Abstract
Multimodal knowledge graphs have recently been successfully applied to tasks such as those relating to information retrieval, question and answer, and recommender systems. In this study, we propose a dual-path fine-tuning mechanism technique with a low-rank adapter and an embedded cueing layer, aiming to improve the generalization and accuracy of the model in analogical reasoning tasks. The low-rank fine-tuning (LoRA) technique with rank-stable scaling factor is used to fine-tune the MKGformer model, and a cue-embedding layer is innovatively added to the input layer, which enables the model to better grasp the scale of the relationship between entities according to the dynamic cue vectors during the fine-tuning process and ensures that the model achieves the best results during training. The experimental results show that the R-MKG model improves several evaluation indexes by more than 20%, which is significantly better than the traditional DoRA and FA-LoRA methods. This research provides technical support for multimodal knowledge graph analogical reasoning. We hope that our work will bring benefits and inspire future research.
1. Introduction
Analogies play a central role in common sense reasoning in humans [], and their use has long been recognized as an effective method of problem solving []. Analogical reasoning, the ability to perceive and use similar relationships between two situations or events, occupies an important place in human cognition and plays an important role in many fields such as education [], engineering [], and computer science []. Given the central role of analogy in human cognition, it is important to understand the extent to which NLP models can handle these more abstract analogies []. The ability to recognize analogies is important in human creativity, innovation, computational creativity, and education. Analogical reasoning, as a profound and illuminating method of thinking, is an integral part of human cognition of the world and problem solving. It is rooted in human beings’ keen insight into the similarities and differences of things. By combining two or more things in different fields and of different natures but with certain common features or laws, it reveals the potential connections and laws between them, and then enables deduction of a new understanding or conclusion. This process not only reflects the flexibility and creativity of human thinking, but also is an important tool for scientific discovery, technological innovation, and even daily decision-making.
The knowledge graph (KG), as an important form of structured knowledge representation, has shown great value in semantic search [], intelligent question and answer [], and other fields. However, traditional knowledge graphs are mainly constructed based on textual information, which makes it difficult to handle multimodal data such as images, audio, and video. With the explosive growth of multimodal data, multimodal knowledge graphs have become a research hotspot, their goal being to build a richer and closer-to-the-real-world knowledge representation system by fusing text, visual, auditory, and other multimodal information [].
By breaking modal barriers, multimodal knowledge graphs promote the evolution of knowledge representation from ‘single text’ to ‘multi-dimensional perception’. Although there are still challenges in data fusion, with the development of multimodal pre-training models [], graph neural networks [], and other technologies, they are expected to become the core infrastructure of the next generation of artificial intelligence, enabling smarter and more anthropomorphic application scenarios. Future research can further explore the deep integration of knowledge-driven and data-driven approaches to achieve comprehensive knowledge and reasoning about the real world.
Combining analogical reasoning with multimodal knowledge graphs not only improves the machine’s ability to understand and reason about multimodal data, but also provides more intelligent solutions for applications such as intelligent question and answer, cross-modal retrieval, and innovative design []. Therefore, research on key technologies of analogical reasoning for multimodal knowledge graphs has become a major direction in the field of artificial intelligence, which has important theoretical significance and application value. The main contributions of this study are as follows:
- (1)
- A low-rank fine-tuning adaptation module based on a rank-stable scaling factor is designed to perform LoRA fine-tuning on the MKGformer model so that the model can meet the requirements of this task.
- (2)
- A dynamic fine-tuning strategy is designed to add a cue-embedding layer module to dynamically adjust the model inputs to ensure that the model achieves optimal results during training.
- (3)
- Experiments show that the method can effectively fine-tune the model for multimodal knowledge graph analogical reasoning, which significantly improves the performance of the model in relevant research in this field, and provides a new solution for applications in the field of multimodal knowledge graph analogical reasoning.
