Abstract
In autonomous-driving real-time semantic segmentation, simultaneously maximizing accuracy, minimizing model size, and sustaining high inference speed remains challenging. This tripartite demand poses significant constraints on the design of lightweight neural networks, as conventional frameworks often suffer from a trade-off between computational efficiency and feature representation capability, thereby limiting their practical deployment in resource-constrained autonomous driving systems. We introduce ISANet, an information supplementary aggregation framework that markedly elevates segmentation accuracy without sacrificing frame rate. ISANet integrates three key components: (i) the Spatial-Supplementary Lightweight Bottleneck Unit (SLBU) that splits channels and employs compensatory branches to extract highly expressive features with minimal parameters; (ii) the Missing Spatial Information Recovery Branch (MSIRB) that recovers spatial details lost during feature extraction; and (iii) the Object Boundary Feature Attention Module (OBFAM) that fuses multi-stage features and strengthens inter-layer information interaction. Evaluated on Cityscapes and CamVid, ISANet attains 76.7% and 73.8% mIoU, respectively, while delivering 58 FPS and 90 FPS with only 1.37 million parameters.
1. Introduction
Semantic segmentation stands as a challenging research direction in the field of autonomous driving. With the growing demand for higher segmentation accuracy in autonomous driving systems, semantic segmentation models have become increasingly complex—this complexity is reflected in larger model sizes and longer running times. Thus, ensuring both high segmentation accuracy and fast inference speed has become a key challenge that must be addressed.
To enhance segmentation accuracy and inference speed, a large number of segmentation networks have been proposed in recent studies. For instance, PSPNet [1] and ICNet [2] introduced composite pyramid structures, which are designed to expand receptive fields and extract feature information across different scales. However, the complexity of these pyramid structures increases computational pressure, thereby exerting a negative impact on segmentation efficiency. BiSeNet [3] put forward a dual-branch segmentation network, enabling the separate acquisition of spatial features and semantic features. RESNet [4] developed a residual structure: by mapping input features to a low-dimensional space before performing convolutional operations, this structure reduces computational load and mitigates overfitting. Additionally, some models have adopted a dual-branch structure to compress input images and boost inference speed, but this image compression leads to the loss of feature information, ultimately lowering segmentation accuracy. Although BiSeNet V2 [5] optimized its fusion module to achieve better segmentation results, it also increased the number of parameters and computational burden, which in turn affects operational efficiency.
Since the advent of BiSeNet V2, an increasing number of models have focused on two core goals: preserving the integrity of spatial information and maintaining the richness of diverse features [6,7,8,9]. ERPNet [10], for example, proposed a feature branch that retains high-resolution information to acquire spatial features, but this method overly depended on abundant spatial feature information, making it unsuitable for processing low-resolution images. DB-Net [11] integrated feature fusion modules into their U-shaped structures to enhance the integrity of spatial features in the encoder; however, as the network depth increased, spatial details continued to be lost, which impaired segmentation accuracy. RoboSeg [12] utilized spatial detail reconstruction to supplement missing spatial information in the feature extraction branch, but this approach increased computational burden and slowed down inference speed.
To tackle these existing issues—while improving segmentation accuracy and enhancing efficiency—this paper proposes a novel ISANet based on lost feature compensation. ISANet is designed with a new multi-aggregation architecture, which includes a Spatial Feature Acquisition Branch (SFAB) and a Missing Spatial Information Recovery Branch (MSIRB). Specifically, the SFAB adopts the Spatial Detail Acquisition Module (SDAM) to improve the richness of spatial features; at the same time, the MSIRB extracts lost spatial details from the feature extraction module, thereby enhancing the integrity of spatial details. These two branches ensure the integrity of spatial features with only a small number of additional parameters, effectively improving segmentation accuracy.
In order to reduce computational burden and boost segmentation efficiency, ISANet does not use a pre-trained model; instead, it designs a Spatial-Supplementary Lightweight Bottleneck Unit (SLBU) to construct the network backbone. The SLBU employs depth-wise separable dilated convolution to expand receptive fields and obtains complete spatial features through compensation branches—this design helps improve the model’s feature extraction capability. Furthermore, the Object Boundary Feature Attention Module (OBFAM) is applied in ISANet to fuse branch information, which further improves segmentation accuracy.
The main contributions are summarized as follows:
- An SLBU is developed for the extraction of feature information. The SLBU has a small number of parameters, yet it can acquire rich semantic features. Moreover, by leveraging compensation branches to supplement the lost spatial details, the SLBU is able to enhance the integrity of spatial features.
- An OBFAM is put forward for the effective fusion of feature information and compensation information. The OBFAM boosts segmentation performance by integrating spatial attention branches and channel attention branches, which in turn strengthens the correlation between features.
- A lightweight real-time semantic segmentation network named ISANet is proposed. This network generates only a small number of parameters but still achieves excellent segmentation accuracy and fast segmentation speed.
To facilitate readers’ understanding of this paper, the structure of the article is organized as follows: Section 2, “Related Work”, systematically reviews the research status and limitations in four key directions, including semantic information utilization, spatial information recovery, attention mechanisms, and real-time semantic segmentation architectures. Section 3, “Proposed Method”, elaborates on the overall architecture of ISANet, covering the design principles of the SLBU and OBFAM, as well as the working mechanisms of the SFAB and MSIRB. Section 4, “Experiments”, introduces the experimental datasets and parameter settings, verifies the effectiveness of each module through ablation experiments, and compares the performance of ISANet with that of existing mainstream models. Section 5, “Conclusion and Future Work”, summarizes the core contributions of ISANet, analyzes the model’s limitations, and proposes future research directions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Semantic Information
Integrating high-quality semantic information—which consists of a large number of image features [13,14,15,16]—can help improve segmentation precision. To enhance the performance of pixel classification, researchers have proposed several models; these models typically achieve this goal by either integrating semantic information from other network stages or preserving more context information from global features. For example, JPANet [17] introduced a connected feature pyramid module to optimize feature utilization; SGCPNet [18] designed a multi-layer feature fusion module, which enables the capture of more context information. RELAXNet [19] promoted the interaction between local information and contextual information, thereby improving both information utilization efficiency and overall segmentation efficiency. In contrast, MFFN [20] developed a lightweight residual module, which performs weighted fusion on feature information from different channels to enhance the richness of features. The experimental results of these models have collectively demonstrated that two strategies can lead to better segmentation outcomes: one obtains comprehensive global context information, and the other expands the receptive field.
