Abstract
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a coronavirus that causes the pandemic Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). There is no current specific treatment for this new coronavirus. In this study, we employed a virtual screening repurposing strategy to search for potential SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors. The databases PDB, ChEMBL, BindingDB and DrugBank were queried with several filtering steps based on ligand-based and structure-based approaches. As a result, we obtained 58 molecules (37 from ChEMBL and 21 from DrugBank) that potentially inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. These molecules have on their chemical structure functional groups that favor stronger docking scores than the inhibitor N3. Several of these molecules are reported experimentally as SARS-CoV Mpro inhibitors. Hence, a combined virtual screening strategy allowed finding chemical compounds with a high potential for the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.
1. Introduction
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a coronavirus that has caused a pandemic designated Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) [1]. This virus is transmitted byrespiratory secretions between humans by direct contact or respiratory droplets. Most infected individuals suffer a mild disease or are asymptomatic. However, elderly people with comorbidities, such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity, are prone to severe pulmonary disease that can cause death. The numbers of cases with severe disease complications are surpassing the capacity of health services around the world. This makes the disease a worrisome threat for public health services worldwide. Due to its recent origin related to bats [2], there is no specific treatment to combat the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The SARS-CoV-2 genome produces 16 non-structural proteins and four structural proteins: spike (S), nucleocapsid (N), membrane (M) and envelope (E). These structural proteins are involved in virus survival within host cells [3]. Due to their evident importance, these proteins are suitable targets to develop new drugs for a pharmacological treatment. Several studies have used drug repurposing strategies that focus on the mechanism of entry, replication, and other viral targets to rapidly identify potential therapeutics [4]. The study by Kumar and Singh, using a small subset of 75 FDA antiviral drugs, found that the antivirals, lopinavir-ritonavir, tipranavir and raltegravir, could bind to SARS-Cov-2 Mpro with similar binding affinity to the inhibitor N3 [5]. Attempts to identify potential scaffolds were made with a pharmacophore model and Activity Cliff Analysis [6]. Thirty-eight structurally diverse compounds were analyzed using a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) fragment-based approach, which identified triclabendazole, emedastine and omeprazole as potential Mpro inhibitors. Oxytetracycline and other twelve structurally potential inhibitors were also identified with a virtual screening approach using 7 million drug-like compounds from the ZINC15 database [7]. Additionally, 23 drugs from 12 different groups were evaluated using an infected cell-based assay, where hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin were the most promising compounds [8]. Another study found withaferin A and artesunate as promising SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors [9]. Moreover, other compounds have been tested for inhibition using computational models. For example, the interface of S protein in its human receptor ACE2 was used as a target to repurpose 47 compounds, applying an in silico docking protocol [10]. The same approach was applied to the prediction of SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) inhibitors that are also involved in the replication and transcription of the virus [11,12]. Some methodologies are based on a consensus score strategy using two different docking tools [13,14] or molecular dynamics (MD) simulation [15,16]. The use of molecular dynamics is useful for binding the free energy calculations and have been used to identify key interacting residues of Mpro in protein-ligand complex analysis [15].
Although SARS-CoV-2 Mpro has been previously analyzed in silico, pre-print studies already mentioned did not explore the wide chemical space available for testing repurposing computational protocols. Hence, in this study, we expand the drug predictions to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Mpro by mining the PDB, ChEMBL, BindingDB and DrugBank databases through a virtual screening protocol with a combination of ligand-based and structure-based approaches. To this end, different cheminformatics and molecular modeling techniques were applied according to the information retrieved from each database. As a result, we obtained potential drug candidates different from previous reports that could inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro protein.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Data Preparation
The crystallized structure of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro in complex with the inhibitor N3 (PDB ID: 6LU7) was downloaded from the protein data bank (PDB). The DoGSiteScorer tool [17] from the Proteins Plus server was used to identify the residues corresponding to the N3 binding site on 6LU7. This binding site was structurally aligned against 157,521 protein structures obtained from the PDB using the TM-align tool [18]. The alignment score can have any value from 0 to 1, where structures with a score higher than 0.5 assume the same fold. Therefore, proteins with structures scored above 0.5 were searched on ChEMBL and BindingDB to retrieve compounds with known inhibition activity.
On the other hand, 1,940,733 compounds were analyzed from the ChEMBL database. Lipinski’s rule of five was applied to these compounds, to obtain potential orally administered drugs. Additionally, 10,695 approved and experimental drugs retrieved from DrugBank were analyzed.