2. Related Work
2.1. Analogical Reasoning with Multimodal Knowledge Graphs
Recent research on analogical reasoning for multimodal knowledge graphs has made significant progress. Zhang et al. [] and Chen et al. [] proposed a multilevel fusion hybrid converter, MKGformer, to solve the analogical reasoning problem. A hybrid converter architecture with unified inputs and outputs is utilized to perform various multimodal knowledge mapping tasks. Multi-level fusion is proposed to integrate visual and textual representations through coarse-grained prefixes and suffixes. Visual and textual representations are integrated through coarse-grained prefix-guided interactions and fine-grained relevance-aware fusion modules. The algorithm utilizes a transformer baseline strategy of multimodal knowledge graph embedding and multimodal pre-training, which significantly improves the analogical inference performance of the model. However, the method still has limitations in that some entity relationships are not intuitive and the model is unable to understand the scale of relationships between entities. However, LoRA fine-tuning in multimodal knowledge graph analogical reasoning research can effectively address the limitations of traditional methods in terms of generalization ability and training efficiency through its powerful optimization.
2.2. Efficient Parameter Fine-Tuning Technology
When fine-tuning the model, it is particularly important to improve the efficiency of parameter fine-tuning []. In addition to the traditional additive and selective fine-tuning methods, parameter-heavy fine-tuning methods are gradually becoming the focus of research, and a low-rank fine-tuning method called LoRA (Low-Rank Adaption) has been proposed by Hu et al. []. LoRA is a highly efficient model fine-tuning technique, which aims at adapting the pre-trained model with very low computational cost. The core idea is to train only a small portion of the model parameters, not the full amount of parameters, by introducing a low-rank matrix decomposition, thus significantly reducing the memory footprint and computational overhead. The core advantage is that only the new low-rank matrix is fine-tuned, the original parameters are frozen, the training speed is faster, and the memory requirement is reduced by more than 50%. LoRA can be flexibly inserted into the attention layer (Q/V matrix) or the fully connected layer of the transformer to meet different task requirements, and LoRA fine-tuning is suitable for different computing resources, task requirements, and performance goals. In multimodal knowledge graph analogical reasoning, where multiple modal data need to be processed simultaneously and model performance is greatly reduced with a large number of parameters, LoRA fine-tuning will greatly reduce the number of training parameters, thus improving model performance. Moreover, in the process of analogical inference, it is necessary to ensure that the basic semantics of the entity remain unchanged, and the LoRA fine-tuning model will precisely freeze the backbone network to ensure that the semantics of the entity will not be changed due to fine-tuning.
3. R-MKG Modeling Approach
3.1. Task Definition
Analogical reasoning, a form of logical reasoning, is a method of reasoning based on the principle of similarity, in which possible relationships between things are inferred by analyzing the similarities between two or more things. When we are given something, we can identify something else related to it by inferring the relationship. For example, given a set of analogous entity examples (, ) and a query entity , we can reason from the relationship between the analogous entity examples to the entity ea that corresponds to the query entity , using a statement of the form a is to b as c is to d, as shown in Figure 1.
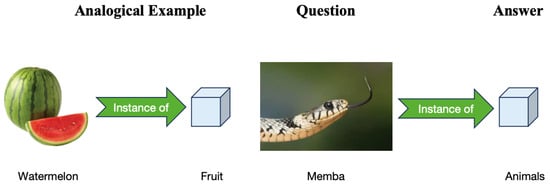
Figure 1.
Given a set of entity instances (watermelon, fruit) and a query entity (mamba), thereby inferring the corresponding entity (animal).
3.2. R-MKG Model
The R-MKG model proposed in this paper contains two main modules: the cue-embedding layer module and the low-rank fine-tuning adaptation module based on the rank-stable scaling factor. The overall architecture of the R-MKG model is shown in Figure 2.
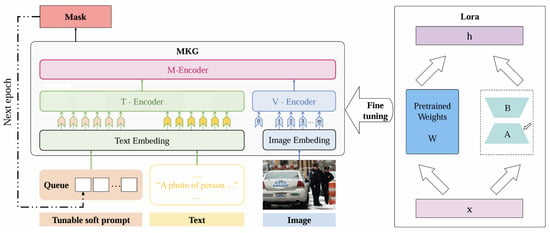
Figure 2.
