Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Targeting Peptides and Their Applications in Tumor Imaging Probe Construction: Current Advances and Future Perspectives
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. EGFR-Targeting Peptides and Their Development Methods
| No. | Sequence | Targeting Selectivity | Development Approaches | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pep1 | HTSDQTN | EGFR WT | Phage display | [24] |
| Pep2 | SYPIPDT | EGFR WT | Phage display | [24] |
| Pep3 | QRHKPRE | EGFR WT | Phage display | [35] |
| Pep4 | YHWYGYTPQNVI | EGFR WT, EGFR vIII | Phage display | [25] |
| Pep5 | YHWYGYTPENVI | EGFR WT, EGFR vIII | Structure-based peptide design | [30] |
| Pep6 | YHWYGYTPQNYI | EGFR WT, EGFR vIII | Structure-based peptide design | [31] |
| Pep7 | CHVPGSTIC | EGFR WT, EGFR vIII | Phage display | [26] |
| Pep8 | CVAAMGSTC | EGFR WT, EGFR vIII | Phage display | [26] |
| Pep9 | CEKMVATHC | EGFR WT | Phage display | [36] |
| Pep10 | CPSDEHHTC | EGFR WT | Phage display | [36] |
| Pep11 | VLGREEWSTSYW | EGFR vIII | Phage display | [37] |
| Pep12 | LARLLT | EGFR WT | Computer-aided design | [38] |
| Pep13 | KYFPPLALYNPTEYFY | EGFR WT | one-bead-one-compound library | [39] |
| Pep14 | STHHYYP | EGFR L858R | Structure-based in silico design | [40] |
| Pep15 | HTHYYLP | EGFR L858R | Structure-based in silico design | [40] |
| Pep16 | CMYIEALDKYAC (CY12) | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [41] |
| Pep17 | CY12-63, CY12-81 and CY12-83 | EGFR WT | Structure-based in silico design | [42] |
| Pep18 | YARAAARQARAKNHVIKYLETLLYSQQQLAKYWEAFL | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [29] |
| Pep19 | FMRRRHIVRKRTLRRLLQERE | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [43] |
| Pep20 | AEYLR | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [44] |
| Pep21 | EYINQ | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [44] |
| Pep22 | PDYQQD | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [44] |
| Pep23 | NYQQN | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [45] |
| Pep24 | RAHEEIYHFFFAKKK | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [46] |
| Pep25 | SYRRPSQIRY | EGFR WT | Antibody fragment | [47] |
| Pep26 | FALGEA | EGFR vIII | Positional scanning synthetic combinatorial library | [48] |
| Pep27 | CQTPYYMNTC | EGFR WT | Structure-based peptide design | [49] |
| Pep28 | LLCSLYPGSSL | EGFR WT | Ribosome display selection | [50] |
3. Construction of EGFR-Targeting Peptide-Based Imaging Probes
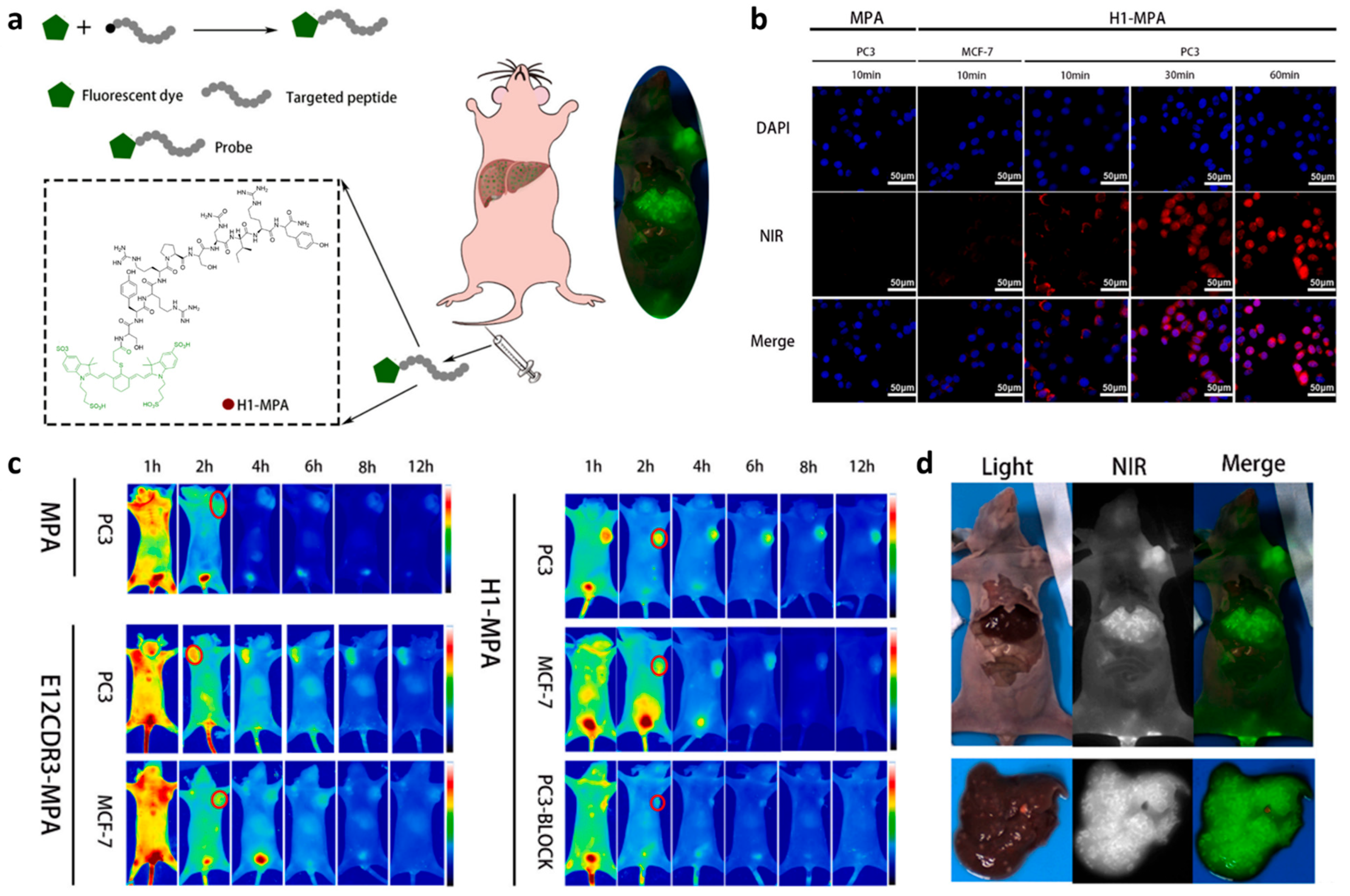
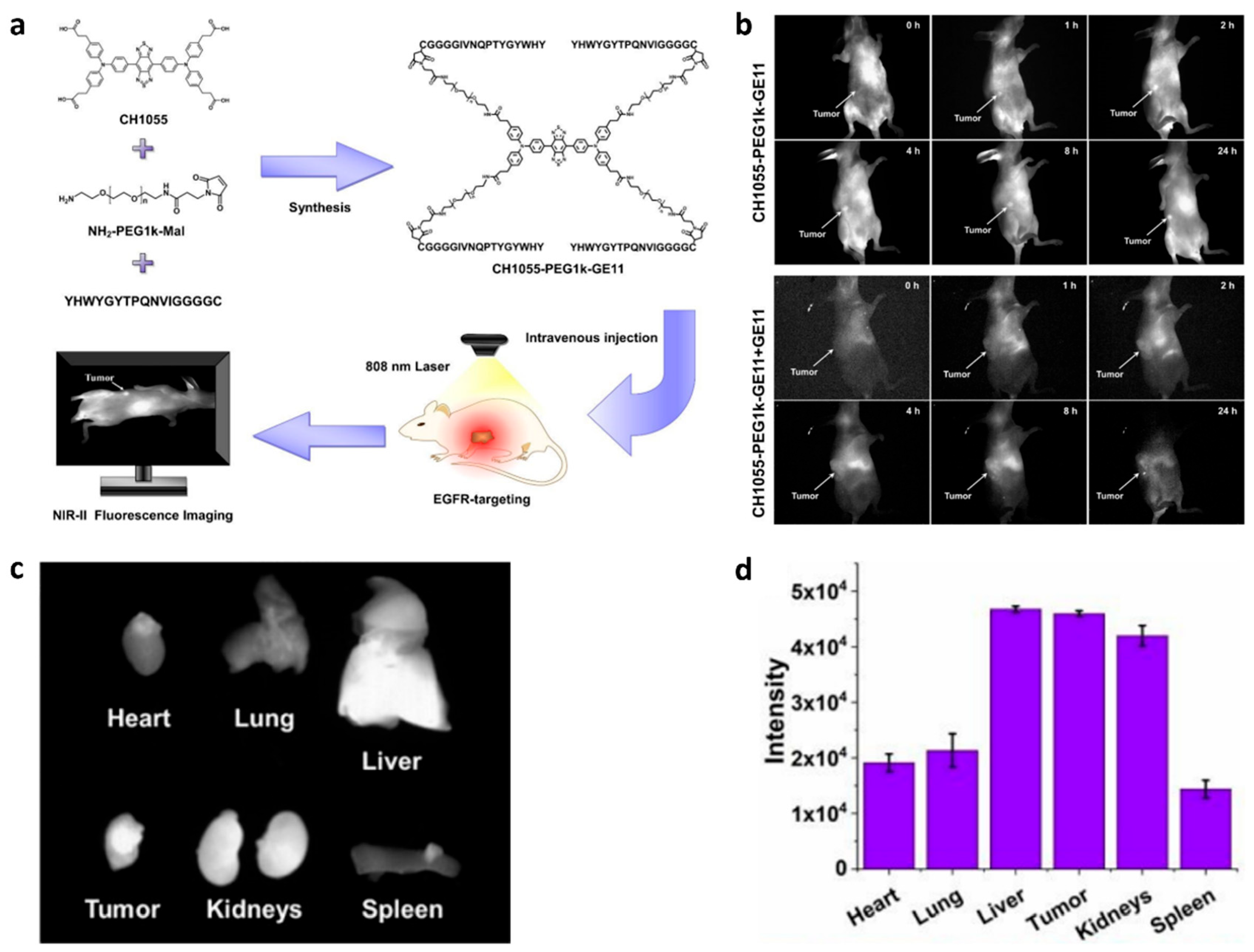
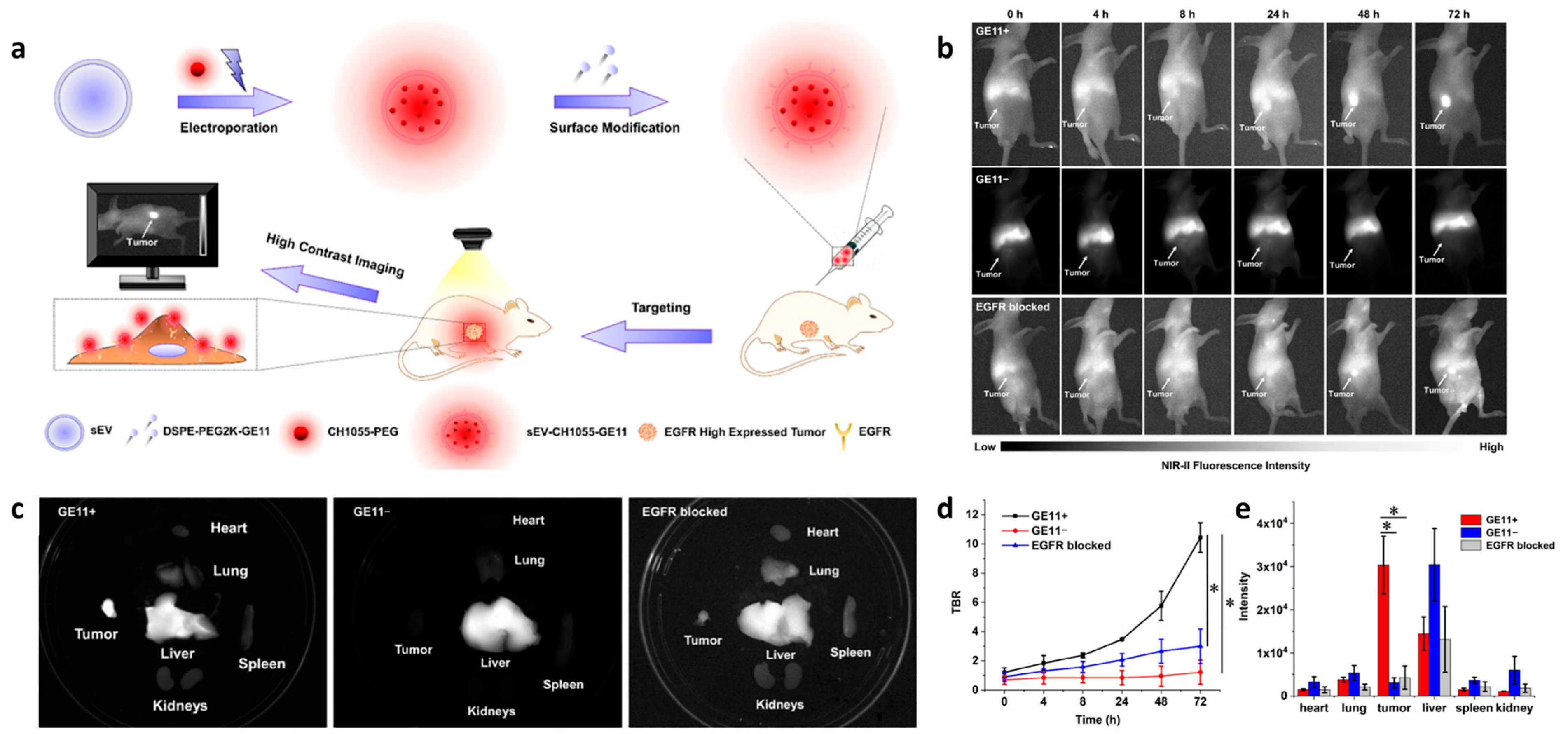
3.1. Fluorescence Imaging
3.2. PET/CT
3.3. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
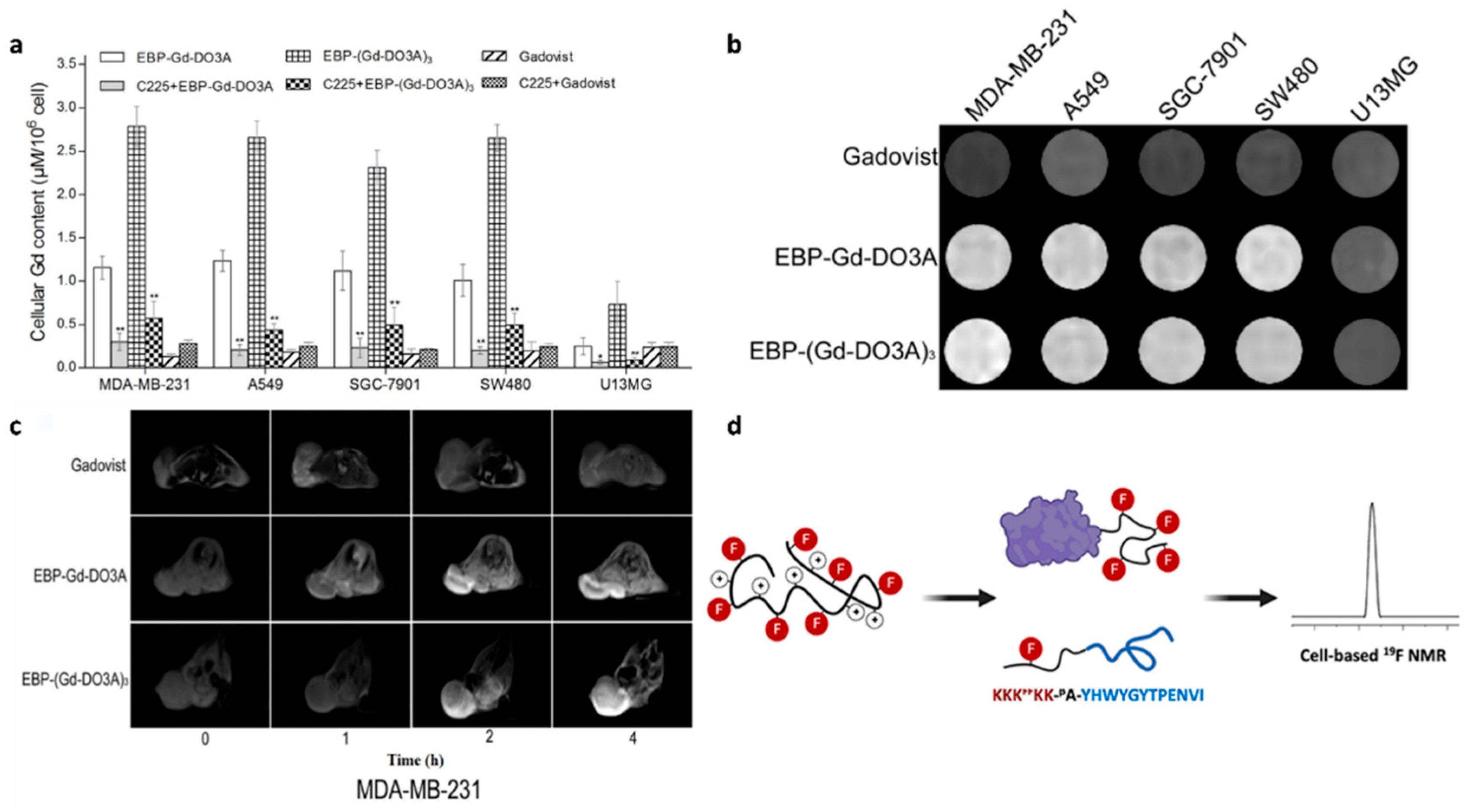
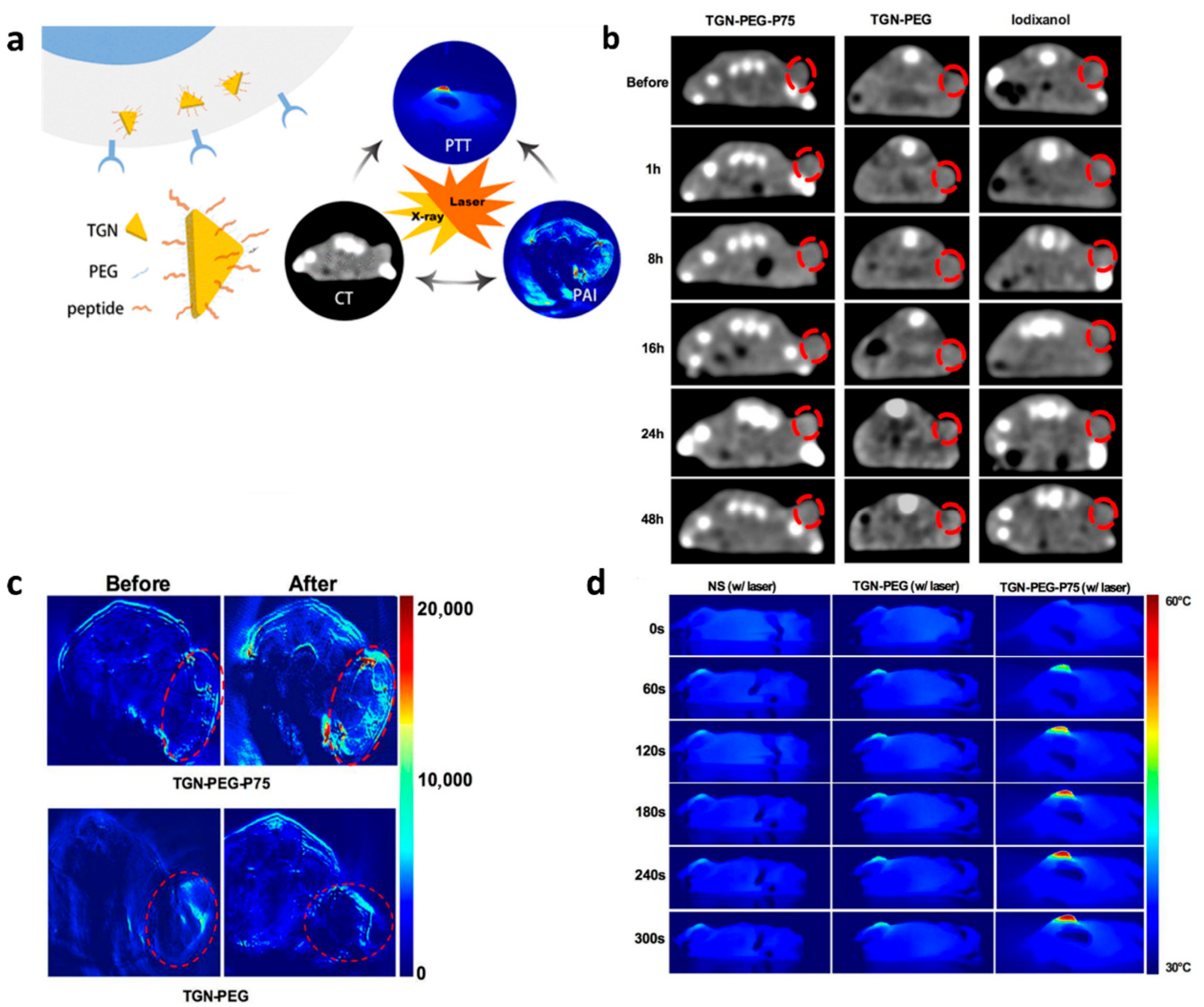
3.4. Multimodality Imaging
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphrey, M.B.; Quaim, L.; Rahimi, N.; Varacallo, M.A. Biochemistry, epidermal growth factor receptor. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, W.-L.; Feng, P.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Chen, K.-Y.; Sun, W.-L.; Van Hiep, N.; Luo, C.-S.; Wu, S.-M. The Role of EREG/EGFR Pathway in Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigismund, S.; Avanzato, D.; Lanzetti, L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaux, C.; Wynes, M.W.; Kato, Y.; Tran, C.; Asuncion, B.R.; Zhao, J.M.; Gustavson, M.