT+/−, n = 32; TauT−/−, n = 12) (Figure 3C). In addition, a reduction in body weights of female TauT−/− mice was observed between P10 onward (WT, n = 16; TauT+/−, n = 32; TauT−/−, n = 15) (Figure 3D). The difference in body weight seems to become apparent around P20 when mice start self-feeding. Notably, the difference in body weights between WT and TauT−/− mice was greater in male mice than in female mice.
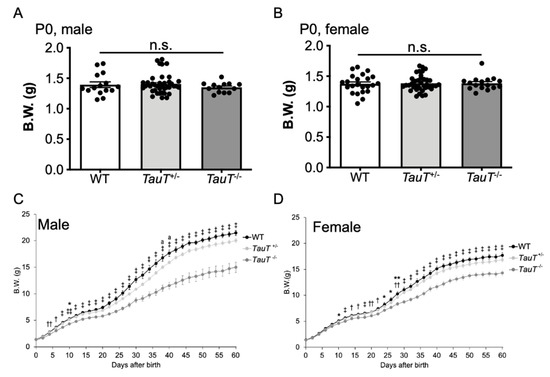
Figure 3.
TauT−/− mice exhibited lower body weights during development. (A) Body weights of male WT, TauT+/−, and TauT−/− pups at P0. Closed circles represent animals. (B) Body weights of female WT, TauT+/−, and TauT−/− pups at P0. (C) Changes in body weights of male WT, TauT+/−, and TauT−/− mice during development. (D) Changes in body weights of female WT, TauT+/−, and TauT−/− mice during development. Error bars represent S.E.M. * p < 0.05 TauT−/− vs. WT, ** p < 0.01 TauT−/− vs. WT, † p < 0.05 TauT−/− vs. WT and TauT+/−, ‡ p < 0.01 TauT−/− vs. WT and TauT+/−, †† p < 0.05 TauT−/− vs. TauT+/−, ‡‡ p < 0.01 TauT−/− vs. TauT+/−, and a p < 0.05 TauT+/− vs. WT by Kruskal-Wallis test.
2.5. Body Weight Changes during 60% Food Restriction Were Similar in WT and TauT−/− Mice
A previous report showed that the weight of visceral fat was significantly less in TauT−/− mice compared with WT mice; however, when fed a high-fat diet, TauT−/− mice exhibited body weights comparable to WT mice and dramatically increased abdominal fat after 16 weeks [29]. Therefore, we examined the effect of a 60% food restriction. Mice were given a food pellet equal to 60% of daily food intake before the onset of the dark phase for 2 weeks. Subsequently, mice were given food ad libitum for 2 weeks. Body weights were measured every day. Body weights were markedly decreased during the first 5 days after starting 60% food restriction, then gradually decreased in both WT and TauT−/− mice (WT, n = 7; TauT−/−, n = 7; Figure 4A,B). After WT and TauT−/− mice were given food ad libitum; their body weights increased in both WT and TauT−/− mice. Indeed, the remarkable weight loss observed during the first 5 days after starting 60% food restriction gradually recovered in both WT and TauT−/− mice (Figure 4C). On the first day, mice were given food ad libitum; the weight gain was significantly lower in TauT−/− mice (2.9 ± 0.1 g) compared with WT mice (4.2 ± 0.2 g). Thus, TauT−/− mice showed an apparent disturbance of body weight recovery after food restriction compared with WT mice, although their body weight reduction during food restriction was comparable.
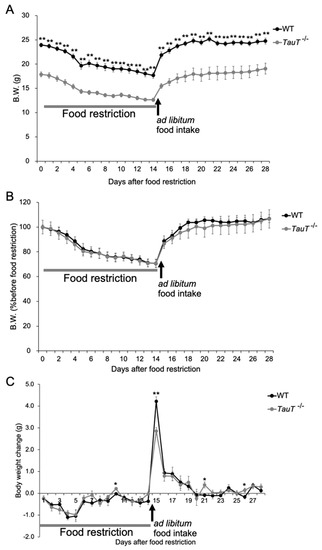
Figure 4.
