B Cells and Double-Negative B Cells (CD27−IgD−) Are Related to Acute Pancreatitis Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects and Sample Collection
2.2. Flow Cytometry
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Immune Profile of Acute Pancreatitis Patients at Hospital Admission
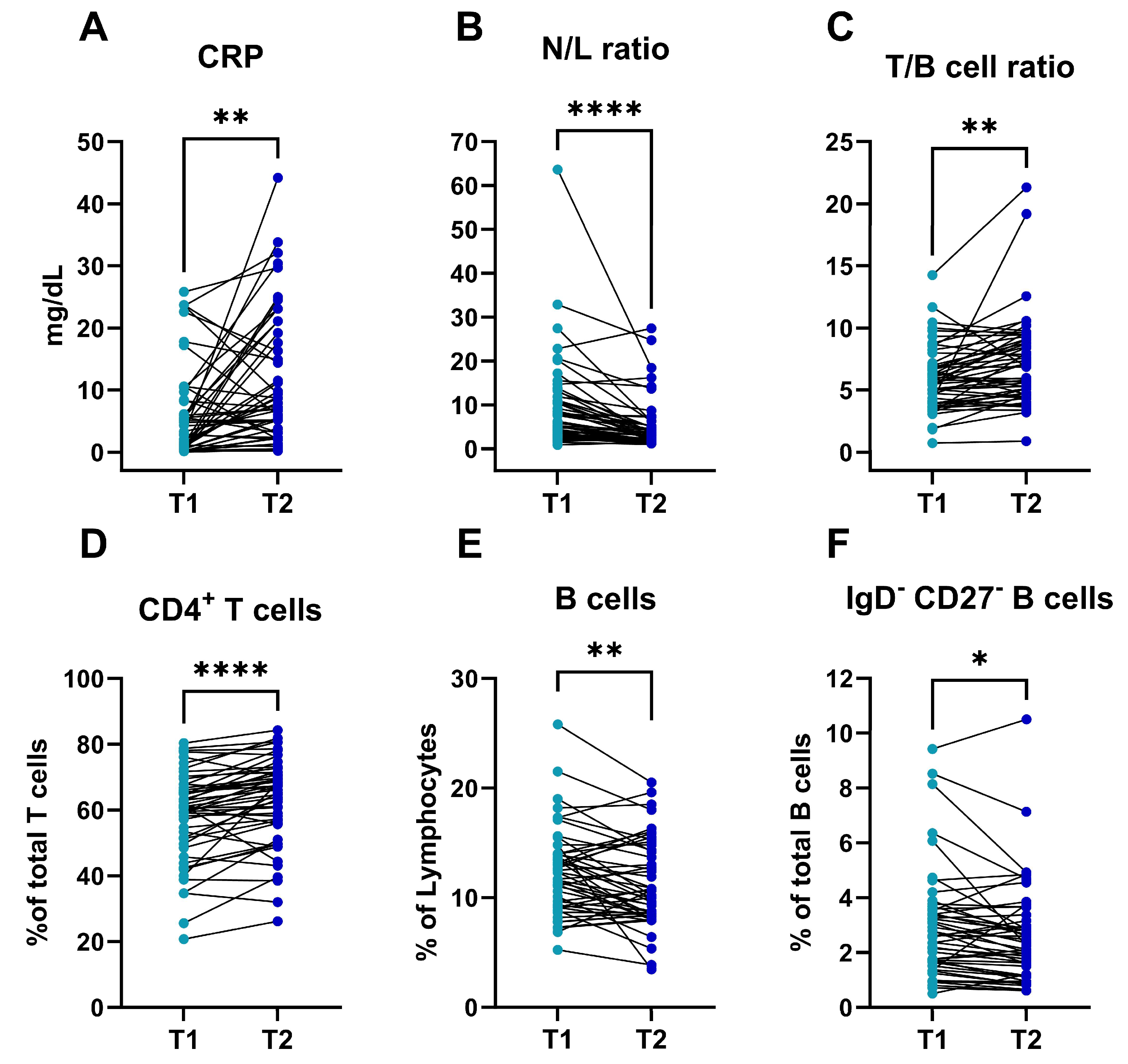
3.2. Dynamics of the Immune Profile in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis during the First 48 H after Diagnosis
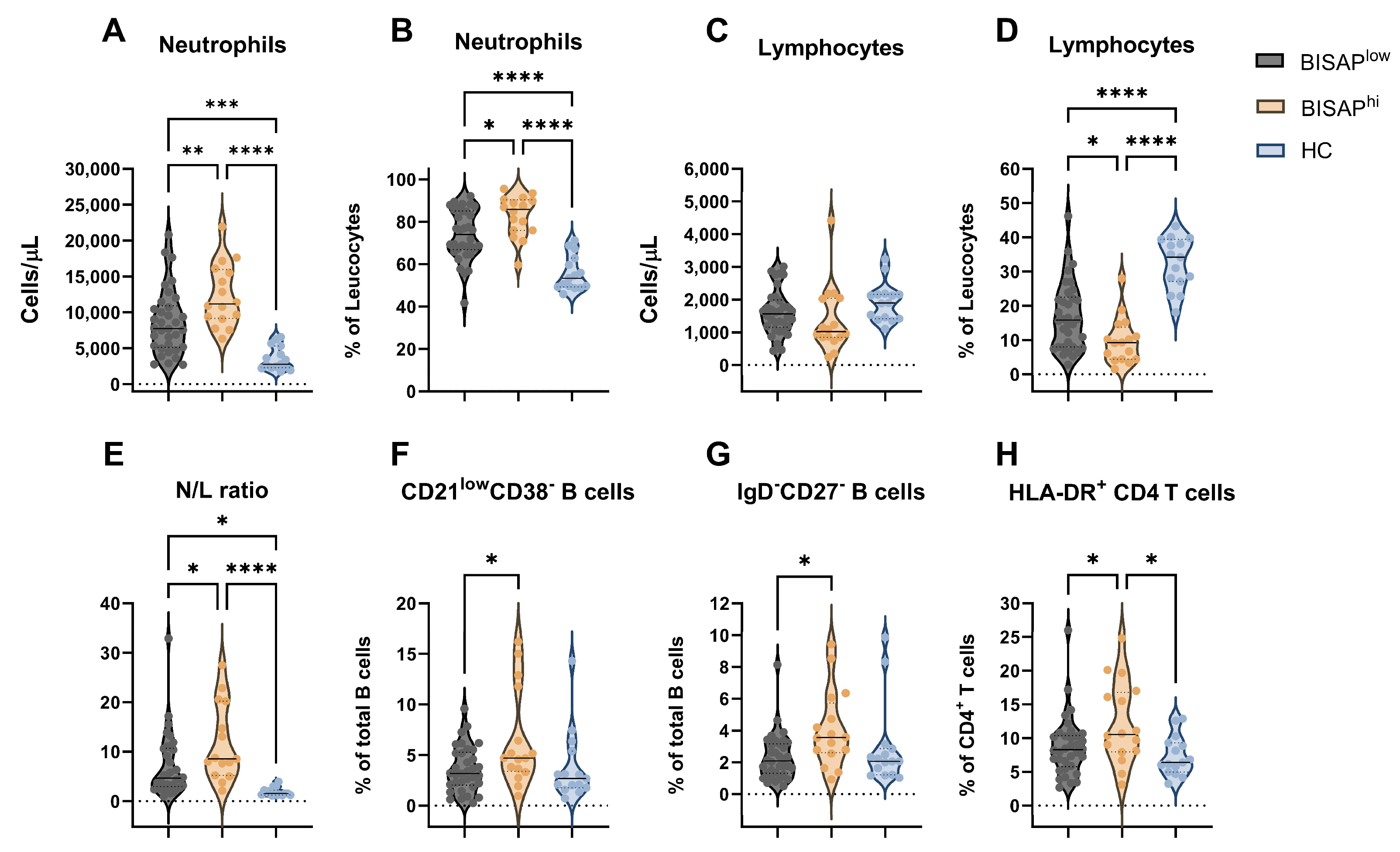
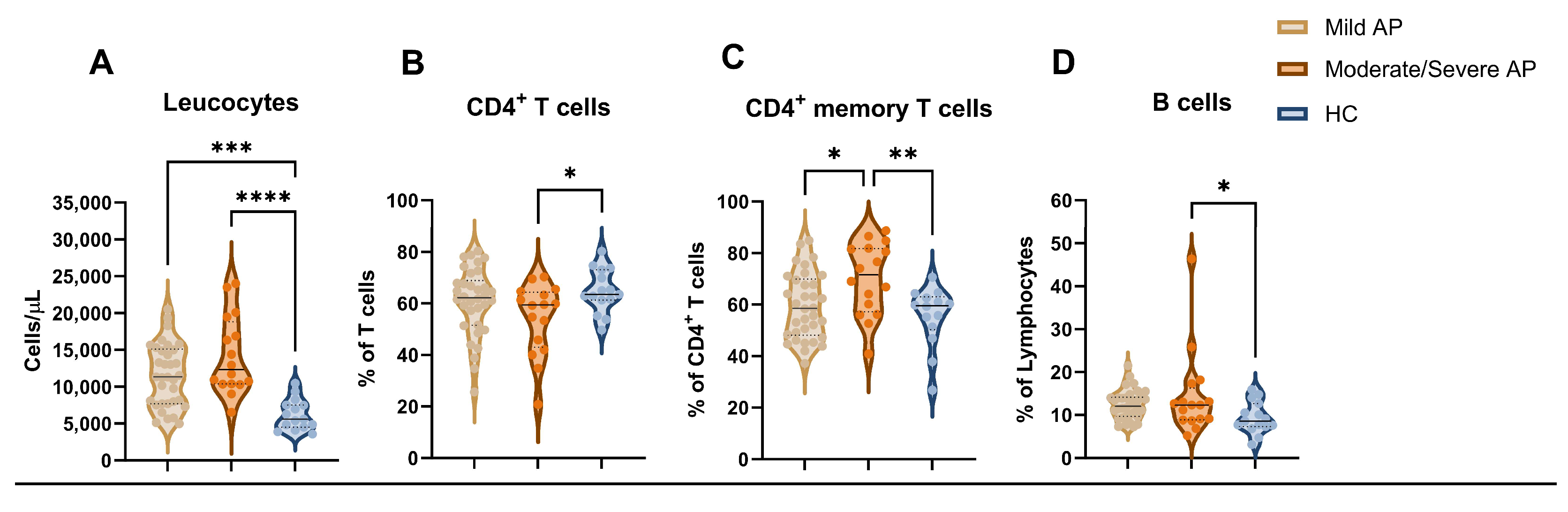
3.3. Early Variations in the Immune Profile and Its Relation to Severity in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis
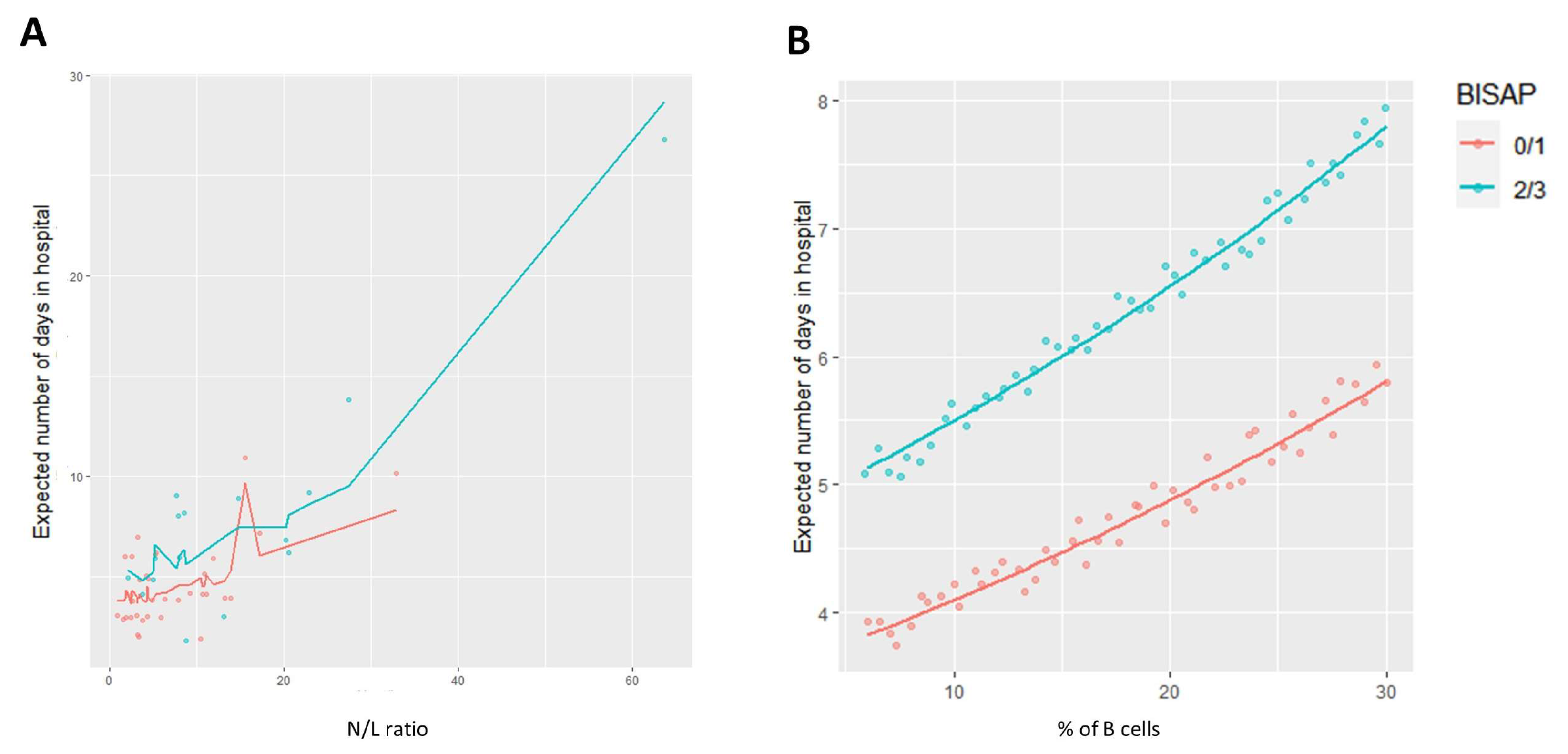
3.4. Length of Stay and the Immune Profile: Exploring Relations for Patient Monitoring and Follow Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, B.U.; Johannes, R.S.; Sun, X.; Tabak, Y.; Conwell, D.L.; Banks, P.A. The early prediction of mortality in acute pancreatitis: A large population-based study. Gut 2008, 57, 1698–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mederos, M.A.; Reber, H.A.; Girgis, M.D. Acute Pancreatitis: A Review. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, C.; Gou, S.; Yin, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, C. The reduction of peripheral blood CD4+ T cell indicates persistent organ failure in acute pancreatitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Xiao, P.; Xie, Y.; Geng, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, T.; Li, L.; et al. Role of Interleukin-17 in Acute Pancreatitis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 674803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.H.; Hu, C.; Cai, W.H.; Chen, W.W.; Zhang, X.X.; Shi, N.; Hang, W.; Ma, Y.; Lin, T.; Lin, Z.; et al. Plasma cytokines can help to identify the development of severe acute pancreatitis on admission. Medicine 2017, 96, e7312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yu, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, R. Decreased levels of regulatory B cells in patients with acute pancreatitis: Association with the severity of the disease. Oncotarget 2018, 90, 