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Gaire, F.; Matsubayashi, J.; et al. EGFR protein expression in non-small cell lung cancer predicts response to an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor—A novel antibody for immunohistochemistry or AQUA technology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7796–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, F.; Forrester, S.J.; Eguchi, S.; Zhang, M.Z.; Harris, R.C. Expression and Function of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Physiology and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1025–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnari, J.; Graziano, P.; Muscarella, L.A.; Rossi, A.; Grillo, L.R.; Montrone, G.; Di Lorenzo, A.; Bronzini, M.; Leone, A. Rapid EGFR evaluation from used H&E, IHC and FISH diagnostic slides with the Idylla platform. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 75, 338–344. [Google Scholar]
- Rotter, L.K.; Berisha, N.; Hsu, H.T.; Burns, K.H.; Andreou, C.; Kircher, M.F. Visualizing surface marker expression and intratumoral heterogeneity with SERRS-NPs imaging. Nanotheranostics 2022, 6, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Safdari, Y.; Tash Shamsabadi, F. Near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging of EGFR-Overexpressing Tumors in the Mouse Xenograft Model Using scFv-IRDye800CW and Cetuximab-IRDye800CW. Mol. Imaging 2022, 2022, 9589820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, B.; Wang, W. Construction of Targeting-Peptide-Based Imaging Reagents and Their Application in Bioimaging. Chem. Biomed. Imaging 2024, 2, 233–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samkoe, K.S.; Sardar, H.S.; Gunn, J.R.; Elliott, J.T.; Mansur, S.; Feldwisch, J.; Pogue, B.W.; Linos, K.; Paulsen, K.D.; Henderson, E.R. First-in-Human Study of ABY-029, a Novel Fluorescent Peptide that Targets EGFR, Applied to Soft-Tissue Sarcomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2025, 24, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samkoe, K.S.; Sardar, H.S.; Bates, B.D.; Tselepidakis, N.N.; Gunn, J.R.; Hoffer-Hawlik, K.A.; Feldwisch, J.; Pogue, B.W.; Paulsen, K.D.; Henderson, E.R. Preclinical imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor with ABY-029 in soft-tissue sarcoma for fluorescence-guided surgery and tumor detection. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 119, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samkoe, K.S.; Gunn, J.R.; Marra, K.; Hull, S.M.; Moodie, K.L.; Feldwisch, J.; Strong, T.V.; Draney, D.R.; Hoopes, P.J.; Roberts, D.W.; et al. Toxicity and Pharmacokinetic Profile for Single-Dose Injection of ABY-029: A Fluorescent Anti-EGFR Synthetic Affibody Molecule for Human Use. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2017, 19, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhingra, S.; Shrestha, P.; Chowdhury, A.; Zhou, Z.; Jois, S.D.; Vicente, M.d.G.H. The Synthesis of BODIPY-TKI Conjugates and Investigation of Their Ability to Target the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Targets 2023, 1, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.; Butch, C.J.; Wang, Z. A novel near-infrared EGFR targeting probe for metastatic lymph node imaging in preclinical mouse models. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Mei, C.