Abstract
In practical application, the gathered multi-view data typically misses samples, known as incomplete multi-view data. Most existing incomplete multi-view clustering methods obtain consensus information in multi-view data by completing incomplete data using zero, mean values, etc. These approaches often ignore the higher-order relationship and structural information between different views. To alleviate the above problems, we propose enhanced tensor incomplete multi-view clustering with dual adaptive weight (ETIMC), which can acquire the higher-order relationship, and structural information between multiple perspectives, adaptively recover the missing samples and distinguish the contribution degree of different views. Specifically, the embedded representations obtained from incomplete multi-view data are stacked into a third-order tensor to capture the higher-order relationship. Then, a consensus matrix can be drawn from these potential representations via a self-weighting mechanism. Additionally, we adaptively reconstruct the missing samples while capturing structural information by the hypergraph Laplacian item. Moreover, we integrate the embedded representation of each view, tensor constraints, hypergraph Laplacian regularization, and dual adaptive weighted mechanisms into a unified framework. Experimental results on natural and synthetic incomplete datasets show the superiority of ETIMC.
1. Introduction
Real-world data generally stems from multiple channels or sensors and is considered multi-view data. For example, people can be identified by their faces, fingerprints, and voices; doctors can diagnose patients in different ways, including interviews, tests, and X-rays. Fusing information from distinct perspectives or multiple ways can comprehensively analyze data, inspiring many multi-perspective clustering techniques. Multi-view clustering aims to separate data into their clusters by obtaining valuable knowledge from diverse viewpoints. So far, the proposed multi-perspective clustering approaches can be roughly divided into feature-driven (e.g., subspace-based [1,2,3]) and relationship-driven (e.g., graph-based [4,5,6]) methods. These methods can process complete data well. When there are missing samples, it is difficult for these methods to comprehensively capture the complementary information between different perspectives, resulting in the algorithm performance degradation.
Multi-view data obtained from different angles suffer from missing samples that are ubiquitous in reality. For example, in the questionnaire survey, many surveys are anonymous for privacy reasons. In disease diagnosis, the patient cannot undergo a comprehensive examination owing to force majeure. It is difficult for previous multi-view clustering methods to deal with incomplete multi-view data directly. Therefore, many incomplete multi-view clustering methods emerge. The work [7] is an earlier method to solve incomplete multi-view data, but it needs at least one complete view. The method proposed by Gao et al. [8] can handle the case of more than two perspectives, which uses the mean value of all samples to fill incomplete data while introducing interference factors such as noise in the filling process. To avoid the above problems, the method proposed by many scholars is to infer missing samples in learning. For example, the work [9] proposed a method, called incomplete multi-modal visual data grouping (IMG), IMG first completed data by Laplacian regularization to obtain structural information between perspectives, then bridges complete and incomplete instances. Wen et al. [10] introduced the incomplete multi-view tensor spectral clustering with missing-view inferring (IMVTSC-MVI), which incorporated the feature space-based missing-view inferring and manifold space-based similarity graph learning into a unified framework. However, IMG and IMVTSC-MVC use traditional graph theory to save the original data of geometric structure and lose important information to some extent. Our proposed ETIMC applies hypergraphs to obtain structural information from incomplete multi-view data. Hypergraphs can connect multiple vertices (more than two), thus exploring more comprehensive information.
The methods mentioned above are not flexible when tackling intricate incomplete multi-view data, so a suite of algorithms based on weighting mechanisms has been proposed to add distinct weights to missing and no missing samples. DAIMC [11] employs weighted NMF to solve the problem of incomplete data by assigning zero weight to missing samples in each view and appropriate weight to those that are not missing. After that, OSINN [12] proposed an interpretable Orthogonal Non-negative Matrix Factorization into a clustering layer. However, these methods are predefined weights and cannot adjust the weights adaptively according to changes in the model. Meanwhile, extra parameters will be introduced, thus increasing the cost of model tuning. In addition, the above method does not pay attention to the higher-order relationship between different perspectives, which is helpful to enhance the clustering performance because it can explore more abundant information. Therefore, Li et al. [13] proposed a novel tensor approach to capture block-diagonal structural and higher-order information from different views. Based on the higher-order relationship, it can acquire the membership degree between the observed sample and the missing instance and further obtain the consensus representation of separability. Zhang et al. [14] introduced an enhanced tensor low-rank and sparse representation recovery(ETLSRR), which constructed a three-way tensor by stacking graphs to explore higher-order relationships. To alleviate the negative influence of missing views and data noise, ETLSRR decomposed the tensor into two parts: a sparse tensor and an intrinsic tensor, which models the noise and underlying true data similarities, respectively. All the tensor methods mentioned above solve the minimization problem via the nuclear norm. Compared with the nuclear norm, the Schatten-p norm has an adjustable parameter p, which can reduce the proportion of large singular values in the objective function. Therefore, our work chooses the Schatten-p norm to solve the minimization problem of the tensor.
