Abstract
Sun exposure can affect the skin in various ways leading to short- and long-term consequences. Waxes are often used to optimize the rheological behavior of products and provide an even sunscreen film on the skin, which can boost the sun protection factor (SPF) of ultraviolet (UV) filters. In this study, a biobased wax, alkenones, sourced from commercially available and sustainable microalgae was evaluated as an SPF booster in sunscreens. Thirty-five sunscreens were formulated using three waxes and four organic liquid UV filters. Products were tested for pH, viscosity, spreadability, stability, as well as in vitro SPF and water resistance. Alkenones’ in vitro SPF boosting capacity was similar to beeswax and cetyl alcohol with three “reef-safe” UV filters. None of the waxes used provided significant water resistance, however, using film-former water resistance could be built into the products. A key finding is that alkenones increased the in vitro SPF without increasing apparent viscosity. All products had a skin-compatible pH and they all remained stable at 25 °C for 10 weeks. Overall, the alkenones’ performance was comparable to those of the comparator waxes. Our in vitro results indicate that alkenones offer a sustainable, biobased, non-animal derived choice as an SPF booster for organic sunscreens.
Keywords:
alkenones; Isochrysis sp.; wax; organic liquid UV filter; sunscreen; in vitro SPF; water resistance 1. Introduction
Sun exposure can affect the skin in various ways, including reddening, irritation, and tanning on the short term, as well as premature wrinkling and skin cancer development on the longer term [1]. Sunscreens allow for appropriate protection from ultraviolet (UV) radiation when properly formulated and applied [2,3]. Providing a uniform sunscreen film with a uniform thickness over the entire skin surface is considered a key element of providing appropriate protection [4,5]. Achieving an even coverage with the thickness of the sunscreen film being consistent over a larger surface area may be challenging due to furrows on the skin surface making the skin an uneven substrate [6]. Products with a low viscosity tend to flow downward into the skin furrows leaving areas uncovered and exposed to the sunlight. One approach that formulators can use is to optimize the rheological behavior of the sunscreen via incorporating rheological additives [7]. Waxes are commonly used in sunscreens as thickeners to build viscosity, help product application, and create a homogenous, even film on the skin, which eventually can create a higher sun protection factor (SPF) [8].
In recent decades [9], the move toward green, sustainable, natural ingredients in cosmetic and personal care products has been growing. A more recent trend within the natural product category is vegan products and claims [10]. With the rising popularity of vegan cosmetic products, plant-derived cosmetic raw ingredients are also becoming more popular compared to animal-derived cosmetic ingredients. The global vegan cosmetics market is expected to register a compound annual growth rate of 7.1% between 2018 and 2023 according to a forecast [10,11]. Beeswax is a commonly used wax in sunscreens to build viscosity, however, it is considered an ingredient of animal origin [12,13].
Alkenones are a family of unique lipids biosynthesized by certain haptophyte microalgae [14], including the industrially grown Isochrysis sp. (Chromista, Haptophyta) [15]. As an off-white waxy solid at room temperature (Figure 1) with a melting point range of 71.1–77.4 °C, these compounds appear similar to beeswax. However, in contrast to beeswax, alkenones being sourced from microalgae can be considered vegan. They are also a renewable and green wax, derived from non-genetically modified organisms (i.e., non-GMO), which fits well into the natural and vegan trend. Additionally, the wax is biobased (USDA BioPreferred, [16]) and of marine origin. Marine-based ingredients, including microalgae-sourced ingredients are becoming popular [17] in cosmetics due to their natural origin and richness in vitamins [18], minerals [19], proteins, and essential fatty acids [20]. Given their waxy nature and reasonably high melting point, we argue that alkenones represent an attractive and as-yet-undeveloped class of natural ingredients that may find useful application in a variety of cosmetic and personal care formulations. The alkenones used in this study have been previously described and characterized extensively [20,21,22].
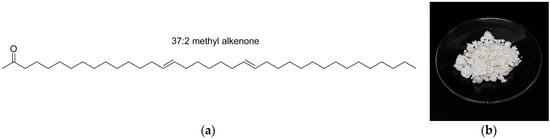
Figure 1.
(a) Structure of a common alkenone, i.e., 37:2 methyl alkenone, isolated from Isochyrsis microalgae. Alkenones contain trans double bonds and a methyl or ethyl ketone; (b) Alkenones wax.
In a previous study [23], we found that alkenones displayed promising properties for their potential use in sunscreens. Specifically, alkenones formed a stable mix with a liquid organic UV filter, i.e., ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, and thickened the UV filter well in that particular concentration (i.e., 10% alkenones). In the same study, alkenones created relatively low viscosity skin creams (i.e., 1470 ± 10 cP at 1 s−1 at room temperature) [23].
