Unlocking the “Code” of Green Innovation Based on Machine Learning: Evidence from Manufacturing Enterprises in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Literature
2.1. GIP
2.2. The Strategic Tripod Framework
3. Preliminaries
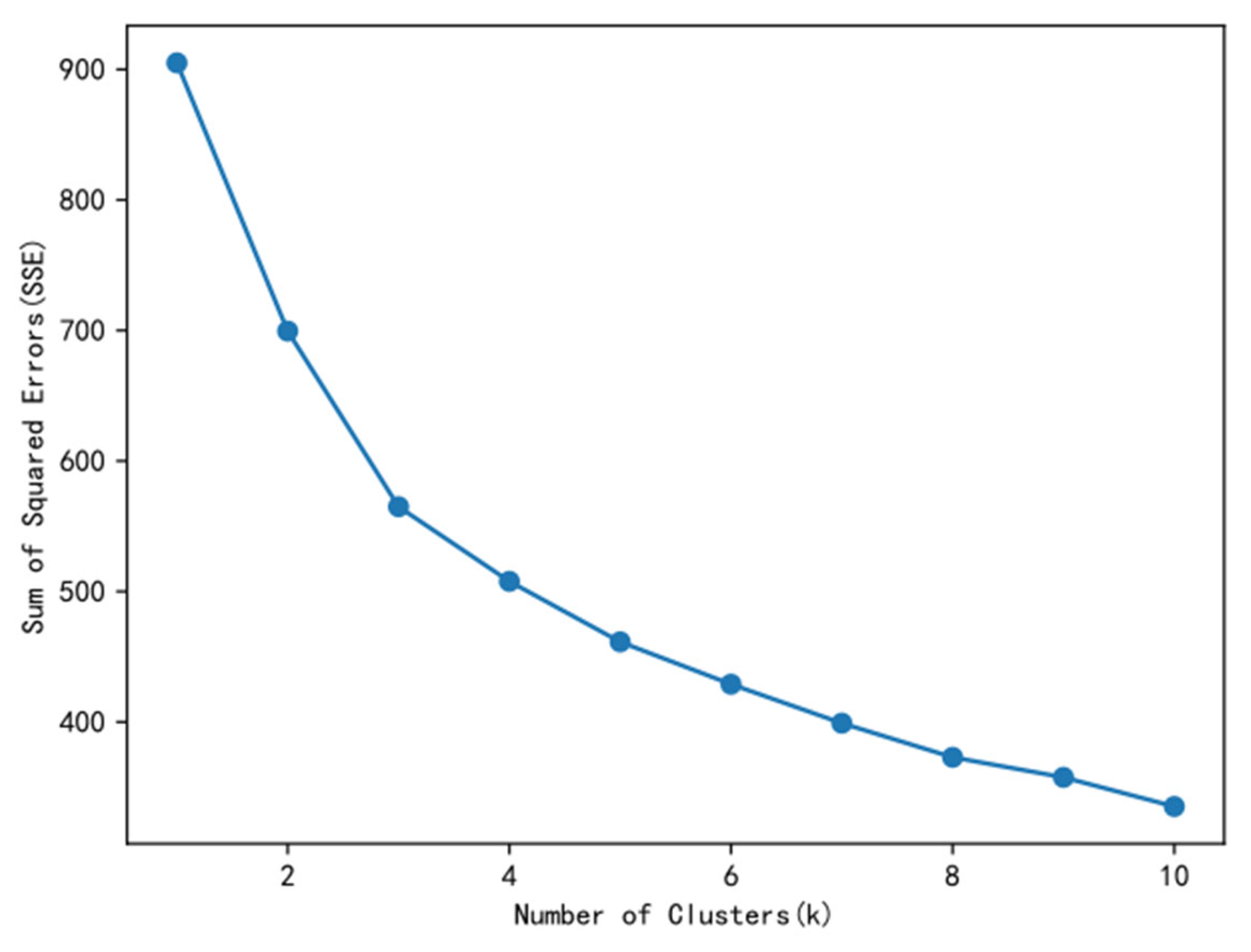
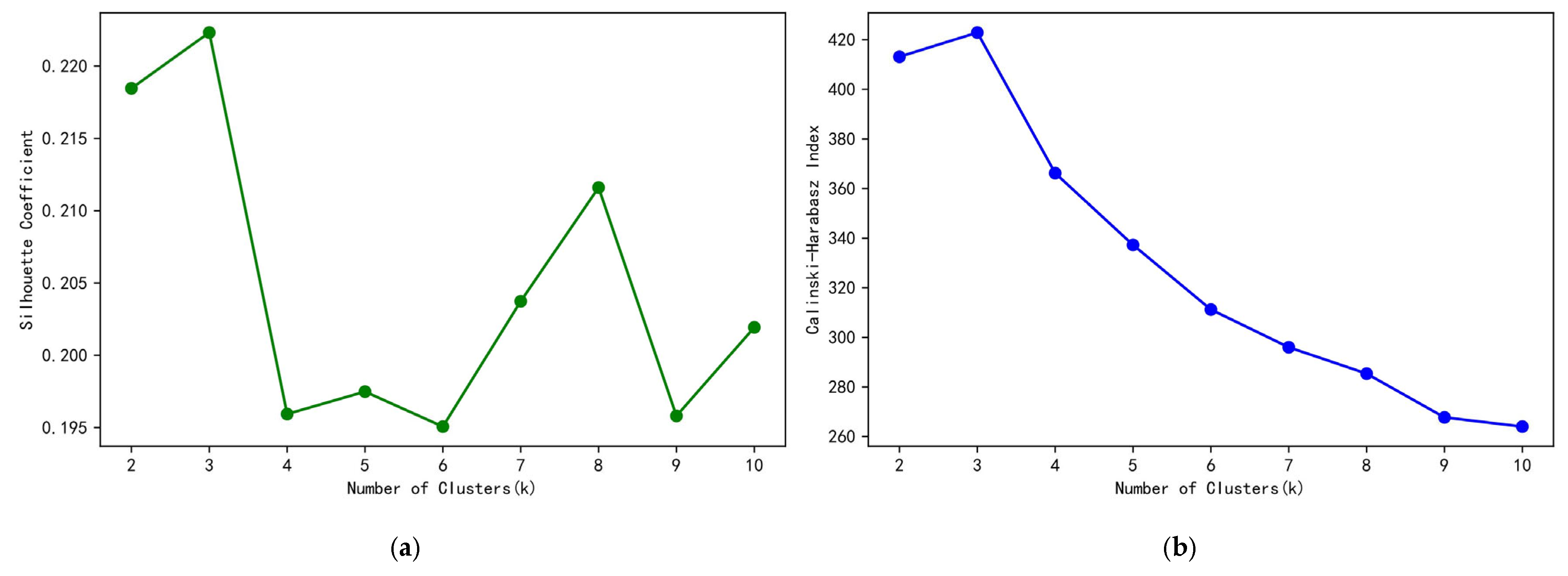
3.1. K-Means Algorithm
3.2. CART Algorithm
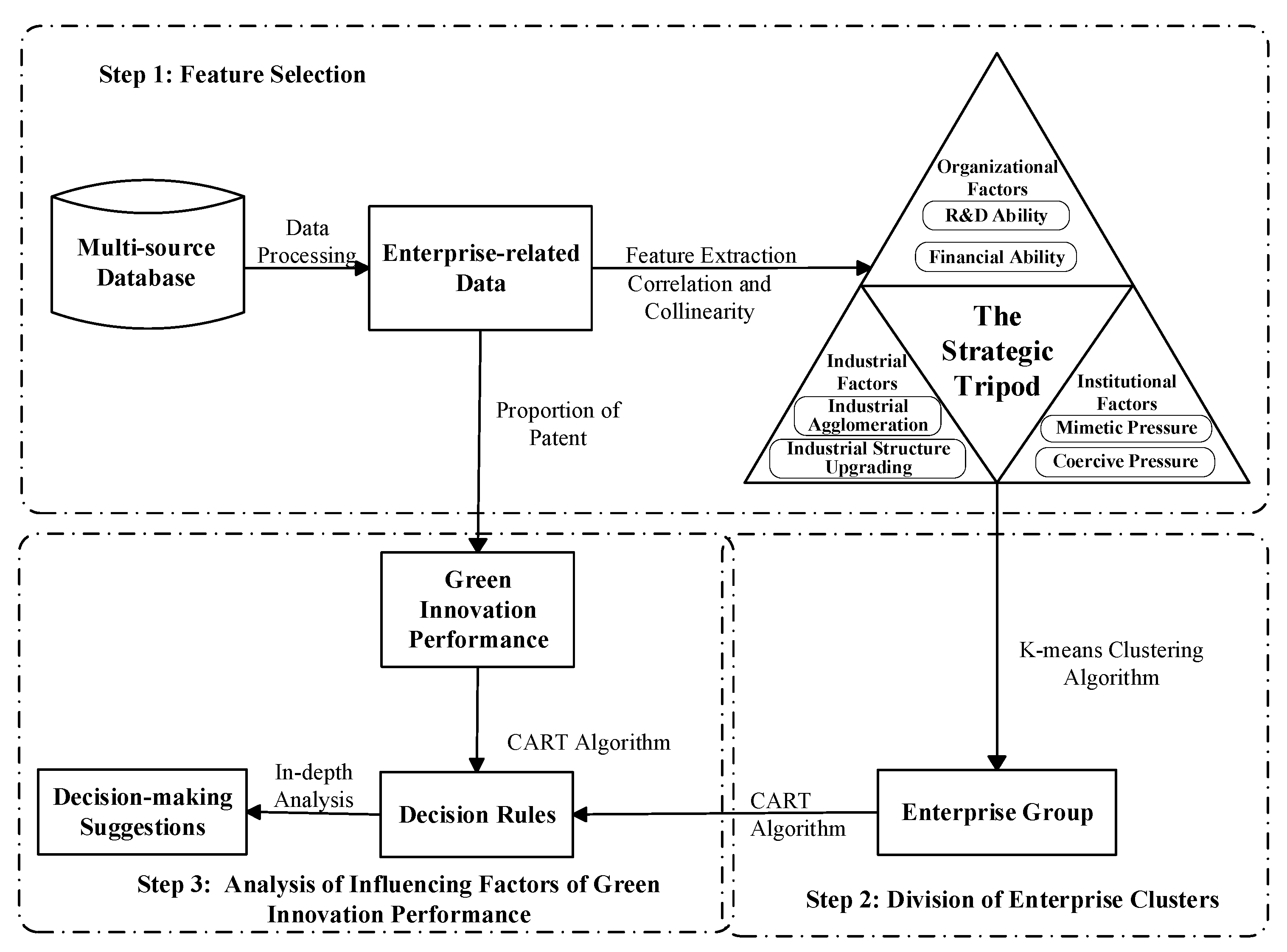
4. Research Framework and Variable Selection
4.1. Research Framework
4.2. Variable Selection
4.2.1. Dependent Variable—GIP
4.2.2. Independent Variables—Strategic Tripod Framework
- (1)
- The organizational level
- (2)
- The industrial level
- (3)
- The institutional level
5. Classification and Characteristic Analysis
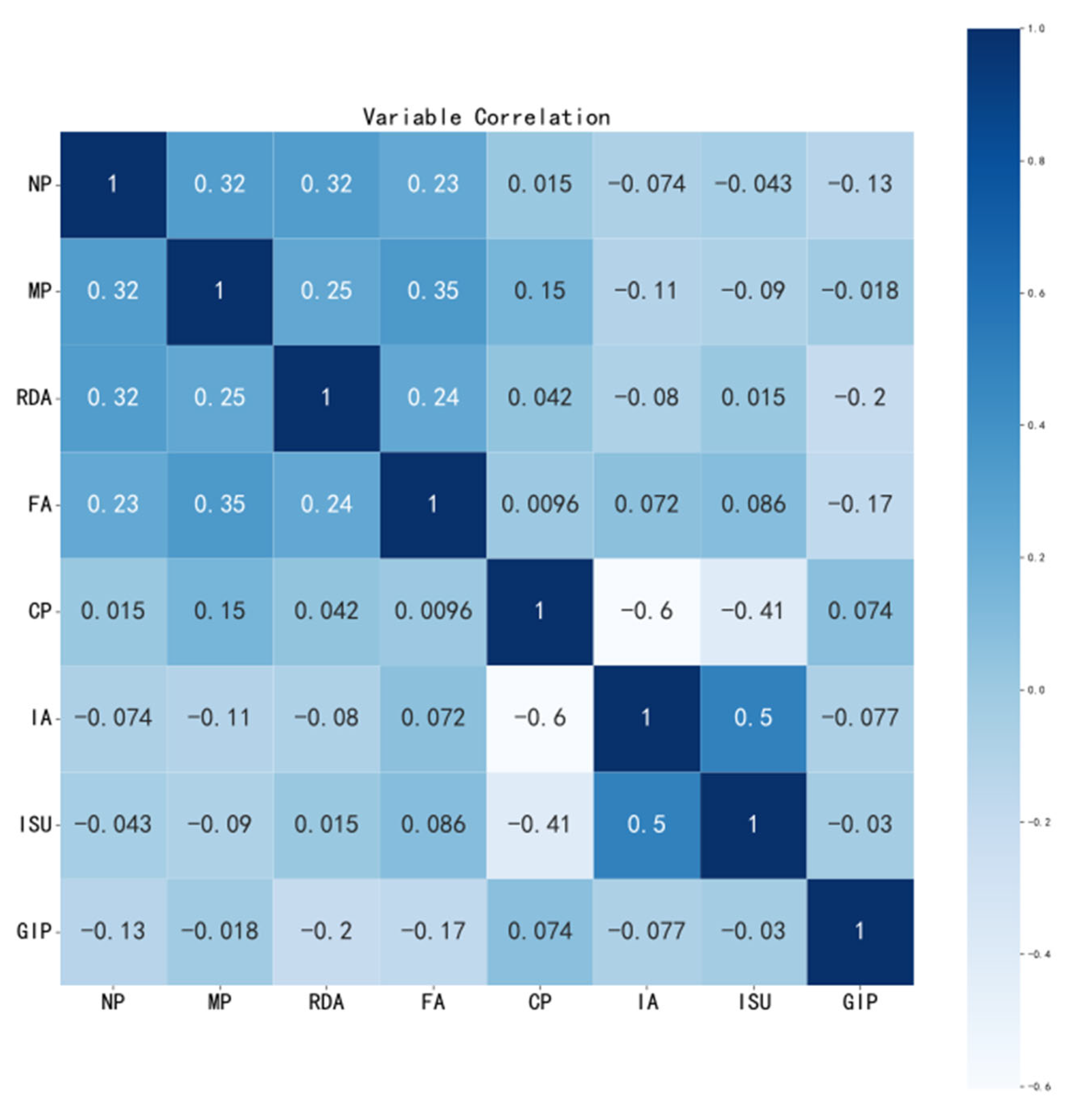
5.1. Data Source and Processing
5.2. Division of Manufacturing Enterprises
5.3. Characteristics Analysis of Manufacturing Enterprises
6. Analysis of Influencing Factors on GIP
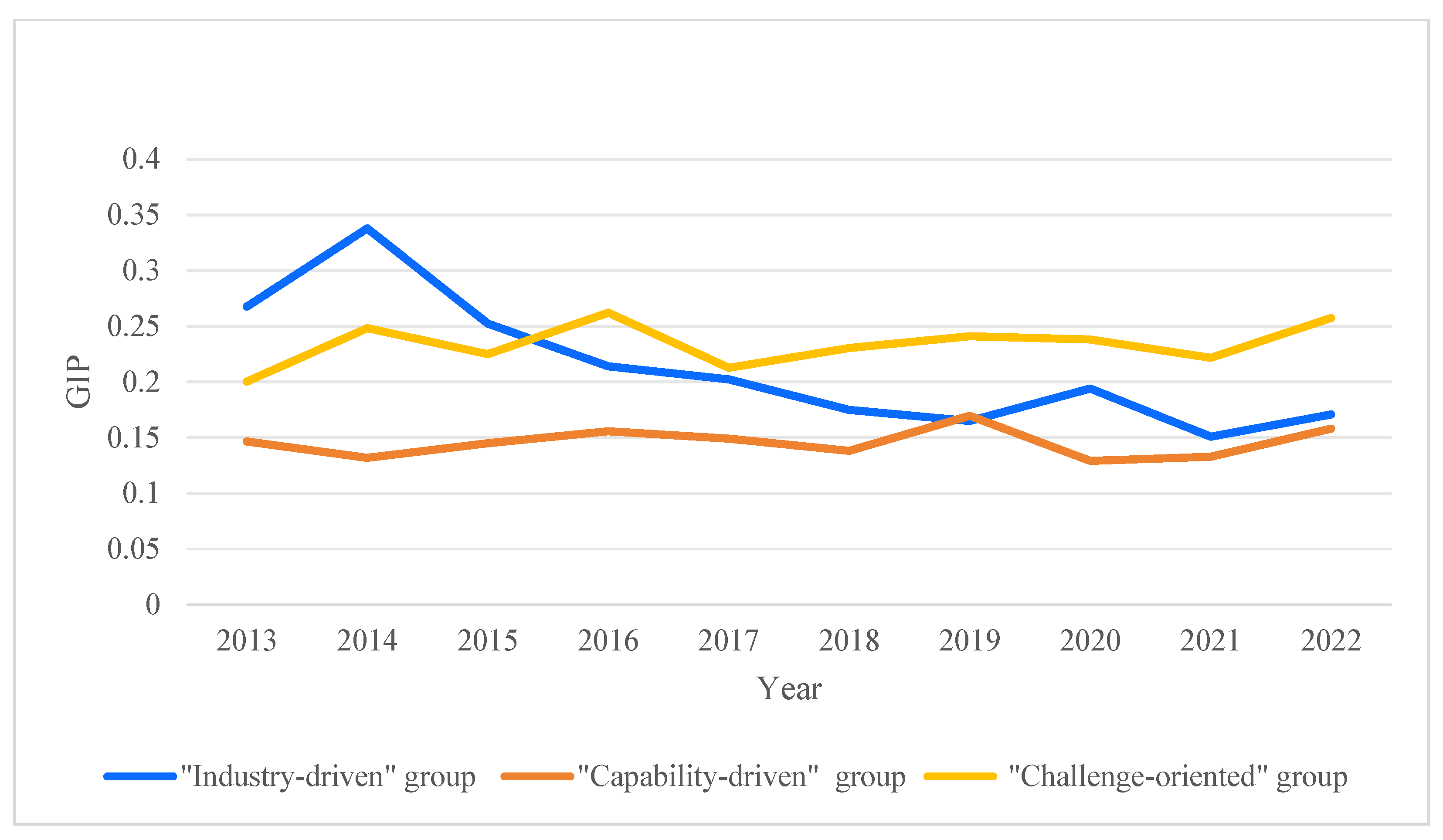
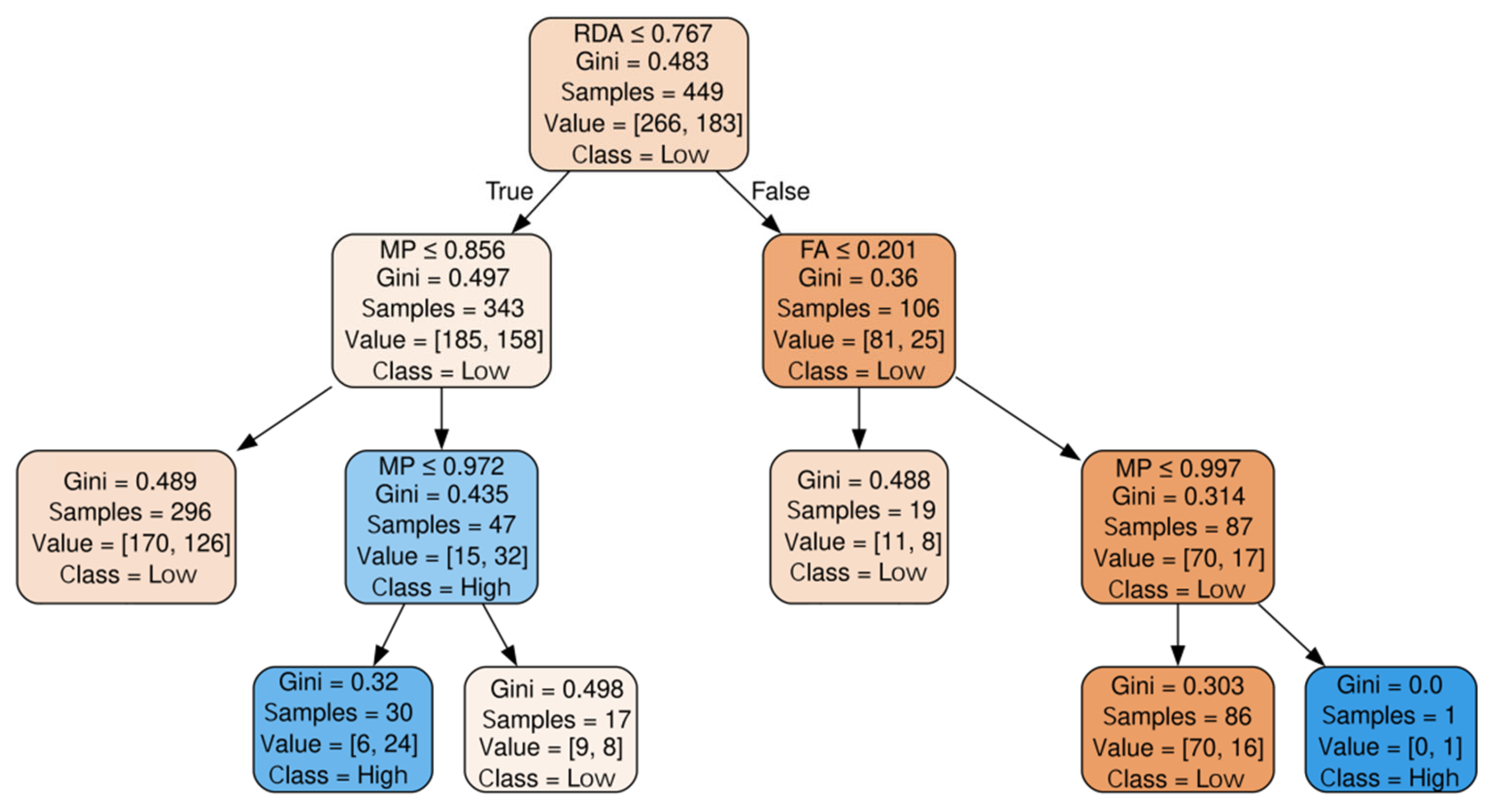
6.1. “Industry-Driven” Enterprises Cluster
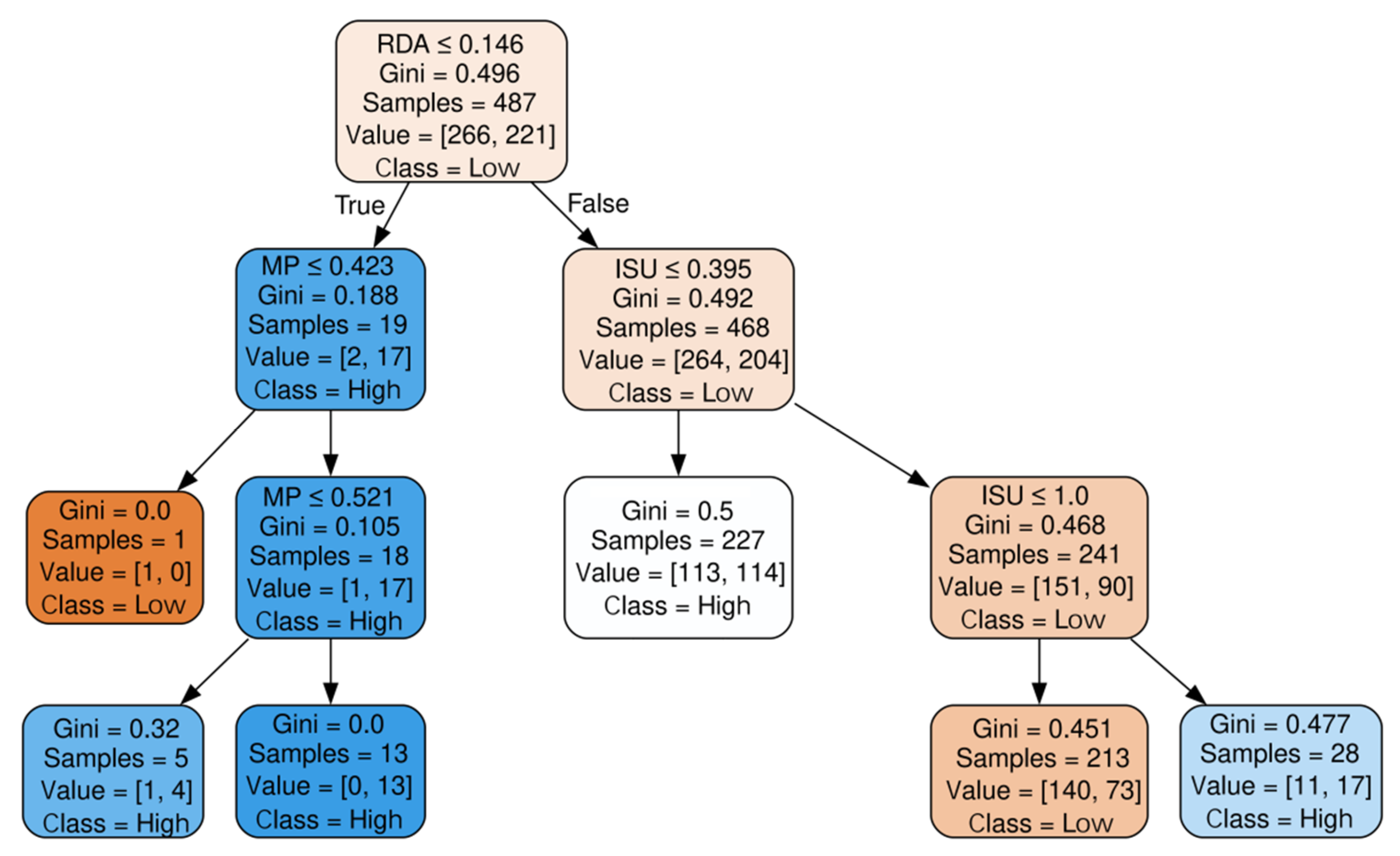
6.2. “Capability-Driven” Enterprises Cluster
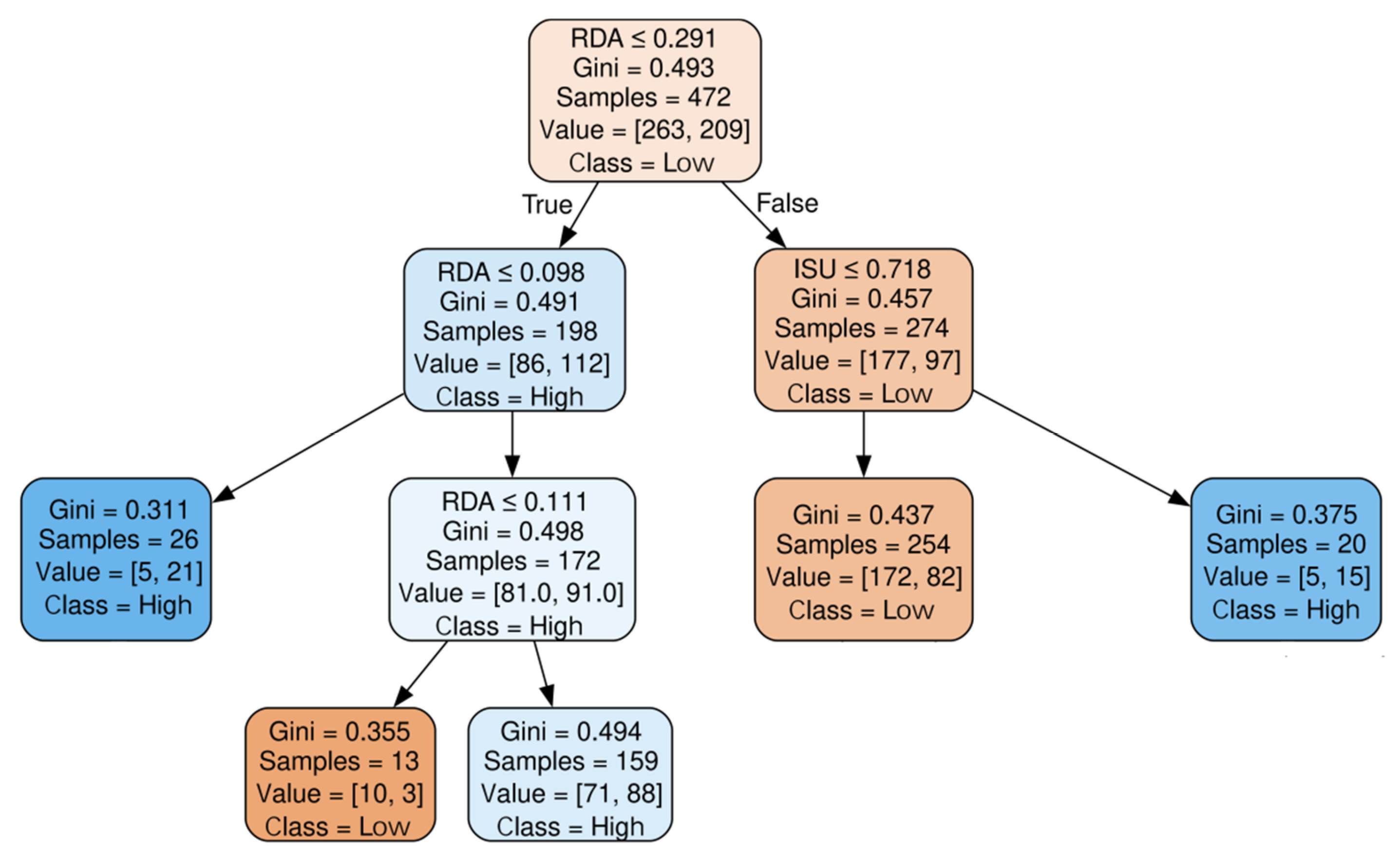
6.3. “Challenge-Oriented” Enterprises Cluster
7. Conclusions and Discussion
7.1. Research Conclusions
7.2. Theoretical Contributions
7.3. Managerial Implications
7.3.1. Enterprise Side
7.3.2. Government Side
7.4. Innovations and Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GIP | Green innovation performance |
| RDA | R&D ability |
| FA | Financial ability |
| IA | Industrial agglomeration |
| ISU | Industrial structure upgrading |
| CP | Coercive pressure |