Changes in body weights following 60% food restriction in WT and TauT−/− mice. (A) Changes in body weight after 60% food restriction and recovery (food ad libitum) in WT mice and TauT−/− mice. (B) Body weight changes are shown as a percentage of the initial body weight before 60% food restriction. (C) Body weight loss or gain after 60% food restriction and recovery (food ad libitum) in WT mice and TauT−/− mice. Error bars represent S.E.M. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by Kruskal-Wallis test.
2.6. Comprehensive Analysis of Protein Kinases and Target Proteins
Metabolic processes are commonly regulated by a series of phosphorylation events by kinases. Therefore, we performed an active site-directed competition binding assay to quantitatively measure interactions between kinases and target proteins to compare differences between WT and TauT−/− mice. Nineteen proteins showed significant changes in expression levels between WT and TauT−/− mice. Moreover, three proteins exhibited significant changes in the phosphorylation of analyzed sites (Table S1). The most prominent protein alteration was phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) at tyrosine 705, which was increased by 9449% in the brains of TauT−/− mice compared with WT mice.
3. Discussion
We have shown that taurine deficiency in mice decreased anxiety-like behaviors, abolished startle responses, and reduced muscular endurance. Furthermore, taurine deficiency caused lower body weight gain during development. Our findings demonstrate the importance of taurine in brain function, muscular endurance, and energy metabolism.
Our results show that TauT−/− mice exhibited decreased anxiety-like behaviors, as indicated by reduced time in the closed arm of the elevated plus maze test and increased time spent in the center square. Time spent exploring the center square has been suggested to reflect decision-making underlying approach-avoidance conflict and risk assessment. Although TauT−/− mice exhibit visual dysfunction due to retinal degeneration [11] and hearing loss [13], the elevated plus maze test is based on mouse exploratory patterns that avoid open spaces and are motivated by thigmotaxis; the tendency to be close to vertical surfaces is far more reliant on tactile inputs compared with vision [33]. Therefore, we consider that visual dysfunction and hearing loss have little effect on our behavioral tests. Taurine is present at high concentrations in the brain [11], whereby it acts as a partial agonist of GABAA [34] and glycine receptors [35]. Although the physiological roles of taurine in the brain are still not fully understood, taurine is required for normal nervous system development [22]. In the developing brain, the taurine concentration is 3–4 times higher than present in the adult brain [18]. After the first postnatal week, taurine concentrations are downregulated [18]. Kittens from taurine-deficient mothers exhibit smaller brain weights and abnormal morphologies in the visual cortex [36] and cerebellum [37]. Ambient taurine in the mouse developing fetal cerebral cortex tonically activates GABAA receptors and slows radial migration [23]. In addition, taurine increases the proliferation of neural stem cells [24,38]. Taurine modulates the switch of GABA responses from depolarizing to hyperpolarizing by suppressing KCC2 in the embryonic brain via WNK kinase signaling [25]. In the adult brain, taurine also activates extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus [39]. TauT−/− mice show impaired GABAergic inhibition in the striatum [40]. Therefore, taurine deficiency in the brain may cause structural deficits or an imbalance in inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission in neuronal circuits controlling anxiety behavior, thereby causing abnormal behavior in TauT−/− mice.
TauT−/− mice did not show startle responses to startle stimuli. Taurine is present at high concentrations in the organ of Corti [41] and inferior colliculus [42]. Since taurine concentrations are relatively high in glia [43], TauT knockout in glia cells may exacerbate degeneration of auditory nerve fibers, resulting in hearing loss [13]. Six-month-old TauT−/− mice reportedly show 20-dB higher auditory brainstem response thresholds due to accelerated losses of outer and inner hair cells [13,44]. Taurine reduces neuronal activity via glycine receptors in the rat inferior colliculus [45]. In addition, taurine serves as a neuromodulator to enhance GABAergic and glycinergic transmission in the rat anteroventral cochlear nucleus [46]. Therefore, taurine may regulate neurotransmission of the central auditory system and its deficiency appears to cause difficulty hearing. The auditory brainstem response should be measured to precisely show TauT−/− mice exhibit hearing loss. Further experiment is needed at this point.