In this study, our goal was to investigate whether and to what extent the alkenones can thicken selected “reef-safe” organic liquid UV filters, and whether alkenones can increase the SPF of sunscreens. In 2018, Hawaii issued a ban on two organic UV filters, octinoxate (also known as OM cinnamate) and oxybenzone due to concerns on the impact of UV filters on coral reefs [24]. Many companies are likely to reformulate their sunscreens to offer “reef-safe” options for consumers by 2021 when the ban goes into effect, otherwise, products that contain any or both of the banned UV filters will be prescription-only products in Hawaii. Since the “reef-safe” organic UV filters will soon be under greater scrutiny, we aimed to study the performance of the alkenones with these UV filters. We also aimed to evaluate whether the alkenones can provide any water-resistance to the sunscreen products. The goal of this study was to explore the alkenones’ potential function in sunscreens. The sunscreen formulas were kept fairly simple to be able to measure differences between sunscreens. Formula optimization and achieving a specific SPF value were not goals in this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The marine microalgae Isochrysis was purchased from Necton S.A. (Olhão, Portugal). Alkenones were isolated and purified from the Isochrysis biomass as previously described [25]. Ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate (OM cinnamate, OMC), homosalate, octocrylene, beeswax, and cetyl alcohol were purchased from Making Cosmetics (Snoqualmie, WA, USA). The following ingredients were received as gifts: octyl salicylate (Neo Heliopan OS, Symrise, Branchburg, NJ, USA); a blend of propylene glycol, diazolidinyl urea, methylparaben, and propylparaben (Germaben II, Ashland, Covington, KY, USA); propanediol (DuPont Tate & Lyle Bio Products, Loudon, TN, USA); heptyl undecylenate (LexFeel Natural, Inolex, Philadelphia, PA, USA); a blend of dimethicone and dimethicone/vinyltrimethylsiloxysilicate crosspolymer (Belsil Reg 1102, Wacker, Adrian, MI, USA); and polyglyceryl-10-stearate (Polyaldo 10-1-S, Lonza, South Plainfield, NJ, USA). All ingredients were of cosmetic grade. Deionized (DI) water was provided by the University of Toledo Health Science Campus.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Formulation of Sunscreens
Thirty-five sunscreen products were formulated using four different organic liquid UV filters and three different waxes. As for the UV filters, we started with OM cinnamate (OMC; INCI: ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate) due to having promising preliminary results with this ingredient. However, because of the recent legislation passed in Hawaii in 2018 [24], we selected three additional “reef-safe” UV filters. These UV filters included homosalate (H; INCI: homosalate), octocrylene (O; INCI: octocrylene), and octyl salicylate (OS; INCI: ethylhexyl salicylate). Given the waxy nature of the alkenones at room temperature, waxes were selected as comparators. The waxes included alkenones (Group A), beeswax (Group B), and cetyl alcohol (Group C).
First, a group of twelve sunscreens were formulated. Series 1 contained OMC; series 2, H; series 3, O; and series 4, OS. The twelve sunscreen formulas can be found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sunscreen formulas.
Then, the above twelve sunscreens were formulated again (Series 5–8) all including an extra ingredient: a silicone resin in phase A (INCI: dimethicone and dimethicone/ vinyltrimethylsiloxysilicate crosspolymer). This ingredient is claimed to provide water resistance to formulations [26]. We included this ingredient in the sunscreens to evaluate how the SPF would change in the water-resistance test, compared to the waxes used alone without any silicone resin. The silicone resin was used in 1% in phase A, and the amount of water was decreased by 1% (w/w) in phase B.
Additionally, we formulated eleven control sunscreens for comparison purposes. Eight controls did not contain any waxes, while three controls did not contain any UV filter (Table 2).

Table 2.
Control sunscreen formulas.
All sunscreens were water-in-oil emulsions and they were all formulated identically. Phase A was heated to 75 °C. Phase B was combined in a separate glass beaker and heated to 75 °C. When both phases reached the same temperature, they were removed from the heat, and the oil phase was added to the water phase using a homogenizer (IKA Works, Inc., Wilmington, NC, USA). The mixture was homogenized at 2800 rpm for one minute; 4600 rpm for two minutes; and 7600 rpm for another three minutes. The emulsion was allowed to cool with continuous propeller-stirring. Phase C was added when the emulsion reached 45 °C. The emulsion was allowed to cool to room temperature under continuous mixing. Water loss was checked by weighing the sunscreens, and evaporated water was replaced. The emulsion was mixed again and was then homogenized for one minute. Then, each sunscreen was stored in clear plastic jars.
