Lipidomics Revealed Aberrant Metabolism of Lipids Including FAHFAs in Renal Tissue in the Progression of Lupus Nephritis in a Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
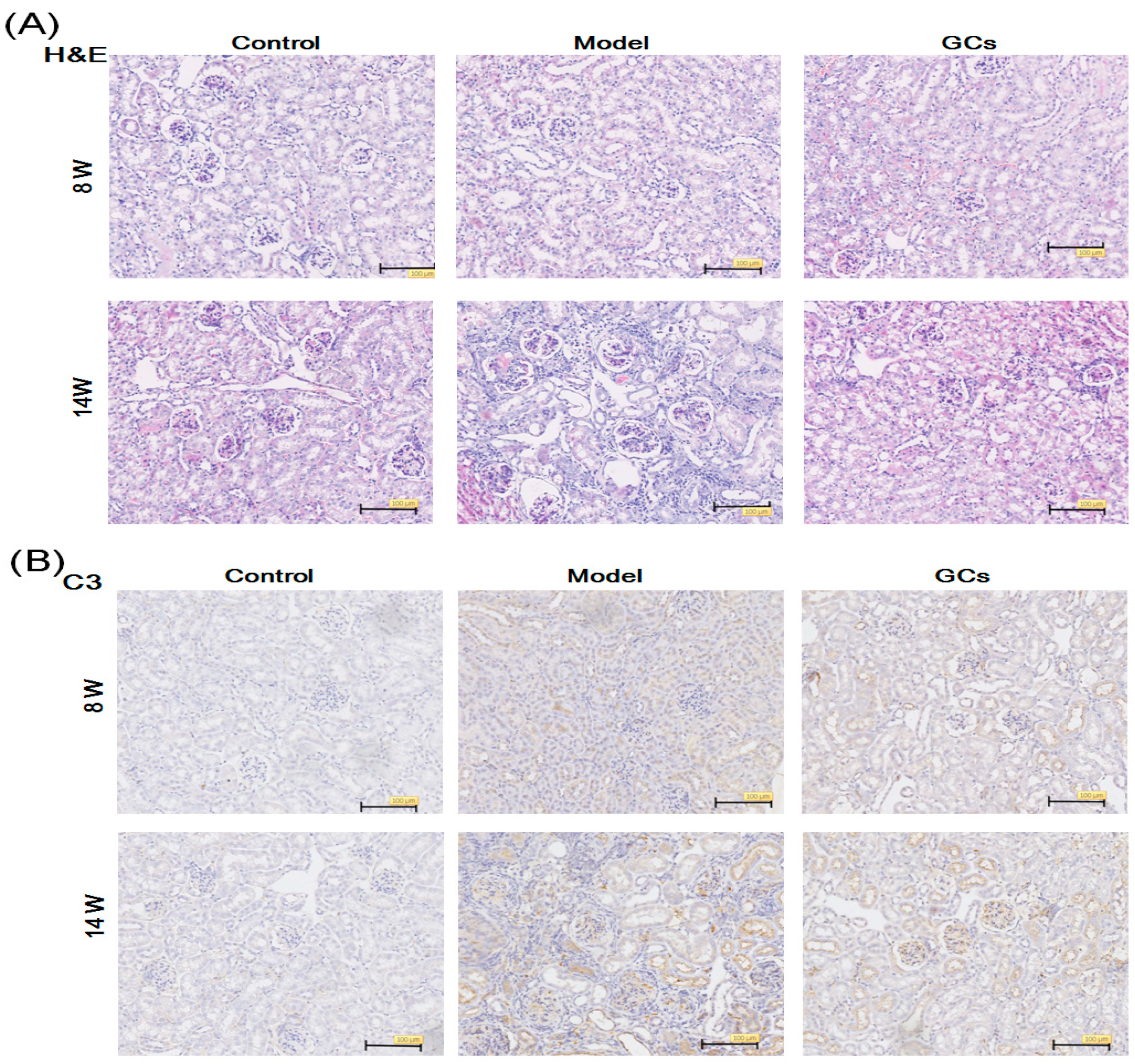
2.1. The Renal Histopathological Changes of MRL/lpr Mice
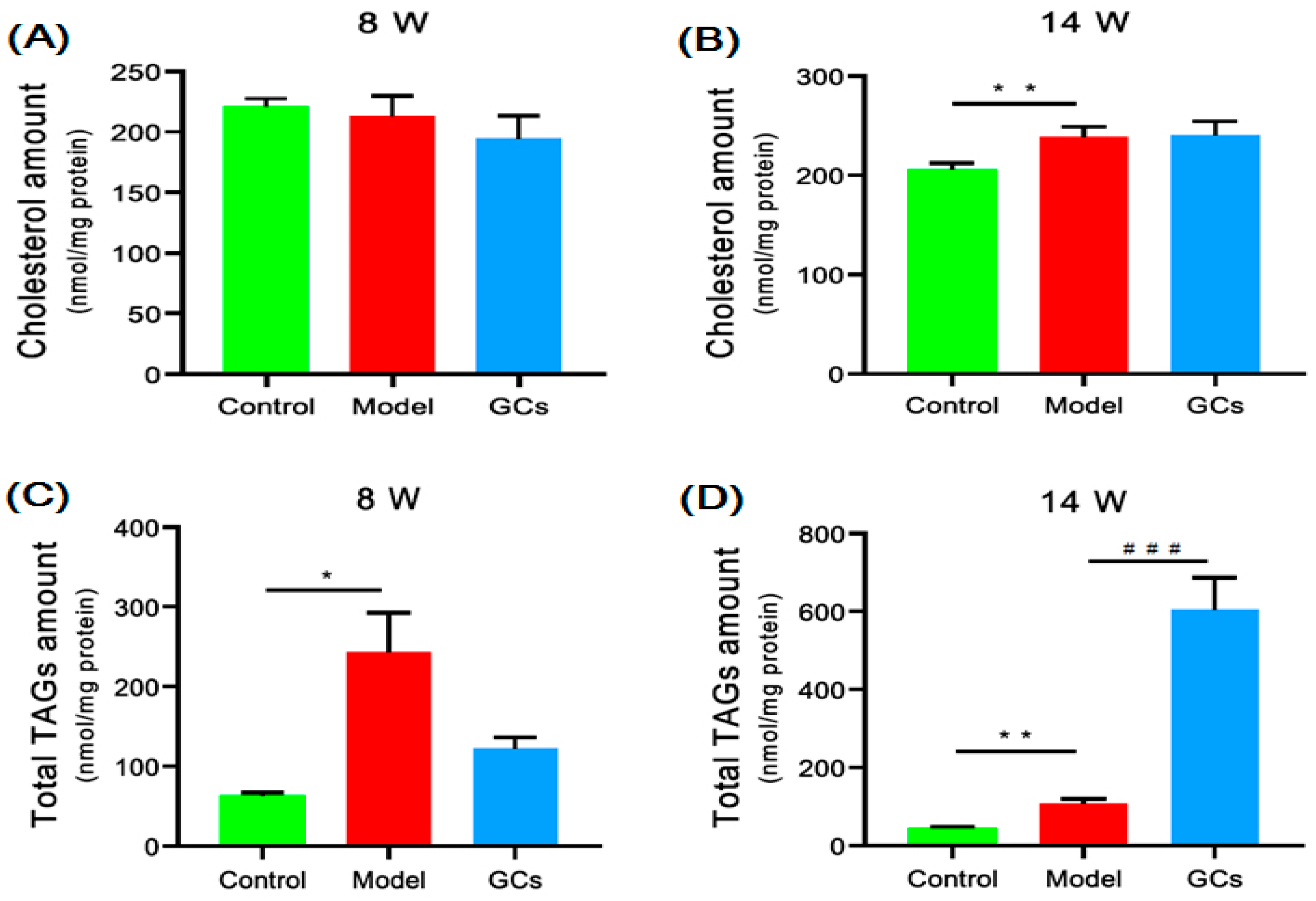
2.2. Cholesterol and TAGs Accumulated in Renal Tissues of MRL/lpr Mice
2.3. Lipidomics Analysis Revealed Significant Increases in Lysophospholipid Species and Elevated Lipid Peroxidation in Kidneys from MRL/lpr Mice
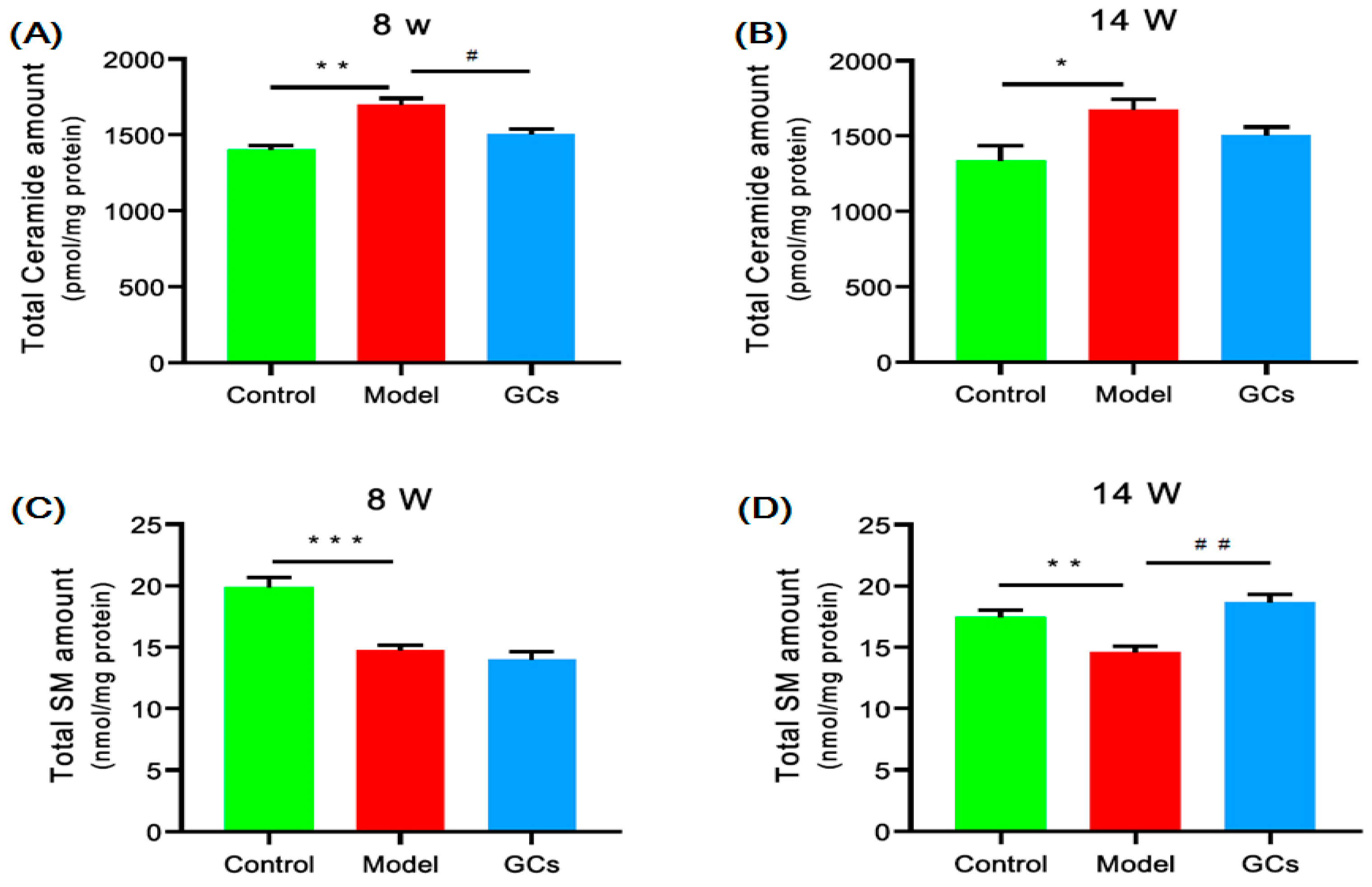
2.4. Lipidomics Analysis Revealed Significant Aberrant Metabolism of Sphingolipids in Renal Tissues from MRL/lpr Mice
2.5. Lipidomics Analysis Showed Marked Elevation of FAHFAs Contents in Renal Tissues from MRL/lpr Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animal Experiments
4.3. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Detection of Cytokines
4.5. Preparation of Lipid Extracts from Kidney Samples
4.6. Lipid Analysis, and Data Processing and Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FAHFAs | fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids |
| GCs | glucocorticoids |
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxyalkenals |
| ICs | immune complexes |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| LN | lupus nephritis |
| lysoPC | choline lysoglycerophospholipid |
| lysoPE | ethanolamine lysoglycerophospholipid |
| MDMS-SL | multidimensional mass spectrometry-based shotgun lipidomics |
| PE | ethanolamine glycerophospholipid |
| PC | choline glycerophospholipid |
| SM | sphingomyelin |
| TAG | triacylglycerol |
References
- Lisnevskaia, L.; Murphy, G.; Isenberg, D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet 2014, 384, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, C.; Putterman, C. Genetics and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichlin, M.; Fesmire, J.; Quintero-Del-Rio, A.I.; Wolfson-Reichlin, M. Autoantibodies to lipoprotein lipase and dyslipidemia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis. Rheum. 2002, 46, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borba, E.F.; Bonfa, E.; Vinagre, C.G.C.; Ramires, J.A.F.; Maranhao, R.C. Chylomicron metabolism is markedly altered in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis. Rheum. 