Abstract
In this paper, we propose a novel Poisson process generator that uses multiple thermal noise amplifiers (TNAs) as a source of randomness and controls its event rate via a frequency-locked loop (FLL). The increase in the number of TNAs extends the effective bandwidth of amplified thermal noise and hence enhances the maximum event rate the proposed architecture can generate. Verilog-A simulation of the proposed Poisson process generator shows that its maximum event rate can be increased by a factor of 26.5 when the number of TNAs increases from 1 to 10. In order to realize parallel stochastic simulations of the biochemical reaction network, we present a fundamental reaction building block with continuous-time multiplication and addition using an AND gate and a 1-bit current-steering digital-to-analog converter, respectively. Stochastic biochemical reactions consisting of the fundamental reaction building blocks are simulated in Verilog-A, demonstrating that the simulation results are consistent with those of conventional Gillespie algorithm. An increase in the number of TNAs to accelerate the Poisson events and the use of digital AND gates for robust reaction rate calculations allow for faster and more accurate stochastic simulations of biochemical reactions than previous parallel stochastic simulators.
1. Introduction
As cells often process signals with a low or medium number of molecules and exploit the stochasticity in their cellular functions [1,2,3,4,5], the stochastic simulation of biochemical reaction networks is essential in systems and computational biology. Although the Gillespie algorithm [6] and its variants [7,8,9,10,11,12,13] have been presented for the software simulation of stochastic biochemical reactions, there is a problem where the simulation time increases proportionally as the size of the biochemical reaction network increases. This is because of the intrinsic limitation of software simulation that cannot process the correlated stochastic reactions in parallel.
There have been several attempts to implement hardware specialized for parallel simulation of stochastic biochemical reactions in order to solve the problem of long simulation times in software [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24]. Ref. [14] presented a field-programmable gate array (FPGA)-based parallel stochastic simulator by comparing random numbers with the number of molecules of each reactant and performing a logic AND operation on the comparators’ outputs. However, pseudo-random number generators that are not truly random were used, and the reaction events with a time interval within one clock cycle cannot be simulated. In [15,16,17], BiCMOS cytomorphic chips based on log-domain analog circuits were presented for continuous-time parallel stochastic simulation. Although random pulses generated with amplified thermal noise were incorporated into the core transistor circuits for modeling high intrinsic noise levels [16], stochastic simulation of reactions with a few molecules was unfeasible. This is because the random pulses corresponding to Poisson events have different widths each time, making it difficult to count the molecules accurately.
In this paper, we propose a novel Poisson process generator that uses multiple thermal noise amplifiers (TNAs) as the random source and controls its event rate via a frequency-locked loop (FLL). Unlike the previous work in [16], the use of multiple TNAs enables the Poisson process generator to enhance its maximum event rate by extending the effective bandwidth of amplified thermal noise. In addition, a pulse-width equalizer is included to precisely map each output pulse to a single molecular event. For parallel stochastic simulation of biochemical reactions, we also propose a fundamental reaction building block with an AND gate and a current-steering DAC. Advantageously, the calculation of reaction rates using such asynchronous time-based circuits can achieve higher accuracy than the conventional analog calculation based on translinear circuits. It also enables digital routing between fundamental reaction building blocks without using analog-to-digital converters that were used for routing between chips in [15,17].
This paper is organized as follows: Section 2 describes the operation principle of the proposed Poisson process generator and the effect of increasing the number of thermal noise amplifiers. Next, Section 3 introduces the architecture in which the event rate of the Poisson process is determined by the continuous-time multiplication using an AND gate. Section 4 presents the fundamental reaction building block for parallel stochastic simulation of biochemical reactions. Then, Section 5 provides Verilog-A simulation results of bidirectional second order reactions and amyloid-beta turnover in Alzheimer’s disease that show good agreement with those of the Gillespie algorithm. Finally, Section 6 summarizes our main conclusions.