2.2.2. In Vitro SPF
A polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) plate (Labsphere, North Sutton, NH, USA) was tared on an analytical balance with a readability of 0.001 grams. Per the method detailed in the FDA 2011 Final Rule on over-the-counter sunscreen testing [27,28], 0.050 g of sunscreen was placed on each PMMA plate. Using a finger cot, the sunscreen was spread in a circular motion for thirty seconds, in a vertical motion for fifteen seconds, and then in a horizontal motion for another fifteen seconds to ensure the plate was completely covered as evenly as possible. The plate was placed in the dark for fifteen minutes and then taken to the in vitro SPF tester (LabSphere 2000S, Labsphere, North Sutton, NH, USA). SPF was scanned in five different locations on each plate. The test was repeated three times for each sunscreen.
2.2.3. Water-Resistance Testing
Sunscreens were applied to the PPMA plate as described above. The PMMA plate was suspended in a beaker of DI water using binder clips for 20 minutes. The water temperature was kept at skin temperature (32 ± 0.5°C), and the water was stirred continuously at 460 rpm using a magnetic stir bar. After 20 minutes, the PMMA plate was removed from the beaker and placed on a solid surface to let air dry. After complete drying, the in vitro SPF method described above was used to measure the SPF.
2.2.4. Viscosity
A Brookfield viscometer DV-I (Brookfield Engineering Laboratories, Middleboro, MA, USA) was used with a concentric cylinder spindle (#29) and a small sample adapter to determine the viscosity of the sunscreens. The tests were performed at 21 °C. The shear rates ranged from 0–25 s−1. All measurements were done in triplicate.
2.2.5. pH Testing
pH of the sunscreens was determined using a pH meter (Mettler Toledo Seven Compact, Billerica, MA, USA). The meter was calibrated with standard buffer solutions of pH 4, 7, and 10 before each analysis. The electrode was dipped directly into the formulations, and readings were recorded in triplicate for each sample.
2.2.6. Spreadability Testing
Spreadability of each sunscreen was determined using TA.XTPlus texture analyzer (Texture Technologies Corp., Hamilton, MA, USA) with a spreadability fixture comprising of male and female Perspex 90-degree cones at room temperature. The instrument was calibrated using 2-kg load cell at the beginning of testing. For probe calibration, the male cone was manually lowered into the empty female cone (sample holder) to make sure the two cones aligned and fit perfectly. Probe and height calibration was done at the beginning of testing. To determine spreadability, each sample was placed into the female cone and pressed down using a metal spatula to eliminate air pockets. The test mode was set to ‘measure compression’ and target mode was set to ‘distance’. Trigger force was 2.3 g, and the male cone’s penetration distance was 11 mm. The pre-test, test, and post-test speeds were set to 3.0, 3.0, and 3.0 mm/sec, respectively. Exponent stable micro systems software (version 6.1.10.0) was used to generate spreadability curves.
2.2.7. Stability Testing
Samples of sunscreens were placed into 1.5 mL centrifuge tubes (four tubes for each sunscreen), and those tubes were placed into stability cabinets. Stability of sunscreens was monitored at two temperatures, room temperature (25 °C) and an elevated temperature (45 °C) in stability cabinets for 10 weeks. Samples were checked visually at day 1 and weeks 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10.
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. In Vitro SPF and Water Resistance
In order to select comparators for alkenones, a detailed literature search was done on marketed sunscreen products. Waxes commonly used in marketed sunscreens were identified, and two comparator waxes were selected for this study, including beeswax and cetyl alcohol. Beeswax is an animal-derived natural ingredient; cetyl alcohol is a synthetic ingredient. Both ingredients are commonly used as thickeners.
The in vitro SPF of the control-A, control-B, and control-C formulas (i.e., sunscreens that did not contain any UV filter, only the cosmetic ingredients) was below 0.9 indicating that the sunscreen base only had negligible UV absorption.
The in vitro SPF of sunscreens was compared to the in vitro SPF provided by 5% UV filter alone, and also to a control formula. The control formula was similar to the sunscreen formula; the only difference was that it did not contain any wax. It can be seen in Figure 2 that the in vitro SPF of the 5% UV filter alone was lower in most cases than the in vitro SPF of the control formula. The explanation for this lies in the composition of the control formulas. All control formulas contained the same emollient, i.e., heptyl undecylenate, which is a good solvent for most liquid UV filters. Emollients that are good solvents for a given UV filter can increase the SPF of the UV filter [29]. This is why we observed an increase in the in vitro SPF even without using a wax in the formula. Octocrylene was an exception, the in vitro SPF of 5% octocrylene was higher than that of the control formula. Heptyl undecylenate was a good solvent for the three other UV filters, but not for octocrylene.