36067–36082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formanchuk, T.; Shaprinskiy, V.; Formanchuk, A. Clinical and simple laboratory data associated with fatal outcomes in patients with acute pancreatitis. Acta Fac. Medicae Naissensis 2022, 39, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragomi, P.; Hinton, A.; Pothoulakis, I.; Talukdar, R.; Kochhar, R.; Goenka, M.K.; Gulla, A.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Singh, V.K.; Bogado, M.F.; et al. The Modified Pancreatitis Activity Scoring System Shows Distinct Trajectories in Acute Pancreatitis: An International Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1334–1342.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shi, J.; Zhang, R.; Ni, J.; Habtezion, A.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Xue, J. Expanded CD14 hi CD16−Immunosuppressive Monocytes Predict Disease Severity in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Vaz, P.; Abrantes, A.M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Gouveia, A.; Botelho, M.F.; Tralhão, J.G. Multifactorial Scores and Biomarkers of Prognosis of Acute Pancreatitis: Applications to Research and Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Yao, W.; Li, H.; Qian, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, H.; Shi, L.; Lin, X. B and NK Cells Closely Correlate with the Condition of Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 7568410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Hu, F. Double-negative (DN) B cells: An under-recognized effector memory B cell subset in autoimmunity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2021, 205, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.K.Y.; Gong, L.; Kwong, D.L.W.; Lee, V.H.F.; Lee, A.W.M.; Guan, X.Y.; Kam, A.W.; Dai, W. Functions of double-negative B cells in autoimmune diseases, infections, and cancers. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S. Classification of acute pancreatitis-2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Muddana, V.; Yadav, D.; O’Connell, M.; Sanders, M.K.