| MP | Mimetic pressure |
| CART | Classification and regression tree |
References
- Matviienko, H.; Pylypenko, O.; Putintsev, A.; Chumak, O.; Gordiichuk, S. European Union policy on financing eco—Innovations in the transition to a green economy. Cuest. Polít. 2022, 40, 28–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.C. The United States—China race for green transformation: Institutions, incentives, and green industrial policies. J. Chin. Polit. Sci. 2024, 29, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, K.; Oates, W.E.; Portney, P.R. Tightening Environmental Standards; The Benefit-Cost or the No-Cost Paradigm? J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Linde, C.D. Toward a New Conception of the Environment-Competitiveness Relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 1995, 9, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Shi, Z.; Han, D.; Zeng, J. Agglomeration of the New Energy Industry and Green Innovation Efficiency: Does the Spatial Mismatch of R&D Resources Matter? J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135453. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; An, K.K.; Jang, S. Threshold Effect and Mechanism of Tourism Industrial Agglomeration on Green Innovation Efficiency: Evidence from Coastal Urban Agglomerations in China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 246, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.P.; Lin, L.; Huang, Y. Industrial Collaborative Agglomeration, Marketization, and Green Innovation: Evidence from China’s Provincial Panel Data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, J. Impact of Industrial Structure Upgrading