2.2. Spatial Information
As the number of convolutional layers increases and as downsampling modules are continuously employed, spatial information is inevitably lost—and this lost information is difficult to recover. Consequently, enhancing the integrity of spatial features and acquiring complete spatial details have become critical to improving segmentation accuracy. To address this challenge, various models have developed specialized solutions. Specifically, LEDNet [21] and EFRNet [22] integrate features from different network stages, which helps improve the richness of spatial features. DSANet [23] proposes a spatial encoding module, enabling the acquisition of relatively complete spatial details. SFANet [24] designs a stage-aware Feature Enhancement Block, which functions to strengthen the correlation of spatial features across different stages. DFFNet [25] integrates multi-level features to jointly learn spatial and semantic information with low computational overhead. SEDNet [26] employs a feature fusion module to combine features from different stages and utilizes channel attention based on Atrous Convolution to expand the receptive field. This design avoids dimensionality reduction during the learning process and enhances the integrity of spatial features. MSDSeg [27] introduces a cross-layer Attention Fusion Module, which effectively fuses multi-layer feature information and narrows the discrepancy between high-level and low-level features. Additionally, it leverages a Feature Enhancement Head based on global average-pooling and global max-pooling to improve the detection performance of objects and their boundaries. These approaches optimize spatial information from a single dimension (e.g., fusion, encoding, attention), failing to establish a closed-loop framework for lost information detection, targeted recovery, and efficient fusion. This results in significant trade-offs among spatial detail integrity, computational efficiency, and scene adaptability.
2.3. Attention Mechanism
In recent years, the widespread application of attention mechanisms in the field of deep learning originated from the transformer architecture proposed by Vaswani et al. [28,29]. In their work “Attention is All You Need”, they proposed a pure attention architecture that abandons the sequential dependence of traditional recurrent neural networks (RNNs). By capturing global feature dependencies and enabling parallel computation through self-attention mechanisms, this architecture not only laid the foundation for the development of attention models but also promoted their gradual penetration from the field of natural language processing (NLP) to multiple domains such as computer vision (CV) and finance. Currently, attention mechanisms have been implemented and demonstrated value in various fields: In the NLP field, Longformer [30] addresses long-text processing issues using sliding window attention, while Reformer [31] reduces computational complexity via locality-sensitive hashing (LSH). In the CV field (especially in the direction of semantic segmentation), ECANet [32] and BiAttnNet [33] filter semantic details through detail branches; WFDCNet [34] and AaSeg [35] enhance feature dependencies by fusing channel and spatial attention; LETNet [36], Seaformer [37], and DARGS [38] optimize accuracy and speed through structural fusion or unit innovation; additionally, Performer [39] improves model efficiency by means of random projection. In the finance field, Helformer combines attention mechanisms with transformers for cryptocurrency prediction, achieving an 8–12% higher accuracy than traditional models [40]. Overall, the core advantage of attention mechanisms lies in accurately capturing critical feature dependencies: they not only optimize feature mapping and strengthen inter-level correlations but also reduce noise interference during fusion—this is particularly prominent in semantic segmentation, where they can directly improve accuracy. Cross-domain practices have all confirmed their role in optimizing model performance.
2.4. Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Structure
Current real-time semantic segmentation models still face the challenge of improving the model’s segmentation accuracy while ensuring model inference efficiency and reducing the number of model parameters. Early studies [1,2,4] adopted the dilated architecture (Figure 1a), which acquires rich semantic features through dilated convolution. However, due to the frequent use of downsampling, it fails to extract complete spatial details, thereby affecting segmentation accuracy. The multi-pathway architecture (Figure 1b) is designed with dedicated extraction paths for different features to ensure the richness of feature information [3,5,41,42]. Nevertheless, the lack of information interaction between branches leads to an increase in parameters and a reduction in segmentation efficiency. The encoder–decoder architecture (Figure 1c) was applied in studies [14,23,43]; it extracts feature information through encoding and restores image resolution through decoding. However, spatial features may be lost during the resolution restoration process, which impairs accuracy. The attention architecture (Figure 1d) aggregates features in a selective manner: the feature at each position is a weighted sum of features from all positions, and this aggregation can be implemented across either the channel or spatial dimension [26,27]. However, the attention architecture struggles to recover the spatial information lost during feature extraction operations, ultimately affecting the model’s segmentation accuracy. Through the “compensation–recovery–fusion” tripartite design, ISANet achieves accurate extraction of lost features, thereby improving the model’s segmentation accuracy without additional increases in the number of parameters and computational burden.
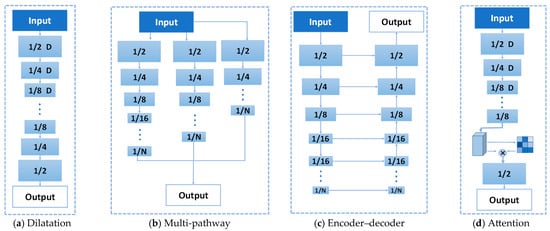
Figure 1.
Real-time semantic segmentation model structure comparison. (a) Dilation architecture. (b) Multi-pathway architecture. (c) Encoder–decoder architecture. (d) Attention architecture.