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson’s, APACHE-II, and CTSI Scores in Predicting Organ Failure, Complications, and Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 435–441, quiz 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finak, G.; Langweiler, M.; Jaimes, M.; Malek, M.; Taghiyar, J.; Korin, Y.; Raddassi, K.; Devine, L.; Obermoser, G.; Pekalski, M.L.; et al. Standardizing Flow Cytometry Immunophenotyping Analysis from the Human ImmunoPhenotyping Consortium. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiber, C.; Zeileis, A. Applied Econometrics with R; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-387-77316-2. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, S.G.; Habtezion, A.; Gukovskaya, A.; Lugea, A.; Jeon, C.; Yadav, D.; Hegyi, P.; Venglovecz, V.; Sutton, R.; Pandol, S.J. Critical thresholds: Key to unlocking the door to the prevention and specific treatments for acute pancreatitis. Gut 2021, 70, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkowska, J.; Zielinska, N.; Tubbs, R.S.; Podgórski, M.; Dłubek-Ruxer, J.; Olewnik, Ł. Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.U.; Batech, M.; Quezada, M.; Lew, D.; Fujikawa, K.; Kung, J.; Jamil, L.; Chen, W.; Afghani, E.; Reicher, S.; et al. Dynamic Measurement of Disease Activity in Acute Pancreatitis: The Pancreatitis Activity Scoring System. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gukovskaya, A.S.; Vaquero, E.; Zaninovic, V.; Gorelick, F.S.; Lusis, A.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Holland, S.; Pandol, S.J. Neutrophils and NADPH oxidase mediate intrapancreatic trypsin activation in murine experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.J.; Papachristou, G.I. New insights into acute pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gukovskaya, A.S.; Gukovsky, I.; Algül, H.; Habtezion, A. Autophagy, Inflammation, and Immune Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmary, P.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Cai, W.; Huang, W.; Mukherjee, R.; Halloran, C.; Beyer, G.; Sutton, R. Acute Pancreatitis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Drugs 2022, 82, 1251–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanza, C.; Caputo, G.; Tornatore, G.; Romenskaya, T.; Piccioni, A.; Franceschi, F.; Artico, M.; Taurone, S.; Savioli, G.; Longhitano, Y. Cellular Immuno-Profile in Septic Human Host: A Scoping Review. Biology 2022, 11, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, M.; Qi, X.; Xu, Z.; Cai, Q.; Sheng, H.; Chen, E.; Zhao, B.; et al. Leukocyte cell population data from the blood cell analyzer as a predictive marker for severity of acute pancreatitis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.J.; Neal, C.P.; Ngu, W.S.; Dennison, A.R.; Garcea, G. Early warning score independently predicts adverse outcome and mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 811–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietruczuk, M.; Dabrowska, M.I.; Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska, U.; Dabrowski, A. Alteration of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Wong, F.L.; Cao, Y.; Lau, H.Y.; Huang, J.; Puneet, P.; Chevali, L. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, K.; Glenn, H.; Delaney, A.; Andersen, C.R.; Sasson, S.C. Fire in the belly: A scoping review of the immunopathological mechanisms of acute pancreatitis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1077414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, K.J.; Kell, M.R.; Coates, C.; Murphy, T.; Reynolds, J.V. Serum antigen(s) drive the proinflammatory T cell response in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 2003, 90, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Hou, C.; Zhu, X.; Peng, Y.; Guo, F.; Zhang, K.; Miao, Y. New Predictor of Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis: CD4+ T Lymphocytes and CD19+ B Lymphocytes. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, D.; Kondo, M.; Chen, H.; Kelsoe, G. Effects of acute and chronic inflammation on B-cell development and differentiation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, C.; Bosma, A. Immune regulatory function of B cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.M.; Liu, Y.S.; Davies, S.P.; Brown, R.M.; Kelly, D.A.; Scheel-Toellner, D.; Reynolds, C.M.; Stamataki, Z. The Role of B Cells in Adult and Paediatric Liver Injury. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 729143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centuori, S.M.; Gomes, C.J.; Kim, S.S.; Putnam, C.W.; Larsen, B.T.; Garland, L.L.; Mount, D.W.; Martinez, J.D. Double-negative (CD27-IgD-) B cells are expanded in NSCLC and inversely correlate with affinity-matured B cell populations. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Kwong, D.L.W.; Dai, W.; Wu, P.; Li, S.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fang, X.; Liu, L.; et al. Comprehensive single-cell sequencing reveals the stromal dynamics and tumor-specific characteristics in the microenvironment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gapp, J.; Hall, A.G.; Walters, R.W.; Jahann, D.; Kassim, T.; Reddymasu, S. Trends and Outcomes of Hospitalizations Related to Acute Pancreatitis: Epidemiology From 2001 to 2014 in the United States. Pancreas 2019, 48, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandalia, A.; Wamsteker, E.-J.; DiMagno, M.J. Recent advances in understanding and managing acute pancreatitis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.; Young, B.; Morton, J.; Behrns, K.; Shaheen, N. Are health related outcomes in acute pancreatitis improving? An analysis of national trends in the U.S. from 1997 to 2003. JOP 2008, 9, 408–414. [Google Scholar]
- Tarar, M.Y.; Khalid, A.; Choo, X.Y.; Khurshid, S.; Tumeh, H.; Muhammad, K. Use of the C-Reactive Protein (CRP)/Albumin Ratio as a Severity Tool in Acute Pancreatitis: Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e29243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongprasobchai, S.; Vibhatavata, P.; Apisarnthanarak, P. Severity, Treatment, and Outcome of Acute Pancreatitis in Thailand: The First Comprehensive Review Using Revised Atlanta Classification. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Huang, W.; Huang, K. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in sepsis: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, B.; Jaglall, N.; Atallah, J.P.; Lamet, A.; Raja-Surya, V.; Farah, B.; Lesser, M.; Widmann, W.D. Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Adverse outcomes of Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2011, 11, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | AP (n = 50) | HC (n = 15) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 59.9 (14.6) | 61.1 (14.3) | n.s. a |
| Gender, n (%) | n.s. b | ||
| Male | 23 (46) | 7 (47) | |
| Female | 27 (54) | 8 (53) | |
| BMI, kg/m2, mean (SD) | 29.0 (5.8) | 26.8 (3.1) | n.s. a |