TauT−/− mice exhibited reduced body weights during the developmental period, although no difference was observed at birth. TauT−/− mice reportedly show lower body weights and less abdominal fat at 3 months, although both food and water intake were unchanged [12,29]. TauT−/− mice also exhibit lower weights of heart and tibial anterior muscle [12], as well as lower fasting blood glucose levels and tolerance against glucose injection [29]. Skeletal muscle lactate content is higher in TauT−/− mice than in WT mice [15], suggesting that the glycolytic pathway may be accelerated in TauT−/− mice. Acceleration of glycolysis can enhance glucose disposal from blood. In addition, several genes involved in the oxidation of fatty acids are downregulated in TauT−/− mice [15], suggesting that their fatty acid utilization is reduced. Accordingly, glucose disposal may be enhanced in TauT−/− mice as a compensatory mechanism. Therefore, imbalances in energy production and expenditure likely cause a reduction in body weight during development. Plasma insulin levels were lower in TauT−/− mice compared with WT mice due to decreased numbers of beta cells in the pancreas [29]. Insulin promotes the conversion of glucose into fat. Therefore, lower insulin levels may reduce the conversion of glucose into fat, which may cause reductions in fat and body weight in TauT−/− mice during development. In our comprehensive analysis of protein kinases and target proteins, STAT3 phosphorylation was significantly increased in TauT−/− mouse brains. Leptin, a hormone synthesized and released from adipose tissue, plays a central role in the long-term control of body weight, acting mainly in the central nervous system to induce satiety, energy expenditure, and glycolysis through the STAT3 pathway [47,48]. Leptin binding to the long isoform of leptin receptor (LepRb) results in its dimerization, leading to the formation of the LepRb/Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) complex. The activated JAK2 phosphorylates itself and also Tyr985, Tyr1077, and Tyr1138 in LepRb. STAT3 binds to phospho-Tyr1077 in LepRb and are subsequently phosphorylated. Active STAT3 dimers then translocate to the nucleus and activate the transcription of their target genes, which mediate leptin’s anorexigenic effect. Therefore, there is a possibility that enhanced leptin signaling causes body weight and fat reduction in TauT−/− mice during development. Taurine depletion did not affect body weight loss during 60% food restriction. Significant body weight reduction in TauT−/− mice compared to WT mice was still observed during the food restriction and recovery period. TauT−/− mice exhibited a significant reduction in body weight gain compared to WT mice on the first day of ad libitum food after food restriction. Phosphorylated STAT3 activates anorexigenic neurons that express proopiomelanocortin while inhibiting orexigenic neurons that express Agouti-related protein, thereby inhibiting food intake and increasing energy expenditure [47]. Combined with a previous report of TauT−/− mice showing reduced abdominal fat weights [29], the present results show that extremely high levels of STAT3 phosphorylation may activate leptin’s anorexigenic effect, thereby reducing food intake in TauT−/− mice even on the first day of ad libitum food after food restriction and disturb body weight recovery. The difference in body weights between WT and TauT−/− mice was greater in male mice compared with female mice. The mechanism of these sex differences is unclear, but a previous paper showed that taurine supplementation increased the level of testosterone in male rats [49], that increased skeletal muscle. Therefore, there is a possibility that taurine depletion may reduce testosterone levels, which leads to a reduction of muscle mass, and results in body weight loss, especially in male mice. Further studies are needed to show the sex differences in weight regulation by taurine.