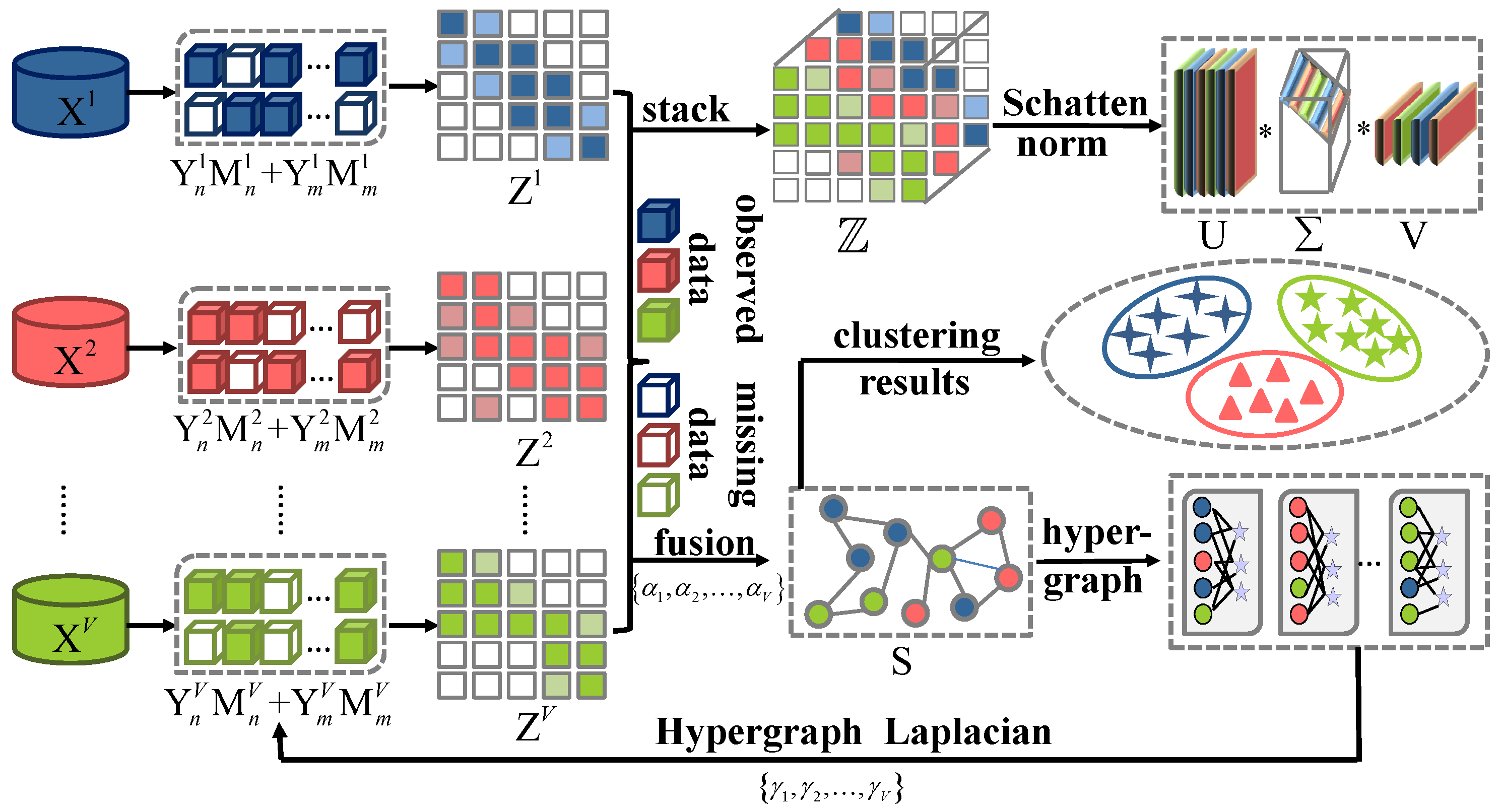
Inspired by the above analysis, this paper proposes an enhanced tensor incomplete multi-view clustering via dual adaptive weight (ETIMC). ETIMC can adaptively recover incomplete data, obtain consistent, structural, and higher-order information among recovered data, and allocate reasonable weights to different perspectives via an adaptive weighted mechanism. Figure 1 illustrates the entire framework of the proposed ETIMC. Specifically, we first stack the low-dimensional representations obtained by subspace learning into a third-order tensor to explore the higher-order relationship between perspectives and use the Schatten-p norm to solve the tensor to increase the flexibility and ensure the low-rank characteristics. We then learn the consensus representation from the obtained low-dimensional representation via an adaptive weighted mechanism. Subsequently, we apply adaptive hypergraph Laplacian constraints to recover missing samples and acquire higher-order structural information between perspectives. The highlights of this article are summarized as follows:
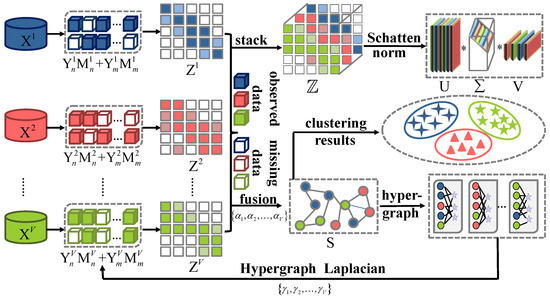
Figure 1.
The entire construction process of ETIMC. Firstly, the potential representation is generated from , and then the corresponding operation is performed on separately. We stack into a third-order tensor to explore the higher-order relationship among multiple views while solving the minimum value of the tensor by the Schatten-p norm. Learn consensus representation from of distinct perspectives while assigning diverse weights to different perspectives to highlight the contributions of multiple perspectives. In addition, we apply the hypergraph Laplacian and self-weighting mechanisms to adaptively recover the missing samples and preserve the higher-order local geometry of the original data.
- The proposed ETIMC can obtain the higher-order information from the incomplete multi-view data, solving the tensor minimization problem with the Schatten-p norm to increase flexibility and ensuring the low-rank characteristics.
- The adaptive hypergraph Laplacian mechanism can recover the missing samples by hypergraph neighbors and preserve the higher-order local geometry structure of the original data.
- The proposed ETIMC considers the differences among multiple perspectives via a self-weighting mechanism, which contributes to identifying the contribution of each low-dimensional representation in learning consensus representations.
2. Related Work
Most previous multi-view clustering methods assume that the samples in each view are complete. However, in practical applications, data from different perspectives are usually missing, leading to the clustering performance deterioration. Currently, existing incomplete multi-view clustering methods are often divided into two categories. One is to complete the missing view and then perform the corresponding operation. For example, the work [7] proposes to fill in the incomplete perspective through the kernel method, but it needs at least one complete perspective as a reference. Therefore, there are some improved works filling in all missing views using 0 or the mean. For example, Gao et al. [8] filled in incomplete perspectives utilizing the mean of all samples. In addition, the work [15] introduced a multiple-kernel K-means approach with incomplete kernels (MKKM-IK), which applies the standard multiple-kernel clustering (MKC) algorithms to an interpolated kernel matrix, integrating interpolation and clustering into a unified learning process. The other is to learn the latent representation from incomplete multi-view data directly. For example, Wen et al. proposed a method, called adaptive graph completion based on incomplete multi-view clustering [16], which developed a joint framework for graph completion and consensus representation learning. Liu et al. [17] introduced a method of localized sparse incomplete multi-view clustering (LSIMVC), LSIMVC intends to learn a sparse and structured consensus latent representation from the incomplete multi-view data by optimizing a sparse regularized and novel graph embedded multi-view matrix factorization model. What our work has in common with the above methods is the processing of incomplete multi-view data. The difference is that our work is not limited to having a complete view, nor does it construct the missing data by filling in 0 or the mean. Our proposed ETIMC is to reconstruct the incomplete sample adaptively.