| Cause (%) | - | - | |
| Gallstone | 23 (46) | ||
| Alcoholic | 5 (10) | ||
| Unknown | 21 (42) | ||
| Other | 1 (2) | ||
| Severity, n (%) | - | - | |
| Mild | 34 (66) | ||
| Moderate | 13 (28) | ||
| Severe | 3 (6) | ||
| 30-day mortality, n (%) | 0 (0) | - | - |
| ICU, n (%) | 3 (6) | - | - |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 1 (2) | - | - |
| BISAP score, n (%) | - | - | |
| 0 | 14 (28) | ||
| 1 | 20 (40) | ||
| 2 | 9 (18) | ||
| 3 | 7 (14) | ||
| AP criteria, n (%) | - | - | |
| 2 | 26 (52) | ||
| 3 | 24 (48) | ||
| LOS, days, median [IQR] | 6 [3–6] | - | - |
| AP at Admission (T1) (n = 50) | AP at 48 h (T2) (n = 50) | HC (n = 15) | T1 vs. HC a | T2-T1 d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucocytes, cells/µL | 12,395 (4733) | 8785 (4257) | 6197 (2077) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils, % | 76.76 (11.89) | 65.98 (12.85) | 55.76 (8.23) | <0.001 b | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils, cells/µL | 9864 (4764) | 6160 (4148) | 3570 (1642) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Eosinophils, % | 1.10 (1.26) | 2.45 (1.44) | 3.26 (3.05) | 0.017 | <0.001 |
| Eosinophils, cells/µL | 111 (122) | 183 (108) | 179 (136) | 0.071 b | <0.001 |
| Basophils, % | 0.29 (0.17) | 0.43 (0.23) | 0.69 (0.22) | <0.001 b | <0.001 |
| Basophils, cells/µL | 32 (17) | 34 (16) | 43 (20) | 0.034 b | 0.413 |
| Lymphocytes, % | 14.67 (9.63) | 22.5 (10.7) | 32.4 (7.56) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes, cells/µL | 1545 (801) | 1689 (719) | 1934 (593) | 0.087 b | 0.043 |
| Monocytes, % | 7.17 (2.83) | 8.63 (2.93) | 7.89 (2.50) | 0.382 b | <0.001 |
| Monocytes, cells/µL | 843 (369) | 720 (313) | 471 (150) | <0.0001 | 0.008 |
| Platelets, ×109/L | 245 (77) | 228 (76) | 207 (53) | 0.075 b | 0.001 |
| N/L ratio # | 6.07 [3.26–12.17] | 2.66 [1.87–5.28] | 1.56 [1.23–2.23] | <0.001 c | <0.001 e |
| CRP, mg/dL | 5.82 (7.37) | 11.02 (10.66) | - | - | 0.001 |
| BISAPlow (n = 34) | BISAPhi (n = 16) | HC (n = 15) | p-Value a | p-Value b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BISAPlow vs. BISAPhi | BISAPlow vs. HC | BISAPhi vs. HC | |||||