3. Proposed Method
In this section, the proposed ISANet will be introduced as follows: (1) SLBU; (2) OBFAM; (3) the overall structure of the ISANet. The detailed structure of the proposed ISANet is shown in Figure 2.
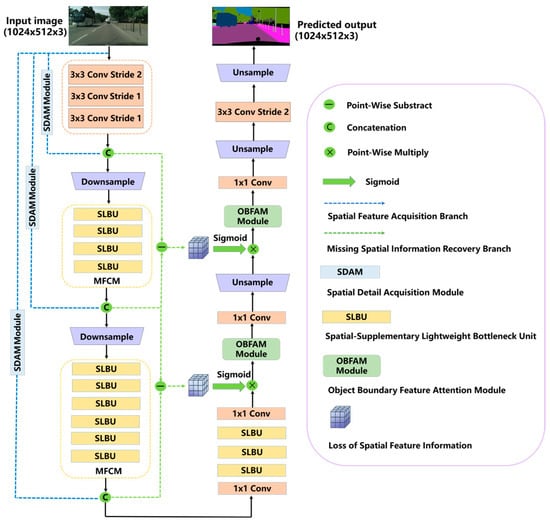
Figure 2.
The complete architecture of our proposed ISANet. The blue dashed line indicates the SFAB, and the green-dashed line indicates the MSIRB.
3.1. Spatial-Supplementary Lightweight Bottleneck Unit (SLBU)
The traditional residual bottleneck unit mainly aims to efficiently extract contextual and spatial information from feature maps, as shown in Figure 3a–c. Yet, these methods often neglect the loss of spatial details during feature extraction, leading to less-than-ideal segmentation results. To address this, we propose the SLBU: it is designed with a lost information compensation branch, which can effectively supplement lost spatial information while extracting feature information at each stage.
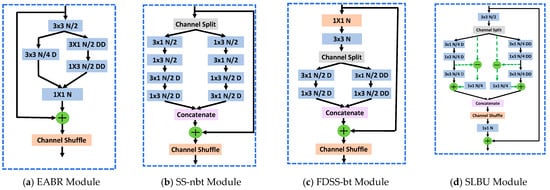
Figure 3.
Comparison with other network bottleneck residual modules. “N” is the number of output channels, “D” indicates depth-wise separable convolution, and “DD” denotes depth-wise dilated separable convolution. (a) EABR Module of RELAXNet [19]. (b) SS-nbt Module of LEDNet [21]. (c) FDSS-bt Module of DFFNet [25]. (d) The proposed SLBU. The green dotted line in (d) represents the reuse of the spatial details lost in feature extraction.
As shown in Figure 3d, the SLBU integrates a green-dashed “lost-information compensation” route. Incoming channels are first split into two parallel processing streams; this design not only reduces FLOPs but also promotes the generation of complementary encodings. The first stream employs depth-wise separable convolutions to capture neighboring fine-grained cues, while the second stream leverages deeply stacked dilated convolutions to model long-range contextual information. Within each stream, traditional n × n depth-wise kernels are substituted with consecutive n × 1 and 1 × n depth-wise operators. This modification expands the receptive span while reducing the per-pixel computational workload [44,45,46,47]. To alleviate the gridding artifacts typically caused by dilated convolutions [48], the SLBU adopts a steadily increasing dilation schedule (from small to large), which helps smooth the sampling lattice [49]. A subsequent channel shuffle operation re-establishes inter-group connectivity and further enhances the model’s representational capacity.
To visually demonstrate the proposed SLBU, the detailed steps are shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: SLBU |
| Input: input image |
| Output: feature map |
| 1: |
| 2: |
| 3: |
| 4: |
| 5: |
| 6: |
| 7: |
| 8: |
| 9: |
Here, denotes a depth-wise convolution with an kernel, followed by BatchNorm and PReLU operations. denotes a depth-wise separable convolution with an kernel, followed by BatchNorm and PReLU operations. represents the channel split operation, denotes the feature fusion operation, and denotes the channel shuffle.
3.2. Object Boundary Feature Attention Module (OBFAM)
Most semantic segmentation models utilize skip connections for fusing feature information across different stages. Nevertheless, the characteristic information of distinct locations exhibits unique attribute features: high-level features contain abundant contextual information, yet their spatial information remains incomplete due to downsampling processes; in contrast, low-level features retain relatively complete spatial information, but their contextual information is insufficient. Thus, fusing low-level and high-level features via skip connections may not yield optimal fusion performance.
To resolve this issue, numerous segmentation networks have incorporated attention mechanisms to selectively highlight salient features and fuse them at various stages of feature maps [50,51,52,53]. Correspondingly, we propose the OBFAM to efficiently fuse supplementary spatial features by extracting branches for model features. As illustrated in Figure 4, OBFAM comprises spatial and channel attention branches. For the channel attention branch, global average-pooling (GAP) and 1 × 1 standard convolution are employed to capture channel feature information. This design better fits the nonlinearity degree between channels, enhances inter-channel correlation, and reduces computational overhead. For the spatial attention branch, average-pooled and max-pooled features are acquired through parallel average-pooling and max-pooling operations, respectively, endowing the branch with superior spatial representation capability.
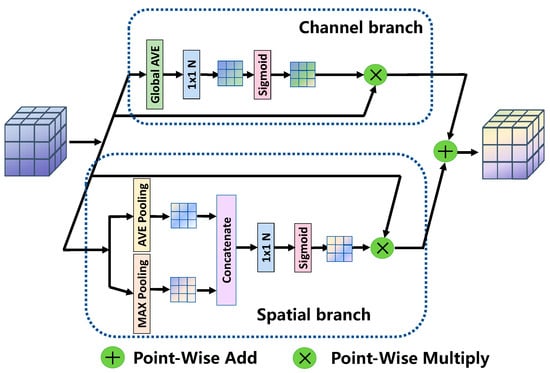
Figure 4.
The structure of OBFAM.