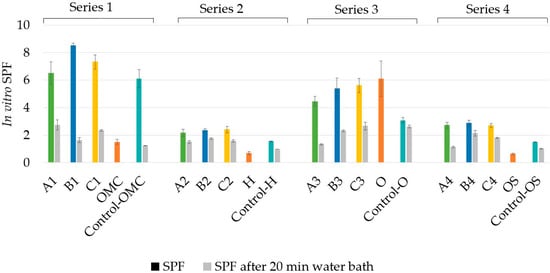
Figure 2.
In vitro sun protection factor (SPF) of Series 1–4 sunscreens compared to the individual ultraviolet (UV) filters and control formulas. OMC: OM cinnamate; H: homosalate; O: octocrylene; OS: octyl salicylate; Si: silicone resin; A: alkenones; B: beeswax; C: cetyl alcohol.
When comparing the sunscreens to each other within one series, the type of wax was the only difference. Thus, the differences seen between sunscreen A, B, and C can be attributed to the wax used (i.e., alkenones-A, beeswax-B, and cetyl alcohol-C).
In the case of Series 1 (OMC), all waxes boosted the in vitro SPF significantly (p < 0.05) compared 5% OMC alone, however, only beeswax enhanced the in vitro SPF significantly (p < 0.05) compared to the control formula. The percent boost of the in vitro SPF is shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Percent boost of in vitro sun protection factor (SPF) compared to the individual ultraviolet (UV) filter and the control formulas.
In the case of Series 2 (H), all waxes boosted the in vitro SPF significantly (p < 0.05) compared to both the UV filter alone and the control formula. With this particular UV filter, all three waxes worked similarly. Even though the waxes did not provide the same level of thickness to the sunscreens (as it is discussed below), they all enhanced the in vitro SPF to the same level.
As for Series 3 (O), none of the sunscreens boosted the in vitro SPF compared to the UV filter alone. Octocrylene is a very viscous liquid organic sunscreen with poor spreading, which explains the high standard deviation of the pure UV filter. The control formula’s SPF significantly decreased compared to that of the 5% UV filter, which can be contributed to the quality of the solvent. As mentioned above, heptyl undecylenate is not a good solvent for octocrylene, according to our previous studies. The solvent mixes with the UV filter, but it is not able to boost the SPF well. Compared to the control formula, all three waxes boosted the in vitro SPF significantly (p < 0.05), however, the values were still lower than that of the 5% UV filter.
As for Series 4 (OS), all waxes boosted the in vitro SPF significantly (p < 0.05) compared to that of both the UV filter alone and the control formula. Similar to Series 2, all three waxes performed statistically the same and boosted the in vitro SPF to the same level.
As for water-resistance, none of the waxes provided good water resistance properties to the sunscreens. The in vitro SPF values before and after the water resistance test were significantly different (p < 0.05) for all twelve sunscreens. Waxes are usually used as thickeners in sunscreens to build viscosity and increase the thickness of the sunscreen film on the skin. Some waxes are good film-formers, however, polymeric film-formers are often incorporated into the formulations. Film-formers are able to create an even film on the skin and increase water-resistance [30]. In order to test whether water resistance can be added to the products, we formulated a second set of sunscreens. This second set contained a silicone resin, which is known to add water resistance properties to sunscreens. The in vitro SPF and water resistance results are shown in Figure 3.
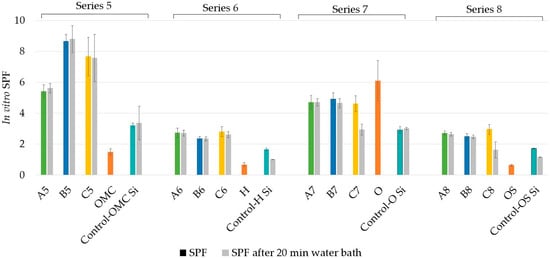
Figure 3.
In vitro sun protection factor (SPF) of Series 5–8 sunscreens compared to that of the individual ultraviolet (UV) filters and control formulas. OMC: OM cinnamate; H: homosalate; O: octocrylene; OS: octyl salicylate; Si: silicone resin; A: alkenones; B: beeswax; C: cetyl alcohol.