Research on incomplete multi-view clustering has increasingly shifted toward deep learning-based solutions, which can be broadly grouped into imputation-based, inference-based, and generative approaches. Early deep methods primarily focused on learning robust latent representations under missing-view scenarios. Wen et al. [18] introduced one of the first deep frameworks capable of adaptively extracting consensus information from view-specific latent embeddings, followed by Wen et al. [19], who further enhanced representation quality through a structured network designed to capture higher-order relationships. Subsequent works expanded the scope to inference-driven strategies. Lin et al. [20] established the connection between data recovery and consistency learning, employing contrastive loss to infer missing views, whereas Jin et al. [21] improved the reliability of such inference by aligning prototype sets to strengthen cross-view structural consistency. In parallel, imputation-oriented models explored feature-level reliability: Li et al. [22] adopted weighted imputation based on dual-view co-occurrence but overlooked differences in feature informativeness, which was subsequently addressed by Li et al. [23] through the incorporation of prototypes and attention mechanisms to enhance cross-view correlations. More recent efforts (2024–2025) have increasingly employed generative modeling to handle incomplete multi-view data. Wen et al. [24] pioneered the use of diffusion models for view generation, though such models remain limited for non-image modalities; Chen et al. [25] mitigated this issue by utilizing variational autoencoders to capture structural consensus in a modality-agnostic manner. Complementary advances, including dual-view representation learning [26] and adaptive cross-view modeling [27], continue to extend deep incomplete multi-view clustering toward more robust and expressive representation learning frameworks.
3. Methods
In this part, we first elaborate on the construction process of the proposed ETIMC, then give the entire optimization procedure of ETIMC, and finally provide the computational complexity of ETIMC.
3.1. Problem Formulation
Suppose is no missing instance of the vth view, where and are the dimension and sample size of the vth perspective, respectively. It is not easy to extract diversified information from multi-view data with missing samples. Therefore, we construct the following equation:
where is the missing instances. By matrix transformation, we reconstruct Equation (1) as follows:
where and are projection matrices corresponding to and , respectively.
Inspired by t-SVD-MSC [28], the tensor-based multi-view approach can capture higher-order information between different perspectives. Hence, we construct an incomplete multi-view clustering model based on tensors, which can be expressed as follows:
where is the operation that fuses together. is the representation matrix from the the vth perspective. It describes the subspace structure of vth view, so satisfying the constraint . Additionally, we impose non-negative and symmetric constraints on to make more discriminant and preserve the potential relationship between data samples. Then we stack from each view into a third-order tensor to capture higher-order information between different views. We add a low-rank constraint for to obtain more valuable information because low-rank means that the elements are linearly related. However, the rank is non-convex while the nuclear norm is convex, so the nuclear norm is a convex approximation of the low-rank constraint. Based on the above considerations, Equation (3) is rewritten as follows:
Despite the fact that the nuclear norm can enforce the low-rank property of tensors and has been widely used in multi-view clustering, it ignores the differentiation among singular values. Since the nuclear norm penalizes all singular values equally, it inevitably shrinks the dominant singular components excessively, whereas larger singular values often capture more discriminative or informative structures in real-world multi-view data. To preserve the essential structural information in the representation matrices, it is desirable to shrink larger singular values less aggressively. This motivates us to employ the Schatten-p norm, which allows flexible control of the shrinkage degree on singular values by adjusting the parameter . Moreover, the Schatten-p norm provides a much tighter and more accurate approximation to the tensor rank function compared with the convex nuclear norm. This property has been theoretically justified in Theorem 1.
Theorem 1
(Tight Low-Rank Approximation of Schatten-p Norm). Let be a third-order tensor and denote its mode-k singular values. For , the Schatten-p norm is a strictly closer approximation to the tensor rank than the convex tensor nuclear norm. Specifically,
Thus, minimizing the Schatten-p norm induces a stronger low-rank constraint and yields more robust structural recovery for incomplete multi-view data.
Building on Theorem 1, we extend the Schatten-p norm from the single-matrix case to the multi-view tensor setting. By jointly modeling into a third-order tensor , the Schatten-p regularization directly exploits the high-order correlations among multiple views while simultaneously enforcing low-rankness in each view-specific representation.
Based on Theorem 1 and its natural extension to tensors, the multi-view Schatten-p norm is defined as
where denotes the j-th singular value of the view-specific matrix . This formulation simultaneously promotes low-rankness in each view and preserves their shared high-order structures across views.
Equation (5) can extract the specific-view and higher-order information from the incomplete multi-view data, which can obtain better performance. Motivated by [29], consistent information from different perspectives also contributes to performance. Therefore, the representation matrix obtained from each view learns the consensus matrix, and the specific model is shown as
where is the consensus matrix. is the parameter that needs to be adjusted, which is time-consuming and laborious. Hence, we have introduced an adaptive weighting mechanism to assign reasonable weights to different perspectives, and the model is defined as follows:
where can be solved by Lagrangian function. Specifically refer to [30], the solution of is described as follows:
Motivated by [31], preserving the local geometric structure of the original samples is essential for improving clustering performance. Many previous methods impose a Laplacian constraint on the learned affinity matrix to encode structural information. However, the traditional graph Laplacian only models pairwise relations and therefore cannot capture richer high-order sample interactions.