R-MKG model architecture diagram.
The R-MKG model cleverly adopts the dynamic cue-embedding strategy, an innovative design that introduces an additional cue-embedding layer in the input layer of the MKGformer model. The core purpose of this strategy is to guide the model to capture key features in the data more accurately by dynamically adjusting the cue information at different stages of training, so as to optimize its performance during the training process and ensure that the model can achieve the best results. This dynamic adjustment not only enhances the adaptability of the model, but also significantly improves its ability to handle complex tasks. Further, the R-MKG model creatively employs LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation), a fine-tuning technique in the low-rank fine-tuning adaptation module based on the rank stabilization scaling factor, to fine-tune the MKG model, which, with its high efficiency and lightweight advantage, can achieve significant performance enhancement of the model without significantly increasing the model parameters. By means of low-rank decomposition, LoRA is able to capture task-specific information and effectively incorporate it into the pre-trained model, enabling the fine-tuned model to not only maintain its original generalization ability, but also better adapt to the needs of a specific task. Within this design framework of the R-MKG model, the application of LoRA fine-tuning techniques ensures the proficiency and accuracy of the model output results. Whether it is understanding domain-specific expertise or the ability to handle complex tasks, the R-MKG model is able to demonstrate superior performance. This strategy of combining dynamic cue embedding and the LoRA fine-tuning technique not only provides new ideas for model training and optimization, but also provides a solid technical guarantee of meeting the professional requirements of the research task.
3.3. Cue-Embedded Layer Module
There is an essential difference between the discrete token encoding of hard cues and the continuous feature space of vision. Fixed prefixes cannot establish a dynamic mapping relationship between modalities, and cue parameters and multimodal encoder parameters cannot be optimized collaboratively. In order to enhance the predictive ability of the model, we innovatively added a cue-embedding layer to the input layer. The core of this layer is the introduction of dynamic soft prompts, which exist as embedding vectors that provide additional contextual information and guidance to the model to better understand the input and make accurate predictions. The advantage of dynamic soft prompts lies in their flexibility and learnability, which can be adapted and optimized according to the specific needs of the task, thus adapting to different analogical reasoning scenarios more than traditional hard prompts (such as fixed templates or rules).
Initialization method: For textual cues, the word embedding layer of the pre-trained BERT is used for initialization, with a dimension of 768 (consistent with the hidden layer of MKGformer). For visual cues, image patch features are extracted through Vision Transformer (ViT), with a dimension of 768.
Input sequence construction:
Text side:
Visual side: After the image patch features are encoded by ViT, they interact with the text prompts in M-Encoder.
As an example of mixed analogical reasoning, analogical instances (,) and analogical question–answer pairs (, ?) are used as inputs, with the goal of predicting the missing answer entity . A cue-embedding layer is added to the input layer by adding dynamic soft prompts, which use embedding vectors as cues.
During the model training process, the parameters in the cue-embedding layer are updated and optimized by means of a backpropagation algorithm. These parameters include the embedding vector of the soft cue word itself and the weights and bias terms associated with it. The dynamic soft cue word implementation of the cue-embedding layer is shown in Equation (2).
where is the feature code, whose formula is shown in Equation (3).
is the input sample, is a lightweight feature extraction network with parameter , and d is the hidden layer dimension.
To avoid gradient vanishing, an exponential linear unit (ELU) activation function is added. The formula is shown in Equation (4).
prompts the embedding layer normalization, which serves to ensure training stability and mitigate internal covariate bias, as shown in Equation (5).
where , are the mean and standard deviation of feature dimensions, , are the learnable scaling and offset parameters, and is the numerical stability term, which is set to in this paper.
Each dynamic soft cue word uniquely depends on the encoded feature of , and similar samples produce similar cues, the formula for which is shown in Equation (6).
where L is the Lipshitz constant.
The dynamic soft cues enable the model to better capture the scale of relationships between entities based on dynamic cue vectors.
