Abstract
The term “acne-like eruptions” encompasses a variety of skin conditions resembling acne vulgaris. While both acne-like dermatoses and true acne are frequently observed in clinical settings, differentiating between the two might be challenging. Similar to acne, the lesions of acne-like eruptions may exhibit papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. However, contrary to acne, comedones are uncommon but may still be observed in certain types of acne-like eruptions. Moreover, acne-like eruptions can be differentiated from acne based on their sudden onset, the propensity to occur across all age groups, the monomorphic appearance of lesions, and the distributions extending outside the seborrheic regions. The development of acne-like eruptions cannot be attributed to a single underlying mechanism; nevertheless, various factors such as patient age, infections, occupation, habits, cosmetics, and medications may be involved. The observed lesions may not respond to standard acne therapy, necessitating that treatment strategies are tailored in accordance with the identified causative agents. The following review aims to outline distinct entities of acne-like eruptions and present features that set them apart from true acne. Acne-like eruptions in the adult population, infectious diseases resembling acne, and acne-like eruptions resulting from exposure to chemical and physical agents are addressed in this paper. An understanding of the clinical presentation, pathophysiology, and epidemiology of this group of dermatoses is pivotal for a precise diagnosis and provision of appropriate care.
1. Background
Acne represents the most widely prevalent skin disorder worldwide [1]. This chronic inflammatory condition impacts the pilosebaceous unit, with a predilection for regions containing densely distributed sebaceous glands, as seen on the face, upper chest, back, and neck [2]. The follicular lesion characteristic of acne is the result of a complex interplay of various factors and may present with a comedo, papule, pustule, nodule, or cyst [3]. The global prevalence of acne is estimated at 9.4% among the population [4], ranking as the eighth most encountered disease on a global scale [5]. Due to its substantial presence, it is not uncommon for other cutaneous disorders that share similarities with acne to be misidentified as such. Such dermatoses bearing resemblance but not related to genuine acne vulgaris are referred to as “acneiform eruptions” or, more recently, “acne-like eruptions” [6]. Acne-like eruptions are a group of many skin disorders exhibiting papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts where, compared to acne, the occurrence of comedones is less frequent. They may be caused by a wide variety of factors, including infections, medications, genetic disorders, and hormonal and metabolic imbalances. Due to the discrepancy in the literature regarding the term “acneiform eruptions” [7,8,9] and the diagnoses that fall under it [8,10,11], for the scope of this paper, we will refer to acne-like eruptions throughout the article. In this narrative review, we will present different entities of acne-like eruptions by classifying them into three main groups. By categorizing them according to age and offending agents, this translates to acne-like eruptions in the adult population, infectious diseases resembling acne, and acne-like eruptions due to chemical and physical agents.
2. Acne-like Eruptions in the Adult Population
Various lesions sharing common features with acne can present in adulthood. Most dermatoses presented in the following chapter display high prevalence rates and, as such, should be included in the differential diagnosis when evaluating patients with lesions resembling acne. Recognition of the characteristic and distinguishing clinical features of these eruptions can facilitate the correct diagnosis.
2.1. Rosacea
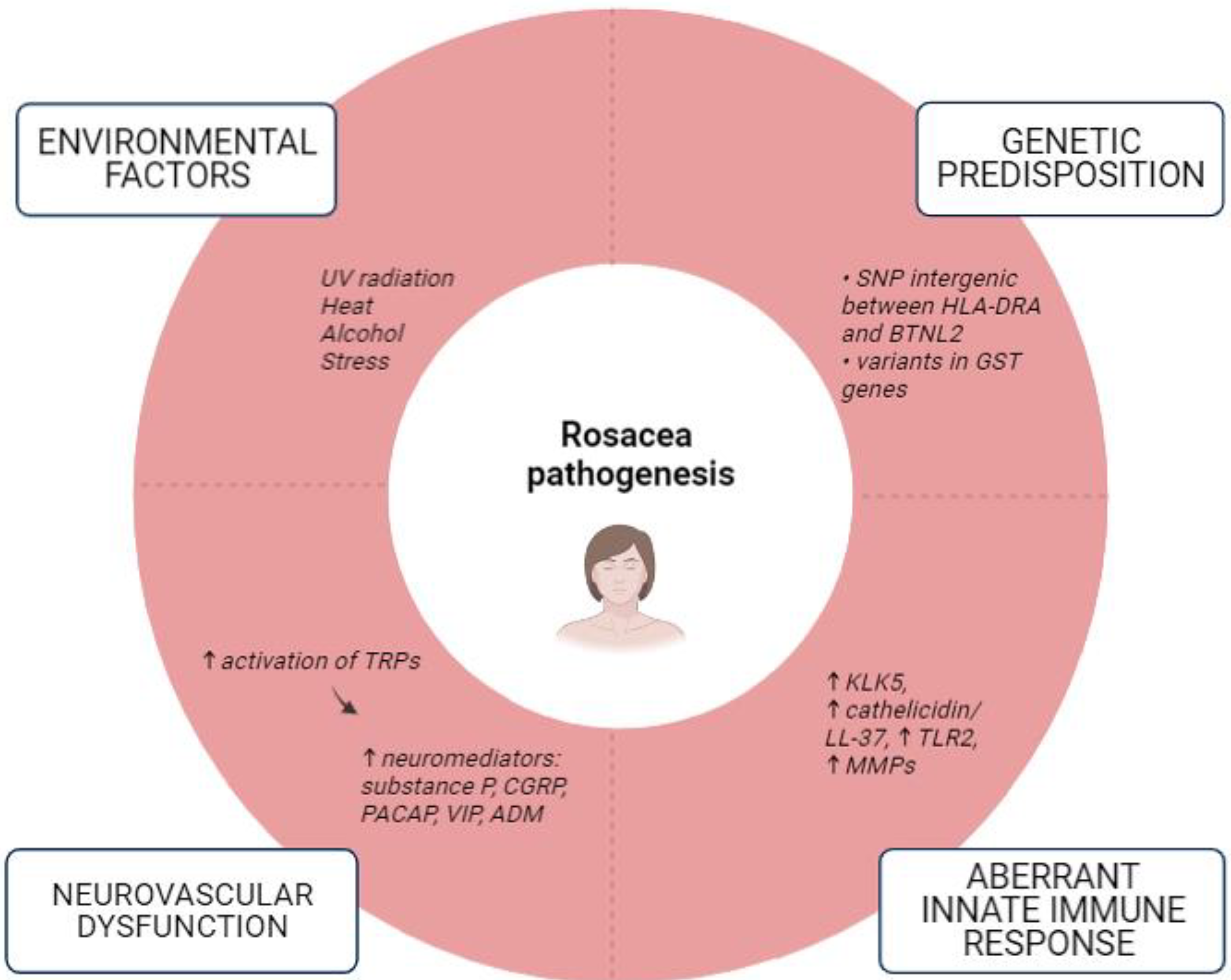
Rosacea is a chronic, relapsing, and prevalent inflammatory condition primarily involving the convex central facial with acne-like papules, pustules, erythema, and telangiectases. Although a wide array of presentations is possible, rosacea typically affects fair-skinned individuals, the majority of whom are females over the age of 40 [12,13]. The pathophysiology has not been fully elucidated, but an individual’s genetic profile, environmental factors, neurogenic inflammation, vascular hyperreactivity, and alterations in immune response all appear to have a contributory role (Figure 1) [14]. Moreover, although a number of studies suggest an association between rosacea and the skin and gut microbiota, it remains uncertain whether altered microbiota and dysbiosis initiate inflammation or if they are consequential effects of changes in the skin microenvironment [14,15,16]. Unlike acne vulgaris, rosacea does not display comedones or seborrhea, it is a relapsing disorder with a symmetrical facial distribution, and it may be accompanied by secondary features such as stinging, burning, edema, dryness, and ocular manifestations [17]. Different therapeutic techniques may be used to control the relapsing nature of the disease. This may include trigger avoidance, topical agents (such as brimonidine tartrate, ivermectin, azelaic acid, and metronidazole), oral antibiotics, vascular lasers, and light-based therapies [11,18].
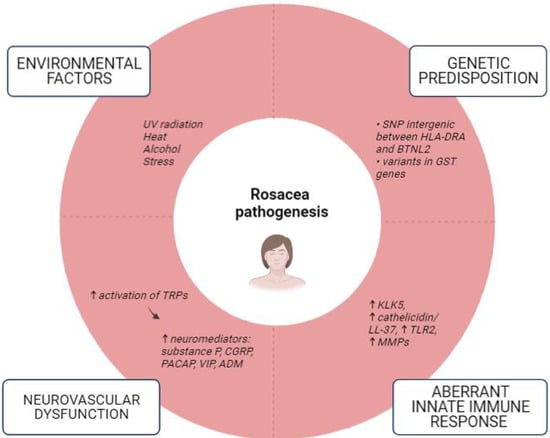
Figure 1.
Factors implicated in the pathogenesis of rosacea (a modified scheme based on Parać E. [19]). Created with https://www.biorender.com/, (accessed on 2 May 2023). Abbreviations: ADM—Adrenomedullin; BTNL2—Butyrophilin-like 2; CGRP—Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide; GST—Glutathione-S-Transferase; HLA-DRA—Human Leukocyte Antigen-DRA; KLK5—Kallikrein 5; LL-37—Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide; MMPs—Matrix Metalloproteinases; PACAP—Pituitary Adenylate Cyclase-Activating Polypeptide; SNP—Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms; TRPs—Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) Cation Channels; VIP—Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide; ↑—increased; ↓—decreased.