on Green Innovation: Evidence from Chinese Cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 3887–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; Jin, S. Managerial Ability and Green Innovation: The Moderating Effect of Directors’ and Officers’ Insurance in China. J. Int. Trade Commer. 2024, 20, 17–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Sheng, Z. Policy orientation, knowledge dynamic ability and green innovation: A mediation model based on China provincial panel data. Zb. Rad. Ekon. Fak. Rij. 2021, 39, 9–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Kou, F.R.; Zhuang, Y. Offensive or defensive? The influence of corporate strategic aggressiveness on corporate performance from the perspective of supply chain. Manag. Rev. 2025, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Chen, X.J. Meaningful green innovation: From the perspective of strategic tripod. Sci. Sci. Manag. Sci. Technol. 2022, 43, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Fussler, C.; James, P. Driving Eco-Innovation: A Breakthrough Discipline for Innovation and Sustainability; Pitman Publishing: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.G.; Liu, F.H.; Wu, J. A Strategy Tripod Perspective on ISO 9001 Adoption: Evidence from Chinese Manufacturing Firms. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 70, 3990–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, S.L.; Gao, H.; Wang, C.Y. Research on the influence of air pollution on green technology innovation of listed companies in heavy pollution industries. Chin. J. Manag. 2023, 20, 400–410. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Chin, W.; Liu, Y.D.; He, K. Do institutional pressures promote green innovation? The effects of cross-functional coopetition in green supply chain management. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2022, 53, 743–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Chen, C.T. Exploring institutional pressures, firm green slack, green product innovation and green new product success: Evidence from Taiwan’s high-tech industries. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 174, 121196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherazi, K.; Zhang, P.C.; Ghazanfar, F.; Khan, Q.T.A. Why is institutional pressure insufficient to develop green innovation in manufacturing firms? The role of green high-performance work systems and managerial environmental concern. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2023, 68, 1622–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.Y.; Jia, Y.H.; Zou, H.L. Is institutional pressure the mother of green innovation? Examining the moderating effect of absorptive capacity. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deltas, G.; Harrington, D.R.; Khanna, M. Oligopolies with (somewhat) environmentally conscious consumers: Market equilibrium and regulatory intervention. J. Econ. Manag. Strategy 2013, 22, 640–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Pang, M.Y.; Jin, J.H.; Tao, X.Y.; Dong, H.M. Research on the influencing factors of green innovation performance of heavy polluting enterprises based on machine learning. Sci. Res. Manag. 2025. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1567.G3.20250623.1329.004 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Riaz, M.; Jie, W.; Sherani, S.; Chang, S. Assessing the role of organizational strategic factors in stimulating green innovation performance: Moderating effects of green absorptive capacity. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2024, 30, 1013–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Z.; Zeng, J.W.; Wang, D.; Su, Y. Research on co-evolution of enterprise green innovation system based on knowledge behavior. J. Ind. Eng. Eng. Manag. 2020, 34, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.M. Digital transformation and corporates’ green technology innovation performance—The mediating role of knowledge sharing. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 62, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.W.; Sun, L.S.; Pinkham, B.; Hao, C. The institution-based view as a third leg for a strategy tripod. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2009, 23, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E. Competitive Strategy: Techniques for Analyzing Industries and Competitors; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- DiMaggio, P.J.; Powell, W.W. The iron cage revisited: Institutional isomorphism and collective rationality in organizational fields. Am. Sociol. Rev. 1983, 48, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, R. Successful industrial innovation: Critical factors for the 1990s. R&D Manag. 1992, 22, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Luo, D.K.; Wang, L.W.; Zhou, T.Z. Foreign ownership and bribery in Chinese listed firms: An institutional perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2024, 174, 114530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangelico, R.M.; Pujari, D.; Pontrandolfo, P. Green product innovation in manufacturing firms: A sustainability-oriented dynamic capability perspective. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2017, 26, 490–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.B.; Chai, H.Q.; Shao, J.; Feng, T.; Newman, A. Green entrepreneurial orientation for enhancing firm performance: A dynamic capability perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Wu, P.J. The impact of high-tech industrial agglomeration on China’s green innovation efficiency: A spatial econometric analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 11, 1167918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ji, Y. Can Informal Environmental Regulation Promote Green Innovation? A Quasi-Natural Experiment Based on Environmental Information Disclosure Policy. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 2795–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Rogers, D.S. A framework of sustainable supply chain management: Moving toward new theory. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2008, 38, 360–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, T.; Woerter, M. Competitive pressure and diversification into green R&D. Rev. Ind. Organ. 2018, 55, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangi, T.A.; Wei, Z.L.; Zhang, L.Q.; Bao, Y.C.; Khoso, W.M. Profiting from Frugal Innovation: A Strategy-Tripod-View and Evidence from China. Creat. Innov. Manag. 2025, 34, 579–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punhani, A.; Faujdar, N.; Mishra, K.K.; Subramanian, M. Binning-Based Silhouette Approach to Find the Optimal Cluster Using K-Means. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 115025–115032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.H.; Li, H.L. R&D team network configurations, knowledge diversity and breakthrough innovation: A combined effect framework. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2024, 28, 2285–2303. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.P.; Li, H.L.; Lin, C.P.; Wan, X.J. The Influence of Knowledge Base on the Dual-Innovation Performance of Firms. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 879640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.H.; Qiao, L.; Singh, A.K. Advanced machine learning on cognitive computing for human behavior analysis. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2021, 8, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.J.; Li, J.M.; Lai, J.; Zhang, L.P. Technological Catch-Up Performance: The Interplay Between Collaboration Networks and Knowledge Networks. Systems 2025, 13, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Rhee, S.-Y.; Hyun, E.-J. Knowledge Exploitation, Inventor Characteristics, and Green Innovation Performance in Automotive Firms. Systems 2025, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.Y.; Hu, D.M.; Wang, X.H. Climate disasters and processing of green patents. J. Econ. Surv. 2024, 38, 1983–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wang, W.N.; Han, D.N. The Impact of Female Executives’ Cognitive Imprints on Corporate Green Innovation. Sci. Res. Manag. 2025. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1567.G3.20250701.1409.004 (accessed on 20 August 2025).