Most current methods use prefix tuning, which freezes the LM parameters and only optimizes task-specific prefix vectors, or prompt tuning, which adds adjustable tags at the input, and is suitable for few-shot learning. Our prompt-embedding layer achieves a breakthrough in interactivity, adaptability, and efficiency over traditional methods by integrating dynamic feedback, multimodal context awareness, and lightweight parameter design.
3.4. Low-Rank Fine-Tuning Adaptation Module Based on Rank-Stable Scaling Factors
LoRA builds on the Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) technique, which enables efficient fine-tuning by introducing trainable low-rank adapters in selected layers of the pre-trained model. The LoRA technique performs the fine-tuning by adding a low-rank matrix to the original weight matrices by expressing the update part as the product of two smaller matrices B and A, as shown in Equation (7).
In Equation (7), B and A are two small matrices obtained by low-rank matrix factorization. , , r is the rank of the Adapter, .
Directly updating the complete W requires tuning parameters, whereas with the low-rank decomposition, only B and A need to be updated, and the number of parameters is reduced from to , since the dimensions of each of B and A are . The original matrix diagram is shown in Figure 3.
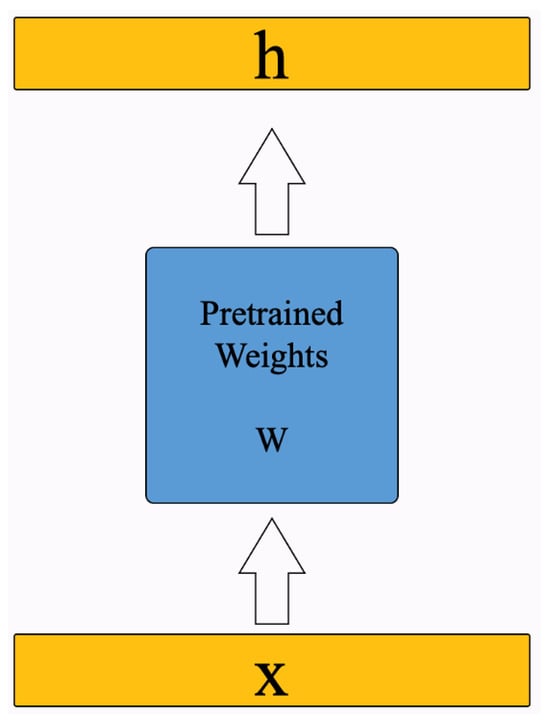
Figure 3.
Original model weight matrix.
A comparison of the model structures reveals that the LoRA fine-tuning method not only greatly reduces the number of training parameters, but also maintains the expressive power of the model. The original weights of the model in the pre-training are frozen, , and only the parameters of A, B are updated. A is initialized using a normal distribution, and B is initialized using all zeros to ensure that the initial state does not change the pre-training weights W so that the training process can start from the original pre-training state. In short, the first forward pass of the model should be based on the original pre-training weights W, not on random Lora weights.
LoRA introduced a rank stabilization scaling factor; this factor corrects the limitation by dividing the LoRA adapter by its rank. Without any scaling, the learning is blocked and the performance of the model fails to improve even at a higher adapter’s rank. LORA, through this scaling mechanism, makes the learning at higher rank more effective while avoiding explosion or reduction in the activation and gradient magnitude. In LoRA, expression of the Adapter is shown in Equation (8).
When fine-tuning the MKGformer using LoRA, for the model’s weight matrix , it can be updated by this method. While the model is being trained, W is frozen and no gradient update is performed, while the Adapter is trainable. Assume that the model input is x and its output h, as represented in Equation (9).
The model complexity can be controlled and overfitting prevented using the regularization method, as shown in Equation (10).
In Equation (10), is the regularization term, is the regularization coefficient, and is the Frobenius coefficient, which is used to measure the size of the matrix.
The Low-Rank Adaptation (LORA) process can be optimized by introducing a rank-stable scaling factor. The core of LORA is its ability to significantly reduce the number of trainable parameters, and also to make the model more efficient and stable when fine-tuning, improving model performance, which is particularly important in resource-constrained environments.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Environment Configuration
The hardware environment for the research experiments was a 13th Gen Intel® Core™i9-13900K processor with 32GB of RAM (Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA), an Ubuntu 18.04.6 LTS operating system, a GeForce RTX 4090 GPU, and dependency on a runtime framework of python3 + Cuda 12.1 + Pytorch-cuda 11.8 + tersorflow 2.16.1 + jupyter 1.0.0.