2.2. Demodicosis
Demodex mite is an obligatory ectoparasite that dwells in or in close proximity to the hair follicle. While skin colonization with these mites does not usually elicit any symptoms, they may lead to detrimental effects when in significant numbers [20,21]. An excessive population of Demodex parasitic mites responsible for human demodicosis can be attributed to various conditions, including end-stage renal disease, immunodeficiencies, obesity, and diabetes mellitus [22,23,24]. Furthermore, an increase in their density has been demonstrated following the prolonged use of topical corticosteroids [25]. Since demodicosis can mimic other dermatological conditions, it is frequently underdiagnosed and misdiagnosed [26]. Demodicosis may be classified into four clinical forms, each of which is named after the skin condition it resembles; rosacea type, perioral type, pityriasis folliculorum, and acne type. The latter clinically imitates acne vulgaris and presents with localized, non-scaly follicular pustules. The determination of mite density can be conducted through direct microscopic examination or standardized skin surface biopsy [20]. Treatment options include topical and systemic ivermectin, topical and systemic metronidazole, and topical and light therapy, such as intense pulsed light (IPL) [11,27].
2.3. Perioral Dermatitis
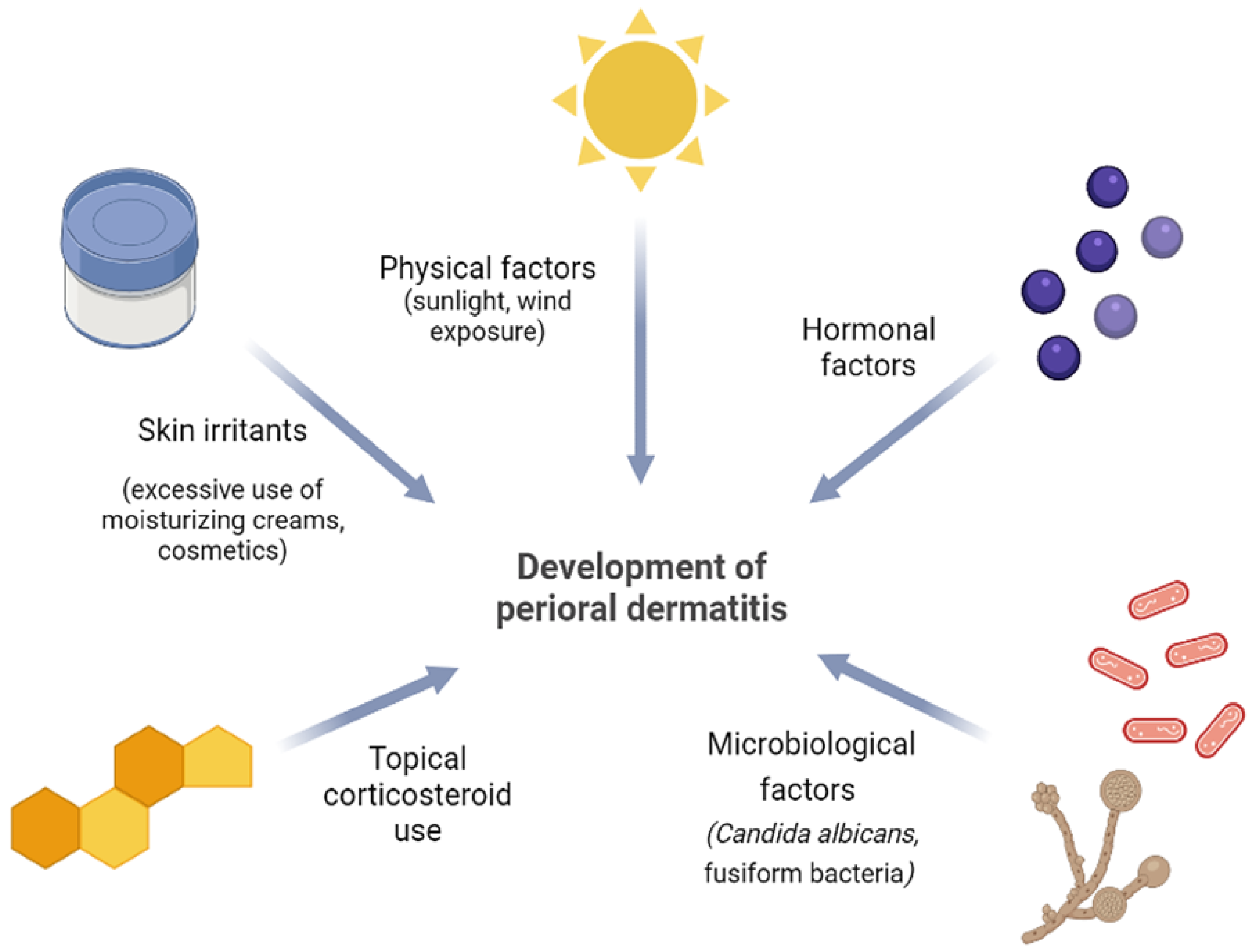
Perioral (periorificial) dermatitis (PD) is a common acne-like facial dermatosis that primarily afflicts individuals with fair complexion, particularly women aged 15 to 45. Classic PD presents with many 1 to 2 mm large papules and pustules situated on discernible erythema of the perioral region. The narrow zone surrounding the vermilion border is typically spared [28,29]. The etiopathogenesis of this condition has yet to be established. Nevertheless, apart from the well-documented relationship between PD and topical corticosteroids, ongoing research is investigating the potential involvement of hormones, ultraviolet light, skin irritants, and microbiological agents in the formation of PD lesions [28]. Furthermore, epidermal barrier dysfunction can exacerbate PD. The occurrence of lesions may additionally be associated with secondary deficiencies of vitamins or minerals, the use of sunscreen, and excessive exposure to environmental factors such as wind and heat (Figure 2) [30]. The choice of treatment is contingent upon the state and extent of the disease. It includes “zero therapy”, i.e., complete withdrawal of offending agents, topical metronidazole, azelaic acid, erythromycin, and pimecrolimus, or in severe disease forms, oral tetracyclines [28,29].
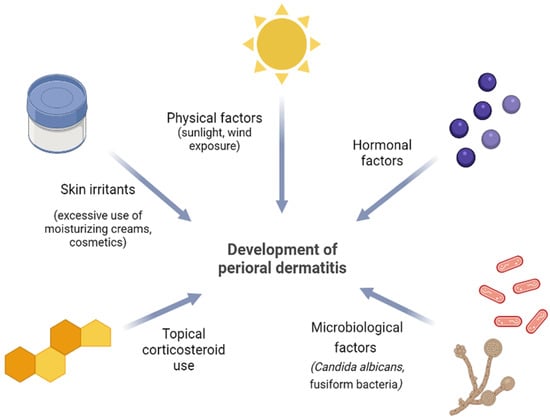
Figure 2.
Proposed etiopathogenic factors in the development of perioral dermatitis (an original scheme reproduced from Parać E. [19]). Created with https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 2 May 2023).
2.4. Hidradenitis Suppurativa
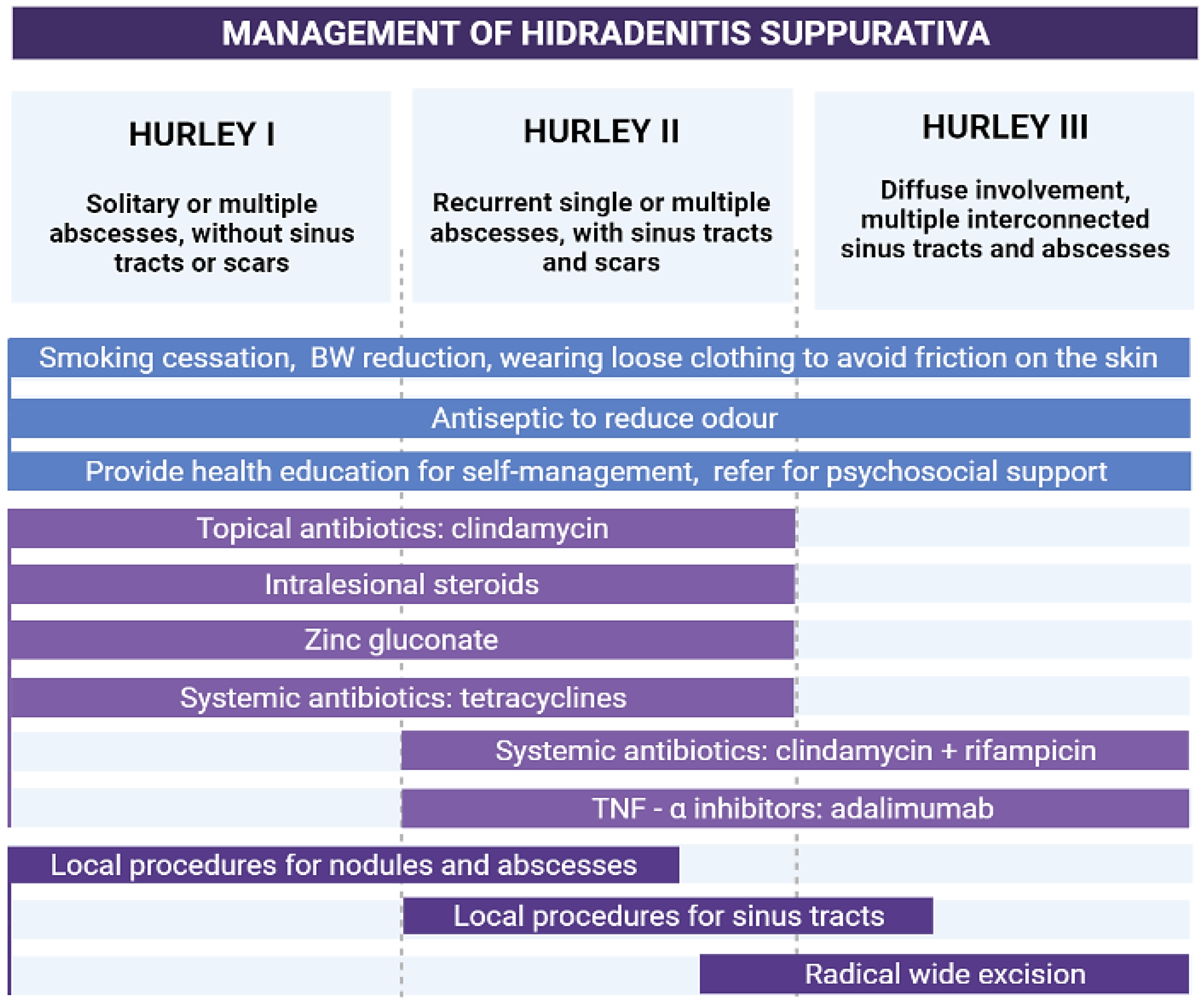
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), also known as acne inversa, is a debilitating chronic inflammatory skin disorder that affects the pilosebaceous units of the apocrine-gland-rich intertriginous areas of the body. It presents with tender and deep papular, pustular, or nodular lesions, or abscesses, which may progress and form sinus tracts and scars. The onset of HS generally occurs in the early stages of adulthood and can be attributed to different environmental and genetic factors. Among the proposed risk factors, smoking and obesity are the most significant ones associated with the disease. HS has been linked to several accompanying conditions, such as autoinflammatory syndromes, inflammatory bowel disease, spondyloarthritis, and metabolic syndrome, as well as other disorders of follicular occlusion, particularly conglobate acne [31,32,33]. Due to the characteristic painful and odorous lesions, patients afflicted with HS commonly report psychological disturbances and impaired quality of life [34]. The Hurley staging system is used to stratify patients into three stages in accordance with the disease severity. Hurley stage I, particularly when accompanied by acne as comorbidity or when observed in ectopic sites, should be considered in the differential diagnosis of acne-like eruptions. One of the characteristic clinical signs of HS is the presence of double- or multiple-ended comedones, also known as “tombstone” comedones. Various treatment options are available for HS lesions (Figure 3) [35,36].
