Design of a Memristor-Based Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)
Abstract
1. Introduction
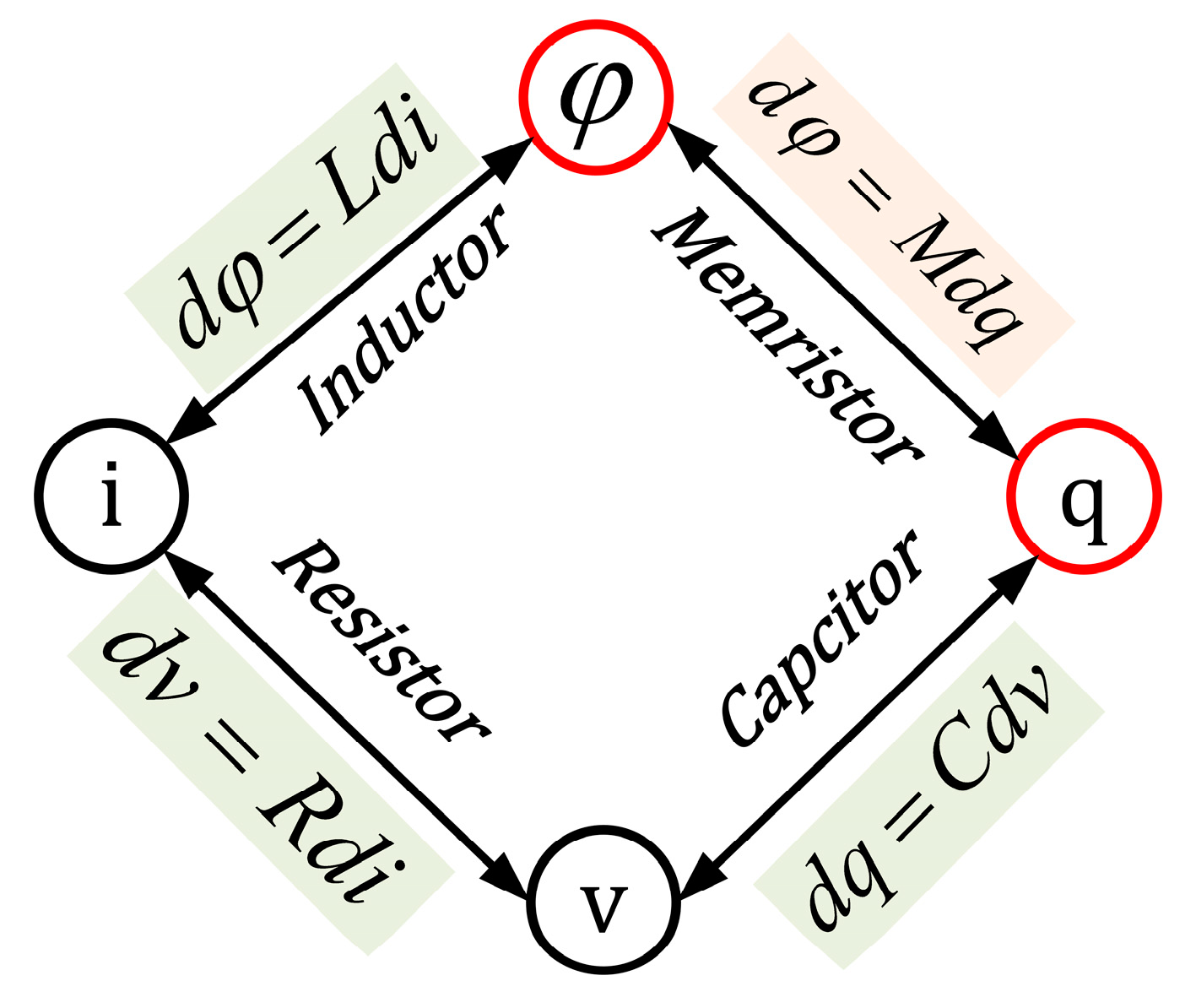
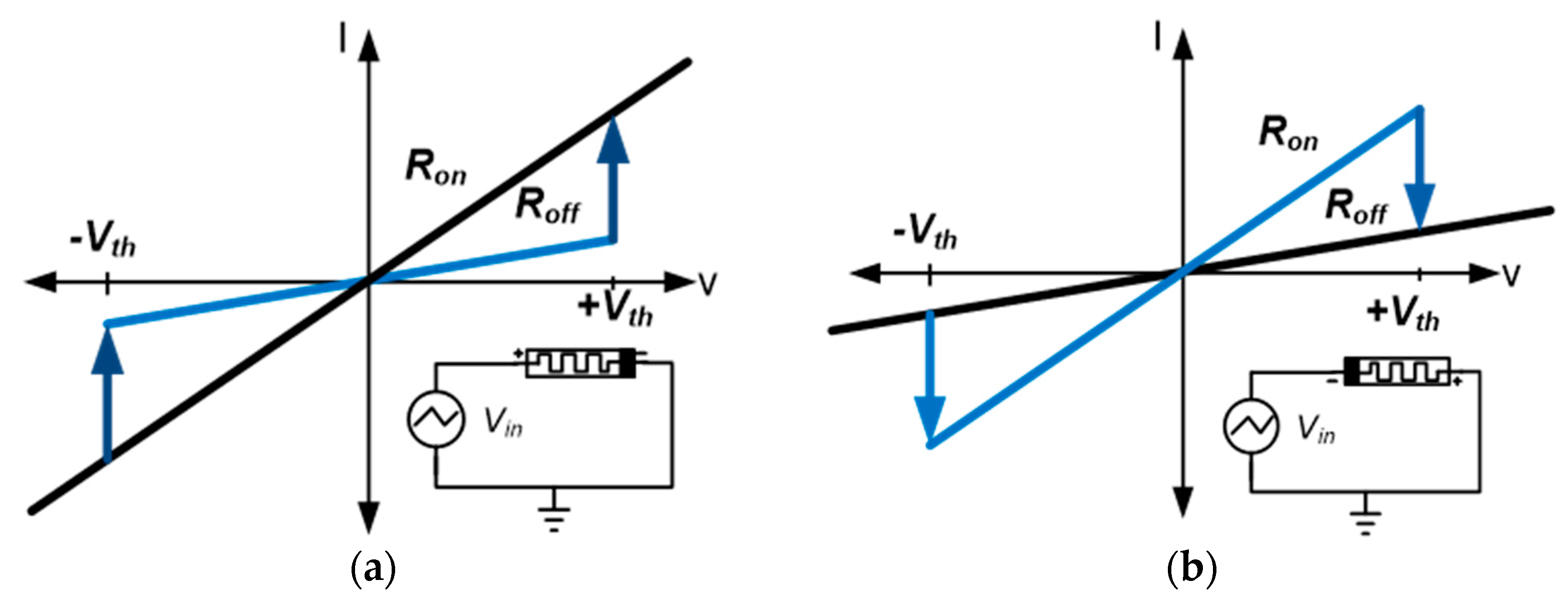
2. Memristive Element Characteristics
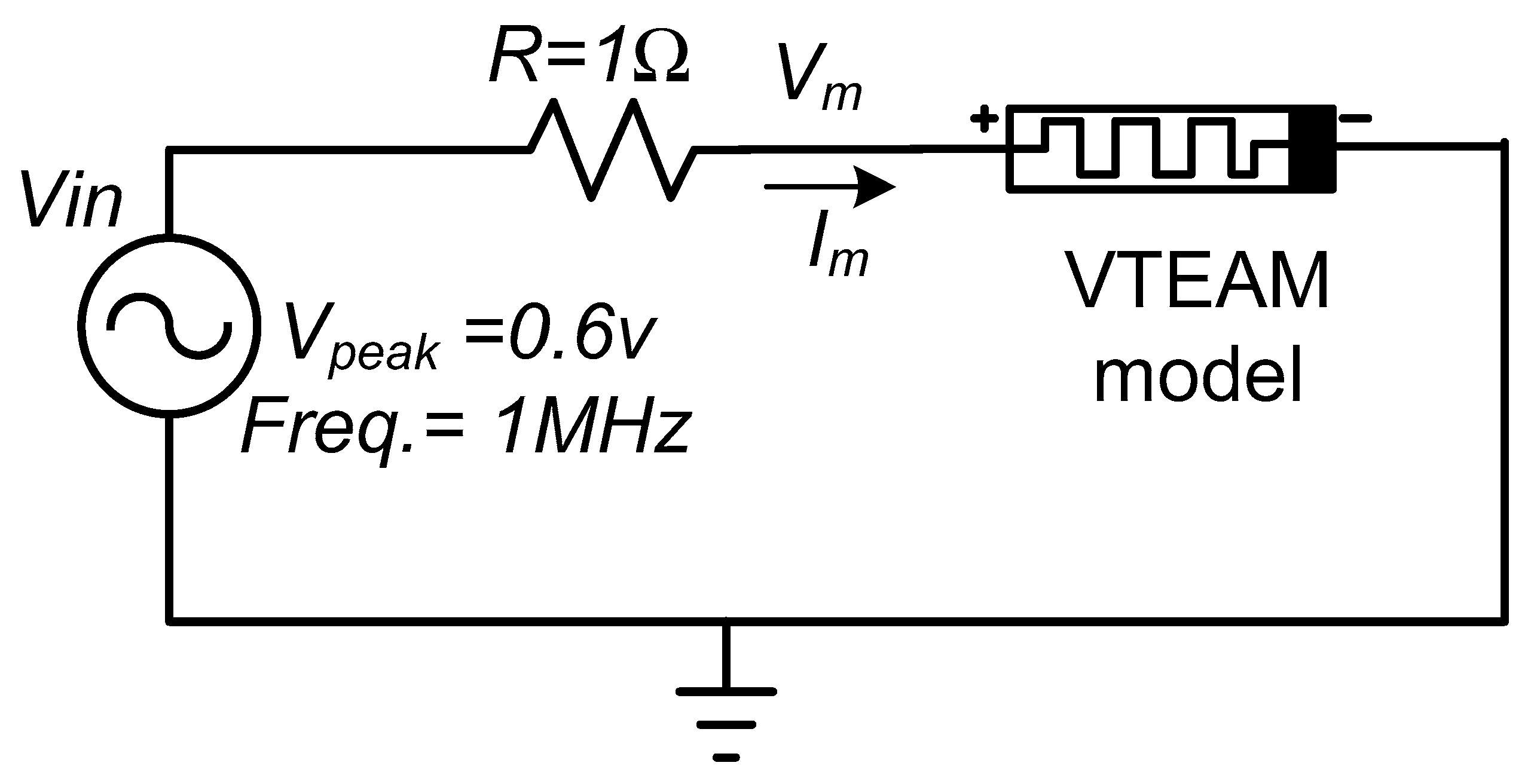
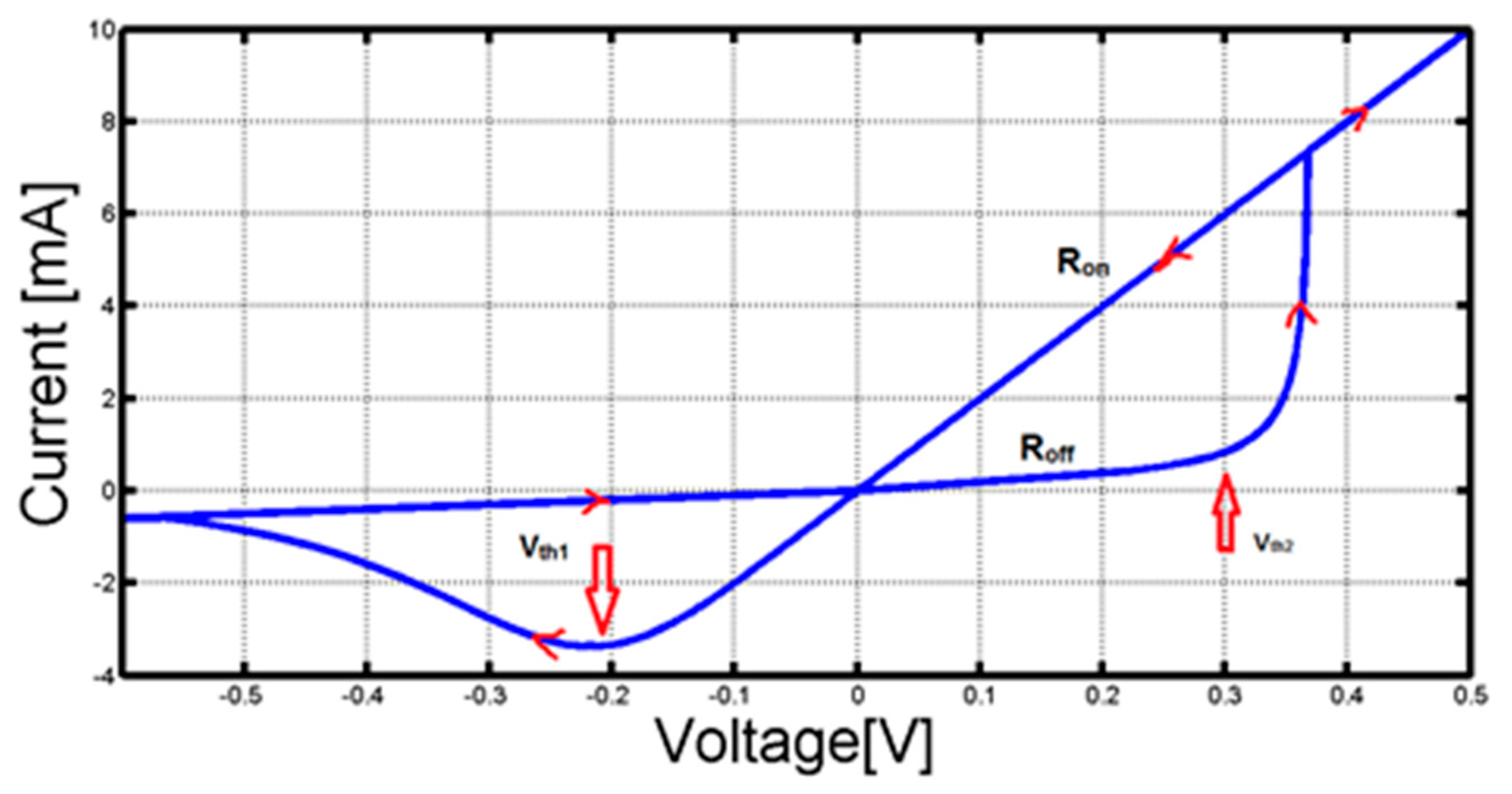
Memristor Setup and Characteristic
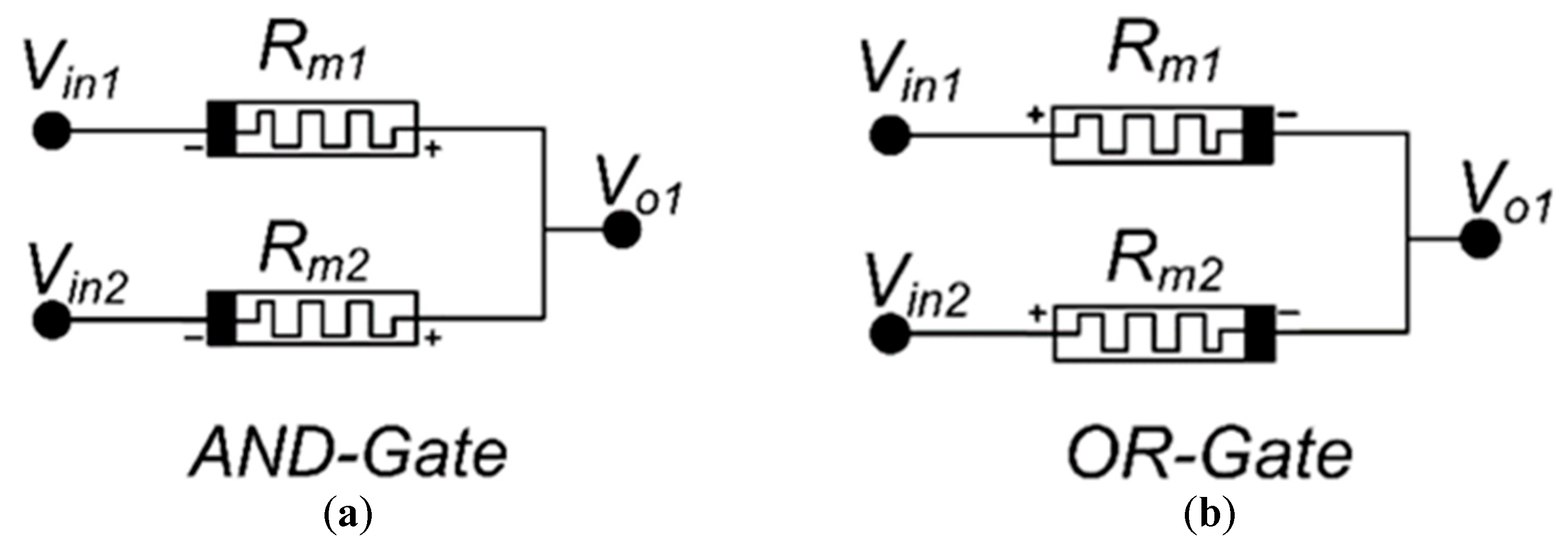
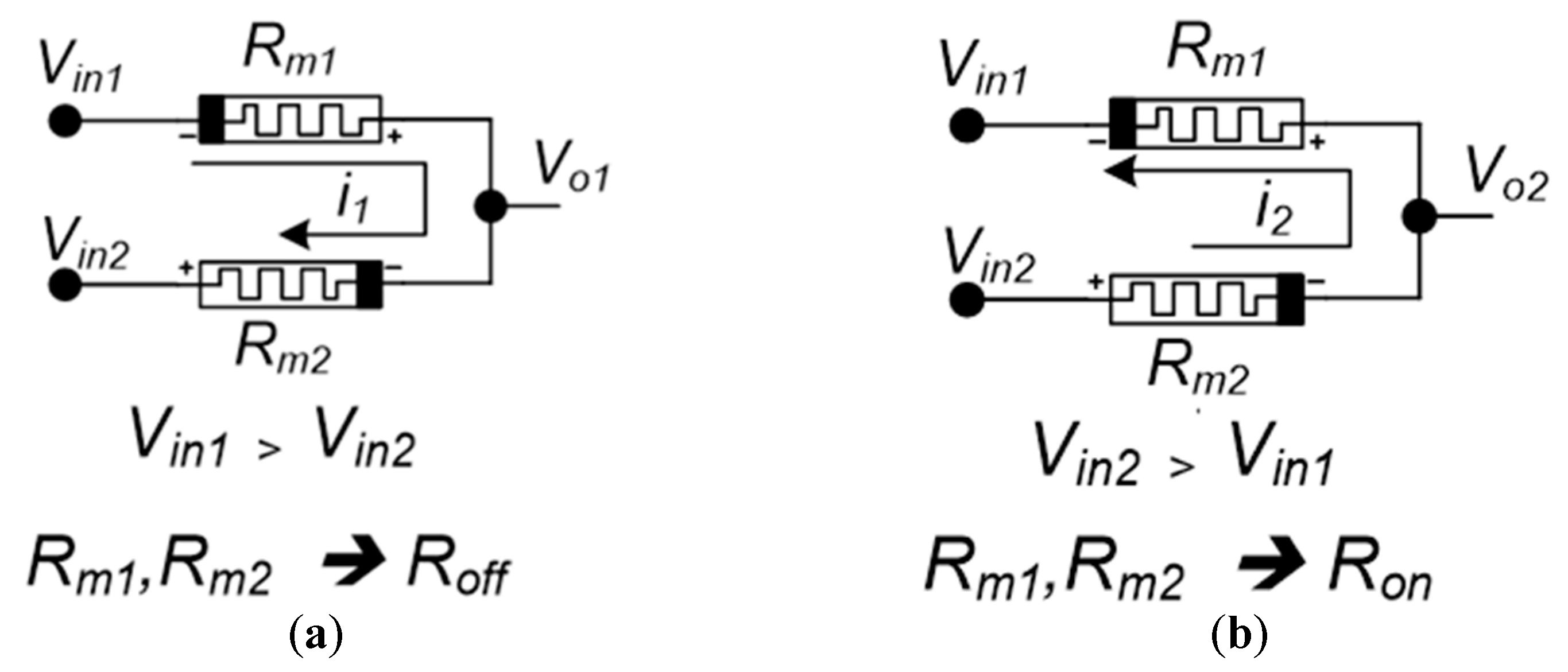
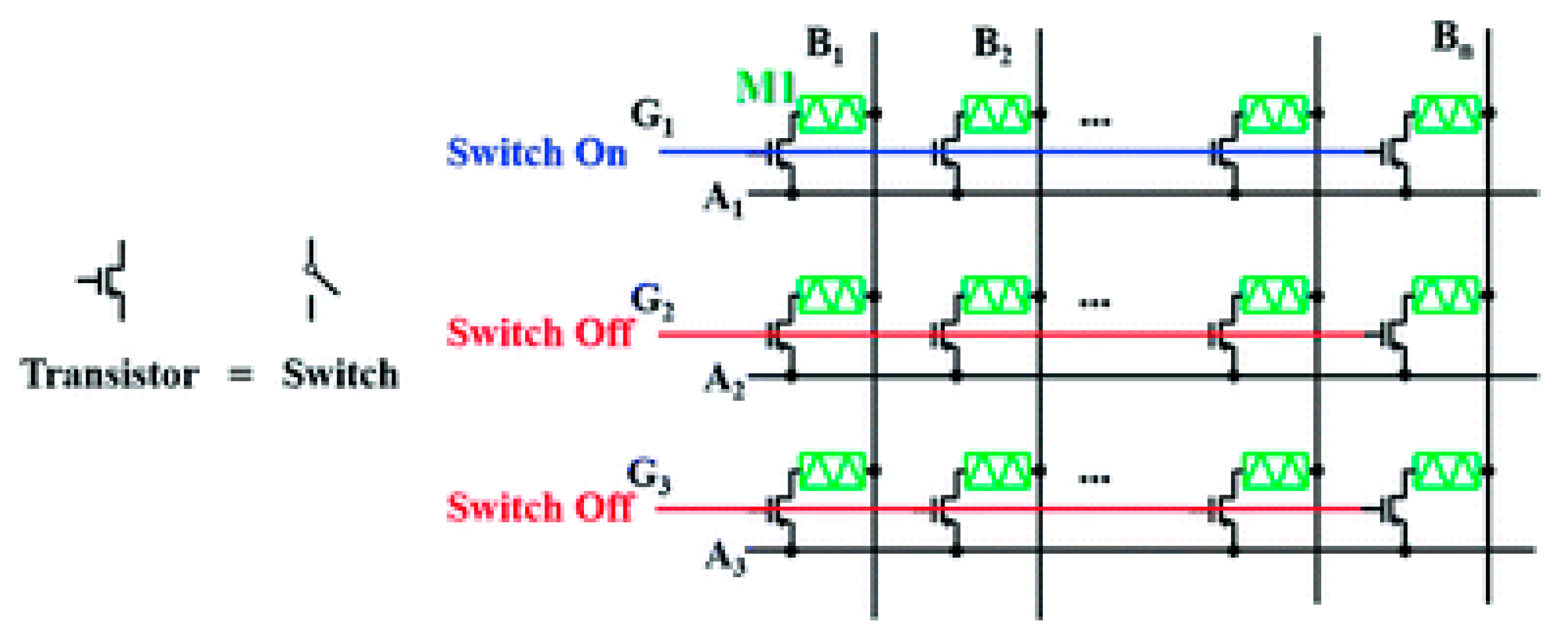
3. Memristor Ratioed Logic (MRL)
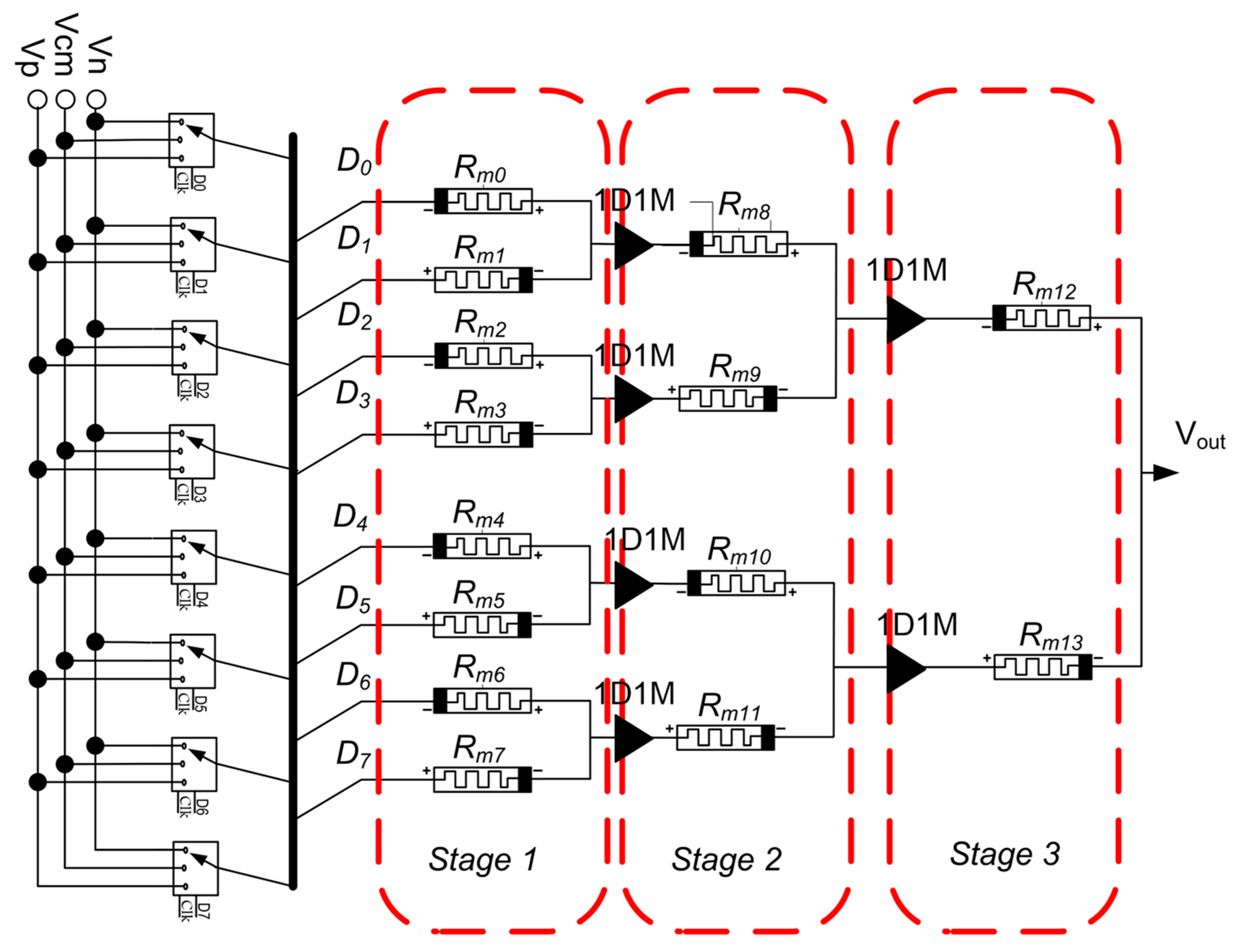
4. Proposed DAC Cell Based on Memristor Technology
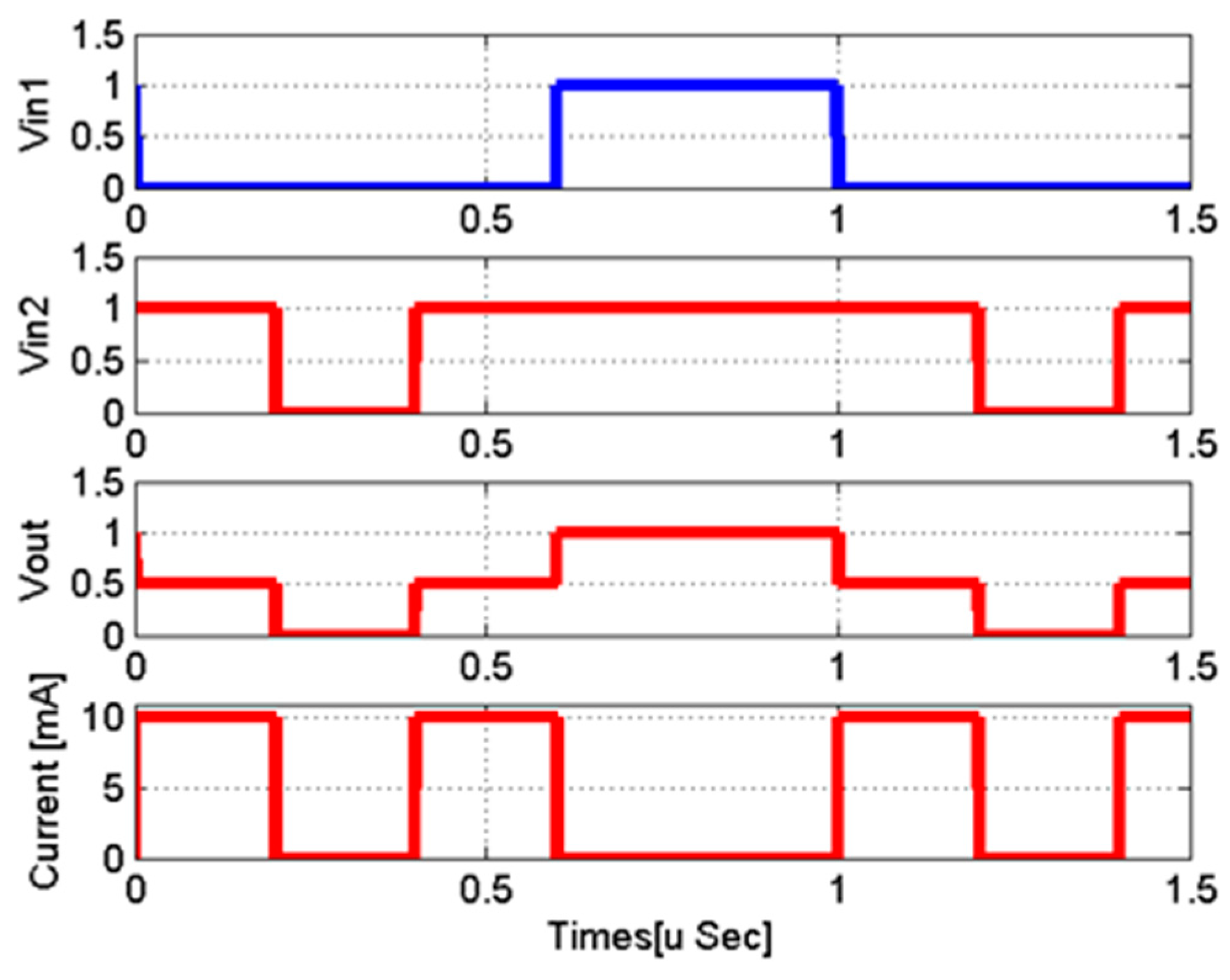
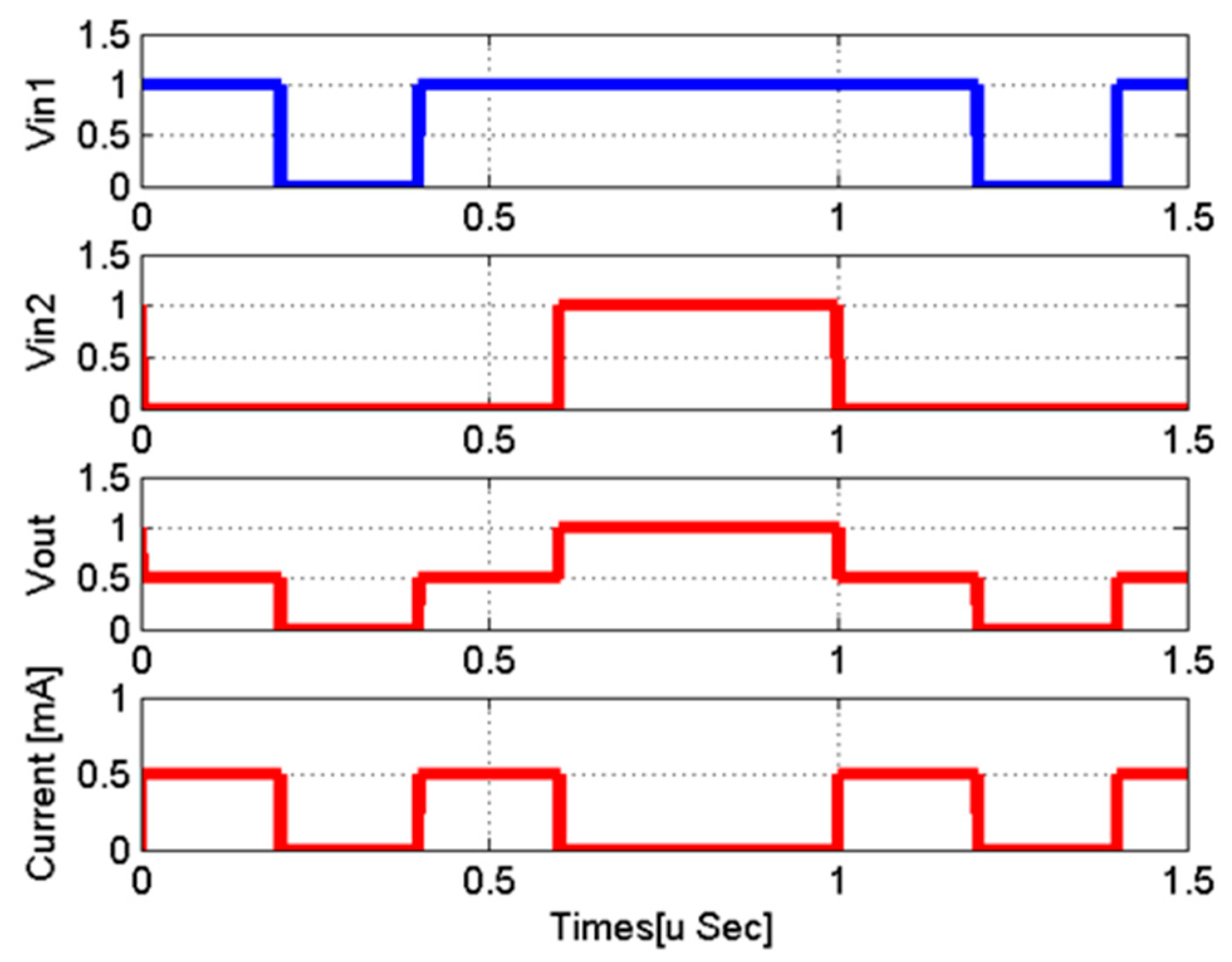
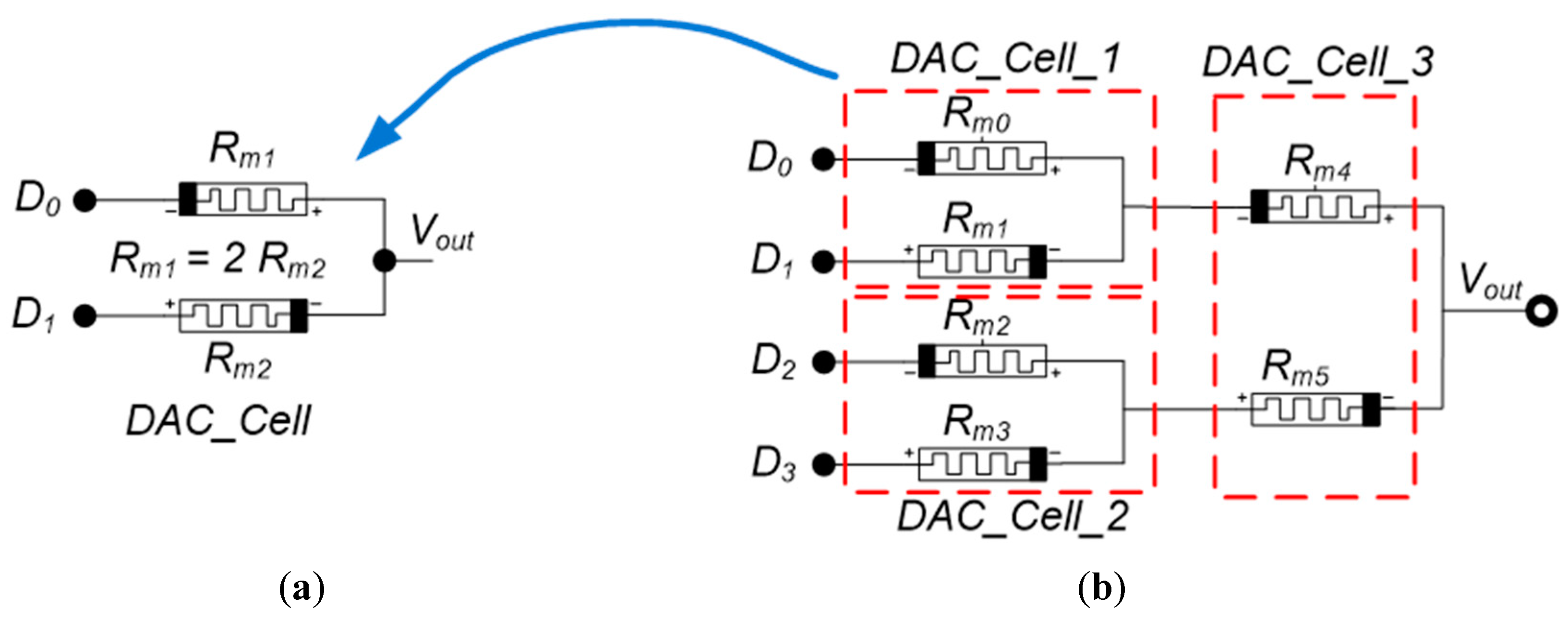
4.1. DAC Cell Based on a Memristor Device
4.2. Design of the Thermometer Code to Analog Converter Based on Memristor
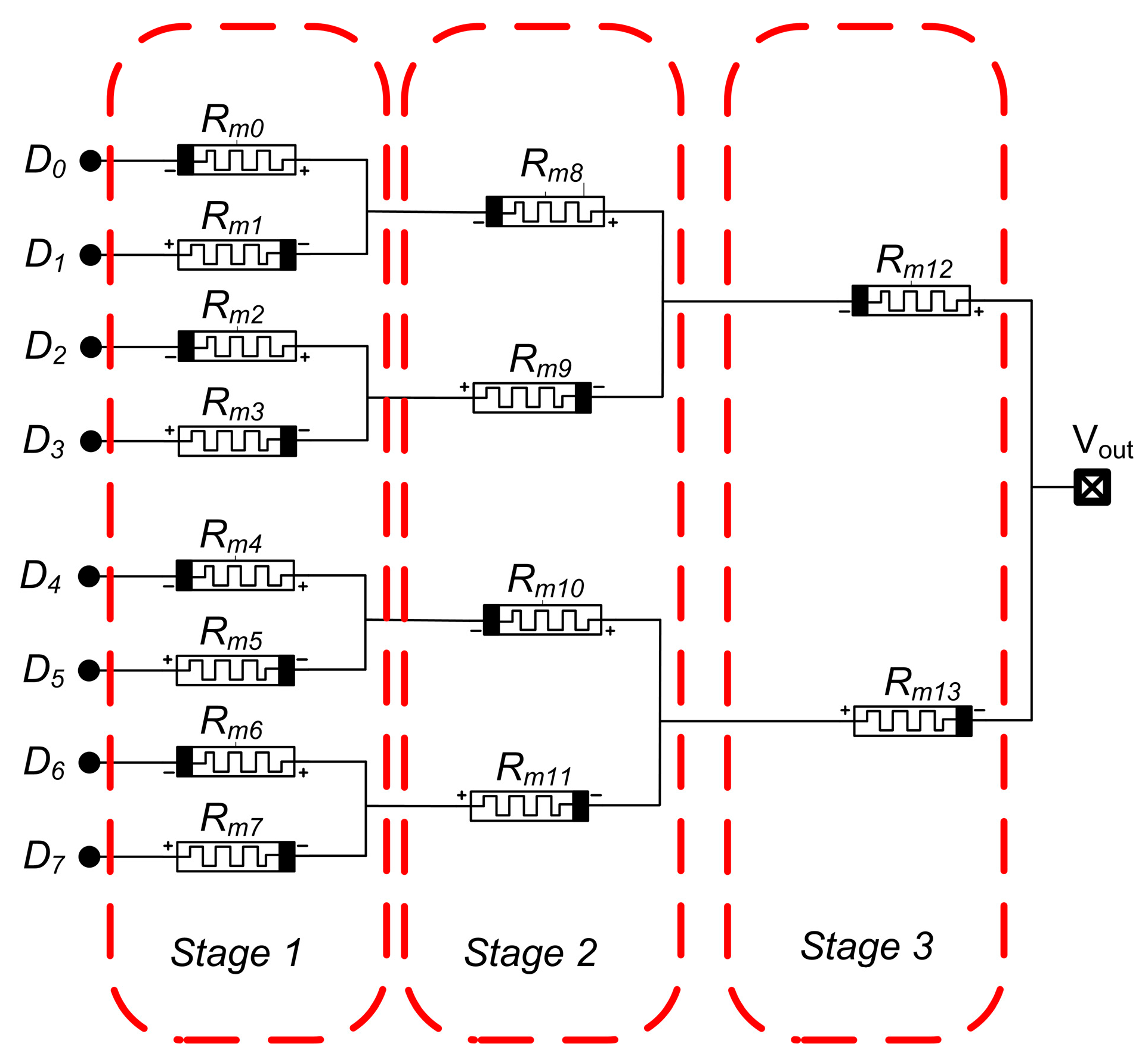
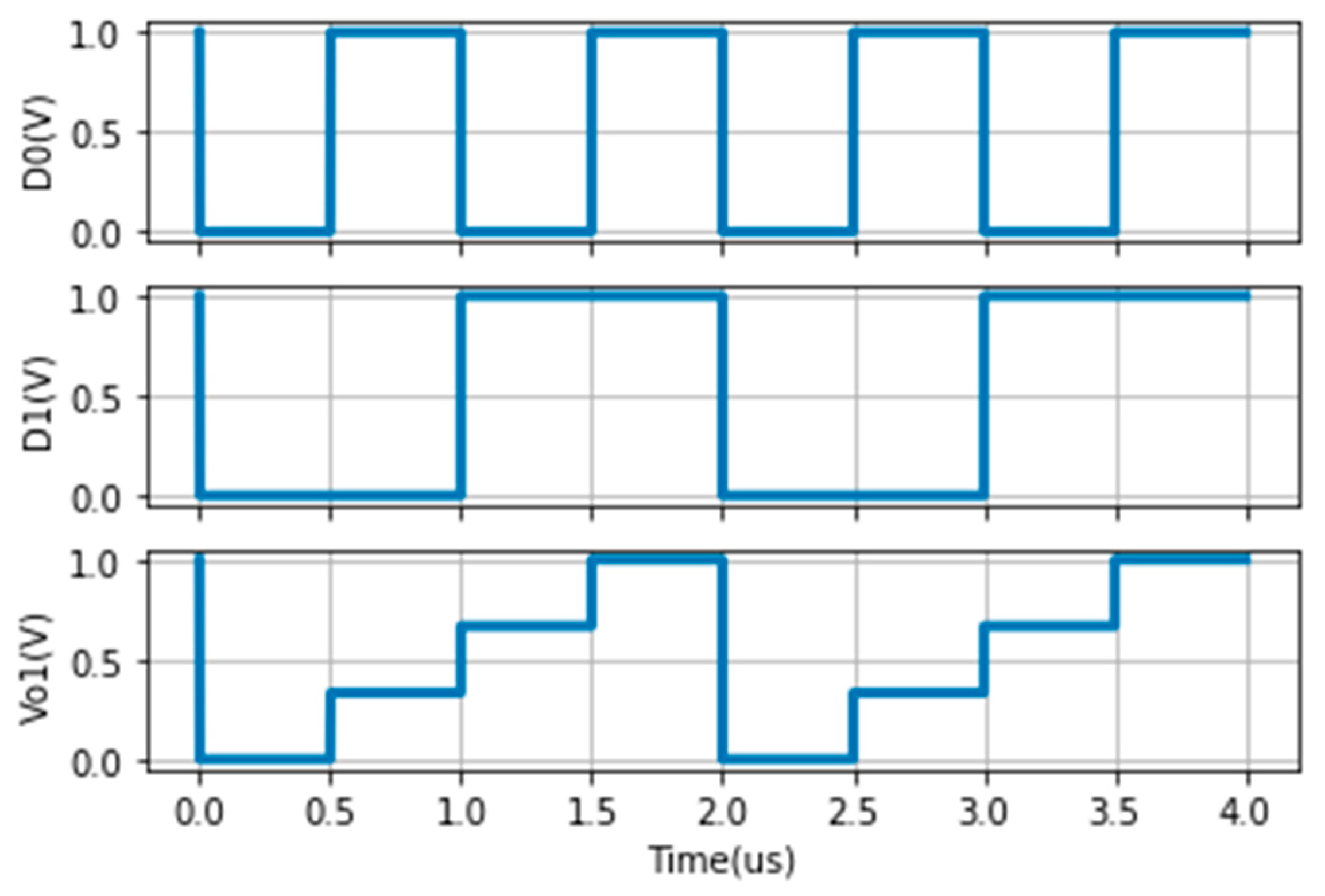
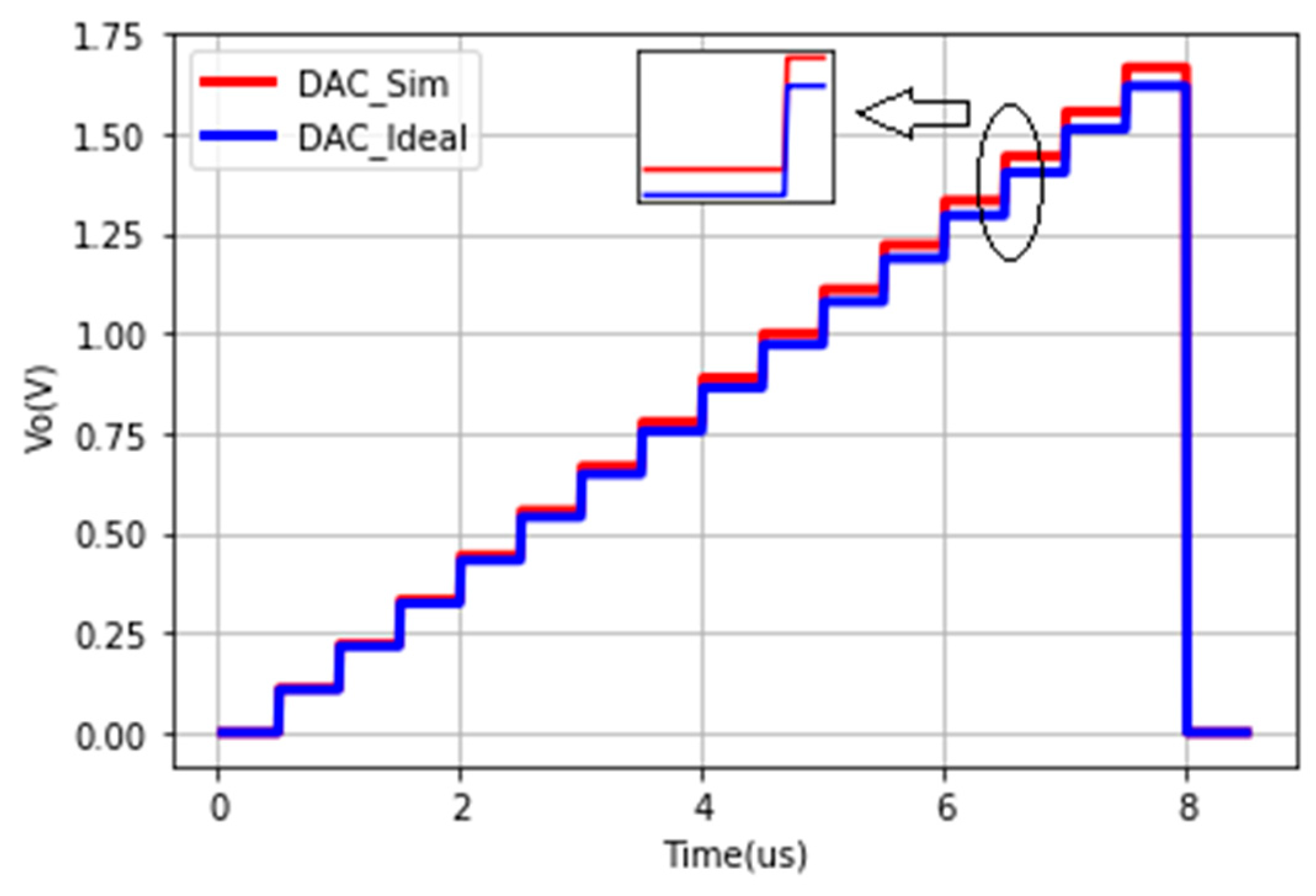
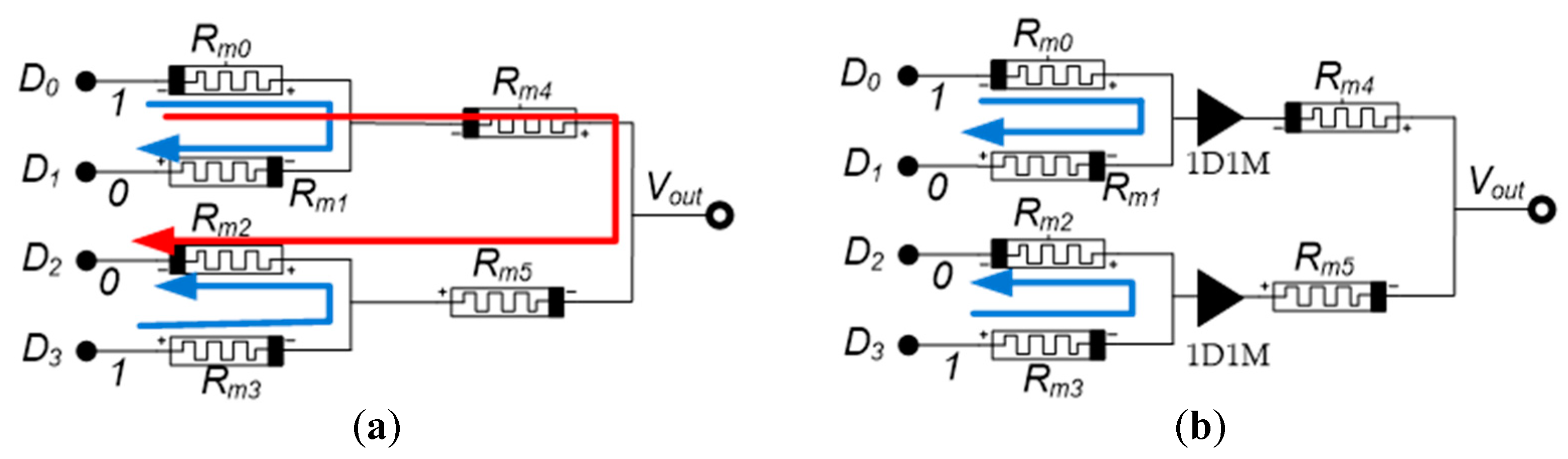
4.3. Binary-Weighted DAC Cell-Based on Memristor
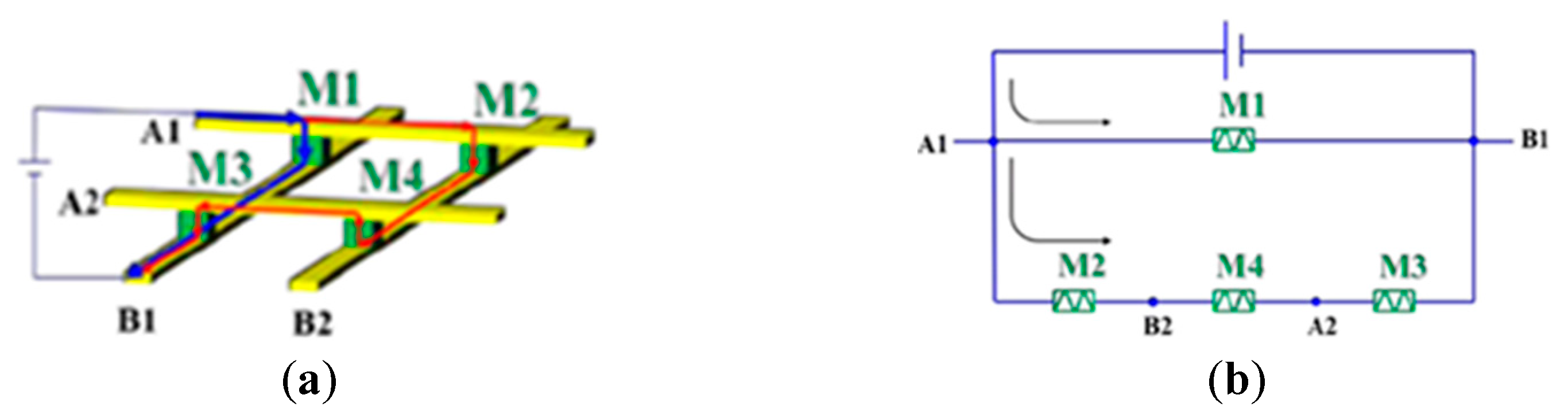
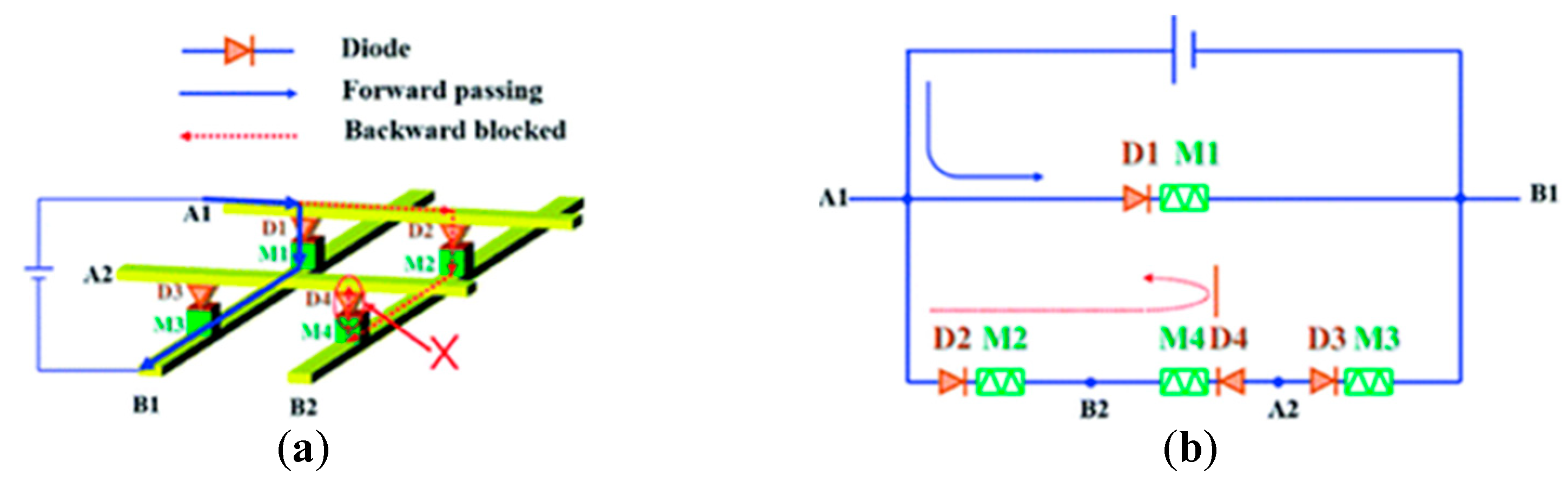
4.4. Sneak Path Problem in a Binary-Weighted DAC-Based Memristor
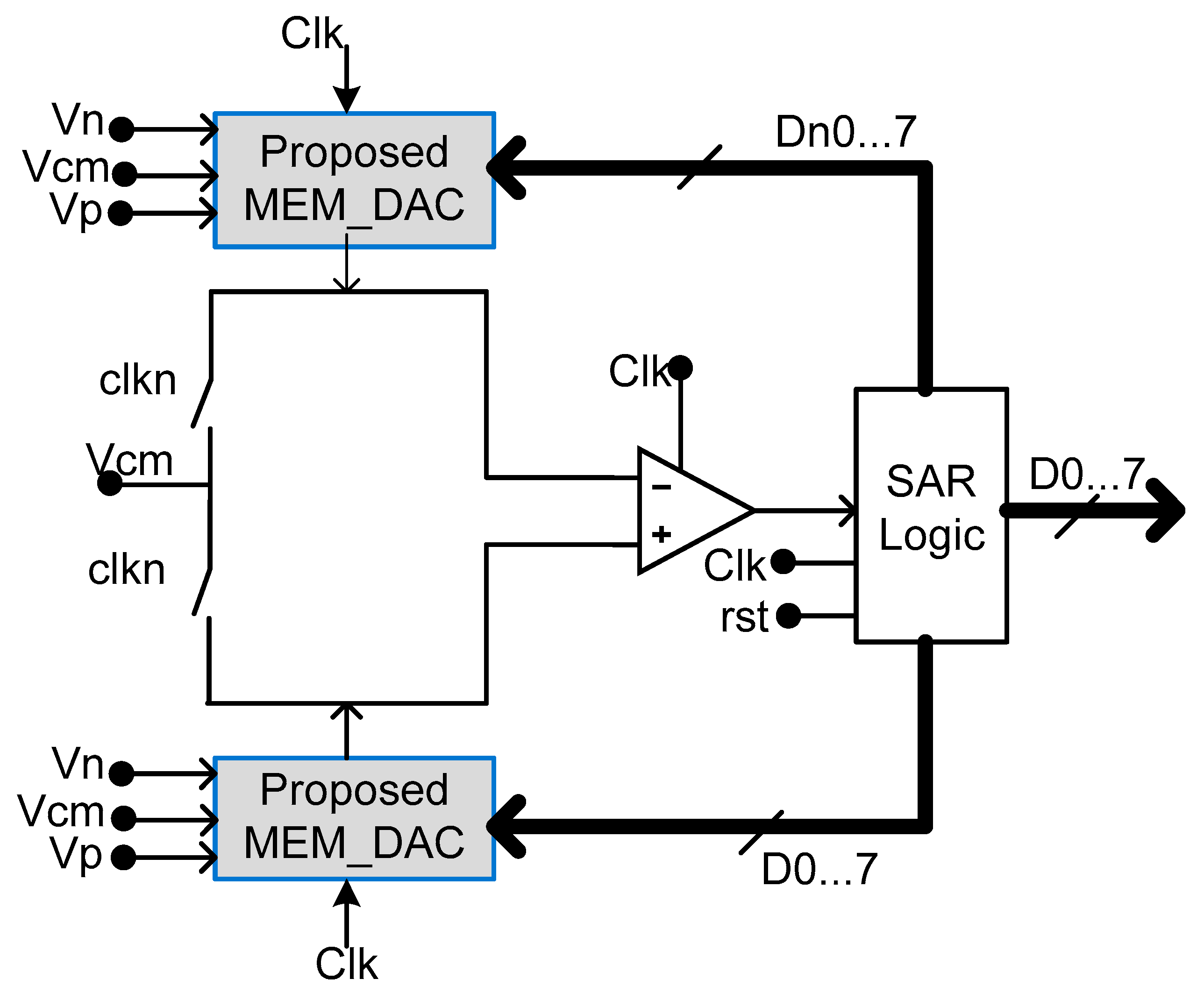
5. Memristor DAC-Based Successive Approximation Register (SAR)-ADC
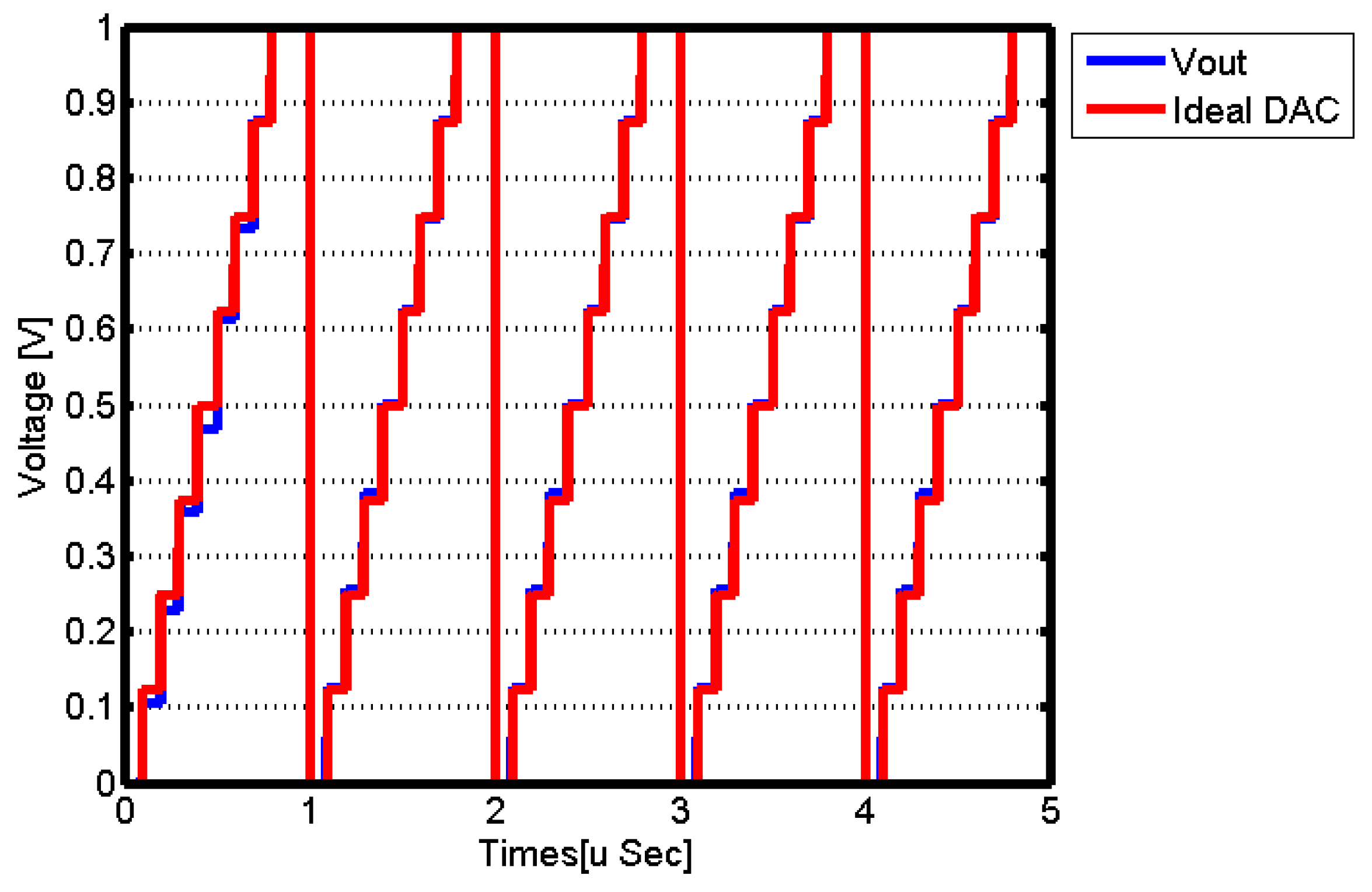
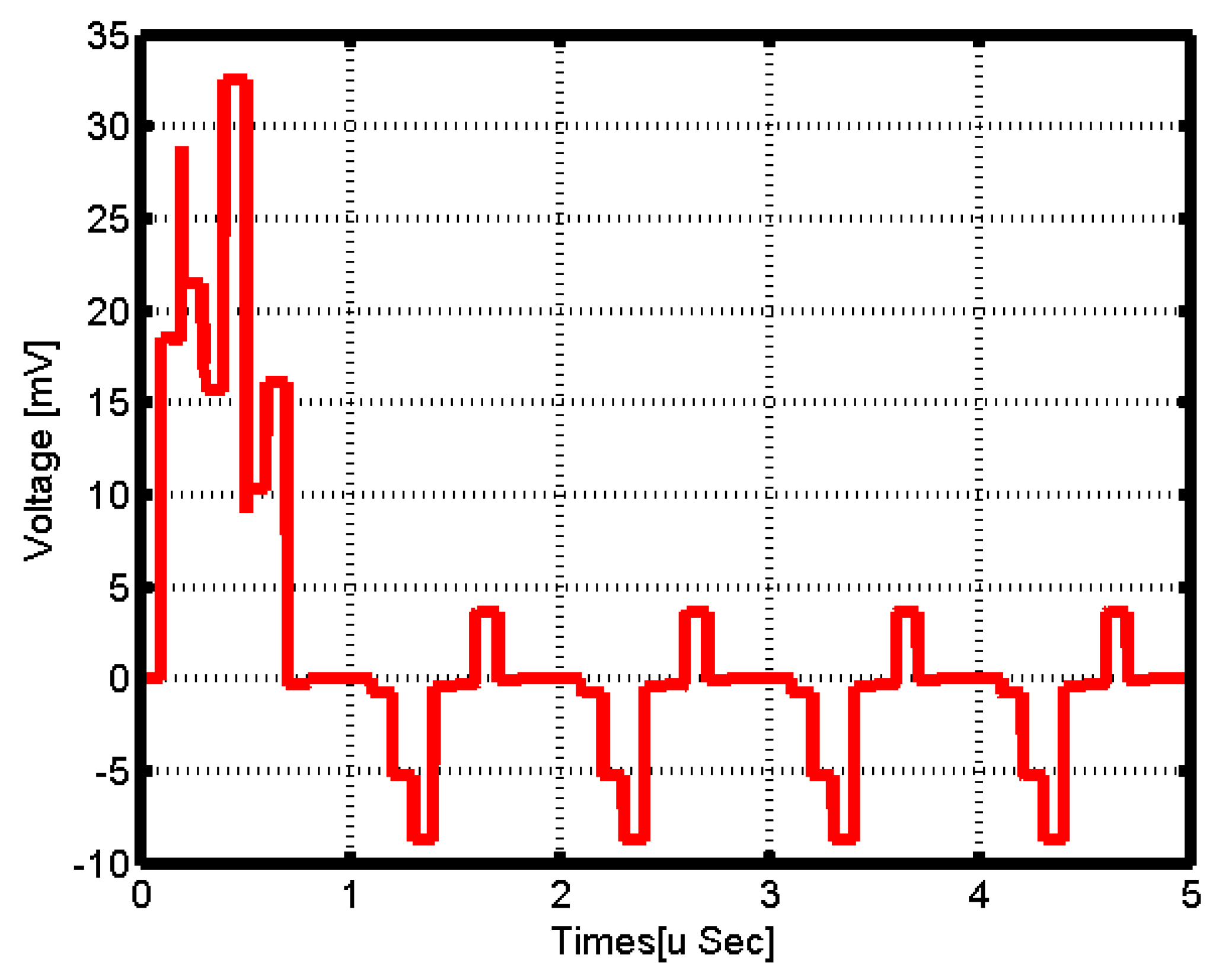