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D. NIR-II Navigation with an EGFR-Targeted Probe Improves Imaging Resolution and Sensitivity of Detecting Micrometastases in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Xenograft Models. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 3563–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, M.; Mei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, H.; Li, D. Preclinical evaluation of a novel EGFR&c-Met bispecific near infrared probe for visualization of esophageal cancer and metastatic lymph nodes. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Sui, X.; Jiang, G.; Li, Y.; et al. Application of Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor-Targeted Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Near-Infrared II Dual-Modal Probe in Lung Cancer Diagnosis and Surgical Resection. Mol. Pharm. 2025, 22, 1198–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Shen, B.; Sun, X. Analysis of Progress and Challenges of EGFR-Targeted Molecular Imaging in Cancer With a Focus on Affibody Molecules. Mol. Imaging 2019, 18, 1536012118823473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.J.; Awan, S.Z.; Joshi, T.; Daniels, M.A.; Porciani, D.; Burke, D.H. Anti-EGFR aptamer exhibits direct anti-cancer effects in NSCLC cells harboring EGFR L858R mutations. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.J.; Guldenpfennig, C.; Guan, Y.; Winkler, C.; Beecher, M.; Beedy, M.; Berendzen, A.F.; Ma, L.; Daniels, M.A.; Burke, D.H.; et al. Targeting lung cancer with clinically relevant EGFR mutations using anti-EGFR RNA aptamer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 34, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ahmadyousefi, Y.; Salimi, Z.; Mirzaei, R.; Najafi, R.; Amirheidari, B.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Kheshti, J.; Safari, A.; Soleimani, M. Innovative Diagnostic Peptide-Based Technologies for Cancer Diagnosis: Focus on EGFR-Targeting Peptides. ChemMedChem 2023, 18, e202200506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pei, P.; Lei, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yin, D.; Zhang, F. A Promising NIR-II Fluorescent Sensor for Peptide-Mediated Long-Term Monitoring of Kidney Dysfunction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 15809–15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Peptides and peptide hormones for molecular imaging and disease diagnosis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3087–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh-Mivehroud, M.; Mahmoudpour, A.; Dastmalchi, S. Identification of new peptide ligands for epidermal growth factor receptor using phage display and computationally modeling their mode of binding. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 79, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Gu, J. Identification and characterization of a novel peptide ligand of epidermal growth factor receptor for targeted delivery of therapeutics. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1978–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, O.; Zaporozhets, A.; Tobi, D.; Bazylevich, A.; Firer, M.A.; Patsenker, L.; Gellerman, G.; Lubin, B.C.R. Novel Cyclic Peptides for Targeting EGFR and EGRvIII Mutation for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.M.; Sable, R.; Singh, S.; Vicente, M.G.H.; Jois, S.D. Peptide ligands for targeting the extracellular domain of EGFR: Comparison between linear and cyclic peptides. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2018, 91, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Lin, T.; Basu, R.; Ritchey, J.; Wang, S.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Pei, D.; Kara, L.B.; Cheng, X. Design of target specific peptide inhibitors using generative deep learning and molecular dynamics simulations. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, B.; Chen, C.Y.; Christofferson, M.; Montfort, W.R.; Schroeder, J. Sorting nexin-dependent therapeutic targeting of oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossein-Nejad-Ariani, H.; Althagafi, E.; Kaur, K. Small Peptide Ligands for Targeting EGFR in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, S.; Taschauer, A.; Geppl, E.; Pirhofer, V.; Schauer, M.; Poschl, S.; Kopp, F.; Richter, L.; Ecker, G.F.; Sami, H.; et al. Structure-based peptide ligand design for improved epidermal growth factor receptor targeted gene delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 176, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, D.; Mori, S.; Chadli, A.; Panda, S.S. Natural Cyclic Peptides: Synthetic Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Junod, S.L.; Zhang, S.; Buuh, Z.Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Kaneria, K.H.; Kafley, P.; Cohen, C.; Maloney, R.; et al. Unprotected peptide macrocyclization and stapling via a fluorine-thiol displacement reaction. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentilucci, L.; De Marco, R.; Cerisoli, L. Chemical modifications designed to improve peptide stability: Incorporation of non-natural amino acids, pseudo-peptide bonds, and cyclization. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3185–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Joshi, B.P.; Duan, X.; Pant, A.; Qiu, Z.; Kuick, R.; Owens, S.R.; Wang, T.D. EGFR Overexpressed in Colonic Neoplasia Can be Detected on Wide-Field Endoscopic Imaging. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2015, 6, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, N.; Aloisio, A.; Lupia, A.; Zimbo, A.M.; Mimmi, S.; Maisano, D.; Russo, R.; Marino, F.; Scalise, M.; Chiarella, E.; et al. Development of Cyclic Peptides Targeting the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Mesenchymal Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Subtype. Cells 2023, 12, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, S.; Adhya, I.; Lebleu, C.; Dumpati, R.; Rehan, A.; Chall, S.; Dai, J.; Errasti, G.; Delacroix, T.; Chakrabarti, R. Identification of a novel peptide ligand for the cancer-specific receptor mutation EGFRvIII using high-throughput sequencing of phage-selected peptides. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Liu, D.; Peng, J.; Deng, H.; Guo, Y.; Xu, L.X.; Miller, A.D.; Xu, Y. Novel peptide ligand directs liposomes toward EGF-R high-expressing cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1396–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Lai, W.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Z.; Tian, J.; Geng, L.; Fang, Q. Tumor detection using magnetosome nanoparticles functionalized with a newly screened EGFR/HER2 targeting peptide. Biomaterials 2017, 115, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, F.; Ganjalikhany, M.R. Structure-based inhibitory peptide design targeting peptide-substrate binding site in EGFR tyrosine kinase. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, S.; Duan, J.; Liu, X.; Bock, S.; Tian, Y.; Huang, Z. Biological evaluation of a novel doxorubicin-peptide conjugate for targeted delivery to EGF receptor-overexpressing tumor cells. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahjono, D.H. Design, synthesis, and activity assay of functionalized Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ligands as anticancer candidate for NSCLC. Rep. Grant-Support. Res. Asahi Glass Found. 2022, 91, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, M.R.; Su, H.Y.; Broka, D.; Goverdhan, A.; Schroeder, J.A. Inactive ERBB receptors cooperate with reactive oxygen species to suppress cancer progression. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1996–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.-Y.; Yue, L.-L.; Tai, L.-Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.-Y.; Xing, G.-H.; Yang, X.-G.; Sun, M.-S.; Pan, W.-S. A novel small peptide as an epidermal growth factor receptor targeting ligand for nanodelivery in vitro. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Kuroda, Y.; Hirose, M.; Kato, M.; Murakami, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakano, M.; Handa, T. Inhibition of autophosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor by a small peptide not employing an ATP-competitive mechanism. Biopolymers 2008, 89, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, K.; Sasaki, T.; Wang, Q.; Kuriyan, J. A highly efficient peptide substrate for EGFR activates the kinase by inducing aggregation. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, Z.; Gu, Y. Near-infrared targeted EGFR fluorescent probe for tumor imaging and diagnosis. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 393, 134102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denholt, C.L.; Hansen, P.R.; Pedersen, N.; Poulsen, H.S.; Gillings, N.; Kjaer, A. Identification of novel peptide ligands for the cancer-specific receptor mutation EFGRvIII using a mixture-based synthetic combinatorial library. Biopolymers 2009, 91, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, T.; Suzuki, M.; Takakura, H.; Hanaoka, H. Synthesis and biological evaluation of EGFR binding peptides for near-infrared photoimmunotherapy. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2024, 105, 117717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiwacharoenchai, N.; Kiriwan, D.; Chang, S.-Y.; Weng, C.C.; Li, Y.-K.; Tabtimmai, L.; Choowongkomon, K. EGFRp4 Peptides: A Novel Strategy for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Inhibitor. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 26848–26856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Pang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, M.; Tu, L.; Li, Q.; Sharma, A.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, Y. Near-infrared metal agents assisting precision medicine: From strategic design to bioimaging and therapeutic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 4392–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Liu, H.; Tang, B.; Wu, M. A NIR-II fluorescent probe for high contrast non-invasive imaging of tumor with a high EGFR-expression. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 9635–9642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.Y.; Liu, H.M.; Yu, Z.L.; Chen, G.; Wu, M. Nanometer-Sized and Near-Infrared-II Fluorescent Extracellular Vesicles for Noninvasive High-Contrast Imaging of Tumors with High EGFR Expression. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 11481–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongarora, B.G.; Fontenot, K.R.; Hu, X.; Sehgal, I.; Satyanarayana-Jois, S.D.; Vicente, M.G. Phthalocyanine-peptide conjugates for epidermal growth factor receptor targeting. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 3725–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Q.; Oldham, K.R.; Wang, T.D. Visualizing epithelial expression of EGFR in vivo with distal scanning side-viewing confocal endomicroscope. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, T.-S.; Joshi, B.; Zhou, J.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Wamsteker, E.J.; Kwon, R.S.; Appelman, H.; Beer, D.G.; et al. Multiplexed endoscopic imaging of Barrett's neoplasia using targeted fluorescent heptapeptides in a phase 1 proof-of-concept study. Gut 2021, 70, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.M.; Zhou, Z.; Singh, S.S.; Sibrian-Vazquez, M.; Jois, S.D.; Henriques Vicente, M.D.G. Targeting EGFR Overexpression at the Surface of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Exploiting Amidated BODIPY-Peptide Conjugates. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 96, 581–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Williams, T.M.; Zhou, Z.; Fronczek, F.R.; Sibrian-Vazquez, M.; Jois, S.D.; Vicente, M.G.H. Synthesis of BODIPY-Peptide Conjugates for Fluorescence Labeling of EGFR Overexpressing Cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 1566–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
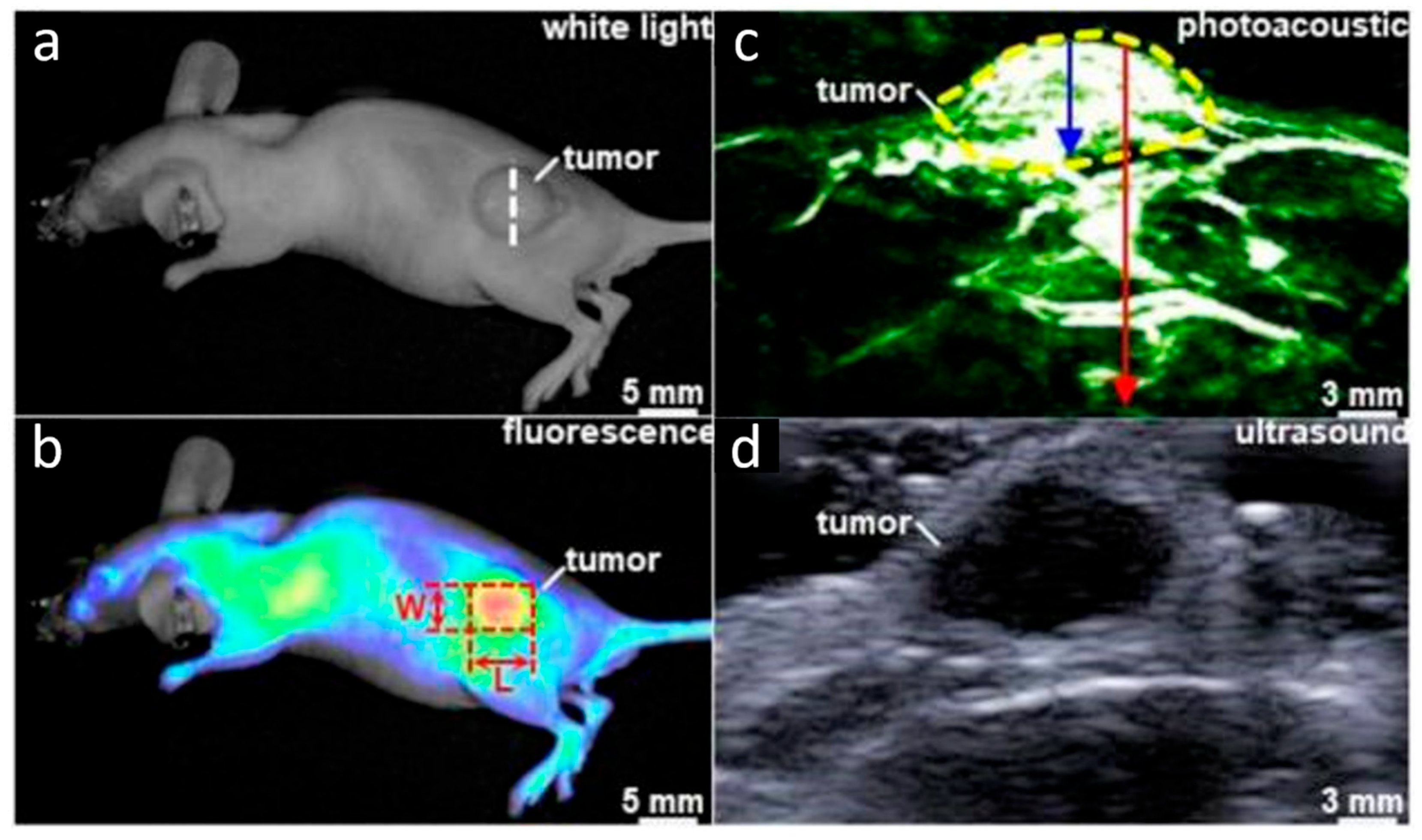
- Chen, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, T.D. Dual-modal in vivo fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging using a heterodimeric peptide. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13196–13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Pan, W. Small peptide-modified nanostructured lipid carriers distribution and targeting to EGFR-overexpressing tumor in vivo. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2014, 42, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J.; Duan, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.D. In vivo fluorescence imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft using near-infrared labeled epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) peptide. Biomed. Opt. Express. 2016, 7, 3163–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; Hu, Z.; Tian, J. New and effective EGFR-targeted fluorescence imaging technology for intraoperative rapid determination of lung cancer in freshly isolated tissue. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2023, 50, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.L.; Ou, Z.; Ximendes, E.; Cui, H.; Keck, C.H.C.; Jaque, D.; Hong, G. Near-infrared II fluorescence imaging. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers. 2024, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denholt, C.L.; Binderup, T.; Stockhausen, M.-T.; Poulsen, H.S.; Spang-Thomsen, M.; Hansen, P.R.; Gillings, N.; Kjær, A. Evaluation of 4-[18F]fluorobenzoyl-FALGEA-NH2 as a positron emission tomography tracer for epidermal growth factor receptor mutation variant III imaging in cancer. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2011, 38, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