| Leucocytes, cells/µL | 11,246 (4556) | 14,836 (4264) | 6197 (2077) | <0.001 | 0.013 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| N/L ratio # | 7.09 [6.36) | 11.71 (7.75) | 1.89 (0.83) | <0.001 | 0.040 | 0.018 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils, % | 73.9 (11.86) | 82.83 (9.72) | 55.76 (8.23) | <0.001 | 0.020 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils, cells/µL | 8669 (4527) | 12,403 (4350) | 3570 (1642) | <0.001 | 0.009 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Lymphocytes % | 16.96 (9.99) | 9.81 (6.79) | 32.40 (7.56) | <0.001 | 0.025 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| CD4+ T cells, % | 60.68 (10.82) | 54.14 (17.69) | 64.86 (8.38) | 0.058 | 0.200 | 0.526 | 0.050 |
| HLA-DR+ CD4+ T cells, % | 8.781 (4.47) | 12.18 (6.07) | 7.37 (2.93) | 0.014 | 0.048 | 0.589 | 0.015 |
| CD45RO−CCR4+ CD4+ T cells, % | 3.32 (1.71) | 2.05 (1.67) | 3.77 (1.55) | 0.014 | 0.043 | 0.683 | 0.018 |
| CD45RO+CCR4− CD4+ T cells, % | 22.06 (8.88) | 29.10 (11.78) | 21.95 (8.54) | 0.050 | 0.056 | 0.999 | 0.118 |
| Total B cells, % | 13.26 (6.66) | 12.65 (5.28) | 9.39 (3.65) | 0.099 | 0.935 | 0.085 | 0.265 |
| CD21dimCD38− B cells, % | 3.61 (2.25) | 6.45 (4.76) | 3.81 (3.48) | 0.018 | 0.017 | 0.980 | 0.075 |
| CD27−IgD− B cells, % | 2.33 (1.47) | 4.09 (2.42) | 2.91 (2.61) | 0.021 | 0.015 | 0.629 | 0.240 |
| CRP at admission, mg/dL # | 2.05 [0.38–5.50] | 7.15 [1.00–16.00] | - | - | 0.024 c | - | - |
| CRP at 48 h, mg/dL # | 5.32 [2.15–10.23] | 15.60 [7.58–28.05] | - | - | 0.010 c | - | - |
| LOS, days | 4.60 (2.00) | 8.00 (5.82) | - | - | 0.035 d | - | - |
| Mild AP (n = 34) | Moderate/ Severe AP (n = 16) | HC (n = 15) | p-Value a | p-Value b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild AP vs. Moderate/Severe AP | Mild AP vs. HC | Moderate/ Severe AP vs. HC | |||||
| Leucocytes, cells/µL | 11,535 (4266) | 14,223 (5283) | 6197 (2077) | <0.0001 | 0.093 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Basophils, cells/µL | 28 (13) | 41 (21) | 43 (20) | 0.005 | 0.037 | 0.013 | 0.916 |
| Platelets ×109/L | 228 (60) | 282 (95) | 207 (53) | 0.008 | 0.029 | 0.594 | 0.009 |
| Total CD4 T cells, % | 60.72 (13.12) | 54.06 (13.81) | 64.86 (8.38) | 0.055 | 0.187 | 0.532 | 0.047 |
| Total CD45RO+ CD4 T cells, % | 59.34 (12.76) | 70.03 (14.04) | 55.48 (11.61) | 0.006 | 0.022 | 0.613 | 0.008 |