2. Proposed Poisson Process Generator
2.1. Operation Principle
The architecture and the operation of the proposed Poisson process generator are shown in Figure 1a and Figure 1b, respectively, where the number of thermal noise amplifiers (TNAs) is 2 in Figure 1b. N number of TNAs provide N amplified thermal noises that are independently and identically distributed. Note that the TNA can be implemented with cascaded common source amplifier stages and a large dominant pole capacitor at the output node of the first stage [16]. Furthermore, N comparators generate pulses corresponding to Poisson events whenever each amplified thermal noise becomes lower than a common threshold voltage Vth(t). A pulse width equalizer based on a D flip-flop produces Poisson events with the same pulse width. As shown in Figure 1a, the event rate of the Poisson process is controlled through an FLL which compares and matches it with the VCO output frequency set by the input voltage Vλ(t). The XOR logic gate generates a high only in an odd number of high inputs and collects N parallel Poisson pulses into one signal. In order to compare the frequency of the VCO output with a duty cycle of 0.5, the XOR output is divided by two in the frequency domain [16]. When the VCO gain and offset frequency are KVCO and fos, respectively, the mean frequency of each output channel of the proposed Poisson process generator (fPPG (t)) is as follows.
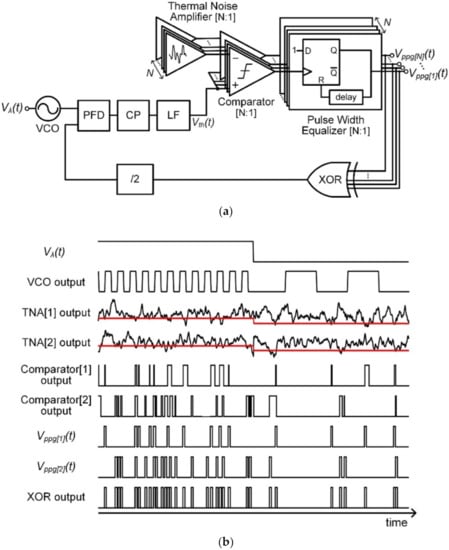
Figure 1.
(a) Block diagram of the proposed Poisson process generator using multiple TNAs. (b) Operation of the proposed Poisson process generator when N = 2.
2.2. Effect of Increasing N
The Poisson process is best understood intuitively as a continuous-time analog of the Bernoulli process. Moreover, the success in a Bernoulli trial corresponds to the transition in which the output of the TNA is higher than the threshold voltage Vth(t) and then lowered in the proposed Poisson process generator (Figure 1a). Moreover, the consecutive success in Bernoulli trials corresponds to the case where the TNA output becomes lower than the threshold voltage for a period as long as a multiple of its bandwidth reciprocal. In this case, the problem is that the proposed Poisson process generator produces only one pulse, not multiple pulses corresponding to consecutive successes. By placing the threshold voltage away from the mean of amplified thermal noise, the probability of consecutive successes can be reduced. However, it lowers the maximum rate that the proposed architecture can generate, slowing down the stochastic simulation of biochemical reactions that will be described in Section 4.
The maximum event rate of the proposed Poisson process generator can be improved by increasing the number of thermal noise amplifiers, N, in Figure 1a. Assuming that the amplified thermal noises obtained from N number of TNAs are independent, the effective bandwidth of amplified thermal noise is extended by a factor of N, and hence the rate of Poisson events increases in proportion to N. In order to verify the improvement of the event rate by increasing N, the Poisson process generation in Figure 1a was simulated using Verilog-A. Note that the bandwidth of amplified thermal noise was set to 160 MHz in the simulation. Figure 2 shows the simulated time-interval histograms of N-channel outputs when N is 1 and 10, respectively. For each N, it also shows the simulation results when the threshold voltage (Vth) is the mean of the amplified thermal noise (μVTNA) and as low as 1.5 times its standard deviation (1.5σVTNA) from the mean, respectively.
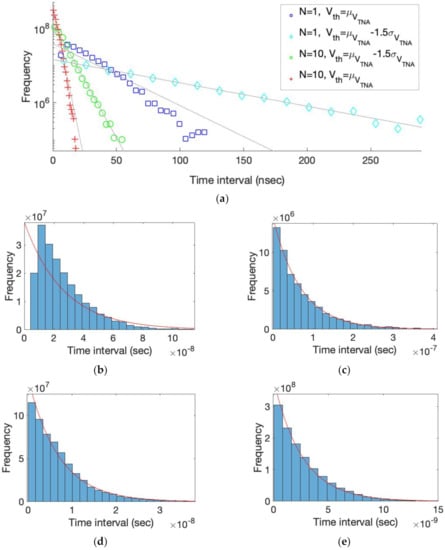
Figure 2.