Taurine contents in skeletal muscle are high [11,12]. TauT−/− mice reportedly show reduced swimming endurance times [12], as well as decreased maximum running speed and endurance duration in treadmill running tests [26,27], suggesting they exhibit exercise intolerance. Notably, taurine supplementation prolonged the time to exhaustion during treadmill running [50]. TauT−/− mice show decreased myofiber size and myofiber disruption [12]. We previously performed LC-MS-based metabolome analysis and suggested that organic osmolytes such as betaine, glycerophosphocholine, and amino acids were increased in the heart muscle of TauT−/− mice by compensating mechanisms for taurine depletion [51], although the expression of related gene expressions, such as betaine/GABA transporter-1 (BGT-1; Slc6a12), carnitine transporter Slc22a4 and Slc22a5 are not changed [52]. The mRNA expressions of heat shock protein 700 (Hsp70), the amino acid transporters (Slc38a2; ATA2), DnaJ (Hsp40) homolog, subfamily B, member 1 (Dnajb1), tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 12a (Tnfrsf12a), and S100 calcium-binding proteins (S100A4, S100A9), which are upregulated by osmotic stress, are elevated in both heart and skeletal muscle of the TauT−/− mice [15], suggesting that dysfunction of osmoregulatory system impairs the tibial anterior muscle volume regulation. Taurine depletion reduced muscular endurance in this study, supporting previous findings of an important role for taurine in the maintenance of skeletal muscle function. Furthermore, STAT3 signaling plays important roles in regulating skeletal muscle mass, repair, and diseases [53]. Chronic activation of the interleukin 6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in muscle wasting. Activated STAT3 promotes skeletal muscle atrophy in muscle diseases, such as muscular dystrophy, cancer, and sepsis [54,55]. Therefore, very high levels of STAT3 phosphorylation may cause skeletal muscle abnormalities, thereby decreasing muscle endurance in TauT−/− mice.
The limitation of this study is that we used whole-body TauT knockout mice. Since taurine is ubiquitous and is abundant free amino acid in the heart, retina, skeletal muscle, brain, and leukocytes [1,2], whole body TauT knockout causes various effects. Therefore, to demonstrate the functional role of taurine in specific tissue precisely, we need to generate tissue-specific TauT knockout mice. If we knockout TauT in a specific region of the brain, we can demonstrate the role of taurine in the behavior, excluding the effects of vision dysfunction and hearing loss. If we generate the time-specific TauT knockout mice, we can demonstrate the role of taurine at specific time points during development and in the adult mice. Further studies are needed to determine the precise role of taurine using cell/tissue- and time-specific TauT knockout mice. We have shown the effects of taurine depletion on anxiety-like behavior, startle response, muscular endurance, and body weight during development. However, the detailed mechanism by which taurine depletion causes such effects remains unclear. We have shown that TauT−/− mice did not show startle responses. This result suggests that TauT−/− mice might have hearing difficulty. However, we need to perform the auditory brainstem response test to confirm hearing difficulty in TauT−/− mice and to locate hearing deficits along the auditory nerve pathway. Because TauT−/− mice showed degeneration in the inner ear and auditory nerve, it is speculated that taurine has a role in the regulating survival of cells related to auditory function. Since taurine also acts as a partial agonist of GABAA and glycine receptors, taurine might have a role in modulating the neurotransmission in the auditory nerve tract. Further studies are needed to show the underlying mechanisms of our results.
In conclusion, the present study suggests that taurine plays important roles in the maintenance of mouse behavior, hearing, body weight, and skeletal muscle function.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
TauT-KO and littermate mice (C57BL/6 background) were used. The generation of TauT KO-mice was previously described [12]. Heterozygous TauT-KO male and female mice were mated, and homozygous TauT-KO (TauT−/−, male n = 51, female n = 17), heterozygous TauT-KO (TauT+/−, male n = 62, female n = 39), and wild-type (WT, male n = 60, female n = 24) mice were used for experiments. Genotyping for TauT-KO mice was carried out by PCR of mouse tail DNA using the following primers: 5′-GGTGTCACTAAGACGTGAGTTG-3′, 5′-CAGACAGCACAAAGTCGATCT-3′, and 5′-TGCTAAAGCGCATGCTCCAGACTG-3′. Mice were kept in a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on at 07:00 a.m.) with access to food and water ad libitum unless otherwise noted. All experimental procedures were approved by the institutional animal care and use committee of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine. With regard to the ethical use of animals for experimentation, all efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering.