| Total B cells, % | 12.45 (3.40) | 14.38 (9.88) | 9.39 (3.65) | 0.057 | 0.510 | 0.204 | 0.047 |
| CRP at admission, mg/dL # | 1.45 [0.29–5.53] | 5.70 [2.25–10.60] | - | - | 0.035 c | - | - |
| CRP at 48 h, mg/dL # | 6.45 [1.83–12.00] | 13.20 [4.13–29.05] | - | - | 0.035 c | - | - |
| Parameter | eEstimate | eSD | e95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Constant | 2.974 | 1.15 | 2.262–3.916 | <0.001 |
| N/L ratio | 1.024 | 1.004 | 1.015–1.033 | <0.001 | |
| B cells (%) | 1.018 | 1.009 | 1.000–1.034 | 0.047 | |
| BISAP score of 2/3 | 1.343 | 1.147 | 1.024–1.755 | 0.031 | |
| Model 2 | Constant | 1.734 | 1.192 | 1.224–2.440 | 0.002 |
| HLA-DR+ CD4 T cells (%) | 1.034 | 1.012 | 1.011–1.057 | 0.003 | |
| B cells (%) | 1.039 | 1.007 | 1.024–1.053 | <0.001 | |
| BISAP [2/3] | 1.459 | 1.141 | 1.126–1.890 | 0.004 | |
| Caused by gallstones | 1.349 | 1.152 | 1.021–1.780 | 0.035 | |
| Model Performance | |||||
| Pseudo-R2 | Overdispersion | Residual deviance | AICc | ||
| Model 1 | 0.723 | 0.526 | 26.96 | 208.8 | |
| Model 2 | 0.635 | 0.803 | 35.54 | 219.9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malheiro, F.; Ângelo-Dias, M.; Lopes, T.; Azeredo-Lopes, S.; Martins, C.; Borrego, L.M. B Cells and Double-Negative B Cells (CD27−IgD−) Are Related to Acute Pancreatitis Severity. Diseases 2024, 12, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010018
Malheiro F, Ângelo-Dias M, Lopes T, Azeredo-Lopes S, Martins C, Borrego LM. B Cells and Double-Negative B Cells (CD27−IgD−) Are Related to Acute Pancreatitis Severity. Diseases. 2024; 12(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalheiro, Filipa, Miguel Ângelo-Dias, Teresa Lopes, Sofia Azeredo-Lopes, Catarina Martins, and Luis Miguel Borrego. 2024. "B Cells and Double-Negative B Cells (CD27−IgD−) Are Related to Acute Pancreatitis Severity" Diseases 12, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010018
APA StyleMalheiro, F., Ângelo-Dias, M., Lopes, T., Azeredo-Lopes, S., Martins, C., & Borrego, L. M. (2024). B Cells and Double-Negative B Cells (CD27−IgD−) Are Related to Acute Pancreatitis Severity. Diseases, 12(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases12010018