(a) Simulated time-interval histograms of the Poisson process generation in Figure 1a. (b) N = 1, Vth(t) = μVTNA, mean event rate = 38.02 MHz. (c) N = 1, Vth(t) = μVTNA − 1.5 σVTNA, mean event rate = 14.4 MHz. (d) N = 10, Vth(t) = μVTNA − 1.5 σVTNA, mean event rate = 142.4 MHz. (e) N = 10, Vth(t) = μVTNA, mean event rate = 382 MHz.
Figure 2b shows a time-interval histogram, the simulated statistics of the inter-event rate vs. time, when N is 1 and Vth is μVTNA. Note that the mean event rate of the simulated Poisson process is 38.02 MHz. When Vth is located at μVTNA, the probability of success, the transition in which the output of the TNA is higher than Vth and then lowered, is 0.5. Therefore, an ideal time-interval histogram should follow the exponential distribution with the mean event rate of 80 MHz. However, since the proposed Poisson process generator recognizes the consecutive successes that occur frequently at Vth = μVTNA, as only one success, the simulated mean event rate is reduced to 38.02 MHz. In addition, as shown in Figure 2b, it can be seen that the simulated time interval histogram does not follow the exponential distribution indicated by the red line, severely lacking events with relatively short time intervals.
Figure 2c shows a simulated time-interval histogram with N = 1 and Vth = μVTNA − 1.5 σVTNA, where the mean event rate of the simulated Poisson process is 14.4 MHz. Although the simulated mean event rate is decreased by a factor of 2.64 than that of Figure 2b, the simulated time-interval histogram follows the exponential distribution well by placing Vth as far away from μVTNA as 1.5 σVTNA to reduce the probability of consecutive successes. Figure 2d shows a simulated time-interval histogram with N = 10 and Vth = μVTNA − 1.5 σVTNA. It can be seen that the simulated histogram is in good agreement with an exponential distribution as the probability of consecutive successes is low as shown in Figure 2c. The mean event rate of the simulated Poisson process is 142.4 MHz, which is 9.87 times higher than that of Figure 2c. This is because the effective bandwidth that the amplified thermal noise is extended with is in proportion to 10, the number of TNAs in Figure 2d.
Figure 2e shows a simulated time-interval histogram with N = 10 and Vth = μVTNA, where the mean event rate of the simulated Poisson process is 382 MHz. Interestingly, the simulated histogram still follows an exponential distribution even when the threshold voltage is μVTNA. This is because short time intervals that were insufficient in Figure 2b due to the omission of consecutive success are filled with those produced by serializing parallel Poisson events obtained from 10 TNAs. Therefore, increasing N in the proposed Poisson process generator provides an additional acceleration that can be achieved by placing the threshold voltage close to μVTNA. From Figure 2c,e, when N is increased by a factor of 10, it can be observed that the maximum event rate of the proposed Poisson process generator is increased by a factor of 26.5.
3. Stochastic Multiplication Using AND Gate
According to the law of mass action, the rate of a chemical reaction is proportional to the product of the reactant concentrations. It is necessary to implement the multiplication of the concentration of the reactants and a reaction constant to apply the proposed Poisson process generator described in Section 2 to the stochastic simulation of biochemical reactions. As shown in Figure 3a, the multiplication is performed first, and the result can be applied as an input to the Poisson process generator. However, analog multipliers, including a translinear current-mode circuit [15,16,17], are difficult to achieve with high accuracy due to device mismatch, PVT variations, and limited dynamic range.
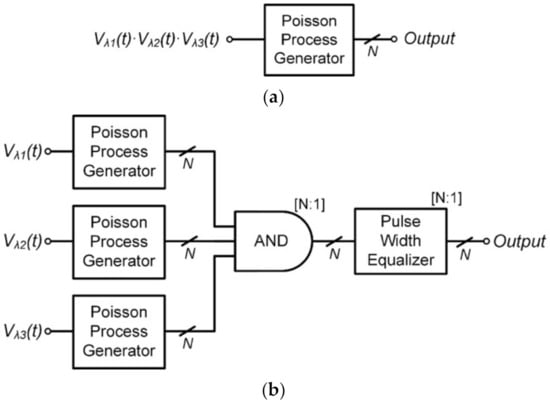
Figure 3.