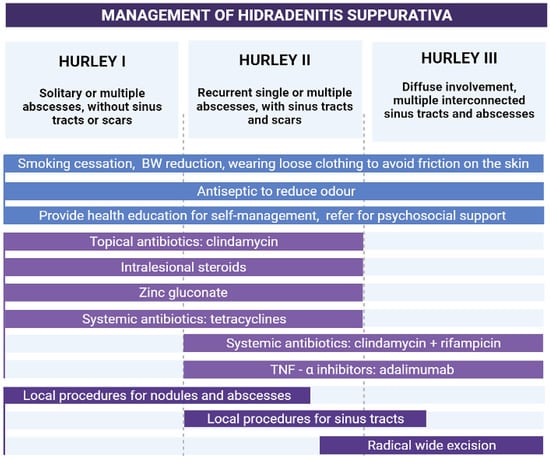
Figure 3.
Treatment recommendations for hidradenitis suppurativa based on the Hurley staging system (an original scheme reproduced form Parać E. [19]). Created with https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 2 May 2023). Abbreviation: BW—body weight.
2.5. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae
Pseudofolliculitis barbae (PFB) is an inflammatory condition of the hair follicle presenting with erythematous papules and pustules that may occur in any site where hair is shaved or plucked. The lesions predominantly occur on the face and neck of men due to shaving. Interestingly, the moustache area is typically unaffected [37,38]. PFB is more commonly seen in populations with tightly curled, coarse hair, due to the specific hair morphology that causes emerging hairs to penetrate epidermal and dermal skin layers, creating extra-follicular or intra-follicular lesions, respectively [37,38]. The eruptions are quite similar to those of acne vulgaris, but the absence of comedones is the crucial distinguishing feature of PFB [39]. The primary focus of treatment is to halt all hair removal methods to facilitate the resolution of the inflammatory response. Nevertheless, painful, pruritic, or more advanced lesions may require specific measures. Topical clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide, steroids, keratolytic agents, and triamcinolone injections have proven to be effective [37,40]. The definite treatment method entails the removal of the hair follicles, where laser and intense pulsed light (IPL) depilation are effective and convenient options [41]. These systems employ different wavelengths to selectively target specific chromophores, in this case, melanin, resulting in the destruction of the follicle. Its application in individuals with darker skin had previously been limited due to concerns about post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and scarring. Nowadays, laser devices that employ longer wavelengths, such as the long-pulsed diode laser (810 nm) and the neodymium: yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG) laser (1064 nm) are suitable for these patients, as they reach the root of the follicle while having minimal impact on the epidermal melanin [37,40,41].
2.6. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis
Eosinophilic pustular folliculitis (EPF), also termed Ofuji disease, is a rare, non-infectious inflammatory skin condition presenting with papulopustules, whose distinctive histological feature is the presence of eosinophilic infiltrates surrounding the pilosebaceous unit. The disease can be divided into three variants: immunosuppression-associated EPF (IS-EPF), infancy-associated EPF (I-EPF), and classic EPF. The latter variant was initially documented by Ofuji in 1970 in Japan, and it still continues to be predominantly observed among Japanese individuals. It develops in seborrheic regions of otherwise healthy individuals, with popular and pustular lesions that merge into plaques and may be accompanied by pruritus [42,43]. Conversely, the most frequently encountered EPF eruption is IS-EPF, which primarily affects HIV-infected patients. A hallmark feature of IS-EPF is extreme and persistent pruritus accompanying the lesions, resulting in frequently severely excoriated papules and pustules [44]. Given the recurrent nature and unknown pathogenesis of EPF, finding an effective therapeutic approach is challenging. While topical steroids may be the attempted first-line treatment for all disease variants, a definitive regimen is tailored according to the specific EPF variant [42,43,44].
2.7. Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a multiorgan granulomatous disease of an unknown origin, notably presenting with pulmonary manifestations [45]. However, among extrapulmonary manifestations, the skin is one of the most commonly affected organs; up to one third of patients present with skin involvement [46]. Different types of skin lesions are associated with sarcoidosis, and they are grouped into “specific” or “non-specific” lesions based on the presence or absence of distinctive sarcoidosic granulomas [45]. Among specific lesions, maculopapular eruptions predominate. These monomorphic lesions are typically located on the face and present with small papules that may coalesce into annular lesions or plaques. In contrast to acne vulgaris, comedones and pustules are absent in sarcoid lesions [45,47].
2.8. Papular Granuloma Annulare
Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common inflammatory dermatological disorder that frequently presents with annular plaques consisting of intradermal papules. The localized variant of GA is the most commonly observed type, and most often, it manifests with a ringed lesion [48,49]. Conversely, the less typical papular presentation of GA lacks the characteristic ring and hence may be misinterpreted as an acne eruption. However, acne can be excluded due to dissimilar affected areas, no epidermal change, the absence of comedones and pustules, and a uniform morphology of GA lesions when compared to acne [50]. GA can appear at any age; nevertheless, it is predominantly observed in children and young adults, with a twofold higher incidence in females compared to males. The lesions are typically located on the extremities [48,51]. Despite the uncertain etiology, GA has been linked to viral infections, malignancies, thyroid disease, hyperlipidemia, trauma, and certain drugs [48,52]. In most cases, the eruption is asymptomatic and may exhibit a self-limiting course over time. However, since GA can demonstrate a relapsing nature, topical steroids or intralesional triamcinolone injections may be employed as a treatment modality [49,53].
2.9. Periorificial Granulomatous Dermatitis
Periorificial granulomatous dermatitis (PGD) is interchangeable with Gianotti-type perioral dermatitis, childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis, and facial Afro-Caribbean childhood eruption (FACE) [11]. This condition is quite rare, and most cases are observed in prepubertal children, although cases in adults have also been identified [54,55,56]. The etiology of this eruption is still undetermined. A common assumption is that PGD is a less frequent and granulomatous variant of perioral/periorificial dermatitis (PD) and that the two conditions share the same underlying causes [54,57]. PGD presents with isolated monomorphous 1 to 3 mm large dome-shaped papules that are typically asymptomatic. The hue of the lesions may vary from pink-red to flesh-colored to yellow-brown [54]. PGD consistently involves the face, where papules are chiefly located in the perioral, periorbital, and perinasal regions [57,58]. The involvement of the vermillion border in PGD distinguishes it from other conditions, providing a helpful differentiation from PD [55]. Moreover, PGD is different from acne due to the monomorphous papules, absence of pustules or comedones, perioral placement of lesions, self-limiting character, and the distinctive histology of the disease [11]. Histologically, PGD is characterized by perifollicular noncaseating granulomas with lymphohistiocytic infiltrates. PGD generally exhibits a relatively benign clinical course, with spontaneous resolution occurring over several months or years. To date, no instances of systemic involvement have been reported. Therapeutic intervention is generally not necessary, although topical and oral antibiotics, as well as topical calcineurin inhibitors, could be employed to hasten the resolution process. Nevertheless, it is crucial to carefully consider the benefits of these medications in relation to their potential adverse effects [57,58].