4.2. Experimental Parameter Setting
The experimental parameters of this study are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameter setting.
In order to better set up the experimental parameters and choose more suitable parameters for the experiment, a comparison experimental set up of different parameters is implemented by adjusting the sequence length, the number of parameters in a single pass (batch_size), and the number of training rounds (epochs). The rest of the parameters remain unchanged, and the parameters are explored on the dataset MARS and the knowledge graph MarKG. The effects on the model performance on the dataset MARS and the knowledge graph MarKG are determined, as shown in Figure A1.
The LoRA rank r ∈ 4, 8, 16, 32 is tested for the same task, and the validation set accuracy is recorded with the training time, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparative experiments with different LoRA ranks.
Experiments show that r ≥ 4 is close to full fine-tuning, and r = 8 saturates the performance on most tasks (with minimal benefit from further increases in r). A value of r = 8 achieves 99% of the full fine-tuning performance and the FLOP is only 15 for the full fine-tuning, while r = 64 improves performance by only 0.2%. When r = 8, the model has the lowest volatility loss rate, indicating that the model is the most stable during training, while full fine-tuning causes a surge in variance due to full parameter updates. The standard deviation of accuracy is 1.89, and the 95% confidence interval is (10.35, 13.05), indicating that the results are highly stable. Their validity was verified by independent sample t-test analysis (t = −5.00, p = 0.0011). Therefore, in this paper, r is chosen to be 8.
The LoRA scaling factor is tested for the same task, and the validation set accuracy and training time are recorded, as shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Comparative experiments with different LoRA scaling factors.
According to Table 3, accuracy improves with increasing , but the growth slows down beyond 16 (only 0.1% improvement from = 16 to 32). The training time varies less (45–52 min) and the time saving rate is stable between 57% and 63%. And for = 16, the volatility loss rate is the lowest and the model is the most stable.Therefore, = 16 may be the optimal choice to achieve 99.1% full performance and 60% time saving. In pursuit of a performance balance, the r = 8, = 16 combination (about 89.6% accuracy and around 50% time saving) is chosen for experiments in this section.
4.3. Datasets
The datasets we use are the MARS public dataset and the MarKG public knowledge graph, as shown in Table 4. MARS has 10,685 training instances, 1228 validation instances, and 1415 test instances, for a total of 13,328 instances. MarKG focuses on knowledge-intensive reasoning across multiple modalities. MarKG was developed from seed entities and relations in E-KAR.MarKG and has 11,292 entities, 192 relations, and 76,424 images, including 2063 analog entities and 27 analog relations.

Table 4.
Comparison between MARS and previous analogical reasoning datasets. “Size” is the amount of data in the dataset, “KB” refers to the knowledge base, and MarKG focuses on knowledge-intensive reasoning across multiple modalities.
4.4. Assessment of Indicators
Evaluation of the performance of a model’s results is an important element. Ordinary evaluation methods cannot reflect one-to-many entities, and due to the limited search space, the internal knowledge of the model cannot be fully explored. Therefore, in this paper, we optimize the model and select Hits@k and MRR as the evaluation metrics. The calculation of Hits@k is based on the concept of mean reciprocal ranking (MRR). Specifically, for each test triad, the model predicts a ranked list and then calculates the ranked inverse of the correct answer in that list. The value of Hits@k is 1 if the correct answer is in the Top-1 position, and 0 if it is not in the Top-1 position. Ultimately, the value of Hits@1 is the average of the Hits@k values for all test triples. Both metrics are in the range [0, 1]. The larger the range, the better the performance. The clicks at the k metric (Hits@k) are calculated by counting the number of times the correct entity appears in the first k positions in the prediction. Based on the prediction scores of each entity in the set of candidate entities, the scores are ranked to produce a ranking for each entity. The golden entity rank of the i-th triple entity is the reciprocal of as . The mean reciprocal rank (MRR) is the average of the reciprocal ranks of all the triples in the knowledge graph, which is computed as shown in Equation (11).
where is the total number of datasets.