Block diagram of Poisson process generation in which the event rate is determined by (a) conventional analog multiplication and (b) proposed stochastic multiplication of logic AND gate.
In order to alleviate this problem, we propose the Poisson process generation in which the event rate is determined by the stochastic multiplication of digital logic AND gates, as shown in Figure 3b. The output pulse from one of the three Poisson process generators in Figure 3b passes through the AND gate only when the outputs of the other two Poisson process generators are both HIGH. Therefore, the mean frequency of the AND gate output can be obtained as
where fPPGi is the mean frequency of each output channel of the Poisson process generator that receives Vλi(t) as an input voltage. Phighi is the probability that the output of the i-th Poisson process generator is HIGH, and can be represented as
where τPW is the width of the output pulse of the Poisson process generator. In order to treat each pulse from the AND gates as an occurrence of the Poisson event, their widths are equalized via the pulse width equalizers. By applying (3) to (2), the output rate of the proposed architecture in Figure 3b, the mean rate of the Poisson events obtained from the outputs of N channel AND gates, can be obtained as the following equation.
The time-interval histogram obtained by simulating the proposed architecture of Figure 3b in Verilog-A is shown in Figure 4. Note that the Poisson process generators transmitting their outputs to the AND gates are all set to the same condition as the simulation in Figure 2e, where N is 10, fppg is 38.2 MHz and τPW is 6.25 ns. It can be seen that the simulated histogram follows the exponential distribution well even after passing through the AND gate. The simulated mean frequency of the output Poisson events is 67.9 MHz, which is close to the theoretical value of 75 MHz from (4). The difference between the simulated frequency and the theoretical value arises from the nonzero setup time of the pulse width equalizer where the output pulses of the AND gate with a width shorter than the setup time are omitted.
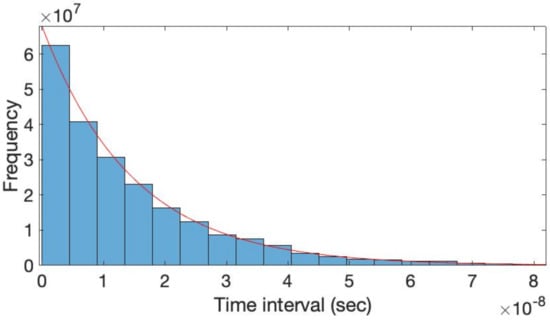
Figure 4.
Time-interval histograms of the simulated output of Figure 3b.
4. Fundamental Reaction Building Block
Figure 5 shows the fundamental reaction building block for the stochastic simulation of association reaction A + B → C and dissociation reaction C → B + A, where Ka and Kd are its reaction constant, respectively. V[A], V[B], and V[C] represent the voltage corresponding to the concentrations of reactant A, B, and C, respectively. Moreover, Vka and VKd denote the voltage corresponding to the reaction constant Ka and Kd, respectively. Additionally, V[1] is the voltage at which the reactant concentration is 1. Stochastic events of the association reaction and the dissociation reaction with a rate of Ka[A][B] and Kd[C], respectively, are generated from the proposed architecture of Figure 3b. V[A], V[B], and V[C] are updated by 1-bit current-steering digital-to-analog converters (DACs) shown in Figure 5. Since the reaction order of the dissociation reaction is less than that of the association reaction by 1, V[1] is applied to the input of the Poisson process generator that does not have a corresponding input.
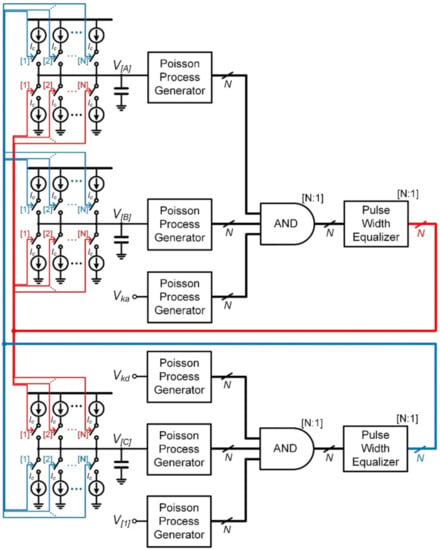
Figure 5.