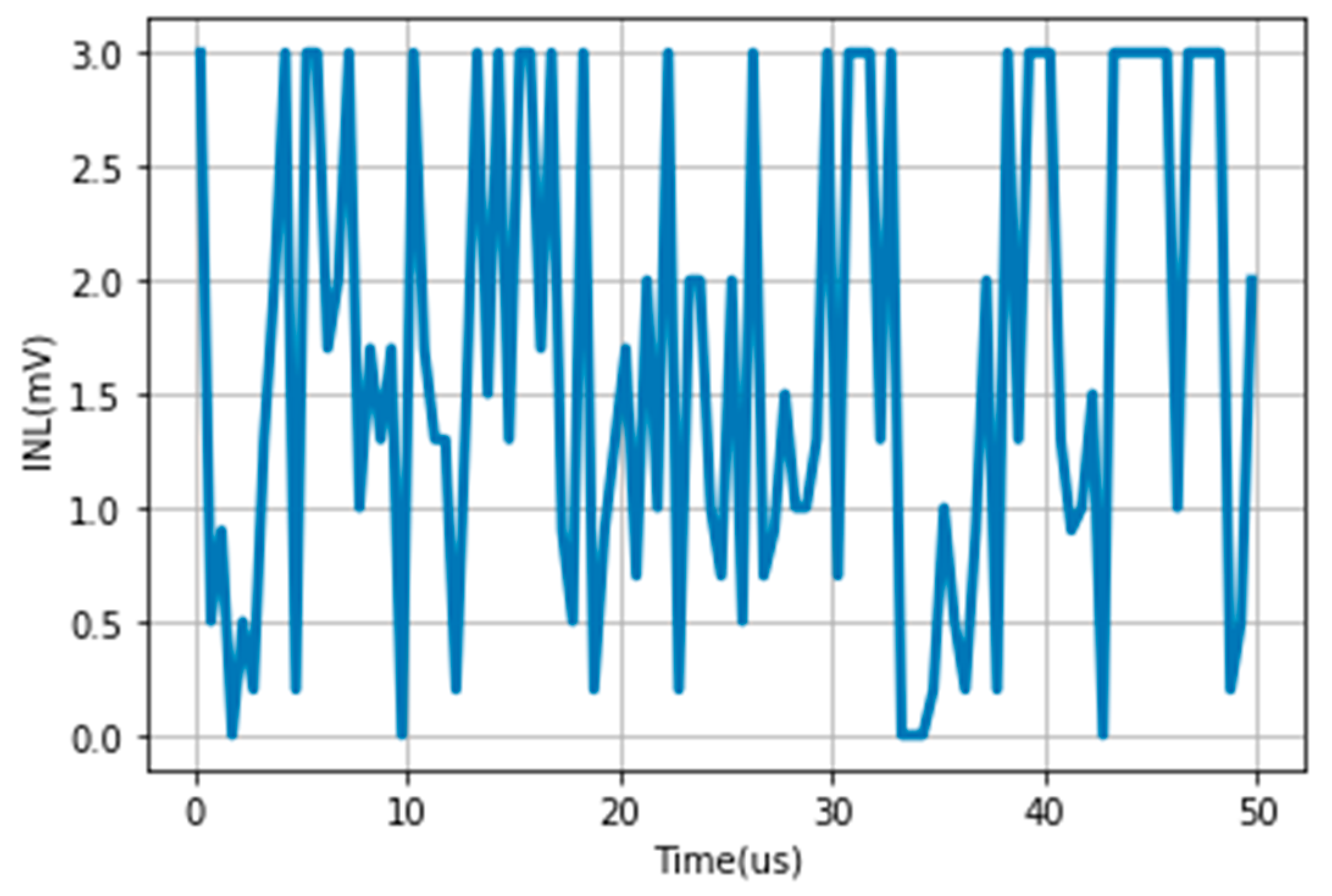
Performance of the Proposed SAR-ADC Memristor-Based Circuit
6. Proposed Memristor DAC Comparison
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chua, L. Memristor-The missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marani, R.; Gelao, G.; Perri, A.G. A review on memristor applications. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.06899. [Google Scholar]
- van de Plassche, R.J. CMOS Integrated Analog-to-Digital and Digital to—Analog Converters; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, M. Review on Various Memristor Models, Characteristics, Potential Applications, and Future Works. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2019, 20, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danial, L.; Wainstein, N.; Kraus, S.; Kvatinsky, S. DIDACTIC: A Data-Intelligent Digital-to-Analog Converter with a Trainable Integrated Circuit using Memristors. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Circuits Syst. 2017, 8, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Merrikh-Bayat, F.; Alibart, F.; Guo, X.; Hoskins, B.D.; Cheng, K.-T.; Strukov, D.B. Digital-to- Analog and Analog-to-Digital Conversion with Metal Oxide Memristors for Ultra-Low Power Computing. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures (NANOARCH), Brooklyn, NY, USA, 15–17 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, F.; Correll, J.M.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Bothra, V.; Zhang, Z.; Flynn, M.P.; Lu, W.D. A fully integrated reprogrammable memristor–CMOS system for efficient multiply–accumulate operations. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakheel, M.M.; Hassanein, A.M.; Fouad, R.A.; Radwan, A.G. Memristor-based data converter circuits. In Proceedings of the 2016 28th International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), Giza, Egypt, 17–20 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Du, L.; Li, Y. A/D converter architectures for energy-efficient vision processor. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.01681. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaie, N.; Alzahmi, A.; Shamsi, H.; Byun, G.Y. Three-Dimensional Pipeline ADC Utilizing TSV/Design Optimization and Memristor Ratioed Logic. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2018, 26, 2619–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Satat, G.; Wald, N.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. Memristor-based material implication (IMPLY) logic:Design principles and methodologies. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2014, 22, 2054–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, M. Modeling and Simulation of the Programmable Metallizationcells (PMCs) and Diamond-Based Power Devices. Ph.D. Thesis, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Humood1, K.; Mohammad1, B.; Abunahla1, H.; Azzam, A. On-chip tunable Memristor-based flash-ADC converter forartificial intelligence applications. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2019, 14, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidana, M.A.; Fahmyb, H.A.H.; Hussaina, M.M.; Salamaa, K.N. Memristor-based Memory: The Sneak Paths Problem and Solutions. Microelectron. J. 2013, 44, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, F. Addressing the sneak-path problem in crossbar RRAM devices using memristor-based one Schottky diode-one resistor array. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Ramadan, M.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A. VTEAM: A General Model for Voltage-Controlled memristors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2015, 62, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, E.; Laiho, M. Stateful Implication Logic with Memristors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Nanoscale Architectures, San Francisco, CA, USA, 30–31 July 2009; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Belousov, D.; Liman, S.; Satat, G.; Wald, N.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. MAGIC–memristor aided LoGIC. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvatinsky, S.; Wald, N.; Satat, G.; Friedman, E.G.; Kolodny, A.; Weiser, U.C. MRL-Memristor Ratioed Logic. In Proceedings of the 2012 13th International Workshop on Cellular Nanoscale Networks and their Applications, Turin, Italy, 29–31 August 2012; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Hudec, B.; Hsu, C.W.; Wang, I.T.; Lai, W.L.; Chang, C.C.; Wang, T.; Fröhlich, K.; Ho, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Hou, T.-H. 3D resistive RAM cell design for high-density storage class memory—A review. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2016, 59, 061403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gi, S.; Yeo, I.; Chu, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, B. Fundamental issues of implementing hardware neural networks using memristor. In Proceedings of the 2015 International SoC Design Conference (ISOCC), Gyeongju, Korea, 2–5 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Zeng, F. Recent progress in resistive random access memories: Materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 83, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, J.Y.; Song, S.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Yoon, K.J.; Park, T.H.; Kwon, D.E.; Lim, H.; Kim, G.H.; Jeong, D.S.; Hwang, C.S. A review of three-dimensional resistive switching cross-bar array memories from the integration and materials property points of view. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5316–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zheng, G.; Tian, B.; Dkhil, B.; Duan, C. Research progress on solutions to the sneak path issue in memristor crossbar arrays. Nanoscale Adv. 2020, 2, 1811–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chang, S.; Huang, G.; Lin, Y. A 10-bit 50-MS/s SAR ADC With a Monotonic Capacitor Switching Procedure. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, G.A. A 6.25GHz, 2.7_w at 0.5V, double-tail comparator using charge-steering approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 35th National Radio Science Conference (NRSC), Cairo, Egypt, 20–22 March 2018; pp. 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- ChoS, H.; Lee, C.K.; Kwon, J.K.A. A 550μW 10b 40MS/s SAR ADC with multistep additiononly digital error correction. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 1 November 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Chang, S.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y. 10-bit 30-MS/s SAR ADC Using a Switchback Switching Method. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2013, 21, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Z. A 12-Bit 10 MS/s SAR ADC with High Linearity and Energy-Efficient Switching. