1. Error in Figure
In the original publication [1], there were mistakes in Figures 4 and 8 as published.
1.1. Figure 4
In the original publication, there was a mistake in Figure 4 as published. The incorrect image for ‘αSMA, IL-1RA treated’ was included due to unclear labeling of the image file. The corrected Figure 4 appears below.
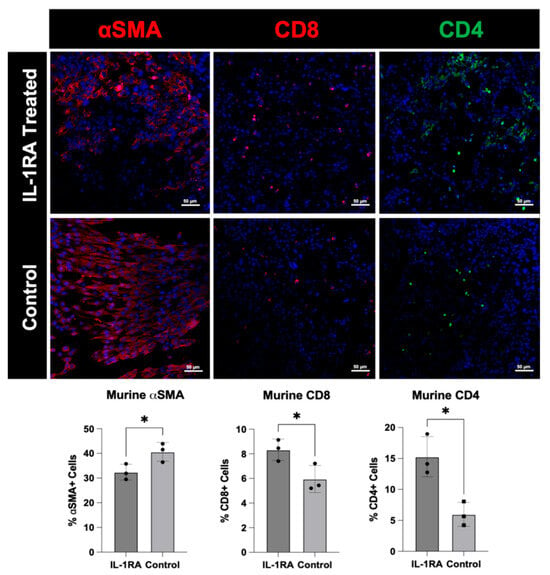
Figure 4.
Immunofluorescence staining of murine pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) organoids harvested on day 14. The tumor organoids were either untreated control (bottom row) or treated with IL-1RA (top row). IL-1RA treatment significantly decreased expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (p < 0.05), and significantly increased the expression of CD4+ (p < 0.05) and CD8+ (p < 0.05) immune cells. The single asterisk (*) indicates that the p value is less than or equal to 0.05, but greater than 0.01.
1.2. Figure 8
In the original publication, there was a mistake in Figure 8 as published. The incorrect image for ‘CD8, IL-1RA treated’ was included due to unclear labeling of the image file. The corrected Figure 8 appears below.
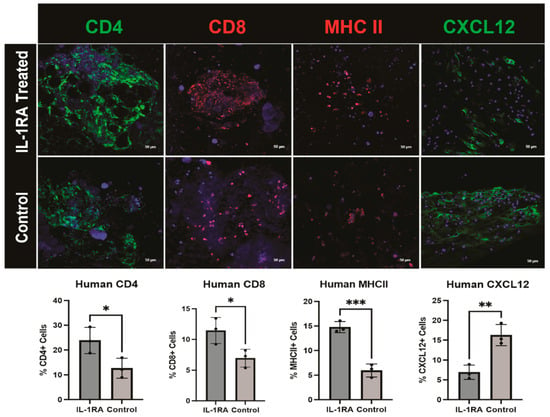
Figure 8.
Immunofluorescence staining of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) organoids harvested on day 14. The tumor organoids were either untreated control (bottom row) or treated with IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) (top row). There was significantly increased expression of CD4 (p < 0.05) and CD8 (p < 0.05) immune cell markers following treatment. The single asterisk (*) indicates that the p value is less than or equal to 0.05, but greater than 0.01. Major histocompatibility complex II (MHCII), a macrophage and antigen-presenting CAF (apCAF) marker, is significantly increased with IL-1RA treatment (p < 0.001). Three asterisks (***) indicate that the p value is less than or equal to 0.001, but greater than 0.0001. IL-1RA treatment significantly decreases C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12), a marker of immunomodulatory CAFs (iCAFs) (p < 0.01). Two asterisks (**) indicate that the p value is less than or equal to 0.01, but greater than 0.001.
The authors state that the scientific conclusions are unaffected.
This correction was approved by the Academic Editor. The original publication has also been updated.
Reference
- Morgan, A.G.; Griffin, M.F.; Longaker, M.T.; Norton, J.A. Precision Medicine: IL-1RA and Pancreatic Cancer Organoids. Biology 2025, 14, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).