Fundamental reaction building block for stochastic simulation of bidirectional second-order reaction: A + B ↔ C.
From (1) and (4), the mean rate of association reaction (λa) and the mean rate of dissociation reaction (λd) can be obtained as follows
where the offset frequency of the VCO is assumed to be much less than the oscillation frequency [25]. Consequently, the simulation speed of the proposed fundamental reaction building block is scaled by 24Kvco3V[1]3τPW2/N2 than the actual biochemical reaction rate. The upper limit of V[1] to be maximized for fast simulation is determined by the maximum event rate that the proposed Poisson process generator of Figure 1a can produce. As discussed in Section 2, it can be increased proportionally when N is small and even more than that when N approaches 10.
When a large-scale biochemical reaction network is constructed using the proposed architecture in Figure 5, the routing between reaction building blocks is achieved via asynchronous digital pulses corresponding to the event stream of the Poisson process. Thus, unlike the previous works that use analog-to-digital converters for routing between chips [15,16,17], it has the advantage of implementing the large-scale stochastic biochemical reaction network without errors due to synchronization or quantization.
5. Stochastic Simulation Results of Biochemical Reactions
Gillespie stochastic simulation results from COPASI [26] and Verilog-A simulation results of Figure 5 for the bidirectional second-order reaction (A + B → C and C → A + B) are shown in Figure 6a,b, respectively, where Ka = 80, Kd = 800, and the initial value of [A], [B], and [C] is 600, 400, and 0. In the simulation presented in Figure 5, V[1] was 5 mV, the output pulse width of pulse width equalizers was 5 ns, and the output current of current sources in the current steering DAC was 100 μA. For each Poisson process generator, N was set to 5, KVCO was set to 25 MHz/V, and the TNA bandwidth was set to 200 MHz. In addition, a second-order passive loop filter with two 1 pF capacitors and one 860 kΩ resistor was used in the FLL. From (5) and (6), the simulated reaction rates of Figure 6b are scaled up by 21 than the actual biochemical reaction rates. It can be seen that the simulation results of Figure 5 are in good agreement with those of conventional Gillespie’s algorithm.
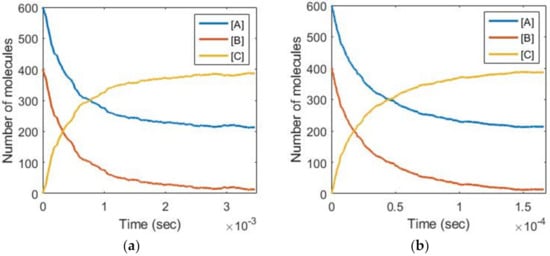
Figure 6.
Simulation results of (a) Gillespie stochastic algorithm and (b) the proposed architecture of Figure 5 for the reactions: A + B ↔ C. Note that the simulated reaction rates of (b) are scaled up by 21 than the actual biochemical reaction rates.
In order to verify the stochastic simulation of very-low-molecule-number biochemical reactions that were not feasible in [16], we simulated the following stochastic model of amyloid-beta (Aβ) turnover [27], which is widely used in research studies for Alzheimer’s disease.
Due to a slight decrease in Kdeg, the number of Aβ molecules can exceed a normal basal level (four in [27]) for short periods of time, and it may cause dimerization of Aβ monomers, which can initiate the aggregation process of Alzheimer’s disease.
Figure 7 shows an architecture based on the proposed fundamental reaction building block of Figure 5 for the stochastic simulation of Aβ turnover in (7). Since (7) consists of a zero-order association reaction and a first-order dissociation reaction, only two Poisson process generators are required for the AND gate-based stochastic multiplication.