To overcome this limitation, we incorporate a hyper-Laplacian regularization on the latent representation. Our motivation is twofold. First, based on the learned consensus representation , we construct a k-nearest-neighbor hypergraph to complete the relational structure of missing instances. Second, hypergraphs provide a mathematically more expressive framework: each hyperedge can connect multiple vertices simultaneously, enabling the model to encode group-level dependencies across views. This property leads to a high-order Laplacian operator of the form , where denotes the incidence matrix, is the diagonal hyperedge-weight matrix, and and represent the vertex and hyperedge degree matrices. Unlike its pairwise counterpart , the hyper-Laplacian retains a tensor-like aggregation of multi-way relations, providing a more faithful representation of the underlying geometric structure. By embedding this higher-order regularization into our model, we are able to better preserve cross-view structural consistency and accurately infer missing samples. Based on these considerations, we design the following model:
where B is the set of edges in the graph. And , , , and are the weight of the edge, the degree of the edge, the ith missing sample, and the jth no missing sample, respectively. To facilitate matrix operation, Equation (11) can be reformulated as
where denotes the hyper-Laplacian constructed on . is the second adaptive weighting proposed in this paper, which is used to reduce the cost of parameter tuning. Refer to [32]; can be solved by the Lagrange function, and its solution is shown as
where .
By merging Equations (5), (8) and (11), the objective function of the proposed method is designed as follows:
where is a hyperparameter utilized to equilibrate the consensus term. Here, the term corresponds to the Enhanced Tensor component, as the Schatten-p norm enforces a stronger multi-view low-rank tensor structure. Meanwhile, the two learnable weights and in the second and third terms implement the Dual Adaptive Weight mechanism, controlling the contributions of each view in hypergraph structure preservation and consensus learning, respectively.
3.2. Optimization
We adopt ADMM approach to resolve the matrix variable and tensor of the proposed ETIMC. For the convenience of the solution, we introduce the auxiliary tensor , and the Lagrange function of Equation (13) is shown as
(1) Fixed other matrix variables except , the optimization problem of can be solved by the following formula:
Let the derivative of Equation (15) in regard to be 0, and we can obtain the resolution of as
To better obtain the potential representation of the original data, is further optimized and the final solution of is
where .
(2) Fixed other matrix variables except , can be resolved by the following equation:
Let the derivative of Equation (18) in regard to be 0, and we can obtain the resolution of as
(3) By fixing all matrix variables except , the optimization problem can be formulated as
Let us define . Then the objective function can be rewritten as
The derivative of the first term with respect to is given by
Similarly, the derivative of the second term is
By summing the two derivatives and setting the result to zero, we obtain the gradient equation,
Solving this equation for yields the closed-form solution
where .
(4) By fixing the other matrix variables except tensor , the issue became
To solve , we need to introduce the following Theorem 2:
Theorem 2.
Assume , make , for the following equation , We can obtain the solution of as
where denotes the ith frontal slice that can be solved by the Lemma 1 of [33]. Hence, the solution of in Equation (26) can be achieved by the following formula:
(5) Update the multiplier ,
To sum up, the entire optimization procedure for solving Equation (13) is summarized in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Optimization procedure of ETIMC |
|
3.3. Computational Complexity
For the proposed ETIMC, the main calculation cost involves , , and . Concretely, updating takes and solving the subproblem of costs . Updating the tensor involves two stages of costs, namely singular value decomposition, fft and ifft operations. Thus, the total cost is . In summary, the overall computational complexity of the proposed ETIMC is for every iteration.
To provide a more concrete comparison, we further report the estimated running times of ETIMC and two representative baselines (EE-R and UEAF) under the same CPU environment. Based on their theoretical complexities—EE-R: , UEAF: , and ETIMC: —we convert the dominant operation counts into runtime estimates normalized by the same computational throughput. Table 1 summarizes the results on ThreeSources, BBCSport, and BBC. The empirical training times of ETIMC are 4.33 s, 4.63 s, and 11.79 s, respectively, which align well with the complexity-derived estimates and confirm that ETIMC’s runtime grows proportionally with dataset scale. Although ETIMC incurs higher computational overhead, the hypergraph Laplacian mechanism and tensor regularization significantly improve clustering performance, rendering the additional cost worthwhile.

Table 1.
Runtime comparison (in seconds).
4. Experiment
4.1. Experiment Settings
To estimate the presented ETIMC, we selected three natural incomplete multi-view datasets, including ThreeSources (http://mlg.ucd.ie/datasets/3sources.html, accessed on 17 January 2025), BBCSport (http://mlg.ucd.ie/datasets/bbc.html, accessed on 17 January 2025), and BBC (http://mlg.ucd.ie/datasets/bbc.html, accessed on 17 January 2025). Meanwhile, we also chose a commonly utilized complete multi-view dataset named ORL (https://cam-orl.co.uk/facedatabase.html, accessed on 17 January 2025) can be constructed as incomplete data. We develop incomplete multi-view datasets by distinct pairing ratios () ranging from 0.1 to 0.9, with a step size of 0.2, where is the number of instances, and N is a randomly picked pair of samples that can be found in all perspectives. To avoid cases where all views of a sample are missing, we generate missing entries under a random-missing mechanism while enforcing the constraint that each instance retains at least one available view. This ensures both the reproducibility of the experimental setup and the feasibility of downstream reconstruction. A summary of these datasets is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of four real-world datasets.
We select eleven multi-view methods to compare with the proposed ETIMC. The comparison methods include MIC: incomplete multi-view clustering by weighted non-negative matrix decomposition; MKKM and MKKM-MKC: learning consensus representation via kernel-based multi-view methods; AWP: the consensus representation is obtained from the embedded matrix by an adaptive mechanism; PIC: multi-view clustering methods by weight strategy and spectral perturbation theory; APMC: learning the consensus graph through the anchor graph; UEAF: unifying representation matrix learning and inferences of missing samples into one step to acquire important information from multiple views; EE-R: learning the consensus matrix from the low-dimension representation obtained by incomplete multi-view; FLSD: seeking an embedded representation and consensus representation of each perspective via graphs and semantic constraints. DDMVC [34]: it utilizes contrastive learning and diversity objectives to learn diverse and distinguishable representations. This method achieves consistency across all views while preserving, to some extent, the inherent semantic information of each view; RecFormer [35]: is an information-recovery–driven deep incomplete multi-view clustering model that jointly performs feature learning and missing-data reconstruction through a two-stage self-attention autoencoder and a recurrent graph reconstruction mechanism.
We pick six commonly utilized evaluation criteria to measure the quality of the proposed ETIMC. These criteria include accuracy (ACC), normalized mutual information (NMI), purity (PUR), adjusted rank index (AR), F-score, and Precision, respectively. All evaluation criteria follow the principle that a higher value represents a better clustering effect. All the experimental results are the average values of 10 experiments.