Though both OBFAM and CBAM [52] incorporate spatial and channel attention mechanisms into their designs, the two models differ entirely from each other. In terms of the channel attention mechanism, CBAM compresses the spatial dimension of the input feature map—this compression results in the loss of feature information, which in turn impairs the final segmentation performance. On the contrary, the OBFAM makes use of 1 × 1 convolution, a method that maximizes the preservation of feature information.
When it comes to the spatial attention mechanism, CBAM first concatenates the feature maps generated by two pooling operations, then applies a convolution operation to construct a spatial attention map. This sequence of operations has a negative impact on the model’s inference speed. By contrast, OBFAM adopts a simple addition operation, which effectively balances the relationship between segmentation accuracy and inference speed. The specific implementation steps of EFAM are detailed in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2: OBFAM |
| Input: input image |
| Output: feature map |
| 1: |
| 2: |
| 3: |
Here, denotes the global average-pooling operation, represents a standard convolution with a 1 × 1 kernel, indicates the Sigmoid operation, represents the mean of a tensor with dimension 1, denotes the feature fusion operation, and denotes the maximum value of a tensor with dimension 1.
3.3. Information Supplementary Aggregation Network (ISANet)
The whole network can be split into three branches: the SFAB, the MSIRB, and the main branch of feature extraction. The feature extraction branch includes the Initial Block, the OBFAM, downsampling module, and the MFCM composed of different SLBU. Different dilation rates ranging from minor to large are applied to avoid grid artifacts for better results [48,49], with a series of prime numbers {3,3,7,7,13,13} designed as MFCM dilated rates. The overall network is presented in Figure 2, and the detailed operation configuration is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Detailed architectural configuration of ISANet.
Downsampling Block: The downsampling block employs the initial block structure of Enet [54], and this design works by enlarging the receptive field, enabling more effective collection of context information. That said, excessive downsampling may result in feature maps with low resolution and incomplete spatial information, which in turn exerts a negative impact on segmentation accuracy. In order to balance inference speed and segmentation accuracy, ISANet is configured with only two downsampling blocks; in the end, the size of the sampled image is reduced to 1/8 of the input image.
Spatial Feature Acquisition Branch (SFAB): To make up for the spatial features lost in the process of feature extraction, the SFAB captures feature maps with different resolutions from the input images. Feature extraction for this branch is accomplished through the SDAM, of which specific position is shown by the blue dashed line in Figure 2. Designed as a shallow structure, the SDAM processes feature mapping by utilizing two parallel connections for avg-pooling and max-pooling. After that, a 3 × 3 convolution is used to capture the feature information produced by the feature mapping. Among these operations, max-pooling serves to retain texture information, while avg-pooling is responsible for maintaining scene information—together, they achieve the transfer of feature information across different stages.
Missing Spatial Information Recovery Branch (MSIRB): Through skip connections, the MSIRB restores the lost spatial edge features to the main branch feature map with the corresponding resolution. Meanwhile, it extracts the differential feature maps before and after each MFCM by means of upsampling and 1 × 1 convolution. These differential feature maps contain a large number of spatial edge features that were lost during feature extraction operations. As a consequence, the spatial information of the target feature map can be preserved, and segmentation accuracy is thereby enhanced. This design not only effectively strengthens the correlation of spatial features inside the segmentation network but also increases the richness of edge information and improves segmentation efficiency.
4. Experiments
In this section, datasets and experimental designs are described. The ablation experiments of ISANet main modules are conducted on the urban Cityscapes datasets. Finally, the proposed model is compared with other excellent methods on Cityscapes and CamVid datasets, proving the excellence of the proposed model.
4.1. Experimental Settings
4.1.1. Cityscapes
The urban scene dataset Cityscapes [55] contains images with a resolution of 1024 × 2048, covering 19 semantic categories in total. The dataset is split into three subsets: the training set comprising 2975 images, the validation set comprising 500 images, and the testing set comprising 1525 images. In our experiments, only the images with detailed and accurate labels were utilized for the testing process.
4.1.2. CamVid
CamVid [56] serves as an additional dataset tailored for urban scene tasks in autonomous-driving applications. This dataset features images with a resolution of 360 × 480, covering 11 distinct semantic categories in total. The 367 images included in CamVid are split into three subsets: the training set, the verification set, and the test set. Specifically, the verification set contains 101 images, while the test set comprises 233 images.
4.1.3. Settings
All experiments are carried out on the Python 3.10 platform, with a Titan XP GPU, PyTorch 1.8, CUDA 11.7, and cuDNN V8.4 serving as supporting hardware and software. The evaluation tests for inference speed are performed on a single Titan XP GPU; in these tests, we calculate the average value based on 100 frames, with the measurement unit being FPS. For the data enhancement process, during the model training phase, we employ three strategies for the input images: random horizontal flipping, average subtraction, and random scaling. The specific values included in the random scaling operation are {0.75,1.0,1.25,1.5,1.75,2.0}.
For the Cityscapes, the small-batch stochastic gradient descent (SGD) algorithm [57] is used for model training. Specifically, the batch size is configured as 8, the momentum is set to 0.9, and the weight decay is set to 10−4. In terms of the learning rate strategy, the ‘poly’ strategy is employed; the initial learning rate is set to 4.5 × 10−2, and the corresponding power parameter is 0.9. The calculation formula for the learning rate can be expressed as follows:
Additionally, online hard sample mining losses (OHEM) are used as the loss function for model training. Given that the network does not utilize a pre-training scheme, we set the number of training epochs to 1000, which helps in achieving the optimal training effect.
For the CamVid dataset, the Adam optimizer is employed to optimize the training process. The specific parameters of this optimizer are configured as follows: momentum is set to 0.9, the associated weight decay is 10−4, and the batch size is 8. Meanwhile, the initial learning rate is set to 10−4, and all models are trained for a total of 1000 epochs. With reference to the approach in ENet, a class weighting scheme is applied to the CamVid dataset to address the issue of class imbalance. This class weighting scheme is defined as follows:
where c is an additional super parameter set to 1.10.