4.2. Measurements of Body Weight and Food Restriction
Body weights of male and female mice aged P0–P60 were measured once every 2 days between 16:00 and 19:00 h. For the food-restriction experiment, daily food consumption of WT mice was measured for 10 days and average food consumption per gram of body weight was calculated. After 7 days of individual housing for acclimation, mice were given a food pellet equal to 60% of their average daily food intake. Body weights were measured between 16:00 and 19:00 h for 14 days during 60% food restriction. After food restriction, mice were allowed free access to food, and body weights were measured for an additional 14 days to observe recovery.
4.3. Behavioral Analysis
For the open field test, the size of the open field box was 42 × 42 × 40 cm. Mice were placed in the center of the chamber at the beginning of each test. The movement of each mouse was tracked for 10 min. Locomotor activity was recorded and analyzed using a video tracking system (SMART 3.0; Panlab, Cornellà de Llobregat, Spain). For the elevated plus maze test, we used an elevated plus maze apparatus comprising a central part (6 × 6 cm), two opposing open arms (40 × 6 cm), and two opposing closed arms (40 × 6 × 15 cm). The apparatus was raised 40 cm above the floor. Mice were placed in the center of the apparatus facing the closed arm and allowed to explore the maze for 5 min freely. Time spent and distance traveled in the center, open arms, and closed arms were measured using a video tracking system. For the acoustic startle response test, a startle box system (Panlab, Cornellà de Llobregat, Spain) containing a sound generator and accelerometer was used to record the amplitude of each mouse’s startle response. Mice were placed into a plexiglass cylinder and set on a weight-transducing platform in the sound-attenuating chamber. A white background noise (70 dB) was generated throughout the experiment. The acoustic startle response test began with 5 min of acclimatization. Mice were randomly exposed to startle stimuli (from 60 to 120 dB, 10-dB increments, 40-ms duration) with a variable (10–20 s) inter-stimulus interval to avoid habituation. Each sound intensity was presented six times. The peak amplitude of the startle response was measured.
4.4. Kinexus Protein Microarray
Brains from WT and TauT−/− mice were cut into small pieces and rinsed in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline to remove the blood and other contamination on the surface. Next, brains were wrapped in tinfoil and snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen. Subsequently, brains were shipped in dry ice to Kinexus Bioinformatics Corporation (Vancouver, BC, Canada) for Kinexus KAM-880 Antibody Microarray, which includes 518 pan-specific (for expression levels of these phosphoproteins) and 359 phosphorylation-site-specific antibodies (for phosphorylation). Briefly, 50 g of cell lysate from each sample was covalently labeled with a fluorescent dye. Free dye molecules were then removed at the completion of labeling reactions by gel filtration. After blocking non-specific binding sites, an incubation chamber was mounted onto the microarray to permit the loading of WT and TauT−/− samples side by side on the same chip and to prevent mixing of the samples. Following sample incubation, unbound proteins were washed away. Each array produced a pair of 16-bit images, which were captured with a Perkin-Elmer ScanArray Reader laser array scanner (Waltham, MA, USA). Signal quantification was performed with ImaGene 8.0 from BioDiscovery (El Segundo, CA, USA), using the predetermined settings for spot segmentation and background correction. The resultant changes in spot intensity are expressed as the percentages of change for TauT−/− mice compared with WT mice [% change from control (% CFC) = [(globally normalized signal intensity of TauT−/− sample /globally normalized signal intensity of WT sample) × 100] − 100]. Changes of 50% CFC were considered significant changes. Globally normalized signal intensity is the background-corrected intensity value.