The silicone resin did not boost the SPF of the sunscreens (p < 0.05), compared to those of the previous set, i.e., Series 1–4. The resin however significantly increased the water resistance properties of each sunscreen (p < 0.05). For most sunscreens, the SPF did not change significantly after the 20-minute water bath. The only two sunscreens where a significant change was seen were C7 and C8, both included cetyl alcohol. This change may be the consequence of an unfavorable interaction between cetyl alcohol and the resin, resulting in a less water-resistant product.
We also looked at whether the absorption peak (λmax) of the individual sunscreens was shifted by the wax or silicone resin. Cosmetic ingredients should not shift the absorption peak of the UV filters in a sunscreen because it could lead to a change in the UV absorbing capability of the product [31]. All four UV filters used in this study were UVB filters and had their absorption peak around 311 nm. The peaks did not shift significantly due to the waxes or silicone resin in the case of three UV filters, including OMC, H, and OS (Figure 4 and Table 4). In the case of O, the absorption peaks shifted to a shorter wavelength, from 311 nm to ~302 nm. This shift was seen for all formulations containing octocrylene; therefore, an interaction may have caused this phenomenon.
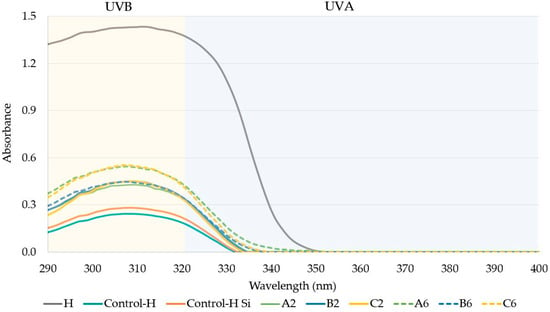
Figure 4.
Ultraviolet (UV) absorption peak of sunscreen made with homosalate as the UV filter. H: homosalate; Si: silicone resin; A: alkenones; B: beeswax; C: cetyl alcohol.

Table 4.
Absorption peak of sunscreens, ultraviolet (UV) filters, and control formulas.
A significantly higher absorption peak was observed for the UV filter (i.e., homosalate) than for any other formulation (Figure 4). To obtain an SPF value for the pure UV filter, the UV filter was spread by itself on the PMMA plate and its SPF was measured. In all other formulations, the UV filter was used at only 5%, and no other ingredients in the formula absorbed light, which resulted in a lower SPF. The same phenomena were seen for all other UV filters in the study.
3.2. Viscosity
All sunscreens and control sunscreens were opaque/white. All products contained the same emulsifier, a wax, which increased the viscosity of the formulations. The water resistance agent, i.e., silicone resin, which was a transparent gel, also added viscosity to the sunscreens. Differences in viscosity between different sunscreens were due to the different waxes and their ability to thicken the emulsions. The viscosity of each sample is reported at 25 s−1, which represents a lower shear application, i.e., when a cream is applied to the skin (Table 5).

Table 5.
Viscosity of the sunscreens at room temperature at 25 s−1.
The sunscreens with the alkenones had consistently the lowest viscosity with each UV filter, which is in correlation with our previous results [23]. The sunscreens with cetyl alcohol wax were the thickest, while products with beeswax were in between the other two samples in terms of their viscosity in each case. All sunscreens had a pseudoplastic behavior.
3.3. pH Testing
The pH of the sunscreens was close to that of the skin, i.e., 4.5–5.5 (Supplementary Materials Table S1). Sunscreens prepared with the alkenones and also containing the silicone resin had a significantly lower pH than the other products (p < 0.05), but this lower pH was still within the skin’s normal pH range. This lower pH was only observed in the case of A5, A6, A7, and A8, which could be the result of an interaction between the alkenones and the silicone resin.
3.4. Spreadability Testing
Spreadability refers to the ease of spreading a product on the application site, i.e., skin. Sunscreens prepared with the alkenones needed the lowest amount of force to spread in all series. This was expected due to the viscosity results. Spreadability and viscosity are related to each other, a rich, thicker cream typically needs a higher force to spread [32]. We found that the silicone resin increased the viscosity of most sunscreens, and the spreading force also increased for most formulations upon adding the silicone resin (Figure 5).
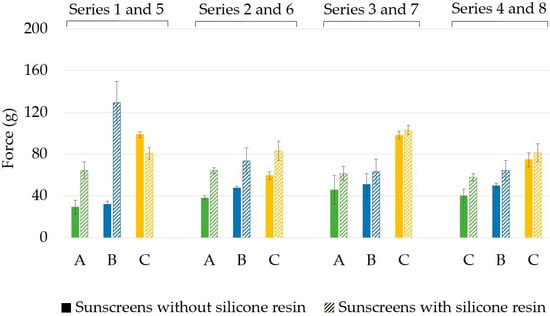
Figure 5.