4.2. Clustering Performance
The clustering performance of our proposed ETIMC and comparison method is shown in Table 3. The best results are displayed in bold. From the table, we can draw the following conclusions:

Table 3.
Clustering performance on natural incomplete datasets.
- Compared with other methods, the proposed ETIMC can achieve optimal performance on these three natural incomplete datasets. For instance, ETIMC is 3.8%, 8.1%, 3.8%, 7.9%, 6.3%, and 7.1% higher in terms of ACC, NMI, PUR, AR, F-score, and Precision than the second-best algorithm in the BBC dataset. This result indicates that hypergraph regularization, Schatten-p norm, and adaptive mechanism contribute to improving the performance of incomplete multi-view clustering.
- The performance of MIC on the three datasets is poor, which indicates that simply completing the incomplete samples using 0 or the mean value is not conducive to improving the performance of incomplete multi-view clustering. This method may introduce unnecessary noise and obtain incorrect information, leading to performance degradation. On the contrary, FLSD processes incomplete multi-view data by saving the locality of missing samples, and it can obtain better clustering results in most circumstances. However, our proposed ETIMC is superior to FLSD, indicating that capturing higher-order information between multiple perspectives applies to processing multi-perspective data.
- PIC, AWP, and UEAF methods outperform other methods in most cases. The reason is that these three methods all apply an adaptive mechanism, indicating that assigning reasonable weights to different views is also beneficial to the clustering results. The ETIMC develops adaptive weights in consensus representation learning and the construction of incomplete data items, which promotes the performance of the whole algorithm to a certain extent.
- The clustering performance of DDMVC and RecFormer shows a clear decline compared with traditional methods, mainly because deep models are well suited for analyzing data distributions in large-scale datasets but face greater difficulty when learning from small-scale data. Consequently, ETIMC exhibits a clear advantage over deep approaches on small datasets.
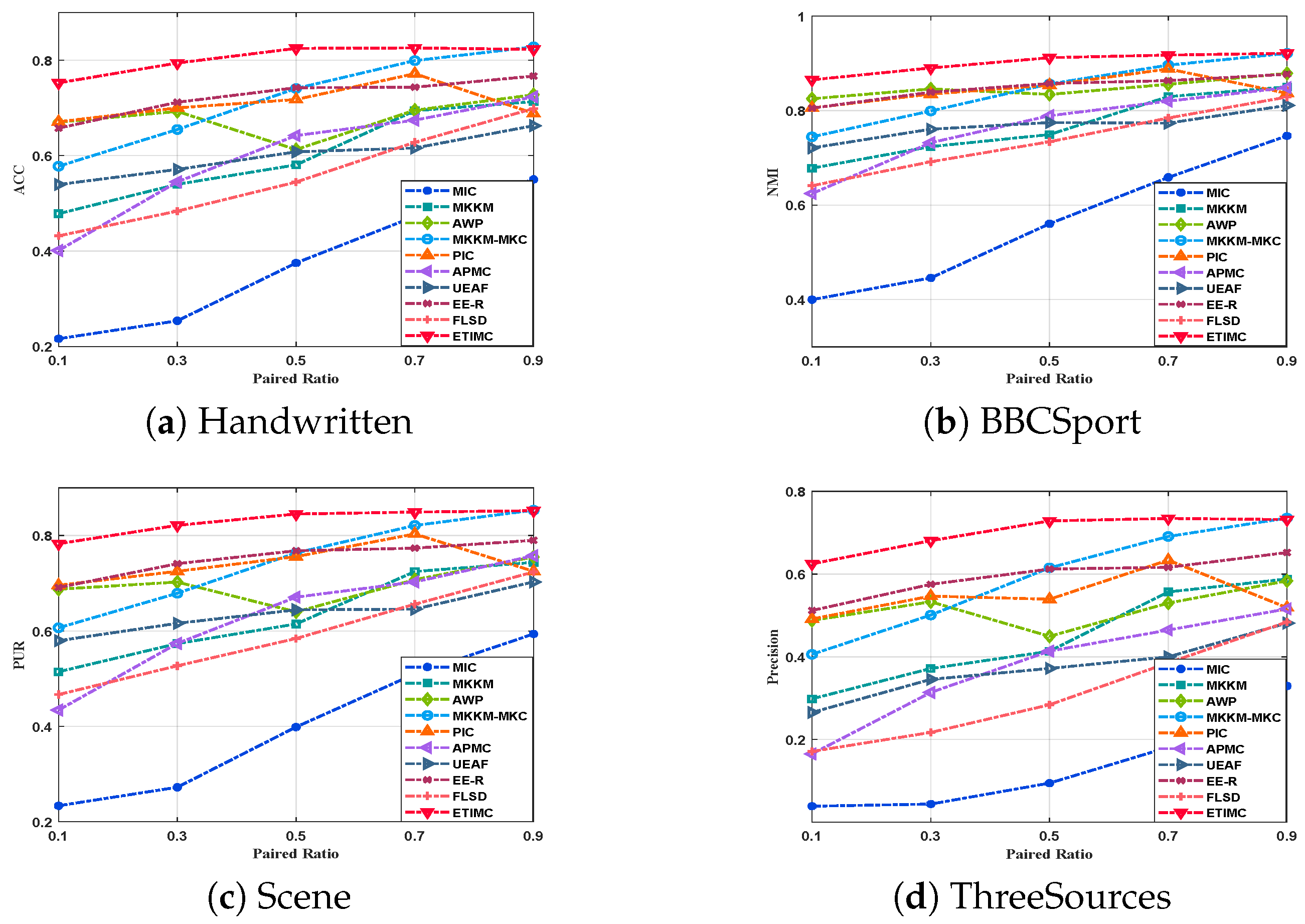
To verify the impact of missing samples on clustering performance, we simulated incomplete data on the ORL complete dataset, and the results are shown in Figure 2. A careful interpretation of Figure 2 leads us to the following conclusions:
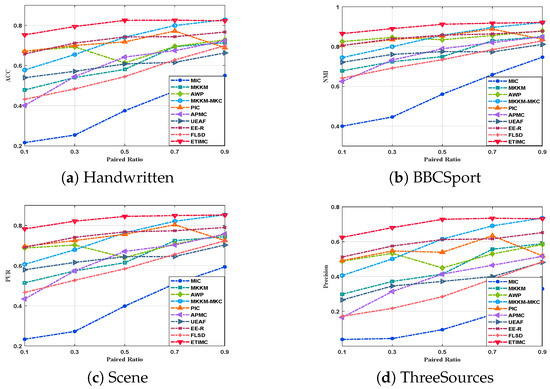
Figure 2.