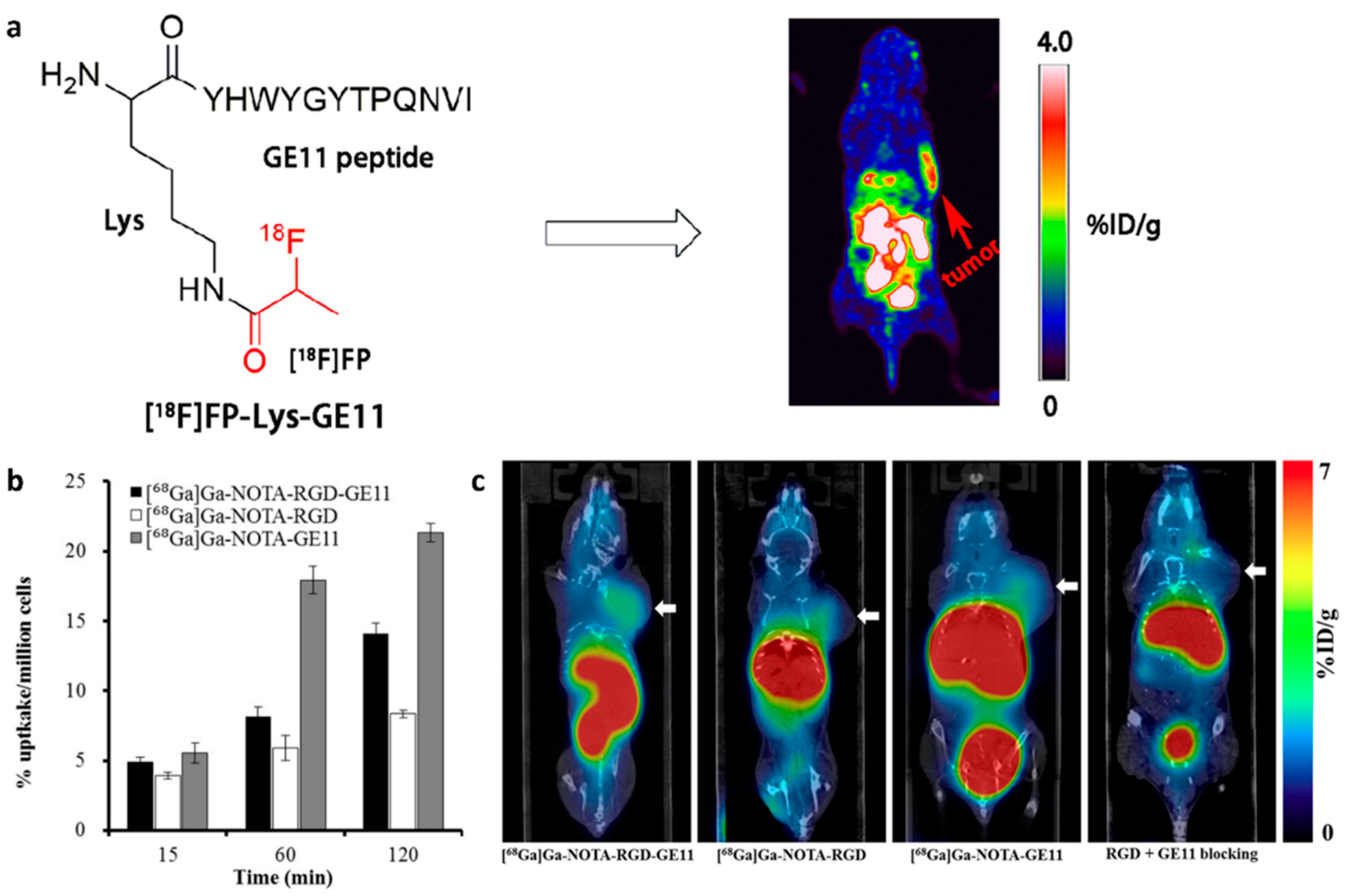
- Li, X.; Hu, K.; Liu, W.; Wei, Y.; Sha, R.; Long, Y.; Han, Y.; Sun, P.; Wu, H.; Li, G.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of [18F]FP-Lys-GE11 as a new radiolabeled peptide probe for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2020, 90–91, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Zhao, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. Synthesis of a novel (99m)Tc labeled GE11 peptide for EGFR SPECT imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 96, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gé, L.G.; Danielsen, M.B.; Nielsen, A.Y.; Skavenborg, M.L.; Langkjær, N.; Thisgaard, H.; McKenzie, C.J. Radiocobalt-Labeling of a Polypyridylamine Chelate Conjugated to GE11 for EGFR-Targeted Theranostics. Molecules 2025, 30, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues Toledo, C.; Tantawy, A.A.; Lima Fuscaldi, L.; Malavolta, L.; de Aguiar Ferreira, C. EGFR- and Integrin αVβ3-Targeting Peptides as Potential Radiometal-Labeled Radiopharmaceuticals for Cancer Theranostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzmann, S.; Ehemann, V.; Schwab, M. Arginine-glycine-aspartic acid (RGD)-peptide binds to both tumor and tumor-endothelial cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 5139–5143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-J.; Chan, C.-H.; Lin, K.-L.; Chen, J.-H.; Tseng, C.-H.; Wang, P.-Y.; Chien, C.-Y.; Yu, H.-M.; Lin, W.-J. 68Ga-labelled NOTA-RGD-GE11 peptide for dual integrin and EGFR-targeted tumour imaging. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2019, 68–69, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xue, X.; Lu, H.; He, Y.; Lu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Tang, N.; Dreyer, C.A.; Quigley, L.; et al. Two-way magnetic resonance tuning and enhanced subtraction imaging for non-invasive and quantitative biological imaging. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, C.; Duan, J.; Ai, S.; Liu, X. MR Molecular Imaging of EGF Receptor-Overexpressing Tumours with Peptide-Targeted Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents. Authorea 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargari, N.R.; Ebrahimi, F.; Akhlaghi, M.; Beiki, D.; Abdi, K.; Abbasi, M.A.; Ramezanpour, S.; Asghari, S.M. Novel Gd-DTPA-peptide for targeted breast tumor magnetic resonance imaging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placidi, M.P.; Botta, M.; Kálmán, F.K.; Hagberg, G.E.; Baranyai, Z.; Krenzer, A.; Rogerson, A.K.; Tóth, I.; Logothetis, N.K.; Angelovski, G. Aryl-phosphonate lanthanide complexes and their fluorinated derivatives: Investigation of their unusual relaxometric behavior and potential application as dual frequency 1H/19F MRI probes. Chemistry 2013, 19, 11644–11660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kirberger, S.E.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Wagner, C.R.; Pomerantz, W.C.K. Design of Highly Fluorinated Peptides for Cell-based 19F NMR. Bioconjug. Chem. 2023, 34, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphandery, E. Biodistribution and targeting properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for treatments of cancer and iron anemia disease. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 573–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