Spreadability of the formulated sunscreens. A: alkenones, B: beeswax, C: cetyl alcohol, 1: OM cinnamate, 2: Homosalate, 3: Octocrylene, 4: Octyl salicylate, 5: OM cinnamate with silicone resin, 6: Homosalate with silicone resin, 7: Octocrylene with silicone resin, 8: Octyl salicylate with silicone resin.
3.5. Sunscreen Stability
The stability of the samples was evaluated for twelve weeks or until any irreversible change was noticed. All samples remained stable at room temperature without any physical signs of instability for twelve weeks. At elevated temperature, most sunscreens started to show signs of a reversible separation (creaming) very early in the stability test, and all of them showed irreversible separation at elevated temperature starting at Week 6 and were, therefore, considered unstable. Results are shown in Table S2.
4. Conclusions
To evaluate how alkenones compared to commonly used waxes, this algae-based wax was formulated into sunscreens containing four different liquid organic UV filters. Three of the four selected UV filters are considered “reef-safe” as of now, including homosalate (H), octocrylene (O), and octyl salicylate (OS), meaning that they are not part of the ban issued by Hawaii in July, 2018. All sunscreens were tested for quality and performance.
The alkenones significantly boosted the in vitro SPF of the three “reef-safe” UV filters (H, O, and OS) compared to the control formulas. The in vitro SPF was similar for the three waxes in the case of these three liquid organic UV filters (i.e., H, O, and OS). As for OMC, the increase in in vitro SPF was significantly higher for beeswax than for the alkenones or cetyl alcohol. We can conclude that the alkenones’ performance in boosting in vitro SPF was similar to that of beeswax and cetyl alcohol in the case of H, O, and OS. This is a notable result considering that these “reef-safe” UV filters will be preferred in the future.
While beeswax and cetyl alcohol significantly thickened the sunscreens, alkenones did not provide a high level of thickness to the products; this was in accordance with our previous results [23]. In our previous study, alkenones only slightly thickened skin creams (i.e., 1470 ± 10 cP at 1 s−1 at room temperature). The creams formulated with alkenones in the previous study were pseudoplastic, however, alkenones did not provide any thixotropic property to the creams. In the current study, the sunscreens formulated with alkenones were pseudoplastic as well. Rheological behavior was not studied. However, it can be assumed that the alkenones would behave the same way as in the previous study, i.e., no thixotropy would be provided. Sunscreens prepared with the alkenones needed the lowest amount of force to spread and had the lowest viscosity. We found that regardless of the lower viscosity and spreading force, the alkenones boosted the in vitro SPF to the same level as the comparator waxes in the case of H and OS, even though beeswax and cetyl alcohol built significantly more viscosity into the sunscreens. Previous studies have demonstrated that the use of waxes in water-in-oil emulsions can increase SPF by shortening the recovery time of the emulsion after spreading [33,34,35]. Recovery time is the time taken to rebuild structure and viscosity in a thixotropic material after is has been subjected to high shear, e.g., spreading on the skin. A short recovery time means that the product maintains an even film over the skin, rather than flowing into the wrinkles. Most waxy materials increase viscosity at low shear, and may not shear-thin fast enough to allow for an even film to form on the skin. Ideally, a thick, consistent film is desired. An explanation to why alkenones increased the SPF without increasing viscosity can be the rheological behavior provided by them. They form pseudoplastic, but not thixotropic, systems and when the sunscreen is applied to the skin, product rheology could lead to faster shear-thinning, allowing for this ideal, even film formation to happen. Increasing the SPF without increasing apparent viscosity is a significant achievement considering consumer preference and product behavior. In general, most consumers prefer lighter creams and lotions as their beach products and daily moisturizers [36]. Sprayable sunscreen emulsion systems are also popular due to their easy application, light feel, and good spreading. Alkenones may be a good choice for sprayable emulsion systems considering the formulated products’ rheology and viscosity.
In this study, viscosity was measured under low shear using a viscometer. Product rheology and film integrity built from the emulsions was more complex than what can be captured in this low-shear evaluation. In order to describe the complex structure built by the waxes and evaluate the behavioral changes in the sunscreens under low and high shear, a more detailed rheological study could be performed.
Results revealed that none of the waxes tested in this study provided water resistance to the sunscreens. However, we proved that water resistance could be built into products by using a film-former, which is a common practice in the cosmetic industry. The silicone resin we selected in this study did not boost the in vitro SPF, however, it significantly increased the water resistance of the sunscreens, and it also thickened the products. The alkenones were compatible with the silicone resin and all other ingredients in the formula, which is an important quality aspect.