The clustering results of different algorithms on four datasets under distinct pairing ratios.
- In different miss rates, our proposed ETIMC is superior to other comparison methods. On the one hand, ETIMC applies a dual adaptive mechanism to capture consistent information in incomplete multi-view data and infer incomplete samples with hypergraph constraints. On the other hand, tensor and hypergraph constraints can explore the higher-order information in incomplete multi-view data, which promotes the clustering performance.
- Generally, as pairing ratios increase, the performances of incomplete data improve. However, the ORL dataset reaches the best when the pairing ratio is 0.5, mainly because the incomplete data may be disturbed by noise. Since the proposed ETIMC adopts the dual adaptive weight mechanism, the hypergraph Laplacian regularization, and tensor constraint to process the incomplete multi-view data. Therefore, ETIMC has the ability to process noise data.
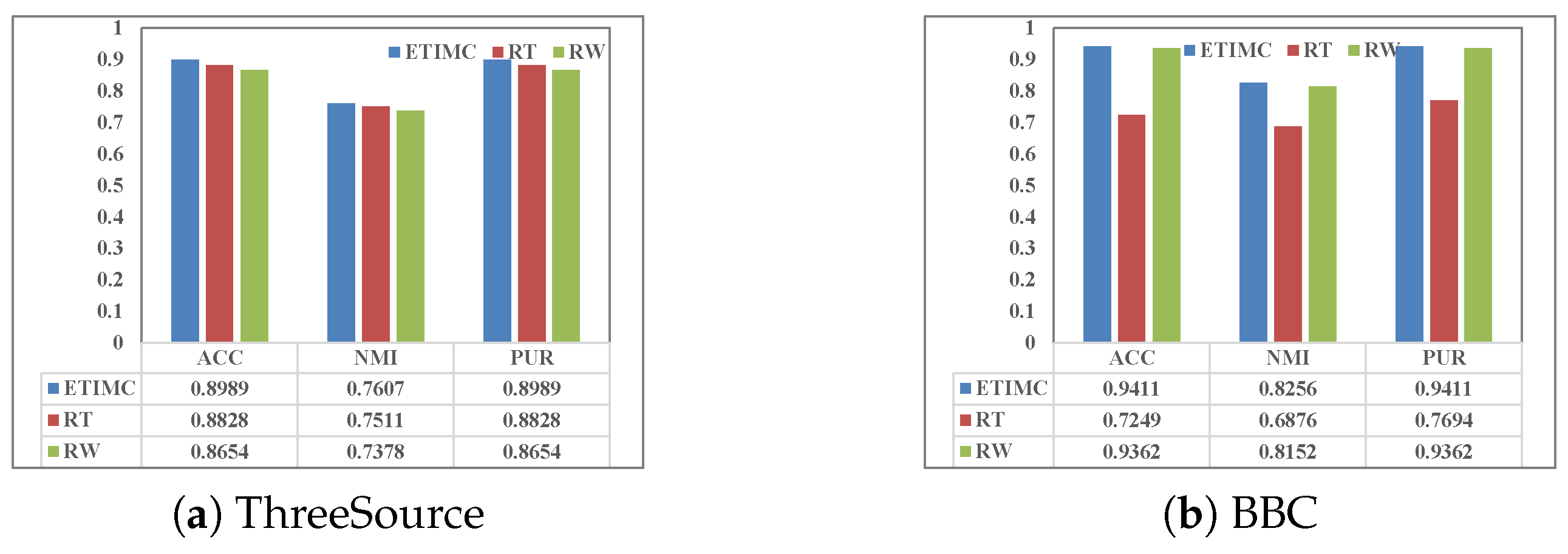
4.3. Ablation Study
In the proposed ETIMC, we stack the embedded representations obtained into third-order tensors to obtain higher-order information in incomplete multi-view data. Additionally, we introduce a dual adaptive weighting mechanism to distinguish the contribution degree of different views and reduce the cost of parameter tuning. To verify the effectiveness of the higher-order relationship and the dual adaptive weighting mechanism, we conducted ablation experiments on three incomplete datasets, shown in Figure 3. We can observe from Figure 3 that the performance of the proposed ETIMC is superior to RT and RW in all datasets, where RT and RW, respectively denote the results after the removal of tensor constraints and the dual adaptive weighting mechanism.
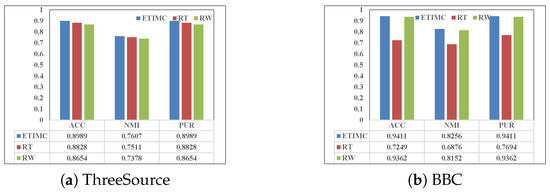
Figure 3.
Ablation studies on three natural incomplete datasets.