All compounds were downloaded in SDF format. Then, MACCS key fingerprint was calculated for each compound. MACCS key is a set of 166 binary values that characterize all the molecular properties of a two-dimensional (2D) chemical structure. The fingerprints were used to calculate compound similarity with the inhibitor N3 using the Tanimoto coefficient. Those compounds with Tanimoto below 0.75 were discarded. Later, the remaining compounds were minimized and converted to mol2 using the pybel library in Python. The prepare_ligand4.py script from MGLTools 1.5.6 [19] was used to add Autodock atom types and Gasteiger charges to each compound.
2.2. Molecular Docking
Autodock vina 1.1.2 software [20] was employed to perform the docking calculations. The structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro in complex with the inhibitor N3 (PDB ID: 6LU7) was used as the receptor. The structure was prepared for docking using the Dock Prep tool from UCSF Chimera 1.14.1 [21]. This tool helps remove water molecules, ions, and unwanted ligands from the crystal. Additionally, it helps to repair the missing side, add hydrogens, and charge. Furthermore, the prepare_receptor4.py script from MGLTools 1.5.6 was used to add Autodock atom types and Gasteiger charges to the protein structure. The receptor was treated as rigid. The conformational search space was determined by settling the coordinates to the center of the inhibitor N3. Like other authors, this was covalently bound to Cys145 in the PDB 6LU7 [15,22]. Therefore, before docking, the unbounded N3 structure with a proper valence was downloaded from the PDB ligand record (http://www.rcsb.org/ligand/PRD_002214). Autodock atom types and charges were added with MGLTools. The docking pose of N3 had a vina score of −7.6 Kcal/mol. This value was used as a cut-off in the structure-based virtual screening.
2.3. Interaction Pattern Calculation
The crystallographic structures of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro with 22 non-covalent ligands on the active site were retrieved from Diamond Light Source (www.diamond.ac.uk/). Protein-ligand Interaction Profiler (PLIP) [23] was used to calculate interactions occurring with each ligand.
3. Results and Discussion
To identify potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro four databases (PDB, ChEMBL, BindingDB and DrugBank) were virtually screened.
3.1. Screening of Known CoV Inhibitors
The diagram in Figure 1 shows the sequential step followed in this section. First, to identify protein structures with a similar binding site to the SARS-CoV-2 MPro, a set of 157,521 proteins contained in the PDB were compared by TMalign. Based on the alignment score, there is a clear difference between the number of structures before and after the value of 0.5. Therefore, a total of 128 crystal structures above this value were selected as similar to the Mpro structure. These structures correspond to 22 unique proteins from 10 different viral species. Once these proteins were identified, a search of active compounds against them was performed at the BindingDB and ChEMBL databases. A total of 328 unique active compounds against SARS-CoV (n = 319), MERS-CoV (n = 3) and 3C-like protease from human-CoV-NL63 (n = 6) were found. Therefore, these compounds were docked on the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro binding site as potential inhibitors. Based on the cut-off of −7.6 Kcal/mol (vina score for inhibitor N3), 144 compounds (Table S1) were selected as potential Mpro binders. The majority of the compounds retrieved from the databases were considered potential binders to SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, due to the high similarity among the proteases mentioned above, especially SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, which showed 96% similarity [24]. The potential binders were clustered in six groups using MACCS key fingerprints and the Tanimoto distance. This helped us to analyze diverse structural binders, highlighting those that could have some advantages on their functional groups for the binding.
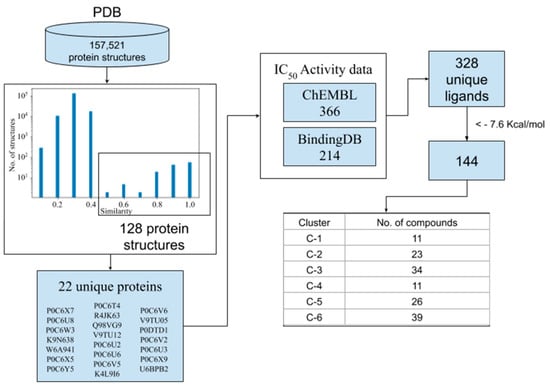
Figure 1.
The selection process of compounds from BindingDB and ChEMBL. Selected compounds were classified into six clusters based on MACCS fingerprint similarity.
The compounds with the highest vina score in each cluster were considered lead drugs. Their structures are shown in Figure 2 along with the IC50 values for SARS-CoV Mpro and the vina score obtained for SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.