5. Experimental Evaluation
5.1. Comparative Experimental Design and Analysis
In order to fairly verify the reliability of the experiments, the comparison experiments in this study used MKG as the baseline model and considered three fine-tuning methods, DoRA (Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation) [], QLoRA (Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation) [], and LoRA-FA (Memory-Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation) [], as well as ViLBERT [], FLAVA [], and MKGformer as comparison models. Twelve combinations were jointly designed for adequate comparative experiments, as shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Comparative experiments.
From detailed analysis of the table, its Hits@1, Hits@10, and MRR values are the highest, which are 0.332, 0.437, and 0.387 respectively, significantly better than all other models including the other three fine-tuning methods. For example, the Hits@1 value of R-MKG is 0.332, and its Hits@10 value is even as high as 0.437, which is much higher than for the other methods. This gap not only verifies the superiority of the R-MKG model structure, but also reflects its stronger representativeness and generalization ability in multimodal knowledge graph analogy reasoning tasks.
5.2. Ablation Experiment
In order to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed fine-tuning method, the LoRA module, the cue-embedded layer module in the R-MKG model is ablated. The specific data are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Ablation experiments.
According to the experimental results in Table 6, after ablating the LoRA module and the cue-embedding module simultaneously, the R-MKG model proposed in this paper decreases in the three evaluation indicators of Hits@1, Hits@10, and MRR. The roles of the LoRA module and the cue-embedding module are more fully reflected. In order to show the comparison effect more clearly, we visualize the results of the ablation experiment, as shown in Figure 4.
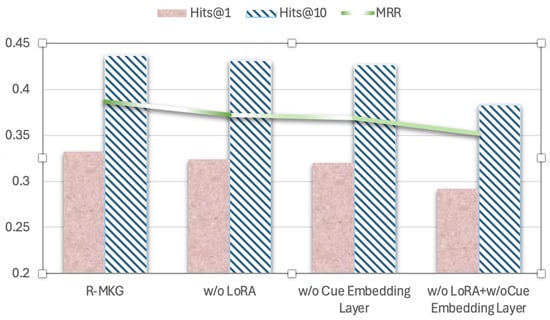
Figure 4.
Comparative experiments.
The LoRA module and the cue-embedding module form a dual enhancement mechanism in the model architecture. Although the loss function constraints are not introduced, the low-rank constraints of LoRA itself form a kind of implicit regularization, which still significantly improves the model performance and inference accuracy. This architecture-level innovation means that the enhancement of model performance is independent of loss function constraints, and provides new ideas for developing lightweight and interpretable inference systems.
5.3. Comparative Experiments with Different Datasets
In order to validate the LoRA-based fine-tuning model proposed in this paper and evaluate its adaptability to different images and texts, COCO (Common Objects in Context), as well as CC (Conceptual Captions) multimodal datasets, FLAVA, and MKGformer, are selected as comparison models. This enables comprehensively verification of the generalization ability of different models under different datasets. During the experimental process, the model structure is kept unchanged, the parameter settings are kept unchanged, and comparison experiments are designed. The specific data are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Comparative experiments on different datasets.
As can be seen from Table 5, the model proposed in this paper demonstrates good generalization and effectiveness, and exhibits high performance across multiple datasets and different sample sizes.
6. Discussion
In this paper, we propose a dual-path fine-tuning mechanism based on the Lora model’s fine-tuning and cue-embedding layer to add incremental matrices of low-rank decomposition to the weight matrix of the MKG model and to add a task-specific cue-embedding layer to optimize the model performance and dynamically adjust the cue vectors during the fine-tuning process to adapt to the different training phases. This is done to ensure that the model achieves the best results during training and remains stable in the later stages to prevent overfitting. The experimental results show that the proposed R-MKG model MRR, Hits@1, and Hits@10 reach 0.387, 0.332, and 0.437. The results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively enhances model performance by increasing the accuracy of analogical reasoning and reducing the number of model parameters to be computed.