2000, 43, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegard, J.; Svenungsson, E.; Wu, R.; Gunnarsson, I.; Lundberg, I.E.; Klareskog, L.; Horkko, S.; Witztum, J.L. Lipid peroxidation is enhanced in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and is associated with arterial and renal disease manifestations. Arthritis. Rheum. 2005, 52, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Grossman, J.; FitzGerald, J.; Dahlin-Lee, E.; Wallace, D.J.; Thong, B.Y.; Badsha, H.; Kalunian, K.; Charles, C.; Navab, M.; et al. Proinflammatory high-density lipoprotein as a biomarker for atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthriris. Rheum. 2006, 54, 2541–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Fang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Wen, C. Oxidative stress leads to reduction of plasmalogen serving as a novel biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2016, 101, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Hu, C.; Zhao, Y.; He, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, C.; Han, X.; et al. Shotgun lipidomics revealed altered profiles of serum lipids in systemic lupus erythematosus closely associated with disease activity. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, X.Z.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F. An update on the lipid nephrotoxicity hypothesis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2009, 5, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X. Lipidomics for studying metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhang, J.; Hong, S.; Li, H.; Lu, L.; Xie, G.; Luo, W.; Du, Y.; Xie, Z.; Han, X.; et al. Oxidative stress-induced aberrant lipid metabolism is an important causal factor for dysfunction of immunocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2021, 163, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckett, A.J.; Wright, D.C.; Riddell, M.C. The effects of glucocorticoids on adipose tissue lipid metabolism. Metabolism 2011, 60, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toller-Kawahisa, J.E.; Canicoba, N.C.; Venancio, V.P.; Kawahisa, R.; Antunes, L.M.; Cunha, T.M.; Marzocchi-Machado, C.M. Systemic lupus erythematosus onset in lupus-prone B6.MRL/lpr mice is influenced by weight gain and is preceded by an increase in neutrophil oxidative burst activity. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 86, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Erythropoietin Treatment Ameliorates Lupus Nephritis of MRL/lpr Mice. Inflammation 2018, 41, 1888–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Chalhoub, N.E.; Sherwin, C.M.; Li, C.; Brunner, H.I. Glucocorticoids pharmacology and their application in the treatment of childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin. Arthritis. Rheum. 