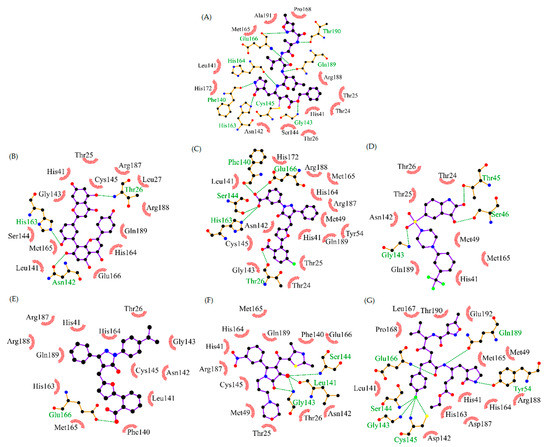
Figure 2.
Potential lead inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro obtained by comparison with others similar proteins. (A) N3 Structure. (B) CHEMBL63354 (D.S.: −10.2 kcal/mol, IC50 = 8.3 μM against 3CL-PRO SARS-CoV). (C) CHEMBL3808795 (D.S.: −9.7 kcal/mol, IC50 = 44.7 μM against 3CL-PRO SARS-CoV). (D) CHEMBL3099535 (D. S: −9.3 kcal/mol, IC50 = 100.0 μM against 3CL-PRO SARS-CoV). (E) 50176857 (D.S.: −8.9 kcal/mol, IC50 = 11.7 μM against 3CL-PRO SARS-CoV). (F) 503435553 (D.S.: −8.2 kcal/mol, IC50 = 101.0 μM against 3CL-PRO SARS-CoV. (G) 11243 (D.S.: −8.0 kcal/mol, IC50 = 100.0 μM against 3CL-PRO SARS-CoV). D.S.: Docking score. Hydrophobic interactions are shown in red and hydrogen bonds in green.
The compound CHEMBL63354 (amentoflavone) is a biflavonoid with a potent inhibitory effect against SARS-CoV Mpro. This compound was the best ranked according to the vina score (−10.2 kcal/mol). As Figure 2 shows, this high affinity could be due to the multiple hydroxyl groups throughout its structure that could bind by H-bonds with the target. Another important structural feature is the presence of several aromatic groups that could lead to π stacking and hydrophobic interactions. In the case of the compounds CHEMBL3808795 and 50176857, the presence of phenyl groups is notable. Both compounds have been shown to be essential for inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV Mpro [12]. These compounds are pyrazolone derivatives. Pyrazolone analogues are present in several pharmaceutically active agents such as anticancer, analgesic, antipyretic, and antiviral [25]. Also, the benzoic acid moiety seems to be an important functional group; it is present in several SARS-CoV Mpro inhibitors [26]. On the other hand, however, CHEMBL3808795, CHEMBL3099535 (a 5-sulfonyl isatin derivative), and 11,243 (a ketomethyl isostere), also have an aromatic-halogen on their structures. According to the interactions predicted by docking, these kinds of chemical groups do not play a particular role in the binding to SARS-CoV Mpro. Furthermore, these compounds have shown a low activity against SARS-CoV [27,28].
3.2. Ligand-Based ChEMBL Database Screening
A ligand-based approach was used to screen 1,940,733 molecules from the ChEMBL database. Figure 3 summarizes this approach. The ChEMBL compounds were compared to inhibitor N3 using MACCS key fingerprints employing the Tanimoto coefficient. Using a cut off = 0.75, a total of 1970 compounds were found to be similar to inhibitor N3. Then, Lipinski’s rule of five was applied to these compounds and 539 compounds displayed this rule. These compounds were analyzed by molecular docking on the active site of SARS-CoV-2 and 174 compounds (Table S2) showed an affinity <−7.6 Kcal/mol, which were clustered as in the previous analysis.
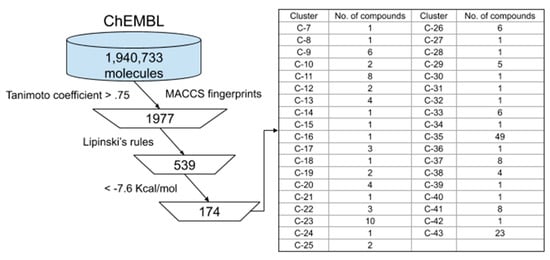
Figure 3.