- Li, H.Y.; Liu, Q.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Fu, S.Y. Environmental, Social and Governance Information Disclosure and Corporate Green Innovation Performance. Stat. Res. 2022, 39, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.I.; Zuo, X. Credit of small and medium sized scientific and technological enterprises based on BP neural network Evaluation research. MATEC Web Conf. 2021, 336, 09010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, X.W.; Lai, Z.J. Do enterprise ownership structures affect financial performance in China’s power and gas industries? J. Util. Policy 2021, 73, 101303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, E.M.; Feser, E.J. Industrial and Regional Clusters: Concepts and Comparative Applications; Regional Research Institute: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.L.; Zhao, J. Environmental regulation, technological innovation and industrial structure upgrading. Sci. Res. Manag. 2018, 39, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, W.R. Institutions and Organizations: Ideas, Interests, and Identities; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, H.T.; Su, L.D. A study on the imitation in corporate information disclosure: Based on institutional theory. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2012, 15, 82–99. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.G. A research on the dynamic mechanism of intellectual transformation among industrial enterprises. Sci. Res. Manag. 2020, 41, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.Y.; Mbanyele, W.; Wei, Z.X.; Li, X. How does green industrial policy affect corporate green innovation? Evidence from the green factory identification in China. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaraan, F.; Elmarzouky, M.; Hussainey, K.; Venkatesh, V.G.; Shi, Y.Y.; Gulko, N. Reinforcing green business strategies with industry 4.0 and governance towards sustainability: Natural-resource-based view and dynamic capability. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 3, 3588–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.P.; Qiu, H.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Li, H.L.; Wan, X.J. How to enhance enterprises’ radical innovation performance through multiple pathways—A machine learning analysis of SRDI enterprises in China. Systems 2025, 13, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primary-Level Indicator | Secondary-Level Indicator | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Debt-paying ability | Current ratio | Current assets/current liabilities |
| Quick ratio | (Current assets—inventory)/current liabilities | |
| Equity-to-liability ratio | Owner’s equity/liabilities | |
| Profitability | Return on assets | (Gross profit + finance expenses)/[(closing balance of total assets + opening balance of total assets)/2] |
| Net profit margin on total assets | Net profit/[(closing balance of total assets + opening balance of total assets)/2] | |
| Net operating margin | Net profit/operating income | |
| Earnings per share | Net profit/total shares | |
| Operating ability | Total asset turnover | Operating income/[(total assets closing balance + total assets opening balance)/2] |
| Turnover of current assets | Operating income/[(closing balance of current assets + beginning balance of current assets)/2] | |
| Development ability | Growth rate of total assets | (Total assets at the end of the current period—total assets at the end of the previous period)/total assets at the end of the previous period |
| Growth rate of operating profit | (Operating profit for the current period-operating profit for the previous period)/operating profit for the previous period |
| Variable Type | Layers | Variable Names | Variable Abbreviations | Measurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Result variable | Green innovation performance | GIP | Number of green innovation patent applications as a percentage of total innovation patent applications | |
| Conditional variable | Organization | R&D ability | RDA | Amount of R&D investment |
| Financial ability | FA | Comprehensive evaluation index system of financial ability | ||
| Industry | Industrial agglomeration | IA | The ratio of manufacturing population to employment in each region | |
| Industrial structure upgrading | ISU | The ratio of output value of high-end technology industries to that of mid-range technology industries | ||
| Institution | Coercive pressure | CP | Pollution control cost per thousand CNY of industrial output value | |
| Normative pressure | NP | Total company news coverage for the year | ||
| Mimetic pressure | MP | Industry averages for environmental disclosures |
| Cluster | Number | Characteristic Variable | GIP (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | CP | RDA | FA | IA | ISU | |||
| Industry-driven | 449 | 0.357 | 0.226 | 0.483 | 0.469 | 0.712 | 0.862 | H: 40.8 L: 59.2 |
| Capability-driven | 487 | 0.771 | 0.613 | 0.724 | 0.795 | 0.336 | 0.438 | H: 45.4 L: 54.6 |
| Challenge-oriented | 472 | 0.338 | 0.645 | 0.417 | 0.233 | 0.237 | 0.321 | H: 44.3 L: 55.7 |
| Cluster | RDA | FA | IA | ISU | CP | MP | Sup (%) | Con (%) | GIP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Industry- driven | ≤0.767 | - | - | - | - | ≤0.856 | 65.9 | 57.4 | L |
| ≤0.767 | - | - | - | - | (0.856, 0.972] | 6.7 | 80.0 | H | |
| ≤0.767 | - | - | - | - | >0.972 | 3.8 | 52.9 | L | |
| >0.767 | ≤0.201 | - | - | - | - | 4.2 | 57.9 | L | |
| >0.767 | >0.201 | - | - | ≤0.997 | 19.2 | 81.4 | L | ||
| >0.767 | >0.201 | - | - | - | >0.997 | 0.2 | 100 | H | |
| Capability- driven | ≤0.146 | - | - | - | - | ≤0.423 | 0.2 | 100 | L |
| ≤0.146 | - | - | - | - | (0.423, 0.521] | 1.0 | 80 | H | |
| ≤0.146 | - | - | - | - | >0.521 | 2.7 | 100 | H | |
| >0.146 | - | - | ≤0.395 | - | - | 46.6 | 50.2 | H | |
| >0.146 | - | - | (0.395, 1.0] | - | - | 43.7 | 65.7 | L | |
| >0.146 | - | - | >1.0 | - | - | 5.7 | 60.7 | H | |
| Challenge- oriented | ≤0.098 | - | - | - | - | - | 5.5 | 80.8 | H |
| (0.098, 0.111] | - | - | - | - | - | 2.8 | 76.9 | L | |
| (0.111, 0.291] | - | - | - | - | - | 33.7 | 55.3 | H | |
| >0.291 | - | - | ≤0.718 | - | - | 53.8 | 67.7 | L | |
| >0.291 | - | - | >0.718 | - | - | 4.2 | 75.0 | H |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, X.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L. Unlocking the “Code” of Green Innovation Based on Machine Learning: Evidence from Manufacturing Enterprises in China. Systems 2025, 13, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090736
Wan X, He Z, Xu Y, Zhang L. Unlocking the “Code” of Green Innovation Based on Machine Learning: Evidence from Manufacturing Enterprises in China. Systems. 2025; 13(9):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090736
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Xiaoji, Zhiyan He, Yutong Xu, and Liping Zhang. 2025. "Unlocking the “Code” of Green Innovation Based on Machine Learning: Evidence from Manufacturing Enterprises in China" Systems 13, no. 9: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090736
APA StyleWan, X., He, Z., Xu, Y., & Zhang, L. (2025). Unlocking the “Code” of Green Innovation Based on Machine Learning: Evidence from Manufacturing Enterprises in China. Systems, 13(9), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090736