2019, 49, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhya, Z.; Borozdenkova, S.; Karim, M.Y. The role of cytokines as biomarkers in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, X.; Chinenov, Y.; Redecha, P.; Madaio, M.; Roelofs, J.J.; Farber, G.; Issuree, P.D.; Donlin, L.; McLlwain, D.R.; Mak, T.W.; et al. iRhom2 promotes lupus nephritis through TNF-alpha and EGFR signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1397–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyebi, L.; Soltani, Z.; Reisin, E. Lipid nephrotoxicity: New concept for an old disease. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2012, 14, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Han, X. Shotgun lipidomics in substantiating lipid peroxidation in redox biology: Methods and applications. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigdon, H.; Kogot-Levin, A.; Park, J.W.; Goldschmidt, R.; Kelly, S.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Scherz, A.; Pewzner-Jung, Y.; Saada, A.; Futerman, A.H. Ablation of ceramide synthase 2 causes chronic oxidative stress due to disruption of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 4947–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yore, M.M.; Syed, I.; Moraes-Vieira, P.M.; Zhang, T.; Herman, M.A.; Homan, E.A.; Patel, R.T.; Lee, J.; Chen, S.; Peroni, O.D.; et al. Discovery of a class of endogenous mammalian lipids with anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. Cell 2014, 159, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, A. What is damaging the kidney in lupus nephritis? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, T.M.; Mizelle, H.L.; Cockrell, K.; Buhner, P. Renal sinus lipomatosis and body composition in hypertensive, obese rabbits. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1995, 19, 869–874. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrara, D.; Montecucco, F.; Dallegri, F.; Carbone, F. Impact of different ectopic fat depots on cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21630–21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, E.U.; Ruan, X.Z.; Chana, R.S.; Brunskill, N.J.; Gaya, J.; Powis, S.H.