The LoRA-based model’s fine-tuning technique proposed in this paper achieves better results in terms of modeling. Existing methods focus on efficient optimization of parameters but fail to fully incorporate explicit constraints of symbolic logic (for example, first-order predicates, rule-based reasoning), which restricts the performance of the models in logically demanding scenarios (for example, causal reasoning). And there are entities that are difficult to visualize, for example, highly semantic phrases such as ‘management’ and ‘control’. The model has a biased understanding of such abstract entities, so we focused on how the model learns and grasps the abstract entities at a deeper level, embedding the logic rules into the loss function or the model structure in a differentiable form, and realizing the synergistic optimization of symbolic reasoning and neural representation.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a Lora-based fine-tuning model for multimodal knowledge graph analogical reasoning. The innovations can be distilled into the following two core contributions: Methodological innovation: a dual-path fine-tuning mechanism with low-rank adapter and cue-embedding layer is proposed, which solves the parameter redundancy problem of traditional fine-tuning by freezing the backbone network and incremental updating of low-rank matrices, and reduces the training cost by 83 compared with full-parameter fine-tuning; Engineering innovation: the design of the rank stabilization scaling factor achieves dynamic rank selection, which, together with the cue-embedding layer, provides the model with dynamic cue vectors, and enhances the model’s complex relational scale adaptability. Experimental validation has shown that this task is quite a daunting challenge that deserves further exploration. We hope that our work will inspire future analogical reasoning and applied research.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Z.Z. and S.Z.; software, Z.Z. and S.Z.; validation, Z.Z., S.Z. and Z.L.; formal analysis, Z.Z. and S.Z.; investigation, Z.Z., S.Z. and Z.A.; resources, Z.Z., S.Z. and C.Z.; data curation, Z.Z., S.Z. and Z.A.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Z.; writing—review and editing, Z.Z. and S.Z.; visualization, Z.Z., S.Z. and Z.Z.; supervision, Z.Z. and S.Z.; project administration, C.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported under the project: Research on the derecycle number of network topology structure graph and its algorithm (61802046). Liaoning Province key research and development plan project (2023JH26/10200015).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
MARS datasets and MarKG are available on request on their official website.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LoRA | Low-Rank Adaptation |
| LoRA-FA | Memory-Efficient Low-Rank Adaptation |
| QLoRA | Quantized Low-Rank Adaptation |
| KG | Knowledge Graph |
| MKG | Multimodal Knowledge Graphs |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| DoRA | Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation |
| ELU | Exponential Linear Units |
| MRR | Mean Reciprocal Ranking |
| COCO | Common Objects in Context |
| CC | Conceptual Captions |
Appendix A
In order to better set up the experimental parameters and choose more suitable parameters for the experiment, a comparison experimental set up of different parameters is carried out by adjusting the sequence length, the number of parameters in a single pass (batch_size), and the number of training rounds (epochs), and the rest of the parameters remain unchanged. The parameters are explored on the dataset MARS and the knowledge graph MarKG on the performance of the model. For the specific parameter settings range: the sequence length takes the values of 256, 128, 64, 32, respectively, and the number of parameters in a single pass takes the values of 64 and 32, forming a total of 8 parameter combinations, with epochs from 10 to 30, and recording the performance trend of each parameter combination under different training rounds. The experimental results are shown in Figure A1.
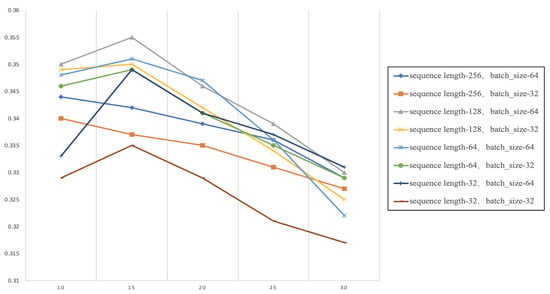
Figure A1.
Experimental results MRR comparison chart.