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 1616–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Huang, D. A 10-Bits 50-MS/s SAR ADC Based on Area- Efficient and Low-Energy Switching Scheme. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28257–28266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fateh, S.; Schonle, P.; Bettini, L.; Rovere, G.; Benini, L.; Huang, Q. A reconfigurable 5-to-14 bit SAR ADC for battery-powered medical instrumentation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 2685–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 3 | [Ω] | 1000 | |
| 1 | [Ω] | 50 | |
| [V] | −0.2 | [nm] | 3 × 10−9 |
| [V] | 0.02 | [nm] | 3 × 10−9 |
| [m/s] | 5 × 10−4 | [nm] | 0 |
| [m/s] | −10 | [nm] | 0 |
| Reference | JSSC’11 [28] | VSLI’13 [29] | CASI’16 [30] | IEEEAccsss’20 [31] | IEEETrans.’15 [32] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 130 nm | 90 nm | 180 nm | 90 nm | 130 nm | 65 nm |
| Supply Voltage (V) | 1.2 | 1 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 |
| Sampling Frequency (MHz) | 40 | 30 | 10 | 50 | 0.072 | 1 |
| SNDR (dB) | 50.6 | 56.8 | 66.9 | 57.6 | 82.9 | 49.3 |
| SFDR (dB) | — | 68.6 | 75.8 | 68.8 | 96.8 | 61 |
| ENOB (bit) | 8.26 | 9.16 | 10.82 | 9.26 | 13.5 | 7.9 |
| Power (uW) | 550 | 980 | 820 | 664 | 130 | 21 |