Virtual screening of compounds from ChEMBL. Selected compounds were classified into 37 clusters based on the MACCS fingerprint similarity.
A total of 37 clusters were obtained from the virtual screening (Table S3), and the compound with the highest negative vina score in each cluster was selected as the lead drug. The top 10 inhibitors from the ChEMBL database are shown in Figure 4.
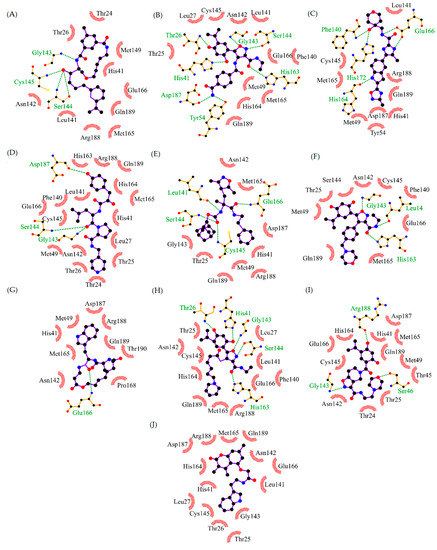
Figure 4.
Top 10 potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro from the ChEMBL database obtained by fingerprints and molecular docking. (A) CHEMBL2047043 (D.S.: −9.6 kcal/mol). (B) CHEMBL1940937 (D.S.: −9.1 kcal/mol). (C) CHEMBL3666013 (D.S.: −8.8 kcal/mol). (D) CHEMBL562054 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol). (E) CHEMBL2047043 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol). (F) CHEMBL3900791 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol). (G) CHEMBL469898 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol). (H) CHEMBL4300783 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol). (I) CHEMBL3233752 (D.S.: −8.3 Kcal/mol). (J) CHEMBL1437444 (D.S.: −8.2 kcal/mol). D.S.: Docking score.
The four leading compounds (CHEMBL1940937, CHEMBL3900791, CHEMBL4300783, and CHEMBL3233752) of this top 10 share a 4-isopropyl-1,3-benzodiol moiety and an isoxazole group. Previous studies against SARS-CoV indicated that compounds with a bulky phenyl group have a potent inhibitory activity [28]. From these four leading compounds, CHEMBL1940937 has the highest vina score, which could be due to the carboxamide group that helps form hydrogen bonds easily. On the other hand, CHEMBL3900791 and CHEMBL3233752 both share a morpholine ring, which is related to several pharmacological activities [29]. The isoxazole group is also present on CHEMBL64623, a CCK-B antagonist. This group could accommodate favorably on the binding site of SARS-CoV Mpro [30]. Additionally, CHEMBL2047043 and CHEMBL469898 have a cyclic structure, but do not have a report of Hsp90 inhibition. CHEMBL2047043 had the highest score; it is a BACE1 inhibitor [31]. This compound is a macrocyclic structure with a hydroxyethylamine component and two benzyl substituents. These aromatic structures have been reported to play an important role in the inhibition of Mpro [28]. The oxygen in the cyclic moiety could bind hydrogen bonds with key residues on the binding site as some carboxylic structures do [6]. CHEMBL469898 is a cyclic depsipeptide [32]. Structures like these have shown an inhibitory activity against proteases; even valinomycin is a potent SARS-CoV inhibitor [33]. The CHEMBL469898 indole group is also present in the compounds CHEMBL3666013 and CHEMBL1437444. The indole group has been reported to be crucial in some compounds to achieve a potent inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV Mpro [26]. The oxadiazole moiety on CHEMBL3666013 seems to improve the docking score compared to isoxazole. In the case of CHEMBL562054, an aeruginosin derivative, the pyridinyl moiety seems to positively influence the docking score. It has been seen that the pyridinyl group improves the inhibitory activity of SARS-CoV Mpro [28].
3.3. Virtual Screening of Approved/Experimental Drugs
Apart from the previous evaluation, 10,695 compounds from the DrugBank database were screened as described in Figure 5. First, Lipinski’s rule was applied, and 5498 compounds were obtained. These compounds were analyzed on the active site of SARS-CoV2 Mpro by molecular docking. As a result, 946 compounds were predicted to bind Mpro better than the inhibitor N3 (Table S4). The compounds were clustered in 21 groups (Table S5) and the lead drug of the top 10 clusters is shown in Figure 6.