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; Wheeler, D.C. Mesangial matrix-activated monocytes express functional scavenger receptors and accumulate intracellular lipid. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Yuan, X.; Gao, H.; Ding, G.; Wang, H. Autophagy activation contributes to lipid accumulation in tubular epithelial cells during kidney fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubicek, T.; Bartlova, M.; Krajickova, J.; Haluzikova, D.; Mraz, M.; Lacinova, Z.; Kudla, M.; Teplan, V.; Haluzik, M. Increased production of proinflammatory cytokines in adipose tissue of patients with end-stage renal disease. Nutrition 2009, 25, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Mei, M.; Yang, S.; Li, Q. Roles of chronic low-grade inflammation in the development of ectopic fat deposition. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 418185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K. 4-Hydroxy-2-nonenal: A product and mediator of oxidative stress. Prog. Lipid Res. 2003, 42, 318–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, K.E.; Andersson, L.; Nilsson, J.; Bjorkbacka, H. Nanomolar concentrations of lysophosphatidylcholine recruit monocytes and induce pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 370, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugesan, G.; Sandhya Rani, M.R.; Gerber, C.E.; Mukhopadhyay, C.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Chisolm, G.M.; Kottke-Marchant, K. Lysophosphatidylcholine regulates human microvascular endothelial cell expression of chemokines. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2003, 35, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balas, L.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Viars, F.; Faugere, J.; Lefort, C.; Caspar-Bauguil, S.; Langin, D.; Durand, T. Regiocontrolled syntheses of FAHFAs and LC-MS/MS differentiation of regioisomers. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 9012–9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Wen, C. Lipidomics revealed idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-induced hepatic lipid disorders corrected with treatment of baicalin in a murine model. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X. Lipid alterations in the earliest clinically recognizable stage of Alzheimer’s disease: Implication of the role of lipids in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2005, 2, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Yang, K.; Cheng, H.; Fikes, K.N.; Gross, R.W. Shotgun lipidomics of phosphoethanolamine-containing lipids in biological samples after one-step in situ derivatization. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Wang, M.; Duan, Q.; Han, X. Sensitive analysis of fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids in biological lipid extracts by shotgun lipidomics after one-step derivatization. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1105, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Cheng, H.; Gross, R.W.; Han, X. Automated lipid identification and quantification by multidimensional mass spectrometry-based shotgun lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 4356–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Luo, W.; Xu, J.; Han, X. Recognition and avoidance of ion source-generated artifacts in lipidomics analysis. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Gross, R.W. Shotgun lipidomics: Electrospray ionization mass spectrometric analysis and quantitation of cellular lipidomes directly from crude extracts of biological samples. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2005, 24, 367–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, C.; Du, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, H.; Duan, Q.; Xie, Z.; Wen, C.; Han, X. Lipidomics Revealed Aberrant Metabolism of Lipids Including FAHFAs in Renal Tissue in the Progression of Lupus Nephritis in a Murine Model. Metabolites 2021, 11, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030142
Hu C, Du Y, Xu X, Li H, Duan Q, Xie Z, Wen C, Han X. Lipidomics Revealed Aberrant Metabolism of Lipids Including FAHFAs in Renal Tissue in the Progression of Lupus Nephritis in a Murine Model. Metabolites. 2021; 11(3):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030142
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Changfeng, Yu Du, Xiaofen Xu, Haichang Li, Qiao Duan, Zhijun Xie, Chengping Wen, and Xianlin Han. 2021. "Lipidomics Revealed Aberrant Metabolism of Lipids Including FAHFAs in Renal Tissue in the Progression of Lupus Nephritis in a Murine Model" Metabolites 11, no. 3: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030142
APA StyleHu, C., Du, Y., Xu, X., Li, H., Duan, Q., Xie, Z., Wen, C., & Han, X. (2021). Lipidomics Revealed Aberrant Metabolism of Lipids Including FAHFAs in Renal Tissue in the Progression of Lupus Nephritis in a Murine Model. Metabolites, 11(3), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030142