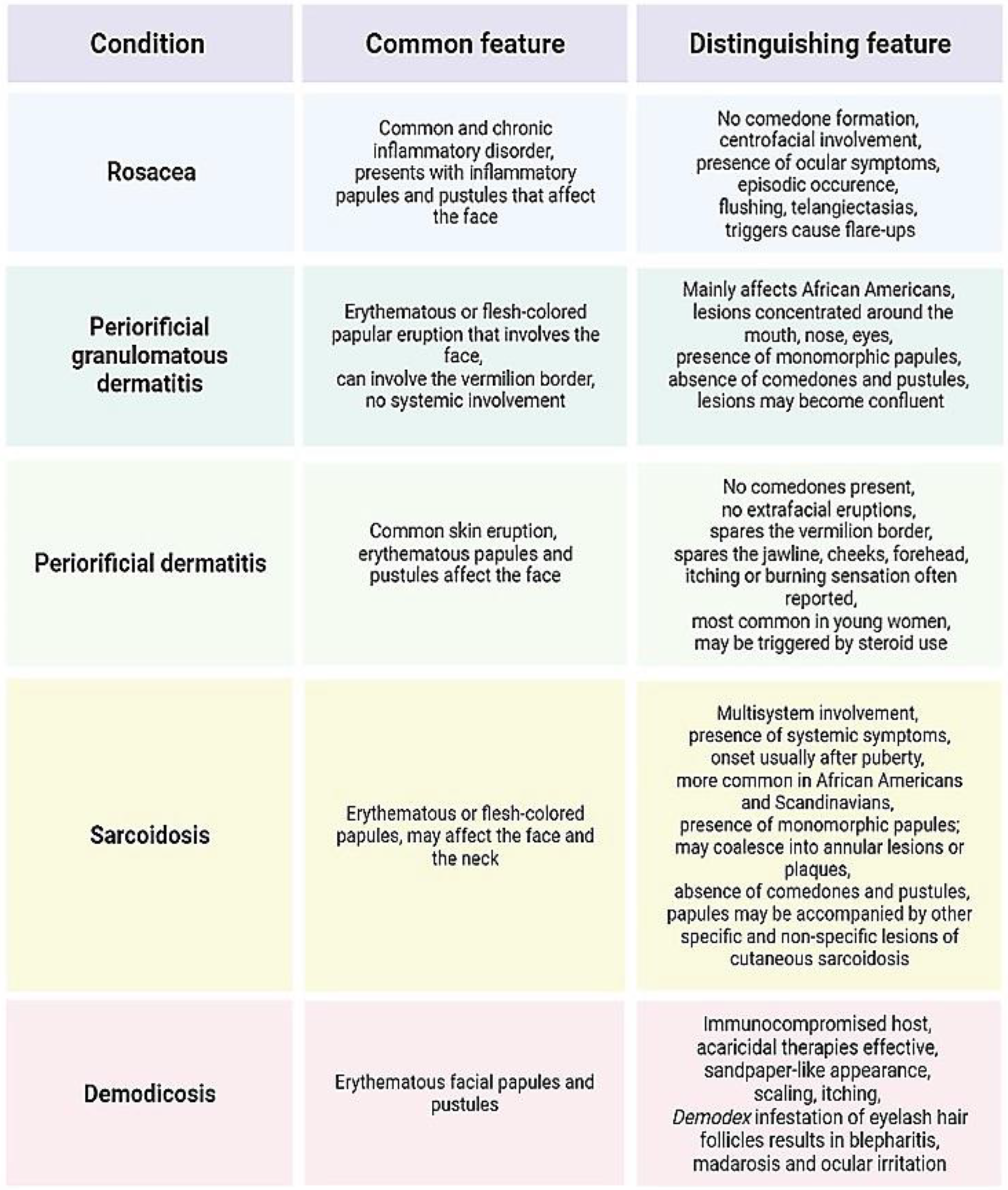
Figure 4 summarizes some of the aforementioned differential diagnoses of acne-like eruptions.
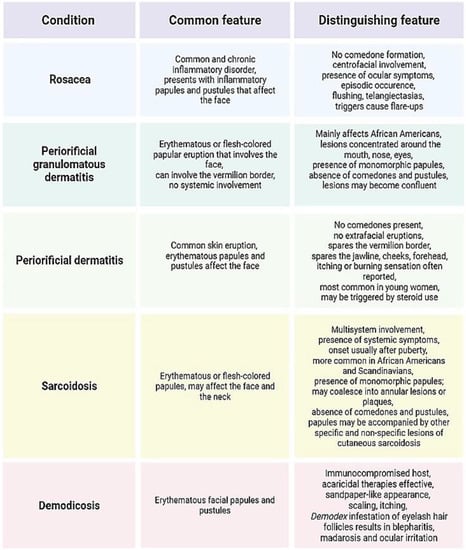
Figure 4.
Comparison of certain acne-like eruptions with acne vulgaris (an original scheme reproduced from Parać E. [19]). Created with https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
3. Infectious Diseases Resembling Acne
The overgrowth of infectious agents, such as Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Malassezia furfur, is commonly implicated in the appearance of acne-like lesions. The diagnosis of the following eruptions is mainly clinical, although confirmation by culture or microscopic examination is possible. Treatment is directed at the organism in question, although some lesions display a self-limiting nature.
3.1. Bacterial Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin disorder characterized by an inflammatory process involving the hair follicle, affecting either the perifollicular region or the follicular opening. The prevailing form of folliculitis is bacterial folliculitis, and Staphylococcus aureus is the primary causative agent [59]. Several factors predispose to increased bacterial skin colonization, namely, the nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus, exposure to chemicals and oils, and occlusion [60]. Additional risk factors include follicular unit manipulation by means of plucking, shaving, or waxing, as well as residing in tropical climates. It is difficult to determine the true incidence of bacterial folliculitis given that many affected individuals do not request medical assistance. This condition may be divided into two distinct clinical types based on the degree of hair follicle involvement. The predominant form of bacterial folliculitis is known as superficial bacterial folliculitis or Bockhart impetigo. It affects the superficial portion of the hair follicle, manifesting as minute folliculocentric pustular eruptions enclosed by erythema which eventually transform into crusted papules. Pruritus and pain are common accompanying symptoms. On the other hand, deep folliculitis arises when the hair follicle is entirely affected. It is characterized by furuncles that initially begin as aching inflammatory nodules and evolve into necrotic lesions in a matter of days [60,61]. Young adult males, diabetics, and immunocompromised patients are more likely to experience furuncles [62]. The management of bacterial folliculitis should target the most likely causative bacteria or the bacteria detected by culture [61].
3.2. Gram-Negative Folliculitis
Gram-negative folliculitis is a follicular pyoderma that arises as a complication of prolonged use of oral antibiotics, among which tetracyclines are most commonly implicated [63]. Oral antibiotic therapy leads to a shift in the composition of the normal skin microflora, causing a decrease in the population of resident Gram-positive microorganisms, namely, Staphylococcus aureus and diphtheroids. Conversely, the quantity of Gram-negative rods such as Enterobacteriaceae correspondingly increases in the nasal mucosa and the adjacent skin. Depending on the particular culprit agents involved, this can lead to the development of either papulopustular lesions (type I) or deep cystic lesions (type II) [64]. Typically, the lesions are localized in the infranasal region and have the potential to extend to the cheeks and chin. Even though the detection of Gram-negative folliculitis is not frequent, it is probably under-reported due to the potential misdiagnosis as an acne exacerbation. Hence, clinicians should consider Gram-negative folliculitis in patients with acne who experience a worsening of pustular or cystic lesions while on antibiotics, and in individuals who fail to see significant improvement in their acne after 3 to 6 months of antibiotic therapy. The preferred treatment for Gram-negative folliculitis is isotretinoin due to its ability to reduce sebum production, thereby creating an unfavorable environment for Gram-negative organisms [63,64].
3.3. Malassezia Folliculitis
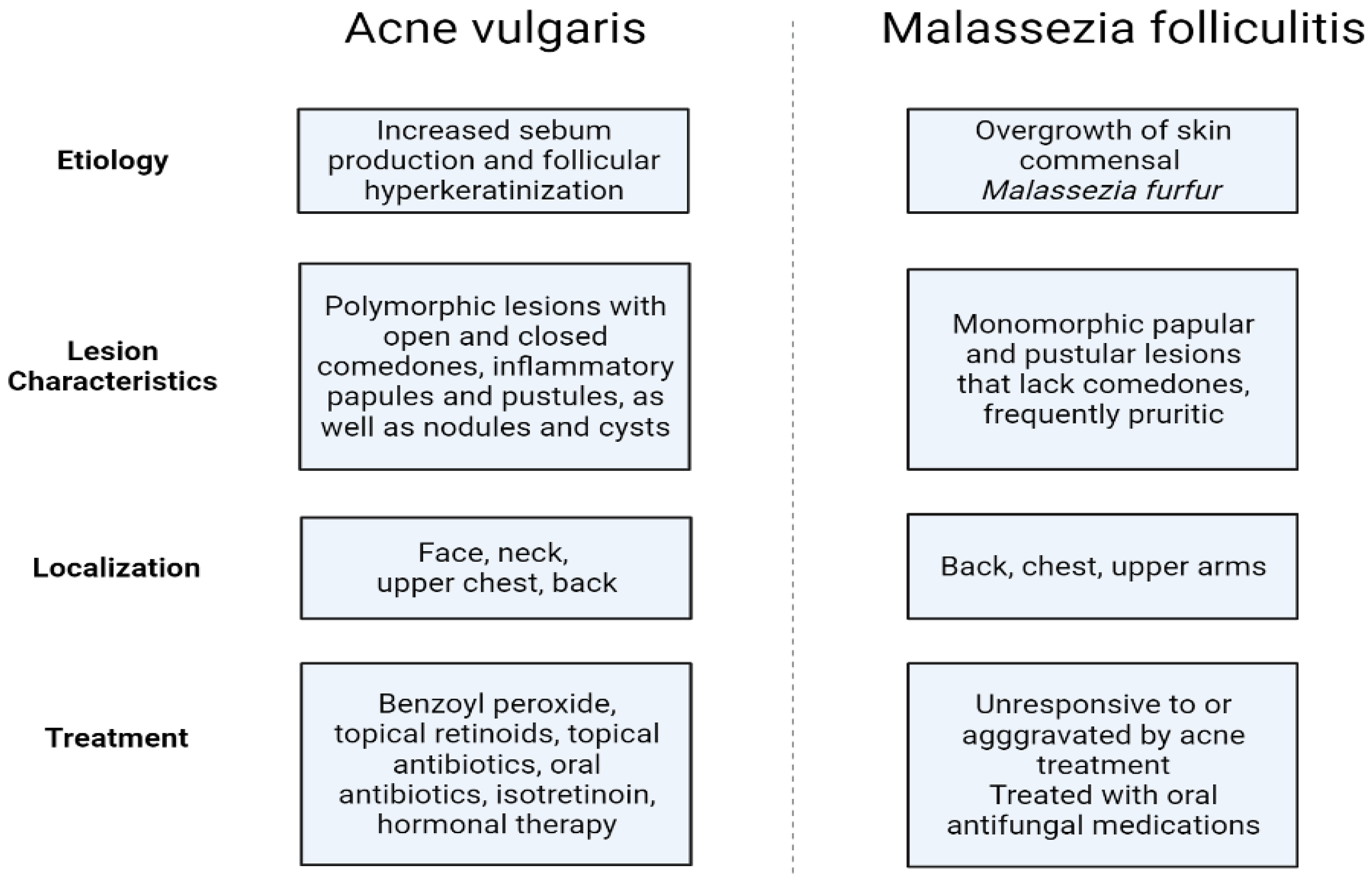
Malassezia folliculitis (MF), formerly termed Pityrosporum folliculitis, is an infectious follicular papulopustular eruption on the torso, face, and upper extremities of young to middle-aged adults. The condition is attributed to yeasts of the Malassezia genus, which are normal skin commensal organisms [65]. The yeasts are lipophilic, so they thrive in the sebaceous-rich environment of hair follicles. Consequently, 90% of people harbor them in their hair follicles and stratum corneum [66]. Malassezia yeasts have been associated with other common dermatological ailments such as pityriasis versicolor and seborrheic dermatitis. Additionally, Malassezia species worsen the head and neck variant of atopic dermatitis and have recently been proposed to contribute to psoriasis [65,67]. MF frequently develops in young individuals due to increased sebum production in those who have taken broad-spectrum antibiotics resulting in changes in their skin microbiota, and in immunocompromised patients. In such circumstances, the commensal yeast Malassezia furfur overgrows and becomes pathogenic [65]. Even though MF is prevalent, it is generally underdiagnosed since it is commonly misinterpreted as acne vulgaris. Contrary to true acne, lesions observed in MF are monomorphic and pruritic, lack comedones, and are responsive to empiric antifungal therapy instead of antibiotics (Figure 5). The diagnosis of the condition is primarily clinical, but confirmation may be achieved by microscopic examination using potassium hydroxide and skin biopsy [68]. The primary modality of therapy remains oral antifungal medications, with topical treatment occasionally required to prevent recurrences [66,67].