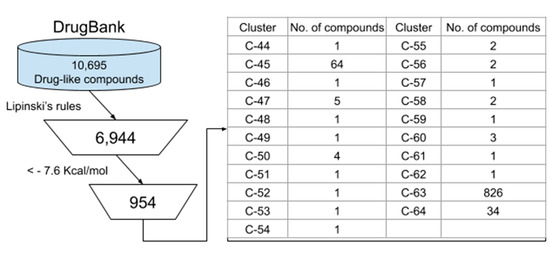
Figure 5.
Virtual screening of compounds from DrugBank. Selected compounds were classified into 21 clusters based on MACCS fingerprint similarity.
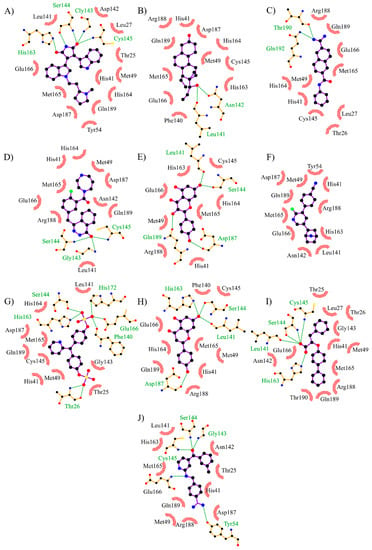
Figure 6.
The top 10 potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro obtained from DrugBank by fingerprints and molecular docking. (A) DB07458 (D.S.: −8.6 kcal/mol) (B) DB09371 (D.S.: −8.5 kcal/mol) (C) DB01977 (D.S.: −8.0 kcal/mol) (D) DB08058 (D.S.: −8.0 kcal/mol) (E) DB01852 (D.S.: −7.9 kcal/mol). (F) DB14029 (D.S.: −7.9 kcal/mol) (G) DB09268 (D.S.: −7.9 kcal/mol) (H) DB07352 (D.S.: −7.8 kcal/mol). (I) DB08121 (D.S.: −7.8 kcal/mol) (J) DB07809 (D.S.: −7.8 kcal/mol). D.S.: Docking score.
DB07458 is shown to have two indole rings on its structure, and just as the compounds from the previous screening (CHEMBL469898, CHEMBL1437444, and CHEMBL3666013), this compound is a protein kinase C inhibitor [34]. On the other hand, the compound DB09371 is an estrogen receptor modulator [35]. These types of compounds have been proposed as candidates for the treatment of COVID-19 [36]. They could act by blocking viral entry into the cell. However, according to our screening it is possible that these compounds also interact with SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. Based on the docking score of the rest of the leaders, it is clear that these two are the most promising inhibitor compounds. The differences in the docking score could indicate which functional groups are unfavorable.
3.4. Analysis of Protein-Ligand Interactions
Virtual screening on SARS-CoV-2 Mpro showed the promiscuity of the binding site. To select the most promising inhibitors, the leaders of each screening were compared to structurally available ligands of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. The Diamond Light Source method has just made available the crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro binding non-covalently to 22 compounds (Table S6). To identify the key interaction for binding the active site, the protein-ligand interaction profiler (PLIP) was used to calculate the molecular interactions on each complex. These interactions are summarized in Figure 7. This figure shows that the most common interaction is the hydrogen bond with the amino acid Glu166. This interaction is very important because Glu166 helps maintain the shape of the active site [24]. Additionally, in flavonoid inhibitors, Glu166 and Gln189 play a key role on the binding force to SARS-CoV Mpro [36]. Moreover, previous studies have shown that His41 plays an important role in the active site stabilizing the binders through hydrogen binding [36,37]. In this study, the results showed that His41 also participated in π-stacking interactions.
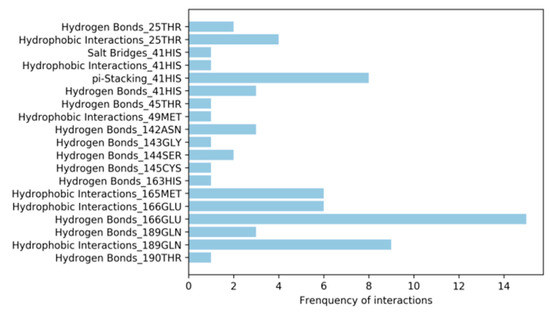
Figure 7.
Non-covalent interactions calculated from 22 known inhibitors from SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.