In summary, our in vitro results suggest that the alkenones can be a great non-animal derived, biobased and renewably-sourced choice as an SPF booster for sunscreens formulated with organic UV filters. Previous studies have suggested that in vitro results may not correlate fully with in vivo results [37,38]. The goal of this study was to explore and evaluate the performance of the alkenones in sunscreens. In this exploratory study, SPF was determined in vitro, which is a common practice during formulation and development. As a next step, in vivo studies are recommended to be performed in order to confirm these in vitro results.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/6/1/11/s1, Table S1: pH of sunscreens and controls, Table S2: Stability results of sunscreens.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.C. and G.B.; Formal analysis, G.B.; Funding acquisition, G.B.; Investigation, A.H. and M.S.A.; Methodology, M.C. and G.B.; Project administration, G.B.; Resources, G.B.; Supervision, G.B.; Visualization, G.B.; Writing—original draft, A.H., M.S.A., and G.B.; Writing—review and editing, G.W.O., C.M.R., M.C., and G.B.
Funding
This research was funded by the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution and the Washington Research Foundation.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the raw ingredient suppliers, including Symrise, Ashland, DuPont Tate & Lyle Bio Products, Inolex, Wacker, and Lonza for donating the ingredients.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Pathak, M.A. Sunscreens: Topical and systemic approaches for protection of human skin against harmful effects of solar radiation. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1982, 7, 285–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A.; Williams, G.; Neale, R.; Hart, V.; Leslie, D.; Parsons, P.; Marks, G.C.; Gaffney, P.; Battistutta, D.; Frost, C.; et al. Daily sunscreen application and betacarotene supplementation in prevention of basal-cell and squamous-cell carcinomas of the skin: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999, 354, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, S.; Wulf, H.C.; Pittelkow, M.R. Photoprotection. Lancet 2007, 370, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Lai, W.; Yan, T.; Wu, Y.; Wan, M.; Yi, J.; Matsui, M.S. Sunburn protection as a function of sunscreen application thickness differs between high and low spfs. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2012, 28, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramura, T.; Mizuno, M.; Asano, H.; Naito, N.; Arakane, K.; Miyachi, Y. Relationship between sun-protection factor and application thickness in high-performance sunscreen: Double application of sunscreen is recommended. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 37, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, V.; Surber, C.; Imanidis, G. Skin surface topography and texture analysis of sun-exposed body sites in view of sunscreen application. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 29, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, J. New and emerging sunscreen technologies. In Clinical Guide to Sunscreens and Photoprotection; Lim, H.L., Draelos, Z.D., Eds.; Informa Healthcare: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 155–168. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, A.; Trevino, M. Film-formers enhance water resistance and spf in sun care products. Cosmet. Toilet. 2004, 119, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- O’Lenick, A.J., Jr. Naturals and Organics in Cosmetics: Trends and Technology; Allured Business Media: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pitman, S. The Rise and Rise of Vegan Claims for Cosmetics. Available online: https://www.cosmeticsdesign.com/Article/2018/09/19/The-rise-and-rise-of-vegan-claims-for-cosmetics (accessed on 27 November 2018).