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Comparisons between the two groups were made using the Mann–Whitney test. Multiple comparisons were made using Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism (version 9.2.0; GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/metabo12070631/s1, Table S1: Effects of taurine depletion on protein expression and phosphorylation by protein microarray analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.W. and A.F.; methodology, M.W., T.I., and A.F.; validation, M.W. and A.F.; investigation, M.W.; data curation, M.W.; writing–original draft preparation, M.W. and A.F.; writing—review and editing, M.W. and A.F.; visualization, M.W. and A.F.; supervision, A.F.; project administration, A.F.; funding acquisition, A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) (#21H02661 to A.F.), Grants-in-Aid for Transformative Research Area “Inducing lifelong plasticity (iPlasticity) by brain rejuvenation: elucidation and manipulation of critical period mechanisms” (#21H05687 to A.F.), Smoking Research Foundation (to A.F.), The Salt Science Research Foundation (to A.F.), Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (#20K06924 to M.W.), and The Japan Epilepsy Research Foundation (to M.W.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hamamatsu University School of Medicine (protocol code 2-53 and 2021.4.27).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Edanz (https://jp.edanz.com/ac) for editing a draft of this manuscript (accessed on 21 April 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chesney, R.W. Taurine: Its biological role and clinical implications. Adv. Pediatr. 1985, 32, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chapman, R.A.; Suleiman, M.S.; Earm, Y.E. Taurine and the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 1993, 27, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxtable, R.J. Actions of taurine. Physiol. Rev. 1992, 72, 101–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Wada, T.; Saigo, K.; Watanabe, K. Taurine as a constituent of mitochondrial tRNAs: New insights into the functions of taurine and human mitochondrial diseases. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6581–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.Q.; Jin, H.; Nguyen, M.; Carr, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Faiman, M.D.; Schloss, J.V.; Wu, J.Y. Role of taurine in regulation of intracellular calcium level and neuroprotective function in cultured neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 66, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís, J.M.; Herranz, A.S.; Herreras, O.; Lerma, J.; del Río, R.M. Does taurine act as an osmoregulatory substance in the rat brain? Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 91, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.S.; Chang, K.J. Taurine protects the liver against lipid peroxidation and membrane disintegration during rat hepatocarcinogenesis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1998, 442, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Martincigh, B.S.; Mundoma, C.; Simoyi, R.H. Antioxidant chemistry: Hypotaurine−taurine oxidation by chlorite. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 9838–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, T.; Kushiro, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Shinohara, K.; Cha, S. mRNA expression of enzymes involved in taurine biosynthesis in rat adipose tissues. Metabolism 2002, 51, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Kwon, H.M.; Yamauchi, A.; Preston, A.S.; Marumo, F.; Handler, J.S. Molecular cloning of the cDNA for an MDCK cell Na+- and Cl−-dependent taurine transporter that is regulated by hypertonicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8230–8234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heller-Stilb, B.; van Roeyen, C.; Rascher, K.; Hartwig, H.G.; Huth, A.; Seeliger, M.W.; Warskulat, U.; Häussinger, D. Disruption of the taurine transporter gene (taut) leads to retinal degeneration in mice. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Kimura, Y.; Uozumi, Y.; Takai, M.; Muraoka, S.; Matsuda, T.; Ueki, K.; Yoshiyama, M.; Ikawa, M.; Okabe, M.; et al. Taurine depletion caused by knocking out the taurine transporter gene leads to cardiomyopathy with cardiac atrophy. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2008, 44, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warskulat, U.; Heller-Stilb, B.; Oermann, E.; Zilles, K.; Haas, H.; Lang, F.; Häussinger, D. Phenotype of the taurine transporter knockout Mouse. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 428, 439–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Oishi, S.; Takai, M.; Kimura, Y.; Uozumi, Y.; Fujio, Y.; Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J. Cardiac and skeletal muscle abnormality in taurine transporter-knockout mice. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Inui, T.; Miyazaki, N.; Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J. Tissue depletion of taurine accelerates skeletal muscle senescence and leads to early death in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Hanahata, Y.; Kine, K.; Murakami, S.; Schaffer, S.W. Tissue taurine depletion induces profibrotic pattern of gene expression and causes aging-related cardiac fibrosis in heart in mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, H.C.; Davis, J.M.; Himwich, W.A. Developmental changes in mouse brain: Weight, water content and free amino acids. J. Neurochem. 1968, 15, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez-Diaz, P.; Miranda-Contreras, L.; Mendoza-Briceño, R.V.; Peña-Contreras, Z.; Palacios-Prü, E. Prenatal and postnatal contents of amino acid neurotransmitters in mouse parietal cortex. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 25, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergeeva, O.A.; Chepkova, A.N.; Doreulee, N.; Eriksson, K.S.; Poelchen, W.; Mönnighoff, I.; Heller-Stilb, B.; Warskulat, U.; Häussinger, D.; Haas, H.L. Taurine-induced long-lasting enhancement of synaptic transmission in mice: Role of transporters. J. Physiol. 2003, 550, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuringer, M.; Sturman, J. Visual acuity loss in rhesus monkey infants fed a taurine-free human infant formula. J. Neurosci. Res. 1987, 18, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuringer, M.; Imaki, H.; Sturman, J.; Moretz, R.; Wisniewski, H. Abnormal visual acuity and retinal morphology in rhesus monkeys fed a taurine-free diet during the first three postnatal months. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1987, 217, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kilb, W.; Fukuda, A. Taurine as an essential neuromodulator during perinatal cortical development. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, T.; Yamada, J.; Akita, T.; Matsushima, Y.; Yanagawa, Y.; Fukuda, A. Roles of taurine-mediated tonic GABAA receptor activation in the radial migration of neurons in the fetal mouse cerebral cortex. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tochitani, S.; Furukawa, T.; Bando, R.; Kondo, S.; Ito, T.; Matsushima, Y.; Kojima, T.; Matsuzaki, H.; Fukuda, A. GABAA receptors and maternally derived raurine regulate the temporal specification of progenitors of excitatory glutamatergic neurons in the mouse developing Cortex. Cereb. Cortex 2021, 31, 4554–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Furukawa, T.; Kumada, T.; Yamada, J.; Wang, T.; Inoue, R.; Fukuda, A. Taurine inhibits K+-Cl− cotransporter KCC2 to regulate embryonic Cl− homeostasis via with-no-lysine (WNK) protein kinase signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20839–20850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Warskulat, U.; Flögel, U.; Jacoby, C.; Hartwig, H.G.; Thewissen, M.; Merx, M.W.; Molojavyi, A.; Heller-Stilb, B.; Schrader, J.; Häussinger, D. Taurine transporter knockout depletes muscle taurine levels and results in severe skeletal muscle impairment but leaves cardiac function uncompromised. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Schaffer, S.W.; Azuma, J. Tissue taurine depletion alters metabolic response to exercise and reduces running capacity in mice. J. Amino Acids 2014, 2014, 964680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yamaji, N.; Murakami, S.; Schaffer, S.W. Induction of growth differentiation factor 15 in skeletal muscle of old taurine transporter knockout mouse. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, T.; Yoshikawa, N.; Ito, H.; Schaffer, S.W. Impact of taurine depletion on glucose control and insulin secretion in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 129, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murakami, S. The physiological and pathophysiological roles of taurine in adipose tissue in relation to obesity. Life Sci. 2017, 186, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Li, B.Y.; Peng, W.Q.; Guo, L.; Tang, Q.Q. Taurine-mediated browning of white adipose tissue is involved in its anti-obesity effect in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15014–15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.; Choi, M. Relation of taurine intake during pregnancy and newborns’ growth. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1155, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Filgueiras, G.B.; Carvalho-Netto, E.F.; Estanislau, C. Aversion in the elevated plus-maze: Role of visual and tactile cues. Behav. Process. 