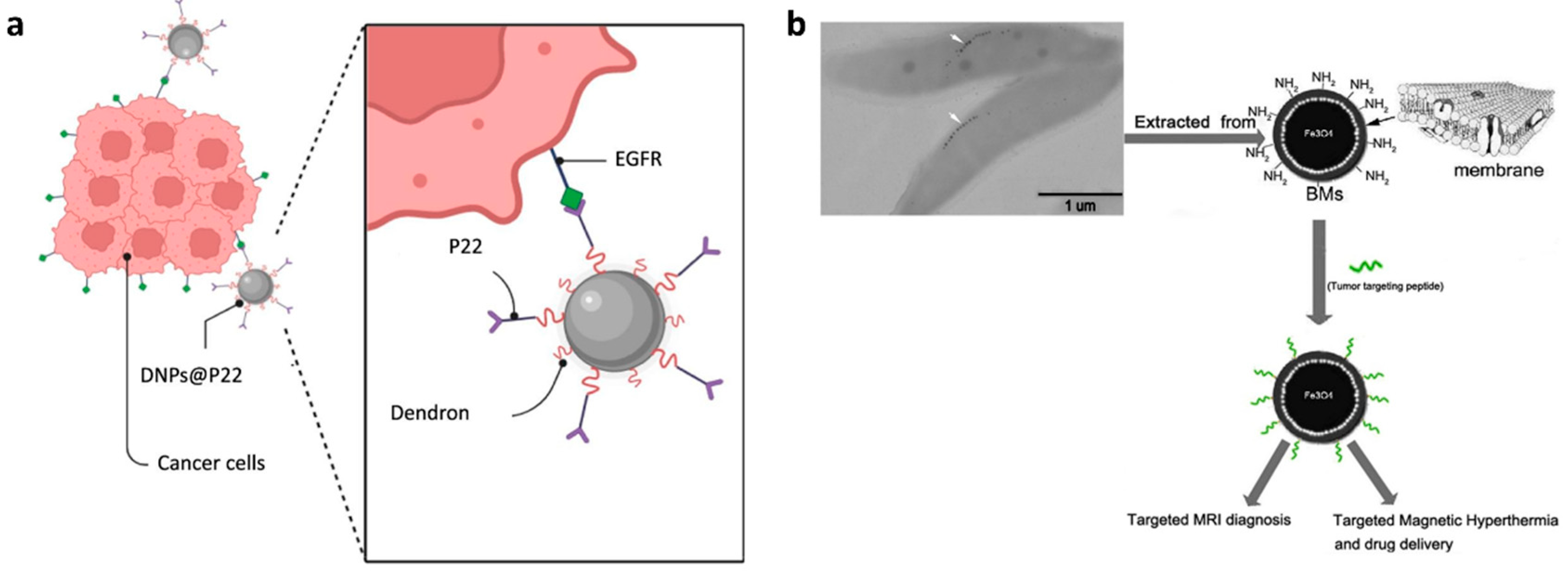
- Freis, B.; Ramírez, M.D.L.Á.; Furgiuele, S.; Journe, F.; Cheignon, C.; Charbonnière, L.J.; Henoumont, C.; Kiefer, C.; Mertz, D.; Affolter-Zbaraszczuk, C.; et al. Bioconjugation studies of an EGF-R targeting ligand on dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles to target head and neck cancer cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
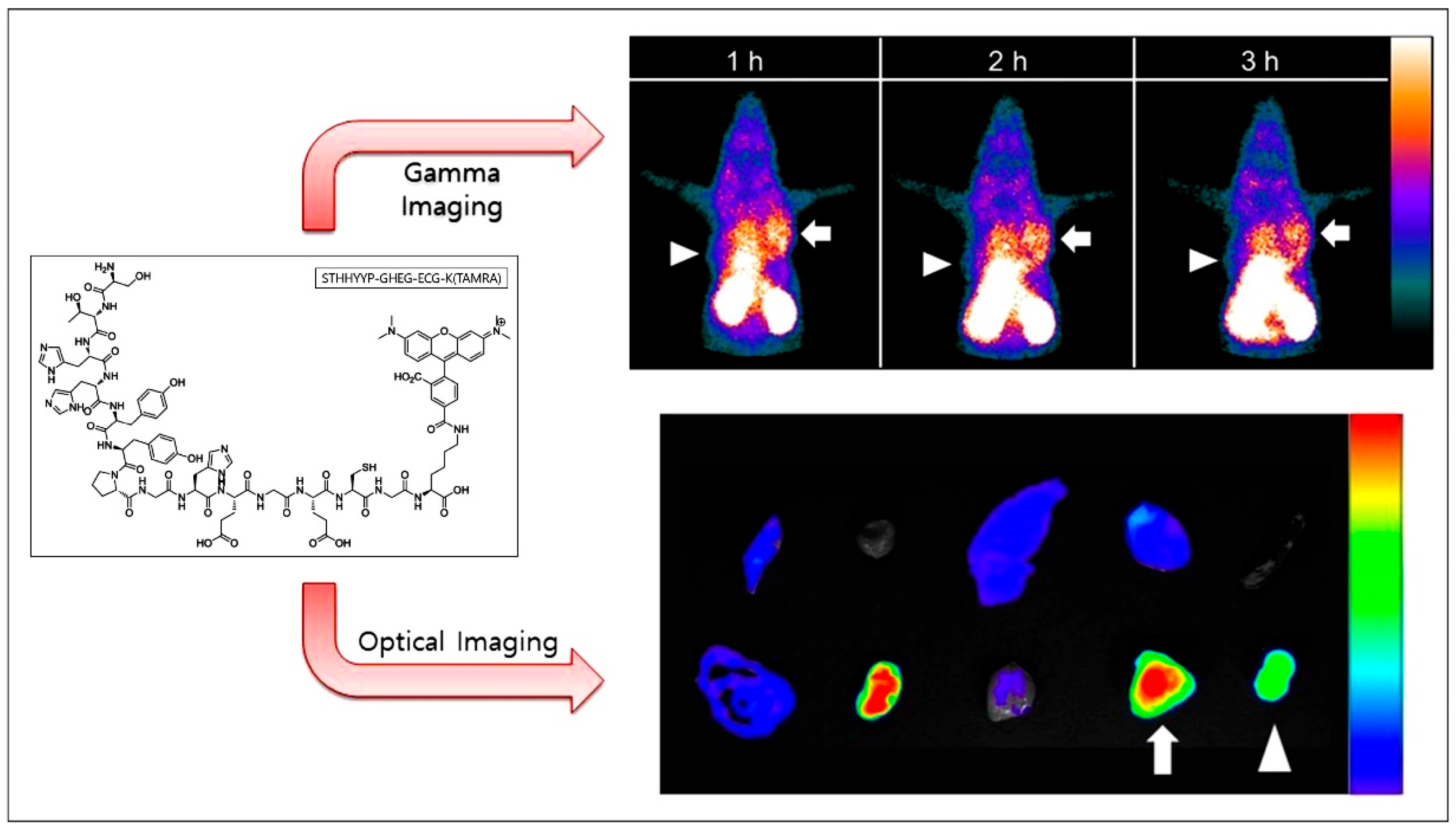
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, D.W. A novel dual-labeled small peptide as a multimodal imaging agent for targeting wild-type EGFR in tumors. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, D.W. A Novel Dual-labeled Peptide for Multimodal Imaging of EGFR with L858R Mutation. Curr. Radiopharm. 2024, 17, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Tian, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Anti-EGFR Peptide-Conjugated Triangular Gold Nanoplates for Computed Tomography/Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16992–17003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.J.; de Campos, L.J.; Xing, H.; Conda-Sheridan, M. Peptide-based therapeutics: Challenges and solutions. Med. Chem. Res. 2024, 33, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailing, T.; Yonghong, P.; Yufeng, Z.; Haitao, T. Challenges for the application of EGFR-targeting peptide GE11 in tumor diagnosis and treatment. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2022, 349, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasdemiroglu, Y.; Gourdie, R.G.; He, J.Q. In vivo degradation forms, anti-degradation strategies, and clinical applications of therapeutic peptides in non-infectious chronic diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 932, 175192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, L.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, Z.; Hu, S.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Targeting Peptides and Their Applications in Tumor Imaging Probe Construction: Current Advances and Future Perspectives. Biology 2025, 14, 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081011
Huang L, Dong Y, Li J, Yang X, Li X, Wu J, Huang J, Zhang Q, Wan Z, Hu S, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Targeting Peptides and Their Applications in Tumor Imaging Probe Construction: Current Advances and Future Perspectives. Biology. 2025; 14(8):1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081011
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Lu, Ying Dong, Jinhang Li, Xinyu Yang, Xiaoqiong Li, Jia Wu, Jinhua Huang, Qiaoxuan Zhang, Zemin Wan, Shuzhi Hu, and et al. 2025. "Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Targeting Peptides and Their Applications in Tumor Imaging Probe Construction: Current Advances and Future Perspectives" Biology 14, no. 8: 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081011
APA StyleHuang, L., Dong, Y., Li, J., Yang, X., Li, X., Wu, J., Huang, J., Zhang, Q., Wan, Z., Hu, S., Feng, R., Li, G., Huang, X., & Zhang, P. (2025). Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-Targeting Peptides and Their Applications in Tumor Imaging Probe Construction: Current Advances and Future Perspectives. Biology, 14(8), 1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14081011