The analyses of these non-covalent interactions were considered to select the most promising inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 from the previous virtual screening. Based on the docking calculations, 64 structurally diverse compounds that bind to SARS-CoV-2 Mpro better than the inhibitor N3 were identified from three different databases (ChEMBL, BindingDB, and DrugBank). The interaction patterns of these compounds were compared with the interactions observed in the 22 known binders. Then, the compounds were ranked based on how many of these interactions were identified according to their docked pose on the binding site. Figure 8 summarizes the top 10 compounds of this ranking.
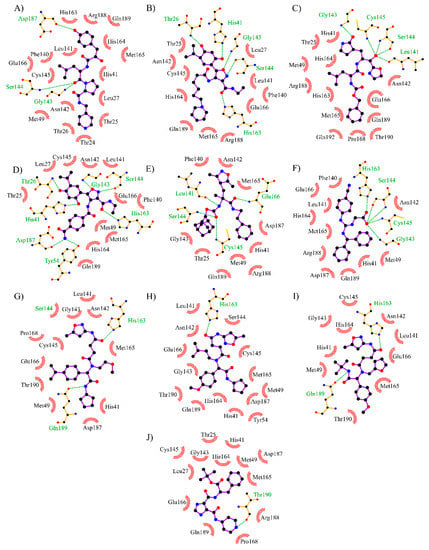
Figure 8.
Top 10 compounds obtained by analyzing the interactions with key residues. The interactions of interest (I. I.) indicate a binding mode similar to the known inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2. (A) CHEMBL562054 (D.S.: −8.4 kcal/mol, 9 I. I.). (B) CHEMBL4300783 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol, 9 I. I.). (C) CHEMBL20247011 (D.S.: −8.1 kcal/mol, 9 I. I.). (D) CHEMBL1940937 (D.S.: −9.1 kcal/mol, 8 I. I.). (E) CHEMBL64623 (D.S.: −8.3 kcal/mol, 8 I. I.). (F) DB07816 (D.S.: −8.5 kcal/mol, 8 I. I.). (G) CHEMBL1383217 (D.S.: −8.1 kcal/mol, 8 I. I.). (H) CHEMBL1866805 (D.S.: −8.0 kcal/mol, 8 I. I.). (I) CHEMBL1392860 (D.S.: −7.7 kcal/mol, 8 I. I.). (J) CHEMBL1740647 (D.S.: −7.7 Kcal/mol, 7 I. I.). D.S.: Docking score.
The top compound was CHEMBL562054, which interacts with three key residues in the binding site. CHEMBL562054 forms hydrogen bonds with Gly143, Ser144, and Cys145. These residues form the oxyanion hole which stabilizes the transition state of Mpro, and they are a common target to achieve its inhibition [2,36]. These interactions also affect the catalytic dyad formed by His41 and Cys145 [18]. The residues Glu166 and Gln189 are at the entrance of the pocket [12], which is blocked through H-bonding. The isoxazole moiety of CHEMBL4300783 binds by H-bond with Gly143, Ser144, and Cys145. In addition, the resorcinol ring destabilizes the catalytic dyad through hydrogen bonding with His41, and Thr26. The rest of the structure interacts hydrophobically with Asn142, Glu166, and Gln189. The next compound CHEMBL2047011 is an α-ketoamide proposed as a potential norovirus 3CL protease inhibitor [1]. This type of inhibitor has already been evaluated against SARS-CoV-2 Mpro showing favorable results [24]. The main features of the docked pose of CHEMBL2047011 are the hydrogen bonds with the oxyanion hole and the catalytic dyad as well as Glu166. The compound DB07816 shows a higher score than the previous compounds. It interacts mainly with its carboxylate group, which forms H-bonds with Leu141, Gly143, Ser144, and Cys145. Additionally, it creates a salt bridge with His163. Apart from these, there are some hydrophobic interactions with His41, Met165, Glu166 and Gln189. Although it seems that the isoxazole moiety could play an important role in Moro inhibition, the docked pose of CHEMBL64623 did not show any interaction of this group with the binding site. The majority of the hydrogen bonding occurs with carbamate atoms.
On the other hand, the compound with the highest score, CHEMBL1940937, forms seven hydrogen bonds. Three of these bonds occur by the isoxazole group. Therefore, although different ligands could have the same interactions, isoxazole favors the docking score. Three compounds, CHEMBL1866805, CHEMBL1392860 and CHEMBL1383217, have similar docked poses, where most of the interactions are hydrogen bonds which occur through the isoxazole and the acetamide moieties. Finally, CHEMBL1740647 is the only compound that forms a π-stacking interaction with His41. It does not have any interaction with the oxyanion hole, but interacts through hydrogen bonding with Glu166 and Gln189.