| FoM (fJ/Conv.-step) | 50 | 57 | 44.2 | 21.68 | 156 | 89 |
| Item | IEEE 2017 [5] | IEEE 2013/ACM [6] | IEEE 2016/ICMM [9] | This Work | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topology | Binary-weighted memristor | Binary-weighted memristor | Current steering memristor | Cascaded memristor | Cascaded memristor |
| DAC Resolutions | 4 bit | 6 bit | 2 bit | 4 bit | 8 bit |
| Number of memristors used | 15 | 63 | 2 * | 9 | 21 |
| Flexibility to increase DAC Resolution | Limited | Limited | Flexible | Flexible | Flexible |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fahmy, G.A.; Zorkany, M. Design of a Memristor-Based Digital to Analog Converter (DAC). Electronics 2021, 10, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10050622
Fahmy GA, Zorkany M. Design of a Memristor-Based Digital to Analog Converter (DAC). Electronics. 2021; 10(5):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10050622
Chicago/Turabian StyleFahmy, Ghazal A., and Mohamed Zorkany. 2021. "Design of a Memristor-Based Digital to Analog Converter (DAC)" Electronics 10, no. 5: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10050622
APA StyleFahmy, G. A., & Zorkany, M. (2021). Design of a Memristor-Based Digital to Analog Converter (DAC). Electronics, 10(5), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10050622