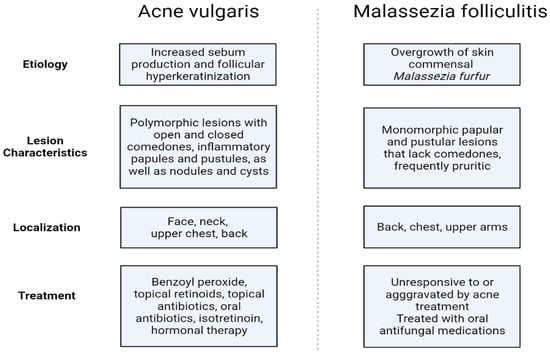
Figure 5.
Differences between acne vulgaris and Malassezia folliculitis (an original scheme reproduced from Parać E. [19]). Created with https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 3 May 2023).
3.4. Hot Tub Folliculitis
Hot tub folliculitis, alternatively known as Pseudomonas folliculitis, is a follicular infection brought on by the Gram-negative opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa). This ubiquitous bacterium is present in freshwater and soil, and can enter the body through skin breaks and hair follicles. The probability of water being contaminated with P. aeruginosa increases in warm, alkaline, or insufficiently chlorinated water. Once the bacterium has reached the skin, it appears that showering does not prevent Pseudomonas folliculitis. The lesions mostly emerge within one to four days following exposure to contaminated whirlpools, hot tubs, or swimming pools. The characteristic pruritic rash initially presents with follicular macules which progress into papules and pustules. A pinpoint vesicle is found in the central area of the lesion. The rash is more commonly found in intertriginous areas or under bathing suits due to the compression of contaminated water in such locations. Other minor symptoms, such as fever, malaise, sore throat, and earache, may be reported, but systemic infection is rare. Without any intervention, the lesions typically resolve spontaneously within 7 to 14 days [69,70,71].
3.5. Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis is a mycotic skin infection caused by Sporothrix schenckii (S. schenckii), a saprophytic fungus that commonly colonizes plants. The infection primarily afflicts gardeners and agricultural workers, usually due to minor injuries with contaminated material. The fungus gains entry into the body through small wounds and abrasions in the skin. In the majority of cases, S. schenckii causes a lymphocutaneous infection [72,73]. Nevertheless, it may potentially present in a fixed cutaneous form [74]. In instances of papulonodular eruptions, it may be mistaken for acne. Culture of tissue specimens is the preferred diagnostic method. Antifungal drugs, such as itraconazole, constitute the mainstay of therapy [73,74,75].
3.6. Cutaneous Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis originates from two distinct soil-borne fungi of the Coccidiodies genus, Coccidioides posadaii and Coccidioides immitis. This fungal infection exhibits a wide range of clinical manifestations, varying from asymptomatic cases to severe and disseminated forms. The most common clinical presentation of the disease is primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis, while cutaneous involvement is one of the most common extrapulmonary manifestations of coccidioidomycosis. Cutaneous coccidioidomycosis can present in three different manners: as an exanthem linked with pulmonary coccidioidomycosis, as a secondary cutaneous infection in disseminated disease, or, infrequently, as a primary cutaneous infection from the direct fungal inoculation. Given the vast array of clinical manifestations, cutaneous coccidioidomycosis may be categorized under “great imitators” [76]. Cutaneous lesions could appear as singular or multiple papulonodules, pustules, abscesses, ulcers, or scars. When observing the aforementioned lesions in patients residing in Coccidiodies-endemic regions, clinicians should be prompted to consider coccidioidomycosis in their differential diagnosis. Confirmation of the diagnosis typically relies on histological examination or fungal isolation [77]. Antifungal medications are employed to treat the condition [76].
3.7. Secondary Syphilis
Secondary syphilis is a systemic condition that results from the hematogenous dissemination of Treponema pallidum. It usually appears between 2–8 weeks following the emergence of the primary chancre. Various cutaneous manifestations of secondary syphilis have been documented, among which acne-like eruptions may also be evident. The clinical presentation typically includes nodules and crusted papules and pustules situated on the trunk, extremities, and face. The lesions are commonly accompanied by concurrent systemic symptoms, including fever, lymphadenopathy, and general malaise. Given syphilis’ designation as “the great mimicker”, it is essential to consider it in the differential diagnosis when evaluating any widespread skin eruption. The diagnosis is established through serologic tests and visualization of spirochetes by dark-field microscopy. Penicillin is the preferred treatment option [78,79].
4. Acne-like Eruptions Resulting from Exposure to Chemical and Physical Agents
Exposure to different chemical and physical agents may lead to the formation of eruptions closely resembling acne vulgaris. However, although clinically similar, any follicle in the body besides the sebaceous follicles can be affected. The eruptions typically present in the skin regions that are in contact with the chemical or physical agent in question. Besides specific treatment, some eruptions show improvement upon elimination of the provoking factors.
4.1. Acne Aestivalis
Acne aestivalis, also known as Mallorca acne, is a seasonal and monomorphous skin eruption that develops following exposure to sunlight [80]. The term “Mallorca acne” was first introduced in the 1970s [81] after Scandinavian individuals, who had vacationed in the Mediterranean, exhibited such lesions. After a period of reduced exposure to the sun during the winter season, the subsequent encounter with high-intensity ultraviolet (UV) radiation triggered an eruption. Eventually, the significance of UV radiation, particularly ultraviolet A (UVA), along with genetic predisposition have become evident in the pathogenesis of Mallorca acne. Since these eruptions emerge during spring, peak in summer, and subside in autumn, they are also classified as polymorphic light eruptions (PLE). The lesions are characterized by uniform, small keratotic nodules, and are devoid of comedones. They are distributed across the back, upper arms, chest, and neck, while the face may be spared. Histological examination of Mallorca acne reveals notable similarities to steroid acne, as they both exhibit focal follicular destruction accompanied by infiltrates of neutrophils [63]. Furthermore, presentations resembling acne aestivalis may arise as a rare side effect of PUVA treatment [82]. The condition poses a therapeutic challenge. It is advised to avoid further sun exposure and the application of oily sunscreens. For symptomatic relief, oral antihistamines can be used, and in severe cases, exfoliating acne medications such as benzoyl peroxide and adapalene may be prescribed. There is insufficient evidence to support the use of oral antibiotics or topical glucocorticoids. Spontaneous improvement is typically observed within several months. However, similar to PLE, patients may experience a recurrence upon re-exposure to UV radiation. As a preventive measure, it is crucial to gradually expose the skin to UV radiation, use gel-based sunscreens, and prioritize staying in shaded areas during the spring and summer months. In cases where symptoms persist despite adherence to preventive measures, UV hardening can be considered during the winter months as a form of light adaptation. This involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of UV light, beginning with very low levels and gradually increasing them [63].
4.2. Acne Mechanica
Acne mechanica refers to the emergence of inflammatory papules and pustules owing to mechanical forces. The condition arises due to the chronic irritation of the pilosebaceous unit, induced by repeated friction exerted on the skin, combined with occlusion, heat, and pressure on the skin [83]. Although acne mechanica and acne vulgaris present similarly, patient history and lifestyle factors can help distinguish between the two conditions. Mechanical obstruction is a significant contributing factor in the development of acne mechanica, and it can be observed in different activities and settings. One notable example showing this phenomenon can be observed in contact sports such as American football. In fact, since acne mechanica appears in players wearing helmets, shoulder pads, and chinstraps, it has been referred to as “football acne” and “sports-induced acne” [84,85].
Moreover, acne mechanica has also been observed in equestrians who wear chinstraps [84] and in violinists whose instruments’ chin rests repeatedly rub against the skin, providing a clinical picture of “fiddler’s neck” [86]. Nonetheless, not all skin changes in areas that have been in contact with the equipment can be solely assigned to “sports-induced acne”. It is important to consider allergic contact dermatitis as a potential alternative diagnosis [84]. The treatment of acne mechanica focuses on identifying and eliminating the causative factors, as this may result in resolution without further intervention. However, in cases where it is required, topical retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and oral antibiotics may be utilized [84,85].