4. Conclusions
In this study, virtual screening of four chemical databases helped to identify potential SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors. Using a docking approach, several structurally diverse compounds were bound to the Mpro binding site with a score higher than the N3 inhibitor. These compounds were clustered based on their structural difference to identify the structural features of potential SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. An analysis of known CoV-inhibitors showed that amentoflavone could be a potent SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor. This compound has several hydroxyl groups that could be related to its high docking score. The ligand-based approaches from the CHEMBL database indicates that Hsp90 inhibitors, such as CHEMBL1940937, CHEMBL3900791, CHEMBL4300783 and CHEMBL3233752, could be other SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors. They highlight the importance of the isoxazoline and morpholine group on the structure of the potential inhibitor Mpro. The molecular docking of the DrugBank database suggests that DB07458 exhibits better interactions than the inhibitor N3 on the active site. Considering this, the indole group seems to play a key role in the binding to Mpro. Finally, a confrontation of protein-ligand interactions from known SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors versus previous compound screening suggests that the best potential lead drug could be CHEMBL562054. This analysis suggested that π-stacking interaction with His41 and hydrogen bonding with Glu166 are the main interactions involved in the ligand binding to Mpro.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2218-0532/88/4/54/s1, Table S1: Results from molecular docking of known CoV inhibitors on SARS-CoV-2 Mpro; Table S2: Compounds obtained from screening the ChEMBL database; Table S3: Leaders from ChEMBL clusters; Table S4: Compounds obtained from screening the DrugBank database; Table S5: Leaders from DrugBank clusters; Table S6: List of non-covalent bindings of SARS-CoV2; Table S7: 2D structure of the predict inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro protein.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.J.-S. and G.R.; methodology, A.J.-S., A.D.P.-G., E.E.L.-R. and F.R.-E.; validation, E.E.L.-R. and F.R.-E.; formal analysis, J.C.V.-R.; data curation, A.D.P.-G. and J.C.V.-R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.J.-S., E.E.L.-R. and G.R.; writing—review and editing, A.J.-S., A.D.P.-G., E.E.L.-R., J.C.V.-R. and F.E.-R.; Project administration and funding acquisition, A.D.P.-G. and G.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Secretaria de Investigacion y Posgrado del Instituto Politecnico Nacional, grant number 20200491.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli., R. Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19); StatPearls, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554776/ (accessed on 15 October 2020).
- Chen, L.R.; Wang, Y.C.; Yi, W.L.; Chou, S.Y.; Chen, S.F.; Lee, T.L.; Wu, Y.T.; Kuo, C.J.; Chen, T.S.S.; Juang, S.H. Synthesis and evaluation of isatin derivatives as effective SARS coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3058–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavizadeh, L.; Ghasemi, S. Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: Their roles in pathogenesis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyr, Z.A.; Gorshkov, K.; Chen, C.Z.; Zheng, W. Drug Discovery Strategies for SARS-CoV-2. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 375, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, Y.; Singh, H.; Patel, C.N. In silico prediction of potential inhibitors for the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 using molecular docking and dynamics simulation based drug-repurposing. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1210–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Ma, R.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Repurposing low-molecular-weight drugs against the main protease of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 7267–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Almes, F.J. Repurposing approved drugs as potential inhibitors of 3CL-protease of SARS-CoV-2: Virtual screening and structure based drug design. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2020, 88, 107351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touret, F.; Gilles, M.; Barral, K.; Nougairède, A.; van Helden, J.; Decroly, E.; de Lamballerie, X.; Coutard, B. In vitro screening of a FDA approved chemical library reveals potential inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Deep, S. In-Silico Drug Repurposing for Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Mpro. 2020. Available online: https://chemrxiv.org/ndownloader/files/22457816 (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Smith, M.; Smith, J.C. Repurposing Therapeutics for COVID-19: Supercomputer-Based Docking to the SARS-CoV-2 Viral Spike Protein and Viral Spike Protein-Human ACE2 Interface. ChemRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and control of covid-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Tan, K.; Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Liang, P. Identification, synthesis and evaluation of SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV 3C-like protease inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3035–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavasotto, C.N.; Di Filippo, J.I. In silico Drug Repurposing for COVID-19: Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins through Docking and Consensus Ranking. Mol. Inform. 