2014, 107, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Schousboe, A. Taurine interaction with neurotransmitter receptors in the CNS: An update. Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, A.C.; Liu, X.; Kriegstein, A.R. Nonsynaptic glycine receptor activation during early neocortical development. Neuron 1998, 20, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palackal, T.; Moretz, R.; Wisniewski, H.; Sturman, J.A. Abnormal visual cortex development in the kitten associated with maternal dietary taurine deprivation. J. Neurosci. Res. 1986, 15, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturman, J.A.; Moretz, R.C.; French, J.H.; Wisniewski, H.M. Taurine deficiency in the developing cat: Persistence of the cerebellar external granule cell layer. J. Neurosci. Res. 1985, 13, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivaraj, M.C.; Marcy, G.; Low, G.; Ryu, J.R.; Zhao, X.; Rosales, F.J.; Goh, E.L.K. Taurine induces proliferation of neural stem cells and synapse development in the developing mouse brain. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, F.; Yue, M.; Chandra, D.; Keramidas, A.; Goldstein, P.A.; Homanics, G.E.; Harrison, N.L. Taurine is a potent activator of extrasynaptic GABAA receptors in the thalamus. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sergeeva, O.A.; Fleischer, W.; Chepkova, A.N.; Warskulat, U.; Häussinger, D.; Siebler, M.; Haas, H.L. GABAA-receptor modification in taurine transporter knockout mice causes striatal disinhibition. J. Physiol. 2007, 585, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, N.J.; Davies, W.E. Cellular localisation of taurine in the organ of Corti. Hear. Res. 1993, 65, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palkovits, M.; Elekes, I.; Láng, T.; Patthy, A. Taurine levels in discrete brain nuclei of rats. J. Neurochem. 1986, 47, 1333–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.C.; Godfrey, D.A. Cochlear damage affects neurotransmitter chemistry in the central auditory system. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, H.; Ding, D.; Müller, M.; Pfister, M.; Warskulat, U.; Häussinger, D.; Salvi, R. Central auditory nerve degeneration in knockout mice lacking the taurine transporter. In Proceedings of the 28th Annual Meeting of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 February 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Tang, Z.Q.; Xu, T.L.; Chen, L. Taurine acts as a glycine receptor agonist in slices of rat inferior colliculus. Hear. Res. 2006, 220, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.Y.; Shi, H.B.; Li, C.Y.; Yin, S.K. Interaction between taurine and GABAA/glycine receptors in neurons of the rat anteroventral cochlear nucleus. Brain Res. 2012, 1472, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Du, T.; Li, C.; Yang, G. STAT3 phosphorylation in central leptin resistance. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douros, J.D.; Baltzegar, D.A.; Reading, B.J.; Seale, A.P.; Lerner, D.T.; Gordon Grau, E.; Borski, R.J. Leptin stimulates cellular glycolysis through a STAT3 dependent mechanism in Tilapia. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Wu, G.; Feng, Y.; Lv, Q.; Lin, S.; Hu, J. Effects of taurine on male reproduction in rats of different ages. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawson, R., Jr.; Biasetti, M.; Messina, S.; Dominy, J. The cytoprotective role of taurine in exercise-induced muscle injury. Amino Acids 2002, 22, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Okazaki, K.; Nakajima, D.; Shibata, D.; Murakami, S.; Schaffer, S. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics to identify taurine-modified metabolites in heart. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Murakami, S.; Schaffer, S. Pathway analysis of a transcriptome and metabolite profile to elucidate a compensatory mechanism for taurine deficiency in the heart of taurine transporter knockout mice. J 2018, 1, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guadagnin, E.; Mázala, D.; Chen, Y.W. STAT3 in skeletal muscle function and disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wada, E.; Tanihata, J.; Iwamura, A.; Takeda, S.; Hayashi, Y.K.; Matsuda, R. Treatment with the anti-IL-6 receptor antibody attenuates muscular dystrophy via promoting skeletal muscle regeneration in dystrophin-/utrophin-deficient mice. Skelet. Muscle 2017, 7, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nunes, A.M.; Wuebbles, R.D.; Sarathy, A.; Fontelonga, T.M.; Deries, M.; Burkin, D.J.; Thorsteinsdóttir, S. Impaired fetal muscle development and JAK-STAT activation mark disease onset and progression in a mouse model for merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2018–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).