- Wood, L. Global Vegan Cosmetics Market 2018–2023. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180907005122/en/Global-Vegan-Cosmetics-Market-2018-2023-Analysis-Product (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Lintner, K. Definitions, legal requirements, and an attempt to harmonize (global?) characterization. In Global Regulatory Issues for the Cosmetics Industry; Lintner, K., Ed.; William Andrew Inc.: Norwich, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 2, p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton, J.L.; Pearce, S.E.M. Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology; Elsevier Advanced Technology: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Volkman, J.K.; Eglinton, G.; Corner, E.D.S.; Forsberg, T.E.V. Long-chain alkenes and alkenones in the marine coccolithophorid emiliania huxleyi. Phytochemistry 1980, 19, 2619–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltgroth, M.L.; Watwood, R.L.; Wolfe, G.V. Production and cellular localization of neutral long-chain lipids in the haptophyte algae isochrysis galbana and emiliana huxleyi. J. Phycol. 2005, 41, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is Biopreferred? Available online: https://www.biopreferred.gov/BioPreferred/faces/pages/AboutBioPreferred.xhtml (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Offredo, H. Marine ingredients for skin care: An ocean of resources. In Harry’s Cosmetology; Rosen, M.R., Ed.; Chemical Publishing Co., Inc.: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.R.; Mular, M.; Miller, I.; Farmer, C.; Trenerry, C. The vitamin content of microalgae used in aquaculture. J. Appl. Phycol. 1999, 11, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kate, B.N.; Banerjee, U.C. Bioactive compounds from cyanobacteria and microalgae: An overview. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2005, 25, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, G.W.; Williams, J.R.; Craig, A.M.; Nelson, R.K.; Gosselin, K.M.; Reddy, C.M. Accessing monomers, surfactants, and the queen bee substance by acrylate cross-metathesis of long-chain alkenones. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2017, 94, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, G.W.; Culler, A.R.; Williams, J.R.; Burlow, N.P.; Gilbert, G.J.; Carmichael, C.A.; Nelson, R.K.; Swarthout, R.F.; Reddy, C.M. Production of jet fuel range hydrocarbons as a coproduct of algal biodiesel by butenolysis of long-chain alkenones. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, G.W.; Yen, T.Q.; Leitch, M.A.; Wilson, G.R.; Brown, E.A.; Rider, D.A.; Reddy, C.M. Alkenones as renewable phase change materials. Renew. Energy 2019, 134, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, K.; Smith, A.; Young, L.; Leitch, M.; Tiwari, A.; Reddy, C.; O’Neil, G.; Liberatore, M.; Chandler, M.; Baki, G. Alkenones as a promising green alternative for waxes in cosmetics and personal care products. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sb2571. Available online: https://www.capitol.hawaii.gov/session2018/bills/SB2571_.HTM (accessed on 10 July 2018).
- O’Neil, G.W.; Williams, J.R.; Wilson-Peltier, J.; Knothe, G.; Reddy, C.M. Experimental protocol for biodiesel production with isolation of alkenones as coproducts from commercial isochrysis algal biomass. J. Vis. Exp. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WACKER. Tehnical Data Sheet for Belsil(r) REG 1102. Available online: https://www.brenntag.com/media/documents/bsi/product_data_sheets/life_science/wacker_silicones_pc/belsil_reg_1102_pds.pdf (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Title 21. Part 201. Subpart g. §201.327 Over-the-Counter Sunscreen Drug Products; Required Labeling Based on Effectiveness Testing. Available online: https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=b7ff601aa9ccc10f7671b082628fcb53&mc=true&node=se21.4.201_1327&rgn=div8 (accessed on 1 August 2018).
- Food and Drug Administration; HHS. Labeling and Effectiveness Testing; Sunscreen Drug Products for Over-the-Counter Human Use; Federal Register; Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 76, pp. 35620–35665. [Google Scholar]
- O’Lenick, T.; Lott, D. The effects of solvents on sunscreens: A new ester to improve efficiency. Cosmet. Toilet. 2013, 126, 431–436. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, M. Uv booster and photoprotection. In Principles and Practice of Photoprotection; Wang, S.Q., Lim, H.L., Eds.; Adis: Berlin, Germany, 2016; pp. 227–245. [Google Scholar]
- Agrapidis-Paloympis, L.E.; Nash, R.A.; Shaath, N.A. The effect of solvents on the ultraviolet absorbance of sunscreens. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1987, 38, 209–221. [Google Scholar]
- Moisturizing Cream Spreadability. Available online: https://www.brookfieldengineering.com/applications/texture-applications/personal-care-products/moisturizing-cream-spreadability (accessed on 11 December 2018).
- Hewitt, J. Factors influencing efficacy of oil-dispersed physical sunscreens. IFSCC Mag. 2000, 3, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, D.G.; Sarruf, F.D.; Oliveira, L.C.D.; Areas, E.P.G.; Kaneko, T.M.; Consiglieri, V.O.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Baby, A.R. Influence of particle size on appearance and in vitro efficacy of sunscreens. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, J.P.; Dahms, G.H. The Influence of Rheology on Efficacy of Physical Sunscreens; IFSCC: Montreux, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Kwa, M.; Agarwal, A.; Rademaker, A.; Kundu, R.V. Sunscreen product performance and other determinants of consumer preferences. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrovska Cvetkovska, A.; Manfredini, S.; Ziosi, P.; Molesini, S.; Dissette, V.; Magri, I.; Scapoli, C.; Carrieri, A.; Durini, E.; Vertuani, S. Factors affecting spf in vitro measurement and correlation with in vivo results. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, M.; Klette, E.; Ruppert, S.; Bimzcok, R.; Klebon, B.; Heinrich, U.; Tronnier, H.; Johncock, W.; Peters, S.; Pflucker, F.; et al. In vitro sun protection factor: Still a challenge with no final answer. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2010, 23, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).