4.3. Acne Cosmetica
Acne cosmetica is a term designating eruptions consisting of multiple comedones induced by the use of cosmetics. Although uncommon nowadays, acne cosmetica was widespread in the 1970s and 1980s, when comedogenic ingredients were prevalently used in cosmetic products. The occlusive nature of used products led to the development of comedones, which would sometimes be accompanied by papules and pustules [87]. Nowadays, skincare product constituents undergo extensive testing, and most agents are labeled “non-comedogenic” [11]. Nonetheless, a subtype of acne cosmetica known as pomade acne (acne venenata) is still common, particularly among individuals who use pomades or scented ointments for their hair. Since pomades are commonly applied to the scalp and the hair, they may affect the adjacent skin areas with acne lesions, such as the temples and the forehead [87,88].
4.4. Radiation Acne
Postradiation acne-like eruptions may arise as a response to both UV and ionizing radiation. Comedo-like papules may appear on the skin regions that have received therapeutic ionizing radiation within a period of two weeks to six months following the exposure. While radiation-induced dermatitis is a significantly more common adverse effect of radiotherapy, a small proportion of treated patients may develop acne-like lesions alongside the resolution of dermatitis. Among the affected individuals, most present with radiation-induced acne on the face, scalp, or neck. The exact mechanism underlying its development remains incompletely understood. It is hypothesized that ionizing radiation may alter the composition of sebum, reduce its production, and stimulate hyperproliferation in pilosebaceous ducts [89,90]. Conversely, excessive UV radiation exposure may lead to the development of a disorder termed Favre–Racouchot syndrome (FRS). Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation, tobacco use, and prior radiotherapy are the most important risk factors for its occurrence [91]. FRS most typically presents in middle-aged Caucasian men with the involvement of the periorbital and malar regions. It is a prevalent dermatosis, affecting roughly 6% of adults over the age of 50. Due to the clinical and histological appearance of the lesions observed in affected individuals, the condition is also referred to as “nodular elastosis with cysts and comedones”. The most effective therapeutic approach combines protective measures, medical treatment (topical or oral retinoids), and extraction [92,93].
4.5. Chloracne
Exposure to polyhalogenated aromatic hydrocarbons can cause an uncommon but severe skin condition called chloracne [94]. These lesions belong to halogenodermas, i.e., skin eruptions associated with reactive halogen elements such as bromine, iodine, and chlorine. The mechanism behind halogenoderma is believed to involve a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction, and the eruptions may have similar clinical features [95]. In the case of chloracne, causative agents, also known as chloracnegens, can be found in occupational and industrial settings, in addition to polluted environments. Due to the potential presence of these substances in industrial waste material and food, they may enter the human body through inhalation, ingestion, and percutaneous absorption [94,96]. Chloracne is linked to one of the most devastating anthropogenic environmental catastrophes in history. The infamous chemical factory explosion near the town of Seveso, Italy, exposed the general population to high levels of dioxins. The “ICMESA plant explosion” resulted in the release of two kilograms of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), leading to severe health consequences [97]. In Japan, there was another considerable polychlorinated hydrocarbon exposure, which led to one of the biggest food poisonings in the world. This event, known as the “Yusho” incident, resulted from the mass contamination of rice bran oil with polychlorinated hydrocarbons [98]. The detrimental effects of chloracnegens are brought about by their immune suppression, carcinogenicity, and endocrine disruption [99]. In more advanced cases, ophthalmopathy, neuropathy, and hepatic dysfunction may develop [100]. In terms of skin alterations, the most distinctive characteristic of dioxin exposure is the development of an acne-like reaction. Chloracne exhibits dissimilarities from other halogenodermas and acne vulgaris. In particular, comedones serve as a hallmark of these lesions and may be present in extensive quantities, affecting all follicles. Notably, these lesions tend to manifest in specific locations, such as the malar crescents, postauricular regions, groin, axilla, and other facial areas. However, the nose is usually unaffected; the feature that was aptly described by Tindall in 1985, when referring to it as an “island in a sea of lesions” [101,102]. In contrast to acne vulgaris, chloracne rarely shows signs of inflammation, exhibits reduced sebum production, and emerges in distinctive locations [103]. In addition to chloracne, other cutaneous manifestations may include grayish skin discoloration, brownish discoloration of the nails, and hypertrichosis [101]. Chloracne is a highly challenging condition to treat, and therapy outcomes are generally unsatisfactory. Retinoic acid and oral antibiotics may provide some relief, but efficacy is limited. Unfortunately, discontinuation of exposure does not result in the resolution of chloracne, and the condition may persist for a long time, up to 15–30 years thereafter [96,101].
4.6. Oil Acne
Among the types of occupational acne, oil acne stands out as the most common form. It occurs due to exposure to mineral oil, which may be found in significant amounts in solvents and greases. Individuals employed in occupations such as marine engineering, the automotive industry, and machine operation may be particularly vulnerable to oil acne as they are exposed to mineral oils that frequently soak their work attire. This exposure can result in mechanical blockage of pilosebaceous glands, forming comedones and inflammatory eruptions, which typically appear on the dorsal surface of the hands, forearms, and thighs. To prevent this condition, it is important to refrain from contact with mineral oils, regularly change clothes, and maintain good personal hygiene. The use of oral tetracyclines and retinoids has demonstrated favorable outcomes [101,104].
4.7. Coal Tar Acne
Coal tar is a viscous, dark liquid obtained as a byproduct of the coal distillation process. While its medical application is beneficial, its industrial use holds far greater importance. It is commonly employed in aluminum and steel production, roofing, and road construction [105]. Coal tar acne, which results from exposure to coal tar, has been identified in nearly 25% of workers who have been exposed to it [106]. The respiratory system, the gastrointestinal system, and the skin all serve as potential entry routes for the development of this acne variant. Accumulation of coal tar fluid in the skin, along with keratin products, can obstruct sebaceous glands and cause coal tar acne to develop on the cheeks, characterized by open comedones. This type of acne does not show inflammatory papules or yellow cysts, the absence of which distinguishes the condition from oil acne and chloracne. Moreover, coal tar acne is more responsive to treatment than chloracne. In order to decrease the incidence of coal tar acne, industry workers should take precautions, follow preventive measures, and avoid potentially hazardous levels of coal tar [101].
4.8. Drug-Induced Acne-like Eruptions
Different medications can potentially cause a condition known as acne medicamentosa, which refers to acne-like eruptions triggered by drugs. The introduction of certain drugs may form acne-like lesions or aggravate pre-existing acne. The presenting lesions are devoid of cysts and comedones, and correspondingly coincide with the introduction or discontinuation of the drug. Although a link between acne and medications has been reported for various drugs, this paper focuses on addressing acne-like eruptions in response to steroid drugs and anticancer treatments.
4.8.1. Steroid Acne
Despite an incomplete understanding of its pathogenesis, the development of acne as a result of corticosteroids has been reported for over 70 years [107]. ‘Steroid acne’ is commonly observed following the administration of high doses of either inhaled, topical, or systemic corticosteroids. These lesions typically display skin-to-pink monomorphic papules and pustules. They usually affect the trunk and the face, and may extend to the shoulder region [108]. The likelihood of patients experiencing corticosteroid-induced acne generally relies on the duration and dosage of the drug, as well as on the individual characteristics of each patient. The underlying mechanism could be attributed to either the direct effects of steroids on epithelial degeneration and inflammation [108], or an elevation in free fatty acids (FFA) in skin lipids, leading to increased bacterial levels [109]. The onset of these eruptions can vary greatly, ranging from immediate manifestation following drug administration to several months after [108,110].
4.8.2. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a tyrosine kinase receptor that normally counteracts signaling pathways for cellular differentiation and proliferation. However, EGFR mutations result in the dysregulation of this pathway, as observed in different cancers such as colorectal, lung, and head and neck cancers. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors (EGFRI) are therefore used as anticancer therapy. This group includes monoclonal antibodies targeting the extracellular domains of EGFR (such as panitumumab and cetuximab), and tyrosine kinase inhibitors targeting the intracellular domains of EGFR (such as gefitinib and erlotinib) [111]. Acne-like eruptions have emerged as a prominent side effect of EGFRI chemotherapy, as their incidence rates in treated patients vary from 53% to 100% [112]. Additionally, the degree of severity is associated with the dosage level. The appearance of skin lesions is the most commonly reported adverse effect of EGFRI, and due to the pruritic nature of presenting papulopustules, the term ‘acneiform rash’ has been introduced. This acne-like reaction is devoid of comedones and appears in seborrheic areas, with occasional involvement of the extremities, abdomen, or lower back. The rash is more frequently reported with EGFR monoclonal antibody drugs. It usually emerges following the initial treatment cycle and reaches its peak incidence between three to four weeks of therapy [113,114]. The management of EGFRI-induced lesions depends on the severity of the condition, which is evaluated using the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI-CTCAE) grading system. Grade 1 eruptions can be effectively managed with topical agents such as clindamycin 2% or metronidazole 0.75%. The management of grade 2 includes topical treatment as in grade 1, but oral minocycline or doxycycline may be prescribed as well. Grade 3 may respond to the same treatment methods as grade 2, although treatment-resistant, symptomatic rashes may require EGFRI dose reduction and oral isotretinoin prescription. An acne-like rash of grade 4 warrants discontinuation of EGFRI therapy. All severity types benefit from general measures such as sun protection and the use of gentle soaps and light emollients. The presence of pruritus at any grade can be controlled with oral antihistamines [115,116]. Prophylactic treatment with oral tetracyclines has demonstrated efficacy, and it may be considered in patients starting EGFRI [114]. The final therapeutic practice is adjusted to the individual patient, and the involvement of a multidisciplinary team contributes to a more successful treatment [11,115].