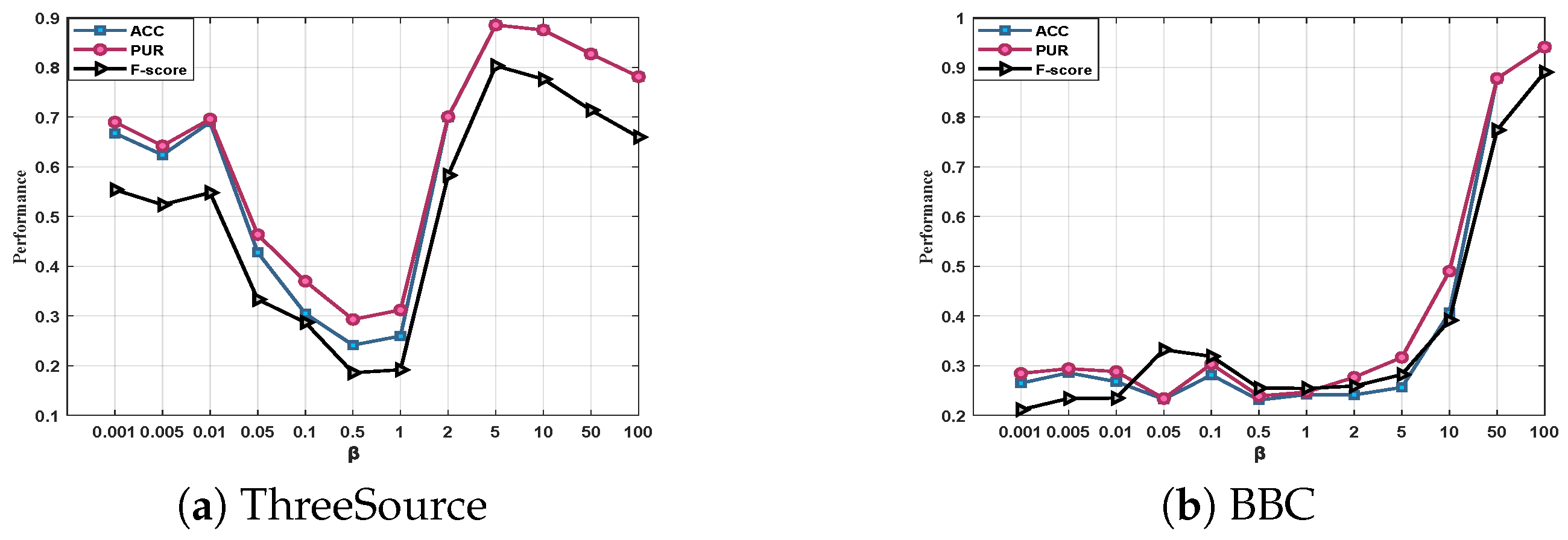
4.4. Parameter Analysis
The proposed ETIMC involves a parameter in Equation (13) that needs to be adjusted. To explore the effect of on the overall clustering performance, we performed parametric analysis experiments on ThreeSources, BBCSport, and BBC incomplete datasets. We report how changes in the range of , shown in Figure 4. As seen from Figure 4, ACC, PUR, and F-score change correspondingly with the constant change in , indicating that ETIMC proposed in this paper is sensitive to .
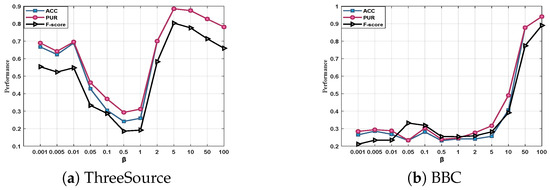
Figure 4.
Parameter analysis on three natural incomplete datasets.
4.5. Convergence Analysis
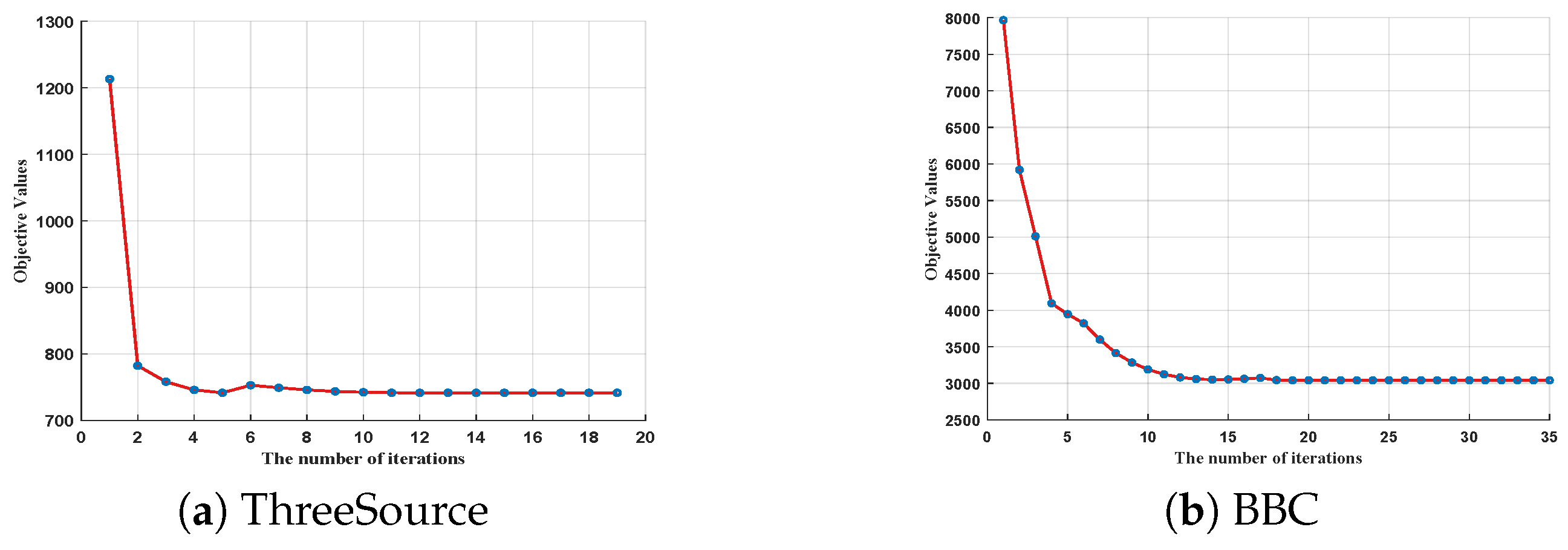
To illustrate the convergence of the proposed ETIMC, Figure 5 shows the change in the value of the objective function with the number of iterations. As can be seen from Figure 5, the objective function values of all three natural incomplete data converge within 30 iterations, indicating that the proposed ETIMC has good convergence.
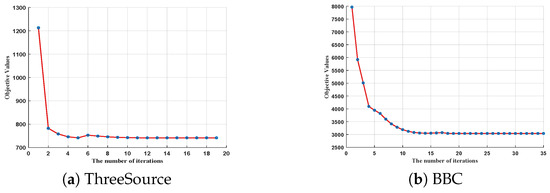
Figure 5.