4.2. Ablation Studies
This section focuses on validating the performance of each module within the entire network, and this validation is carried out through adequate ablation experiments. To analyze the experimental effects, we use the Cityscapes datasets as the experimental basis. Specifically, the ablation experiments themselves are conducted on the Cityscapes training dataset, while the Cityscapes validation dataset is utilized to evaluate the effects of these experiments.
4.2.1. Ablation Study for MFCM
In the ISANet model, the MFCM incorporates SLBU in varying quantities. To explore how the backbone depth and dilated rate influence segmentation efficiency, we designed a series of MFCM modules—each equipped with a different number of SLBU—to conduct comparative experiments. For these experiments, we conducted comparisons using three key metrics: mIoU, FPS, and Params. Here, M and N denote the different numbers of SLBU used in the two MFCM modules, and the specific experimental results are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Evaluation results of different model depth on Cityscapes. M and N represent the number of SLBUs used by the two MFCM.
As displayed in Table 2, both the number of MFCM modules and the configured dilated rate exert a notable influence on segmentation accuracy. The MFCM module is capable of expanding the receptive field to a considerable extent, thereby enabling the acquisition of more abundant feature information. However, with an increase in the number of MFCM modules, the dilated rate will also rise continuously—this phenomenon not only leads to a decline in segmentation accuracy but also generates more model parameters, which in turn has a negative effect on inference speed. For this reason, the SLBU is set with parameters M = 4 and N = 6. Additionally, by examining the experimental groups involving MFCM modules with the same number of SLBUs, it can be observed that better segmentation accuracy is achieved when the dilated rates are set to {2,2} and {3,3,7,7,13,13}, respectively.
4.2.2. Ablation Study of SDAM and MSIRB
This section aims to confirm the advantages of SIEB and MSIRB in enhancing spatial information, and this confirmation is realized through ablation experiments. As presented in Table 3, the MSIRB module manages to improve the segmentation accuracy performance by 3.1%, and it accomplishes this with only a small increase in the number of parameters. For the SFAB, although its parameter count rises by 0.05 M, it achieves a segmentation accuracy of 73.3%—a value significantly higher than the 70.6% segmentation accuracy of the basic model.

Table 3.
Evaluation results of SDAM and MSIRB on Cityscapes.
The results of these four ablation experiments indicate that both MSIRB and SFAB exert a positive effect on the model, effectively boosting the segmentation precision. Taking into account the lightweight structural design goal of ISANet, we integrate the SFAB and MSIRB modules into the model; this integration enables the model to reach a mIoU of 76.7% while maintaining a real-time inference speed of more than 50FPS. Ultimately, the experimental results prove that the proposed SDAM and MSIRB modules can enhance segmentation accuracy without compromising inference speed.
4.2.3. Ablation Study of OBFAM
To conduct comparative analyses on the Cityscapes and CamVid datasets, we compare the classic SE module [51], CBAM [52], and our proposed OBFAM in Table 4 and Table 5. From these two tables, it can be observed that the network integrated with the SE module attained the lowest segmentation accuracy. The reason for this lies in the fact that the SE module only adopts a channel attention mechanism, failing to make effective use of the spatial information contained in feature maps.

Table 4.
Evaluation results of different attention mechanism modules on Cityscapes.

Table 5.
Evaluation results of different attention mechanism modules on CamVid.
In contrast, both OBFAM and CBAM leverage both spatial and channel attention mechanisms—this design allows them to comprehensively enhance the utilization rate of valuable feature information. Although the CBAM module has 0.02M fewer parameters than the OBFAM, it compresses channel information during operation, which leads to the loss of some feature details. As a consequence, CBAM achieves segmentation accuracy that is 0.7% and 1% lower than that of OBFAM on the two datasets, respectively. In terms of inference speed, the parallel structure of the OBFAM gives it a distinct advantage: it reaches high inference speeds of 58FPS and 90FPS, which are significantly faster than the 21FPS and 33FPS achieved by the CBAM module. Ultimately, ablation experiments confirm that the OBFAM is capable of improving segmentation accuracy without sacrificing inference speed.
4.2.4. Ablation Study of SLBU
This section focuses on comparing the performance of the SLBU with that of other advanced bottleneck units. The modules selected for this comparison include the Bottleneck from RESNet [4], the EABR Module from RELAXNet [19], the SS-nbt Module from LEDNet [21], and the FDSS-bt Module fromDFFNet [25]. As presented in Table 6, the experimental network equipped with the Bottleneck module achieves the quickest inference speed, yet it has the lowest segmentation accuracy. The root cause of this lies in the Bottleneck module’s shallow depth and the small number of branches dedicated to feature extraction. In contrast, the bottleneck units used in other experimental networks feature greater model depth and a multi-branch structure—these characteristics enable them to obtain better segmentation accuracy.

Table 6.
Evaluation results of different feature extraction units on Cityscapes.
Compared with the other comparison units, the SLBU is uniquely designed with an additional lost space information reconstruction branch. This branch can enhance the richness of spatial information and thereby improve segmentation accuracy. The effectiveness of this lost space information reconstruction branch is validated by the SLBU-L model: this model, which removes the reconstruction branch, only sees a slight increase in inference speed (merely 5 FPS). While the SLBU-L model has the same number of parameters as the SLBU, its segmentation accuracy is 1.6% lower than that of the SLBU (which retains the reconstruction branch). These results clearly demonstrate the positive effect of the SLBU on boosting the model’s segmentation accuracy. On the whole, the ablation experiments fully confirm that the SLBU exhibits superior performance when compared with the other bottleneck units in the comparison set.