5. Conclusions
Although acne is perceived as a skin condition with easily identifiable characteristics, its distinction from acne-like eruptions may pose a challenge in diagnostics. This group of dermatoses resembling acne vulgaris encloses an extensive number of dermatological conditions, which vary significantly in terms of severity and prevalence. The lesions of acne-like eruptions can manifest as papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts. As opposed to acne, these lesions are not necessarily confined to seborrheic areas and can affect any age group. They may present abruptly and have a monomorphic appearance. Moreover, the presence of comedones is generally uncommon, although they may occur in certain types of acne-like eruptions. Therefore, when evaluating these lesions, it is important to obtain a complete medical history, inquire about concomitant diseases, use of certain products and prescription drugs, exposure to physical and chemical agents, and perform a detailed clinical examination. The implementation of existing knowledge about acne-like eruptions, along with further investigations into the pathophysiology of the conditions that fall under it, is fundamental for achieving an accurate diagnosis and favorable treatment outcomes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.P. and Z.B.M.; methodology, Z.B.M.; software, E.P. and B.Š.; validation, E.P. and Z.B.M.; formal analysis, E.P. and Z.B.M.; investigation, E.P. and Z.B.M.; resources, L.L.-M. and Z.B.M.; data curation, E.P. and B.Š.; writing—original draft preparation, E.P. and Z.B.M.; writing—review and editing, E.P., L.L.-M., B.Š., and Z.B.M.; visualization, E.P.; supervision, L.L.-M. and Z.B.M.; project administration, E.P. and B.Š. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Layton, A.M.; Thiboutot, D.; Tan, J. Reviewing the Global Burden of Acne: How Could We Improve Care to Reduce the Burden? Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 184, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutaria, A.H.; Masood, S.; Schlessinger, J. Acne Vulgaris. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459173 (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Ogé, L.K.; Broussard, A.; Marshall, M.D. Acne Vulgaris: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, R.J.; Johns, N.E.; Williams, H.C.; Bolliger, I.W.; Dellavalle, R.P.; Margolis, D.J.; Marks, R.; Naldi, L.; Weinstock, M.A.; Wulf, S.K.; et al. The Global Burden of Skin Disease in 2010: An Analysis of the Prevalence and Impact of Skin Conditions. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnik, B.; Wenchieh, C. Acne and Rosacea. In Braun-Falco’s Dermatology, 4th ed.; Plewig, G., French, L., Ruzicka, T., Kaufmann, R., Hertl, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1291–1324. [Google Scholar]
- MeSH Browser. Available online: https://meshb.nlm.nih.gov/record/ui?ui=D017486 (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Cheung, M.J.; Taher, M.; Lauzon, G.J. Acneiform facial eruptions: A problem for young women. Can. Fam. Physician 2005, 51, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Kuflik, J.H. Acneiform Eruptions: Practice Essentials. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1072536-differential (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Thiboutot, D.; Zaenglein, A.L. Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestations, and Diagnosis of Acne Vulgaris. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/pathogenesis-clinical-manifestations-and-diagnosis-of-acne-vulgaris (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Dessinioti, C.; Antoniou, C.; Katsambas, A. Acneiform Eruptions. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alia, E.; Feng, H. Rosacea Pathogenesis, Common Triggers, and Dietary Role: The Cause, the Trigger, and the Positive Effects of Different Foods. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 40, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marson, J.W.; Baldwin, H.E. Rosacea: A Wholistic Review and Update from Pathogenesis to Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Dermatol. 2019, 59, e175–e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.S.; Huang, W.W. Rosacea Pathogenesis. Dermatol. Clin. 2018, 36, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S. Microbiota in Rosacea. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21 (Suppl. S1), 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferček, I.; Lugović-Mihić, L.; Tambić-Andrašević, A.; Ćesić, D.; Grginić, A.G.; Bešlić, I.; Mravak-Stipetić, M.; Mihatov-Štefanović, I.; Buntić, A.-M.; Čivljak, R. Features of the Skin Microbiota in Common Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Life 2021, 11, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picardo, M.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Tan, J. Acne and Rosacea. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7 (Suppl. S1), 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tang, K.; Wang, Y.; Fang, R.; Sun, Q. Rosacea Treatment: Review and Update. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parać, E. Acneiform Eruptions. Diploma Thesis, University of Zagreb, School of Medicine, Zagreb, Croatia, 2022. Available online: https://urn.nsk.hr/urn:nbn:hr:105:662849 (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Yun, C.H.; Yun, J.H.; Baek, J.O.; Roh, J.Y.; Lee, J.R. Demodex Mite Density Determinations by Standardized Skin Surface Biopsy and Direct Microscopic Examination and Their Relations with Clinical Types and Distribution Patterns. Ann. Dermatol. 2017, 29, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, P.; Hassan, I. Human Demodex Mite: The Versatile Mite of Dermatological Importance. Indian. J. Dermatol. 2014, 59, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, S.; Pancar Yüksel, E. Increased Demodex Density in Patients Hospitalized for Worsening Heart Failure. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendezu-Quispe, G.; Rojas-Zevallos, J.; Rosales-Rimache, J. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Demodex folliculorum Infestation: A Cross-Sectional Study in Peruvian Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toka Özer, T.; Akyürek, Ö.; Durmaz, S. Association between Demodex folliculorum and Metabolic Syndrome. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 3145–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paichitrojjana, A. Demodex: The Worst Enemies Are the Ones That Used to Be Friends. Dermatol. Rep. 2022, 14, 9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paichitrojjana, A. Demodicosis Imitating Acne Vulgaris: A Case Report. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, E.; Reisinger, A.; French, L.E.; Clanner-Engelshofen, B.M.; Reinholz, M. Comparison of Different Anti-Demodex Strategies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatology 2023, 239, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokos, Z.B.; Kummer, A.; Mosler, E.L.; Čeović, R.; Basta-Juzbašić, A. Perioral dermatitis: Still a therapeutic challenge. Acta Clin. Croat. 2015, 54, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Searle, T.; Ali, F.R.; Al-Niaimi, F. Perioral Dermatitis: Diagnosis, Proposed Etiologies, and Management. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3839–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugović-Mihić, L.; Špiljak, B.; Blagec, T.; Delaš Aždajić, M.; Franceschi, N.; Gašić, A.; Parać, E. Factors Participating in the Occurrence of Inflammation of the Lips (Cheilitis) and Perioral Skin. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakis, G.; Kokolakis, G.; Kaleta, K.; Wolk, K.; Hunger, R.; Sabat, R.; Zouboulis, C.C. Pathogenese der Hidradenitis Suppurativa/Acne Inversa. Hautarzt 2021, 72, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldburg, S.R.; Strober, B.E.; Payette, M.J. Hidradenitis Suppurativa. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pescitelli, L.; Ricceri, F.; Prignano, F. Hidradenitis Suppurativa and Associated Diseases. G. Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 153 (Suppl. S2), 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frings, V.G.; Bauer, B.; Glöditzsch, M.; Goebeler, M.; Presser, D. Assessing the psychological burden of patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek, M.; Walecka, I. Hidradenitis Suppurativa—Known and Unknown Disease. Reumatologia 2018, 56, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Jafari, S.M.; Hunger, R.E.; Schlapbach, C. Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Current Understanding of Pathogenic Mechanisms and Suggestion for Treatment Algorithm. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbiyi, A. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae; Current Treatment Options. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 12, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.G.; Goldstein, A.O. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae; Post, T.W., Ed.; UpToDate: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, A.P. Pseudofolliculitis Barbae and Acne Keloidalis Nuchae. Dermatol. Clin. 2003, 21, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalia, Y.; Khatib, J.; Odens, H.; Patel, T. A Review of Treatments of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 48, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribera, M.; Fernández-Chico, N.; Casals, M. Pseudofoliculitis de la barba [Pseudofolliculitis barbae]. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas 2010, 101, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, M.; Nomura, T.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis: A Review of the Japanese Published Works. J. Dermatol. 2012, 40, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Katoh, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Miyachi, Y.; Kabashima, K. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis: A Proposal of Diagnostic and Therapeutic Algorithms. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1301–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nervi, S.J.; Schwartz, R.A.; Dmochowski, M. Eosinophilic Pustular Folliculitis: A 40 Year Retrospect. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sève, P.; Pacheco, Y.; Durupt, F.; Jamilloux, Y.; Gerfaud-Valentin, M.; Isaac, S.; Boussel, L.; Calender, A.; Androdias, G.; Valeyre, D.; et al. Sarcoidosis: A Clinical Overview from Symptoms to Diagnosis. Cells 2021, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, A.; Rosenbach, M.; Imadojemu, S. Cutaneous Sarcoidosis. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 41, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeichner, J.A. Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology: A Differential Diagnosis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schmieder, S.J.; Harper, C.D.; Schmieder, G.J. Granuloma Annulare. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459377/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Joshi, T.P.; Duvic, M. Granuloma Annulare: An Updated Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatment Options. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 23, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. Papular Granuloma Annulare. In Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology; Zeichner, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Lam, J.M. Granuloma Annulare. Paediatr. Child. Health 2019, 24, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, C.B.; Rosenbach, M. Granuloma annulare: A retrospective series of 133 patients. Cutis 2019, 103, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Khachemoune, A. Granuloma Annulare: A Focused Review of Therapeutic Options. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 19, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambe, S.; Jerajani, H.; Pund, P. Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis Effectively Managed with Oral Isotretinoin. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2018, 9, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qassabi, A.-M.; Al-Busaidi, K.; Al Baccouche, K.; Al Ismaili, A. Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis in an Adult: A Case Report with Review of Literature. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2020, 20, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chintagunta, S.R.; Manchala, S.; Arakkal, G. Granulomatous periorificial dermatitis in an adult: A rare case report. J. Dr. NTR Univ. Health Sci. 2018, 7, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakih, A.; Makhoul, R.; Grozdev, I. Childhood Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 26, 13030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Garijo, N.; Querol-Cisneros, E.; Tomas-Velazquez, A.; Estenaga, A.; Moreno-Artero, E.; Idoate, M.A.; Paricio, J.J.; España, A. Recalcitrant Granulomatous Periorificial Dermatitis with Good Response to Low-Dose Oral Isotretinoin. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2019, 36, 980–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.S.; Lin, P.T.; Tsai, Y.S.; Wang, S.H.; Chi, C.C. Interventions for bacterial folliculitis and boils (furuncles and carbuncles). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2, CD013099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugović-Mihić, L.; Barisić, F.; Bulat, V.; Buljan, M.; Situm, M.; Bradić, L.; Mihić, J. Differential diagnosis of the scalp hair folliculitis. Acta Clin. Croat 2011, 50, 395–402. [Google Scholar]