Convergence analysis on three natural incomplete datasets.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a new method called ETIMC that can tackle multi-view data with missing samples. Different from previous approaches, ETIMC integrates higher-order relational learning, consistent information learning, and inference of incomplete data into one framework. By utilizing tensor constraints, dual adaptive weighted mechanism, and hypergraph Laplacian constraints, ETIMC can infer the internal association information between the missing samples and the available samples, which is conducive to acquiring a more suitable consensus matrix for final clustering tasks. However, the tensor operations in ETIMC impose high computational and memory costs on large-scale data. Future work will focus on introducing complexity-reduction techniques to improve its scalability.
Author Contributions
J.Z., conceptualization, methodology, writing, algorithm, validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation; W.L., investigation, data curation and supervision; Z.X., funding acquisition and formal analysis; C.Z., investigation and data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Postgraduate Research and Innovation Project of Huzhou University under Grant 2025KYCX59, and the Huzhou Science and Technology Plan Project under Grant 2024YZ39.
Data Availability Statement
The data has been presented in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
We confirm that we have given due consideration to the protection of intellectual property associated with this work and that there are no impediments to publication, including the timing of publication, with respect to intellectual property. We confirm that we have followed the regulations of our institutions concerning intellectual property.
References
- Cai, X.; Huang, D.; Zhang, G.-Y.; Wang, C.-D. Seeking commonness and inconsistencies: A jointly smoothed approach to multi-view subspace clustering. Inf. Fusion 2023, 91, 364–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, C.-D. Facilitated low-rank multi-view subspace clustering. Knowl. Based Syst. 2023, 260, 110141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Huang, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chen, C. Subspace-contrastive multi-view clustering. ACM Trans. Knowl. Discov. Data 2024, 18, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Lu, G.-F.; Ji, G.-Y. Robust and optimal neighborhood graph learning for multi-view clustering. Inf. Sci. 2023, 631, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Robust Multi-view Clustering via Graph-oriented High-order Correlations Learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, G.; Xu, K.; Xie, X.; Chen, Y. Global Graph Propagation with Hierarchical Information Transfer for Incomplete Contrastive Multi-view Clustering. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 15713–15721. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, A.; Rai, P.; Daumé, H., III; DuVall, S.L. Multiview clustering with incomplete views. In NIPS Workshop; NeurIPS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; Volume 224, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Peng, Y.; Jian, S. Incomplete multi-view clustering. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing (IIP), Melbourne, Australia, 18–21 November 2016; pp. 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, Y. Incomplete multi-modal visual data grouping. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, New York, NY, USA, 9–15 July 2016; pp. 2392–2398. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Fei, L.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Y. Unified tensor framework for incomplete multi-view clustering and missing-view inferring. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 10273–10281. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Chen, S. Doubly aligned incomplete multi-view clustering. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.02785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Y.; Liu, J. Interpretable unsupervised neural network structure for data clustering via differentiable reconstruction of ONMF and sparse autoencoder. Neural Netw. 2025, 188, 107504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tang, C.; Liu, X.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, E. Tensor-Based Multi-View Block-Diagonal Structure Diffusion for Clustering Incomplete Multi-View Data. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference Multimedia Expo (ICME), Shenzhen, China, 5–9 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Lv, W.; Huang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C. Enhanced tensor low-rank and sparse representation recovery for incomplete multi-view clustering. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 11174–11182. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Zhu, E.; Liu, T.; Kloft, M.; Shen, D.; Yin, J.; Gao, W. Multiple kernel k-means with incomplete kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 42, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Yan, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.; Fei, L.; Zhang, B. Adaptive graph completion based incomplete multi-view clustering. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Z.; Wen, J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C. Localized sparse incomplete multi-view clustering. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 5539–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Fei, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, B. Dimc-net: Deep incomplete multi-view clustering network. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 3753–3761. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fei, L.; Zhang, B.; Xu, Y. Structural Deep Incomplete Multi-view Clustering Network. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, Gold Coast, Australia, 1–5 November 2021; pp. 3538–3542. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Gou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, B.; Lv, J.; Peng, X. Completer: Incomplete multi-view clustering via contrastive prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 11174–11183. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, E. Deep incomplete multi-view clustering with cross-view partial sample and prototype alignment. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 11600–11609. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Ren, Z.; Sun, Y. Dynamic incomplete multi-view imputing and clustering. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3412–3420. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, M.; Hu, P.; Peng, D.; Peng, X. Incomplete multi-view clustering via prototype-based imputation. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Macao, China, 19–25 August 2023; pp. 3911–3919. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Deng, S.; Wong, W.; Chao, G.; Huang, C.; Fei, L.; Xu, Y. Diffusion-based missing-view generation with the application on incomplete multi-view clustering. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024; pp. 52762–52778. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ling, Y.; Xu, J.; Ren, Y.; Huang, S.; Pu, X. Variational graph generator for multiview graph clustering. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 18, 11078–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Gou, Y.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Lv, J.; Peng, X. Dual contrastive prediction for incomplete multi-view representation learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 4447–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Li, C.; Peng, L.; Ren, Y.; Shi, X.; Shen, H.T.; Zhu, X. Adaptive feature projection with distribution alignment for deep incomplete multi-view clustering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Tao, D.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qu, Y. On unifying multi-view self-representations for clustering by tensor multi-rank minimization. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2018, 126, 1157–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Mi, Z.; Fu, X. Tensorial Multi-view Clustering via Low-rank Constrained High-order Graph Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 5307–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Li, J.; Li, X. Self-weighted Multiview Clustering with Multiple Graphs. In Proceedings of the IJCAI, Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 2564–2570. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Qu, Y.; Dai, L.; Tao, D. Hyper-Laplacian regularized multilinear multiview self-representations for clustering and semisupervised learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 50, 572–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S. Unified Low-Rank Tensor Learning and Spectral Embedding for Multi-View Subspace Clustering. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2022, 25, 4972–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, P.; Xia, W.; Xie, D.; Gao, X.; Tao, D. Enhanced tensor RPCA and its application. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 43, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Meng, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, J. Deep multi-view clustering with diverse and discriminative feature learning. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 161, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wen, J.; Wu, Z.; Luo, X.; Huang, C.; Xu, Y. Information Recovery-Driven Deep Incomplete Multiview Clustering Network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 35, 15442–15452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.