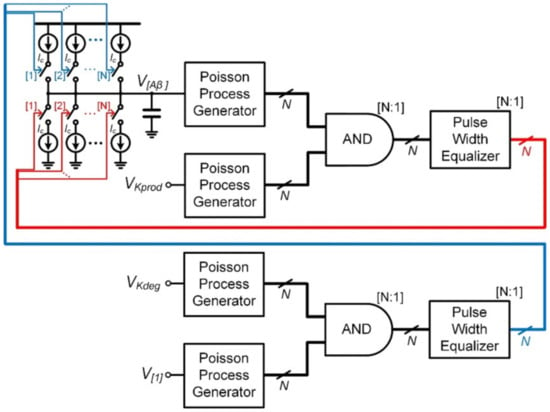
Figure 7.
Fundamental reaction building block for stochastic simulation of the model of amyloid beta (Aβ) turnover.
Gillespie stochastic simulation results of Aβ turnover in (7) are shown in Figure 8a where Kprod = 1.86 × 10−5 molecules/s and Kdeg = 1.5 × 10−5 molecules/s. In order to examine the aggregation process of Alzheimer’s disease in human aging, the simulated time is set to 100 years [27]. The mean and the standard deviation of the simulated number of reactant Aβ ([Aβ]) are 1.296 and 1.159, respectively. Verilog-A simulation results of Figure 7 are shown in Figure 8b where the simulation parameters are set to N = 10, V[1] = 5 mV, τPW = 5 ns, and KVCO = 50 MHz/V, scaling the simulated reaction rates by 3.125 × 109 than the actual biochemical reaction rates. It can be seen that the time taken for 100 years in actual biochemical reactions is shortened to 3.5 ms in Figure 8b. The mean and the standard deviation of the simulated [Aβ] are 1.301 and 1.18, respectively. Figure 8 indicates that the simulation based on the proposed fundamental reaction building blocks is consistent with the Gillespie stochastic simulation, even in the biochemical reactions with very few molecules.
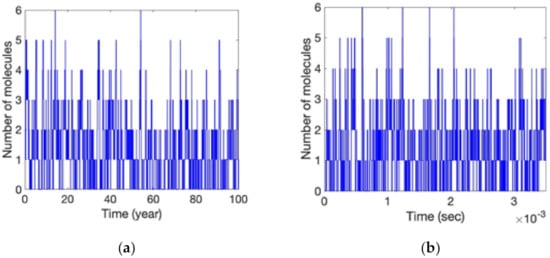
Figure 8.
Simulation results of (a) Gillespie stochastic algorithm and (b) the architecture of Figure 7 for the reactions of Aβ turnover. Note that the simulated reaction rates of (b) are scaled up by 3.125 × 109 than the actual biochemical reaction rates.
6. Conclusions
In this work, we presented a multiple TNAs-based Poisson process generator and fundamental reaction building blocks for parallel stochastic simulation of biochemical reactions. Increasing the number of TNAs to accelerate the Poisson events and employing digital AND gates for robust reaction rate calculations allow for faster and more accurate stochastic simulations of biochemical reactions than previous parallel stochastic simulators.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.K.; methodology, Y.J. (Yeji Jo); software, Y.J. (Yeji Jo); validation, K.M.; formal analysis, Y.J. (Yeji Jo); investigation, Y.J. (Yeonjoo Jeong), J.Y.K., J.P., S.L., I.K., J.-K.P. and G.-W.H.; data curation, Y.J. (Yeji Jo); writing—original draft preparation Y.J. (Yeji Jo); writing—review and editing, J.K.; visualization, Y.J. (Yeji Jo) and K.M.; supervision, J.K.; project administration, J.K.; funding acquisition, J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National R&D Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea(NRF) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT(2021M3F3A2A01037808, 2020M3F3A2A01082329) and by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) through 2E31551.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, T.; Chen, L.; Aihara, K. Molecular communication through stochastic synchronization induced by extracellular fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 178103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gammaitoni, L.; Hänggi, P.; Jung, P.; Marchesoni, F. Stochastic resonance. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1998, 70, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.L.; Gaudet, S.; Albeck, J.G.; Burke, J.M.; Sorger, P.K. Non-genetic origins of cell-to-cell variability in TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Nature 2009, 459, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuer, R. Effects of stochasticity in models of the cell cycle: From quantized cycle times to noise-induced oscillations. J. Theor. Biol. 2004, 228, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kepler, T.B.; Elston, T.C. Stochasticity in transcriptional regulation: Origins, consequences, and mathematical representations. Biophys. J. 2001, 81, 3116–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillespie, D.T. Exact stochastic simulation of coupled chemical reactions. J. Phys. Chem. 1977, 81, 2340–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slepoy, A.; Thompson, A.P.; Plimpton, S.J. A constant-time kinetic Monte Carlo algorithm for simulation of large biochemical reaction networks. J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 205101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, R.; González-Segredo, N.; Sbalzarini, I.F. A new class of highly efficient exact stochastic simulation algorithms for chemical reaction networks. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 130, 244104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, M.A.; Bruck, J. Efficient exact stochastic simulation of chemical systems with many species and many channels. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 1876–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Petzold, L.R.; Rathinam, M.; Gillespie, D.T. The numerical stability of leaping methods for stochastic simulation of chemically reacting systems. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 121, 12169–12178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaw, D.E.; Deneroff, M.M.; Dror, R.O.; Kuskin, J.S.; Larson, R.H.; Salmon, J.K.; Young, C.; Batson, B.; Bowers, K.J.; Chao, J.C.; et al. Anton, a special-purpose machine for molecular dynamics simulation. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 2007, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, D.; Bergmann, F.T.; Sauro, H.M. TinkerCell: Modular CAD tool for synthetic biology. J. Biol. Eng. 2009, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Petzold, L. Efficient parallelization of the stochastic simulation algorithm for chemically reacting systems on the graphics processing unit. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Appl. 2010, 24, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Salwinski, L.; Eisenberg, D. In silico simulation of biological network dynamics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.S.; Kim, J.; Sarpeshkar, R. A cytomorphic chip for quantitative modeling of fundamental bio-molecular circuits. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2015, 9, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Woo, S.S.; Sarpeshkar, R. Fast and precise emulation of stochastic biochemical reaction networks with amplified thermal noise in silicon chips. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.S.; Kim, J.; Sarpeshkar, R. A digitally programmable cytomorphic chip for simulation of arbitrary biochemical reaction networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2018, 12, 360–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarpeshkar, R. Cytomorphic electronics: Cell-inspired electronics for systems and synthetic biology. In Ultra Low Power Bioelectronics: Fundamentals, Biomedical Applications, and Bio-Inspired Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 753–786. [Google Scholar]
- Hanna, H.A.; Danial, L.; Kvatinsky, S.; Daniel, R. Cytomorphic electronics with memristors for modeling fundamental genetic circuits. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2020, 14, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houssein, A.; Papadimitriou, K.I.; Drakakis, E.M. A 1.26 µW Cytomimetic IC Emulating Complex Nonlinear Mammalian Cell Cycle Dynamics: Synthesis, Simulation and Proof-of-Concept Measured Results. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2015, 9, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medley, J.K.; Teo, J.; Woo, S.S.; Hellerstein, J.; Sarpeshkar, R.; Sauro, H.M. A compiler for biological networks on silicon chips. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2020, 16, e1008063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, J.J.; Kim, J.; Woo, S.S.; Sarpeshkar, R. Bio-molecular circuit design with electronic circuit software and cytomorphic chips. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS), Nara, Japan, 17–19 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Beahm, D.R.; Deng, Y.J.; Riley, T.G.; Sarpeshkar, R. Cytomorphic Electronic Systems: A review and perspective. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2021, 15, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Sarpeshkar, R.; Mandal, S. A Compact and Power-Efficient Noise Generator for Stochastic Simulations. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Lansing, MI, USA, 9–11 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanli, K.; Sayedi, S.M.; Dehghani, R.; Jalili, A.; Wikner, J.J. A low power wide tuning-range CMOS current-controlled oscillator. Integration 2016, 55, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoops, S.; Sahle, S.; Gauges, R.; Lee, C.; Pahle, J.; Simus, N.; Singhal, N.; Xu, L.; Mendes, P.; Kummer, U. COPASI- a complex pathway simulator. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 3067–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proctor, C.J.; Pienaar, I.S.; Elson, J.L.; Kirkwood, T.B. Aggregation, impaired degradation and immunization targeting of amyloid-beta dimers in Alzheimer’s disease: A stochastic modelling approach. Mol. Neurodegener. 2012, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).