- Laureano, A.C.; Schwartz, R.A.; Cohen, P.J. Facial Bacterial Infections: Folliculitis. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, H.S.; Nopper, A.J. Superficial Bacterial Skin Infections and Cellulitis. In Principles and Practice of Pediatric Infectious Diseases, 5th ed.; Long, S.S., Prober, C.G., Fischer, M., Eds.; Elsevier—Health Sciences Division: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 436–444. [Google Scholar]
- Plewig, G.; Jansen, T. Acneiform Dermatoses. Dermatology 1998, 196, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böni, R.; Nehrhoff, B. Treatment of Gram-Negative Folliculitis in Patients with Acne. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2003, 4, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, C.; Henning, M.A.S.; Gaitanis, G.; Faergemann, J.; Saunte, D.M. Critical Synthesis of Available Data in Malassezia Folliculitis and a Systematic Review of Treatments. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1672–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, R.M.; Malerich, S.A. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) Folliculitis. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2014, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Saunte, D.M.L.; Gaitanis, G.; Hay, R.J. Malassezia-Associated Skin Diseases, the Use of Diagnostics and Treatment. Front. Cell. Infect. 2020, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgotra, V.; Singh, H. Malassezia (Pityrosporum) Folliculitis Masquerading as Recalcitrant Acne. Cureus 2021, 13, e13534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spernovasilis, N.; Psichogiou, M.; Poulakou, G. Skin Manifestations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 34, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, S.; Hogan, K.; March, S.B.; Butler, R.W. Whirlpool-Associated Folliculitis Caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Report of an Outbreak and Review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1986, 23, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toner, C.B. Pseudomonas Folliculitis; Elston, D.M., Ed.; Medscape: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Revanker, S.G. Sporotrichosis—Infectious Diseases. Available online: https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/fungi/sporotrichosis (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Sizar, O.; Talati, R. Sporotrichosis. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532255 (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Mahlberg, M.J.; Patel, R.; Rosenman, K.; Cheung, W.; Wang, N.; Sanchez, M. Fixed Cutaneous Sporotrichosis. Dermatol. Online J. 2009, 15, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusuhara, M.; Hachisuka, H.; Sasai, Y. Statistical Survey of 150 Cases with Sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 1988, 102, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, S.C.G.; Alanis, J.C.S.; Flores, M.G.; Gonzalez, S.E.G.; Cabrera, L.V.; Candiani, J.O. Coccidioidomycosis and the Skin: A Comprehensive Review. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2015, 90, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocampo-Garza, J.; Castrejón-Pérez, A.D.; Gonzalez-Saldivar, G.; Ocampo-Candiani, J. Cutaneous Coccidioidomycosis: A Great Mimicker. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, bcr2015211680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, W.C.; Bagley, M.P.; Khan, Y.; Schwartz, R.A. Pustular acneiform secondary syphilis. Cutis 1986, 37, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harden, D. Papular and Nodular Lesions of the Scalp, Face, and Neck. Arch. Dermatol. 1997, 133, 1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaess, M.; Kaiser, L.; Sommerfeld, O.; Csuk, R.; Deigner, H.-P. Drug Triggered Pruritus, Rash, Papules, and Blisters—Is AGEP a Clash of an Altered Sphingolipid-Metabolism and Lysosomotropism of Drugs Accumulating in the Skin? Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjorth, N.; Sjolin, K.E.; Sylvest, B.; Thomsen, K. Acne Aestivalis--Mallorca Acne. Acta Derm. Venereol. 1972, 52, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Bleehen, S.S. Acne Induced by PUVA Treatment. BMJ 1977, 2, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mazhar, M.; Simpson, M.; Marathe, K. Inner Thigh Friction as a Cause of Acne Mechanica. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2019, 36, 546–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiman, A. Sports Dermatology Part 1: Common Dermatoses. CMAJ 2004, 171, 851–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, R.; Adams, B.B. Dermatological Problems in the Football Player. Int. J. Dermatol. 2006, 45, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knierim, C.; Goertz, W.; Reifenberger, J.; Homey, B.; Meller, S. Geigerknoten. Hautarzt 2013, 64, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligman, A.M. Acne Cosmetica. Arch. Dermatol. 1972, 106, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewig, G. Pomade Acne. Arch. Dermatol. 1970, 101, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.M.C.; Bardsley, A.F. The Comedo Skin Reaction to Radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2002, 75, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubiche, T.; Sibaud, V. Localized Acne Induced by Radiation Therapy. Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 20, 21545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganelli, A.; Mandel, V.D.; Kaleci, S.; Pellacani, G.; Rossi, E. Favre–Racouchot Disease: Systematic Review and Possible Therapeutic Strategies. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 33, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonthalia, S.; Arora, R.; Chhabra, N.; Khopkar, U. Favre-Racouchot Syndrome. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2014, 5, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platsidaki, E.; Markantoni, V.; Balamoti, E.; Kouris, A.; Rigopoulos, D.; Kontochristopoulos, G. Combination of 30% Salicylic Acid Peels and Mechanical Comedo Extraction for the Treatment of Favre-Racouchot Syndrome. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2019, 27, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger, D.I.; Robinson, C.A.; Schlessinger, J. Chloracne. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459189/ (accessed on 10 April 2023).
- Dyall-Smith, D. Halogenoderma. Available online: https://dermnetnz.org/topics/halogenoderma (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Ju, Q.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Xia, L. Environmental Pollution and Acne-Chloracne. Dermato-Endocrinology 2009, 1, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskenazi, B.; Warner, M.; Brambilla, P.; Signorini, S.; Ames, J.; Mocarelli, P. The Seveso accident: A look at 40 years of health research and beyond. Environ. Int. 2018, 121 Pt 1, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onozuka, D.; Nakamura, Y.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, M. Mortality in Yusho Patients Exposed to Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Polychlorinated Dibenzofurans: A 50-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. Environ. Health 2020, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, D.O. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Routes of Exposure and Effects on Human Health. Rev. Environ. Health 2006, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelclová, D.; Urban, P.; Preiss, J.; Lukáš, E.; Fenclová, Z.; Navrátil, T.; Dubská, Z.; Senholdová, Z. Adverse Health Effects in Humans Exposed to 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin (TCDD). Rev. Environ. Health 2006, 21, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, B.; Cicek, D. Occupational Acne. In Acne and Acneiform Eruptions; Kartal, S.P., Gönül, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 53–67. [Google Scholar]
- Tindall, J.P. Chloracne and Chloracnegens. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1985, 13, 539–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panteleyev, A.A.; Bickers, D.R. Dioxin-Induced Chloracne—Reconstructing the Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of a Classic Environmental Disease. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 705–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokelj, F. Occupational Acne. Clin. Dermatol. 1992, 10, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, G.-A.; Xanthopoulou, E.; Riza, E.; Linos, A. Skin Disease after Occupational Dermal Exposure to Coal Tar: A Review of the Scientific Literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 2015, 54, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, E.; Karpouzis, A.; Zorbas, A.; Bazas, T.; Zorbas, S.; Alexopoulos, E.; Zorbas, I.; Kouskoukis, K.; Konstandinidis, T. Occupational Dermatoses by Type of Work in Greece. Saf. Health Work 2013, 4, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, M.J.; Riddell, J.M., Jr.; Best, W.R. Cutaneous side effects of ACTH cortisone and pregnenolone therapy. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1951, 16, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, R.M. Steroid acne. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1989, 21, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloor, M.; Mildenberger, K.H. On the influence of an external therapy with dexamethasone-21-sodium-m-sulfobenzoate on the amount of free fatty acids in the skin surface lipids. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 1978, 261, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, H.K.; Ezra, N.; Wolverton, S.E. Drug-Induced Acneiform Eruptions. In Acneiform Eruptions in Dermatology; Zeichner, J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 389–404. [Google Scholar]
- Ayati, A.; Moghimi, S.; Salarinejad, S.; Safavi, M.; Pouramiri, B.; Foroumadi, A. A Review on Progression of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Inhibitors as an Efficient Approach in Cancer Targeted Therapy. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segaert, S.; Van Cutsem, E. Clinical Signs, Pathophysiology and Management of Skin Toxicity during Therapy with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrocini, G.; Panariello, L.; Caro, G.; Cacciapuoti, S. Acneiform Rash Induced by EGFR Inhibitors: Review of the Literature and New Insights. Ski. Appendage Disord. 2015, 1, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorji, M.; Joseph, J.; Pavlakis, N.; Smith, S.D. Prevention and Management of Acneiform Rash Associated with EGFR Inhibitor Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 18, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potthoff, K.; Hofheinz, R.; Hassel, J.C.; Volkenandt, M.; Lordick, F.; Hartmann, J.T.; Karthaus, M.; Riess, H.; Lipp, H.P.; Hauschild, A.; et al. Interdisciplinary Management of EGFR-Inhibitor-Induced Skin Reactions: A German Expert Opinion. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, J.; Germetaki, T.; Judge, M.; Paton, N.; Collins, J.; Garbutt, A.; Braun, M.; Fenwick, J.; Saunders, M.P. Management and Grading of EGFR Inhibitor-Induced Cutaneous Toxicity. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).