4.3. Comparison with Other Lightweight SOTA Methods
At the initial stage of model training, the raw images and their corresponding labels are cropped to specific sizes: 512 × 1024 for the Cityscapes dataset and 360 × 480 for the CamVid dataset. This cropping operation helps lower the required amount of computation and reduce the GPU memory consumption. During the testing phase, inference is performed directly using the original size of the dataset images without additional processing.
4.3.1. Results on Cityscapes
As exhibited in Table 7, ISANet achieves the highest IoU in 11 out of 19 categories without utilizing any additional pre-trained data. For the remaining 7 categories where it does not rank first, ISANet still maintains a medium-to-high level of segmentation accuracy. Taking the “Wall” category as an example, ISANet attains an IoU of 54.5%, which is merely 0.1 percentage point lower than the optimal value (85.6% by SEDNet [26]) and significantly outperforms all other comparative models. In the “Terrain” category, ISANet achieves an IoU of 70.4%, trailing only 0.2 percentage points behind the best-performing method (SEDNet [26] with 70.6%). Additionally, ISANet secures a top-two position in categories such as “Fence” and “Truck”, which verifies its competitiveness even in non-top-ranked categories.

Table 7.
Per-class IoU (%) results on Cityscapes. “Avg” represents the average results of all these categories. The best results are shown in bold.
Overall, ISANet ranks first with a mIoU of 76.7%, representing a 0.3 percentage point improvement over the second-ranked SEDNet [26] (76.4%). It also outperforms LBN-AA [60] and LETNet [36] by 3.1 and 3.9 percentage points, respectively. The aforementioned results fully demonstrate that ISANet exhibits superior and comprehensive semantic segmentation performance on the Cityscapes test set.
Table 8 presents quantitative comparisons between ISANet and other lightweight semantic segmentation methods on the Cityscapes. The comparative results show that ISANet is capable of attaining both better segmentation accuracy and faster inference speed, while utilizing a smaller number of parameters. Specifically, models that have the same parameter count as ISANet fail to reach the same level of segmentation accuracy; on the other hand, models that can achieve segmentation accuracy comparable to ISANet demand a larger number of parameters.

Table 8.
Comparison with state-of-the-arts image semantic segmentation methods on Cityscapes dataset. The best results are shown in bold.
SANet achieves 58 FPS on a single TITAN XP GPU, which comfortably exceeds the 30 FPS threshold required for real-time semantic segmentation applications. While some models demonstrate higher raw speed (e.g., BisNet-V2 at 156 FPS and LETNet at 150 FPS), these models achieve 4.1% and 3.9% lower mIoU, respectively, compared to ISANet.
When evaluating computational efficiency through the lens of parameter count, ISANet’s 1.37 M parameters place it among the more lightweight models in the comparison set. Notably, models with fewer parameters (CGNet, FBSNet, and FDDWNet) sacrifice significant accuracy (5.2–5.9% lower mIoU) to achieve their compact size. Conversely, models approaching or exceeding ISANet’s accuracy (SEDNet, SegFormer, Seaformer) require substantially more parameters (4.8–61.8× higher).
The FLOPs metric further highlights ISANet’s efficiency advantage. With 12.6G FLOPs, ISANet delivers the highest mIoU (76.7%) among models with comparable computational complexity. SEDNet, which achieves 76.4% mIoU (only 0.3% lower), requires 65.9G FLOPs—more than 5× the computational cost of ISANet. Meanwhile, SGCPNet, which operates with the lowest computational cost (4.5G FLOPs), lags behind ISANet by 5.8% in mIoU.
ISANet achieves the highest mIoU (76.7%) among all compared methods, representing a clear accuracy advantage:
It outperforms the next highest accuracy (SEDNet at 76.4%) while using 1/5 of the computational resources.
It exceeds the accuracy of lightweight transformer-based models like LETNet by 3.9%.
It outperforms other efficient architectures such as DABNet and BisNet-V2 by 6.6% and 4.1%, respectively.
Qualitative analysis (Figure 5) confirms these quantitative results, with ISANet demonstrating superior segmentation at object boundaries and for small objects including street lamps, billboard outlines, and bus rearview mirrors. Notably, under challenging conditions with strong lighting interference and complex backgrounds, ISANet maintains accurate segmentation without misclassifying building edges as street lamps—a common error observed in DABNet and BiSeNet-V2. This edge preservation capability stems from ISANet’s effective capture and preservation of spatial feature integrity throughout the network.
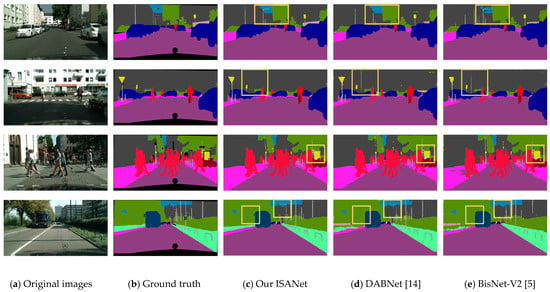
Figure 5.
Semantic segmentation results on Cityscapes. (a) Original images. (b) Ground truth. (c) Our ISANet. (d) DABNet [14]. (e) BisNet-V2 [5].
ISANet’s multi-branch architecture introduces moderate computational overhead compared to the simplest single-branch designs, but this investment is strategically justified by the resulting accuracy gains. The network achieves an optimal balance between segmentation accuracy, computational efficiency, and real-time performance—a critical triad for practical deployment in resource-constrained environments such as autonomous driving systems. This balanced performance distinguishes ISANet from competitors that typically sacrifice either accuracy for speed or efficiency for precision.