2020, 2000115, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, W.R.; Gomes, R.A.S.; Novaes, A.L.; Goulart Trossini, G.H. Ligand and structure-based virtual screening applied to the SARS-CoV-2 main protease: An in silico repurposing study. Future Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Fast Identification of Possible Drug Treatment of Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19) through Computational Drug Repurposing Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 3277–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, V.; Wieder, O.; Garon, A.; Seidel, T.; Urban, E.; Langer, T. A Computational Approach to Identify Potential Novel Inhibitors against the Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Mol. Inform. 2020, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkamer, A.; Kuhn, D.; Rippmann, F.; Rarey, M. Dogsitescorer: A web server for automatic binding site prediction, analysis and druggability assessment. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2074–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. TM-align: A protein structure alignment algorithm based on the TM-score. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. Autodock vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar]
- Culleta, G.; Gulotta, M.R.; Perricone, U.; Zappalà, M.; Almerico, A.M.; Tutone, M. Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 Proteome in the Search of Potential Inhibitors via Structure-Based Pharmacophore Modeling/Docking Approach. Computation 2020, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salentin, S.; Schreiber, S.; Haupt, V.J.; Adasme, M.F.; Schroeder, M. PLIP: Fully automated protein-ligand interaction profiler. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W443–W447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lin, D.; Sun, X.; Curth, U.; Drosten, C.; Sauerhering, L.; Becker, S.; Rox, K.; Hilgenfeld, R. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved a-ketoamide inhibitors. Science 2020, 368, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.F.; Alam, M.M.; Verma, G.; Akhtar, W.; Akhter, M.; Shaquiquzzaman, M. The therapeutic voyage of pyrazole and its analogs: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 170–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Namasivayam, V.; Hayashi, Y.; Jung, S.H. An overview of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3CL protease inhibitors: Peptidomimetics and small molecule chemotherapy. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6595–6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Sharma, A.; Nandi, S.P. Identification of Potent Inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease Enzyme by Molecular Docking Study. ChemRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, H.M.; Niu, G.J.; Shi, E.Z.; Chen, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, W.Q.; Zhou, H.G.; Yang, C. Synthesis, modification and docking studies of 5-sulfonyl isatin derivatives as SARS-CoV 3C-like protease inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Singh, R.K. Morpholine as ubiquitous pharmacophore in medicinal chemistry: Deep insight into the structure-activity relationship (SAR). Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 96, 103578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.J.; Fang, J.M.; Kuo, T.H.; Kuo, C.J.; Liang, P.H.; Huang, H.J.; Wu, Y.T.; Jan, J.T.; Cheng, Y.S.E.; Wong, C.H. Inhibition of the severe acute respiratory syndrome 3CL protease by peptidomimetic α,β-unsaturated esters. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5240–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandgren, V.; Agback, T.; Johansson, P.O.; Lindberg, J.; Kvarnström, I.; Samuelsson, B.; Belda, O.; Dahlgren, A. Highly potent macrocyclic BACE-1 inhibitors incorporating a hydroxyethylamine core: Design, synthesis and X-ray crystal structures of enzyme inhibitor complexes. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4377–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Terracciano, S.; Bruno, I.; D’Amico, E.; Bifulco, G.; Zampella, A.; Sepe, V.; Smith, C.D.; Riccio, R. Synthetic and pharmacological studies on new simplified analogues of the potent actin-targeting Jaspamide. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6580–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Jan, J.T.; Ma, S.H.; Kuo, C.J.; Juan, H.F.; Cheng, Y.S.E.; Hsu, H.H.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, D.; Brik, A.; et al. Small molecules targeting severe acute respiratory syndrome human coronavirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10012–10017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassel, M.; Breitenlechner, C.B.; König, N.; Huber, R.; Engh, R.A.; Bossemeyer, D. The protein kinase C inhibitor bisindolyl maleimide 2 binds with reversed orientations to different conformations of protein kinase A. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 23679–23690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witters, H.; Freyberger, A.; Smits, K.; Vangenechten, C.; Lofink, W.; Weimer, M.; Bremer, S.; Ahr, P.H.J.; Berckmans, P. The assessment of estrogenic or anti-estrogenic activity of chemicals by the human stably transfected estrogen sensitive MELN cell line: Results of test performance and transferability. Reprod. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Shen, J.; Huang, Y.; Martin, W.; Cheng, F. Network-based drug repurposing for novel coronavirus 2019-nCoV/SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 2020, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, D.C.J.; Ji, H.F. A search for medications to treat COVID-19 via in silico molecular docking models of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and 3CL protease. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 35, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).