The experimental results show that when the sequence length = 128 and the batch_size = 64, combined with 15 rounds of training, the model exhibits optimal performance in all three metrics. When the sequence length = 128, the MRR of batch_size = 64 is significantly higher than that of batch_size = 32, and the evaluation index of batch_size = 64 is higher than that of batch_size = 32 even under different epochs. When the batch_size = 64, sequence length = 256 to batch_size = 64, sequence length = 128, the evaluation index tends to increase. But when the sequence length decreases towards 64 as well as 32, the evaluation index tends to decrease irrespective of the value of the epochs. After a variety of parameter combinations, the evaluation index is basically highest at epochs = 15 in all cases.
Although individual parameter combinations may show minor fluctuations in the middle rounds, the evaluation index is highest when the sequence length = 128, batch_size = 64, and epochs = 15. Specific data show that when the sequence length = 128, batch_size = 64, and epoch = 15, the MRR value is 0.355, which is significantly higher than for other parameter combinations. This comparison demonstrates the importance of setting the sequence length reasonably with the number of parameters in a single pass and the number of training rounds. So, the sequence length is set to 128, the number of single pass parameters is set to 64, and the number of training rounds is set to 15 when conducting the experiment.
References
- Wu, B.; Qin, H.; Zareian, A.; Vondrick, C.; Chang, S.-F. Analogical reasoning for visually grounded language acquisition. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2007.11668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prade, H.; Richard, G. Analogical proportions: Why they are useful in AI. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI-21), Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–27 August 2021; pp. 4568–4576. [Google Scholar]
- Thagard, P. Analogy, explanation, and education. J. Res. Sci. Teach. 1992, 29, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugherty, J.L.; Mentzer, N. Analogical reasoning in the engineering design process and technology education applications. J. Technol. Educ. 2008, 19, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, M. Categories and Analogies. In Analogical Reasoning: Perspectives of Artificial Intelligence, Cognitive Science, and Philosophy; Helman, D.H., Ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 3–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z. Analyzing the role of semantic representations in the era of large language models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.01502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Li, Y.; Wen, M.; Liu, Y. KG4Py: A toolkit for generating Python knowledge graph and code semantic search. Conn. Sci. 2022, 34, 1384–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. Design and research of intelligent question-answering (Q&A) system based on high school course knowledge graph. Mobile Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar]
- Simianer, P.; Riezler, S.; Dyer, C. Joint feature selection in distributed stochastic learning for large-scale discriminative training in SMT. In Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Long Papers, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 8–14 July 2012; pp. 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Ji, L.; Shi, B.; Huang, H.; Duan, N.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Bharti, T.; Zhou, M. UniVL: A unified video and language pre-training model for multimodal understanding and generation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.06353. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pan, S.; Chen, F.; Long, G.; Zhang, C.; Yu, P.S. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Hassan, F.H.; Hoon, G.K. The state of the art for cross-modal retrieval: A survey. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 138568–138589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Liang, X.; Deng, S.; Chen, H. Multimodal analogical reasoning over knowledge graphs. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.00312. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, L.; Deng, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, C.; Huang, F.; Si, L.; Chen, H. Hybrid transformer with multi-level fusion for multimodal knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Madrid, Spain, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 904–915. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Valls, V.; Ko, B.; Lee, W.; Leung, K.K.; Tassiulas, L. Model pruning enables efficient federated learning on edge devices. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 34, 10374–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. LoRA: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 25–29 April 2022; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Yin, H.; Molchanov, P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Chen, M. DoRA: Weight-decomposed low-rank adaptation. In Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dettmers, T.; Pagnoni, A.; Holtzman, A.; Zettlemoyer, L. QLORA: Efficient finetuning of quantized LLMs. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 10088–10115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Shi, S.; Chu, X.; Li, B. LoRA-FA: Memory-efficient low-rank adaptation for large language models fine-tuning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.03303. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Batra, D.; Parikh, D.; Lee, S. ViLBERT: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Hu, R.; Goswami, V.; Couairon, G.; Galuba, W.; Rohrbach, M.; Kiela, D. FLAVA: A foundational language and vision alignment model. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 15638–15650. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).