4.3.2. Results on CamVid
We further conducted an evaluation of ISANet’s performance on the CamVid testing dataset and organized the evaluation results into Table 9. When compared to models with a similar parameter size, ISANet achieves higher segmentation accuracy. When pitted against larger models (in terms of parameter count), ISANet delivers better segmentation results while using fewer parameters—this effectively showcases its superior performance. Figure 6 provides a visual comparison of the segmentation results generated by DABNet [14], BiSeNet-V2 [5], and ISANet. As observed in Figure 6, some small objects—particularly slender ones such as street lamps—are prone to being misclassified into other categories or completely omitted. Both DABNet [14] and BiSeNet-V2 [5] exhibit ambiguous and incorrect segmentation of such objects. The fundamental cause of this phenomenon is that small objects contain limited spatial feature information, which is highly susceptible to loss during the feature processing stage. In contrast, ISANet enhances the integrity of spatial features by extracting and fusing the lost spatial features, thereby achieving superior segmentation accuracy compared to the other models. The aforementioned experiments fully demonstrate the excellent performance of ISANet.

Table 9.
Comparison with state-of-the-art image semantic segmentation methods on CamVid. The best results are shown in bold.
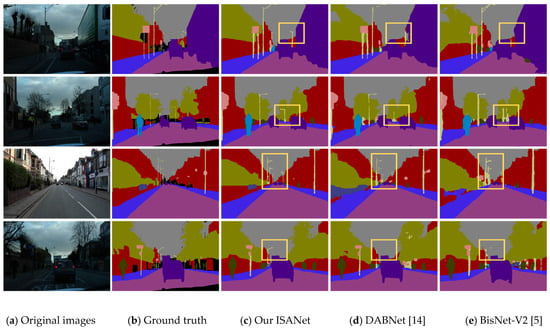
Figure 6.
Semantic segmentation results on CamVid. (a) Original images. (b) Ground truth. (c) Our ISANet. (d) DABNet [14]. (e) BisNet-V2 [5].
5. Conclusions and Discussion
In this paper, we put forward a novel information supplementary aggregation network (ISANet) model. By extracting and utilizing lost spatial features, ISANet strikes an outstanding balance among segmentation accuracy, operational efficiency, and model size. Different from methods that rely on complex structures, ISANet is designed with the Spatial-Supplementary Lightweight Bottleneck Unit (SLBU) and a dedicated feature extraction branch—this design enables the model to acquire more comprehensive feature information and boost inference accuracy. Among these components, the Spatial Feature Acquisition Branch (SFAB) works to enhance the richness of spatial information, while the Missing Spatial Information Recovery Branch (MSIRB) supplements the spatial features that have been lost, thereby improving the precision of edge segmentation. Additionally, the Object Boundary Feature Attention Module (OBFAM) is capable of mitigating noise disturbance and strengthening the interactivity between features. Experimental results show that the proposed ISANet achieves excellent segmentation performance, with the advantages of fewer parameters and real-time inference speed. It should be noted that although ISANet achieves an mIoU improvement through the SLBU and multi-branch design, the increased structural complexity leads to a decrease in inference speed and an increase in computational burden, which still requires comprehensive trade-off considerations in specific deployment scenarios. The current study is conducted based on clear visual images, and the model’s robustness remains to be enhanced when facing diverse and dynamically changing real-world environments. Meanwhile, for low-bandwidth embedded devices, it is also necessary to further optimize the multi-branch structure to ensure that the inference speed can still be guaranteed while improving segmentation accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L. and H.L.; Methodology, F.L.; Software, F.L.; Validation, F.L. and D.H.; Formal analysis, X.Z.; Investigation, D.H.; Resources, F.L.; Data curation, D.H.; Writing—original draft, F.L.; Writing—review & editing, F.L.; Visualization, H.L. and X.Z.; Supervision, F.L. and X.Z.; Funding acquisition, F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by The Liaoning Provincial Education Science “14th Five-Year” Plan Project (Grant No. JG24DB479, 2024) and China University Industry–University Research Innovation Fund—New Generation Information Technology Innovation Project (Grant No. 2023IT80, 2023).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Icnet for real-time semantic segmentation on high-resolution images. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Gao, C.; Yu, G.; Sang, N. Bisenet: Bilateral segmentation network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 325–341. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. Bisenet v2: Bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3051–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Montiel, M.; Lopez, D.A.; Montiel, O. JetSeg: Efficient Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Model for Low-Power GPU-Embedded Systems. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.11419. [Google Scholar]
- Atif, N.; Mazhar, S.; Sarma, D.; Bhuyan, M.K.; Ahamed, S.R. Efficient context integration through factorized pyramidal learning for ultra-lightweight semantic segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Gu, X.; Xiong, J. Cross-cbam: A lightweight network for scene segmentation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.02306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiong, Z.; Bhattacharyya, S.P. PIDNet: A real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 19529–19539. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zou, F.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Li, K. Efficient resolution-preserving network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Shenzhen, China, 18–22 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, D.; Thirupathi Rao, N.; Joshua, E.S.N.; Hu, Y.C. A bi-directional deep learning architecture for lung nodule semantic segmentation. Vis. Comput. 2023, 39, 5245–5261. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Chen, Q. RoboSeg: Real-time semantic segmentation on computationally constrained robots. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Tang, S.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y. CGNet: A light-weight context guided network for semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 30, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Jiang, S.; Yun, I.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Depth-wise asymmetric bottleneck with point-wise aggregation decoder for real-time semantic segmentation in urban scenes. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 27495–27506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Chen, T.; Fan, J.; Lu, Y.; Zuo, C.; Chi, Q. Eadnet: Efficient asymmetric dilated network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 2315–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Singha, T.; Pham, D.S.; Krishna, A.; Gedeon, T. A lightweight multi-scale feature fusion network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Neural Information Processing, Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing, Bali, Indonesia, 8–12 December 2021; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland; pp. 193–205.
- Hu, X.; Jing, L.; Sehar, U. Joint pyramid attention network for real-time semantic segmentation of urban scenes. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 580–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Hong, R.; Cheng, J.; Wang, M. Real-time semantic segmentation via spatial-detail guided context propagation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 36, 4042–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Shi, Y.; Deng, C.; Shi, M. RELAXNet: Residual efficient learning and attention expected fusion network for real-time semantic segmentation. Neurocomputing 2022, 474, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, R.; Yang, K.; Zou, K. MFFN: Image super-resolution via multi-level features fusion network. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 489–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, J.; Xiong, J.; Gao, G.; Wu, X.; Latecki, L.J. Lednet: A lightweight encoder-decoder network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Taipei, Taiwan, 2–25 September 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1860–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Ma, H.; Xue, J.H. EFRNet: A lightweight network with efficient feature fusion and refinement for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shenzhen, China, 5–9 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Elhassan, M.A.; Huang, C.; Yang, C.; Munea, T.L. DSANet: Dilated spatial attention for real-time semantic segmentation in urban street scenes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Yan, Y.; Chen, S.; Xue, J.H.; Wang, H. Stage-aware feature alignment network for real-time semantic segmentation of street scenes. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2021, 32, 4444–4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Tu, W.; Li, K.; Cheng, J. DFFNet: An IoT-perceptive dual feature fusion network for general real-time semantic segmentation. Inf. Sci. 2021, 565, 326–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhao, Z.; Hou, Z.; Yu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhao, X. SEDNet: Real-Time Semantic Segmentation Algorithm Based on STDC. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2025, 2025, 8243407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, F. Lightweight and real-time semantic segmentation network via multi-scale dilated convolutions. Vis. Comput. 2025, 41, 11833–11855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, E.; Wang, W.; Yu, Z.; Anandkumar, A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Luo, P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 12077–12090. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltagy, I.; Peters, M.E.; Cohan, A. Longformer: The long-document transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.05150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaev, N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Levskaya, A. Reformer: The efficient transformer. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2001.04451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Tian, T.; Chen, C.; Guo, X.; Ma, J. Bilateral attention decoder: A lightweight decoder for real-time semantic segmentation. Neural Netw. 2021, 137, 188–199. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, J. BiAttnNet: Bilateral attention for improving real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 29, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, C. Real-time semantic segmentation with weighted factorized-depthwise convolution. Image and Vision Computing 2021, 114, 104269. [Google Scholar]
- Sagar, A. AaSeg: Attention aware network for real time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.04349. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Li, J.; Gao, G.; Lu, H.; Yang, J.; Yue, D. Lightweight real-time semantic segmentation network with efficient transformer and CNN. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 15897–15906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Huang, Z.; Lu, J.; Yu, G.; Zhang, L. Seaformer: Squeeze-enhanced axial transformer for mobile semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xia, R.; Yang, K.; Zou, K. DARGS: Image inpainting algorithm via deep attention residuals group and semantics. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choromanski, K.; Likhosherstov, V.; Dohan, D.; Song, X.; Gane, A.; Sarlos, T.; Hawkins, P.; Davis, J.; Mohiuddin, A.; Kaiser, L.; et al. Rethinking attention with performers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.14794. [Google Scholar]
- Kehinde, T.O.; Adedokun, O.J.; Joseph, A.; Kabirat, K.M.; Akano, H.A.; Olanrewaju, O.A. Helformer: An attention-based deep learning model for cryptocurrency price forecasting. J. Big Data 2025, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Hong, Y.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep Dual-Resolution Networks for Real-Time and Accurate Semantic Segmentation of Traffic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 3448–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senhua, X.U.E.; Liqing, G.A.O.; Liang, W.A.N.; Wei, F.E.N.G. Multi-scale context-aware network for continuous sign language recognition. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2024, 6, 323–337. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Xu, G.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Lu, H.; Yang, J. FBSNet: A Fast Bilateral Symmetrical Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multim. 2023, 25, 3273–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, B.; Wu, Z.; Wan, T. LAANet: Lightweight attention-guided asymmetric network for real-time semantic segmentation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 3573–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V.; Funkhouser, T. Dilated residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 472–480. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnet: Efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 561–580. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.G.; Navab, N.; Wachinger, C. Concurrent spatial and channel ‘squeeze & excitation’in fully convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Granada, Spain, 16–20 September 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Gong, C.; Liu, Z.; Fu, K. SAL: Selection and attention losses for weakly supervised semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2020, 23, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Kim, S.; Culurciello, E. Enet: A deep neural network architecture for real-time semantic segmentation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Computer Vision, Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Brostow, G.J.; Shotton, J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Segmentation and recognition using structure from motion point clouds. In Computer Vision, Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 44–57. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Qiang, Y.; Kang, B.; Wu, X.; Zheng, B. FDDWNet: A lightweight convolutional neural network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 2373–2377. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, G.; Xu, G.; Yu, Y.; Xie, J.; Yang, J.; Yue, D. MSCFNet: A lightweight network with multi-scale context fusion for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 25489–25499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Yan, Y.; Shen, C.; Wang, H. Real-Time High-Performance Semantic Image Segmentation of Urban Street Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 3258–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yu, H.; Fu, Q.; Sun, W.; Jia, W.; Sun, M.; Mao, Z.H. NDNet: Narrow while deep network for real-time semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2020, 22, 5508–5519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, F.; Chu, H.; Hu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Gao, B. MLFNet: Multi-Level Fusion Network for Real-Time Semantic Segmentation of Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Ke, Y. EMFANet: A lightweight network with efficient multi-scale feature aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liang, S.H.; Wu, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L. Mgseg: Multiple granularity-based real-time semantic segmentation network. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7200–7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Dou, F.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, C. BSNet: A bilateral real-time semantic segmentation network based on multi-scale receptive fields. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 102, 104188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qiu, S.; Chen, Z. Real-time semantic segmentation network based on parallel atrous convolution for short-term dense concatenate and attention feature fusion. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntao, C.A.O.; Huang, X.; Shao, J. Aggregation architecture and all-to-one network for real-time semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021—2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 2330–2334. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).